African buffalo (Syncerus caffer caffer) juvenile head.jpg on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The African buffalo (''Syncerus caffer)'' is a large
The African buffalo (''Syncerus caffer)'' is a large
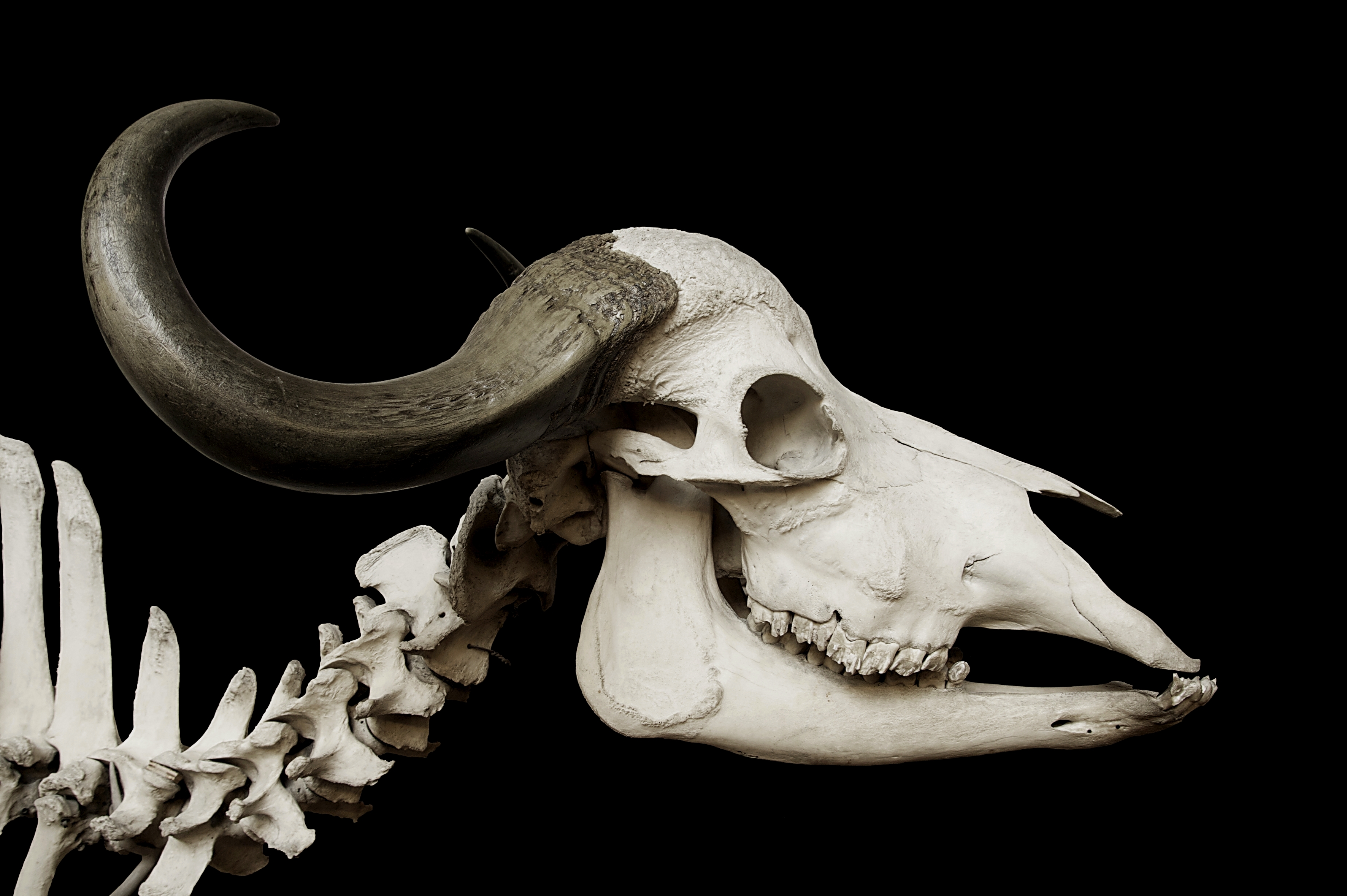 The African buffalo is a very robust species. Its shoulder height can range from and its head-and-body length can range from . The tail can range from long. Compared with other large bovids, it has a long but stocky body (the body length can exceed the wild water buffalo, which is heavier and taller) and short but thickset legs, resulting in a relatively short standing height. Cape buffaloes weigh (males weigh about more than females). In comparison, African forest buffaloes, at , are only half that size. Its head is carried low; its top is located below the backline. The front hooves of the buffalo are wider than the rear, which is associated with the need to support the weight of the front part of the body, which is heavier and more powerful than the back.
Savannah-type buffaloes have black or dark brown coats with age. Old bulls often have whitish circles around their eyes and on their face. Females tend to have more reddish coats. Forest-type buffaloes are 30–40% smaller, reddish brown in colour, with much more hair growth around the ears and with horns that curve back and slightly up. Calves of both types have red coats.
A characteristic feature of the horns of adult male African buffalo (southern and eastern populations) is that the bases come very close together, forming a shield referred to as a "boss". From the base, the horns diverge downwards, then smoothly curve upwards and outwards and in some cases inwards and or backwards. In large bulls, the distance between the ends of the horns can reach upwards of one metre (the record being 64.5 inches 164 cm). The horns form fully when the animal reaches the age of 5 or 6 years old, but the bosses do not become "hard" until it reaches the age of 8 to 9 years old. In cows, the horns are, on average, 10–20% smaller, and they do not have a boss. Forest-type buffalo horns are smaller than those of the savanna-type buffaloes from Southern and East Africa, usually measuring less than , and are almost never fused.
Unlike other large bovines, African buffalo have 52 chromosomes (for comparison, American bison and domestic cattle have 60). This means domestic cattle and bison are unable to create
The African buffalo is a very robust species. Its shoulder height can range from and its head-and-body length can range from . The tail can range from long. Compared with other large bovids, it has a long but stocky body (the body length can exceed the wild water buffalo, which is heavier and taller) and short but thickset legs, resulting in a relatively short standing height. Cape buffaloes weigh (males weigh about more than females). In comparison, African forest buffaloes, at , are only half that size. Its head is carried low; its top is located below the backline. The front hooves of the buffalo are wider than the rear, which is associated with the need to support the weight of the front part of the body, which is heavier and more powerful than the back.
Savannah-type buffaloes have black or dark brown coats with age. Old bulls often have whitish circles around their eyes and on their face. Females tend to have more reddish coats. Forest-type buffaloes are 30–40% smaller, reddish brown in colour, with much more hair growth around the ears and with horns that curve back and slightly up. Calves of both types have red coats.
A characteristic feature of the horns of adult male African buffalo (southern and eastern populations) is that the bases come very close together, forming a shield referred to as a "boss". From the base, the horns diverge downwards, then smoothly curve upwards and outwards and in some cases inwards and or backwards. In large bulls, the distance between the ends of the horns can reach upwards of one metre (the record being 64.5 inches 164 cm). The horns form fully when the animal reaches the age of 5 or 6 years old, but the bosses do not become "hard" until it reaches the age of 8 to 9 years old. In cows, the horns are, on average, 10–20% smaller, and they do not have a boss. Forest-type buffalo horns are smaller than those of the savanna-type buffaloes from Southern and East Africa, usually measuring less than , and are almost never fused.
Unlike other large bovines, African buffalo have 52 chromosomes (for comparison, American bison and domestic cattle have 60). This means domestic cattle and bison are unable to create
The Lake Rudolf Crocodile (''Crocodylus niloticus'' Laurenti) Population
Masters of Science Thesis, The University of East Africa. The cheetah,
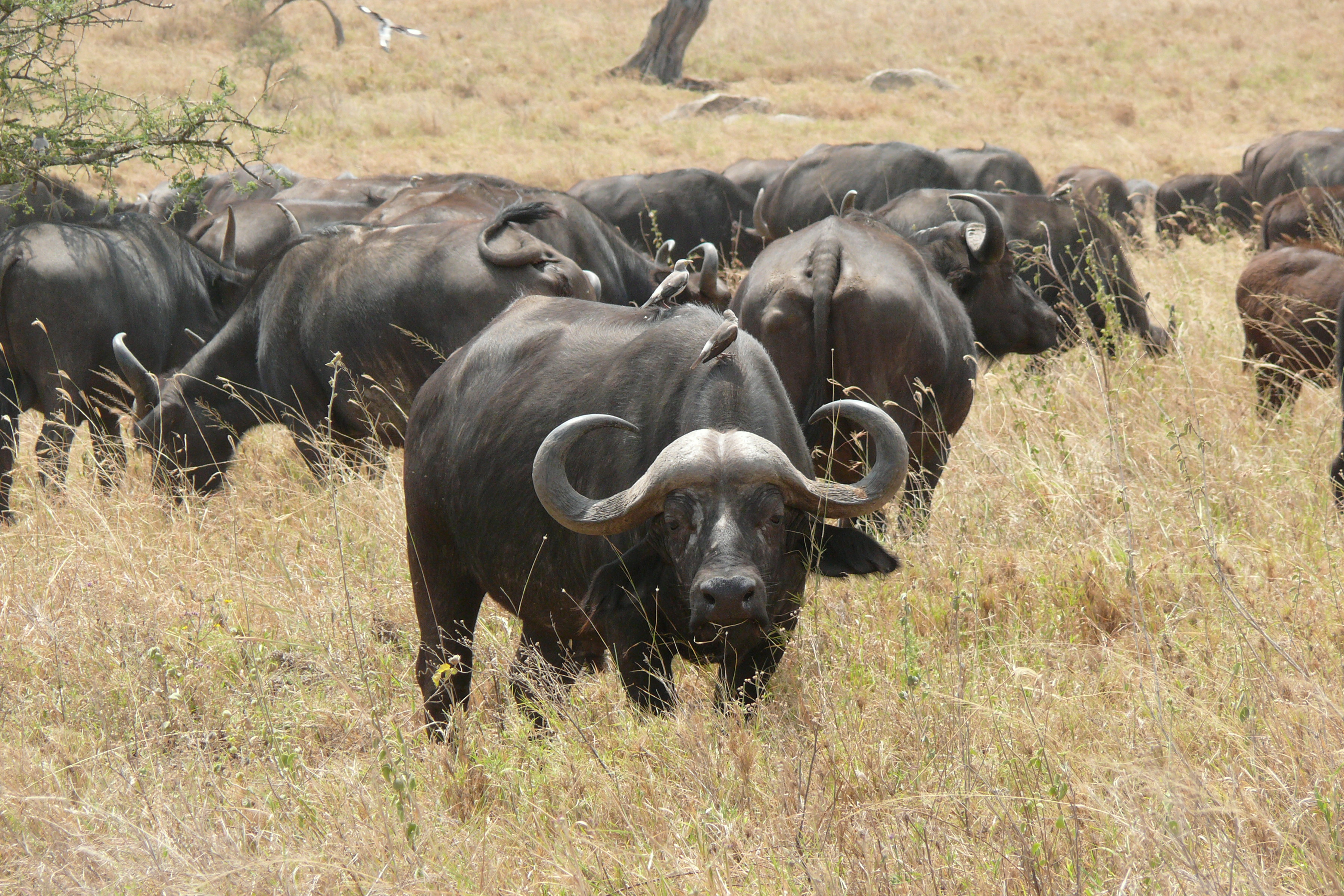 Herd size is highly variable. The core of the herds is made up of related females, and their offspring, in an almost linear dominance hierarchy. The basic herds are surrounded by subherds of subordinate males, high-ranking males and females, and old or invalid animals.
African buffaloes engage in several types of group behavior. Females appear to exhibit a sort of "voting behavior". During resting time, the females stand up, shuffle around, and sit back down again. They sit in the direction they think they should move. After an hour of more shuffling, the females travel in the direction they decide. This decision is communal and not based on hierarchy or dominance.
When chased by
Herd size is highly variable. The core of the herds is made up of related females, and their offspring, in an almost linear dominance hierarchy. The basic herds are surrounded by subherds of subordinate males, high-ranking males and females, and old or invalid animals.
African buffaloes engage in several types of group behavior. Females appear to exhibit a sort of "voting behavior". During resting time, the females stand up, shuffle around, and sit back down again. They sit in the direction they think they should move. After an hour of more shuffling, the females travel in the direction they decide. This decision is communal and not based on hierarchy or dominance.
When chased by  Adult bulls spar in play, dominance interactions, or actual fights. A bull approaches another, lowing, with his horns down, and waits for the other bull to do the same thing. When sparring, the bulls twist their horns from side to side.Sinclair, A. R. E. (1977) ''The African Buffalo''. Chicago, The University of Chicago Press. If the sparring is for play, the bull may rub his opponent's face and body during the sparring session. Actual fights are violent but rare and brief. Calves may also spar in play, but adult females rarely spar at all.
During the dry season, males split from the herd and form bachelor groups. Two types of bachelor herds occur: ones made of males aged four to seven years and those of males 12 years or older. During the wet season, the younger bulls rejoin a herd to mate with the females. They stay with them throughout the season to protect the calves. Some older bulls cease to rejoin the herd, as they can no longer compete with the younger, more aggressive males. The old bachelors are called ''dagga boy''s ("mud covered"), and are considered the most dangerous to humans.
Adult bulls spar in play, dominance interactions, or actual fights. A bull approaches another, lowing, with his horns down, and waits for the other bull to do the same thing. When sparring, the bulls twist their horns from side to side.Sinclair, A. R. E. (1977) ''The African Buffalo''. Chicago, The University of Chicago Press. If the sparring is for play, the bull may rub his opponent's face and body during the sparring session. Actual fights are violent but rare and brief. Calves may also spar in play, but adult females rarely spar at all.
During the dry season, males split from the herd and form bachelor groups. Two types of bachelor herds occur: ones made of males aged four to seven years and those of males 12 years or older. During the wet season, the younger bulls rejoin a herd to mate with the females. They stay with them throughout the season to protect the calves. Some older bulls cease to rejoin the herd, as they can no longer compete with the younger, more aggressive males. The old bachelors are called ''dagga boy''s ("mud covered"), and are considered the most dangerous to humans.
African buffalo (Syncerus caffer) calf 2 weeks.jpg, Two-week-old red calf
At
At Kazinga Channel in Uganda African buffalo (Syncerus caffer caffer) juvenile head.jpg, Calf
At
At Ngorongoro Conservation Area in Tanzania

''The ultimate ungulate page''
''UltimateUngulate.com''. Retrieved January 9, 2007. * Nowak, R.M. and Paradiso, J.L. 1983. ''Walker's Mammals of the World''. Baltimore, Maryland, USA: The Johns Hopkins University Press.
Video:Battle Kruger
No attribution required Free African buffalo Images
African buffalo images
* {{DEFAULTSORT:African buffalo Bovids of Africa Syncerus Extant Middle Pleistocene first appearances Herbivorous mammals Mammals described in 1779 Mammals of Sub-Saharan Africa Taxa named by Anders Sparrman

 The African buffalo (''Syncerus caffer)'' is a large
The African buffalo (''Syncerus caffer)'' is a large sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
n bovine. There are five subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species ...
that are recognized as being valid. ''Syncerus caffer caffer'', the Cape buffalo, is the nominotypical subspecies
In biological classification, subspecies is a rank below species, used for populations that live in different areas and vary in size, shape, or other physical characteristics (morphology), but that can successfully interbreed. Not all species ...
, and the largest one, found in Southern Africa and East Africa
East Africa, Eastern Africa, or East of Africa, is the eastern subregion of the African continent. In the United Nations Statistics Division scheme of geographic regions, 10-11-(16*) territories make up Eastern Africa:
Due to the historical ...
. ''S. c. nanus'' (the forest buffalo) is the smallest subspecies, common in forest areas of Central Africa and West Africa, while ''S. c. brachyceros'' is in West Africa and ''S. c. aequinoctialis'' is in the savannas of East Africa. The adult African buffalo's horns are its characteristic feature: they have fused bases, forming a continuous bone shield across the top of the head, referred to as a "boss".
The African buffalo is more closely related to other buffalo species than it is to other bovids such as American bison or domestic cattle, with its closest living relative being the Asian water buffalo. Its unpredictable temperament may be part of the reason that the African buffalo has never been domesticated, which would also explain why the African buffalo has no domesticated descendants, unlike the wild yak
The wild yak (''Bos mutus'') is a large, wild bovine native to the Himalayas. It is the ancestor of the domestic yak (''Bos grunniens'').
Taxonomy
The ancestor of the wild and domestic yak is thought to have diverged from ''Bos primigenius'' ...
which is an ancestor of the domestic yak. Natural predators of adult African buffaloes include lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large Felidae, cat of the genus ''Panthera'' native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; short, rounded head; round ears; and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphi ...
s, African wild dogs, spotted hyena
The spotted hyena (''Crocuta crocuta''), also known as the laughing hyena, is a hyena species, currently classed as the sole extant member of the genus ''Crocuta'', native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is listed as being of least concern by the IUC ...
s, and Nile crocodiles. As one of the Big Five game animals, the Cape buffalo is a sought-after trophy in hunting.
Description
 The African buffalo is a very robust species. Its shoulder height can range from and its head-and-body length can range from . The tail can range from long. Compared with other large bovids, it has a long but stocky body (the body length can exceed the wild water buffalo, which is heavier and taller) and short but thickset legs, resulting in a relatively short standing height. Cape buffaloes weigh (males weigh about more than females). In comparison, African forest buffaloes, at , are only half that size. Its head is carried low; its top is located below the backline. The front hooves of the buffalo are wider than the rear, which is associated with the need to support the weight of the front part of the body, which is heavier and more powerful than the back.
Savannah-type buffaloes have black or dark brown coats with age. Old bulls often have whitish circles around their eyes and on their face. Females tend to have more reddish coats. Forest-type buffaloes are 30–40% smaller, reddish brown in colour, with much more hair growth around the ears and with horns that curve back and slightly up. Calves of both types have red coats.
A characteristic feature of the horns of adult male African buffalo (southern and eastern populations) is that the bases come very close together, forming a shield referred to as a "boss". From the base, the horns diverge downwards, then smoothly curve upwards and outwards and in some cases inwards and or backwards. In large bulls, the distance between the ends of the horns can reach upwards of one metre (the record being 64.5 inches 164 cm). The horns form fully when the animal reaches the age of 5 or 6 years old, but the bosses do not become "hard" until it reaches the age of 8 to 9 years old. In cows, the horns are, on average, 10–20% smaller, and they do not have a boss. Forest-type buffalo horns are smaller than those of the savanna-type buffaloes from Southern and East Africa, usually measuring less than , and are almost never fused.
Unlike other large bovines, African buffalo have 52 chromosomes (for comparison, American bison and domestic cattle have 60). This means domestic cattle and bison are unable to create
The African buffalo is a very robust species. Its shoulder height can range from and its head-and-body length can range from . The tail can range from long. Compared with other large bovids, it has a long but stocky body (the body length can exceed the wild water buffalo, which is heavier and taller) and short but thickset legs, resulting in a relatively short standing height. Cape buffaloes weigh (males weigh about more than females). In comparison, African forest buffaloes, at , are only half that size. Its head is carried low; its top is located below the backline. The front hooves of the buffalo are wider than the rear, which is associated with the need to support the weight of the front part of the body, which is heavier and more powerful than the back.
Savannah-type buffaloes have black or dark brown coats with age. Old bulls often have whitish circles around their eyes and on their face. Females tend to have more reddish coats. Forest-type buffaloes are 30–40% smaller, reddish brown in colour, with much more hair growth around the ears and with horns that curve back and slightly up. Calves of both types have red coats.
A characteristic feature of the horns of adult male African buffalo (southern and eastern populations) is that the bases come very close together, forming a shield referred to as a "boss". From the base, the horns diverge downwards, then smoothly curve upwards and outwards and in some cases inwards and or backwards. In large bulls, the distance between the ends of the horns can reach upwards of one metre (the record being 64.5 inches 164 cm). The horns form fully when the animal reaches the age of 5 or 6 years old, but the bosses do not become "hard" until it reaches the age of 8 to 9 years old. In cows, the horns are, on average, 10–20% smaller, and they do not have a boss. Forest-type buffalo horns are smaller than those of the savanna-type buffaloes from Southern and East Africa, usually measuring less than , and are almost never fused.
Unlike other large bovines, African buffalo have 52 chromosomes (for comparison, American bison and domestic cattle have 60). This means domestic cattle and bison are unable to create hybrid
Hybrid may refer to:
Science
* Hybrid (biology), an offspring resulting from cross-breeding
** Hybrid grape, grape varieties produced by cross-breeding two ''Vitis'' species
** Hybridity, the property of a hybrid plant which is a union of two dif ...
offspring with cape buffalo.
Subspecies
Ecology
The African buffalo is one of the most successful grazers in Africa. It lives in savannas,swamps
A swamp is a forested wetland.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p. Swamps are considered to be transition zones because both land and water play a role in ...
and floodplains, as well as mopane grasslands, and the forests of the major mountains of Africa. This buffalo prefers a habitat with dense cover, such as reeds and thickets, but can also be found in open woodland.Estes, R. (1991) ''The Behavior Guide to African Mammals, Including Hoofed Mammals, Carnivores, Primates.'' Los Angeles, The University of California Press. pp. 195–200 While not particularly demanding in regard to habitat, they require water daily, and so they depend on perennial sources of water. Like the plains zebra, the buffalo can live on tall, coarse grasses. Herds of buffalo mow down grasses and make way for more selective grazers. When feeding, the buffalo makes use of its tongue and wide incisor row to eat grass more quickly than most other African herbivores. Buffaloes do not stay on trampled or depleted areas for long.
Other than humans, African buffaloes have few predators and are capable of defending themselves against (and killing) lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large Felidae, cat of the genus ''Panthera'' native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; short, rounded head; round ears; and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphi ...
s. Lions kill and eat buffaloes regularly, and in some regions, the buffaloes are the lions' primary prey. It often takes several lions to bring down a single adult buffalo, and the entire pride may join in the hunt. However, several incidents have been reported in which lone adult male lions have successfully brought down adult buffaloes. On very rare occasions, buffaloes and white rhinos
The white rhinoceros, white rhino or square-lipped rhinoceros (''Ceratotherium simum'') is the largest extant species of rhinoceros. It has a wide mouth used for grazing and is the most social of all rhino species. The white rhinoceros consists ...
will fight over territory; due to the rhino's strength and size advantage, the rhino typically wins and the buffalo can die from injuries sustained during the encounter. Rhinos live solitary lives, whereas buffalo (excluding solitary adult bulls) primarily live social lives and thus they do not usually recognize each other as threats. Hippopotamuses and buffalo also do not normally interact, but if the buffalo provokes the hippo or makes it feel threatened, a fight can break out, but this is also rare. Adolescent bull African elephants may harass or kill Cape buffalo, either out of territorial aggression or while in musth; when they do this, the calves are most likely to be killed by the elephant attack as they are defenseless when facing an elephant alone, whereas adults will try to fight back and may survive (or succumb to injuries afterward). The average-sized Nile crocodile typically attacks only old solitary animals and young calves, though they can kill healthy adults. Exceptionally large, old male crocodile
Crocodiles (family (biology), family Crocodylidae) or true crocodiles are large semiaquatic reptiles that live throughout the tropics in Africa, Asia, the Americas and Australia. The term crocodile is sometimes used even more loosely to inclu ...
s may become semi-habitual predators of buffaloes.Graham, A. D. (1968)The Lake Rudolf Crocodile (''Crocodylus niloticus'' Laurenti) Population
Masters of Science Thesis, The University of East Africa. The cheetah,
leopard
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant species in the genus '' Panthera'', a member of the cat family, Felidae. It occurs in a wide range in sub-Saharan Africa, in some parts of Western and Central Asia, Southern Russia, a ...
, African wild dog and spotted hyena
The spotted hyena (''Crocuta crocuta''), also known as the laughing hyena, is a hyena species, currently classed as the sole extant member of the genus ''Crocuta'', native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is listed as being of least concern by the IUC ...
are normally a threat only to newborn calves, though larger clans of hyenas have been recorded killing cows (mainly pregnant ones) and, on rare occasions, full-grown bulls. Large packs of wild dogs have been observed to hunt calves and sick adults.
Diseases
The African buffalo is susceptible to many diseases, including those shared with domestic cattle, such as bovine tuberculosis,corridor disease
Corridor or The Corridor may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
Films
* ''The Corridor'' (1968 film), a 1968 Swedish drama film
* ''The Corridor'' (1995 film), a 1995 Lithuanian drama film
* ''The Corridor'' (2010 film), a 2010 Canadia ...
, and foot-and-mouth disease
Foot-and-mouth disease (FMD) or hoof-and-mouth disease (HMD) is an infectious and sometimes fatal viral disease that affects cloven-hoofed animals, including domestic and wild bovids. The virus causes a high fever lasting two to six days, followe ...
. As with many diseases, these problems remain dormant within a population as long as the health of the animals is good. These diseases do, however, restrict the legal movements of the animals and fencing infected areas from unaffected areas is enforced. Some wardens and game managers have managed to protect and breed "disease-free" herds which become very valuable because they can be transported. Most well-known are Lindsay Hunt's efforts to source uninfected animals from the Kruger National Park
Kruger National Park is a South African National Park and one of the largest game reserves in Africa. It covers an area of in the provinces of Limpopo and Mpumalanga in northeastern South Africa, and extends from north to south and from ea ...
in South Africa. Some disease-free buffaloes in South Africa have been sold to breeders for close to US$130,000.
Social behavior
 Herd size is highly variable. The core of the herds is made up of related females, and their offspring, in an almost linear dominance hierarchy. The basic herds are surrounded by subherds of subordinate males, high-ranking males and females, and old or invalid animals.
African buffaloes engage in several types of group behavior. Females appear to exhibit a sort of "voting behavior". During resting time, the females stand up, shuffle around, and sit back down again. They sit in the direction they think they should move. After an hour of more shuffling, the females travel in the direction they decide. This decision is communal and not based on hierarchy or dominance.
When chased by
Herd size is highly variable. The core of the herds is made up of related females, and their offspring, in an almost linear dominance hierarchy. The basic herds are surrounded by subherds of subordinate males, high-ranking males and females, and old or invalid animals.
African buffaloes engage in several types of group behavior. Females appear to exhibit a sort of "voting behavior". During resting time, the females stand up, shuffle around, and sit back down again. They sit in the direction they think they should move. After an hour of more shuffling, the females travel in the direction they decide. This decision is communal and not based on hierarchy or dominance.
When chased by predators
Predation is a biological interaction where one organism, the predator, kills and eats another organism, its prey. It is one of a family of common feeding behaviours that includes parasitism and micropredation (which usually do not kill the ...
, a herd sticks close together and makes it hard for the predators to pick off one member. Calves are gathered in the middle. A buffalo herd responds to the distress call of a threatened member and tries to rescue it. A calf's distress call gets the attention of not only the mother, but also the herd. Buffaloes engage in mobbing behavior
Mobbing in animals is an antipredator adaptation in which individuals of prey species mob a predator by cooperatively attacking or harassing it, usually to protect their offspring. A simple definition of mobbing is an assemblage of individuals a ...
when fighting off predators. They have been recorded killing lions and chasing lions up trees and keeping them there for two hours, after the lions have killed a member of their group. Lion cubs can get trampled and killed. In one videotaped instance, known as the ''Battle at Kruger
''Battle at Kruger'' is an eight-minute amateur wildlife video that depicts a confrontation between a herd of Cape buffalo, a small group of young lions from a pride, and two crocodiles. The video was shot in September 2004 at the Transport Da ...
'', a calf survived an attack by both lions and a crocodile after intervention of the herd.
Males have a linear dominance hierarchy based on age and size. Since a buffalo is safer when a herd is larger, dominant bulls may rely on subordinate bulls and sometimes tolerate their copulation. The young males keep their distance from the dominant bull, which is recognizable by the thickness of his horns.
 Adult bulls spar in play, dominance interactions, or actual fights. A bull approaches another, lowing, with his horns down, and waits for the other bull to do the same thing. When sparring, the bulls twist their horns from side to side.Sinclair, A. R. E. (1977) ''The African Buffalo''. Chicago, The University of Chicago Press. If the sparring is for play, the bull may rub his opponent's face and body during the sparring session. Actual fights are violent but rare and brief. Calves may also spar in play, but adult females rarely spar at all.
During the dry season, males split from the herd and form bachelor groups. Two types of bachelor herds occur: ones made of males aged four to seven years and those of males 12 years or older. During the wet season, the younger bulls rejoin a herd to mate with the females. They stay with them throughout the season to protect the calves. Some older bulls cease to rejoin the herd, as they can no longer compete with the younger, more aggressive males. The old bachelors are called ''dagga boy''s ("mud covered"), and are considered the most dangerous to humans.
Adult bulls spar in play, dominance interactions, or actual fights. A bull approaches another, lowing, with his horns down, and waits for the other bull to do the same thing. When sparring, the bulls twist their horns from side to side.Sinclair, A. R. E. (1977) ''The African Buffalo''. Chicago, The University of Chicago Press. If the sparring is for play, the bull may rub his opponent's face and body during the sparring session. Actual fights are violent but rare and brief. Calves may also spar in play, but adult females rarely spar at all.
During the dry season, males split from the herd and form bachelor groups. Two types of bachelor herds occur: ones made of males aged four to seven years and those of males 12 years or older. During the wet season, the younger bulls rejoin a herd to mate with the females. They stay with them throughout the season to protect the calves. Some older bulls cease to rejoin the herd, as they can no longer compete with the younger, more aggressive males. The old bachelors are called ''dagga boy''s ("mud covered"), and are considered the most dangerous to humans.
Vocalizations
African buffaloes make various vocalizations. Many calls are lower-pitched versions of those emitted by domestic cattle. They emit low-pitched, two- to four-second calls intermittently at three- to six-second intervals to signal the herd to move. To signal to the herd to change direction, leaders emit "gritty", "creaking gate" sounds. When moving to drinking places, some individuals make long "maaa" calls up to 20 times a minute. When being aggressive, they make explosive grunts that may last long or turn into a rumbling growl. Cows produce croaking calls when looking for their calves. Calves make a similar call of a higher pitch when in distress. When threatened by predators, they make drawn-out "waaaa" calls. Dominant individuals make calls to announce their presence and location. A version of the same call, but more intense, is emitted as a warning to an encroaching inferior. When grazing, they make various sounds, such as brief bellows, grunts, honks, and croaks.Reproduction
Females reach sexual maturity at around five years of age while males are sexually matured at four to six. African buffaloes mate and give birth only during the rainy seasons. Birth peak takes place early in the season, while mating peaks later. A bull closely guards a cow that comes into heat, while keeping other bulls at bay. This is difficult, as cows are quite evasive and attract many males to the scene. By the time a cow is in full estrus, only the most dominant bull in the herd/subherd is there. Cows first calve at five years of age, after agestation
Gestation is the period of development during the carrying of an embryo, and later fetus, inside viviparous animals (the embryo develops within the parent). It is typical for mammals, but also occurs for some non-mammals. Mammals during pregna ...
period of 11.5 months. Newborn calves remain hidden in vegetation for the first few weeks while being nursed occasionally by the mother before joining the main herd. Older calves are held in the centre of the herd for safety. The maternal bond between mother and calf lasts longer than in most bovids. That bonding ends when a new calf is born, and the mother then keeps her previous offspring at bay with horn jabs. Nevertheless, the yearling follows its mother for another year or so. Males leave their mothers when they are two years old and join the bachelor groups. Young calves, unusually for bovids, suckle from behind their mothers, pushing their heads between the mothers' legs.
In the wild African buffaloes have an average lifespan of 11 years but they've been recorded to reach 22 years of age. In captivity they can live for a maximum of 29.5 years though they only live 16 years on average.
At
Kazinga Channel
The Kazinga Channel in Uganda is a wide, long natural channel that links Lake Edward and Lake George (Uganda), Lake George, and a dominant feature of Queen Elizabeth National Park. The channel attracts a varied range of animals and birds, with ...
in Uganda
African buffalo (Syncerus caffer) calf 2 weeks suckling.jpg, Two-week-old calf sucklingAt Kazinga Channel in Uganda African buffalo (Syncerus caffer caffer) juvenile head.jpg, Calf
At
Chobe National Park
Chobe National Park is Botswana's first national park, and also the most biologically diverse. Located in the north of the country, it is Botswana's third largest park, after Central Kalahari Game Reserve and Gemsbok National Park, and has one of ...
in Botswana
Cape Buffalo calf.jpg, Female with red calfAt Ngorongoro Conservation Area in Tanzania
Relationship with humans

Status
The current status of the African buffalo is dependent on the animal's value to both trophy hunters and tourists, paving the way for conservation efforts through anti-poaching patrols, village crop damage payouts, and CAMPFIRE payback programs to local areas. The African buffalo is listed as Near threatened by theIUCN
The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN; officially International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources) is an international organization working in the field of nature conservation and sustainable use of natu ...
, with a decreasing population of 400,000 individuals. While some populations (subspecies) are decreasing, others will remain unchanged in the long term if large, healthy populations continue to persist in a substantial number of national parks, equivalent reserves and hunting zones in southern and eastern Africa."
In the most recent and available census data at continental scale, the total estimated numbers of the three savanna-type African buffalo subspecies (''S. c. caffer'', ''S. c. brachyceros'' and ''S. c. aequinoctialis'') are at 513,000 individuals.
In the past, numbers of African buffaloes suffered their most severe collapse during the great rinderpest epidemic of the 1890s, which, coupled with pleuro-pneumonia
Pleuropneumonia is inflammation of the lungs and pleura, pleurisy being the inflammation of the pleura alone.
See also
* Contagious bovine pleuropneumonia – a disease in cattle
* Contagious caprine pleuropneumonia
Contagious caprine pleurop ...
, caused mortalities as high as 95% among livestock and wild ungulates.
Being a member of the big five game group, a term originally used to describe the five most dangerous animals to hunt, the Cape buffalo is a sought-after trophy, with some hunters paying over $10,000 for the opportunity to hunt one. The larger bulls are targeted for their trophy value, although in some areas, buffaloes are still hunted for meat.
Attacks
One of the "big five" African game, it is known as "the Black Death" or "the widowmaker," and is widely regarded as a very dangerous animal. African buffaloes are sometimes reported to kill more people in Africa than any other animal, although the same claim is also made of hippopotamuses andcrocodile
Crocodiles (family (biology), family Crocodylidae) or true crocodiles are large semiaquatic reptiles that live throughout the tropics in Africa, Asia, the Americas and Australia. The term crocodile is sometimes used even more loosely to inclu ...
s. These numbers may be somewhat overestimated; for example, in the country of Mozambique, attacks, especially fatal ones, were much less frequent on humans than those by hippos, and especially, Nile crocodiles. In Uganda, on the other hand, large herbivores were found to attack more people on average than lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large Felidae, cat of the genus ''Panthera'' native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; short, rounded head; round ears; and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphi ...
s or leopard
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant species in the genus '' Panthera'', a member of the cat family, Felidae. It occurs in a wide range in sub-Saharan Africa, in some parts of Western and Central Asia, Southern Russia, a ...
s and have a higher rate of inflicting fatalities during attacks than the predators (the African buffalo, in particular, killing humans in 49.5% of attacks on them), but hippos and even elephants may still kill more people per annum than buffaloes. African buffaloes are notorious among big-game hunters as very dangerous animals, with wounded animals reported to ambush and attack pursuers.
See also
* Anoa * Gaur * Zebu, the common type of domestic cattle from India: the gaur may have contributed to some zebu breeds.References
Further reading
* Melletti M. and Burton J. (eds). 2014. ''Ecology, Evolution and Behaviour of Wild Cattle. Implications for Conservation'' (Cambridge University Press). http://www.cambridge.org/us/academic/subjects/life-sciences/animal-behaviour/ecology-evolution-and-behaviour-wild-cattle-implications-conservation * ''Ecology and Behaviour of the African Buffalo – Social Inequality and Decision Making'' (Chapman & Hall Wildlife Ecology & Behaviour) * Huffman, B. 2006''The ultimate ungulate page''
''UltimateUngulate.com''. Retrieved January 9, 2007. * Nowak, R.M. and Paradiso, J.L. 1983. ''Walker's Mammals of the World''. Baltimore, Maryland, USA: The Johns Hopkins University Press.
External links
Video:Battle Kruger
No attribution required Free African buffalo Images
African buffalo images
* {{DEFAULTSORT:African buffalo Bovids of Africa Syncerus Extant Middle Pleistocene first appearances Herbivorous mammals Mammals described in 1779 Mammals of Sub-Saharan Africa Taxa named by Anders Sparrman