Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, امارت اسلامی افغانستان is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of
Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
and
South Asia
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth descr ...
. Referred to as the
Heart of Asia, it is bordered by
Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
to the
east and south,
Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
to the
west
West or Occident is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from east and is the direction in which the Sun sets on the Earth.
Etymology
The word "west" is a Germanic word passed into some ...
,
Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan ( or ; tk, Türkmenistan / Түркменистан, ) is a country located in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the sout ...
to the
northwest,
Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked co ...
to the
north
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north ...
,
Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
to the
northeast
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A compass rose is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each se ...
, and
China to the
northeast and east. Occupying of land, the country is predominantly mountainous with plains
in the north and
the southwest, which are separated by the
Hindu Kush
The Hindu Kush is an mountain range in Central and South Asia to the west of the Himalayas. It stretches from central and western Afghanistan, Quote: "The Hindu Kush mountains run along the Afghan border with the North-West Frontier Province ...
mountain range. ,
its population is 40.2 million
(officially estimated to be 32.9 million), composed mostly of ethnic
Pashtuns
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, پښتانه, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically r ...
,
Tajiks
Tajiks ( fa, تاجيک، تاجک, ''Tājīk, Tājek''; tg, Тоҷик) are a Persian-speaking Iranian ethnic group native to Central Asia, living primarily in Afghanistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan. Tajiks are the largest ethnicity in Taj ...
,
Hazaras
The Hazaras ( fa, , Həzārə; haz, , Āzərə) are an ethnic group and the principal component of the population of Afghanistan, native to, and primarily residing in the Hazaristan (Hazarajat) region in central Afghanistan and generally scatt ...
, and
Uzbeks
The Uzbeks ( uz, , , , ) are a Turkic ethnic group native to the wider Central Asian region, being among the largest Turkic ethnic group in the area. They comprise the majority population of Uzbekistan, next to Kazakh and Karakalpak mino ...
.
Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. Acco ...
is the country's largest city and serves as its capital.
Human habitation in Afghanistan dates back to the
Middle Paleolithic era, and the country's
strategic location along the historic
Silk Road has led it to being described, picturesquely, as the ‘roundabout of the ancient world’. Popularly referred to as the
graveyard of empires, the land has historically been home to various peoples and
has witnessed numerous military campaigns, including those by
the Persians
''The Persians'' ( grc, Πέρσαι, ''Persai'', Latinised as ''Persae'') is an Greek tragedy, ancient Greek tragedy written during the Classical Greece, Classical period of Ancient Greece by the Greek tragedian Aeschylus. It is the second and on ...
,
Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
, the
Maurya Empire,
Arab Muslims, the
Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, Монголчууд, , , ; ; russian: Монголы) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal membe ...
, the
British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
, the
Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
, and most recently by
an American-led coalition. Afghanistan also served as the source from which the
Greco-Bactrians
The Bactrian Kingdom, known to historians as the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom or simply Greco-Bactria, was a Hellenistic-era Greek state, and along with the Indo-Greek Kingdom, the easternmost part of the Hellenistic world in Central Asia and the India ...
and the
Mughals
The Mughal Empire was an early-modern empire that controlled much of South Asia between the 16th and 19th centuries. Quote: "Although the first two Timurid emperors and many of their noblemen were recent migrants to the subcontinent, the d ...
, among others, rose to form major empires.
The various conquests and periods in both the
Iranian
Iranian may refer to:
* Iran, a sovereign state
* Iranian peoples, the speakers of the Iranian languages. The term Iranic peoples is also used for this term to distinguish the pan ethnic term from Iranian, used for the people of Iran
* Iranian lan ...
and
Indian
Indian or Indians may refer to:
Peoples South Asia
* Indian people, people of Indian nationality, or people who have an Indian ancestor
** Non-resident Indian, a citizen of India who has temporarily emigrated to another country
* South Asia ...
cultural spheres made the area a center for
Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheisti ...
, Buddhism, Hinduism, and later Islam throughout history.
The modern state of Afghanistan began with the
Durrani dynasty
The Durrani dynasty ( fa, سلسله درانیان; ps, د درانيانو کورنۍ) was founded in 1747 by Ahmad Shah Durrani at Kandahar, Afghanistan. He united the different Pashtun tribes and created the Durrani Empire. which at it ...
in the 18th century, with the
Durrani Afghan Empire being formed by
Ahmad Shah Durrani. The Durrani Empire led conquests in which, at its peak, encompassed land that spanned from
eastern Iran
Eastern Iran consists of the Lut Desert, the mountains ranges bordering Turkmenistan, Afghanistan and Pakistan, and the coastal strip of the Gulf of Oman.
It includes the provinces of North Khorasan, Razavi Khorasan, South Khorasan and Sis ...
to
northern India
North India is a loosely defined region consisting of the northern part of India. The dominant geographical features of North India are the Indo-Gangetic Plain and the Himalayas, which demarcate the region from the Tibetan Plateau and Central ...
. Following its decline and the death of
Ahmad Shah Durrani, and
Timur Shah, it was divided into multiple smaller independent kingdoms, including but not limited to:
Herat
Herāt (; Persian: ) is an oasis city and the third-largest city of Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Selseleh-ye Safē ...
,
Kandahar
Kandahar (; Kandahār, , Qandahār) is a city in Afghanistan, located in the south of the country on the Arghandab River, at an elevation of . It is Afghanistan's second largest city after Kabul, with a population of about 614,118. It is the c ...
and Kabul. Afghanistan would be reunited in the 19th century after wars of unification led by
Dost Mohammad Khan
Dost Mohammad Khan Barakzai (Pashto/Persian: ; 23 December 17929 June 1863), nicknamed the Amir-i Kabir, Also titled Amir al-Mu'minin, was a member of the Barakzai dynasty and one of the prominent rulers of the Emirate of Afghanistan. His 37-year ...
, where he conquered the independent principalities in Afghanistan. Dost Mohammad died in 1863, weeks after
his last campaign to unite Afghanistan, and as a result,
threw Afghanistan back into civil war with his successors. During this time, Afghanistan became a
buffer state
A buffer state is a country geographically lying between two rival or potentially hostile great powers. Its existence can sometimes be thought to prevent conflict between them. A buffer state is sometimes a mutually agreed upon area lying between ...
in the
Great Game
The Great Game is the name for a set of political, diplomatic and military confrontations that occurred through most of the 19th century and the beginning of the 20th century – involving the rivalry of the British Empire and the Russian Empi ...
between the
British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
(in
British-ruled India) and the
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
. From India, the British attempted to subjugate Afghanistan but were repelled in the
First Anglo-Afghan War
The First Anglo-Afghan War ( fa, جنگ اول افغان و انگلیس) was fought between the British Empire and the Emirate of Kabul from 1838 to 1842. The British initially successfully invaded the country taking sides in a succession d ...
. However, the
Second Anglo-Afghan War
The Second Anglo-Afghan War (Dari: جنگ دوم افغان و انگلیس, ps, د افغان-انګرېز دويمه جګړه) was a military conflict fought between the British Raj and the Emirate of Afghanistan from 1878 to 1880, when the l ...
saw a British victory and the successful establishment of British political influence over Afghanistan. Following the
Third Anglo-Afghan War
The Third Anglo-Afghan War; fa, جنگ سوم افغان-انگلیس), also known as the Third Afghan War, the British-Afghan War of 1919, or in Afghanistan as the War of Independence, began on 6 May 1919 when the Emirate of Afghanistan inv ...
in 1919, Afghanistan became free of foreign dominance, and eventually emerged as the independent
Kingdom of Afghanistan
The Kingdom of Afghanistan ( ps, , Dǝ Afġānistān wākmanān; prs, پادشاهی افغانستان, Pādešāhī-ye Afġānistān) was a constitutional monarchy in Central Asia established in 1926 as a successor state to the Emirate of A ...
in June 1926 under
Amanullah Khan
Ghazi Amanullah Khan ( Pashto and Dari: ; 1 June 1892 – 25 April 1960) was the sovereign of Afghanistan from 1919, first as Emir and after 1926 as King, until his abdication in 1929. After the end of the Third Anglo-Afghan War in August 1 ...
. This monarchy lasted almost 50 years, until
Zahir Shah
Mohammed Zahir Shah (Pashto/Dari: , 15 October 1914 – 23 July 2007) was the last king of Afghanistan, reigning from 8 November 1933 until he was deposed on 17 July 1973. Serving for 40 years, Zahir was the longest-serving ruler of Afghanistan s ...
was
overthrown in 1973, following which the
Republic of Afghanistan
A republic () is a "state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th c ...
was established.
Since the late 1970s, Afghanistan's history has been dominated by extensive warfare, including
coups, invasions, insurgencies, and civil wars which would end twice with the victory of the
Islamic fundamentalist
Islamic fundamentalism has been defined as a puritanical, revivalist, and reform movement of Muslims who aim to return to the founding scriptures of Islam. Islamic fundamentalists are of the view that Muslim-majority countries should return t ...
Taliban
The Taliban (; ps, طالبان, ṭālibān, lit=students or 'seekers'), which also refers to itself by its state name, the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a Deobandi Islamic fundamentalist, militant Islamist, jihadist, and Pasht ...
. In 1979 the
Soviet Union invaded Afghanistan.
Mujahideen fought against them in the
Soviet–Afghan War
The Soviet–Afghan War was a protracted armed conflict fought in the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan from 1979 to 1989. It saw extensive fighting between the Soviet Union and the Afghan mujahideen (alongside smaller groups of anti-Sovie ...
and
continued fighting amongst themselves following
Soviet withdrawal in 1989. The Taliban controlled most of the country by 1996, but their
Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan received little international recognition before its overthrow in the 2001
United States invasion of Afghanistan
In late 2001, the United States and its close allies invaded Afghanistan and toppled the Taliban government. The invasion's aims were to dismantle al-Qaeda, which had executed the September 11 attacks, and to deny it a safe base of operatio ...
. The Taliban returned to power in 2021 following Kabul's
capture by the Taliban and the concurrent overthrow of the
Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, ending the
2001–2021 war.
Although initially claiming to form an inclusive government for the country, the Taliban in September 2021 re-established the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan with an
interim government
A provisional government, also called an interim government, an emergency government, or a transitional government, is an emergency governmental authority set up to manage a political transition generally in the cases of a newly formed state or f ...
made up entirely of Taliban members; the regime currently remains internationally unrecognized.
Afghanistan is prominently rich in natural resources, including
lithium
Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid ...
,
iron
Iron () is a chemical element with Symbol (chemistry), symbol Fe (from la, Wikt:ferrum, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 element, group 8 of the periodic table. It is, Abundanc ...
,
zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
, and
copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
, amongst many others. It is also the world's largest producer of
opium, second largest producer of
cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae. The number of species within the genus is disputed. Three species may be recognized: '' Cannabis sativa'', '' C. indica'', and '' C. ruderalis''. Alternative ...
, and third largest of both
saffron
Saffron () is a spice derived from the flower of ''Crocus sativus'', commonly known as the "saffron crocus". The vivid crimson stigma and styles, called threads, are collected and dried for use mainly as a seasoning and colouring agent in ...
and
cashmere. The country is a member of the
South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation
The South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) is the regional intergovernmental organization and geopolitical union of states in South Asia. Its member states are Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan ...
and a founding member of the
Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
An organization or organisation (Commonwealth English; see spelling differences), is an entity—such as a company, an institution, or an association—comprising one or more people and having a particular purpose.
The word is derived from ...
. Due to the effects of war in recent decades, the country has dealt with high levels of
terrorism
Terrorism, in its broadest sense, is the use of criminal violence to provoke a state of terror or fear, mostly with the intention to achieve political or religious aims. The term is used in this regard primarily to refer to intentional violen ...
,
poverty, and
child malnutrition. Afghanistan's economy is the world's 96th-largest, with a
gross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is oft ...
(GDP) of $72.9 billion by
purchasing power parity; the country fares much worse in terms of per-capita GDP (PPP), ranking 169th out of 186 countries .
Etymology
Some scholars suggest that the
root
In vascular plants, the roots are the organs of a plant that are modified to provide anchorage for the plant and take in water and nutrients into the plant body, which allows plants to grow taller and faster. They are most often below the su ...
name "
''Afghān''" is derived from the
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
word ''
Aśvaka
The ''Aśvaka'' (Sanskrit: अश्वक), also known as the Ashvakan, Aśvakayana, or Asvayana and sometimes Latinised as Assacenii, Assacani, or Aspasioi, were a people who lived in what is now eastern Afghanistan and northern Khyber Pakhtun ...
n'' or ''Assakan'', which was the name used for ancient inhabitants of the
Hindu Kush
The Hindu Kush is an mountain range in Central and South Asia to the west of the Himalayas. It stretches from central and western Afghanistan, Quote: "The Hindu Kush mountains run along the Afghan border with the North-West Frontier Province ...
. ''Aśvakan'' literally means "horsemen", "horse breeders", or "
cavalrymen" (from ''
aśva
Ashva () is the Sanskrit word for a horse, one of the significant animals finding references in the Vedas as well as later Hindu scriptures. The word is cognate to Avestan (), Latin '' equus'', Ancient Greek (), Proto-Germanic *''ehwaz'', obsol ...
'' or ''aspa'', the
Sanskrit
Sanskrit (; attributively , ; nominally , , ) is a classical language belonging to the Indo-Aryan branch of the Indo-European languages. It arose in South Asia after its predecessor languages had diffused there from the northwest in the late ...
and
Avestan words for "
horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million yea ...
"). However, others such as Ibrahim Khan have contended that the word Afghan comes from
Bactrian.
Historically, the ethnonym ''Afghān'' was used to refer to ethnic
Pashtuns
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, پښتانه, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically r ...
.
The Arabic and Persian form of the name, ''Afġān'', was first attested in the 10th-century geography book ''
Hudud al-'Alam''. The last part of the name, "''
-stan
The suffix -stan ( fa, ـستان, translit=''stân'' after a vowel; ''estân'' or ''istân'' after a consonant), has the meaning of "a place abounding in" or "a place where anything abounds" in the Persian language. It appears in the names of ...
''", is a Persian suffix meaning "place of". Therefore, "Afghanistan" translates to "land of the Afghans", or "land of the Pashtuns" in a historical sense. According to the third edition of the ''
Encyclopedia of Islam
The ''Encyclopaedia of Islam'' (''EI'') is an encyclopaedia of the academic discipline of Islamic studies published by Brill. It is considered to be the standard reference work in the field of Islamic studies. The first edition was published i ...
'':
Ancient history

Many empires and kingdoms have also risen to power in Afghanistan, such as the
Greco-Bactrians
The Bactrian Kingdom, known to historians as the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom or simply Greco-Bactria, was a Hellenistic-era Greek state, and along with the Indo-Greek Kingdom, the easternmost part of the Hellenistic world in Central Asia and the India ...
,
Indo-Scythians
Indo-Scythians (also called Indo-Sakas) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples of Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into modern day Pakistan and Northwestern India from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th centu ...
,
Kushans,
Kidarites,
Hephthalites
The Hephthalites ( xbc, ηβοδαλο, translit= Ebodalo), sometimes called the White Huns (also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in Sanskrit as the ''Sveta-huna''), were a people who lived in Central Asia during th ...
,
Alkhons,
Nezaks,
Zunbils
Zunbil, also written as Zhunbil, or Rutbils of Zabulistan, was a royal dynasty south of the Hindu Kush in present southern Afghanistan region. They ruled from circa 680 AD until the Saffarid conquest in 870 AD. The Zunbil dynasty was founded by R ...
,
Turk Shahi
The Turk Shahis or Kabul Shahis were a dynasty of Western Turk, or mixed Turko- Hephthalite, origin, that ruled from Kabul and Kapisa to Gandhara in the 7th to 9th centuries AD.
They may have been of Khalaj ethnicity."The new rulers of Kabu ...
s,
Hindu Shahi
The Hindu Shahis (also known as Odi Shahis, Uḍi Śāhis, or Brahman Shahis, 822–1026 CE) were a dynasty that held sway over the Kabul Valley, Gandhara and western Punjab during the early medieval period in the Indian subcontinent. Details ...
s,
Lawiks,
Saffarids
The Saffarid dynasty ( fa, صفاریان, safaryan) was a Persianate dynasty of eastern Iranian origin that ruled over parts of Persia, Greater Khorasan, and eastern Makran from 861 to 1003. One of the first indigenous Persian dynasties to emer ...
,
Samanids People
Samanid
Samanid
Samanid
The Samanid Empire ( fa, سامانیان, Sāmāniyān) also known as the Samanian Empire, Samanid dynasty, Samanid amirate, or simply as the Samanids) was a Persianate Sunni Muslim empire, of Iranian dehqan orig ...
,
Ghaznavids,
Ghurids
The Ghurid dynasty (also spelled Ghorids; fa, دودمان غوریان, translit=Dudmân-e Ğurīyân; self-designation: , ''Šansabānī'') was a Persianate dynasty and a clan of presumably eastern Iranian Tajik origin, which ruled from the ...
,
Khalji
The Khalji or Khilji (Pashto: ; Persian: ) dynasty was a Turco-Afghan dynasty which ruled the Delhi sultanate, covering large parts of the Indian subcontinent for nearly three decades between 1290 and 1320.[Kartids
The Kart dynasty, also known as the Kartids ( fa, آل کرت), was a Sunni Muslim dynasty of Tajik origin closely related to the Ghurids, that ruled over a large part of Khorasan during the 13th and 14th centuries. Ruling from their capita ...]
, Lodi dynasty, Lodis, Sur Empire, Surs, Mughals, and finally, the Hotak dynasty, Hotak and Durrani Empire, Durrani dynasties, which marked the political origins of the modern state. Throughout millennia several cities within the modern day Afghanistan served as capitals of various empires, namely, Bactra (Balkh), Alexandria on the Oxus (Ai-Khanoum), Kapisi, Sigal, Sakastan, Sigal,
Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. Acco ...
, Kunduz, Zaranj, Firozkoh, Herat, Ghazna (Ghazni), Binban (Bamyan), and Kandahar.
The country has been home to various peoples through the ages, among them the ancient Iranian peoples who established the dominant role of Indo-Iranian languages in the region. At multiple points, the land has been incorporated within vast regional empires; among them the Achaemenid Empire, the Macedonian Empire, the
Maurya Empire, and the Islamic Empire. For its success in resisting foreign occupation during the 19th and 20th centuries, Afghanistan has been called the "Graveyard of empires (Afghanistan), graveyard of empires", though it is unknown who coined the phrase.
Prehistory and antiquity
Excavations of prehistoric sites suggest that humans were living in what is now Afghanistan at least 50,000 years ago, and that farming communities in the area were among the earliest in the world. An important site of early historical activities, many believe that Afghanistan compares to Egypt in terms of the historical value of its archaeological sites.

Ancient era
Archaeological exploration done in the 20th century suggests that the geographical area of Afghanistan has been closely connected by culture and trade with its neighbors to the east, west, and north. Artifacts typical of the Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic, Bronze Age, Bronze, and Iron Ages have been found in Afghanistan. Urban civilization is believed to have begun as early as 3000 BCE, and the early city of Mundigak (near Kandahar in the south of the country) was a center of the Helmand culture. More recent findings established that the Indus Valley Civilisation stretched up towards modern-day Afghanistan, making the ancient civilization today part of Pakistan, Afghanistan, and India. In more detail, it extended from what today is northwest Pakistan to northwest India and northeast Afghanistan. An Indus Valley site has been found on the Oxus River at Shortugai in northern Afghanistan.
There are several smaller IVC colonies to be found in Afghanistan as well. An Indus Valley site has been found on the Oxus River at Shortugai in northern Afghanistan, shows Afghanistan to have been a part of Indus Valley civilisation.
After 2000 BCE, successive waves of semi-nomadic people from Central Asia began moving south into Afghanistan; among them were many Indo-European languages, Indo-European-speaking Indo-Iranians. These tribes later migrated further into South Asia, Western Asia, and toward Europe via the area north of the Caspian Sea. The region at the time was referred to as Ariana.

By the middle of the 6th century BCE, the Achaemenids overthrew the Medes and incorporated Arachosia, Aria (satrapy), Aria, and Bactria within its eastern boundaries. An Epigraphy, inscription on the tombstone of Darius I of Persia mentions the Kabulistan, Kabul Valley in a list of the 29 countries that he had conquered. The region of Arachosia, around Kandahar in modern-day southern Afghanistan, used to be primarily Zoroastrian and played a key role in the transfer of the Avesta to Persis, Persia and is thus considered by some to be the "second homeland of Zoroastrianism".
Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
and his Macedonian forces arrived in Afghanistan in 330 BCE after defeating Darius III of Persia a year earlier in the Battle of Gaugamela. Following Alexander's brief occupation, the successor state of the Seleucid Empire controlled the region until 305 BCE when they gave much of it to the
Maurya Empire as part of an alliance treaty. The Mauryans controlled the area south of the
Hindu Kush
The Hindu Kush is an mountain range in Central and South Asia to the west of the Himalayas. It stretches from central and western Afghanistan, Quote: "The Hindu Kush mountains run along the Afghan border with the North-West Frontier Province ...
until they were overthrown in about 185 BCE. Their decline began 60 years after Ashoka's rule ended, leading to the Hellenistic reconquest by the
Greco-Bactrians
The Bactrian Kingdom, known to historians as the Greco-Bactrian Kingdom or simply Greco-Bactria, was a Hellenistic-era Greek state, and along with the Indo-Greek Kingdom, the easternmost part of the Hellenistic world in Central Asia and the India ...
. Much of it soon broke away from them and became part of the Indo-Greek Kingdom. They were defeated and expelled by the
Indo-Scythians
Indo-Scythians (also called Indo-Sakas) were a group of nomadic Iranian peoples of Scythian origin who migrated from Central Asia southward into modern day Pakistan and Northwestern India from the middle of the 2nd century BCE to the 4th centu ...
in the late 2nd century BCE.
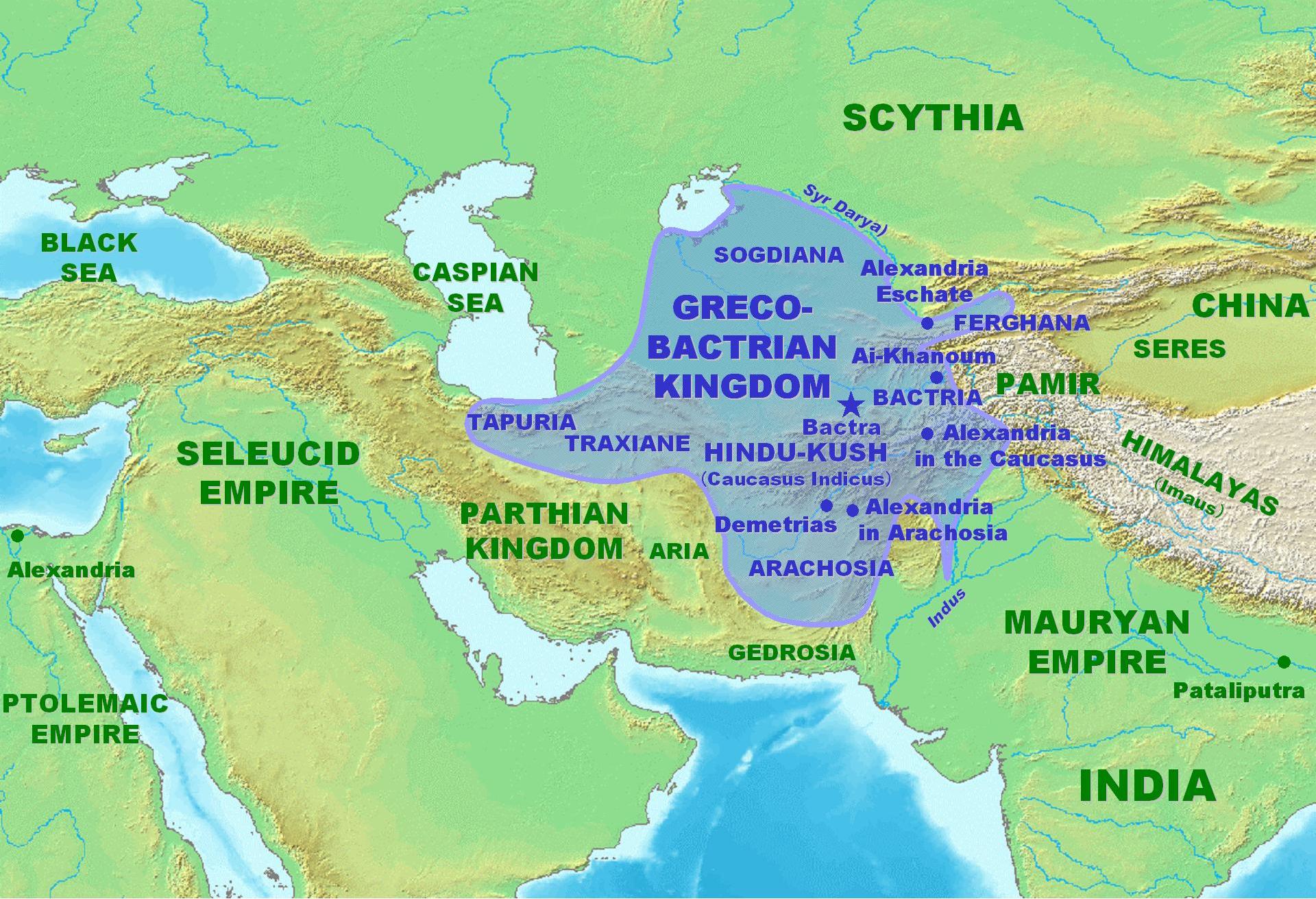
The
Silk Road appeared during the first century BCE, and Afghanistan flourished with trade, with routes to China, India, Persia and north to the cities of Bukhara, Samarkand and Khiva in present-day Uzbekistan. Goods and ideas were exchanged at this center point, such as Chinese silk, Persian silver and Roman gold, while the region of present Afghanistan was mining and trading lapis lazuli stones mainly from the Badakhshan region.
During the first century BCE, the Parthian Empire subjugated the region but lost it to their Indo-Parthian vassals. In the mid-to-late first century CE the vast Kushan Empire, centered in Afghanistan, became great patrons of Buddhist culture, making Buddhism flourish throughout the region. The Kushans were overthrown by the Sassanids in the 3rd century CE, though the Indo-Sassanids continued to rule at least parts of the region. They were followed by the Kidarites who, in turn, was replaced by the
Hephthalites
The Hephthalites ( xbc, ηβοδαλο, translit= Ebodalo), sometimes called the White Huns (also known as the White Hunas, in Iranian as the ''Spet Xyon'' and in Sanskrit as the ''Sveta-huna''), were a people who lived in Central Asia during th ...
. They were replaced by the
Turk Shahi
The Turk Shahis or Kabul Shahis were a dynasty of Western Turk, or mixed Turko- Hephthalite, origin, that ruled from Kabul and Kapisa to Gandhara in the 7th to 9th centuries AD.
They may have been of Khalaj ethnicity."The new rulers of Kabu ...
in the 7th century. The Buddhist Turk Shahi of Kabul was replaced by a Hindu dynasty before the Saffarids conquered the area in 870, this Hindu dynasty was called
Hindu Shahi
The Hindu Shahis (also known as Odi Shahis, Uḍi Śāhis, or Brahman Shahis, 822–1026 CE) were a dynasty that held sway over the Kabul Valley, Gandhara and western Punjab during the early medieval period in the Indian subcontinent. Details ...
. Much of the northeastern and southern areas of the country remained dominated by Buddhist culture.
Medieval history
Islamic conquest

Arab Muslims brought Islam to Herat and Zaranj in 642 CE and began spreading eastward; some of the native inhabitants they encountered accepted it while others revolted. Before the Islamic conquest of Afghanistan, arrival of Islam, the region used to be home to various beliefs and cults, often resulting in Syncretism between the dominant religions such as
Zoroastrianism
Zoroastrianism is an Iranian religion and one of the world's oldest organized faiths, based on the teachings of the Iranian-speaking prophet Zoroaster. It has a dualistic cosmology of good and evil within the framework of a monotheisti ...
,
Buddhism or Greco-Buddhism, Ancient Iranian religions,
Hinduism, Christianity and Judaism.
An exemplification of the syncretism in the region would be that people were patrons of Buddhism but still worshipped local Iranian gods such as Ahura Mazda, Nana (Kushan goddess), Lady Nana, Anahita or Mithra, Mihr(Mithra) and portrayed Greek mythology, Greek Gods like Heracles or Tyche as protectors of Buddha.
The
Zunbils
Zunbil, also written as Zhunbil, or Rutbils of Zabulistan, was a royal dynasty south of the Hindu Kush in present southern Afghanistan region. They ruled from circa 680 AD until the Saffarid conquest in 870 AD. The Zunbil dynasty was founded by R ...
and Kabul Shahi were first conquered in 870 CE by the Saffarid dynasty, Saffarid Muslims of Zaranj. Later, the
Samanids People
Samanid
Samanid
Samanid
The Samanid Empire ( fa, سامانیان, Sāmāniyān) also known as the Samanian Empire, Samanid dynasty, Samanid amirate, or simply as the Samanids) was a Persianate Sunni Muslim empire, of Iranian dehqan orig ...
extended their Islamic influence south of the Hindu Kush. It is reported that Muslims and non-Muslims still lived side by side in Kabul before the
Ghaznavids rose to power in the 10th century.
By the 11th century, Mahmud of Ghazni defeated the remaining Hindu rulers and effectively Islamized the wider region, with the exception of Kafiristan.
Mahmud made Ghazni into an important city and patronized intellectuals such as the historian Al-Biruni and the poet Ferdowsi. The Ghaznavid dynasty was Siege of Lahore (1186), overthrown by the Ghurids in 1186, whose architectural achievements included the remote Minaret of Jam. The Ghurids controlled Afghanistan for less than a century before being conquered by the Khwarazmian dynasty in 1215.
Mongols and Babur with the Lodi Dynasty

In 1219 CE, Genghis Khan and his Mongol invasion of the Khwarazmian Empire, Mongol army overran the region. His troops are said to have annihilated the Khwarazmian cities of Herat and Balkh as well as Bamyan, Afghanistan, Bamyan. The destruction caused by the Mongols forced many locals to return to an agrarian rural society. Mongol rule continued with the Ilkhanate in the northwest while the Khalji dynasty administered the Afghan tribal areas south of the Hindu Kush until the invasion of Timur (aka Tamerlane), who established the Timurid Empire in 1370. Under the rule of Shah Rukh the city served as the focal point of the Timurid Renaissance, whose glory matched Florence of the Italian Renaissance as the center of a cultural rebirth.
In the early 16th century, Babur arrived from Ferghana and captured Kabul from the Arghun dynasty. Babur would go on to conquer the Afghan Lodi dynasty who had ruled the Delhi Sultanate in the First Battle of Panipat. Between the 16th and 18th century, the Uzbek Khanate of Bukhara, Iranian Safavids, and Indian Mughals ruled parts of the territory. During the Medieval Period, the northwestern area of Afghanistan was referred to by the regional name Greater Khorasan, Khorasan. Two of the four capitals of Khorasan (Herat and Balkh) are now located in Afghanistan, while the regions of Kandahar Province, Kandahar, Zabulistan, Ghazni, Kabulistan, and name of Afghanistan, Afghanistan formed the frontier between Khorasan and Hindustan. However, up to the 19th century the term Khorasan was commonly used among natives to describe their country; Sir George Elphinstone wrote with amazement that the country known to outsiders as "Afghanistan" was referred to by its own inhabitants as "Khorasan" and that the first Afghan official whom he met at the border welcomed him to Khorasan.
Modern history
Hotak Dynasty

In 1709, Mirwais Hotak, a local Ghilzai tribal leader, successfully rebelled against the Safavids. He defeated Gurgin Khan and established his own kingdom.
Mirwais died of natural causes in 1715 and was succeeded by his brother Abdul Aziz Hotak, Abdul Aziz, who was soon killed by Mirwais' son Mahmud Hotak, Mahmud for possibly planning to concede territories back to the Safavids. Mahmud led the Afghan army in 1722 to the Persian capital of Isfahan, captured the city after the Battle of Gulnabad and proclaimed himself King of Persia.
The Afghan dynasty was ousted from Persia by Nader Shah after the 1729 Battle of Damghan (1729), Battle of Damghan.
Fall of the Hotak Dynasty

In 1738, Nader Shah and his Afsharid dynasty, forces captured Kandahar in the Siege of Kandahar, the last Hotak stronghold, from Shah Hussain Hotak. Soon after, the Persian and Afghan forces Nader Shah's invasion of India, invaded India, Nader Shah had plundered Delhi, alongside his 16 year old commander,
Ahmad Shah Durrani who had assisted him on these campaigns. Nader Shah was assassinated in 1747.
Rise of the Durrani Empire
After the death of Nader Shah in 1747,
Ahmad Shah Durrani had returned to Kandahar with a contingent of 4,000
Pashtuns
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, پښتانه, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically r ...
. The Abdalis had "unanimously accepted" Ahmad Shah as their new leader. With his acension in 1747, Ahmad Shah had led multiple campaigns against the Mughal Empire, Maratha Empire, and then receding, Afsharid Empire. Ahmad Shah had captured
Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. Acco ...
and Peshawar from the Mughal appointed governor, Nasir Khan. Ahmad Shah had then conquered Herat in 1750, and had also captured Kashmir in 1752. Ahmad Shah had launched two campaigns into Greater Khorasan, Khorasan, (1750–1751) and (1754–1755).
His first campaign had seen the siege of Mashhad, however he was forced to retreat after 4 months. In November 1750, he moved to siege Khanate of Nishapur, Nishapur, however he was unable to capture the city and was forced to retreat in early 1751. Ahmad Shah returned in 1754, he captured Ferdows, Tun, and on 23 July, he sieged Mashhad once again. Mashhad had fallen on 2 December, however Shah rokh was reappointed in 1755. He was forced to give up Torshiz, Bakharz, Torbat-e Jam, Jam, Khaf, Iran, Khaf, and Torbat-e Heydarieh, Turbat-e Haidari to the Afghans. Following this, Ahmad Shah had sieged Khanate of Nishapur, Nishapur once again, and captured it.
Objectives and Invasions of India

Ahmad Shah invaded India 8 times during his reign. With the capture of Peshawar, Ahmad Shah had used this as a convenient striking point to lead his military campaigns into Punjab and India.
Ahmad Shah had sought out multiple reasons for his invasions, Ahmad Shah saw Afghanistan in a dire state, and one that needed to expand and exploit a weak but rich neighboring country, which Ahmad Shah had capitalized on in multiple opportunities during his Invasions of India, he sought the reasons needed to fill his treasury in a war-plunder conquest based economy. Ahmad Shah had launched his first invasion in 1748, crossing the indus river, his armies sacked and absorbed Lahore into the Durrani Empire, Durrani Realm. Ahmad Shah had met Mughal armies at the Battle of Manupur (1748), where he was defeated and forced to retreat to back to Afghanistan. Ahmad Shah had returned the next year in 1749, where he had captured the area around Lahore and Punjab, presenting it as an Afghan victory for this campaign. From 1749 to 1767, Ahmad Shah would lead 6 more invasions, the most important being his sixth invasion, with the Third Battle of Panipat, which created a power vacuum in northern India, halting Maratha Empire, Maratha expansion.
Death of Ahmad Shah and his Successors
Ahmad Shah Durrani had died in October 1772, what followed would be a civil war in succession, with his named successor, Timur Shah Durrani succeeding him after the defeat of his brother, Suleiman Mirza.
Timur Shah Durrani ascended to the throne in November 1772, having defeated a coalition under Shah Wali Khan, the influential prime minister of the Durrani Empire, and Humayun Mirza. Timur Shah began his reign by consolidating power toward himself and people loyal to him, purging Durrani Sardars and influential tribal leaders in
Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. Acco ...
and Kandahar to bring support toward himself. Timur Shah's reforms also saw the capital of the Durrani Empire being shifted from Kandahar to
Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. Acco ...
, being able to cover the empire better as a base of ordination since it was essentially the heartland of the empire. This reform saw
Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. Acco ...
as the modern capital of Afghanistan today. Having consolidated power to himself, Timur Shah would fight multiple series of rebellions to consolidate and hold the empire apart, Timur Shah would also lead campaigns into Punjab against the Sikhs like his father did, however being more successful. Most prominent example of his battles during this campaign would be where Timur Shah led his forces under Zangi Khan Durrani, with over 18,000 men total of Afghan, Qizilbash, and Mongol cavalrymen. Against over 60,000 Sikh men. The Sikhs would lose over 30,000 in this battle and would stage a Durrani resurgence in Punjab.
The Durranis lost Multan in 1772 after Ahmad Shah's death, following this victory by Timur Shah, Timur Shah was able to lay siege to Multan and recapture it, incorporating it into the Durrani empire once again, reintegrating it as a province until the Siege of Multan (1818). Timur Shah would be succeeded by his son, Zaman Shah Durrani after his death on 18 or 20 May 1793. Timur Shah's reign oversaw the attempted stabilization and consolidation of the empire. However, Timur Shah had over 24 sons, a mistake that would plunge the empire in civil war over succession crises.
Zaman Shah Durrani would succeed to the Durrani Empire, Durrani Throne following the death of his father, Timur Shah Durrani. This instigated civil war with his brothers, Mahmud Shah Durrani, and Humayun Mirza revolting against him. With Humayun centered in Kandahar, and Mahmud Shah centered in Herat. Zaman Shah would defeat Humayun and also force the loyalty of Mahmud Shah Durrani. Securing his position on the throne, Zaman Shah had led 3 campaigns into Punjab, with the first two campaigns capturing Lahore, but being forced to retreat due to issues from a possible Qajar Iran, Qajar invasion, or his brother, Mahmud Shah Durrani revolting. Zaman Shah embarked on his third campaign for Punjab in 1800 to deal with a rebellious Ranjit Singh. However, he was forced to withdraw, with his brother, Mahmud Shah Durrani revolting, Zaman Shah would be toppled from his reign, replaced by his brother, Mahmud Shah Durrani. However, just under 2 years in his reign, Mahmud Shah Durrani would be deposed by his brother, Shah Shuja Durrani, on 13 July 1803. Shah Shuja would attempt to consolidate the Durrani Empire, Durrani Realm, which had been long striven by civil war. Shah Shuja would later be deposed by his brother at the Battle of Nimla (1809), where Mahmud Shah Durrani would defeat and force Shah Shuja to flee, with Shah Mahmud usurping the throne again for his second reign beginning on 3 May 1809.
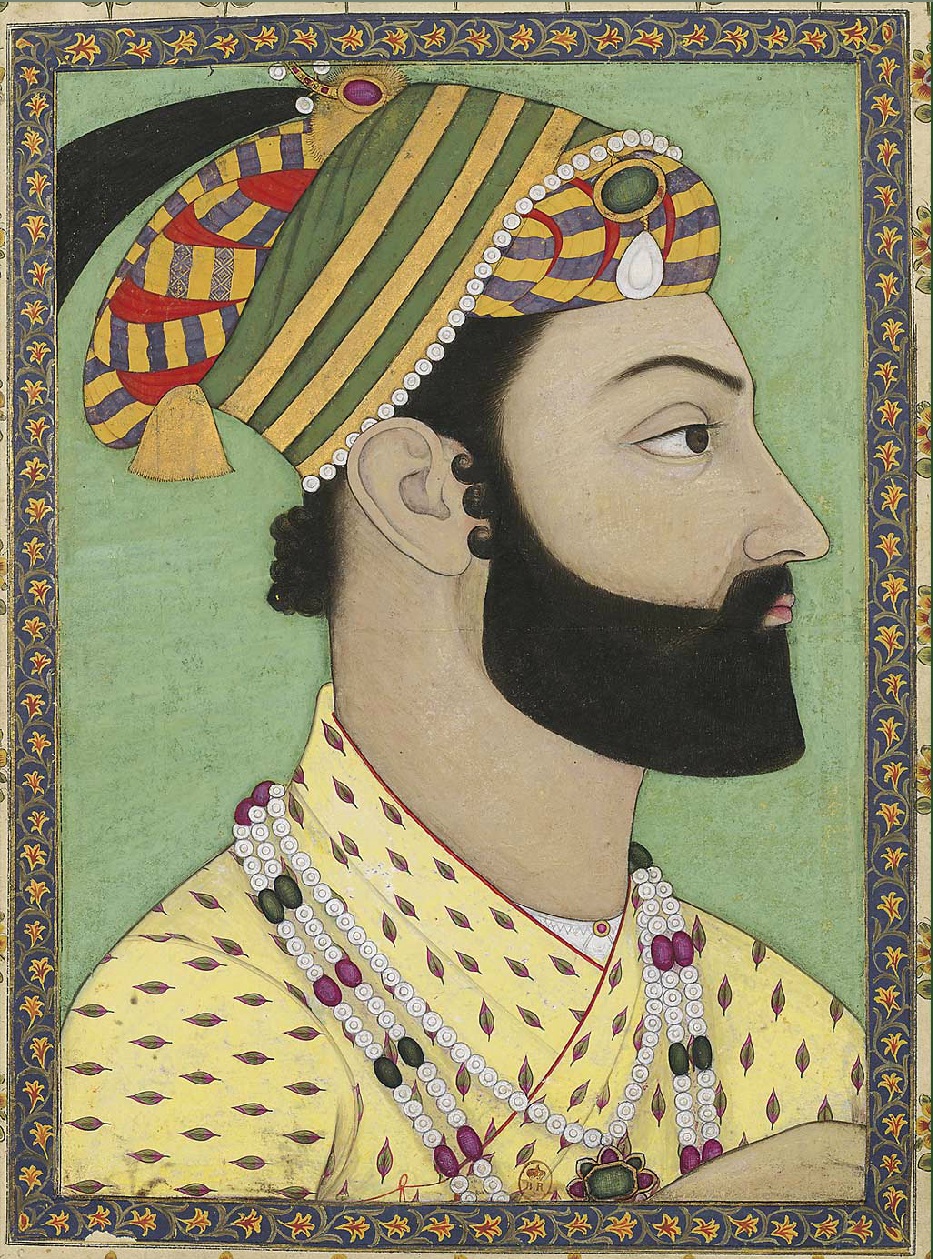
Barakzai dynasty and British wars

By the early 19th century, the Afghan empire was under threat from the Qajar dynasty, Persians in the west and the Sikh Empire in the east. Fateh Khan, leader of the Barakzai dynasty, Barakzai tribe, installed many of his brothers in positions of power throughout the empire, mostly ruling as governors of major cities and provinces. After his murder for apparent treason against the Durrani king. Fateh Khan would be sentenced by Mahmud Shah Durrani, having him executed. His brothers rebelled and divided up the provinces of the empire between themselves. During this turbulent period, Afghanistan had fractured into many states, this included the Principality of Qandahar, Herat (1793–1863), Emirate of Herat, Khanate of Qunduz, Maimana Khanate, and many more states. The most prominent state being the Emirate of Afghanistan, Emirate of Kabul, ruled by Dost Mohammad Khan after he declared himself emir and was bestowed upon the title of Amir al-Mu'minin in summer 1826 following a usurpation of the throne from his brother, Sultan Mohammad Khan.
With the collapse of the Durrani Empire, and the exile of the Sadozai Dynasty while Afghanistan was in this turbulent period of civil war, Punjab and Kashmir were lost to Ranjit Singh ruler of the Sikh Empire, who invaded Khyber Pakhtunkhwa in March 1823 and captured the city of Peshawar from the Peshawar Sardars (one of the many entities that split following the collapse of the Durrani Empire), at the Battle of Nowshera.
In 1837, Dost Mohammad Khan attempted to retake Peshawar and sent a large force under his son, Wazir Akbar Khan, leading to the Battle of Jamrud near the Khyber Pass. Wazir Akbar Khan, Akbar Khan and the Afghan army failed to capture the Jamrud Fort from the Sikh Khalsa Army, but killed Sikh Commander Hari Singh Nalwa, thus ending the Afghan-Sikh Wars. By this time the British were advancing from the east, conquering the Sikh Empire after it had its own period of turbulence following the death of Ranjit Singh, directly bringing the Emirate of Afghanistan, Emirate of Kabul to conflict in the First Anglo-Afghan War, first major conflict during "the Great Game".
In 1838, a British Army, British expeditionary force marched into Afghanistan, invading the Principality of Qandahar, and in August 1839, seized
Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. Acco ...
, forcing Dost Mohammad into exile with other factions and rebels in Afghanistan, while he was replaced with the former Durrani ruler Shah Shuja Durrani, Shah Shuja List of heads of state of Afghanistan, Durrani as the new ruler of
Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. Acco ...
, and unbeknownst to him, a de facto puppet on the throne.
[In Defence of British India: Great Britain in the Middle East, 1775–1842]
By Edward Ingram. Frank Cass & Co, London, 1984. . p7-19 Following an uprising that saw the assassination of Shah Shuja Durrani, Shah Shuja, the 1842 retreat from Kabul of British-Indian forces and the 1842 retreat from Kabul, annihilation of William George Keith Elphinstone, Elphinstone's army, and the punitive expedition of Battle of Kabul (1842), The battle of Kabul that led to its sacking, the British gave up on their attempts to try and subjugate Afghanistan, and allowed Dost Mohammad Khan to return as ruler and withdrew their military forces from Afghanistan. Dost Mohammad Khan would spend most of his reign consolidating the parts of Afghanistan that were lost in the Durrani-Barakzai civil wars. Dost Mohammad Khan would launch numerous campaigns after returning to rule in 1842, ruling only from Kabul, Ghazni, and other cities when he had returned. Dost Mohammad united most of the Afghan realm in his reign, securing the last major state,
Herat
Herāt (; Persian: ) is an oasis city and the third-largest city of Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Selseleh-ye Safē ...
, in the Herat Campaign of 1862–63. Dost Mohammad died on 9 June 1863, a few weeks after his Herat Campaign of 1862–63, campaign to capture
Herat
Herāt (; Persian: ) is an oasis city and the third-largest city of Afghanistan. In 2020, it had an estimated population of 574,276, and serves as the capital of Herat Province, situated south of the Paropamisus Mountains (''Selseleh-ye Safē ...
. Dost Mohammad's successors would fight for the throne of Afghanistan, between Sher Ali Khan, Mohammad Afzal Khan, and Mohammad Azam Khan in the Afghan Civil War (1863–1869). Sher Ali would win this civil war and would go on to rule the realm until In 1878, the British had returned in the
Second Anglo-Afghan War
The Second Anglo-Afghan War (Dari: جنگ دوم افغان و انگلیس, ps, د افغان-انګرېز دويمه جګړه) was a military conflict fought between the British Raj and the Emirate of Afghanistan from 1878 to 1880, when the l ...
which was fought over perceived Russian influence in the region, Abdur Rahman Khan replaced Mohammad Ayub Khan (Emir of Afghanistan), Ayub Khan who had succeeded Sher Ali Khan after his death in 1879. Britain would gain control of Afghanistan's foreign relations as part of the Treaty of Gandamak of 1879, making it an official British Protectorate, British Protected State. In 1893, Amir Abdur Rahman signed an agreement in which the ethnic Pashtun and Baloch people, Baloch territories were divided by the Durand Line, which forms the modern-day border between Pakistan and Afghanistan. Shia Islam in Afghanistan, Shia-dominated Hazarajat and pagan Kafiristan remained politically independent until being Muslim conquests of Afghanistan, conquered by Abdur Rahman Khan in 1891–1896. He was known as the "Iron Amir" for his features and his ruthless methods against tribes. The ''Iron Amir'' viewed railway and telegraph lines coming from the Russian and British as "trojan horses" and therefore prevented railway development in Afghanistan. He died in 1901, succeeded by his son, Habibullah Khan.

During the First World War, when Afghanistan was neutral, Habibullah Khan was met by officials of the Central Powers in the Niedermayer–Hentig Expedition, to declare full independence from the United Kingdom, join them and attack British India, as part of the Hindu–German Conspiracy. Their efforts to bring Afghanistan into the Central Powers failed, but it caused discontent among the population for keeping neutrality against the British. Habibullah was assassinated during a hunting trip in February 1919, and
Amanullah Khan
Ghazi Amanullah Khan ( Pashto and Dari: ; 1 June 1892 – 25 April 1960) was the sovereign of Afghanistan from 1919, first as Emir and after 1926 as King, until his abdication in 1929. After the end of the Third Anglo-Afghan War in August 1 ...
eventually assumed power. A staunch supporter of the 1915–1916 expeditions, Amanullah Khan provoked the
Third Anglo-Afghan War
The Third Anglo-Afghan War; fa, جنگ سوم افغان-انگلیس), also known as the Third Afghan War, the British-Afghan War of 1919, or in Afghanistan as the War of Independence, began on 6 May 1919 when the Emirate of Afghanistan inv ...
, entering British India via the Khyber Pass.

After the end of the Third Anglo-Afghan War and the signing of the Anglo-Afghan Treaty of 1919, Treaty of Rawalpindi on 19 August 1919, Emir of Afghanistan, Emir Amanullah Khan declared the Emirate of Afghanistan a sovereign state, sovereign and fully independent state. He moved to end his country's traditional isolation by establishing diplomatic relations with the international community, particularly with the Soviet Union and the Weimar Republic of Germany. He proclaimed himself King of Afghanistan on 9 June 1926, when the Emirate of Afghanistan became the
Kingdom of Afghanistan
The Kingdom of Afghanistan ( ps, , Dǝ Afġānistān wākmanān; prs, پادشاهی افغانستان, Pādešāhī-ye Afġānistān) was a constitutional monarchy in Central Asia established in 1926 as a successor state to the Emirate of A ...
. Following a 1927–28 tour of Europe and Turkey, he introduced several reforms intended to modernize his nation. A key force behind these reforms was Mahmud Tarzi, an ardent supporter of the education of women. He fought for Article 68 of Afghanistan's 1923 constitution of Afghanistan, constitution, which made elementary education compulsory. The institution of slavery was abolished in the Emirate of Afghanistan in 1923. King Amanullah's wife, Soraya Tarzi, Queen Soraya, was an important figure during this period in the fight for woman's education and against their oppression.
Some of the reforms that were put in place, such as the abolition of the traditional burqa for women and the opening of several co-educational schools, quickly alienated many tribal and religious leaders, and this led to the Afghan Civil War (1928–1929). Faced with the overwhelming armed opposition, King Amanullah abdicated in January 1929, and soon after Kabul fell to Saqqawist forces led by Habibullah Kalakani. Prince Mohammed Nadir Shah, Amanullah's cousin, in turn defeated and killed Kalakani in October 1929, and was declared King Nadir Shah. He abandoned the reforms of King Amanullah in favor of a more gradual approach to modernization, but was assassinated in 1933 by Abdul Khaliq Hazara (assassin), Abdul Khaliq, a fifteen-year-old Hazara people, Hazara student who was an Amanullah loyalist.
Mohammed Zahir Shah, Nadir Shah's 19-year-old son, succeeded to the throne and reigned as King from 1933 to 1973. The Afghan tribal revolts of 1944–1947, tribal revolts of 1944–1947 saw King Zahir's reign challenged by Zadran (Pashtun tribe), Zadran, Safi (Pashtun tribe), Safi, Mangal (Pashtun tribe), Mangal, and Wazir (Pashtun tribe), Wazir tribesmen led by Mazrak Zadran, Salemai, and Faqir Ipi, Mirzali Khan, among others, many of whom were Amanullah loyalists. Close relations with the Muslim states Turkey, the Hashemite Kingdom of Iraq and Pahlavi dynasty, Iran/Persia were also pursued, while further international relations were sought by joining the League of Nations in 1934. The 1930s saw the development of roads, infrastructure, the founding of a Da Afghanistan Bank, national bank, and increased education. Road links in the north played a large part in a growing cotton and textile industry.
The country built close relationships with the Axis powers, with Nazi Germany having the largest share in Afghan development at the time, along with the Kingdom of Italy and the Empire of Japan.
Contemporary history

Until 1946, King Zahir ruled with the assistance of his uncle, who held the post of Prime Minister of Afghanistan, Prime Minister and continued the policies of Nadir Shah. Another of Zahir Shah's uncles, Shah Mahmud Khan, became Prime Minister in 1946 and began an experiment allowing greater political freedom, but reversed the policy when it went further than he expected. He was replaced in 1953 by Mohammed Daoud Khan, the king's cousin and brother-in-law, and a Pashtun nationalist who sought the creation of a Pashtunistan, leading to highly tense relations with Pakistan. During his ten years at the post until 1963, Daoud Khan pressed for social modernization reforms and sought a closer relationship with the Soviet Union. Afterward, the 1964 Constitution of Afghanistan, 1964 constitution was formed, and the first non-royal Prime Minister was sworn in.
King Zahir Shah, like his father Nadir Shah, had a policy of maintaining national independence while pursuing gradual modernization, creating nationalist feeling, and improving relations with the United Kingdom. However, Afghanistan remained neutral and was neither a participant in World War II nor aligned with either power bloc in the Cold War thereafter. However, it was a beneficiary of the latter rivalry as both the Soviet Union and the United States vied for influence by building Afghanistan's main highways, airports, and other vital infrastructure in the post-war period. On a per capita basis, Afghanistan received more Soviet development aid than any other country. Afghanistan had, therefore, good relations with both Cold War enemies. In 1973, while the King was in Italy, Daoud Khan launched a 1973 Afghan coup, bloodless coup and became the first President of Afghanistan, abolishing the monarchy.
Democratic Republic and Soviet war
In April 1978, the communist People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan (PDPA) seized power in a bloody coup d'état against then-President Mohammed Daoud Khan, in what is called the Saur Revolution. The PDPA declared the establishment of the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan, with its first leader named as People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan, People's Democratic Party general secretary Nur Muhammad Taraki. This would trigger a series of events that would dramatically turn Afghanistan from a poor and secluded (albeit peaceful) country to a hotbed of international terrorism. The PDPA initiated various social, symbolic and land distribution reforms that provoked strong opposition, while also brutally oppressing political dissidents. This caused unrest and quickly expanded into a state of War in Afghanistan (1978–present), civil war by 1979, waged by guerrilla ''mujahideen'' (and smaller Maoist guerrillas) against regime forces countrywide. It quickly turned into a proxy war as the Pakistani government provided these rebels with covert training centers, the United States Operation Cyclone, supported them through Pakistan's Inter-Services Intelligence (ISI),
and the Soviet Union sent thousands of military advisers to support the PDPA regime. Meanwhile, there was increasingly hostile friction between the competing factions of the PDPA – the dominant Khalq and the more moderate Parcham.
In September 1979, PDPA General Secretary Taraki was assassinated in an internal coup orchestrated by fellow Khalq member, then-prime minister Hafizullah Amin, who assumed the new general secretary of the People's Democratic Party of Afghanistan, People's Democratic Party. The situation in the country deteriorated under Amin and thousands of people went missing. Displeased with Amin's government, the Soviet Army invaded the country in December 1979, heading for Kabul and killing Amin just three days later. A Soviet-organized regime, led by Parcham's Babrak Karmal but inclusive of both factions (Parcham and Khalq), filled the vacuum. Soviet troops in more substantial numbers were deployed to stabilize Afghanistan under Karmal, marking the beginning of the
Soviet–Afghan War
The Soviet–Afghan War was a protracted armed conflict fought in the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan from 1979 to 1989. It saw extensive fighting between the Soviet Union and the Afghan mujahideen (alongside smaller groups of anti-Sovie ...
. The United States and Pakistan,
[ along with smaller actors like Saudi Arabia and China, continued supporting the rebels, delivering billions of dollars in cash and weapons including two thousand FIM-92 Stinger surface-to-air missiles.][UNICEF]
Land-mines: A deadly inheritance
and displaced about 6 million people who subsequently fled Afghanistan, mainly to Afghans in Pakistan, Pakistan and Afghans in Iran, Iran. Heavy air bombardment destroyed many countryside villages, millions of landmines were planted, and some cities such as Herat and Kandahar were also damaged from bombardment. Pakistan's Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, North-West Frontier Province functioned as an organizational and networking base for the anti-Soviet Afghan resistance, with the province's influential Deobandi ulama playing a major supporting role in promoting the 'jihad'. After the Soviet withdrawal from Afghanistan, Soviet withdrawal, the Afghan Civil War (1989-92), civil war ensued until the communist regime under People's Democratic Party leader Mohammad Najibullah collapsed in 1992.['Mujahidin vs. Communists: Revisiting the battles of Jalalabad and Khost]
. By Anne Stenersen: a Paper presented at the conference ''COIN in Afghanistan: From Mughals to the Americans'', Peace Research Institute Oslo (PRIO), 12–13 February 2012. Retrieved 1 February 2018.
The Soviet-Afghan War had drastic social effects on Afghanistan. The militarization of society led to heavily armed police, private bodyguards, openly armed civil defense groups and other such things becoming the norm in Afghanistan for decades thereafter. The traditional power structure had shifted from clergy, community elders, intelligentsia and military in favor of powerful warlords.
Post–Cold War conflict
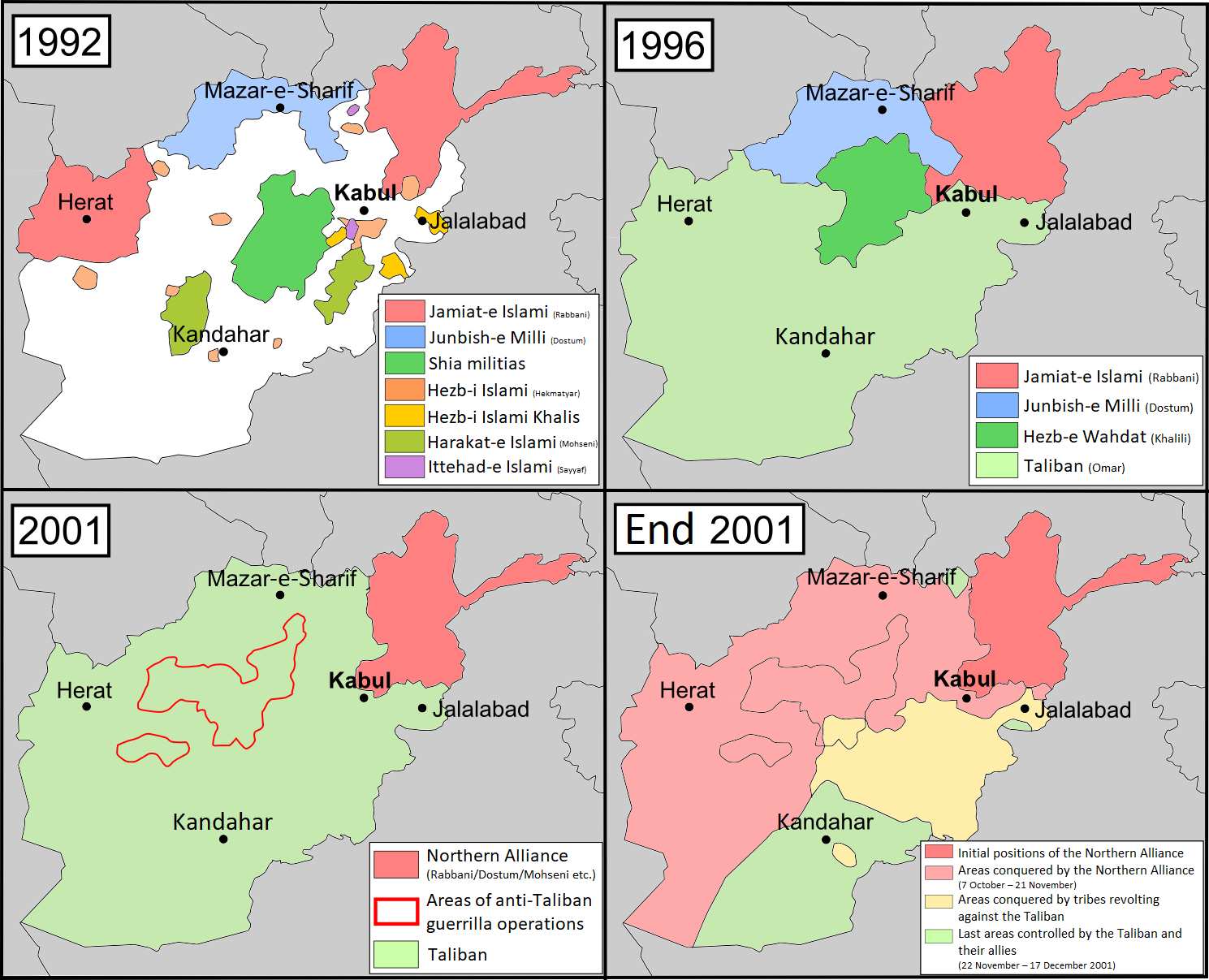 Another civil war broke out after the Peshawar Accords, creation of a dysfunctional coalition Islamic State of Afghanistan, government between leaders of various ''mujahideen'' factions. Amid a state of anarchy and factional infighting,
Another civil war broke out after the Peshawar Accords, creation of a dysfunctional coalition Islamic State of Afghanistan, government between leaders of various ''mujahideen'' factions. Amid a state of anarchy and factional infighting,[GUTMAN, Roy (2008): How We Missed the Story: Osama Bin Laden, the Taliban and the Hijacking of Afghanistan, Endowment of the United States Institute of Peace, 1st ed., Washington D.C.] various ''mujahideen'' factions committed widespread rape, murder and extortion,Taliban
The Taliban (; ps, طالبان, ṭālibān, lit=students or 'seekers'), which also refers to itself by its state name, the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a Deobandi Islamic fundamentalist, militant Islamist, jihadist, and Pasht ...
emerged in September 1994 as a movement and militia of students (''talib'') from Islamic Madrassas in Pakistan, madrassas (schools) in Pakistan,[Matinuddin, Kamal, ''The Taliban Phenomenon, Afghanistan 1994–1997'', Oxford University Press, (1999), pp. 25–26] who soon had military support from Pakistan.[Country profile: Afghanistan (published August 2008)]
(page 3). Library of Congress. Retrieved 13 February 2018. that gained international recognition from 3 countries: Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's second-lar ...
, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates. The Taliban were condemned internationally for the harsh enforcement of their interpretation of Islamic sharia law, which resulted in the brutal treatment of many Afghans, especially Taliban treatment of women, women.
US invasion and Islamic Republic
In October 2001, the United States invasion of Afghanistan, United States invaded Afghanistan to remove the Taliban from power after they refused to hand over Osama Bin Laden, the prime suspect of the September 11 attacks, who was a "guest" of the Taliban and was operating his al-Qaeda network in Afghanistan. In December 2001, after the Taliban government was overthrown, the Afghan Interim Administration under Hamid Karzai was formed. The International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) was established by the UN Security Council to help assist the Karzai administration and provide basic security. By this time, after two decades of war as well as an acute famine at the time, Afghanistan had one of the highest infant mortality, infant and child mortality rates in the world, the lowest life expectancy, much of the population were hungry, and infrastructure was in ruins. Many foreign donors started providing aid and assistance to rebuild the war-torn country.
Taliban forces meanwhile began regrouping inside Pakistan, while more coalition troops entered Afghanistan to help the Reconstruction in Afghanistan, rebuilding process. The Taliban insurgency, Taliban began an insurgency to regain control of Afghanistan. Over the next decade, ISAF and Afghan National Army, Afghan troops led many offensives against the Taliban, but failed to fully defeat them. Afghanistan remained one of the poorest countries in the world because of a lack of foreign investment, Corruption in Afghanistan, government corruption, and the Taliban insurgency.
Meanwhile, Karzai attempted to unite the peoples of the country, and the Afghan government was able to build some democratic structures, adopting a constitution in 2004 with the name Islamic Republic of Afghanistan. Attempts were made, often with the support of foreign donor countries, to improve the country's economy, healthcare, education, transport, and agriculture. ISAF forces also began to train the Afghan National Security Forces. Following 2002, nearly five million Afghan diaspora, Afghans were repatriated.
In December 2001, after the Taliban government was overthrown, the Afghan Interim Administration under Hamid Karzai was formed. The International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) was established by the UN Security Council to help assist the Karzai administration and provide basic security. By this time, after two decades of war as well as an acute famine at the time, Afghanistan had one of the highest infant mortality, infant and child mortality rates in the world, the lowest life expectancy, much of the population were hungry, and infrastructure was in ruins. Many foreign donors started providing aid and assistance to rebuild the war-torn country.
Taliban forces meanwhile began regrouping inside Pakistan, while more coalition troops entered Afghanistan to help the Reconstruction in Afghanistan, rebuilding process. The Taliban insurgency, Taliban began an insurgency to regain control of Afghanistan. Over the next decade, ISAF and Afghan National Army, Afghan troops led many offensives against the Taliban, but failed to fully defeat them. Afghanistan remained one of the poorest countries in the world because of a lack of foreign investment, Corruption in Afghanistan, government corruption, and the Taliban insurgency.
Meanwhile, Karzai attempted to unite the peoples of the country, and the Afghan government was able to build some democratic structures, adopting a constitution in 2004 with the name Islamic Republic of Afghanistan. Attempts were made, often with the support of foreign donor countries, to improve the country's economy, healthcare, education, transport, and agriculture. ISAF forces also began to train the Afghan National Security Forces. Following 2002, nearly five million Afghan diaspora, Afghans were repatriated.[
]
"Body Count – Casualty Figures after 10 Years of the 'War on Terror' – Iraq Afghanistan Pakistan"
(PDF), by IPPNW, Physicians for Global Survival, PGS and Physicians for Social Responsibility, PSR, First international edition (March 2015)
*
*
 On 19 February 2020, the US–Taliban deal was made in Qatar. The 2020 US–Taliban deal was one of the critical events that caused the collapse of the Afghan National Security Forces (ANSF);
On 19 February 2020, the US–Taliban deal was made in Qatar. The 2020 US–Taliban deal was one of the critical events that caused the collapse of the Afghan National Security Forces (ANSF);
Second Taliban era (2021–present)
On 14 April 2021, NATO Secretary General Jens Stoltenberg said the alliance had agreed to start Withdrawal of United States troops from Afghanistan (2020–2021), withdrawing its troops from Afghanistan by 1 May. Soon after the withdrawal of NATO troops started, the Taliban
The Taliban (; ps, طالبان, ṭālibān, lit=students or 'seekers'), which also refers to itself by its state name, the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a Deobandi Islamic fundamentalist, militant Islamist, jihadist, and Pasht ...
launched an 2021 Taliban offensive, offensive against the Afghan government, quickly advancing in front of collapsing Afghan government forces. On 15 August 2021, as the Taliban once again controlled a vast majority of Afghan territory, they Fall of Kabul (2021), re-captured the capital city of Kabul, and many civilians, government officials and foreign diplomats were evacuated. President Ghani fled Afghanistan that day. As of 16 August 2021, an unofficial Coordination Council led by senior statesmen was in the process of coordinating the transfer of the state institutions of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan to the Taliban.Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
.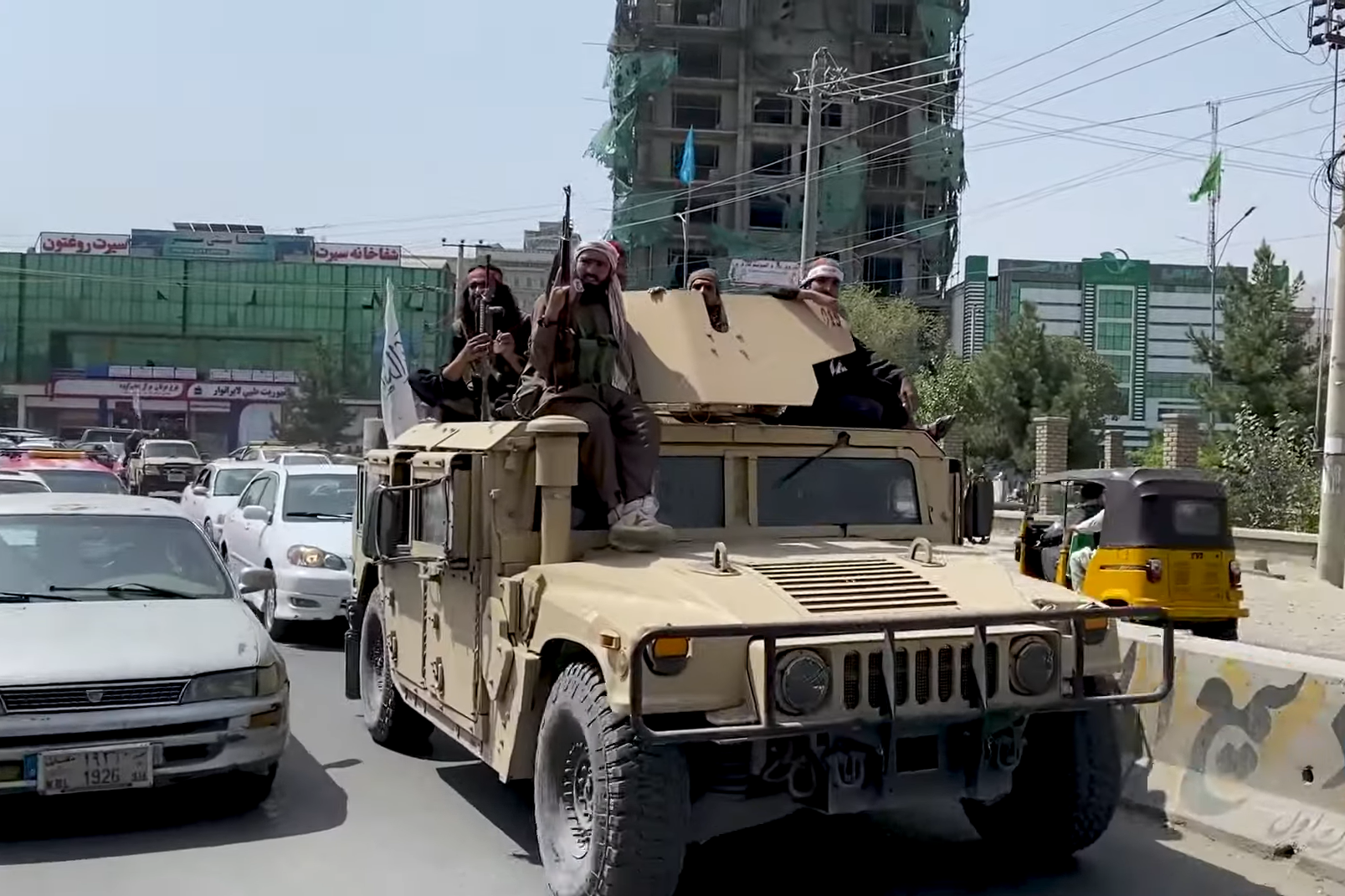 Taliban rule was swiftly restored as its opponents were defeated or left the country. Declaring an "Islamic Emirate", it is apparently led by Head of the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, supreme leader Hibatullah Akhundzada and acting Prime Minister of Afghanistan, Prime Minister Hasan Akhund, who took office on 7 September 2021.
Taliban rule was swiftly restored as its opponents were defeated or left the country. Declaring an "Islamic Emirate", it is apparently led by Head of the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, supreme leader Hibatullah Akhundzada and acting Prime Minister of Afghanistan, Prime Minister Hasan Akhund, who took office on 7 September 2021.
Geography
Afghanistan is located in Southern-Central Asia.[*
*
*
*
*
* ]
At over , Afghanistan is the world's List of countries and dependencies by area, 41st largest country, slightly bigger than France and smaller than Myanmar, and about the size of Texas in the United States. There is no coastline, as Afghanistan is landlocked. Afghanistan shares its longest land border (the Durand Line) with Pakistan to the east and south, followed by borders with Tajikistan to the north-east, Iran to the west, Turkmenistan to the north-west, Uzbekistan to the north and China to the north-east; India recognizes a border with Afghanistan through Pakistani-administered Kashmir. Clockwise from south-west, Afghanistan shares borders with the Sistan and Baluchestan Province, South Khorasan Province and Razavi Khorasan Province of Iran; Ahal Region, Mary Region and Lebap Region of Turkmenistan; Surxondaryo Region of Uzbekistan; Khatlon Region and Gorno-Badakhshan Autonomous Region of Tajikistan; Xinjiang, Xinjiang Uyghur Autonomous Region of China; and the Gilgit-Baltistan, Gilgit-Baltistan territory, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa province and Balochistan, Pakistan, Balochistan province of Pakistan.
The geography in Afghanistan is varied, but is mostly mountainous and rugged, with some unusual mountain ridges accompanied by plateaus and river basins.Hindu Kush
The Hindu Kush is an mountain range in Central and South Asia to the west of the Himalayas. It stretches from central and western Afghanistan, Quote: "The Hindu Kush mountains run along the Afghan border with the North-West Frontier Province ...
range, the western extension of the Himalayas that stretches to eastern Tibet via the Pamir Mountains and Karakoram Mountains in Afghanistan's far north-east. Most of the highest points are in the east consisting of fertile mountain valleys, often considered part of the "Roof of the World". The Hindu Kush ends at the west-central highlands, creating plains in the north and southwest, namely the Turkestan Plains and the Sistan Basin; these two regions consist of rolling grasslands and semi-deserts, and hot windy deserts, respectively. Forests exist in the corridor between Nuristan and Paktika provinces (see East Afghan montane conifer forests), and tundra in the north-east. The country's highest point is Noshaq, at above sea level.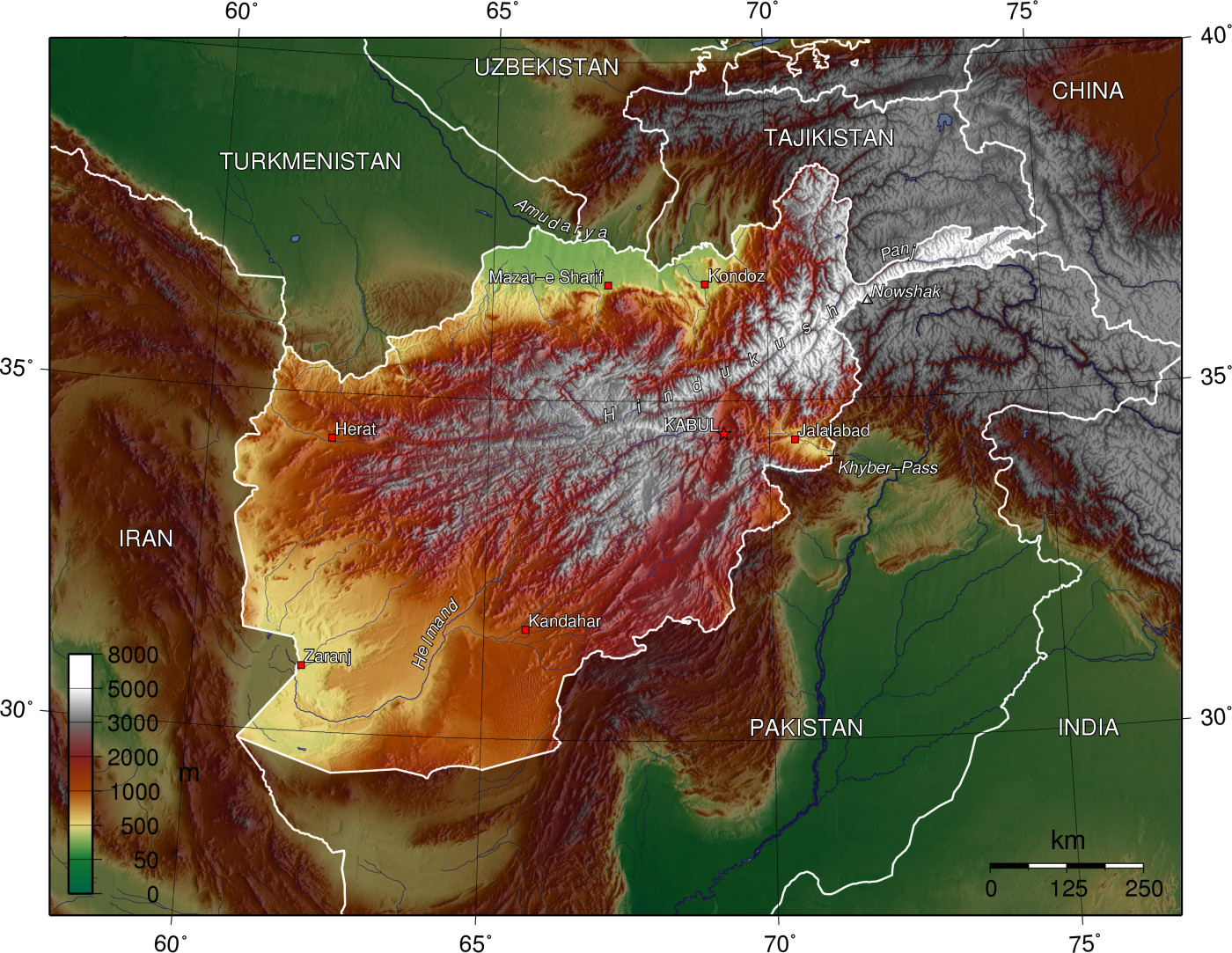 Despite having numerous rivers and list of dams and reservoirs in Afghanistan, reservoirs, large parts of the country are dry. The endorheic Sistan Basin is one of the driest regions in the world. The Amu Darya rises at the north of the Hindu Kush, while the nearby Hari Rud flows west towards Herat, and the Arghandab River from the central region southwards. To the south and west of the Hindu Kush flow a number of streams that are tributaries of the Indus River,
Despite having numerous rivers and list of dams and reservoirs in Afghanistan, reservoirs, large parts of the country are dry. The endorheic Sistan Basin is one of the driest regions in the world. The Amu Darya rises at the north of the Hindu Kush, while the nearby Hari Rud flows west towards Herat, and the Arghandab River from the central region southwards. To the south and west of the Hindu Kush flow a number of streams that are tributaries of the Indus River,Hindu Kush
The Hindu Kush is an mountain range in Central and South Asia to the west of the Himalayas. It stretches from central and western Afghanistan, Quote: "The Hindu Kush mountains run along the Afghan border with the North-West Frontier Province ...
and Pamir Mountains, and the melting snow in the spring season enters the list of rivers of Afghanistan, rivers, lakes, and streams. However, two-thirds of the country's water flows into the neighboring countries of Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, Pakistan, and Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan ( or ; tk, Türkmenistan / Түркменистан, ) is a country located in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the sout ...
. As reported in 2010, the state needs more than US$2 billion to rehabilitate its irrigation systems so that the water is properly managed.
The northeastern Hindu Kush mountain range, in and around the Badakhshan Province of Afghanistan, is in a natural environment#Geological activity, geologically active area where earthquakes may occur almost every year.
Climate
 Afghanistan has a continental climate with harsh winters in the Hazarajat, central highlands, the glaciated northeast (around Nuristan), and the Wakhan Corridor, where the average temperature in January is below and can reach ,
Afghanistan has a continental climate with harsh winters in the Hazarajat, central highlands, the glaciated northeast (around Nuristan), and the Wakhan Corridor, where the average temperature in January is below and can reach ,
Biodiversity
 Several types of mammals exist throughout Afghanistan. Snow leopards, Siberian tigers and brown bears live in the high elevation alpine tundra regions. The Marco Polo sheep exclusively live in the Wakhan Corridor region of north-east Afghanistan. Foxes, wolves, otters, deer, wild sheep, lynx and other big cats populate the mountain forest region of the east. In the semi-desert northern plains, wildlife include a variety of birds, hedgehogs, gophers, and large carnivores such as Golden jackal, jackals and Striped hyena, hyenas.
Several types of mammals exist throughout Afghanistan. Snow leopards, Siberian tigers and brown bears live in the high elevation alpine tundra regions. The Marco Polo sheep exclusively live in the Wakhan Corridor region of north-east Afghanistan. Foxes, wolves, otters, deer, wild sheep, lynx and other big cats populate the mountain forest region of the east. In the semi-desert northern plains, wildlife include a variety of birds, hedgehogs, gophers, and large carnivores such as Golden jackal, jackals and Striped hyena, hyenas.
Demographics
 The population of Afghanistan was estimated at 32.9 million as of 2019 by the Afghanistan Statistics and Information Authority, whereas the UN estimates over 38.0 million. In 1979 the total population was reported to be about 15.5 million. About 23.9% of them are urban area, urbanite, 71.4% live in rural areas, and the remaining 4.7% are nomadic.
The population of Afghanistan was estimated at 32.9 million as of 2019 by the Afghanistan Statistics and Information Authority, whereas the UN estimates over 38.0 million. In 1979 the total population was reported to be about 15.5 million. About 23.9% of them are urban area, urbanite, 71.4% live in rural areas, and the remaining 4.7% are nomadic.
Ethnicity and languages
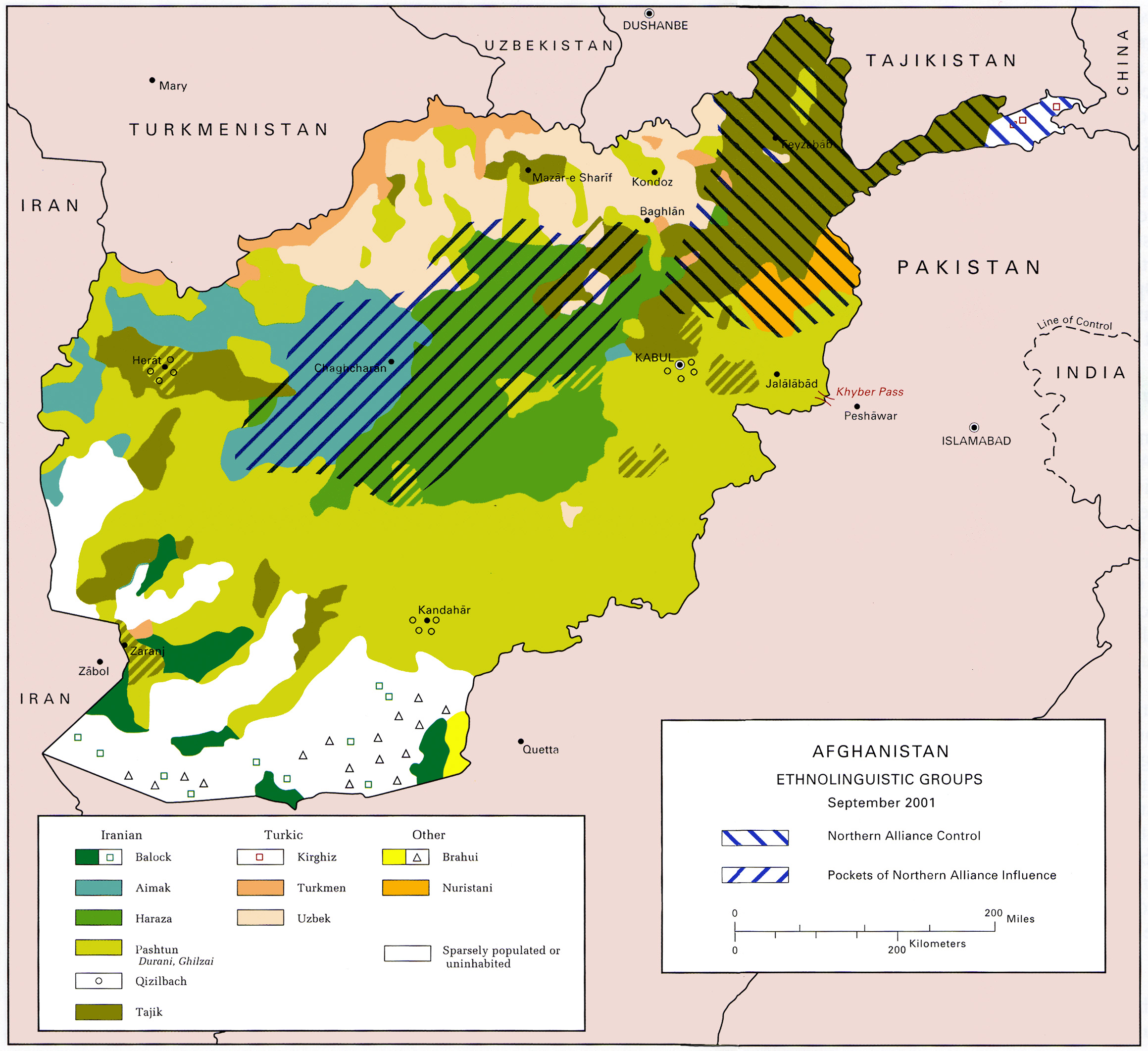 Afghans are divided into several ethnolinguistic groups. Off of sociological research data by The Asia Foundation in 2019, the
Afghans are divided into several ethnolinguistic groups. Off of sociological research data by The Asia Foundation in 2019, the Pashtuns
Pashtuns (, , ; ps, پښتانه, ), also known as Pakhtuns or Pathans, are an Iranian ethnic group who are native to the geographic region of Pashtunistan in the present-day countries of Afghanistan and Pakistan. They were historically r ...
are the largest ethnic group, comprising 39%, followed by Tajiks
Tajiks ( fa, تاجيک، تاجک, ''Tājīk, Tājek''; tg, Тоҷик) are a Persian-speaking Iranian ethnic group native to Central Asia, living primarily in Afghanistan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan. Tajiks are the largest ethnicity in Taj ...
, comprising 37%.[See:
*2019:
*2018: ] of the country's population. The other two major ethnic groups are the Hazaras
The Hazaras ( fa, , Həzārə; haz, , Āzərə) are an ethnic group and the principal component of the population of Afghanistan, native to, and primarily residing in the Hazaristan (Hazarajat) region in central Afghanistan and generally scatt ...
and Uzbeks
The Uzbeks ( uz, , , , ) are a Turkic ethnic group native to the wider Central Asian region, being among the largest Turkic ethnic group in the area. They comprise the majority population of Uzbekistan, next to Kazakh and Karakalpak mino ...
. A further 10 other ethnic groups are recognized and each are represented in the Afghan National Anthem.
Dari and Pashto are the official languages of Afghanistan; bilingualism is very common. Dari, which is a variety of and mutually intelligible with Persian language, Persian (and very often called 'Farsi' by some Afghans like in Iran) functions as the lingua franca in Kabul as well as in much of the northern and northwestern parts of the country.[The ''Encyc. Iranica'' makes clear in the article on Afghanistan — Ethnography that "The term Farsiwan also has the regional forms Parsiwan and Parsiban. In religion they are Imami Shia. In the literature they are often mistakenly referred to as Tajik.]
Dupree, Louis (1982) "Afghanistan: (iv.) Ethnography", in ''Encyclopædia Iranica''
Online Edition 2006. Pashto is the native tongue of the Pashtuns, although many of them are also fluent in Dari while some non-Pashtuns are fluent in Pashto. Despite the Pashtuns having been dominant in Afghan politics for centuries, Dari remained the preferred language for government and bureaucracy.
According to The World Factbook, CIA World Factbook, Dari Persian is spoken by 78% (First language, L1 + Second language, L2) and functions as the lingua franca, while Pashto is spoken by 50%, Uzbek 10%, English 5%, Turkmen 2%, Urdu 2%, Pashayi 1%, Nuristani 1%, Arabic 1%, and Balochi 1% (2021 est). Data represent the most widely spoken languages; shares sum to more than 100% because there is much bilingualism in the country and because respondents were allowed to select more than one language.There are a number of smaller regional languages, including Uzbek language, Uzbek, Turkmen language, Turkmen, Balochi language, Balochi, Pashayi language, Pashayi, and Nuristani languages, Nuristani.
When it comes to foreign languages among the populace, many are able to speak or understand Hindustani language, Hindustani (Urdu-Hindi), partly due to returning Afghan refugees from Pakistan and the popularity of Bollywood films respectively.[The Asia Foundation]
''Afghanistan in 2018: A Survey of the Afghan People''.
and has been gaining popularity as of the 2000s. Some Afghans retain some ability in Russian, which was taught in public schools during the 1980s.
Religion
 The CIA estimated in 2009 that 99.7% of the Afghan population was Muslim
The CIA estimated in 2009 that 99.7% of the Afghan population was Muslim
Urbanization
As estimated by the CIA World Factbook, 26% of the population was urbanized as of 2020. This is one of the lowest figures in the world; in Asia it is only higher than Cambodia, Nepal and Sri Lanka. Urbanization has increased rapidly, particularly in the capital Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. Acco ...
, due to returning refugees from Pakistan and Iran after 2001, internally displaced people, and rural migrants. Urbanization in Afghanistan is different from typical urbanization in that it is centered on just a few cities.
Education
 Education in Afghanistan includes K–12 and higher education, which is overseen by the Ministry of Education (Afghanistan), Ministry of Education and the Ministry of Higher Education (Afghanistan), Ministry of Higher Education. There are over 16,000 schools in the country and roughly 9 million students. Of this, about 60% are males and 40% females. However, the new regime has thus far forbidden girls and female teachers from returning to secondary schools. Over 174,000 students are enrolled in different List of universities in Afghanistan, universities around the country. About 21% of these are females.
Education in Afghanistan includes K–12 and higher education, which is overseen by the Ministry of Education (Afghanistan), Ministry of Education and the Ministry of Higher Education (Afghanistan), Ministry of Higher Education. There are over 16,000 schools in the country and roughly 9 million students. Of this, about 60% are males and 40% females. However, the new regime has thus far forbidden girls and female teachers from returning to secondary schools. Over 174,000 students are enrolled in different List of universities in Afghanistan, universities around the country. About 21% of these are females.
Health
 According to the Human Development Index, Afghanistan is the List of countries by Human Development Index, 15th least developed country in the world. The average List of countries by life expectancy, life expectancy is estimated to be around 60 years.
According to the Human Development Index, Afghanistan is the List of countries by Human Development Index, 15th least developed country in the world. The average List of countries by life expectancy, life expectancy is estimated to be around 60 years.
Governance
 Following the effective collapse of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan during the 2021 Taliban offensive, the Taliban declared the country an Islamic Emirate. A new caretaker government was announced on 7 September.
Following the effective collapse of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan during the 2021 Taliban offensive, the Taliban declared the country an Islamic Emirate. A new caretaker government was announced on 7 September.
Development of Taliban government
On 17 August 2021, the leader of the Taliban-affiliated Hezb-e Islami Gulbuddin, Hezb-e-Islami Gulbuddin party, Gulbuddin Hekmatyar, met with both Hamid Karzai, the former President of Afghanistan, and Abdullah Abdullah, the former chairman of the High Council for National Reconciliation and former Chief Executive (Afghanistan), Chief Executive, in Doha, Qatar, with the aim of forming a national unity government. President Ashraf Ghani, having fled the country during the Taliban advance to either Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
or Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked co ...
, emerged in the United Arab Emirates and said that he supported such negotiations and was in talks to return to Afghanistan. Many figures within the Taliban generally agreed that continuation of the 2004 Constitution of Afghanistan may, if correctly applied, be workable as the basis for the new religious state as their objections to the former government were political, and not religious.
Administrative divisions
Afghanistan is administratively divided into 34 provinces (''wilayat''). Each province has a governor and a capital. The country is further divided into nearly 400 provincial Districts of Afghanistan, districts, each of which normally covers a city or several villages. Each district is represented by a district governor.
The list of current governors of Afghanistan, provincial governors are now appointed by the Prime Minister of Afghanistan, and the district governors are selected by the provincial governors. The provincial governors are representatives of the central government in Kabul and are responsible for all administrative and formal issues within their provinces. There are also provincial councils that are elected through direct and general elections for four years. The functions of provincial councils are to take part in provincial development planning and to participate in the monitoring and appraisal of other provincial governance institutions.
According to article 140 of the constitution and the presidential decree on electoral law, mayors of cities should be elected through free and direct elections for a four-year term. In practice however, mayors are appointed by the government.
The following is a list of all the 34 provinces in alphabetical order:
 # Badakhshan Province, Badakhshan
# Badghis Province, Badghis
# Baghlan Province, Baghlan
# Balkh Province, Balkh
# Bamyan Province, Bamyan
# Daykundi Province, Daykundi
# Farah Province, Farah
# Faryab Province, Faryab
# Ghazni Province, Ghazni
# Ghor Province, Ghor
# Helmand Province, Helmand
# Herat Province, Herat
# Jowzjan Province, Jowzjan
# Kabul Province, Kabul
# Kandahar Province, Kandahar
# Kapisa Province, Kapisa
# Khost Province, Khost
# Kunar Province, Kunar
# Kunduz Province, Kunduz
# Laghman Province, Laghman
# Logar Province, Logar
# Nangarhar Province, Nangarhar
# Nimruz Province, Nimruz
# Nuristan Province, Nuristan
# Oruzgan Province, Oruzgan
# Paktia Province, Paktia
# Paktika Province, Paktika
# Panjshir Province, Panjshir
# Parwan Province, Parwan
# Samangan Province, Samangan
# Sar-e Pol Province, Sar-e Pol
# Takhar Province, Takhar
# Wardak Province, Wardak
# Zabul Province, Zabul
# Badakhshan Province, Badakhshan
# Badghis Province, Badghis
# Baghlan Province, Baghlan
# Balkh Province, Balkh
# Bamyan Province, Bamyan
# Daykundi Province, Daykundi
# Farah Province, Farah
# Faryab Province, Faryab
# Ghazni Province, Ghazni
# Ghor Province, Ghor
# Helmand Province, Helmand
# Herat Province, Herat
# Jowzjan Province, Jowzjan
# Kabul Province, Kabul
# Kandahar Province, Kandahar
# Kapisa Province, Kapisa
# Khost Province, Khost
# Kunar Province, Kunar
# Kunduz Province, Kunduz
# Laghman Province, Laghman
# Logar Province, Logar
# Nangarhar Province, Nangarhar
# Nimruz Province, Nimruz
# Nuristan Province, Nuristan
# Oruzgan Province, Oruzgan
# Paktia Province, Paktia
# Paktika Province, Paktika
# Panjshir Province, Panjshir
# Parwan Province, Parwan
# Samangan Province, Samangan
# Sar-e Pol Province, Sar-e Pol
# Takhar Province, Takhar
# Wardak Province, Wardak
# Zabul Province, Zabul
Foreign relations
Afghanistan became a member of the United Nations in 1946. Historically, Afghanistan had strong relations with Germany, one of the first countries to recognize Afghanistan's independence in 1919; the Soviet Union, which provided much aid and military training for Afghanistan's forces and includes the signing of a Treaty of Friendship in 1921 and 1978; and Afghanistan–India relations, India, with which a friendship treaty was signed in 1950. Relations with Afghanistan–Pakistan relations, Pakistan have often been tense for various reasons such as the Durand Line border issue and alleged Pakistani involvement in Afghan insurgent groups.
The present Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan is currently internationally Recognition of the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, unrecognized, but has had notable unofficial ties with Afghanistan–China relations, China, Pakistan, and Qatar. Under the previous Islamic Republic of Afghanistan, it enjoyed cordial relations with a number of NATO and allied nations, particularly the Afghanistan–United States relations, United States, Afghanistan–Canada relations, Canada, Afghanistan–United Kingdom relations, United Kingdom, Afghanistan–Germany relations, Germany, Australia, and Afghanistan–Turkey relations, Turkey. In 2012, the United States and the then-republic in Afghanistan signed their US–Afghanistan Strategic Partnership Agreement, Strategic Partnership Agreement in which Afghanistan became a major non-NATO ally. Such qualification was rescinded by US President Joe Biden in July 2022.
Military
The Armed Forces of the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan captured a large amount of weapons, hardware, vehicles, aerocrafts, and equipment from the Afghan National Security Forces following the 2021 Taliban offensive and the Fall of Kabul (2021), Fall of Kabul. The total value of the captured equipment has been estimated at US$83 billion.
Human rights
Homosexuality is taboo in Afghan society; according to the Penal Code, homosexual intimacy is punished by up to a year in prison. With implementing Sharia law offenders can be Death penalty for homosexuality, punished by death. However an ancient tradition involving male homosexual acts between children and older men (typically wealthy warlords or elite people) called ''bacha bazi'' persists.
Religious minorities such as Sikhs, Hindus, and Christians have reportedly faced persecution in the country.
Economy
 Afghanistan's nominal GDP was $21.7 billion in 2018, or $72.9 billion by purchasing power parity (PPP).
Afghanistan's nominal GDP was $21.7 billion in 2018, or $72.9 billion by purchasing power parity (PPP). One of the main drivers for the current economic recovery is the return of over 5 million Afghan diaspora, expatriates, who brought with them entrepreneurship and wealth-creating skills as well as much needed funds to start up businesses. Many Afghans are now involved in construction, which is one of the largest industries in the country. Some of the major national construction projects include the $35 billion New Kabul City next to the capital, the Aino Mena project in Kandahar, and the Ghazi Amanullah Khan Town near Jalalabad. Similar development projects have also begun in Herat, Mazar-e-Sharif, and other cities. An estimated 400,000 people enter the labor market each year.
Several small companies and factories began operating in different parts of the country, which not only provide revenues to the government but also create new jobs. Improvements to the business environment have resulted in more than $1.5 billion in Telecommunication, telecom investment and created more than 100,000 jobs since 2003. Afghan rugs are becoming popular again, allowing many carpet dealers around the country to hire more workers; in 2016–17 it was the fourth most exported group of items.
Afghanistan is a member of WTO, SAARC, Economic Cooperation Organization, ECO, and OIC. It holds an observer status in Shanghai Cooperation Organisation, SCO. In 2018, a majority of imports come from either Iran, China, Pakistan and Kazakhstan, while 84% of exports are to Pakistan and India.
Since the Taliban's takeover of the country in August 2021, the United States has Afghan frozen assets, frozen about $9 billion in assets belonging to the Da Afghanistan Bank, Afghan central bank, blocking the Taliban from accessing billions of dollars held in U.S. bank accounts.
One of the main drivers for the current economic recovery is the return of over 5 million Afghan diaspora, expatriates, who brought with them entrepreneurship and wealth-creating skills as well as much needed funds to start up businesses. Many Afghans are now involved in construction, which is one of the largest industries in the country. Some of the major national construction projects include the $35 billion New Kabul City next to the capital, the Aino Mena project in Kandahar, and the Ghazi Amanullah Khan Town near Jalalabad. Similar development projects have also begun in Herat, Mazar-e-Sharif, and other cities. An estimated 400,000 people enter the labor market each year.
Several small companies and factories began operating in different parts of the country, which not only provide revenues to the government but also create new jobs. Improvements to the business environment have resulted in more than $1.5 billion in Telecommunication, telecom investment and created more than 100,000 jobs since 2003. Afghan rugs are becoming popular again, allowing many carpet dealers around the country to hire more workers; in 2016–17 it was the fourth most exported group of items.
Afghanistan is a member of WTO, SAARC, Economic Cooperation Organization, ECO, and OIC. It holds an observer status in Shanghai Cooperation Organisation, SCO. In 2018, a majority of imports come from either Iran, China, Pakistan and Kazakhstan, while 84% of exports are to Pakistan and India.
Since the Taliban's takeover of the country in August 2021, the United States has Afghan frozen assets, frozen about $9 billion in assets belonging to the Da Afghanistan Bank, Afghan central bank, blocking the Taliban from accessing billions of dollars held in U.S. bank accounts.
Agriculture
 Agricultural production is the backbone of Afghanistan's economy and has traditionally dominated the economy, employing about 40% of the workforce as of 2018. The country is known for producing pomegranate production in Afghanistan, pomegranates, grapes, apricots, melons, and several other fresh and dry fruits. It is also known as the world's largest producer of Opium production in Afghanistan, opium – as much as 16% or more of the nation's economy is derived from the cultivation and sale of opium. It is also one of the world's top producers of
Agricultural production is the backbone of Afghanistan's economy and has traditionally dominated the economy, employing about 40% of the workforce as of 2018. The country is known for producing pomegranate production in Afghanistan, pomegranates, grapes, apricots, melons, and several other fresh and dry fruits. It is also known as the world's largest producer of Opium production in Afghanistan, opium – as much as 16% or more of the nation's economy is derived from the cultivation and sale of opium. It is also one of the world's top producers of cannabis
''Cannabis'' () is a genus of flowering plants in the family Cannabaceae. The number of species within the genus is disputed. Three species may be recognized: '' Cannabis sativa'', '' C. indica'', and '' C. ruderalis''. Alternative ...
.
Saffron, the most expensive spice, grows in Afghanistan, particularly Herat Province. In recent years, there has been an uptick in saffron production, which authorities and farmers trying to replace poppy cultivation. Between 2012 and 2019, the saffron cultivated and produced in Afghanistan was consecutively ranked the world's best by the International Taste and Quality Institute. Production hit record high in 2019 (19,469 kg of saffron), and one kilogram is sold domestically between $634 and $1147.
The availability of cheap diesel-powered water pumps imported from China and Pakistan, and in the 2010s, of cheap solar power to pump water, resulted in expansion of agriculture and population in the southwestern deserts of Afghanistan in Kandahar Province, Helmand Province and Nimruz Province in the 2010s. Wells have gradually been deepened, but water resources are limited. Opium is the major crop, but as of 2022, was under attack by the new Taliban government which, in order to suppress opium production, was systematically suppressing water pumping.
Mining
 The country's natural resources include: coal, copper, iron ore,
The country's natural resources include: coal, copper, iron ore, lithium
Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid ...
, uranium, rare earth elements, chromite, gold, zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
, talc, barite, sulfur, lead, marble, precious and semi-precious stones, natural gas, and petroleum.lithium
Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid ...
, copper, gold, coal, iron ore, and other minerals.[
]
Infrastructure
Energy
 According to the World Bank, 98% of the rural population have access to electricity in 2018, up from 28% in 2008. Overall the figure stands at 98.7%. As of 2016, Afghanistan produces 1,400 megawatts of power, but still imports the majority of electricity via transmission lines from Iran and the Central Asian states. The majority of electricity production is via hydropower, helped by the amount of rivers and streams that flow from the mountains. However electricity is not always reliable and blackouts happen, including in Kabul.
According to the World Bank, 98% of the rural population have access to electricity in 2018, up from 28% in 2008. Overall the figure stands at 98.7%. As of 2016, Afghanistan produces 1,400 megawatts of power, but still imports the majority of electricity via transmission lines from Iran and the Central Asian states. The majority of electricity production is via hydropower, helped by the amount of rivers and streams that flow from the mountains. However electricity is not always reliable and blackouts happen, including in Kabul.
Tourism
 Tourism is a small industry in Afghanistan due to security issues. Nevertheless, some 20,000 foreign tourists visit the country annually as of 2016. In particular an important region for domestic and international tourism is the picturesque Bamyan Valley, which includes lakes, canyons and historical sites, helped by the fact it is in a safe area away from insurgent activity. Smaller numbers visit and trek in regions such as the Wakhan Valley, which is also one of the world's most remote communities. From the late 1960s onwards, Afghanistan was a popular stop on the famous hippie trail, attracting many Europeans and Americans. Coming from Iran, the trail traveled through various Afghan provinces and cities including Herat, Kandahar and
Tourism is a small industry in Afghanistan due to security issues. Nevertheless, some 20,000 foreign tourists visit the country annually as of 2016. In particular an important region for domestic and international tourism is the picturesque Bamyan Valley, which includes lakes, canyons and historical sites, helped by the fact it is in a safe area away from insurgent activity. Smaller numbers visit and trek in regions such as the Wakhan Valley, which is also one of the world's most remote communities. From the late 1960s onwards, Afghanistan was a popular stop on the famous hippie trail, attracting many Europeans and Americans. Coming from Iran, the trail traveled through various Afghan provinces and cities including Herat, Kandahar and Kabul
Kabul (; ps, , ; , ) is the capital and largest city of Afghanistan. Located in the eastern half of the country, it is also a municipality, forming part of the Kabul Province; it is administratively divided into 22 municipal districts. Acco ...
before crossing to northern Pakistan, northern India, and Nepal. Tourism peaked in 1977, the year before the start of political instability and armed conflict.
 The city of Ghazni has significant history and historical sites, and together with Bamyan city have in recent years been voted Islamic Cultural Capital and South Asia Cultural Capital respectively. The cities of Herat, Kandahar, Balkh, and Zaranj are also very historic. The Minaret of Jam in the Hari River, Afghanistan, Hari River valley is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. A cloak reputedly worn by Islam's prophet Muhammad is kept inside the Shrine of the Cloak in Kandahar, a city founded by
The city of Ghazni has significant history and historical sites, and together with Bamyan city have in recent years been voted Islamic Cultural Capital and South Asia Cultural Capital respectively. The cities of Herat, Kandahar, Balkh, and Zaranj are also very historic. The Minaret of Jam in the Hari River, Afghanistan, Hari River valley is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. A cloak reputedly worn by Islam's prophet Muhammad is kept inside the Shrine of the Cloak in Kandahar, a city founded by Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
and the first capital of Afghanistan. The citadel of Alexander in the western city of Herat has been renovated in recent years and is a popular attraction. In the north of the country is the Shrine of Ali, believed by many to be the location where Ali was buried. The National Museum of Afghanistan is located in Kabul and hosts a large number of Buddhist, Bactrian Greek and early Islamic antiquities; the museum suffered greatly by civil war but has been slowly restoring since the early 2000s.
Communication
Telecommunication services in Afghanistan are provided by Afghan Telecom, Afghan Wireless, Etisalat, MTN Group, and Roshan (telco), Roshan. The country uses its own space satellite called Afghansat 1, which provides services to millions of phone, internet, and television subscribers. By 2001 following years of civil war, telecommunications was virtually a non-existent sector, but by 2016 it had grown to a $2 billion industry, with 22 million mobile phone subscribers and 5 million internet users. The sector employs at least 120,000 people nationwide.
Transportation
 Due to Afghanistan's geography, transport between various parts of the country has historically been difficult. The backbone of Afghanistan's road network is Highway 1 (Afghanistan), Highway 1, often called the "Ring Road", which extends for and connects five major cities: Kabul, Ghazni, Kandahar, Herat and Mazar-i-Sharif, with spurs to Kunduz and Jalalabad and various border crossings, while skirting around the mountains of the Hindu Kush.
The Ring Road is crucially important for domestic and international trade and the economy. A key portion of the Ring Road is the Salang Tunnel, completed in 1964, which facilitates travel through the Hindu Kush mountain range and connects northern and southern Afghanistan. It is the only land route that connects Central Asia to the Indian subcontinent. Several mountain passes allow travel between the Hindu Kush in other areas. Serious traffic accidents are common on Afghan roads and highways, particularly on the Kabul–Kandahar Highway, Kabul–Kandahar and the Kabul–Jalalabad Road. Traveling by bus in Afghanistan remains dangerous due to militant activities.
Due to Afghanistan's geography, transport between various parts of the country has historically been difficult. The backbone of Afghanistan's road network is Highway 1 (Afghanistan), Highway 1, often called the "Ring Road", which extends for and connects five major cities: Kabul, Ghazni, Kandahar, Herat and Mazar-i-Sharif, with spurs to Kunduz and Jalalabad and various border crossings, while skirting around the mountains of the Hindu Kush.
The Ring Road is crucially important for domestic and international trade and the economy. A key portion of the Ring Road is the Salang Tunnel, completed in 1964, which facilitates travel through the Hindu Kush mountain range and connects northern and southern Afghanistan. It is the only land route that connects Central Asia to the Indian subcontinent. Several mountain passes allow travel between the Hindu Kush in other areas. Serious traffic accidents are common on Afghan roads and highways, particularly on the Kabul–Kandahar Highway, Kabul–Kandahar and the Kabul–Jalalabad Road. Traveling by bus in Afghanistan remains dangerous due to militant activities.
 Air transport in Afghanistan is provided by the national carrier, Ariana Afghan Airlines,
Air transport in Afghanistan is provided by the national carrier, Ariana Afghan Airlines,Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan ( or ; tk, Türkmenistan / Түркменистан, ) is a country located in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the sout ...
border (where it continues as part of Turkmen Railways); and a short link from Aqina across the Turkmen border to Kerki, which is planned to be extended further across Afghanistan. These lines are used for freight only and there is no passenger service. A rail line between Khaf, Iran, Khaf, Iran and Herat, western Afghanistan, intended for both freight and passengers, is under construction as of 2019. About of the line will lie on the Afghan side. There are various proposals for the construction of additional rail lines in the country.
Private vehicle ownership has increased substantially since the early 2000s. Taxis are yellow in color and consist of both cars and auto rickshaws. In rural Afghanistan, villagers often use donkeys, mules or horse
The horse (''Equus ferus caballus'') is a domesticated, one-toed, hoofed mammal. It belongs to the taxonomic family Equidae and is one of two extant subspecies of ''Equus ferus''. The horse has evolved over the past 45 to 55 million yea ...
s to transport or carry goods. Camels are primarily used by the Kochi nomads.
Culture
Afghans have both common cultural features and those that differ between the regions of Afghanistan, each with distinctive cultures partly as a result of geographic obstacles that divide the country.Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a subregion, region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes t ...
and the Iranian Plateau. The remaining Afghans are culturally Persianization, Persian and Turkic peoples, Turkic. Some non-Pashtuns who live in proximity with Pashtuns have adopted Pashtunwali in a process called Pashtunization, while some Pashtuns have been Persianized. Those who have lived in Pakistan and Iran over the last 30 years have been further influenced by the cultures of those neighboring nations. The Afghan people are known to be strongly religious.[Heathcote, Tony (1980, 2003) "The Afghan Wars 1839–1919", Sellmount Staplehurst.] There are various ethnic groups in Afghanistan, Afghan tribes, and an estimated 2–3 million Kochi people, nomads. Afghan culture is deeply Islamic culture, Islamic, but pre-Islamic practices persist. One example is ''bacha bazi'', a term for activities involving sexual relations between older men and younger adolescent men, or boys. In the villages, families typically occupy mudbrick houses, or compounds with mudbrick or stone walled houses. Villages typically have a headman (''malik''), a master for water distribution (''mirab'') and a religious teacher (''mullah''). Men would typically work on the fields, joined by women during harvest.
In the villages, families typically occupy mudbrick houses, or compounds with mudbrick or stone walled houses. Villages typically have a headman (''malik''), a master for water distribution (''mirab'') and a religious teacher (''mullah''). Men would typically work on the fields, joined by women during harvest.Taliban
The Taliban (; ps, طالبان, ṭālibān, lit=students or 'seekers'), which also refers to itself by its state name, the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, is a Deobandi Islamic fundamentalist, militant Islamist, jihadist, and Pasht ...
enforced this dress on women when they were in power. Another popular dress is the ''chapan'' which acts as a coat. The ''Karakul (hat), karakul'' is a hat made from the fur of a specific regional breed of sheep. It was favored by former kings of Afghanistan and became known to much of the world in the 21st century when it was constantly worn by President Hamid Karzai. The ''pakol'' is another traditional hat originating from the far east of the country; it was popularly worn by the guerrilla leader Ahmad Shah Massoud. The ''Mazari hat'' originates from northern Afghanistan.
Architecture
 The nation has a complex history that has survived either in its current cultures or in the form of various languages and monuments. Afghanistan contains many remnants from all ages, including Ancient Greece, Greek and Buddhist stupas, monasteries, monuments, temples and Islamic minarets. Among the most well known are the Great Mosque of Herat, the Blue Mosque (Mazar-i-Sharif), Blue Mosque, the Minaret of Jam, the Chil Zena, the Qala-i Bost in Lashkargah, the ancient Greek city of Ai-Khanoum. However, many of its historic monuments have been damaged in modern times due to the civil wars. The two famous Buddhas of Bamiyan were destroyed by the Taliban, who regarded them as idolatrous. Despite that, archaeologists are still finding Buddhist relics in different parts of the country, some of them dating back to the 2nd century. As there was no colonialism in the modern era in Afghanistan, European-style architecture is rare but does exist: the Victory Arch at Paghman and the Darul Aman Palace in Kabul were built in this style in the 1920s by the Afghans themselves.
The nation has a complex history that has survived either in its current cultures or in the form of various languages and monuments. Afghanistan contains many remnants from all ages, including Ancient Greece, Greek and Buddhist stupas, monasteries, monuments, temples and Islamic minarets. Among the most well known are the Great Mosque of Herat, the Blue Mosque (Mazar-i-Sharif), Blue Mosque, the Minaret of Jam, the Chil Zena, the Qala-i Bost in Lashkargah, the ancient Greek city of Ai-Khanoum. However, many of its historic monuments have been damaged in modern times due to the civil wars. The two famous Buddhas of Bamiyan were destroyed by the Taliban, who regarded them as idolatrous. Despite that, archaeologists are still finding Buddhist relics in different parts of the country, some of them dating back to the 2nd century. As there was no colonialism in the modern era in Afghanistan, European-style architecture is rare but does exist: the Victory Arch at Paghman and the Darul Aman Palace in Kabul were built in this style in the 1920s by the Afghans themselves.
Art and ceramics
 Carpet weaving is an ancient practice in Afghanistan, and many of these are still Handicraft, handmade by tribal and nomadic people today.
Carpet weaving is an ancient practice in Afghanistan, and many of these are still Handicraft, handmade by tribal and nomadic people today.Soviet–Afghan War
The Soviet–Afghan War was a protracted armed conflict fought in the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan from 1979 to 1989. It saw extensive fighting between the Soviet Union and the Afghan mujahideen (alongside smaller groups of anti-Sovie ...
, "war rugs", a variant of Afghan rugs, were created with designs representing pain and misery caused by the conflict. Every province has its own specific characteristics in making rugs. In some of the Turkic-populated areas in the north-west, bride and wedding ceremony prices are driven by the bride's weaving skills.
Pottery has been crafted in Afghanistan for millennia. The village of Istalif, north of Kabul, is in particular a major center, known for its unique turquoise and green pottery, and their methods of crafting have remained the same for centuries. Much of ''lapis lazuli'' stones were earthed in modern-day Afghanistan which were used in Chinese porcelain as cobalt blue, later used in ancient Mesopotamia and Turkey.
The lands of Afghanistan have a long history of art, with the world's earliest known usage of oil painting found in cave murals in the country. A notable art style that developed in Afghanistan and eastern Pakistan is Gandhara Art, produced by a fusion of Greco-Roman art and Buddhist art between the 1st and 7th centuries CE. Later eras saw increased use of the Persian miniature style, with Kamaleddin Behzad of Herat being one of the most notable miniature artists of the Timurid dynasty, Timurid and early Safavid periods. Since the 1900s, the nation began to use Western techniques in art. Abdul Ghafoor Breshna was a prominent Afghan painter and sketch artist from Kabul during the 20th century.
Media and entertainment
Afghanistan has around 350 List of radio stations in Afghanistan, radio stations and over 200 television stations.
Music
 Afghan classical music has close historical links with Indian classical music and use the same Hindustani terminology and theories like raga. Genres of this style of music include ghazal (poetic music) and instruments such as the Indian tabla, sitar and harmonium, and local instruments like zerbaghali, as well as dayereh and tanbur which are also known in Central Asia, the Caucusus and the Middle East. The Rubab (instrument), rubab is the country's national instrument and precurses the Indian sarod instrument. Some of the famous artists of classical music include Ustad Sarahang and Abdul Rahim Sarban, Sarban.
Afghan classical music has close historical links with Indian classical music and use the same Hindustani terminology and theories like raga. Genres of this style of music include ghazal (poetic music) and instruments such as the Indian tabla, sitar and harmonium, and local instruments like zerbaghali, as well as dayereh and tanbur which are also known in Central Asia, the Caucusus and the Middle East. The Rubab (instrument), rubab is the country's national instrument and precurses the Indian sarod instrument. Some of the famous artists of classical music include Ustad Sarahang and Abdul Rahim Sarban, Sarban.
Cuisine
 Afghan cuisine is largely based upon the nation's chief crops, such as wheat, maize, barley and rice. Accompanying these staples are native fruits and vegetables as well as dairy products such as milk, yogurt and whey. Kabuli palaw is the national dish of Afghanistan.
Afghan cuisine is largely based upon the nation's chief crops, such as wheat, maize, barley and rice. Accompanying these staples are native fruits and vegetables as well as dairy products such as milk, yogurt and whey. Kabuli palaw is the national dish of Afghanistan.
Literature
Classic Persian literature, Persian and Pashto poetry are a cherished part of Afghan culture. Poetry has always been one of the major educational pillars in the region, to the level that it has integrated itself into culture. One of the poetic styles is called Landay (poetry), landay. A popular theme in Afghan folklore and mythology are Dev (mythology), Divs, monstrous creatures. Thursdays are traditionally "poetry night" in the city of Herat when men, women and children gather and recite both ancient and modern poems.
The Afghan region has produced countless Persian-speaking poets and writers from the Middle Ages to the present day, among which three mystical authors are considered true national glories (although claimed with equal ardor by Iran), namely: Khwaja Abdullah Ansari of Herat, a great mystic and Sufi saint in the 11th century, Sanai of Ghazni, author of mystical poems in the 12th century, and, finally, Rumi of Balkh, in the 13th century, considered the persophonist throughout the world as the greatest mystical poet of the entire Muslim world. The Afghan Pashto literature, although quantitatively remarkable and in great growth in the last century, has always had an essentially local meaning and importance, feeling the influence of both Persian literature and the contiguous literatures of India. Both main literatures, from the second half of the nineteenth century, have shown themselves to be sensitive to genres (novel, theater), movements and stylistic features imported from Europe.
Khushal Khan Khattak of the 17th century is considered the national poet. Other notable poets include Rabi'a Balkhi, Jami, Rahman Baba, Khalilullah Khalili, and Parween Pazhwak.
Holidays and festivals
 Afghanistan's official New Year starts with Nowruz, an ancient tradition that started as a Zoroastrian celebration in present-day Iran, and with which it shares the annual celebration along with several other countries. It occurs every year at the March equinox, vernal equinox. Nauruz in Afghanistan, In Afghanistan, Nowruz is typically celebrated with music and dance, as well as holding buzkashi tournaments.
Yaldā, another nationally celebrated ancient tradition, commemorates the ancient goddess Mithra and marks the longest night of the year on the eve of the winter solstice (; usually falling on 20 or 21 December), during which families gather together to recite poetry and eat fruits—particularly the red fruits watermelon and pomegranate, as well as mixed nuts.
Religious festivals are also celebrated; as a predominantly Muslim country, Islamic events and festivals such as Ramadan, Eid al-Fitr and Ashura are widely celebrated annually in Afghanistan. The Sikh festival of Vaisakhi is celebrated by the Sikh community and the Hindu festival Diwali by the Hindu community.
Afghan Independence Day, National Independence Day is celebrated on 19 August to mark the Anglo-Afghan Treaty of 1919 under King
Afghanistan's official New Year starts with Nowruz, an ancient tradition that started as a Zoroastrian celebration in present-day Iran, and with which it shares the annual celebration along with several other countries. It occurs every year at the March equinox, vernal equinox. Nauruz in Afghanistan, In Afghanistan, Nowruz is typically celebrated with music and dance, as well as holding buzkashi tournaments.
Yaldā, another nationally celebrated ancient tradition, commemorates the ancient goddess Mithra and marks the longest night of the year on the eve of the winter solstice (; usually falling on 20 or 21 December), during which families gather together to recite poetry and eat fruits—particularly the red fruits watermelon and pomegranate, as well as mixed nuts.
Religious festivals are also celebrated; as a predominantly Muslim country, Islamic events and festivals such as Ramadan, Eid al-Fitr and Ashura are widely celebrated annually in Afghanistan. The Sikh festival of Vaisakhi is celebrated by the Sikh community and the Hindu festival Diwali by the Hindu community.
Afghan Independence Day, National Independence Day is celebrated on 19 August to mark the Anglo-Afghan Treaty of 1919 under King Amanullah Khan
Ghazi Amanullah Khan ( Pashto and Dari: ; 1 June 1892 – 25 April 1960) was the sovereign of Afghanistan from 1919, first as Emir and after 1926 as King, until his abdication in 1929. After the end of the Third Anglo-Afghan War in August 1 ...
and the country's full independence. Several international celebrations are also officially held in Afghanistan, such as International Workers' Day and International Women's Day. Some regional festivals include the Pamir Festival, which celebrates the culture of the Wakhi people, Wakhi and Kyrgyz people, Kyrgyz peoples, the Red Flower Festival (during Nowruz) in Mazar-i-Sharif and the Damboora Festival in Bamyan Province.
Sports
 Sport in Afghanistan is managed by the Afghan Sports Federation. Cricket and Association football are the two most popular sports in the country. The Afghan Sports Federation promotes cricket, association football, basketball, volleyball, golf, team handball, handball, boxing, taekwondo, Olympic weightlifting, weightlifting, bodybuilding, track and field, ice skating, skating, bowling, snooker, chess, and other sports.
Afghanistan's sports teams are increasingly celebrating titles at international events. Afghanistan national basketball team, basketball team won the first team sports title at the 2010 South Asian Games. Later that year, the country's Afghanistan national cricket team, cricket team followed it with the winning of 2009–10 ICC Intercontinental Cup.
Sport in Afghanistan is managed by the Afghan Sports Federation. Cricket and Association football are the two most popular sports in the country. The Afghan Sports Federation promotes cricket, association football, basketball, volleyball, golf, team handball, handball, boxing, taekwondo, Olympic weightlifting, weightlifting, bodybuilding, track and field, ice skating, skating, bowling, snooker, chess, and other sports.
Afghanistan's sports teams are increasingly celebrating titles at international events. Afghanistan national basketball team, basketball team won the first team sports title at the 2010 South Asian Games. Later that year, the country's Afghanistan national cricket team, cricket team followed it with the winning of 2009–10 ICC Intercontinental Cup.
See also
* Outline of Afghanistan
Explanatory notes
References
Citations
General and cited sources
*
Further reading
External links
Afghanistan
''The World Factbook''. Central Intelligence Agency.
*
*
*
Research Guide to Afghanistan
{{Authority control
Afghanistan,
1709 establishments in Asia
Central Asian countries
Countries in Asia
Emirates
Iranian countries and territories
Iranian Plateau
Islamic states
Landlocked countries
Least developed countries
Member states of the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation
Member states of the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation
Member states of the United Nations
Pashto-speaking countries and territories
Persian-speaking countries and territories
South Asian countries
States and territories established in 1709
States and territories established in 1747
Theocracies
Totalitarian states
 Many empires and kingdoms have also risen to power in Afghanistan, such as the
Many empires and kingdoms have also risen to power in Afghanistan, such as the 
 By the middle of the 6th century BCE, the Achaemenids overthrew the Medes and incorporated Arachosia, Aria (satrapy), Aria, and Bactria within its eastern boundaries. An Epigraphy, inscription on the tombstone of Darius I of Persia mentions the Kabulistan, Kabul Valley in a list of the 29 countries that he had conquered. The region of Arachosia, around Kandahar in modern-day southern Afghanistan, used to be primarily Zoroastrian and played a key role in the transfer of the Avesta to Persis, Persia and is thus considered by some to be the "second homeland of Zoroastrianism".
By the middle of the 6th century BCE, the Achaemenids overthrew the Medes and incorporated Arachosia, Aria (satrapy), Aria, and Bactria within its eastern boundaries. An Epigraphy, inscription on the tombstone of Darius I of Persia mentions the Kabulistan, Kabul Valley in a list of the 29 countries that he had conquered. The region of Arachosia, around Kandahar in modern-day southern Afghanistan, used to be primarily Zoroastrian and played a key role in the transfer of the Avesta to Persis, Persia and is thus considered by some to be the "second homeland of Zoroastrianism".
 The Silk Road appeared during the first century BCE, and Afghanistan flourished with trade, with routes to China, India, Persia and north to the cities of Bukhara, Samarkand and Khiva in present-day Uzbekistan. Goods and ideas were exchanged at this center point, such as Chinese silk, Persian silver and Roman gold, while the region of present Afghanistan was mining and trading lapis lazuli stones mainly from the Badakhshan region.
During the first century BCE, the Parthian Empire subjugated the region but lost it to their Indo-Parthian vassals. In the mid-to-late first century CE the vast Kushan Empire, centered in Afghanistan, became great patrons of Buddhist culture, making Buddhism flourish throughout the region. The Kushans were overthrown by the Sassanids in the 3rd century CE, though the Indo-Sassanids continued to rule at least parts of the region. They were followed by the Kidarites who, in turn, was replaced by the
The Silk Road appeared during the first century BCE, and Afghanistan flourished with trade, with routes to China, India, Persia and north to the cities of Bukhara, Samarkand and Khiva in present-day Uzbekistan. Goods and ideas were exchanged at this center point, such as Chinese silk, Persian silver and Roman gold, while the region of present Afghanistan was mining and trading lapis lazuli stones mainly from the Badakhshan region.
During the first century BCE, the Parthian Empire subjugated the region but lost it to their Indo-Parthian vassals. In the mid-to-late first century CE the vast Kushan Empire, centered in Afghanistan, became great patrons of Buddhist culture, making Buddhism flourish throughout the region. The Kushans were overthrown by the Sassanids in the 3rd century CE, though the Indo-Sassanids continued to rule at least parts of the region. They were followed by the Kidarites who, in turn, was replaced by the  Arab Muslims brought Islam to Herat and Zaranj in 642 CE and began spreading eastward; some of the native inhabitants they encountered accepted it while others revolted. Before the Islamic conquest of Afghanistan, arrival of Islam, the region used to be home to various beliefs and cults, often resulting in Syncretism between the dominant religions such as
Arab Muslims brought Islam to Herat and Zaranj in 642 CE and began spreading eastward; some of the native inhabitants they encountered accepted it while others revolted. Before the Islamic conquest of Afghanistan, arrival of Islam, the region used to be home to various beliefs and cults, often resulting in Syncretism between the dominant religions such as  In 1709, Mirwais Hotak, a local Ghilzai tribal leader, successfully rebelled against the Safavids. He defeated Gurgin Khan and established his own kingdom. Mirwais died of natural causes in 1715 and was succeeded by his brother Abdul Aziz Hotak, Abdul Aziz, who was soon killed by Mirwais' son Mahmud Hotak, Mahmud for possibly planning to concede territories back to the Safavids. Mahmud led the Afghan army in 1722 to the Persian capital of Isfahan, captured the city after the Battle of Gulnabad and proclaimed himself King of Persia. The Afghan dynasty was ousted from Persia by Nader Shah after the 1729 Battle of Damghan (1729), Battle of Damghan.
In 1709, Mirwais Hotak, a local Ghilzai tribal leader, successfully rebelled against the Safavids. He defeated Gurgin Khan and established his own kingdom. Mirwais died of natural causes in 1715 and was succeeded by his brother Abdul Aziz Hotak, Abdul Aziz, who was soon killed by Mirwais' son Mahmud Hotak, Mahmud for possibly planning to concede territories back to the Safavids. Mahmud led the Afghan army in 1722 to the Persian capital of Isfahan, captured the city after the Battle of Gulnabad and proclaimed himself King of Persia. The Afghan dynasty was ousted from Persia by Nader Shah after the 1729 Battle of Damghan (1729), Battle of Damghan.
 In 1738, Nader Shah and his Afsharid dynasty, forces captured Kandahar in the Siege of Kandahar, the last Hotak stronghold, from Shah Hussain Hotak. Soon after, the Persian and Afghan forces Nader Shah's invasion of India, invaded India, Nader Shah had plundered Delhi, alongside his 16 year old commander, Ahmad Shah Durrani who had assisted him on these campaigns. Nader Shah was assassinated in 1747.
In 1738, Nader Shah and his Afsharid dynasty, forces captured Kandahar in the Siege of Kandahar, the last Hotak stronghold, from Shah Hussain Hotak. Soon after, the Persian and Afghan forces Nader Shah's invasion of India, invaded India, Nader Shah had plundered Delhi, alongside his 16 year old commander, Ahmad Shah Durrani who had assisted him on these campaigns. Nader Shah was assassinated in 1747.
 Ahmad Shah invaded India 8 times during his reign. With the capture of Peshawar, Ahmad Shah had used this as a convenient striking point to lead his military campaigns into Punjab and India.
Ahmad Shah had sought out multiple reasons for his invasions, Ahmad Shah saw Afghanistan in a dire state, and one that needed to expand and exploit a weak but rich neighboring country, which Ahmad Shah had capitalized on in multiple opportunities during his Invasions of India, he sought the reasons needed to fill his treasury in a war-plunder conquest based economy. Ahmad Shah had launched his first invasion in 1748, crossing the indus river, his armies sacked and absorbed Lahore into the Durrani Empire, Durrani Realm. Ahmad Shah had met Mughal armies at the Battle of Manupur (1748), where he was defeated and forced to retreat to back to Afghanistan. Ahmad Shah had returned the next year in 1749, where he had captured the area around Lahore and Punjab, presenting it as an Afghan victory for this campaign. From 1749 to 1767, Ahmad Shah would lead 6 more invasions, the most important being his sixth invasion, with the Third Battle of Panipat, which created a power vacuum in northern India, halting Maratha Empire, Maratha expansion.
Ahmad Shah invaded India 8 times during his reign. With the capture of Peshawar, Ahmad Shah had used this as a convenient striking point to lead his military campaigns into Punjab and India.
Ahmad Shah had sought out multiple reasons for his invasions, Ahmad Shah saw Afghanistan in a dire state, and one that needed to expand and exploit a weak but rich neighboring country, which Ahmad Shah had capitalized on in multiple opportunities during his Invasions of India, he sought the reasons needed to fill his treasury in a war-plunder conquest based economy. Ahmad Shah had launched his first invasion in 1748, crossing the indus river, his armies sacked and absorbed Lahore into the Durrani Empire, Durrani Realm. Ahmad Shah had met Mughal armies at the Battle of Manupur (1748), where he was defeated and forced to retreat to back to Afghanistan. Ahmad Shah had returned the next year in 1749, where he had captured the area around Lahore and Punjab, presenting it as an Afghan victory for this campaign. From 1749 to 1767, Ahmad Shah would lead 6 more invasions, the most important being his sixth invasion, with the Third Battle of Panipat, which created a power vacuum in northern India, halting Maratha Empire, Maratha expansion.
 By the early 19th century, the Afghan empire was under threat from the Qajar dynasty, Persians in the west and the Sikh Empire in the east. Fateh Khan, leader of the Barakzai dynasty, Barakzai tribe, installed many of his brothers in positions of power throughout the empire, mostly ruling as governors of major cities and provinces. After his murder for apparent treason against the Durrani king. Fateh Khan would be sentenced by Mahmud Shah Durrani, having him executed. His brothers rebelled and divided up the provinces of the empire between themselves. During this turbulent period, Afghanistan had fractured into many states, this included the Principality of Qandahar, Herat (1793–1863), Emirate of Herat, Khanate of Qunduz, Maimana Khanate, and many more states. The most prominent state being the Emirate of Afghanistan, Emirate of Kabul, ruled by Dost Mohammad Khan after he declared himself emir and was bestowed upon the title of Amir al-Mu'minin in summer 1826 following a usurpation of the throne from his brother, Sultan Mohammad Khan. With the collapse of the Durrani Empire, and the exile of the Sadozai Dynasty while Afghanistan was in this turbulent period of civil war, Punjab and Kashmir were lost to Ranjit Singh ruler of the Sikh Empire, who invaded Khyber Pakhtunkhwa in March 1823 and captured the city of Peshawar from the Peshawar Sardars (one of the many entities that split following the collapse of the Durrani Empire), at the Battle of Nowshera. In 1837, Dost Mohammad Khan attempted to retake Peshawar and sent a large force under his son, Wazir Akbar Khan, leading to the Battle of Jamrud near the Khyber Pass. Wazir Akbar Khan, Akbar Khan and the Afghan army failed to capture the Jamrud Fort from the Sikh Khalsa Army, but killed Sikh Commander Hari Singh Nalwa, thus ending the Afghan-Sikh Wars. By this time the British were advancing from the east, conquering the Sikh Empire after it had its own period of turbulence following the death of Ranjit Singh, directly bringing the Emirate of Afghanistan, Emirate of Kabul to conflict in the First Anglo-Afghan War, first major conflict during "the Great Game".
In 1838, a British Army, British expeditionary force marched into Afghanistan, invading the Principality of Qandahar, and in August 1839, seized
By the early 19th century, the Afghan empire was under threat from the Qajar dynasty, Persians in the west and the Sikh Empire in the east. Fateh Khan, leader of the Barakzai dynasty, Barakzai tribe, installed many of his brothers in positions of power throughout the empire, mostly ruling as governors of major cities and provinces. After his murder for apparent treason against the Durrani king. Fateh Khan would be sentenced by Mahmud Shah Durrani, having him executed. His brothers rebelled and divided up the provinces of the empire between themselves. During this turbulent period, Afghanistan had fractured into many states, this included the Principality of Qandahar, Herat (1793–1863), Emirate of Herat, Khanate of Qunduz, Maimana Khanate, and many more states. The most prominent state being the Emirate of Afghanistan, Emirate of Kabul, ruled by Dost Mohammad Khan after he declared himself emir and was bestowed upon the title of Amir al-Mu'minin in summer 1826 following a usurpation of the throne from his brother, Sultan Mohammad Khan. With the collapse of the Durrani Empire, and the exile of the Sadozai Dynasty while Afghanistan was in this turbulent period of civil war, Punjab and Kashmir were lost to Ranjit Singh ruler of the Sikh Empire, who invaded Khyber Pakhtunkhwa in March 1823 and captured the city of Peshawar from the Peshawar Sardars (one of the many entities that split following the collapse of the Durrani Empire), at the Battle of Nowshera. In 1837, Dost Mohammad Khan attempted to retake Peshawar and sent a large force under his son, Wazir Akbar Khan, leading to the Battle of Jamrud near the Khyber Pass. Wazir Akbar Khan, Akbar Khan and the Afghan army failed to capture the Jamrud Fort from the Sikh Khalsa Army, but killed Sikh Commander Hari Singh Nalwa, thus ending the Afghan-Sikh Wars. By this time the British were advancing from the east, conquering the Sikh Empire after it had its own period of turbulence following the death of Ranjit Singh, directly bringing the Emirate of Afghanistan, Emirate of Kabul to conflict in the First Anglo-Afghan War, first major conflict during "the Great Game".
In 1838, a British Army, British expeditionary force marched into Afghanistan, invading the Principality of Qandahar, and in August 1839, seized  During the First World War, when Afghanistan was neutral, Habibullah Khan was met by officials of the Central Powers in the Niedermayer–Hentig Expedition, to declare full independence from the United Kingdom, join them and attack British India, as part of the Hindu–German Conspiracy. Their efforts to bring Afghanistan into the Central Powers failed, but it caused discontent among the population for keeping neutrality against the British. Habibullah was assassinated during a hunting trip in February 1919, and
During the First World War, when Afghanistan was neutral, Habibullah Khan was met by officials of the Central Powers in the Niedermayer–Hentig Expedition, to declare full independence from the United Kingdom, join them and attack British India, as part of the Hindu–German Conspiracy. Their efforts to bring Afghanistan into the Central Powers failed, but it caused discontent among the population for keeping neutrality against the British. Habibullah was assassinated during a hunting trip in February 1919, and  After the end of the Third Anglo-Afghan War and the signing of the Anglo-Afghan Treaty of 1919, Treaty of Rawalpindi on 19 August 1919, Emir of Afghanistan, Emir Amanullah Khan declared the Emirate of Afghanistan a sovereign state, sovereign and fully independent state. He moved to end his country's traditional isolation by establishing diplomatic relations with the international community, particularly with the Soviet Union and the Weimar Republic of Germany. He proclaimed himself King of Afghanistan on 9 June 1926, when the Emirate of Afghanistan became the
After the end of the Third Anglo-Afghan War and the signing of the Anglo-Afghan Treaty of 1919, Treaty of Rawalpindi on 19 August 1919, Emir of Afghanistan, Emir Amanullah Khan declared the Emirate of Afghanistan a sovereign state, sovereign and fully independent state. He moved to end his country's traditional isolation by establishing diplomatic relations with the international community, particularly with the Soviet Union and the Weimar Republic of Germany. He proclaimed himself King of Afghanistan on 9 June 1926, when the Emirate of Afghanistan became the  Until 1946, King Zahir ruled with the assistance of his uncle, who held the post of Prime Minister of Afghanistan, Prime Minister and continued the policies of Nadir Shah. Another of Zahir Shah's uncles, Shah Mahmud Khan, became Prime Minister in 1946 and began an experiment allowing greater political freedom, but reversed the policy when it went further than he expected. He was replaced in 1953 by Mohammed Daoud Khan, the king's cousin and brother-in-law, and a Pashtun nationalist who sought the creation of a Pashtunistan, leading to highly tense relations with Pakistan. During his ten years at the post until 1963, Daoud Khan pressed for social modernization reforms and sought a closer relationship with the Soviet Union. Afterward, the 1964 Constitution of Afghanistan, 1964 constitution was formed, and the first non-royal Prime Minister was sworn in.
King Zahir Shah, like his father Nadir Shah, had a policy of maintaining national independence while pursuing gradual modernization, creating nationalist feeling, and improving relations with the United Kingdom. However, Afghanistan remained neutral and was neither a participant in World War II nor aligned with either power bloc in the Cold War thereafter. However, it was a beneficiary of the latter rivalry as both the Soviet Union and the United States vied for influence by building Afghanistan's main highways, airports, and other vital infrastructure in the post-war period. On a per capita basis, Afghanistan received more Soviet development aid than any other country. Afghanistan had, therefore, good relations with both Cold War enemies. In 1973, while the King was in Italy, Daoud Khan launched a 1973 Afghan coup, bloodless coup and became the first President of Afghanistan, abolishing the monarchy.
Until 1946, King Zahir ruled with the assistance of his uncle, who held the post of Prime Minister of Afghanistan, Prime Minister and continued the policies of Nadir Shah. Another of Zahir Shah's uncles, Shah Mahmud Khan, became Prime Minister in 1946 and began an experiment allowing greater political freedom, but reversed the policy when it went further than he expected. He was replaced in 1953 by Mohammed Daoud Khan, the king's cousin and brother-in-law, and a Pashtun nationalist who sought the creation of a Pashtunistan, leading to highly tense relations with Pakistan. During his ten years at the post until 1963, Daoud Khan pressed for social modernization reforms and sought a closer relationship with the Soviet Union. Afterward, the 1964 Constitution of Afghanistan, 1964 constitution was formed, and the first non-royal Prime Minister was sworn in.
King Zahir Shah, like his father Nadir Shah, had a policy of maintaining national independence while pursuing gradual modernization, creating nationalist feeling, and improving relations with the United Kingdom. However, Afghanistan remained neutral and was neither a participant in World War II nor aligned with either power bloc in the Cold War thereafter. However, it was a beneficiary of the latter rivalry as both the Soviet Union and the United States vied for influence by building Afghanistan's main highways, airports, and other vital infrastructure in the post-war period. On a per capita basis, Afghanistan received more Soviet development aid than any other country. Afghanistan had, therefore, good relations with both Cold War enemies. In 1973, while the King was in Italy, Daoud Khan launched a 1973 Afghan coup, bloodless coup and became the first President of Afghanistan, abolishing the monarchy.
 Another civil war broke out after the Peshawar Accords, creation of a dysfunctional coalition Islamic State of Afghanistan, government between leaders of various ''mujahideen'' factions. Amid a state of anarchy and factional infighting,GUTMAN, Roy (2008): How We Missed the Story: Osama Bin Laden, the Taliban and the Hijacking of Afghanistan, Endowment of the United States Institute of Peace, 1st ed., Washington D.C. various ''mujahideen'' factions committed widespread rape, murder and extortion, while Kabul was heavily bombarded and partially destroyed by the fighting. Several failed reconciliations and alliances occurred between different leaders. The
Another civil war broke out after the Peshawar Accords, creation of a dysfunctional coalition Islamic State of Afghanistan, government between leaders of various ''mujahideen'' factions. Amid a state of anarchy and factional infighting,GUTMAN, Roy (2008): How We Missed the Story: Osama Bin Laden, the Taliban and the Hijacking of Afghanistan, Endowment of the United States Institute of Peace, 1st ed., Washington D.C. various ''mujahideen'' factions committed widespread rape, murder and extortion, while Kabul was heavily bombarded and partially destroyed by the fighting. Several failed reconciliations and alliances occurred between different leaders. The  In December 2001, after the Taliban government was overthrown, the Afghan Interim Administration under Hamid Karzai was formed. The International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) was established by the UN Security Council to help assist the Karzai administration and provide basic security. By this time, after two decades of war as well as an acute famine at the time, Afghanistan had one of the highest infant mortality, infant and child mortality rates in the world, the lowest life expectancy, much of the population were hungry, and infrastructure was in ruins. Many foreign donors started providing aid and assistance to rebuild the war-torn country.
Taliban forces meanwhile began regrouping inside Pakistan, while more coalition troops entered Afghanistan to help the Reconstruction in Afghanistan, rebuilding process. The Taliban insurgency, Taliban began an insurgency to regain control of Afghanistan. Over the next decade, ISAF and Afghan National Army, Afghan troops led many offensives against the Taliban, but failed to fully defeat them. Afghanistan remained one of the poorest countries in the world because of a lack of foreign investment, Corruption in Afghanistan, government corruption, and the Taliban insurgency.
Meanwhile, Karzai attempted to unite the peoples of the country, and the Afghan government was able to build some democratic structures, adopting a constitution in 2004 with the name Islamic Republic of Afghanistan. Attempts were made, often with the support of foreign donor countries, to improve the country's economy, healthcare, education, transport, and agriculture. ISAF forces also began to train the Afghan National Security Forces. Following 2002, nearly five million Afghan diaspora, Afghans were repatriated. The number of NATO troops present in Afghanistan peaked at 140,000 in 2011, dropping to about 16,000 in 2018.
In September 2014 Ashraf Ghani became president after the Afghan presidential election, 2014, 2014 presidential election where for the first time in Afghanistan's history power was democratically transferred. On 28 December 2014, NATO formally ended ISAF combat operations in Afghanistan and transferred full security responsibility to the Afghan government. The NATO-led Operation Resolute Support was formed the same day as a successor to ISAF. Thousands of NATO troops remained in the country to train and advise Afghan government forces and continue their fight against the Taliban. It was estimated in 2015 that "about 147,000 people have been killed in the Afghanistan war since 2001. More than 38,000 of those killed have been civilians". A report titled ''Body Count'' concluded that 106,000–170,000 civilians had been killed as a result of the fighting in Afghanistan at the hands of all parties to the conflict.
In December 2001, after the Taliban government was overthrown, the Afghan Interim Administration under Hamid Karzai was formed. The International Security Assistance Force (ISAF) was established by the UN Security Council to help assist the Karzai administration and provide basic security. By this time, after two decades of war as well as an acute famine at the time, Afghanistan had one of the highest infant mortality, infant and child mortality rates in the world, the lowest life expectancy, much of the population were hungry, and infrastructure was in ruins. Many foreign donors started providing aid and assistance to rebuild the war-torn country.
Taliban forces meanwhile began regrouping inside Pakistan, while more coalition troops entered Afghanistan to help the Reconstruction in Afghanistan, rebuilding process. The Taliban insurgency, Taliban began an insurgency to regain control of Afghanistan. Over the next decade, ISAF and Afghan National Army, Afghan troops led many offensives against the Taliban, but failed to fully defeat them. Afghanistan remained one of the poorest countries in the world because of a lack of foreign investment, Corruption in Afghanistan, government corruption, and the Taliban insurgency.
Meanwhile, Karzai attempted to unite the peoples of the country, and the Afghan government was able to build some democratic structures, adopting a constitution in 2004 with the name Islamic Republic of Afghanistan. Attempts were made, often with the support of foreign donor countries, to improve the country's economy, healthcare, education, transport, and agriculture. ISAF forces also began to train the Afghan National Security Forces. Following 2002, nearly five million Afghan diaspora, Afghans were repatriated. The number of NATO troops present in Afghanistan peaked at 140,000 in 2011, dropping to about 16,000 in 2018.
In September 2014 Ashraf Ghani became president after the Afghan presidential election, 2014, 2014 presidential election where for the first time in Afghanistan's history power was democratically transferred. On 28 December 2014, NATO formally ended ISAF combat operations in Afghanistan and transferred full security responsibility to the Afghan government. The NATO-led Operation Resolute Support was formed the same day as a successor to ISAF. Thousands of NATO troops remained in the country to train and advise Afghan government forces and continue their fight against the Taliban. It was estimated in 2015 that "about 147,000 people have been killed in the Afghanistan war since 2001. More than 38,000 of those killed have been civilians". A report titled ''Body Count'' concluded that 106,000–170,000 civilians had been killed as a result of the fighting in Afghanistan at the hands of all parties to the conflict.
 On 19 February 2020, the US–Taliban deal was made in Qatar. The 2020 US–Taliban deal was one of the critical events that caused the collapse of the Afghan National Security Forces (ANSF); following the signing of the deal, the US dramatically reduced the number of air attacks and deprived the ANSF of a critical edge in fighting the Taliban insurgency, leading to the Taliban takeover of Kabul.
On 19 February 2020, the US–Taliban deal was made in Qatar. The 2020 US–Taliban deal was one of the critical events that caused the collapse of the Afghan National Security Forces (ANSF); following the signing of the deal, the US dramatically reduced the number of air attacks and deprived the ANSF of a critical edge in fighting the Taliban insurgency, leading to the Taliban takeover of Kabul.
 Taliban rule was swiftly restored as its opponents were defeated or left the country. Declaring an "Islamic Emirate", it is apparently led by Head of the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, supreme leader Hibatullah Akhundzada and acting Prime Minister of Afghanistan, Prime Minister Hasan Akhund, who took office on 7 September 2021. Akhund is one of the four founders of the Taliban and was a deputy Prime Minister in their previous Emirate; his appointment was seen as a compromise between moderates and hardliners. A Cabinet of Afghanistan, new, all-male cabinet was formed including Abdul Hakim Ishaqzai as Minister of Justice. On 20 September 2021, Secretary-General of the United Nations, United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres received a letter from acting Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Afghanistan), minister of Foreign Affairs Amir Khan Muttaqi to formally claim Afghanistan's seat as a member state for their official spokesman in Doha, Suhail Shaheen, and asked to address the United Nations General Assembly, General Assembly. During the previous Taliban rule from 1996 to 2001, the United Nations never recognized their representatives and chose to work with the then-government in exile instead.
Western nations have suspended most humanitarian aid to Afghanistan following the Taliban's takeover of the country in August 2021 and the World Bank and International Monetary Fund also halted payments. In October 2021, more than half of Afghanistan's 39 million people faced an acute Food security, food shortage. On 11 November 2021, the ''Human Rights Watch'' reported that Afghanistan was facing widespread famine due to an economic and banking crisis.
Though the state of war in the country has ended as of 2021, armed conflict persists in some regions amid Islamic State–Taliban conflict, fighting between the Taliban and the local branch of the Islamic State, as well as an anti-Taliban Republican insurgency in Afghanistan, Republican insurgency. A year into Taliban rule, former president Hamid Karzai said in an interview: "In terms of [an] end to widespread fighting and conflict, we are happy — there's more stability, there's more security. But in terms of Afghanistan having a government that all Afghan people find themselves [in], we still have a way to go. In terms of the economy of the country, it's a disaster."
Taliban rule was swiftly restored as its opponents were defeated or left the country. Declaring an "Islamic Emirate", it is apparently led by Head of the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan, supreme leader Hibatullah Akhundzada and acting Prime Minister of Afghanistan, Prime Minister Hasan Akhund, who took office on 7 September 2021. Akhund is one of the four founders of the Taliban and was a deputy Prime Minister in their previous Emirate; his appointment was seen as a compromise between moderates and hardliners. A Cabinet of Afghanistan, new, all-male cabinet was formed including Abdul Hakim Ishaqzai as Minister of Justice. On 20 September 2021, Secretary-General of the United Nations, United Nations Secretary-General António Guterres received a letter from acting Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Afghanistan), minister of Foreign Affairs Amir Khan Muttaqi to formally claim Afghanistan's seat as a member state for their official spokesman in Doha, Suhail Shaheen, and asked to address the United Nations General Assembly, General Assembly. During the previous Taliban rule from 1996 to 2001, the United Nations never recognized their representatives and chose to work with the then-government in exile instead.
Western nations have suspended most humanitarian aid to Afghanistan following the Taliban's takeover of the country in August 2021 and the World Bank and International Monetary Fund also halted payments. In October 2021, more than half of Afghanistan's 39 million people faced an acute Food security, food shortage. On 11 November 2021, the ''Human Rights Watch'' reported that Afghanistan was facing widespread famine due to an economic and banking crisis.
Though the state of war in the country has ended as of 2021, armed conflict persists in some regions amid Islamic State–Taliban conflict, fighting between the Taliban and the local branch of the Islamic State, as well as an anti-Taliban Republican insurgency in Afghanistan, Republican insurgency. A year into Taliban rule, former president Hamid Karzai said in an interview: "In terms of [an] end to widespread fighting and conflict, we are happy — there's more stability, there's more security. But in terms of Afghanistan having a government that all Afghan people find themselves [in], we still have a way to go. In terms of the economy of the country, it's a disaster."
 Despite having numerous rivers and list of dams and reservoirs in Afghanistan, reservoirs, large parts of the country are dry. The endorheic Sistan Basin is one of the driest regions in the world. The Amu Darya rises at the north of the Hindu Kush, while the nearby Hari Rud flows west towards Herat, and the Arghandab River from the central region southwards. To the south and west of the Hindu Kush flow a number of streams that are tributaries of the Indus River, such as the Helmand River. One exception is the Kabul River which flows in an easterly direction to the Indus ending at the Indian Ocean. Afghanistan receives heavy snow during the winter in the
Despite having numerous rivers and list of dams and reservoirs in Afghanistan, reservoirs, large parts of the country are dry. The endorheic Sistan Basin is one of the driest regions in the world. The Amu Darya rises at the north of the Hindu Kush, while the nearby Hari Rud flows west towards Herat, and the Arghandab River from the central region southwards. To the south and west of the Hindu Kush flow a number of streams that are tributaries of the Indus River, such as the Helmand River. One exception is the Kabul River which flows in an easterly direction to the Indus ending at the Indian Ocean. Afghanistan receives heavy snow during the winter in the  Several types of mammals exist throughout Afghanistan. Snow leopards, Siberian tigers and brown bears live in the high elevation alpine tundra regions. The Marco Polo sheep exclusively live in the Wakhan Corridor region of north-east Afghanistan. Foxes, wolves, otters, deer, wild sheep, lynx and other big cats populate the mountain forest region of the east. In the semi-desert northern plains, wildlife include a variety of birds, hedgehogs, gophers, and large carnivores such as Golden jackal, jackals and Striped hyena, hyenas.
Gazelles, wild boar, wild pigs and jackals populate the steppe plains of the south and west, while mongoose and cheetahs exist in the semi-desert south. Marmots and ibex also live in the high mountains of Afghanistan, and pheasants exist in some parts of the country. The Afghan hound is a native breed of dog known for its fast speed and its long hair; it is relatively known in the west.
Endemic fauna of Afghanistan includes the Afghan flying squirrel, Afghan snowfinch, Afghanodon (or the "Paghman mountain salamander"), ''Stigmella kasyi'', ''Vulcaniella kabulensis'', Afghan leopard gecko, ''Wheeleria parviflorellus'', amongst others. Endemic flora include ''Iris afghanica''. Afghanistan has a wide variety of birds despite its relatively arid climate – an estimated 460 species of which 235 breed within.
The forest region of Afghanistan has vegetation such as pine trees, spruce trees, fir trees and larches, whereas the steppe grassland regions consist of broadleaf trees, short grass, perennial plants and shrublands. The colder high elevation regions are composed of hardy grasses and small flowering plants. Several regions are designated List of protected areas of Afghanistan, protected areas; there are three national parks: Band-e Amir, Wakhan National Park, Wakhan and Nuristan National Park, Nuristan. Afghanistan had a 2018 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 8.85/10, ranking it 15th globally out of 172 countries.
Several types of mammals exist throughout Afghanistan. Snow leopards, Siberian tigers and brown bears live in the high elevation alpine tundra regions. The Marco Polo sheep exclusively live in the Wakhan Corridor region of north-east Afghanistan. Foxes, wolves, otters, deer, wild sheep, lynx and other big cats populate the mountain forest region of the east. In the semi-desert northern plains, wildlife include a variety of birds, hedgehogs, gophers, and large carnivores such as Golden jackal, jackals and Striped hyena, hyenas.
Gazelles, wild boar, wild pigs and jackals populate the steppe plains of the south and west, while mongoose and cheetahs exist in the semi-desert south. Marmots and ibex also live in the high mountains of Afghanistan, and pheasants exist in some parts of the country. The Afghan hound is a native breed of dog known for its fast speed and its long hair; it is relatively known in the west.
Endemic fauna of Afghanistan includes the Afghan flying squirrel, Afghan snowfinch, Afghanodon (or the "Paghman mountain salamander"), ''Stigmella kasyi'', ''Vulcaniella kabulensis'', Afghan leopard gecko, ''Wheeleria parviflorellus'', amongst others. Endemic flora include ''Iris afghanica''. Afghanistan has a wide variety of birds despite its relatively arid climate – an estimated 460 species of which 235 breed within.
The forest region of Afghanistan has vegetation such as pine trees, spruce trees, fir trees and larches, whereas the steppe grassland regions consist of broadleaf trees, short grass, perennial plants and shrublands. The colder high elevation regions are composed of hardy grasses and small flowering plants. Several regions are designated List of protected areas of Afghanistan, protected areas; there are three national parks: Band-e Amir, Wakhan National Park, Wakhan and Nuristan National Park, Nuristan. Afghanistan had a 2018 Forest Landscape Integrity Index mean score of 8.85/10, ranking it 15th globally out of 172 countries.
 The population of Afghanistan was estimated at 32.9 million as of 2019 by the Afghanistan Statistics and Information Authority, whereas the UN estimates over 38.0 million. In 1979 the total population was reported to be about 15.5 million. About 23.9% of them are urban area, urbanite, 71.4% live in rural areas, and the remaining 4.7% are nomadic. An additional 3 million or so Afghans are temporarily housed in neighboring Afghans in Pakistan, Pakistan and Afghans in Iran, Iran, most of whom were born and raised in those two countries. As of 2013, Afghanistan was the largest refugee-producing country in the world, a title held for 32 years.
The current population growth rate is 2.37%, one of the highest in the world outside of Africa. This population is expected to reach 82 million by 2050 if current population trends continue. The population of Afghanistan increased steadily until the 1980s, when civil war caused millions to flee to other countries such as Pakistan. Millions have since returned and the war conditions contribute to the country having the highest fertility rate outside Africa. Afghanistan's healthcare has recovered since the turn of the century, causing falls in infant mortality and increases in life expectancy, although it has the lowest life expectance of any country outside Africa. This (along with other factors such as returning refugees) caused rapid population growth in the 2000s that has only recently started to slow down. The Gini coefficient in 2008 was 27.8.
The population of Afghanistan was estimated at 32.9 million as of 2019 by the Afghanistan Statistics and Information Authority, whereas the UN estimates over 38.0 million. In 1979 the total population was reported to be about 15.5 million. About 23.9% of them are urban area, urbanite, 71.4% live in rural areas, and the remaining 4.7% are nomadic. An additional 3 million or so Afghans are temporarily housed in neighboring Afghans in Pakistan, Pakistan and Afghans in Iran, Iran, most of whom were born and raised in those two countries. As of 2013, Afghanistan was the largest refugee-producing country in the world, a title held for 32 years.
The current population growth rate is 2.37%, one of the highest in the world outside of Africa. This population is expected to reach 82 million by 2050 if current population trends continue. The population of Afghanistan increased steadily until the 1980s, when civil war caused millions to flee to other countries such as Pakistan. Millions have since returned and the war conditions contribute to the country having the highest fertility rate outside Africa. Afghanistan's healthcare has recovered since the turn of the century, causing falls in infant mortality and increases in life expectancy, although it has the lowest life expectance of any country outside Africa. This (along with other factors such as returning refugees) caused rapid population growth in the 2000s that has only recently started to slow down. The Gini coefficient in 2008 was 27.8.
 Afghans are divided into several ethnolinguistic groups. Off of sociological research data by The Asia Foundation in 2019, the
Afghans are divided into several ethnolinguistic groups. Off of sociological research data by The Asia Foundation in 2019, the  The CIA estimated in 2009 that 99.7% of the Afghan population was Muslim and most are thought to adhere to the Sunni Hanafi school. According to Pew Research Center, as much as 90% are of the Sunni denomination, 7% Shia and 3% non-denominational Muslim, non-denominational. The CIA Factbook variously estimates up to 89.7% Sunni or up to 15% Shia.
Afghan Sikhism in Afghanistan, Sikhs and Hinduism in Afghanistan, Hindus are also found in certain major cities (namely Kabul, Jalalabad, Ghazni, Kandahar) accompanied by gurdwaras and mandirs. According to Deutsche Welle in September 2021, 250 remain in the country after 67 were evacuated to India.
There was a small History of the Jews in Afghanistan, Jewish community in Afghanistan, living mainly in Herat and Kabul. Over the years, this small community was forced leave due to decades of warfare and religious persecution. By the end of the twentieth century, the entire community had emigrated to Israel and the United States, with the exception of one person, Herat-born Zablon Simintov. He remained for years, being the caretaker of the only remaining Afghan synagogue. After the second Taliban takeover, he left Afghanistan for the United States.
Afghan Christians, who number 500–8,000, practice their faith secretly due to intense societal opposition, and there are no public churches.
The CIA estimated in 2009 that 99.7% of the Afghan population was Muslim and most are thought to adhere to the Sunni Hanafi school. According to Pew Research Center, as much as 90% are of the Sunni denomination, 7% Shia and 3% non-denominational Muslim, non-denominational. The CIA Factbook variously estimates up to 89.7% Sunni or up to 15% Shia.
Afghan Sikhism in Afghanistan, Sikhs and Hinduism in Afghanistan, Hindus are also found in certain major cities (namely Kabul, Jalalabad, Ghazni, Kandahar) accompanied by gurdwaras and mandirs. According to Deutsche Welle in September 2021, 250 remain in the country after 67 were evacuated to India.
There was a small History of the Jews in Afghanistan, Jewish community in Afghanistan, living mainly in Herat and Kabul. Over the years, this small community was forced leave due to decades of warfare and religious persecution. By the end of the twentieth century, the entire community had emigrated to Israel and the United States, with the exception of one person, Herat-born Zablon Simintov. He remained for years, being the caretaker of the only remaining Afghan synagogue. After the second Taliban takeover, he left Afghanistan for the United States.
Afghan Christians, who number 500–8,000, practice their faith secretly due to intense societal opposition, and there are no public churches.
 Education in Afghanistan includes K–12 and higher education, which is overseen by the Ministry of Education (Afghanistan), Ministry of Education and the Ministry of Higher Education (Afghanistan), Ministry of Higher Education. There are over 16,000 schools in the country and roughly 9 million students. Of this, about 60% are males and 40% females. However, the new regime has thus far forbidden girls and female teachers from returning to secondary schools. Over 174,000 students are enrolled in different List of universities in Afghanistan, universities around the country. About 21% of these are females. Former Education Minister Ghulam Farooq Wardak had stated that construction of 8,000 schools is required for the remaining children who are deprived of formal learning. As of 2018 the literacy rate of the population age 15 and older is 43.02% (males 55.48% and females 29.81%).
The top universities in Afghanistan are the American University of Afghanistan (AUAF) followed by Kabul University (KU), both of which are located in Kabul. The National Military Academy of Afghanistan, modeled after the United States Military Academy at West Point, was a four-year military development institution dedicated to graduating officers for the Afghan Armed Forces. The Afghan Defense University was constructed near Qargha in Kabul. Major universities outside of Kabul include Kandahar University in the south, Herat University in the northwest, Balkh University and Kunduz University in the north, Nangarhar University and Khost University in the east. Kabul University was founded in 1932 and is a respected institute that played a significant part in the country's education; from the 1960s the Kabul University was also a hotbed of radical political ideologies such as Marxism and Islamism, which played major parts in society, politics and the war that began in 1978.
After the Taliban regained power in 2021, it became unclear to what extent female education would continue in the country. In March 2022, after they had been closed for some time, it was announced that girl's schools after 6th grade would be reopened shortly. However, shortly before reopening, the order was rescinded and schools for older girls remained closed.
Education in Afghanistan includes K–12 and higher education, which is overseen by the Ministry of Education (Afghanistan), Ministry of Education and the Ministry of Higher Education (Afghanistan), Ministry of Higher Education. There are over 16,000 schools in the country and roughly 9 million students. Of this, about 60% are males and 40% females. However, the new regime has thus far forbidden girls and female teachers from returning to secondary schools. Over 174,000 students are enrolled in different List of universities in Afghanistan, universities around the country. About 21% of these are females. Former Education Minister Ghulam Farooq Wardak had stated that construction of 8,000 schools is required for the remaining children who are deprived of formal learning. As of 2018 the literacy rate of the population age 15 and older is 43.02% (males 55.48% and females 29.81%).
The top universities in Afghanistan are the American University of Afghanistan (AUAF) followed by Kabul University (KU), both of which are located in Kabul. The National Military Academy of Afghanistan, modeled after the United States Military Academy at West Point, was a four-year military development institution dedicated to graduating officers for the Afghan Armed Forces. The Afghan Defense University was constructed near Qargha in Kabul. Major universities outside of Kabul include Kandahar University in the south, Herat University in the northwest, Balkh University and Kunduz University in the north, Nangarhar University and Khost University in the east. Kabul University was founded in 1932 and is a respected institute that played a significant part in the country's education; from the 1960s the Kabul University was also a hotbed of radical political ideologies such as Marxism and Islamism, which played major parts in society, politics and the war that began in 1978.
After the Taliban regained power in 2021, it became unclear to what extent female education would continue in the country. In March 2022, after they had been closed for some time, it was announced that girl's schools after 6th grade would be reopened shortly. However, shortly before reopening, the order was rescinded and schools for older girls remained closed.
 According to the Human Development Index, Afghanistan is the List of countries by Human Development Index, 15th least developed country in the world. The average List of countries by life expectancy, life expectancy is estimated to be around 60 years. The country's maternal mortality rate is 396 deaths/100,000 live births and its infant mortality rate is 66 to 112.8 deaths in every 1,000 live births. The Ministry of Public Health (Afghanistan), Ministry of Public Health plans to cut the infant mortality rate to 400 for every 100,000 live births before 2020. The country has more than 3,000 midwifery, midwives, with an additional 300 to 400 being trained each year.
There are over 100 hospitals in Afghanistan, with the most advanced treatments being available in Kabul. The French Medical Institute for Children and Indira Gandhi Children's Hospital in Kabul are the leading children's hospitals in the country. Some of the other leading hospitals in Kabul include the Jamhuriat Hospital and Jinnah Hospital (Kabul), Jinnah Hospital. In spite of all this, many Afghans travel to Pakistan and India for advanced treatment.
It was reported in 2006 that nearly 60% of the Afghan population lives within a two-hour walk of the nearest health facility. Disability rate is also high in Afghanistan due to the decades of war. It was reported recently that about 80,000 people are missing limbs. Non-governmental charities such as Save the Children and Mahboba's Promise assist orphans in association with governmental structures. Demographic and Health Surveys is working with the Indian Institute of Health Management Research and others to conduct a survey in Afghanistan focusing on maternal death, among other things.
According to the Human Development Index, Afghanistan is the List of countries by Human Development Index, 15th least developed country in the world. The average List of countries by life expectancy, life expectancy is estimated to be around 60 years. The country's maternal mortality rate is 396 deaths/100,000 live births and its infant mortality rate is 66 to 112.8 deaths in every 1,000 live births. The Ministry of Public Health (Afghanistan), Ministry of Public Health plans to cut the infant mortality rate to 400 for every 100,000 live births before 2020. The country has more than 3,000 midwifery, midwives, with an additional 300 to 400 being trained each year.
There are over 100 hospitals in Afghanistan, with the most advanced treatments being available in Kabul. The French Medical Institute for Children and Indira Gandhi Children's Hospital in Kabul are the leading children's hospitals in the country. Some of the other leading hospitals in Kabul include the Jamhuriat Hospital and Jinnah Hospital (Kabul), Jinnah Hospital. In spite of all this, many Afghans travel to Pakistan and India for advanced treatment.
It was reported in 2006 that nearly 60% of the Afghan population lives within a two-hour walk of the nearest health facility. Disability rate is also high in Afghanistan due to the decades of war. It was reported recently that about 80,000 people are missing limbs. Non-governmental charities such as Save the Children and Mahboba's Promise assist orphans in association with governmental structures. Demographic and Health Surveys is working with the Indian Institute of Health Management Research and others to conduct a survey in Afghanistan focusing on maternal death, among other things.
 Following the effective collapse of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan during the 2021 Taliban offensive, the Taliban declared the country an Islamic Emirate. A new caretaker government was announced on 7 September. As of 8 September 2021, no other country had formally recognized the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan as the ''de jure'' government of Afghanistan.
A traditional instrument of governance in Afghanistan is the ''loya jirga'' (grand assembly), a Pashtun consultative meeting that was mainly organized for choosing a new head of state, adopting a new constitution, or to settle national or regional issue such as war. Loya jirgas have been held since at least 1747, with the most recent one occurring in August 2020.
Following the effective collapse of the Islamic Republic of Afghanistan during the 2021 Taliban offensive, the Taliban declared the country an Islamic Emirate. A new caretaker government was announced on 7 September. As of 8 September 2021, no other country had formally recognized the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan as the ''de jure'' government of Afghanistan.
A traditional instrument of governance in Afghanistan is the ''loya jirga'' (grand assembly), a Pashtun consultative meeting that was mainly organized for choosing a new head of state, adopting a new constitution, or to settle national or regional issue such as war. Loya jirgas have been held since at least 1747, with the most recent one occurring in August 2020.
 # Badakhshan Province, Badakhshan
# Badghis Province, Badghis
# Baghlan Province, Baghlan
# Balkh Province, Balkh
# Bamyan Province, Bamyan
# Daykundi Province, Daykundi
# Farah Province, Farah
# Faryab Province, Faryab
# Ghazni Province, Ghazni
# Ghor Province, Ghor
# Helmand Province, Helmand
# Herat Province, Herat
# Jowzjan Province, Jowzjan
# Kabul Province, Kabul
# Kandahar Province, Kandahar
# Kapisa Province, Kapisa
# Khost Province, Khost
# Kunar Province, Kunar
# Kunduz Province, Kunduz
# Laghman Province, Laghman
# Logar Province, Logar
# Nangarhar Province, Nangarhar
# Nimruz Province, Nimruz
# Nuristan Province, Nuristan
# Oruzgan Province, Oruzgan
# Paktia Province, Paktia
# Paktika Province, Paktika
# Panjshir Province, Panjshir
# Parwan Province, Parwan
# Samangan Province, Samangan
# Sar-e Pol Province, Sar-e Pol
# Takhar Province, Takhar
# Wardak Province, Wardak
# Zabul Province, Zabul
# Badakhshan Province, Badakhshan
# Badghis Province, Badghis
# Baghlan Province, Baghlan
# Balkh Province, Balkh
# Bamyan Province, Bamyan
# Daykundi Province, Daykundi
# Farah Province, Farah
# Faryab Province, Faryab
# Ghazni Province, Ghazni
# Ghor Province, Ghor
# Helmand Province, Helmand
# Herat Province, Herat
# Jowzjan Province, Jowzjan
# Kabul Province, Kabul
# Kandahar Province, Kandahar
# Kapisa Province, Kapisa
# Khost Province, Khost
# Kunar Province, Kunar
# Kunduz Province, Kunduz
# Laghman Province, Laghman
# Logar Province, Logar
# Nangarhar Province, Nangarhar
# Nimruz Province, Nimruz
# Nuristan Province, Nuristan
# Oruzgan Province, Oruzgan
# Paktia Province, Paktia
# Paktika Province, Paktika
# Panjshir Province, Panjshir
# Parwan Province, Parwan
# Samangan Province, Samangan
# Sar-e Pol Province, Sar-e Pol
# Takhar Province, Takhar
# Wardak Province, Wardak
# Zabul Province, Zabul
 Afghanistan's nominal GDP was $21.7 billion in 2018, or $72.9 billion by purchasing power parity (PPP). Its List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita, GDP per capita is $2,024 (PPP). Despite having $1 trillion or more in mineral deposits, it remains one of the world's least developed countries. Afghanistan's rough physical geography and its landlocked status has been cited as reasons why the country has always been among the least developed in the modern era – a factor where progress is also slowed by contemporary conflict and political instability. The country imports over $7 billion worth of goods but exports only $784 million, mainly fruits and Nut (fruit), nuts. It has $2.8 billion in external debt. The service sector contributed the most to the GDP (55.9%) followed by agriculture (23%) and industry (21.1%).
While the nation's current account deficit is largely financed with donor money, only a small portion is provided directly to the government budget. The rest is provided to non-budgetary expenditure and donor-designated projects through the United Nations system and non-governmental organizations.
Da Afghanistan Bank serves as the central bank of the nation and the Afghan afghani, Afghani (AFN) is the national currency, with an exchange rate of about 75 Afghanis to 1 US dollar. A number of local and foreign banks operate in the country, including the Afghanistan International Bank, New Kabul Bank, Azizi Bank, Pashtany Bank, Standard Chartered Bank, and the First MicroFinance Bank-Afghanistan, First Micro Finance Bank.
Afghanistan's nominal GDP was $21.7 billion in 2018, or $72.9 billion by purchasing power parity (PPP). Its List of countries by GDP (PPP) per capita, GDP per capita is $2,024 (PPP). Despite having $1 trillion or more in mineral deposits, it remains one of the world's least developed countries. Afghanistan's rough physical geography and its landlocked status has been cited as reasons why the country has always been among the least developed in the modern era – a factor where progress is also slowed by contemporary conflict and political instability. The country imports over $7 billion worth of goods but exports only $784 million, mainly fruits and Nut (fruit), nuts. It has $2.8 billion in external debt. The service sector contributed the most to the GDP (55.9%) followed by agriculture (23%) and industry (21.1%).
While the nation's current account deficit is largely financed with donor money, only a small portion is provided directly to the government budget. The rest is provided to non-budgetary expenditure and donor-designated projects through the United Nations system and non-governmental organizations.
Da Afghanistan Bank serves as the central bank of the nation and the Afghan afghani, Afghani (AFN) is the national currency, with an exchange rate of about 75 Afghanis to 1 US dollar. A number of local and foreign banks operate in the country, including the Afghanistan International Bank, New Kabul Bank, Azizi Bank, Pashtany Bank, Standard Chartered Bank, and the First MicroFinance Bank-Afghanistan, First Micro Finance Bank.
 One of the main drivers for the current economic recovery is the return of over 5 million Afghan diaspora, expatriates, who brought with them entrepreneurship and wealth-creating skills as well as much needed funds to start up businesses. Many Afghans are now involved in construction, which is one of the largest industries in the country. Some of the major national construction projects include the $35 billion New Kabul City next to the capital, the Aino Mena project in Kandahar, and the Ghazi Amanullah Khan Town near Jalalabad. Similar development projects have also begun in Herat, Mazar-e-Sharif, and other cities. An estimated 400,000 people enter the labor market each year.
Several small companies and factories began operating in different parts of the country, which not only provide revenues to the government but also create new jobs. Improvements to the business environment have resulted in more than $1.5 billion in Telecommunication, telecom investment and created more than 100,000 jobs since 2003. Afghan rugs are becoming popular again, allowing many carpet dealers around the country to hire more workers; in 2016–17 it was the fourth most exported group of items.
Afghanistan is a member of WTO, SAARC, Economic Cooperation Organization, ECO, and OIC. It holds an observer status in Shanghai Cooperation Organisation, SCO. In 2018, a majority of imports come from either Iran, China, Pakistan and Kazakhstan, while 84% of exports are to Pakistan and India.
Since the Taliban's takeover of the country in August 2021, the United States has Afghan frozen assets, frozen about $9 billion in assets belonging to the Da Afghanistan Bank, Afghan central bank, blocking the Taliban from accessing billions of dollars held in U.S. bank accounts.
One of the main drivers for the current economic recovery is the return of over 5 million Afghan diaspora, expatriates, who brought with them entrepreneurship and wealth-creating skills as well as much needed funds to start up businesses. Many Afghans are now involved in construction, which is one of the largest industries in the country. Some of the major national construction projects include the $35 billion New Kabul City next to the capital, the Aino Mena project in Kandahar, and the Ghazi Amanullah Khan Town near Jalalabad. Similar development projects have also begun in Herat, Mazar-e-Sharif, and other cities. An estimated 400,000 people enter the labor market each year.
Several small companies and factories began operating in different parts of the country, which not only provide revenues to the government but also create new jobs. Improvements to the business environment have resulted in more than $1.5 billion in Telecommunication, telecom investment and created more than 100,000 jobs since 2003. Afghan rugs are becoming popular again, allowing many carpet dealers around the country to hire more workers; in 2016–17 it was the fourth most exported group of items.
Afghanistan is a member of WTO, SAARC, Economic Cooperation Organization, ECO, and OIC. It holds an observer status in Shanghai Cooperation Organisation, SCO. In 2018, a majority of imports come from either Iran, China, Pakistan and Kazakhstan, while 84% of exports are to Pakistan and India.
Since the Taliban's takeover of the country in August 2021, the United States has Afghan frozen assets, frozen about $9 billion in assets belonging to the Da Afghanistan Bank, Afghan central bank, blocking the Taliban from accessing billions of dollars held in U.S. bank accounts.
 Agricultural production is the backbone of Afghanistan's economy and has traditionally dominated the economy, employing about 40% of the workforce as of 2018. The country is known for producing pomegranate production in Afghanistan, pomegranates, grapes, apricots, melons, and several other fresh and dry fruits. It is also known as the world's largest producer of Opium production in Afghanistan, opium – as much as 16% or more of the nation's economy is derived from the cultivation and sale of opium. It is also one of the world's top producers of
Agricultural production is the backbone of Afghanistan's economy and has traditionally dominated the economy, employing about 40% of the workforce as of 2018. The country is known for producing pomegranate production in Afghanistan, pomegranates, grapes, apricots, melons, and several other fresh and dry fruits. It is also known as the world's largest producer of Opium production in Afghanistan, opium – as much as 16% or more of the nation's economy is derived from the cultivation and sale of opium. It is also one of the world's top producers of  The country's natural resources include: coal, copper, iron ore,
The country's natural resources include: coal, copper, iron ore,  Tourism is a small industry in Afghanistan due to security issues. Nevertheless, some 20,000 foreign tourists visit the country annually as of 2016. In particular an important region for domestic and international tourism is the picturesque Bamyan Valley, which includes lakes, canyons and historical sites, helped by the fact it is in a safe area away from insurgent activity. Smaller numbers visit and trek in regions such as the Wakhan Valley, which is also one of the world's most remote communities. From the late 1960s onwards, Afghanistan was a popular stop on the famous hippie trail, attracting many Europeans and Americans. Coming from Iran, the trail traveled through various Afghan provinces and cities including Herat, Kandahar and
Tourism is a small industry in Afghanistan due to security issues. Nevertheless, some 20,000 foreign tourists visit the country annually as of 2016. In particular an important region for domestic and international tourism is the picturesque Bamyan Valley, which includes lakes, canyons and historical sites, helped by the fact it is in a safe area away from insurgent activity. Smaller numbers visit and trek in regions such as the Wakhan Valley, which is also one of the world's most remote communities. From the late 1960s onwards, Afghanistan was a popular stop on the famous hippie trail, attracting many Europeans and Americans. Coming from Iran, the trail traveled through various Afghan provinces and cities including Herat, Kandahar and  The city of Ghazni has significant history and historical sites, and together with Bamyan city have in recent years been voted Islamic Cultural Capital and South Asia Cultural Capital respectively. The cities of Herat, Kandahar, Balkh, and Zaranj are also very historic. The Minaret of Jam in the Hari River, Afghanistan, Hari River valley is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. A cloak reputedly worn by Islam's prophet Muhammad is kept inside the Shrine of the Cloak in Kandahar, a city founded by
The city of Ghazni has significant history and historical sites, and together with Bamyan city have in recent years been voted Islamic Cultural Capital and South Asia Cultural Capital respectively. The cities of Herat, Kandahar, Balkh, and Zaranj are also very historic. The Minaret of Jam in the Hari River, Afghanistan, Hari River valley is a UNESCO World Heritage Site. A cloak reputedly worn by Islam's prophet Muhammad is kept inside the Shrine of the Cloak in Kandahar, a city founded by  Due to Afghanistan's geography, transport between various parts of the country has historically been difficult. The backbone of Afghanistan's road network is Highway 1 (Afghanistan), Highway 1, often called the "Ring Road", which extends for and connects five major cities: Kabul, Ghazni, Kandahar, Herat and Mazar-i-Sharif, with spurs to Kunduz and Jalalabad and various border crossings, while skirting around the mountains of the Hindu Kush.
The Ring Road is crucially important for domestic and international trade and the economy. A key portion of the Ring Road is the Salang Tunnel, completed in 1964, which facilitates travel through the Hindu Kush mountain range and connects northern and southern Afghanistan. It is the only land route that connects Central Asia to the Indian subcontinent. Several mountain passes allow travel between the Hindu Kush in other areas. Serious traffic accidents are common on Afghan roads and highways, particularly on the Kabul–Kandahar Highway, Kabul–Kandahar and the Kabul–Jalalabad Road. Traveling by bus in Afghanistan remains dangerous due to militant activities.
Due to Afghanistan's geography, transport between various parts of the country has historically been difficult. The backbone of Afghanistan's road network is Highway 1 (Afghanistan), Highway 1, often called the "Ring Road", which extends for and connects five major cities: Kabul, Ghazni, Kandahar, Herat and Mazar-i-Sharif, with spurs to Kunduz and Jalalabad and various border crossings, while skirting around the mountains of the Hindu Kush.
The Ring Road is crucially important for domestic and international trade and the economy. A key portion of the Ring Road is the Salang Tunnel, completed in 1964, which facilitates travel through the Hindu Kush mountain range and connects northern and southern Afghanistan. It is the only land route that connects Central Asia to the Indian subcontinent. Several mountain passes allow travel between the Hindu Kush in other areas. Serious traffic accidents are common on Afghan roads and highways, particularly on the Kabul–Kandahar Highway, Kabul–Kandahar and the Kabul–Jalalabad Road. Traveling by bus in Afghanistan remains dangerous due to militant activities.
 Air transport in Afghanistan is provided by the national carrier, Ariana Afghan Airlines, and by the private company Kam Air. Airlines from a number of countries also provide flights in and out of the country. These include Air India, Emirates (airline), Emirates, Gulf Air, Iran Aseman Airlines, Pakistan International Airlines, and Turkish Airlines. The country has four international airports: Hamid Karzai International Airport (formerly Kabul International Airport), Kandahar International Airport, Herat International Airport, and Mazar-e Sharif International Airport. Including domestic airports, there are 43. Bagram Air Base is a major military airfield.
The country has three rail links: one, a line from Mazar-i-Sharif to the Afghanistan–Uzbekistan Friendship Bridge, Uzbekistan border; a long line from Toraghundi to the
Air transport in Afghanistan is provided by the national carrier, Ariana Afghan Airlines, and by the private company Kam Air. Airlines from a number of countries also provide flights in and out of the country. These include Air India, Emirates (airline), Emirates, Gulf Air, Iran Aseman Airlines, Pakistan International Airlines, and Turkish Airlines. The country has four international airports: Hamid Karzai International Airport (formerly Kabul International Airport), Kandahar International Airport, Herat International Airport, and Mazar-e Sharif International Airport. Including domestic airports, there are 43. Bagram Air Base is a major military airfield.
The country has three rail links: one, a line from Mazar-i-Sharif to the Afghanistan–Uzbekistan Friendship Bridge, Uzbekistan border; a long line from Toraghundi to the  In the villages, families typically occupy mudbrick houses, or compounds with mudbrick or stone walled houses. Villages typically have a headman (''malik''), a master for water distribution (''mirab'') and a religious teacher (''mullah''). Men would typically work on the fields, joined by women during harvest. About 15% of the population are nomadic, locally called ''Kochi people, kochis''. When nomads pass villages they often buy supplies such as tea, wheat and kerosene from the villagers; villagers buy wool and milk from the nomads.
Afghan clothing for both men and women typically consists of various forms of shalwar kameez, especially ''perahan tunban'' and ''khet partug''. Women would normally wear a ''chador'' for head covering; some women, typically from highly conservative communities, wear the ''burqa'', a full body covering. These were worn by some women of the Pashtun community well before Islam came to the region, but the
In the villages, families typically occupy mudbrick houses, or compounds with mudbrick or stone walled houses. Villages typically have a headman (''malik''), a master for water distribution (''mirab'') and a religious teacher (''mullah''). Men would typically work on the fields, joined by women during harvest. About 15% of the population are nomadic, locally called ''Kochi people, kochis''. When nomads pass villages they often buy supplies such as tea, wheat and kerosene from the villagers; villagers buy wool and milk from the nomads.
Afghan clothing for both men and women typically consists of various forms of shalwar kameez, especially ''perahan tunban'' and ''khet partug''. Women would normally wear a ''chador'' for head covering; some women, typically from highly conservative communities, wear the ''burqa'', a full body covering. These were worn by some women of the Pashtun community well before Islam came to the region, but the  The nation has a complex history that has survived either in its current cultures or in the form of various languages and monuments. Afghanistan contains many remnants from all ages, including Ancient Greece, Greek and Buddhist stupas, monasteries, monuments, temples and Islamic minarets. Among the most well known are the Great Mosque of Herat, the Blue Mosque (Mazar-i-Sharif), Blue Mosque, the Minaret of Jam, the Chil Zena, the Qala-i Bost in Lashkargah, the ancient Greek city of Ai-Khanoum. However, many of its historic monuments have been damaged in modern times due to the civil wars. The two famous Buddhas of Bamiyan were destroyed by the Taliban, who regarded them as idolatrous. Despite that, archaeologists are still finding Buddhist relics in different parts of the country, some of them dating back to the 2nd century. As there was no colonialism in the modern era in Afghanistan, European-style architecture is rare but does exist: the Victory Arch at Paghman and the Darul Aman Palace in Kabul were built in this style in the 1920s by the Afghans themselves.
The nation has a complex history that has survived either in its current cultures or in the form of various languages and monuments. Afghanistan contains many remnants from all ages, including Ancient Greece, Greek and Buddhist stupas, monasteries, monuments, temples and Islamic minarets. Among the most well known are the Great Mosque of Herat, the Blue Mosque (Mazar-i-Sharif), Blue Mosque, the Minaret of Jam, the Chil Zena, the Qala-i Bost in Lashkargah, the ancient Greek city of Ai-Khanoum. However, many of its historic monuments have been damaged in modern times due to the civil wars. The two famous Buddhas of Bamiyan were destroyed by the Taliban, who regarded them as idolatrous. Despite that, archaeologists are still finding Buddhist relics in different parts of the country, some of them dating back to the 2nd century. As there was no colonialism in the modern era in Afghanistan, European-style architecture is rare but does exist: the Victory Arch at Paghman and the Darul Aman Palace in Kabul were built in this style in the 1920s by the Afghans themselves.
 Carpet weaving is an ancient practice in Afghanistan, and many of these are still Handicraft, handmade by tribal and nomadic people today. Carpets have been produced in the region for thousands of years and traditionally done by women. Some crafters express their feelings through the designs of rugs; for example after the outbreak of the
Carpet weaving is an ancient practice in Afghanistan, and many of these are still Handicraft, handmade by tribal and nomadic people today. Carpets have been produced in the region for thousands of years and traditionally done by women. Some crafters express their feelings through the designs of rugs; for example after the outbreak of the  Afghan classical music has close historical links with Indian classical music and use the same Hindustani terminology and theories like raga. Genres of this style of music include ghazal (poetic music) and instruments such as the Indian tabla, sitar and harmonium, and local instruments like zerbaghali, as well as dayereh and tanbur which are also known in Central Asia, the Caucusus and the Middle East. The Rubab (instrument), rubab is the country's national instrument and precurses the Indian sarod instrument. Some of the famous artists of classical music include Ustad Sarahang and Abdul Rahim Sarban, Sarban.
Pop music developed in the 1950s through Radio Kabul and was influential in social change. During this time female artists also started appearing, at first Mermon Parwin. Perhaps the most famous artist of this genre was Ahmad Zahir, who synthesized many genres and continues to be renowned for his voice and rich lyrics long after his death in 1979. Other notable masters of traditional or popular Afghan music include Nashenas, Ubaidullah Jan, Mahwash, Ahmad Wali, Farhad Darya, and Naghma.
Attan is the national dance of Afghanistan, a group dance popularly performed by Afghans of all backgrounds. The dance is considered part of Afghan identity.
Afghan classical music has close historical links with Indian classical music and use the same Hindustani terminology and theories like raga. Genres of this style of music include ghazal (poetic music) and instruments such as the Indian tabla, sitar and harmonium, and local instruments like zerbaghali, as well as dayereh and tanbur which are also known in Central Asia, the Caucusus and the Middle East. The Rubab (instrument), rubab is the country's national instrument and precurses the Indian sarod instrument. Some of the famous artists of classical music include Ustad Sarahang and Abdul Rahim Sarban, Sarban.
Pop music developed in the 1950s through Radio Kabul and was influential in social change. During this time female artists also started appearing, at first Mermon Parwin. Perhaps the most famous artist of this genre was Ahmad Zahir, who synthesized many genres and continues to be renowned for his voice and rich lyrics long after his death in 1979. Other notable masters of traditional or popular Afghan music include Nashenas, Ubaidullah Jan, Mahwash, Ahmad Wali, Farhad Darya, and Naghma.
Attan is the national dance of Afghanistan, a group dance popularly performed by Afghans of all backgrounds. The dance is considered part of Afghan identity.
 Afghan cuisine is largely based upon the nation's chief crops, such as wheat, maize, barley and rice. Accompanying these staples are native fruits and vegetables as well as dairy products such as milk, yogurt and whey. Kabuli palaw is the national dish of Afghanistan. The nation's culinary specialties reflect its ethnic and geographic diversity. Afghanistan is known for its high quality Pomegranate production in Afghanistan, pomegranates, grapes, and sweet melons. Tea is a favorite drink among Afghans, and a typical diet consists of naan, yoghurts, rice and meat.
Afghan cuisine is largely based upon the nation's chief crops, such as wheat, maize, barley and rice. Accompanying these staples are native fruits and vegetables as well as dairy products such as milk, yogurt and whey. Kabuli palaw is the national dish of Afghanistan. The nation's culinary specialties reflect its ethnic and geographic diversity. Afghanistan is known for its high quality Pomegranate production in Afghanistan, pomegranates, grapes, and sweet melons. Tea is a favorite drink among Afghans, and a typical diet consists of naan, yoghurts, rice and meat.
 Afghanistan's official New Year starts with Nowruz, an ancient tradition that started as a Zoroastrian celebration in present-day Iran, and with which it shares the annual celebration along with several other countries. It occurs every year at the March equinox, vernal equinox. Nauruz in Afghanistan, In Afghanistan, Nowruz is typically celebrated with music and dance, as well as holding buzkashi tournaments.
Yaldā, another nationally celebrated ancient tradition, commemorates the ancient goddess Mithra and marks the longest night of the year on the eve of the winter solstice (; usually falling on 20 or 21 December), during which families gather together to recite poetry and eat fruits—particularly the red fruits watermelon and pomegranate, as well as mixed nuts.
Religious festivals are also celebrated; as a predominantly Muslim country, Islamic events and festivals such as Ramadan, Eid al-Fitr and Ashura are widely celebrated annually in Afghanistan. The Sikh festival of Vaisakhi is celebrated by the Sikh community and the Hindu festival Diwali by the Hindu community.
Afghan Independence Day, National Independence Day is celebrated on 19 August to mark the Anglo-Afghan Treaty of 1919 under King
Afghanistan's official New Year starts with Nowruz, an ancient tradition that started as a Zoroastrian celebration in present-day Iran, and with which it shares the annual celebration along with several other countries. It occurs every year at the March equinox, vernal equinox. Nauruz in Afghanistan, In Afghanistan, Nowruz is typically celebrated with music and dance, as well as holding buzkashi tournaments.
Yaldā, another nationally celebrated ancient tradition, commemorates the ancient goddess Mithra and marks the longest night of the year on the eve of the winter solstice (; usually falling on 20 or 21 December), during which families gather together to recite poetry and eat fruits—particularly the red fruits watermelon and pomegranate, as well as mixed nuts.
Religious festivals are also celebrated; as a predominantly Muslim country, Islamic events and festivals such as Ramadan, Eid al-Fitr and Ashura are widely celebrated annually in Afghanistan. The Sikh festival of Vaisakhi is celebrated by the Sikh community and the Hindu festival Diwali by the Hindu community.
Afghan Independence Day, National Independence Day is celebrated on 19 August to mark the Anglo-Afghan Treaty of 1919 under King  Sport in Afghanistan is managed by the Afghan Sports Federation. Cricket and Association football are the two most popular sports in the country. The Afghan Sports Federation promotes cricket, association football, basketball, volleyball, golf, team handball, handball, boxing, taekwondo, Olympic weightlifting, weightlifting, bodybuilding, track and field, ice skating, skating, bowling, snooker, chess, and other sports.
Afghanistan's sports teams are increasingly celebrating titles at international events. Afghanistan national basketball team, basketball team won the first team sports title at the 2010 South Asian Games. Later that year, the country's Afghanistan national cricket team, cricket team followed it with the winning of 2009–10 ICC Intercontinental Cup. In 2012, the country's Afghanistan national 3x3 team, 3x3 basketball team won the gold medal at the 3-on-3 basketball at the 2012 Asian Beach Games, 2012 Asian Beach Games. In 2013, Afghanistan's Afghanistan national football team, football team followed as it won the SAFF Championship.
The Afghan national cricket team, which was formed in 2001, participated in the 2009 ICC World Cup Qualifier, 2010 ICC World Cricket League Division One and the 2010 ICC World Twenty20. It won the ACC Twenty20 Cup in 2007, 2009, 2011 and 2013. The team eventually made it and played in the 2015 Cricket World Cup. The Afghanistan Cricket Board (ACB) is the official governing body of the sport and is headquartered in Kabul. The Alokozay Kabul International Cricket Ground serves as the nation's main cricket stadium. There are several other stadiums throughout the country, including the Ghazi Amanullah Khan International Cricket Stadium near Jalalabad. Domestically, cricket is played between teams from different provinces.
The Afghanistan national football team has been competing in international Association football, football since 1941. The national team plays its home games at the Ghazi Stadium in Kabul, while football in Afghanistan is governed by the Afghanistan Football Federation. The national team has never competed or qualified for the FIFA World Cup but has recently won an international football trophy in 2013. The country also has a national team in the sport of futsal, a 5-a-side variation of football.
The traditional and the national sport of Afghanistan is buzkashi, mainly popular in the north, but also having a following in other parts of the country. It is similar to polo, played by horsemen in two teams, each trying to grab and hold a goat carcass. The Afghan Hound (a type of running dog) originated in Afghanistan and was formerly used in wolf hunting with dogs, wolf hunting. In 2002, traveler Rory Stewart reported that dogs were still used for wolf hunting in remote areas.
Sport in Afghanistan is managed by the Afghan Sports Federation. Cricket and Association football are the two most popular sports in the country. The Afghan Sports Federation promotes cricket, association football, basketball, volleyball, golf, team handball, handball, boxing, taekwondo, Olympic weightlifting, weightlifting, bodybuilding, track and field, ice skating, skating, bowling, snooker, chess, and other sports.
Afghanistan's sports teams are increasingly celebrating titles at international events. Afghanistan national basketball team, basketball team won the first team sports title at the 2010 South Asian Games. Later that year, the country's Afghanistan national cricket team, cricket team followed it with the winning of 2009–10 ICC Intercontinental Cup. In 2012, the country's Afghanistan national 3x3 team, 3x3 basketball team won the gold medal at the 3-on-3 basketball at the 2012 Asian Beach Games, 2012 Asian Beach Games. In 2013, Afghanistan's Afghanistan national football team, football team followed as it won the SAFF Championship.
The Afghan national cricket team, which was formed in 2001, participated in the 2009 ICC World Cup Qualifier, 2010 ICC World Cricket League Division One and the 2010 ICC World Twenty20. It won the ACC Twenty20 Cup in 2007, 2009, 2011 and 2013. The team eventually made it and played in the 2015 Cricket World Cup. The Afghanistan Cricket Board (ACB) is the official governing body of the sport and is headquartered in Kabul. The Alokozay Kabul International Cricket Ground serves as the nation's main cricket stadium. There are several other stadiums throughout the country, including the Ghazi Amanullah Khan International Cricket Stadium near Jalalabad. Domestically, cricket is played between teams from different provinces.
The Afghanistan national football team has been competing in international Association football, football since 1941. The national team plays its home games at the Ghazi Stadium in Kabul, while football in Afghanistan is governed by the Afghanistan Football Federation. The national team has never competed or qualified for the FIFA World Cup but has recently won an international football trophy in 2013. The country also has a national team in the sport of futsal, a 5-a-side variation of football.
The traditional and the national sport of Afghanistan is buzkashi, mainly popular in the north, but also having a following in other parts of the country. It is similar to polo, played by horsemen in two teams, each trying to grab and hold a goat carcass. The Afghan Hound (a type of running dog) originated in Afghanistan and was formerly used in wolf hunting with dogs, wolf hunting. In 2002, traveler Rory Stewart reported that dogs were still used for wolf hunting in remote areas.