Fasciolopsis buski on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Fasciolopsis'' () is a
 ''Fasciolopsis buski'' is commonly called the giant intestinal
''Fasciolopsis buski'' is commonly called the giant intestinal
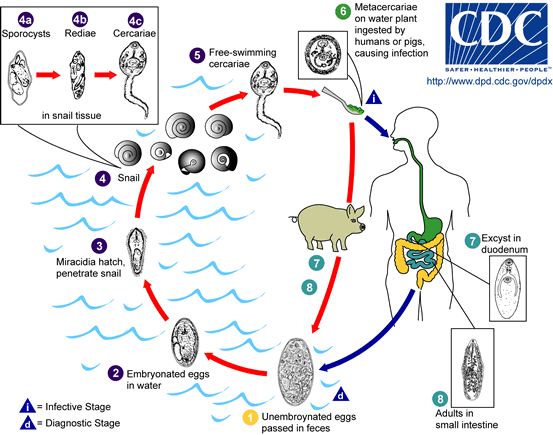 Adults produce over 25,000 eggs every day; these take up to seven weeks to mature and hatch at 27–32 °C. Immature, un
Adults produce over 25,000 eggs every day; these take up to seven weeks to mature and hatch at 27–32 °C. Immature, un
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
BioLib
The Taxonomicon
ZipcodeZoo
*Fasciolopsiasis in children: Clinical,Sociodemographic Profile and outcome. Indian Journal of Medical Microbiology2017 vol 35, issue 4 page 551-554 DOI:10.4103/ijmm.IJMM_17_7 * http://www.ijmm.org/text.asp?2017/35/4/551/224440 {{Taxonbar, from=Q3279537 Fasciolidae Trematode genera Monotypic protostome genera Parasitic helminths of humans
genus
Genus ( plural genera ) is a taxonomic rank used in the biological classification of extant taxon, living and fossil organisms as well as Virus classification#ICTV classification, viruses. In the hierarchy of biological classification, genus com ...
of trematode
Trematoda is a class of flatworms known as flukes. They are obligate internal parasites with a complex life cycle requiring at least two hosts. The intermediate host, in which asexual reproduction occurs, is usually a snail. The definitive host ...
s. They are also known as giant intestinal flukes.
Only one species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriate s ...
is recognised: ''Fasciolopsis buski''. It is a notable parasite of medical importance in humans and veterinary importance in pigs. It is prevalent in Southern and Eastern Asia. The term for infestation with ''Fasciolopsis'' is fasciolopsiasis
Fasciolopsiasis results from an infection by the trematode ''Fasciolopsis buski'', the largest intestinal fluke of humans (up to 7.5 cm in length).
Signs and symptoms
Most infections are light, almost asymptomatic. In heavy infections, sympto ...
.
''Fasciolopsis buski''
fluke
Fluke may refer to:
Biology
* Fluke (fish), a species of marine flatfish
* Fluke (tail), the lobes of the tail of a cetacean, such as dolphins or whales, ichthyosaurs, mosasaurs
Mosasaurs (from Latin ''Mosa'' meaning the 'Meuse', and Greek ...
, because it is an exceptionally large parasitic fluke, and the largest known to parasitise humans. Its size is variable and a mature specimen might be as little as 2 cm long, but the body may grow to a length of 7.5 cm and a width of 2.5 cm. It is a common parasite
Parasitism is a close relationship between species, where one organism, the parasite, lives on or inside another organism, the host, causing it some harm, and is adapted structurally to this way of life. The entomologist E. O. Wilson has ...
of humans and pigs and is most prevalent in Southern
Southern may refer to:
Businesses
* China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China
* Southern Airways, defunct US airline
* Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US
* Southern Airways Express, M ...
and Southeastern Asia
Southeast Asia, also spelled South East Asia and South-East Asia, and also known as Southeastern Asia, South-eastern Asia or SEA, is the geographical south-eastern region of Asia, consisting of the regions that are situated south of mainland ...
. It is a member of the family
Family (from la, familia) is a Social group, group of people related either by consanguinity (by recognized birth) or Affinity (law), affinity (by marriage or other relationship). The purpose of the family is to maintain the well-being of its ...
Fasciolidae
Fasciolidae is a family of trematodes and includes several parasites involved in the veterinary and medical sciences, which cause the disease Fasciolosis. Fasciolidae is divided into five genera by Olson et al. 2003. The family's various species ...
in the order Plagiorchiida
Plagiorchiida is a large order of trematodes, synonymous to Echinostomida. They belong to the Digenea, a large subclass of flukes. This order contains relatively few significant parasites of humans.
The following families are placed here, organ ...
. The Echinostomida are members of the class
Class or The Class may refer to:
Common uses not otherwise categorized
* Class (biology), a taxonomic rank
* Class (knowledge representation), a collection of individuals or objects
* Class (philosophy), an analytical concept used differentl ...
Trematoda
Trematoda is a Class (biology), class of flatworms known as flukes. They are obligate parasite, obligate internal Parasitism, parasites with a complex biological life cycle, life cycle requiring at least two Host_(biology), hosts. The intermedia ...
, the flukes. The fluke differs from most species that parasitise large mammals, in that they inhabit the gut rather than the liver as ''Fasciola
''Fasciola'', commonly known as the liver fluke, is a genus of parasitic trematodes. There are two species within the genus ''Fasciola'': ''Fasciola'' ''hepatica'' and ''Fasciola'' ''gigantica'', as well as hybrids between the two species. Bot ...
'' species do. ''Fasciolopsis buski'' generally occupies the upper region of the small intestine
The small intestine or small bowel is an organ in the gastrointestinal tract where most of the absorption of nutrients from food takes place. It lies between the stomach and large intestine, and receives bile and pancreatic juice through the p ...
, but in heavy infestations can also be found in the stomach
The stomach is a muscular, hollow organ in the gastrointestinal tract of humans and many other animals, including several invertebrates. The stomach has a dilated structure and functions as a vital organ in the digestive system. The stomach i ...
and lower regions of the intestine. ''Fasciolopsis buski'' is the cause of the pathological condition fasciolopsiasis
Fasciolopsiasis results from an infection by the trematode ''Fasciolopsis buski'', the largest intestinal fluke of humans (up to 7.5 cm in length).
Signs and symptoms
Most infections are light, almost asymptomatic. In heavy infections, sympto ...
.
In London, George Busk
George Busk FRS FRAI (12 August 1807 – 10 August 1886) was a British naval surgeon, zoologist and palaeontologist.
Early life, family and education
Busk was born in St. Petersburg, Russia. He was the son of the merchant Robert Busk and his ...
first described ''Fasciolopsis buski'' in 1843 after finding it in the duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine m ...
of a sailor. After years of careful study and self experimentation, in 1925, Claude Heman Barlow determined its life cycle in humans.
Morphology
''Fasciolopsis buski'' is a large,dorsoventrally
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ...
flattened fluke characterized by a blunt anterior
Standard anatomical terms of location are used to unambiguously describe the anatomy of animals, including humans. The terms, typically derived from Latin or Greek roots, describe something in its standard anatomical position. This position prov ...
end, undulating, unbranched ceca (sac-like cavities with single openings), tandem dendritic
Dendrite derives from the Greek word "dendron" meaning ( "tree-like"), and may refer to:
Biology
*Dendrite, a branched projection of a neuron
*Dendrite (non-neuronal), branching projections of certain skin cells and immune cells
Physical
* Dendr ...
testes
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testoster ...
, branched ovaries
The ovary is an organ in the female reproductive system that produces an ovum. When released, this travels down the fallopian tube into the uterus, where it may become fertilized by a sperm. There is an ovary () found on each side of the body. T ...
, and ventral suckers to attach itself to the host
A host is a person responsible for guests at an event or for providing hospitality during it.
Host may also refer to:
Places
* Host, Pennsylvania, a village in Berks County
People
*Jim Host (born 1937), American businessman
* Michel Host ...
. The acetabulum
The acetabulum (), also called the cotyloid cavity, is a concave surface of the pelvis. The head of the femur meets with the pelvis at the acetabulum, forming the hip joint.
Structure
There are three bones of the ''os coxae'' (hip bone) that c ...
is larger than the oral sucker. The fluke has extensive vitelline
Vitelline may refer to:
Embryology
* Vitelline arteries, arteries that bring blood to the yolk sac
* Vitelline circulation, the system of blood flowing between an embryo and its yolk sac
* Vitelline cyst, a developmental defect relating to the c ...
follicles. It can be distinguished from other fasciolids by a lack of cephalic
A head is the part of an organism which usually includes the ears, brain, forehead, cheeks, chin, eyes, nose, and mouth, each of which aid in various sensory functions such as sight, hearing, smell, and taste. Some very simple animals may ...
cone or "shoulders" and the unbranched ceca.
Life cycle
 Adults produce over 25,000 eggs every day; these take up to seven weeks to mature and hatch at 27–32 °C. Immature, un
Adults produce over 25,000 eggs every day; these take up to seven weeks to mature and hatch at 27–32 °C. Immature, unembryonated Embryonated, unembryonated and de-embryonated are terms generally used in reference to eggs or, in botany, to seeds. The words are often used as professional jargon rather than as universally applicable terms or concepts. Examples of relevant fields ...
eggs are discharged into the intestine and stool. In two weeks, eggs become embryonated in water, and after about seven weeks, tiny parasitic organisms called miracidia
Trematodes are parasitic flatworms of the class ''Trematoda'', specifically parasitic flukes with two suckers: one ventral and the other oral. Trematodes are covered by a tegument, that protects the organism from the environment by providing secr ...
hatch from the eggs, which then go on to invade a suitable snail
A snail is, in loose terms, a shelled gastropod. The name is most often applied to land snails, terrestrial pulmonate gastropod molluscs. However, the common name ''snail'' is also used for most of the members of the molluscan class Gastro ...
intermediate host. Several species in the genera ''Segmentina
''Segmentina'' is a genus of very small, air-breathing, freshwater snails, aquatic gastropod mollusks or micromollusks in the family Planorbidae, the ramshorn snails.
Albrecht et al. (2007)Albrecht C., Kuhn K. & Streit B. (2007). "A molecul ...
'' and '' Hippeutis'' serve as intermediate hosts. In the snail the parasite undergoes several developmental stages (sporocysts, rediae, and cercariae). The cercariae
Trematodes are parasitic flatworms of the class ''Trematoda'', specifically parasitic flukes with two suckers: one ventral and the other oral. Trematodes are covered by a tegument, that protects the organism from the environment by providing secr ...
are released from the snail and encyst as metacercariae
Trematodes are parasitic flatworms of the class ''Trematoda'', specifically parasitic flukes with two suckers: one ventral and the other oral. Trematodes are covered by a tegument, that protects the organism from the environment by providing secr ...
on aquatic plants such as water chestnut Water chestnut may refer to either of two plants (both sometimes used in Chinese cuisine):
* The Chinese water chestnut ('' Eleocharis dulcis''), eaten for its crisp corm
* The water caltrop
The water caltrop is any of three extant species of th ...
, water caltrop
The water caltrop is any of three extant species of the genus ''Trapa'': ''Trapa natans'', ''Trapa bicornis'' and the endangered ''Trapa rossica''. It is also known as buffalo nut, bat nut, devil pod, ling gok (Chinese: 菱角), ling nut, lin kok ...
, lotus, bamboo
Bamboos are a diverse group of evergreen perennial flowering plants making up the subfamily Bambusoideae of the grass family Poaceae. Giant bamboos are the largest members of the grass family. The origin of the word "bamboo" is uncertain, bu ...
, and other edible plants. The mammalian
Mammals () are a group of vertebrate animals constituting the class (biology), class Mammalia (), characterized by the presence of mammary glands which in Female#Mammalian female, females produce milk for feeding (nursing) their young, a ...
final host becomes infected by ingesting metacercariae
Trematodes are parasitic flatworms of the class ''Trematoda'', specifically parasitic flukes with two suckers: one ventral and the other oral. Trematodes are covered by a tegument, that protects the organism from the environment by providing secr ...
on the aquatic plants. After ingestion, the metacercariae excyst in the duodenum
The duodenum is the first section of the small intestine in most higher vertebrates, including mammals, reptiles, and birds. In fish, the divisions of the small intestine are not as clear, and the terms anterior intestine or proximal intestine m ...
in about three months and attach to the intestinal wall. There they develop into adults (20 to 75 mm by 8 to 20 mm) in approximately three months, remaining attached to the intestinal wall of the mammalian hosts (humans and pigs). The adults have a life span of about one year.
References
External links
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
BioLib
The Taxonomicon
ZipcodeZoo
*Fasciolopsiasis in children: Clinical,Sociodemographic Profile and outcome. Indian Journal of Medical Microbiology2017 vol 35, issue 4 page 551-554 DOI:10.4103/ijmm.IJMM_17_7 * http://www.ijmm.org/text.asp?2017/35/4/551/224440 {{Taxonbar, from=Q3279537 Fasciolidae Trematode genera Monotypic protostome genera Parasitic helminths of humans