F-111E on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The General Dynamics F-111 Aardvark is a retired supersonic, medium-range,
 The Air Force and the Navy could agree only on swing-wing, two-seat, twin-engine design features. The Air Force wanted a tandem-seat aircraft for low-level penetration ground-attack, while the Navy wanted a shorter, high altitude interceptor with side-by-side seating to allow the pilot and Naval Flight Officer, radar operator to share the radar display. Also, the Air Force wanted the aircraft designed for 7.33 g with Mach 2.5 speed at altitude and Mach 1.2 speed at low level with an approximate length of . The Navy had less strenuous requirements of 6 g with Mach 2 speed at altitude and high subsonic speed (approx. Mach 0.9) at low level with a length of . The Navy also wanted the aircraft with a nose large enough for a diameter radar dish.Miller 1982, pp. 11–15.
McNamara developed a basic set of requirements for TFX based largely on the Air Force's requirements and, on 1 September 1961, ordered the Air Force to develop it. A request for proposals (RFP) for the TFX was provided to industry in October 1961. In December, proposals were received from Boeing,
The Air Force and the Navy could agree only on swing-wing, two-seat, twin-engine design features. The Air Force wanted a tandem-seat aircraft for low-level penetration ground-attack, while the Navy wanted a shorter, high altitude interceptor with side-by-side seating to allow the pilot and Naval Flight Officer, radar operator to share the radar display. Also, the Air Force wanted the aircraft designed for 7.33 g with Mach 2.5 speed at altitude and Mach 1.2 speed at low level with an approximate length of . The Navy had less strenuous requirements of 6 g with Mach 2 speed at altitude and high subsonic speed (approx. Mach 0.9) at low level with a length of . The Navy also wanted the aircraft with a nose large enough for a diameter radar dish.Miller 1982, pp. 11–15.
McNamara developed a basic set of requirements for TFX based largely on the Air Force's requirements and, on 1 September 1961, ordered the Air Force to develop it. A request for proposals (RFP) for the TFX was provided to industry in October 1961. In December, proposals were received from Boeing,
"General Dynamics F-111A."
''USAAC/USAAF/USAF Fighters'', 23 December 1999. Retrieved: 5 October 2009. A team of engineers at General Dynamics was led by Robert H. Widmer. Lacking experience with carrier-based fighters, General Dynamics teamed with Grumman for the assembly and testing of the F-111B aircraft. In addition, Grumman would also build the F-111A's aft fuselage and the landing gear. The General Dynamics and Grumman team faced ambitious requirements for range, weapons load, and aircraft weight. The F-111 design also included new features on a production military aircraft, such as variable-geometry wings and afterburning turbofan engines.Miller 1982, pp. 17, 19. The F-111A mockup was inspected in September 1963. The first test F-111A was rolled out of Air Force Plant 4, Plant 4 of General Dynamics' Fort Worth, Texas, facility on 15 October 1964. It was powered by YTF30-P-1 turbofans and used a set of ejector seats as the escape capsule was not yet available. The F-111A first flew on 21 December 1964 from Carswell Air Force Base, Texas, U.S. The F-111B was also equipped with ejector seats and first flew on 18 May 1965.Baugher, Joe
"General Dynamics/Grumman F-111B."
''USAAC/USAAF/USAF Fighters'', 7 November 2004. Retrieved: 5 October 2009. Initially there were compressor surge and stall issues in certain parts of the flight regime. NASA, the Air Force, and General Dynamics studies resulted in the engine inlet design being modified in 1965–66, culminating with the "Triple Plow I" and "Triple Plow II" designs.Gunston 1978, pp. 25–27. The F-111A achieved a speed of Mach 1.3 in February 1965 with an interim intake design. Cracks in the F-111's wingbox, wing attach points were first discovered in 1968 during ground fatigue testing; an F-111 crashed the following year due to this issue. The attach structure required redesign and testing to ensure adequate design and workmanship.Miller 1982, pp. 31, 47. Flight testing of the F-111A ran through 1973.Logan 1998, p. 32. The F-111B was canceled by the Navy in 1968 due to weight and performance issues, along with the need for additional fighter requirements. The F-111C model was developed for Australia. Subsequently, the improved F-111E, F-111D, F-111F models were developed for the U.S. Air Force. The strategic bomber FB-111A and the EF-111 electronic warfare versions were later developed for the USAF. Production ended in 1976,Miller 1982, p. 65. after 563 F-111 aircraft were built.
 The F-111 was an all-weather attack aircraft, capable of low-level penetration of enemy defenses to deliver ordnance on the target. The F-111 featured variable-sweep wing, variable-geometry wings, an internal weapons bay and a cockpit with side-by-side seating. The cockpit was part of an escape crew capsule.Eden 2004, pp. 196–201. The wing sweep varied between 16 degrees and 72.5 degrees (full forward to full sweep). The wing included leading edge slats and flap (aircraft), double slotted flaps over its full length.Miller 1982, pp. 80–81. The airframe was made up mostly of aluminium alloys with steel, titanium and other materials used in places.Logan 1998, pp. 17–18. The fuselage was made of a semi-monocoque structure with stiffened panels and honeycomb structure panels for skin. The horizontal stabilizer was an all-moving stabilator.
The F-111 used a three-point landing gear arrangement, with a two-wheel nose gear and two single-wheel main landing gear units. The landing gear door for the main gear, which was positioned in the center of the fuselage, also served as a air brake (aircraft), speed brake in flight.Logan 1998, p. 19. Most F-111 variants included a terrain-following radar system connected to the autopilot. The aircraft was powered by two Pratt & Whitney TF30 afterburning turbofan engines. The F-111's variable-geometry wings, escape capsule, terrain following radar and afterburning turbofans were new technologies for production aircraft.Logan 1998, p. 14.
The F-111 was an all-weather attack aircraft, capable of low-level penetration of enemy defenses to deliver ordnance on the target. The F-111 featured variable-sweep wing, variable-geometry wings, an internal weapons bay and a cockpit with side-by-side seating. The cockpit was part of an escape crew capsule.Eden 2004, pp. 196–201. The wing sweep varied between 16 degrees and 72.5 degrees (full forward to full sweep). The wing included leading edge slats and flap (aircraft), double slotted flaps over its full length.Miller 1982, pp. 80–81. The airframe was made up mostly of aluminium alloys with steel, titanium and other materials used in places.Logan 1998, pp. 17–18. The fuselage was made of a semi-monocoque structure with stiffened panels and honeycomb structure panels for skin. The horizontal stabilizer was an all-moving stabilator.
The F-111 used a three-point landing gear arrangement, with a two-wheel nose gear and two single-wheel main landing gear units. The landing gear door for the main gear, which was positioned in the center of the fuselage, also served as a air brake (aircraft), speed brake in flight.Logan 1998, p. 19. Most F-111 variants included a terrain-following radar system connected to the autopilot. The aircraft was powered by two Pratt & Whitney TF30 afterburning turbofan engines. The F-111's variable-geometry wings, escape capsule, terrain following radar and afterburning turbofans were new technologies for production aircraft.Logan 1998, p. 14.

 Each wing was equipped with four underwing pylons. The inner two pylons on each wing rotated to align with the fuselage, while the outer two were fixed. Each pylon had a capacity of . Various bombs and missiles could be carried on the pylons. Auxiliary fuel drop tanks with capacity each could be fitted.Gunston 1983, pp. 30–31.
The design of the F-111's fuselage prevented the carriage of external weapons under the fuselage, but two stations were available on the underside for electronic countermeasures (ECM) pods and/or datalink pods; one station was on the weapons bay, and the other on the rear fuselage between the engines. The F-111's maximum practical weapons load was limited, since the fixed pylons could not be used with the wings fully swept.Logan 1998, p. 18.
Tactical F-111s were fitted with shoulder rails on the four inner swiveling pylons to mount AIM-9 Sidewinder air-to-air missiles for self-defense. Australian F-111Cs were equipped to launch the Harpoon (missile), Harpoon anti-ship missile, and the Popeye (missile), Popeye stand-off missile.Logan 1998, p. 28. FB-111As could carry the same conventional ordnance as the tactical variants, but their wing pylons were more commonly used for either fuel tanks or strategic nuclear gravity bombs. They could carry up to four AGM-69 SRAM nuclear missiles on the pylons.Gunston 1983, p. 49.
Each wing was equipped with four underwing pylons. The inner two pylons on each wing rotated to align with the fuselage, while the outer two were fixed. Each pylon had a capacity of . Various bombs and missiles could be carried on the pylons. Auxiliary fuel drop tanks with capacity each could be fitted.Gunston 1983, pp. 30–31.
The design of the F-111's fuselage prevented the carriage of external weapons under the fuselage, but two stations were available on the underside for electronic countermeasures (ECM) pods and/or datalink pods; one station was on the weapons bay, and the other on the rear fuselage between the engines. The F-111's maximum practical weapons load was limited, since the fixed pylons could not be used with the wings fully swept.Logan 1998, p. 18.
Tactical F-111s were fitted with shoulder rails on the four inner swiveling pylons to mount AIM-9 Sidewinder air-to-air missiles for self-defense. Australian F-111Cs were equipped to launch the Harpoon (missile), Harpoon anti-ship missile, and the Popeye (missile), Popeye stand-off missile.Logan 1998, p. 28. FB-111As could carry the same conventional ordnance as the tactical variants, but their wing pylons were more commonly used for either fuel tanks or strategic nuclear gravity bombs. They could carry up to four AGM-69 SRAM nuclear missiles on the pylons.Gunston 1983, p. 49.
 The first of six initial production F-111s was delivered on 17 July 1967 to fighter squadrons at Nellis Air Force Base.Logan 1998, p. 33. These aircraft were used for crew training. 428th Fighter Squadron, 428th Tactical Fighter Squadron achieved initial operational capability on 28 April 1968.
After early testing, a detachment of six aircraft from the 474th Tactical Fighter Wing (474th TFW Roadrunners) were sent in March 1968 to Southeast Asia for Combat Lancer testing in real combat conditions in the Vietnam War. During the deployment, 55 night missions were flown against targets in North Vietnam, but two aircraft had been lost. 66–0022 was lost on 28 March, and 66-0017 on 30 March. Replacement aircraft left Nellis, but the loss of a third F-111A (66-0024) on 22 April halted F-111A combat operations. The squadron returned to the United States in November. The cause of the first two losses is unknown as the wreckages were never recovered. It turned out that the third loss was traced to a failure of a hydraulic control-valve rod for the horizontal stabilizer which caused the aircraft to pitch up uncontrollably. Further inspection of the remaining fleet of F-111As revealed 42 aircraft with the same potential failures. It is speculated that this failure could also have contributed to the two earlier losses had the failure caused a pitch down while at low altitude. It was not until 1971 that 474 TFW was fully operational.
The word "aardvark" is Afrikaans for "earthpig" and reflects the look of the long nose of the aircraft that might remind one of the nose of the aardvark. The name is attributed to F-111A Instructor Pilot Al Mateczun in 1969, as the aircraft had not received an official Air Force name.
September 1972 saw the F-111 back in Southeast Asia, stationed at Takhli Royal Thai Air Force Base, Takhli Air Base, Thailand. F-111As from Nellis AFB participated in the final month of Operation Linebacker and later flew 154 low-level missions in the Operation Linebacker II aerial offensive against the North Vietnamese, who called the aircraft "Whispering Death". They also supported regional aerial operations against other communist forces such as Operation Phou Phiang III during the Laotian Civil War in Laos. Crews described their flying in Vietnam as "speed is life", "one pass, haul ass", and "you do more than one pass in a target area you die". The F-111's ability with terrain-following radar ("the best in the fighter world", according to F-111 pilot Richard Crandall) to fly as low as above ground level at or faster in most weather conditions made it very effective; missions did not require tankers or ECM support, and they could operate in weather that grounded most other aircraft. One F-111 could carry the bomb load of four McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom IIs. The worth of the new aircraft was beginning to show; F-111s flew more than 4,000 combat missions in Vietnam with only six combat losses.Logan 1998, pp. 283–284.
From 30 July 1973 F-111As of the 347th Rescue Wing, 347th Tactical Fighter Wing (347th TFW) were stationed at Takhli Air Base. The 347th TFW conducted bombing missions in Cambodia in support of Khmer Republic forces until 15 August 1973 when US combat support ceased in accordance with the Case–Church Amendment. The 347th TFW was stationed at Korat Royal Thai Air Force Base from 12 July 1974 until 30 June 1975. In May 1975 347th TFW F-111s provided air support during the Mayaguez incident, ''Mayaguez'' incident.
One of the most unusual missions occurred on 14 February 1986, when two FB-111s of the 509th Bombardment Wing were dispatched from then Pease Air Force Base, New Hampshire to Tinker Air Force Base, Oklahoma to pick up a heart for transplant. The aircraft landed at Bradley International Airport to deliver the organ to a waiting ambulance.
The first of six initial production F-111s was delivered on 17 July 1967 to fighter squadrons at Nellis Air Force Base.Logan 1998, p. 33. These aircraft were used for crew training. 428th Fighter Squadron, 428th Tactical Fighter Squadron achieved initial operational capability on 28 April 1968.
After early testing, a detachment of six aircraft from the 474th Tactical Fighter Wing (474th TFW Roadrunners) were sent in March 1968 to Southeast Asia for Combat Lancer testing in real combat conditions in the Vietnam War. During the deployment, 55 night missions were flown against targets in North Vietnam, but two aircraft had been lost. 66–0022 was lost on 28 March, and 66-0017 on 30 March. Replacement aircraft left Nellis, but the loss of a third F-111A (66-0024) on 22 April halted F-111A combat operations. The squadron returned to the United States in November. The cause of the first two losses is unknown as the wreckages were never recovered. It turned out that the third loss was traced to a failure of a hydraulic control-valve rod for the horizontal stabilizer which caused the aircraft to pitch up uncontrollably. Further inspection of the remaining fleet of F-111As revealed 42 aircraft with the same potential failures. It is speculated that this failure could also have contributed to the two earlier losses had the failure caused a pitch down while at low altitude. It was not until 1971 that 474 TFW was fully operational.
The word "aardvark" is Afrikaans for "earthpig" and reflects the look of the long nose of the aircraft that might remind one of the nose of the aardvark. The name is attributed to F-111A Instructor Pilot Al Mateczun in 1969, as the aircraft had not received an official Air Force name.
September 1972 saw the F-111 back in Southeast Asia, stationed at Takhli Royal Thai Air Force Base, Takhli Air Base, Thailand. F-111As from Nellis AFB participated in the final month of Operation Linebacker and later flew 154 low-level missions in the Operation Linebacker II aerial offensive against the North Vietnamese, who called the aircraft "Whispering Death". They also supported regional aerial operations against other communist forces such as Operation Phou Phiang III during the Laotian Civil War in Laos. Crews described their flying in Vietnam as "speed is life", "one pass, haul ass", and "you do more than one pass in a target area you die". The F-111's ability with terrain-following radar ("the best in the fighter world", according to F-111 pilot Richard Crandall) to fly as low as above ground level at or faster in most weather conditions made it very effective; missions did not require tankers or ECM support, and they could operate in weather that grounded most other aircraft. One F-111 could carry the bomb load of four McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom IIs. The worth of the new aircraft was beginning to show; F-111s flew more than 4,000 combat missions in Vietnam with only six combat losses.Logan 1998, pp. 283–284.
From 30 July 1973 F-111As of the 347th Rescue Wing, 347th Tactical Fighter Wing (347th TFW) were stationed at Takhli Air Base. The 347th TFW conducted bombing missions in Cambodia in support of Khmer Republic forces until 15 August 1973 when US combat support ceased in accordance with the Case–Church Amendment. The 347th TFW was stationed at Korat Royal Thai Air Force Base from 12 July 1974 until 30 June 1975. In May 1975 347th TFW F-111s provided air support during the Mayaguez incident, ''Mayaguez'' incident.
One of the most unusual missions occurred on 14 February 1986, when two FB-111s of the 509th Bombardment Wing were dispatched from then Pease Air Force Base, New Hampshire to Tinker Air Force Base, Oklahoma to pick up a heart for transplant. The aircraft landed at Bradley International Airport to deliver the organ to a waiting ambulance.
 On 14 April 1986, 18 F-111s and approximately 25 Navy aircraft conducted air strikes against Libya under 1986 United States bombing of Libya, Operation El Dorado Canyon. The 18 F-111s of the 48th Fighter Wing, 48th Tactical Fighter Wing and 4 EF-111As from the 20th Fighter Wing, 20th Tactical Fighter Wing flew what turned out to be the longest fighter combat mission in history. The round-trip flight between RAF Lakenheath/RAF Upper Heyford, United Kingdom and Libya of spanned 13 hours. One F-111 was lost over Libya and crashed into the Mediterranean Sea, probably shot down.Walter J. Boyne, Boyne, Walter J.]
On 14 April 1986, 18 F-111s and approximately 25 Navy aircraft conducted air strikes against Libya under 1986 United States bombing of Libya, Operation El Dorado Canyon. The 18 F-111s of the 48th Fighter Wing, 48th Tactical Fighter Wing and 4 EF-111As from the 20th Fighter Wing, 20th Tactical Fighter Wing flew what turned out to be the longest fighter combat mission in history. The round-trip flight between RAF Lakenheath/RAF Upper Heyford, United Kingdom and Libya of spanned 13 hours. One F-111 was lost over Libya and crashed into the Mediterranean Sea, probably shot down.Walter J. Boyne, Boyne, Walter J.]
"El Dorado Canyon."
''Air Force Magazine'', March 1999. F-111s participated in the Gulf War (Operation Desert Storm) in 1991. During Desert Storm, F-111Fs completed 3.2 successful strike missions for every unsuccessful one, better than any other U.S. strike aircraft used in the operation."GAO/NS-97-134, Operation Desert Storm, Evaluation of the Air Campaign."
''US General Accounting Office'', June 1997. The group of 66 F-111Fs dropped almost 80% of the war's laser-guided bombs, including the penetrating bunker-buster GBU-28. Eighteen F-111Es were also deployed during the operation. The F-111s were credited with destroying more than 1,500 Iraqi tanks and armored vehicles."Air Force Performance in Desert Storm", p. 4.
''U.S. Air Force,'' April 1991. Their use in the anti-armor role was dubbed "tank plinking". The F-111 was in service with the USAF from 1967 through 1998. The FB-111s were operated by Strategic Air Command from 1969 before conversion to F-111G and transferred to Air Combat Command (ACC) until their retirement in 1993. At a ceremony marking the F-111's USAF retirement, on 27 July 1996, it was officially named Aardvark, its long-standing unofficial name."Fact Sheet: General Dynamics F-111D to F."
''National Museum of the United States Air Force.'' Retrieved: 1 August 2010. The USAF retired the EF-111 electronic warfare variant in 1998.Gershanoff, H
''Journal of Electronic Defense'', 1 December 1998.
 The purchase proved to be highly successful for the RAAF. Although it never saw combat, the F-111C was the fastest, longest range combat aircraft in Southeast Asia, providing Australia with independent strike capability.Stephens 2006, p. 290. Leonardus Benjamin Moerdani, Benny Murdani told Kim Beazley that when others became upset with Australia during Cabinet of Indonesia, Indonesian cabinet meetings, Murdani told them "Do you realise the Australians have a bomber that can put a bomb through that window on to the table here in front of us?"
Australian F-111s were ready to attack Indonesian forces during the establishment of East Timor's independence and the deployment of the Australian-led International Force for East Timor. In 2006, an RAAF F-111 scuttled the North Korean ship ''Pong Su'' on 23 March 2006.
Because of the high maintenance time required for every flight hour, the F-111's retirement began with the F-111G models operated by No. 6 Squadron in late 2007. Twenty-four F/A-18F Super Hornets were procured as an interim replacement while the F-35 program was delayed. The last F-111s were retired on 3 December 2010.
The purchase proved to be highly successful for the RAAF. Although it never saw combat, the F-111C was the fastest, longest range combat aircraft in Southeast Asia, providing Australia with independent strike capability.Stephens 2006, p. 290. Leonardus Benjamin Moerdani, Benny Murdani told Kim Beazley that when others became upset with Australia during Cabinet of Indonesia, Indonesian cabinet meetings, Murdani told them "Do you realise the Australians have a bomber that can put a bomb through that window on to the table here in front of us?"
Australian F-111s were ready to attack Indonesian forces during the establishment of East Timor's independence and the deployment of the Australian-led International Force for East Timor. In 2006, an RAAF F-111 scuttled the North Korean ship ''Pong Su'' on 23 March 2006.
Because of the high maintenance time required for every flight hour, the F-111's retirement began with the F-111G models operated by No. 6 Squadron in late 2007. Twenty-four F/A-18F Super Hornets were procured as an interim replacement while the F-35 program was delayed. The last F-111s were retired on 3 December 2010.
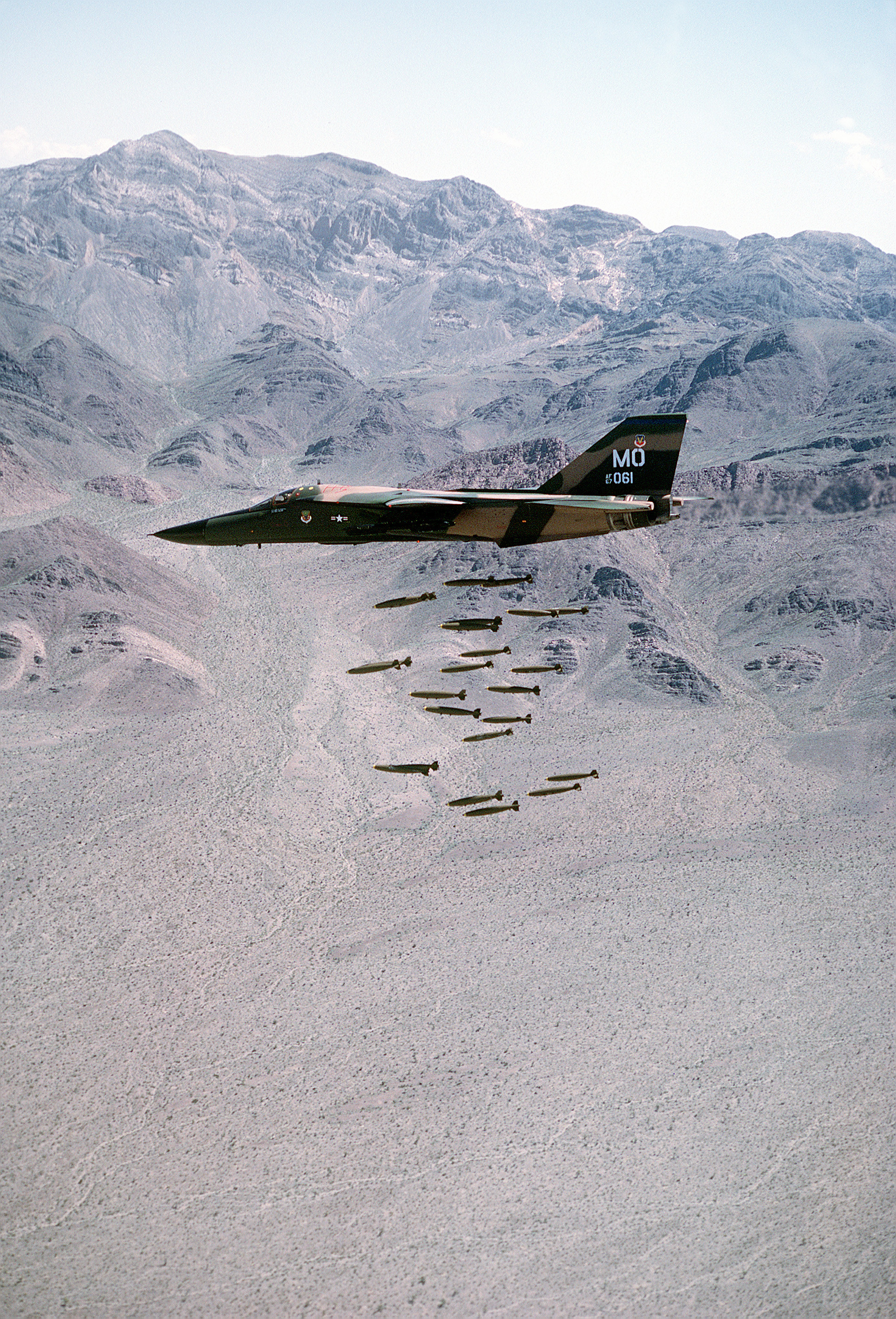 The F-111A was the initial production version of the F-111. Early A-models used the TF30-P-1 engine. Most A-models used the TF30-P-3 engine with 12,000 lbf (53 kN) dry and 18,500 lbf (82 kN) afterburning thrust and "Triple Plow I" variable intakes, providing a maximum speed of Mach 2.3 (1,450 mph, 2,300 km/h) at altitude.Miller 1982, pp. 26, 66. The variant had a maximum takeoff weight of and an empty weight of .Logan 1998, p. 302.
The A-model's Mark I avionics suite included the General Electric AN/APQ-113 attack radar mated to a separate Texas Instruments AN/APQ-110 terrain-following radar lower in the nose and a Litton Industries, Litton AJQ-20 inertial navigation and nav/attack system. The terrain-following radar (TFR) was integrated into the automatic flight control system, allowing for "hands-off" flight at high speeds and low levels (down to ).Gunston 1978, pp. 46–47.
Total production of the F-111As was 159, including 30 pre-production aircraft that were later brought up to production standards.Miller 1982, p. 26. 42 F-111As were converted to EF-111A Ravens for an electronic warfare tactical electronic jamming role. In 1982, four surviving F-111As were provided to Australia as attrition replacements and modified to F-111C standard; these were fitted with the longer-span wings and reinforced landing gear of the C-model.Logan 1998, p. 263.
Three pre-production F-111A were provided to NASA for various testing duties. The 13th F-111A was fitted with new wing designs for the Transonic Aircraft Technology and Advanced Fighter Technology Integration programs in the 1970s and 1980s. It was retired to the National Museum of the United States Air Force, United States Air Force Museum at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base in 1989. The remaining unconverted F-111As were mothballed at 309th Aerospace Maintenance and Regeneration Group, Aerospace Maintenance and Regeneration Center at Davis-Monthan Air Force Base in June 1991.
The F-111A was the initial production version of the F-111. Early A-models used the TF30-P-1 engine. Most A-models used the TF30-P-3 engine with 12,000 lbf (53 kN) dry and 18,500 lbf (82 kN) afterburning thrust and "Triple Plow I" variable intakes, providing a maximum speed of Mach 2.3 (1,450 mph, 2,300 km/h) at altitude.Miller 1982, pp. 26, 66. The variant had a maximum takeoff weight of and an empty weight of .Logan 1998, p. 302.
The A-model's Mark I avionics suite included the General Electric AN/APQ-113 attack radar mated to a separate Texas Instruments AN/APQ-110 terrain-following radar lower in the nose and a Litton Industries, Litton AJQ-20 inertial navigation and nav/attack system. The terrain-following radar (TFR) was integrated into the automatic flight control system, allowing for "hands-off" flight at high speeds and low levels (down to ).Gunston 1978, pp. 46–47.
Total production of the F-111As was 159, including 30 pre-production aircraft that were later brought up to production standards.Miller 1982, p. 26. 42 F-111As were converted to EF-111A Ravens for an electronic warfare tactical electronic jamming role. In 1982, four surviving F-111As were provided to Australia as attrition replacements and modified to F-111C standard; these were fitted with the longer-span wings and reinforced landing gear of the C-model.Logan 1998, p. 263.
Three pre-production F-111A were provided to NASA for various testing duties. The 13th F-111A was fitted with new wing designs for the Transonic Aircraft Technology and Advanced Fighter Technology Integration programs in the 1970s and 1980s. It was retired to the National Museum of the United States Air Force, United States Air Force Museum at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base in 1989. The remaining unconverted F-111As were mothballed at 309th Aerospace Maintenance and Regeneration Group, Aerospace Maintenance and Regeneration Center at Davis-Monthan Air Force Base in June 1991.
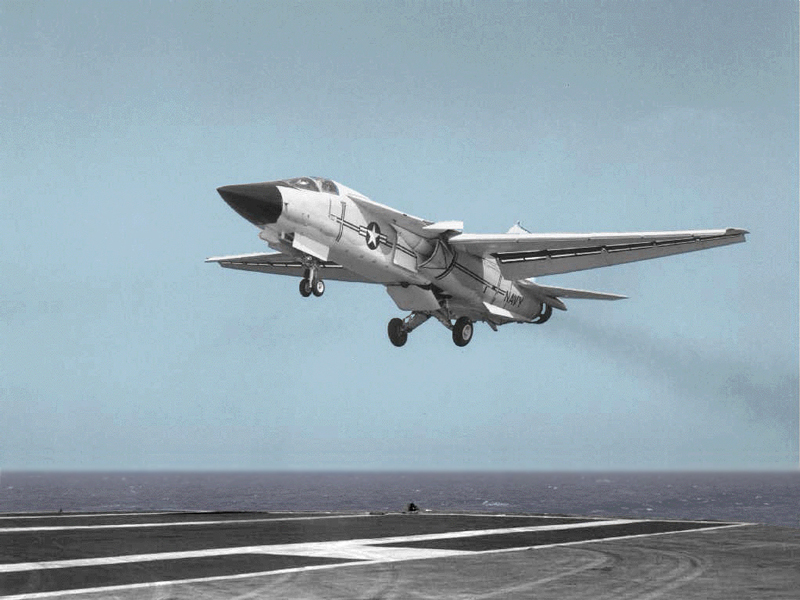 The F-111B was to be a fleet air defense (FAD) fighter for the U.S. Navy, fulfilling a naval requirement for a carrier-based fighter aircraft capable of carrying heavy, long-range missiles to defend aircraft carriers and their battle groups from Soviet bombers and fighter-bombers equipped with anti-ship missiles. General Dynamics, lacking experience with carrier-based aircraft, partnered with Grumman for this version. The F-111B suffered development problems and Navy requirements changed to an aircraft with maneuverability for dogfighting. The swing-wing configuration, TF-30 engines, AIM-54 Phoenix air-to-air missiles and AWG-9 radar developed for this aircraft were used on its replacement, the Grumman F-14 Tomcat. The Tomcat would be large enough to carry the AWG-9 and Phoenix weapons system while exceeding both the F-111's and the F-4's maneuverability. Seven aircraft were completed for testing but the model never entered fleet service.
The F-111B was to be a fleet air defense (FAD) fighter for the U.S. Navy, fulfilling a naval requirement for a carrier-based fighter aircraft capable of carrying heavy, long-range missiles to defend aircraft carriers and their battle groups from Soviet bombers and fighter-bombers equipped with anti-ship missiles. General Dynamics, lacking experience with carrier-based aircraft, partnered with Grumman for this version. The F-111B suffered development problems and Navy requirements changed to an aircraft with maneuverability for dogfighting. The swing-wing configuration, TF-30 engines, AIM-54 Phoenix air-to-air missiles and AWG-9 radar developed for this aircraft were used on its replacement, the Grumman F-14 Tomcat. The Tomcat would be large enough to carry the AWG-9 and Phoenix weapons system while exceeding both the F-111's and the F-4's maneuverability. Seven aircraft were completed for testing but the model never entered fleet service.
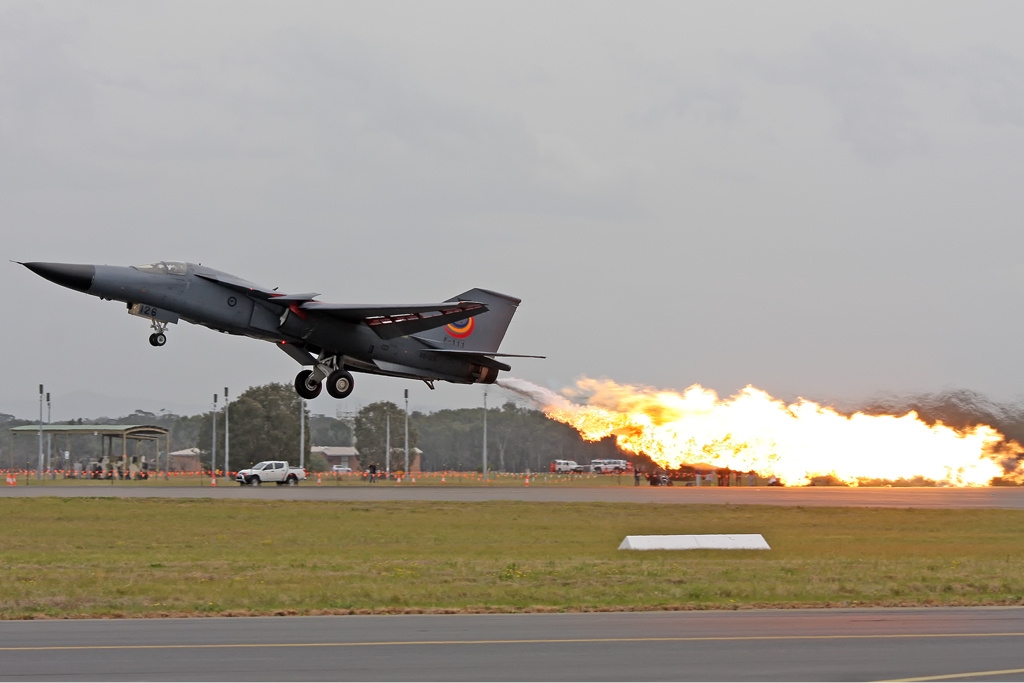 The F-111C is the export version for Australia, combining the F-111A with longer F-111B wings and strengthened FB-111A landing gear. Australia ordered 24 F-111s and, following delays, the
The F-111C is the export version for Australia, combining the F-111A with longer F-111B wings and strengthened FB-111A landing gear. Australia ordered 24 F-111s and, following delays, the
Boeing Australia. Retrieved: 3 July 2009. In the 1990s, F-111C aircraft underwent a comprehensive digital avionics upgrade (known as the AUP) which introduced new nav/attack systems (PAVE TACK Laser /infrared targeting system) and flight control computers. The RAAF retired its last F-111Cs in December 2010.
"General Dynamics FB-111A."
''joebaugher.com,'' 22 December 1999. Retrieved: 5 October 2009. The FB-111A had new electronics, known as the SAC Mark IIB avionics suite. For the FB-111A the system used an attack radar improved from the F-111A's system, along with components that would be used later on the F-111D, including the inertial navigation system, digital computers, and multi-function displays.Logan 1998, pp. 215–218. The SAC Mark IIB kit included custom items added to support the strategic mission, such as a star tracker navigation system mounted forward of the cockpit, a satellite communications receiver, and an automatic stores release system, replacing the manual stores release system used on other F-111 variants. Armament for the strategic bombing role was the Boeing AGM-69 SRAM (short-range attack missile); two could be carried in the internal weapons bay and four more on the inner underwing pylons. Nuclear gravity bombs were also typical FB armament. Fuel tanks were often carried on the third non-swivelling pylon of each wing. The FB-111A had a total weapon load of .
The FB-111A had new electronics, known as the SAC Mark IIB avionics suite. For the FB-111A the system used an attack radar improved from the F-111A's system, along with components that would be used later on the F-111D, including the inertial navigation system, digital computers, and multi-function displays.Logan 1998, pp. 215–218. The SAC Mark IIB kit included custom items added to support the strategic mission, such as a star tracker navigation system mounted forward of the cockpit, a satellite communications receiver, and an automatic stores release system, replacing the manual stores release system used on other F-111 variants. Armament for the strategic bombing role was the Boeing AGM-69 SRAM (short-range attack missile); two could be carried in the internal weapons bay and four more on the inner underwing pylons. Nuclear gravity bombs were also typical FB armament. Fuel tanks were often carried on the third non-swivelling pylon of each wing. The FB-111A had a total weapon load of .
 Multiple advanced FB-111 strategic bomber designs were proposed by General Dynamics in the 1970s. The first design, referred to as "FB-111G" within the company, was a larger aircraft with more powerful engines with more payload and range. The next was a lengthened "FB-111H" that featured more powerful General Electric F101 turbofan engines, a 12 ft 8.5 in longer fuselage and redesigned fixed intakes. The rear landing gear were moved outward so armament could be carried on the fuselage there. The FB-111H was offered as an alternative to the Rockwell B-1 Lancer, B-1A in 1975.Logan 1998, pp. 247–248.Miller 1982, pp. 59–62, 73–77. The similar FB-111B/C was offered in 1979 without success.Logan 1998, pp. 249–251.
The FB-111A became surplus to SAC's needs after the introduction of the B-1B Lancer. The remaining FB-111s were subsequently reconfigured for tactical use and redesignated ''F-111G''. The conversions began in 1989 and ended after 34 F-111G conversions were completed. With the disestablishment of SAC, the FB-111As and F-111Gs were transferred to the newly established Air Combat Command (ACC). They were used primarily for training.Logan 1998, p. 206. The remaining FB-111As were retired in 1991 and the F-111Gs were retired in 1993.Logan 1998, pp. 206, 218. Australia bought 15 F-111Gs in 1993 to supplement its F-111Cs. They were retired in 2007.
Multiple advanced FB-111 strategic bomber designs were proposed by General Dynamics in the 1970s. The first design, referred to as "FB-111G" within the company, was a larger aircraft with more powerful engines with more payload and range. The next was a lengthened "FB-111H" that featured more powerful General Electric F101 turbofan engines, a 12 ft 8.5 in longer fuselage and redesigned fixed intakes. The rear landing gear were moved outward so armament could be carried on the fuselage there. The FB-111H was offered as an alternative to the Rockwell B-1 Lancer, B-1A in 1975.Logan 1998, pp. 247–248.Miller 1982, pp. 59–62, 73–77. The similar FB-111B/C was offered in 1979 without success.Logan 1998, pp. 249–251.
The FB-111A became surplus to SAC's needs after the introduction of the B-1B Lancer. The remaining FB-111s were subsequently reconfigured for tactical use and redesignated ''F-111G''. The conversions began in 1989 and ended after 34 F-111G conversions were completed. With the disestablishment of SAC, the FB-111As and F-111Gs were transferred to the newly established Air Combat Command (ACC). They were used primarily for training.Logan 1998, p. 206. The remaining FB-111As were retired in 1991 and the F-111Gs were retired in 1993.Logan 1998, pp. 206, 218. Australia bought 15 F-111Gs in 1993 to supplement its F-111Cs. They were retired in 2007.
"Grumman EF-111A Raven."
''USAAC/USAAF/USAF Fighters'', 20 December 1999. Retrieved: 5 October 2009.
 ;
*
;
*


''RAAF Museum.'' Retrieved: 11 March 2013.
 * 68-0055 – Museum of Aviation (Warner Robins), Museum of Aviation, Robins AFB, Warner Robins, Georgia (nicknamed "Heartbreaker")
* 68-0058 – Air Force Armament Museum, Eglin AFB, Valparaiso, Florida
;F-111F
* 70-2364 – In the median strip of U.S. Route 70 in New Mexico, U.S. Highway 70, in Portales, New Mexico
* 70-2390 – National Museum of the United States Air Force, Wright-Patterson AFB, Dayton, Ohio
* 70-2408 – Santa Fe County Municipal, Santa Fe, New Mexico
* 74-0178 – Aviation Heritage Park, Bowling Green, Kentucky
; FB-111A / F-111G
* 67-0159 – Aerospace Museum of California, McClellan AFB (formerly), Sacramento, California (FB-111A development aircraft, converted to F-111G)
* 68-0239 – K. I. Sawyer Heritage Air Museum, formerly K.I. Sawyer AFB, Marquette, Michigan (nicknamed the "Rough Night"); converted to F-111G
* 68-0245 – March Field Air Museum, March Air Reserve Base, March ARB, Riverside, California (nicknamed "Ready Teddy")
* 68-0248 – South Dakota Air and Space Museum, Ellsworth AFB, South Dakota (nicknamed "Free For All")
* 68-0267 – Strategic Air Command & Aerospace Museum in Ashland, Nebraska (nicknamed "Black Widow")
* 68-0275 – Kelly Field Heritage Museum, Lackland AFB / Kelly Field San Antonio, Texas (painted in tactical scheme)
* 68-0284 – Barksdale Global Power Museum, Barksdale AFB, Bossier City, Louisiana
* 68-0286 – Clyde Lewis Airpark (adjacent to former Plattsburgh AFB), Plattsburgh, New York (nicknamed "SAC Time")
* 68-0287 – Wings Over the Rockies Air and Space Museum (former Lowry AFB), Denver, Colorado
* 69-6507 – Castle Air Museum (former Castle AFB), Atwater, California (nicknamed "Madam Queen")
* 69-6509 – Whiteman AFB, Knob Noster, Missouri (gate guard) (Converted to F-111G; nicknamed "The Spirit of the Seacoast")
* 68-0055 – Museum of Aviation (Warner Robins), Museum of Aviation, Robins AFB, Warner Robins, Georgia (nicknamed "Heartbreaker")
* 68-0058 – Air Force Armament Museum, Eglin AFB, Valparaiso, Florida
;F-111F
* 70-2364 – In the median strip of U.S. Route 70 in New Mexico, U.S. Highway 70, in Portales, New Mexico
* 70-2390 – National Museum of the United States Air Force, Wright-Patterson AFB, Dayton, Ohio
* 70-2408 – Santa Fe County Municipal, Santa Fe, New Mexico
* 74-0178 – Aviation Heritage Park, Bowling Green, Kentucky
; FB-111A / F-111G
* 67-0159 – Aerospace Museum of California, McClellan AFB (formerly), Sacramento, California (FB-111A development aircraft, converted to F-111G)
* 68-0239 – K. I. Sawyer Heritage Air Museum, formerly K.I. Sawyer AFB, Marquette, Michigan (nicknamed the "Rough Night"); converted to F-111G
* 68-0245 – March Field Air Museum, March Air Reserve Base, March ARB, Riverside, California (nicknamed "Ready Teddy")
* 68-0248 – South Dakota Air and Space Museum, Ellsworth AFB, South Dakota (nicknamed "Free For All")
* 68-0267 – Strategic Air Command & Aerospace Museum in Ashland, Nebraska (nicknamed "Black Widow")
* 68-0275 – Kelly Field Heritage Museum, Lackland AFB / Kelly Field San Antonio, Texas (painted in tactical scheme)
* 68-0284 – Barksdale Global Power Museum, Barksdale AFB, Bossier City, Louisiana
* 68-0286 – Clyde Lewis Airpark (adjacent to former Plattsburgh AFB), Plattsburgh, New York (nicknamed "SAC Time")
* 68-0287 – Wings Over the Rockies Air and Space Museum (former Lowry AFB), Denver, Colorado
* 69-6507 – Castle Air Museum (former Castle AFB), Atwater, California (nicknamed "Madam Queen")
* 69-6509 – Whiteman AFB, Knob Noster, Missouri (gate guard) (Converted to F-111G; nicknamed "The Spirit of the Seacoast")

"Voyager - Spacecraft - Golden Record - Sounds of Earth."
''NASA,'' 17 August 2008. Retrieved: 1 August 2010.
''Encyclopedia of US Air Force Aircraft and Missile Systems: Volume 1 Post-World War II Fighters 1945-1973''.
Washington, D.C.: Office of Air Force History, 1978. . * Lax, Mark
''From Controversy to Cutting Edge: A History of the F-111 in Australian Service''.
Canberra, Australia: Air Power Development Centre, Department of Defence (Australia), 2010. . * Logan, Don. ''General Dynamics F-111 Aardvark''. Atglen, Pennsylvania: Schiffer Military History, 1998. . * * Miller, Jay. ''General Dynamics F-111 "Aardvark"''. Fallbrook, California: Aero Publishers, 1982. . *Poore, Richard. ''Premature Fielding of an Immature Weapons System?''. Air Enthusiast 115, January–February 2005, p. 74 * Spick, Mike. '' B-1B'' (Modern Fighting Aircraft). New York: Prentice Hall, 1986. . * Thomason, Tommy. ''Grumman Navy F-111B Swing Wing'' (Navy Fighters No. 41). Simi Valley, California: Steve Ginter, 1998. . * Thornborough, Anthony M. ''F-111 Aardvark''. London: Arms and Armour, 1989. . * Thornborough, Anthony M. and Peter E. Davies. ''F-111 Success in Action''. London: Arms and Armour Press Ltd., 1989. . * Wilson, Stewart. ''Lincoln, Canberra and F-111 in Australian Service''. Weston Creek, ACT, Australia: Aerospace Publications, 1989. .
F-111 page on USAF National Museum web site
F-111.net
F-111 profile on Aerospaceweb.org
"The Truth About the Amazing F-111". ''Popular Science,'' May 1968
{{Authority control General Dynamics aircraft, F-111 1960s United States attack aircraft, F-111 Aardvark Variable-sweep-wing aircraft Twinjets Aircraft first flown in 1964 Shoulder-wing aircraft
multirole
A multirole combat aircraft (MRCA) is a combat aircraft intended to perform different roles in combat. These roles can include air to air combat, air support,
aerial bombing, reconnaissance, electronic warfare, and suppression of air defens ...
combat aircraft. Production variants of the F-111 had roles that included ground attack (e.g. interdiction), strategic bombing (including nuclear weapons capabilities), reconnaissance and electronic warfare. Developed in the 1960s by General Dynamics
General Dynamics Corporation (GD) is an American publicly traded, aerospace and defense corporation headquartered in Reston, Virginia. As of 2020, it was the fifth-largest defense contractor in the world by arms sales, and 5th largest in the Uni ...
, the F-111 entered service in 1967 with the United States Air Force (USAF). The Royal Australian Air Force
"Through Adversity to the Stars"
, colours =
, colours_label =
, march =
, mascot =
, anniversaries = RAAF Anniversary Commemoration ...
(RAAF) also ordered the type and began operating the F-111C
The General Dynamics F-111C (nicknamed "Pig") is a variant of the F-111 Aardvark medium-range interdictor and tactical strike aircraft, developed by General Dynamics to meet Australian requirements. The design was based on the F-111A model but ...
variant in 1973.
The F-111 pioneered several technologies for production aircraft, including variable-sweep wings, afterburning turbofan engines, and automated terrain-following radar for low-level
High-level and low-level, as technical terms, are used to classify, describe and point to specific goals of a systematic operation; and are applied in a wide range of contexts, such as, for instance, in domains as widely varied as computer scienc ...
, high-speed flight. Its design influenced later variable-sweep wing aircraft, and some of its advanced features have since become commonplace. The F-111 suffered a variety of problems during initial development.
A fighter variant, the F-111B, was not accepted for production. The F-111B was intended to perform aircraft carrier-based roles with the US Navy, including long-range interception.
USAF F-111s were retired during the 1990s with the F-111Fs in 1996 and EF-111s in 1998. The F-111 was replaced in USAF service by the F-15E Strike Eagle for medium-range precision strike missions, while the supersonic bomber role has been assumed by the B-1B Lancer. The RAAF continued to operate the type until December 2010, when the last F-111C was retired.
The name Aardvark was derived from perceived similarities of the aircraft to the animal of the same name: a long nose and low-level, terrain-following capabilities. The word aardvark originated in the Afrikaans language, as a contraction of "earth-pig", and this was the source of the F-111's nickname of "Pig", during its Australian service.
Development
Early requirements
The May1960 U-2 incident
On 1 May 1960, a United States U-2 spy plane was shot down by the Soviet Air Defence Forces while conducting photographic aerial reconnaissance deep inside Soviet territory. The single-seat aircraft, flown by American pilot Francis Gary Power ...
, in which an American CIA
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian intelligence agency, foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gat ...
U-2 reconnaissance plane was shot down over the USSR, stunned the United States government. Besides greatly damaging US–Soviet relations, the incident showed that the Soviet Union had developed a surface-to-air missile
A surface-to-air missile (SAM), also known as a ground-to-air missile (GTAM) or surface-to-air guided weapon (SAGW), is a missile designed to be launched from the ground to destroy aircraft or other missiles. It is one type of anti-aircraft syst ...
that could reach aircraft above 60,000 feet (18,000 meters). The United States Air Force Strategic Air Command (SAC) and the RAF Bomber Command's plans to send subsonic, high-altitude B-47 and V bomber formations into the USSR were now much less viable.Lax 2010, p. 15.
By 1960, SAC had begun moving to Terrain mask, low-level penetration, which greatly reduced radar detection distances. At the time, SAMs were ineffective against low-flying aircraft, and interceptor aircraft had less of a speed advantage at low altitudes.Spick 1986, pp. 4–7. The Air Force's Tactical Air Command (TAC) was largely concerned with the fighter-bomber and deep strike/interdiction roles. TAC was in the process of receiving its latest design, the Republic F-105 Thunderchief, which was designed to deliver nuclear weapons fast and far, but required long runways.Gunston 1978, pp. 12–13. A simpler Variable-sweep wing, variable geometry wing configuration with the pivot points farther out from the aircraft's centerline was reported by NASA in 1958, which made swing-wings viable.Thomason 1998, pp. 5–6. This led Air Force leaders to encourage its use.Miller 1982, pp. 10–11. In June 1960, the USAF issued specification SOR 183 for a long-range interdiction/strike aircraft able to penetrate Soviet Union, Soviet air defenses at very low altitudes and high speeds. The specification also called for the aircraft to operate from short, unprepared airstrips.
In the 1950s, the United States Navy sought a long-range, high-endurance interceptor aircraft to protect its carrier battle groups against long-range anti-ship missiles launched from Soviet jet bombers and submarines. The Navy needed a fleet air defense (FAD) fighter with a more powerful radar, and longer range missiles than the McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II, F-4 Phantom II to intercept both enemy bombers and missiles.Thomason 1998, pp. 3–5. Seeking a FAD fighter, the Navy started with the subsonic aircraft, subsonic, straight-winged aircraft, the Douglas F6D Missileer in the late 1950s. The Missileer was designed to carry six long-range missiles and loiter for five hours, but would be defenseless after firing its missiles. The program was formally canceled in 1961. The Navy had tried variable geometry wings with the XF10F Jaguar, but abandoned it in the early 1950s. It was NASA's simplification which made the variable geometry wings practical. By 1960, increases in aircraft weights required improved high-lift devices, such as variable geometry wings.Miller 1982, p. 11. Variable geometry offered high speeds, and maneuverability with heavier payloads, long range, and the ability to take off and land in shorter distances.
Tactical Fighter Experimental (TFX)
The U.S. Air Force and Navy were both seeking new aircraft when Robert McNamara was appointed United States Secretary of Defense, Secretary of Defense in January 1961.Miller 1982, p. 13. The aircraft sought by the two armed services shared the need to carry heavy armament and fuel loads, feature high supersonic speed, twin engines and two seats, and probably use Variable-sweep wing, variable geometry wings. On 14 February 1961, McNamara formally directed the services to study the development of a single aircraft that would satisfy both requirements. Early studies indicated that the best option was to base the design on the Air Force requirement, and use a modified version for the Navy. In June 1961, Secretary McNamara ordered the go ahead of Tactical Fighter Experimental (TFX), despite Air Force and Navy efforts to keep their programs separate. The Air Force and the Navy could agree only on swing-wing, two-seat, twin-engine design features. The Air Force wanted a tandem-seat aircraft for low-level penetration ground-attack, while the Navy wanted a shorter, high altitude interceptor with side-by-side seating to allow the pilot and Naval Flight Officer, radar operator to share the radar display. Also, the Air Force wanted the aircraft designed for 7.33 g with Mach 2.5 speed at altitude and Mach 1.2 speed at low level with an approximate length of . The Navy had less strenuous requirements of 6 g with Mach 2 speed at altitude and high subsonic speed (approx. Mach 0.9) at low level with a length of . The Navy also wanted the aircraft with a nose large enough for a diameter radar dish.Miller 1982, pp. 11–15.
McNamara developed a basic set of requirements for TFX based largely on the Air Force's requirements and, on 1 September 1961, ordered the Air Force to develop it. A request for proposals (RFP) for the TFX was provided to industry in October 1961. In December, proposals were received from Boeing,
The Air Force and the Navy could agree only on swing-wing, two-seat, twin-engine design features. The Air Force wanted a tandem-seat aircraft for low-level penetration ground-attack, while the Navy wanted a shorter, high altitude interceptor with side-by-side seating to allow the pilot and Naval Flight Officer, radar operator to share the radar display. Also, the Air Force wanted the aircraft designed for 7.33 g with Mach 2.5 speed at altitude and Mach 1.2 speed at low level with an approximate length of . The Navy had less strenuous requirements of 6 g with Mach 2 speed at altitude and high subsonic speed (approx. Mach 0.9) at low level with a length of . The Navy also wanted the aircraft with a nose large enough for a diameter radar dish.Miller 1982, pp. 11–15.
McNamara developed a basic set of requirements for TFX based largely on the Air Force's requirements and, on 1 September 1961, ordered the Air Force to develop it. A request for proposals (RFP) for the TFX was provided to industry in October 1961. In December, proposals were received from Boeing, General Dynamics
General Dynamics Corporation (GD) is an American publicly traded, aerospace and defense corporation headquartered in Reston, Virginia. As of 2020, it was the fifth-largest defense contractor in the world by arms sales, and 5th largest in the Uni ...
, Lockheed Corporation, Lockheed, McDonnell Aircraft, McDonnell, North American Aviation, North American and Republic Aviation, Republic. The evaluation group found all the proposals lacking, but Boeing and General Dynamics were selected to submit enhanced designs. Boeing's Boeing 818, proposal was recommended by the selection board in January 1962, with the exception of the engine, which was not considered acceptable. Switching to a crew escape capsule, instead of ejection seats and alterations to radar and missile storage were also needed. Both companies provided updated proposals in April 1962. Air Force reviewers favored Boeing's offering, while the Navy found both submissions unacceptable for its operations. Two more rounds of updates to the proposals were conducted, with Boeing being picked by the selection board.
In November 1962, McNamara selected General Dynamics' proposal due to its greater commonality between Air Force and Navy versions. The Boeing aircraft shared less than half of the major structural components. General Dynamics signed the TFX contract in December 1962. A Congressional investigation followed, but would not change the selection.
Design phase
The F-111A and B variants used the same airframe structural components and Pratt & Whitney TF30, Pratt & Whitney TF30-P-1 turbofan engines. They featured side-by-side crew seating in an escape capsule as required by the Navy. The General Dynamics/Grumman F-111B, F-111B's nose was shorter so as to fit on existing carrier elevator decks, and had wingtips to improve on-station endurance time. The Navy version would carry an AN/AWG-9 Pulse-Doppler radar and AIM-54 Phoenix missiles. The Air Force version would carry the AN/APQ-113 attack radar and the AN/APQ-110 terrain-following radar and air-to-ground armament.Baugher, Joe"General Dynamics F-111A."
''USAAC/USAAF/USAF Fighters'', 23 December 1999. Retrieved: 5 October 2009. A team of engineers at General Dynamics was led by Robert H. Widmer. Lacking experience with carrier-based fighters, General Dynamics teamed with Grumman for the assembly and testing of the F-111B aircraft. In addition, Grumman would also build the F-111A's aft fuselage and the landing gear. The General Dynamics and Grumman team faced ambitious requirements for range, weapons load, and aircraft weight. The F-111 design also included new features on a production military aircraft, such as variable-geometry wings and afterburning turbofan engines.Miller 1982, pp. 17, 19. The F-111A mockup was inspected in September 1963. The first test F-111A was rolled out of Air Force Plant 4, Plant 4 of General Dynamics' Fort Worth, Texas, facility on 15 October 1964. It was powered by YTF30-P-1 turbofans and used a set of ejector seats as the escape capsule was not yet available. The F-111A first flew on 21 December 1964 from Carswell Air Force Base, Texas, U.S. The F-111B was also equipped with ejector seats and first flew on 18 May 1965.Baugher, Joe
"General Dynamics/Grumman F-111B."
''USAAC/USAAF/USAF Fighters'', 7 November 2004. Retrieved: 5 October 2009. Initially there were compressor surge and stall issues in certain parts of the flight regime. NASA, the Air Force, and General Dynamics studies resulted in the engine inlet design being modified in 1965–66, culminating with the "Triple Plow I" and "Triple Plow II" designs.Gunston 1978, pp. 25–27. The F-111A achieved a speed of Mach 1.3 in February 1965 with an interim intake design. Cracks in the F-111's wingbox, wing attach points were first discovered in 1968 during ground fatigue testing; an F-111 crashed the following year due to this issue. The attach structure required redesign and testing to ensure adequate design and workmanship.Miller 1982, pp. 31, 47. Flight testing of the F-111A ran through 1973.Logan 1998, p. 32. The F-111B was canceled by the Navy in 1968 due to weight and performance issues, along with the need for additional fighter requirements. The F-111C model was developed for Australia. Subsequently, the improved F-111E, F-111D, F-111F models were developed for the U.S. Air Force. The strategic bomber FB-111A and the EF-111 electronic warfare versions were later developed for the USAF. Production ended in 1976,Miller 1982, p. 65. after 563 F-111 aircraft were built.
Design
Overview
 The F-111 was an all-weather attack aircraft, capable of low-level penetration of enemy defenses to deliver ordnance on the target. The F-111 featured variable-sweep wing, variable-geometry wings, an internal weapons bay and a cockpit with side-by-side seating. The cockpit was part of an escape crew capsule.Eden 2004, pp. 196–201. The wing sweep varied between 16 degrees and 72.5 degrees (full forward to full sweep). The wing included leading edge slats and flap (aircraft), double slotted flaps over its full length.Miller 1982, pp. 80–81. The airframe was made up mostly of aluminium alloys with steel, titanium and other materials used in places.Logan 1998, pp. 17–18. The fuselage was made of a semi-monocoque structure with stiffened panels and honeycomb structure panels for skin. The horizontal stabilizer was an all-moving stabilator.
The F-111 used a three-point landing gear arrangement, with a two-wheel nose gear and two single-wheel main landing gear units. The landing gear door for the main gear, which was positioned in the center of the fuselage, also served as a air brake (aircraft), speed brake in flight.Logan 1998, p. 19. Most F-111 variants included a terrain-following radar system connected to the autopilot. The aircraft was powered by two Pratt & Whitney TF30 afterburning turbofan engines. The F-111's variable-geometry wings, escape capsule, terrain following radar and afterburning turbofans were new technologies for production aircraft.Logan 1998, p. 14.
The F-111 was an all-weather attack aircraft, capable of low-level penetration of enemy defenses to deliver ordnance on the target. The F-111 featured variable-sweep wing, variable-geometry wings, an internal weapons bay and a cockpit with side-by-side seating. The cockpit was part of an escape crew capsule.Eden 2004, pp. 196–201. The wing sweep varied between 16 degrees and 72.5 degrees (full forward to full sweep). The wing included leading edge slats and flap (aircraft), double slotted flaps over its full length.Miller 1982, pp. 80–81. The airframe was made up mostly of aluminium alloys with steel, titanium and other materials used in places.Logan 1998, pp. 17–18. The fuselage was made of a semi-monocoque structure with stiffened panels and honeycomb structure panels for skin. The horizontal stabilizer was an all-moving stabilator.
The F-111 used a three-point landing gear arrangement, with a two-wheel nose gear and two single-wheel main landing gear units. The landing gear door for the main gear, which was positioned in the center of the fuselage, also served as a air brake (aircraft), speed brake in flight.Logan 1998, p. 19. Most F-111 variants included a terrain-following radar system connected to the autopilot. The aircraft was powered by two Pratt & Whitney TF30 afterburning turbofan engines. The F-111's variable-geometry wings, escape capsule, terrain following radar and afterburning turbofans were new technologies for production aircraft.Logan 1998, p. 14.
Armament

Weapons bay
The F-111 featured an internal weapons bay that could carry bombs, a removable 20 mm M61 Vulcan, M61 cannon or auxiliary fuel tanks.Logan 1998, pp. 20, 21, 28. For bombs, the bay could hold two 750 lb (340 kg) M117 bomb, M117 conventional bombs, one nuclear weapon, nuclear bomb or practice bombs. The F-111B for the US Navy was to carry two AIM-54 Phoenix long-range air-to-air missiles in the bay. The cannon had a large 2,084-round ammunition tank, and its muzzle was covered by a fairing; however, it was rarely fitted on F-111s.Gunston 1983, p. 30. The F-111C and F-111F were equipped to carry the Pave Tack, AN/AVQ-26 Pave Tack targeting system on a rotating carriage that kept the pod protected within the weapons bay when not in use. Pave Tack featured a forward looking infrared (FLIR) sensor, optical camera and laser rangefinder/Laser designator, designator. The Pave Tack pod allowed the F-111 to designate targets and drop laser-guided bombs on them. Australian RF-111Cs carried a pallet of sensors and cameras for aerial reconnaissance use.Miller 1982, p. 31. The FB-111 could carry two AGM-69 SRAM air-to-surface nuclear missiles in its weapons bay.Gunston 1983, p. 31. General Dynamics trialed an arrangement with two AIM-9 Sidewinder air-to-air missiles carried on rails in a trapeze arrangement from the bay, but this was not adopted. Early F-111 models had radars equipped to guide the AIM-7 Sparrow medium-range air-to-air missile, but it was never fitted.Gunston 1983, pp. 23–24.External ordnance
 Each wing was equipped with four underwing pylons. The inner two pylons on each wing rotated to align with the fuselage, while the outer two were fixed. Each pylon had a capacity of . Various bombs and missiles could be carried on the pylons. Auxiliary fuel drop tanks with capacity each could be fitted.Gunston 1983, pp. 30–31.
The design of the F-111's fuselage prevented the carriage of external weapons under the fuselage, but two stations were available on the underside for electronic countermeasures (ECM) pods and/or datalink pods; one station was on the weapons bay, and the other on the rear fuselage between the engines. The F-111's maximum practical weapons load was limited, since the fixed pylons could not be used with the wings fully swept.Logan 1998, p. 18.
Tactical F-111s were fitted with shoulder rails on the four inner swiveling pylons to mount AIM-9 Sidewinder air-to-air missiles for self-defense. Australian F-111Cs were equipped to launch the Harpoon (missile), Harpoon anti-ship missile, and the Popeye (missile), Popeye stand-off missile.Logan 1998, p. 28. FB-111As could carry the same conventional ordnance as the tactical variants, but their wing pylons were more commonly used for either fuel tanks or strategic nuclear gravity bombs. They could carry up to four AGM-69 SRAM nuclear missiles on the pylons.Gunston 1983, p. 49.
Each wing was equipped with four underwing pylons. The inner two pylons on each wing rotated to align with the fuselage, while the outer two were fixed. Each pylon had a capacity of . Various bombs and missiles could be carried on the pylons. Auxiliary fuel drop tanks with capacity each could be fitted.Gunston 1983, pp. 30–31.
The design of the F-111's fuselage prevented the carriage of external weapons under the fuselage, but two stations were available on the underside for electronic countermeasures (ECM) pods and/or datalink pods; one station was on the weapons bay, and the other on the rear fuselage between the engines. The F-111's maximum practical weapons load was limited, since the fixed pylons could not be used with the wings fully swept.Logan 1998, p. 18.
Tactical F-111s were fitted with shoulder rails on the four inner swiveling pylons to mount AIM-9 Sidewinder air-to-air missiles for self-defense. Australian F-111Cs were equipped to launch the Harpoon (missile), Harpoon anti-ship missile, and the Popeye (missile), Popeye stand-off missile.Logan 1998, p. 28. FB-111As could carry the same conventional ordnance as the tactical variants, but their wing pylons were more commonly used for either fuel tanks or strategic nuclear gravity bombs. They could carry up to four AGM-69 SRAM nuclear missiles on the pylons.Gunston 1983, p. 49.
Historical significance
The F-111 was the first production variable-geometry wing aircraft. Several other types have followed with similar swing-wing configuration, including the Soviet Union, Soviet Sukhoi Su-17 "Fitter" (1965), Mikoyan-Gurevich MiG-23 "Flogger" (1967), Tupolev Tu-22M "Backfire" (1969), Sukhoi Su-24 "Fencer" (1970) and Tupolev Tu-160 "Blackjack" (1981); the U.S. Rockwell B-1 Lancer bomber (1974); and the European Panavia Tornado (1974). The Sukhoi Su-24 was very similar to the F-111.Gunston 1983, p. 3. The U.S. Navy's role intended for the F-111B was instead filled by another variable-geometry design, the Grumman F-14 Tomcat.Operational history
U.S. Air Force
 The first of six initial production F-111s was delivered on 17 July 1967 to fighter squadrons at Nellis Air Force Base.Logan 1998, p. 33. These aircraft were used for crew training. 428th Fighter Squadron, 428th Tactical Fighter Squadron achieved initial operational capability on 28 April 1968.
After early testing, a detachment of six aircraft from the 474th Tactical Fighter Wing (474th TFW Roadrunners) were sent in March 1968 to Southeast Asia for Combat Lancer testing in real combat conditions in the Vietnam War. During the deployment, 55 night missions were flown against targets in North Vietnam, but two aircraft had been lost. 66–0022 was lost on 28 March, and 66-0017 on 30 March. Replacement aircraft left Nellis, but the loss of a third F-111A (66-0024) on 22 April halted F-111A combat operations. The squadron returned to the United States in November. The cause of the first two losses is unknown as the wreckages were never recovered. It turned out that the third loss was traced to a failure of a hydraulic control-valve rod for the horizontal stabilizer which caused the aircraft to pitch up uncontrollably. Further inspection of the remaining fleet of F-111As revealed 42 aircraft with the same potential failures. It is speculated that this failure could also have contributed to the two earlier losses had the failure caused a pitch down while at low altitude. It was not until 1971 that 474 TFW was fully operational.
The word "aardvark" is Afrikaans for "earthpig" and reflects the look of the long nose of the aircraft that might remind one of the nose of the aardvark. The name is attributed to F-111A Instructor Pilot Al Mateczun in 1969, as the aircraft had not received an official Air Force name.
September 1972 saw the F-111 back in Southeast Asia, stationed at Takhli Royal Thai Air Force Base, Takhli Air Base, Thailand. F-111As from Nellis AFB participated in the final month of Operation Linebacker and later flew 154 low-level missions in the Operation Linebacker II aerial offensive against the North Vietnamese, who called the aircraft "Whispering Death". They also supported regional aerial operations against other communist forces such as Operation Phou Phiang III during the Laotian Civil War in Laos. Crews described their flying in Vietnam as "speed is life", "one pass, haul ass", and "you do more than one pass in a target area you die". The F-111's ability with terrain-following radar ("the best in the fighter world", according to F-111 pilot Richard Crandall) to fly as low as above ground level at or faster in most weather conditions made it very effective; missions did not require tankers or ECM support, and they could operate in weather that grounded most other aircraft. One F-111 could carry the bomb load of four McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom IIs. The worth of the new aircraft was beginning to show; F-111s flew more than 4,000 combat missions in Vietnam with only six combat losses.Logan 1998, pp. 283–284.
From 30 July 1973 F-111As of the 347th Rescue Wing, 347th Tactical Fighter Wing (347th TFW) were stationed at Takhli Air Base. The 347th TFW conducted bombing missions in Cambodia in support of Khmer Republic forces until 15 August 1973 when US combat support ceased in accordance with the Case–Church Amendment. The 347th TFW was stationed at Korat Royal Thai Air Force Base from 12 July 1974 until 30 June 1975. In May 1975 347th TFW F-111s provided air support during the Mayaguez incident, ''Mayaguez'' incident.
One of the most unusual missions occurred on 14 February 1986, when two FB-111s of the 509th Bombardment Wing were dispatched from then Pease Air Force Base, New Hampshire to Tinker Air Force Base, Oklahoma to pick up a heart for transplant. The aircraft landed at Bradley International Airport to deliver the organ to a waiting ambulance.
The first of six initial production F-111s was delivered on 17 July 1967 to fighter squadrons at Nellis Air Force Base.Logan 1998, p. 33. These aircraft were used for crew training. 428th Fighter Squadron, 428th Tactical Fighter Squadron achieved initial operational capability on 28 April 1968.
After early testing, a detachment of six aircraft from the 474th Tactical Fighter Wing (474th TFW Roadrunners) were sent in March 1968 to Southeast Asia for Combat Lancer testing in real combat conditions in the Vietnam War. During the deployment, 55 night missions were flown against targets in North Vietnam, but two aircraft had been lost. 66–0022 was lost on 28 March, and 66-0017 on 30 March. Replacement aircraft left Nellis, but the loss of a third F-111A (66-0024) on 22 April halted F-111A combat operations. The squadron returned to the United States in November. The cause of the first two losses is unknown as the wreckages were never recovered. It turned out that the third loss was traced to a failure of a hydraulic control-valve rod for the horizontal stabilizer which caused the aircraft to pitch up uncontrollably. Further inspection of the remaining fleet of F-111As revealed 42 aircraft with the same potential failures. It is speculated that this failure could also have contributed to the two earlier losses had the failure caused a pitch down while at low altitude. It was not until 1971 that 474 TFW was fully operational.
The word "aardvark" is Afrikaans for "earthpig" and reflects the look of the long nose of the aircraft that might remind one of the nose of the aardvark. The name is attributed to F-111A Instructor Pilot Al Mateczun in 1969, as the aircraft had not received an official Air Force name.
September 1972 saw the F-111 back in Southeast Asia, stationed at Takhli Royal Thai Air Force Base, Takhli Air Base, Thailand. F-111As from Nellis AFB participated in the final month of Operation Linebacker and later flew 154 low-level missions in the Operation Linebacker II aerial offensive against the North Vietnamese, who called the aircraft "Whispering Death". They also supported regional aerial operations against other communist forces such as Operation Phou Phiang III during the Laotian Civil War in Laos. Crews described their flying in Vietnam as "speed is life", "one pass, haul ass", and "you do more than one pass in a target area you die". The F-111's ability with terrain-following radar ("the best in the fighter world", according to F-111 pilot Richard Crandall) to fly as low as above ground level at or faster in most weather conditions made it very effective; missions did not require tankers or ECM support, and they could operate in weather that grounded most other aircraft. One F-111 could carry the bomb load of four McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom IIs. The worth of the new aircraft was beginning to show; F-111s flew more than 4,000 combat missions in Vietnam with only six combat losses.Logan 1998, pp. 283–284.
From 30 July 1973 F-111As of the 347th Rescue Wing, 347th Tactical Fighter Wing (347th TFW) were stationed at Takhli Air Base. The 347th TFW conducted bombing missions in Cambodia in support of Khmer Republic forces until 15 August 1973 when US combat support ceased in accordance with the Case–Church Amendment. The 347th TFW was stationed at Korat Royal Thai Air Force Base from 12 July 1974 until 30 June 1975. In May 1975 347th TFW F-111s provided air support during the Mayaguez incident, ''Mayaguez'' incident.
One of the most unusual missions occurred on 14 February 1986, when two FB-111s of the 509th Bombardment Wing were dispatched from then Pease Air Force Base, New Hampshire to Tinker Air Force Base, Oklahoma to pick up a heart for transplant. The aircraft landed at Bradley International Airport to deliver the organ to a waiting ambulance.
 On 14 April 1986, 18 F-111s and approximately 25 Navy aircraft conducted air strikes against Libya under 1986 United States bombing of Libya, Operation El Dorado Canyon. The 18 F-111s of the 48th Fighter Wing, 48th Tactical Fighter Wing and 4 EF-111As from the 20th Fighter Wing, 20th Tactical Fighter Wing flew what turned out to be the longest fighter combat mission in history. The round-trip flight between RAF Lakenheath/RAF Upper Heyford, United Kingdom and Libya of spanned 13 hours. One F-111 was lost over Libya and crashed into the Mediterranean Sea, probably shot down.Walter J. Boyne, Boyne, Walter J.]
On 14 April 1986, 18 F-111s and approximately 25 Navy aircraft conducted air strikes against Libya under 1986 United States bombing of Libya, Operation El Dorado Canyon. The 18 F-111s of the 48th Fighter Wing, 48th Tactical Fighter Wing and 4 EF-111As from the 20th Fighter Wing, 20th Tactical Fighter Wing flew what turned out to be the longest fighter combat mission in history. The round-trip flight between RAF Lakenheath/RAF Upper Heyford, United Kingdom and Libya of spanned 13 hours. One F-111 was lost over Libya and crashed into the Mediterranean Sea, probably shot down.Walter J. Boyne, Boyne, Walter J.]"El Dorado Canyon."
''Air Force Magazine'', March 1999. F-111s participated in the Gulf War (Operation Desert Storm) in 1991. During Desert Storm, F-111Fs completed 3.2 successful strike missions for every unsuccessful one, better than any other U.S. strike aircraft used in the operation."GAO/NS-97-134, Operation Desert Storm, Evaluation of the Air Campaign."
''US General Accounting Office'', June 1997. The group of 66 F-111Fs dropped almost 80% of the war's laser-guided bombs, including the penetrating bunker-buster GBU-28. Eighteen F-111Es were also deployed during the operation. The F-111s were credited with destroying more than 1,500 Iraqi tanks and armored vehicles."Air Force Performance in Desert Storm", p. 4.
''U.S. Air Force,'' April 1991. Their use in the anti-armor role was dubbed "tank plinking". The F-111 was in service with the USAF from 1967 through 1998. The FB-111s were operated by Strategic Air Command from 1969 before conversion to F-111G and transferred to Air Combat Command (ACC) until their retirement in 1993. At a ceremony marking the F-111's USAF retirement, on 27 July 1996, it was officially named Aardvark, its long-standing unofficial name."Fact Sheet: General Dynamics F-111D to F."
''National Museum of the United States Air Force.'' Retrieved: 1 August 2010. The USAF retired the EF-111 electronic warfare variant in 1998.Gershanoff, H
''Journal of Electronic Defense'', 1 December 1998.
Royal Australian Air Force
The Australian government ordered 24 F-111C aircraft to replace the RAAF's English Electric Canberras in the bombing and tactical strike role.Gunston 1978, p. 62. While the first aircraft was officially handed over in September 1968, structural issues delayed the entry into service.Wilson 1989, p. 152. The first F-111C was accepted at Nellis Air Force Base on 15 March 1973.Wilson and Pittaway 2010, p. 47. The RAAF's first six F-111Cs arrived at Amberley on 1 July 1973, and three subsequent flights of six F-111s arrived on 27 July, 28 September and 4 December. F-111Cs were allocated to No. 1 Squadron RAAF, No. 1 Squadron and No. 6 Squadron RAAF, No. 6 Squadron, under the control of No. 82 Wing RAAF, No. 82 Wing. In Australia, the F-111 was affectionately known as the "Pig". The purchase proved to be highly successful for the RAAF. Although it never saw combat, the F-111C was the fastest, longest range combat aircraft in Southeast Asia, providing Australia with independent strike capability.Stephens 2006, p. 290. Leonardus Benjamin Moerdani, Benny Murdani told Kim Beazley that when others became upset with Australia during Cabinet of Indonesia, Indonesian cabinet meetings, Murdani told them "Do you realise the Australians have a bomber that can put a bomb through that window on to the table here in front of us?"
Australian F-111s were ready to attack Indonesian forces during the establishment of East Timor's independence and the deployment of the Australian-led International Force for East Timor. In 2006, an RAAF F-111 scuttled the North Korean ship ''Pong Su'' on 23 March 2006.
Because of the high maintenance time required for every flight hour, the F-111's retirement began with the F-111G models operated by No. 6 Squadron in late 2007. Twenty-four F/A-18F Super Hornets were procured as an interim replacement while the F-35 program was delayed. The last F-111s were retired on 3 December 2010.
The purchase proved to be highly successful for the RAAF. Although it never saw combat, the F-111C was the fastest, longest range combat aircraft in Southeast Asia, providing Australia with independent strike capability.Stephens 2006, p. 290. Leonardus Benjamin Moerdani, Benny Murdani told Kim Beazley that when others became upset with Australia during Cabinet of Indonesia, Indonesian cabinet meetings, Murdani told them "Do you realise the Australians have a bomber that can put a bomb through that window on to the table here in front of us?"
Australian F-111s were ready to attack Indonesian forces during the establishment of East Timor's independence and the deployment of the Australian-led International Force for East Timor. In 2006, an RAAF F-111 scuttled the North Korean ship ''Pong Su'' on 23 March 2006.
Because of the high maintenance time required for every flight hour, the F-111's retirement began with the F-111G models operated by No. 6 Squadron in late 2007. Twenty-four F/A-18F Super Hornets were procured as an interim replacement while the F-35 program was delayed. The last F-111s were retired on 3 December 2010.
Variants
F-111A
 The F-111A was the initial production version of the F-111. Early A-models used the TF30-P-1 engine. Most A-models used the TF30-P-3 engine with 12,000 lbf (53 kN) dry and 18,500 lbf (82 kN) afterburning thrust and "Triple Plow I" variable intakes, providing a maximum speed of Mach 2.3 (1,450 mph, 2,300 km/h) at altitude.Miller 1982, pp. 26, 66. The variant had a maximum takeoff weight of and an empty weight of .Logan 1998, p. 302.
The A-model's Mark I avionics suite included the General Electric AN/APQ-113 attack radar mated to a separate Texas Instruments AN/APQ-110 terrain-following radar lower in the nose and a Litton Industries, Litton AJQ-20 inertial navigation and nav/attack system. The terrain-following radar (TFR) was integrated into the automatic flight control system, allowing for "hands-off" flight at high speeds and low levels (down to ).Gunston 1978, pp. 46–47.
Total production of the F-111As was 159, including 30 pre-production aircraft that were later brought up to production standards.Miller 1982, p. 26. 42 F-111As were converted to EF-111A Ravens for an electronic warfare tactical electronic jamming role. In 1982, four surviving F-111As were provided to Australia as attrition replacements and modified to F-111C standard; these were fitted with the longer-span wings and reinforced landing gear of the C-model.Logan 1998, p. 263.
Three pre-production F-111A were provided to NASA for various testing duties. The 13th F-111A was fitted with new wing designs for the Transonic Aircraft Technology and Advanced Fighter Technology Integration programs in the 1970s and 1980s. It was retired to the National Museum of the United States Air Force, United States Air Force Museum at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base in 1989. The remaining unconverted F-111As were mothballed at 309th Aerospace Maintenance and Regeneration Group, Aerospace Maintenance and Regeneration Center at Davis-Monthan Air Force Base in June 1991.
The F-111A was the initial production version of the F-111. Early A-models used the TF30-P-1 engine. Most A-models used the TF30-P-3 engine with 12,000 lbf (53 kN) dry and 18,500 lbf (82 kN) afterburning thrust and "Triple Plow I" variable intakes, providing a maximum speed of Mach 2.3 (1,450 mph, 2,300 km/h) at altitude.Miller 1982, pp. 26, 66. The variant had a maximum takeoff weight of and an empty weight of .Logan 1998, p. 302.
The A-model's Mark I avionics suite included the General Electric AN/APQ-113 attack radar mated to a separate Texas Instruments AN/APQ-110 terrain-following radar lower in the nose and a Litton Industries, Litton AJQ-20 inertial navigation and nav/attack system. The terrain-following radar (TFR) was integrated into the automatic flight control system, allowing for "hands-off" flight at high speeds and low levels (down to ).Gunston 1978, pp. 46–47.
Total production of the F-111As was 159, including 30 pre-production aircraft that were later brought up to production standards.Miller 1982, p. 26. 42 F-111As were converted to EF-111A Ravens for an electronic warfare tactical electronic jamming role. In 1982, four surviving F-111As were provided to Australia as attrition replacements and modified to F-111C standard; these were fitted with the longer-span wings and reinforced landing gear of the C-model.Logan 1998, p. 263.
Three pre-production F-111A were provided to NASA for various testing duties. The 13th F-111A was fitted with new wing designs for the Transonic Aircraft Technology and Advanced Fighter Technology Integration programs in the 1970s and 1980s. It was retired to the National Museum of the United States Air Force, United States Air Force Museum at Wright-Patterson Air Force Base in 1989. The remaining unconverted F-111As were mothballed at 309th Aerospace Maintenance and Regeneration Group, Aerospace Maintenance and Regeneration Center at Davis-Monthan Air Force Base in June 1991.
F-111B
 The F-111B was to be a fleet air defense (FAD) fighter for the U.S. Navy, fulfilling a naval requirement for a carrier-based fighter aircraft capable of carrying heavy, long-range missiles to defend aircraft carriers and their battle groups from Soviet bombers and fighter-bombers equipped with anti-ship missiles. General Dynamics, lacking experience with carrier-based aircraft, partnered with Grumman for this version. The F-111B suffered development problems and Navy requirements changed to an aircraft with maneuverability for dogfighting. The swing-wing configuration, TF-30 engines, AIM-54 Phoenix air-to-air missiles and AWG-9 radar developed for this aircraft were used on its replacement, the Grumman F-14 Tomcat. The Tomcat would be large enough to carry the AWG-9 and Phoenix weapons system while exceeding both the F-111's and the F-4's maneuverability. Seven aircraft were completed for testing but the model never entered fleet service.
The F-111B was to be a fleet air defense (FAD) fighter for the U.S. Navy, fulfilling a naval requirement for a carrier-based fighter aircraft capable of carrying heavy, long-range missiles to defend aircraft carriers and their battle groups from Soviet bombers and fighter-bombers equipped with anti-ship missiles. General Dynamics, lacking experience with carrier-based aircraft, partnered with Grumman for this version. The F-111B suffered development problems and Navy requirements changed to an aircraft with maneuverability for dogfighting. The swing-wing configuration, TF-30 engines, AIM-54 Phoenix air-to-air missiles and AWG-9 radar developed for this aircraft were used on its replacement, the Grumman F-14 Tomcat. The Tomcat would be large enough to carry the AWG-9 and Phoenix weapons system while exceeding both the F-111's and the F-4's maneuverability. Seven aircraft were completed for testing but the model never entered fleet service.
F-111C
 The F-111C is the export version for Australia, combining the F-111A with longer F-111B wings and strengthened FB-111A landing gear. Australia ordered 24 F-111s and, following delays, the
The F-111C is the export version for Australia, combining the F-111A with longer F-111B wings and strengthened FB-111A landing gear. Australia ordered 24 F-111s and, following delays, the Royal Australian Air Force
"Through Adversity to the Stars"
, colours =
, colours_label =
, march =
, mascot =
, anniversaries = RAAF Anniversary Commemoration ...
accepted the aircraft in 1973.Logan 1998, p. 261. Four of these were converted to the RF-111C reconnaissance variant in 1979–80. Australia also purchased four ex-USAF F-111As and converted them to C standard."F/RF-111C Modifications and Support"Boeing Australia. Retrieved: 3 July 2009. In the 1990s, F-111C aircraft underwent a comprehensive digital avionics upgrade (known as the AUP) which introduced new nav/attack systems (PAVE TACK Laser /infrared targeting system) and flight control computers. The RAAF retired its last F-111Cs in December 2010.
F-111D
The F-111D was an upgraded F-111A equipped with newer Mark II avionics, more powerful engines, improved intake geometry, and an early glass cockpit. The variant was first ordered in 1967 and delivered from 1970–73. The F-111D reached initial operational capability in 1972. Deliveries were delayed due to avionics issues. 96 F-111Ds were built.Logan 1998, pp. 26, 106–107. The sole operator of this variant was the 27th TFW stationed at Cannon AFB, New Mexico. The F-111D used the new Triple Plow II intakes, which were located four inches (100 mm) further away from the airframe to prevent engine ingestion of the sluggish boundary layer air that was known to cause stalls in the TF30 turbofans. It had more powerful TF30-P-9 engines with 12,000 lbf (53 kN) dry and 18,500 lbf (82 kN) afterburning thrust.Knaack 1978, pp. 250–252. The Mark II avionics were digitally integrated microprocessor systems, some of the first used by the USAF, offering tremendous capability, but substantial problems. The Rockwell International, Rockwell Autonetics digital bombing-navigation system included inertial navigation system, AN/APQ-130 attack radar system and Doppler radar. It also included digital computer set and multi-function displays (MFDs). The terrain-following radar was the Sperry Corporation, Sperry AN/APQ-128.Logan 1998, pp. 26–27. The attack radar featured a Doppler beam-sharpening, moving target indication (MTI), and Continuous-wave radar for guiding semi-active radar homing missiles.Gunston 1978, pp. 94–95. It took years to improve the reliability of the avionics, but issues were never fully addressed. According to Crandall, "The truth is that the D model didn't work. They parked every single one of them in Fort Worth for several years as they worked to fix the bugs". The F-111D was withdrawn from service in 1991 and 1992.Logan 1998, p. 108.F-111E
A simplified, interim variant ordered after the F-111D was delayed, the F-111E used the Triple Plow II intakes, but retained the F-111A's TF30-P-3 engines and Mark I avionics.Gunston 1978, pp. 74–76. The weapon stores management system was improved and other small changes made.Miller 1982, p. 32. Crandall described the F-111E as "all analog, just like the A model, but It worked". The E-model was first ordered in 1968 and delivered from 1969–71. It achieved initial operational capability in 1969.Logan 1998, pp. 137–138. The variant's first flight occurred on 20 August 1969. 94 F-111Es were built. Many F-111Es were assigned to the 20th TFW at Upper Heyford, UK until 1991. The avionics were upgraded on some E-models as part of an Avionics Modernization Program. The variant served in 1990-91 during the Gulf War. Some F-111Es received improved TF30-P-109 engines in the early 1990s. All F-111Es were retired to AMARC by 1995.Logan 1998, p. 138.F-111F
Crandall described the F-111F as "the Cadillac of the F-111 force". It was the final variant produced for Tactical Air Command, with a modern, but less expensive, Mark IIB avionics system.Gunston 1978, pp. 95–97. The USAF approved development of the variant in 1969. It also included the more powerful TF30-P-100 engine and strengthened wing carry-through box. 106 were produced between 1970 and 1976.Logan 1998, pp. 169–171. The F-111F's Mark IIB avionics suite used a simplified version of the FB-111A's radar, the AN/APQ-144, lacking some of the strategic bomber's operating modes but adding a new 2.5 mi (4.0 km) display ring. Although it was tested with digital moving-target indicator (MTI) capacity, it was not used in production sets. The Mark IIB avionics combined some Mark II components with FB-111A components, such as the AN/APQ-146 terrain-following radar. The F-111E's weapon management system was also included.Logan 1998, pp. 27, 169. The F-model could reach Mach 1.2 at sea level on full afterburner. It used the Triple Plow II intakes, along with the substantially more powerful TF30-P-100 turbofan with 25,100 lbf (112 kN) afterburning thrust, 35% more thrust than the F-111A and E. An adjustable engine nozzle was added to decrease drag. The P-100 engine greatly improved the F-111F's performance.Gunston 1978, p. 96. The engines were upgraded to the TF30-P-109 version,Logan 1998, p. 301. later in the 1985–86 timeframe. In the early 1980s, the F-111F began to be equipped with the AVQ-26 Pave Tack forward looking infrared (FLIR) and laser designator system, which provided for the delivery of precision laser-guided munitions and was mounted in the internal weapons bay. The Pacer Strike avionics update program replaced analog equipment with new digital equipment and multi-function displays.Logan 1998, pp. 28–29. The last USAF F-111s were withdrawn from service in 1996, replaced by the McDonnell Douglas F-15E Strike Eagle.F-111K
The British government canceled the BAC TSR-2 strike aircraft in 1965, citing the lower costs for the TFX and ordered 50 F-111K aircraft in February 1967 for the Royal Air Force.Gunston 1978, pp. 84–87. The F-111K was to be supplemented later by the AFVG, Anglo-French Variable Geometry Aircraft then under development. The F-111K was based on the F-111A with longer F-111B wings, FB-111 landing gear, Mark II navigation/fire control system, and British supplied mission systems. Other changes included weapons bay modifications, addition of a centerline pylon, a retractable refueling probe, provisions for a reconnaissance pallet, and a higher gross weight with the use of FB-111A landing gear.Logan 1998, pp. 278–80. In January 1968, the United Kingdom terminated its F-111K order, citing higher cost; increased costs along with devaluation of the Pound sterling, pound had raised the cost to around £3 million each. The first two F-111Ks (one strike/recon F-111K and one trainer/strike TF-111K) were in the final stages of assembly when the order was canceled. All of the components that had been assembled for the production of the main F-111K fleet that shared commonality were diverted to the FB-111A program, while the two aircraft under construction were re-designated as YF-111As with the intention that they be used as test aircraft in the F-111A program. Ultimately however, the two F-111Ks were never operated as test aircraft – in July 1968, almost exactly a year after the first airframe began construction, the US Air Force decided not to take them over, and General Dynamics were ordered to use them for component recovery.FB-111A / F-111G
The FB-111A was a strategic bomber version of the F-111 for the USAF Strategic Air Command. With Air Force's Rockwell B-1 Lancer, Advanced Manned Strategic Aircraft program proceeding slowly, and concerns of fatigue failures in the Boeing B-52 Stratofortress, B-52 fleet, the service needed an interim bomber quickly. The FB-111A was selected in 1965 to replace the supersonic Convair B-58 Hustler and early B-52 variants.Logan 1998, p. 215. The Air Force signed a contract for the FB-111A in 1966. In 1968, plans called for 263 FB-111s, but the total was reduced to 76 in 1969. The first production aircraft flew in 1968.Miller 1982, pp. 38–41. Deliveries began in 1969 and ended in 1971. When the UK canceled its order for the F-111K in 1968, components for the 48 F-111Ks in manufacturing were diverted to FB-111A production.Gunston 1978, p. 87.Logan 1998, pp. 278–279. The FB-111A featured longer F-111B wings for greater range and load-carrying ability.Miller 1982, pp. 38–43. The bomber variant had a redesigned aft fuselage and its maximum speed was limited to Mach 2.Logan 1998, p. 216–218. Its fuel capacity was increased by 585 gallons (2,214 L) and it used stronger landing gear to compensate for the higher maximum takeoff weight of 119,250 lb (54,105 kg). All but the first aircraft had the Triple Plow II intakes and the TF30-P-7 with 12,500 lbf (56 kN) dry and 20,350 lbf (90 kN) afterburning thrust.Baugher, Joe"General Dynamics FB-111A."
''joebaugher.com,'' 22 December 1999. Retrieved: 5 October 2009.
 The FB-111A had new electronics, known as the SAC Mark IIB avionics suite. For the FB-111A the system used an attack radar improved from the F-111A's system, along with components that would be used later on the F-111D, including the inertial navigation system, digital computers, and multi-function displays.Logan 1998, pp. 215–218. The SAC Mark IIB kit included custom items added to support the strategic mission, such as a star tracker navigation system mounted forward of the cockpit, a satellite communications receiver, and an automatic stores release system, replacing the manual stores release system used on other F-111 variants. Armament for the strategic bombing role was the Boeing AGM-69 SRAM (short-range attack missile); two could be carried in the internal weapons bay and four more on the inner underwing pylons. Nuclear gravity bombs were also typical FB armament. Fuel tanks were often carried on the third non-swivelling pylon of each wing. The FB-111A had a total weapon load of .
The FB-111A had new electronics, known as the SAC Mark IIB avionics suite. For the FB-111A the system used an attack radar improved from the F-111A's system, along with components that would be used later on the F-111D, including the inertial navigation system, digital computers, and multi-function displays.Logan 1998, pp. 215–218. The SAC Mark IIB kit included custom items added to support the strategic mission, such as a star tracker navigation system mounted forward of the cockpit, a satellite communications receiver, and an automatic stores release system, replacing the manual stores release system used on other F-111 variants. Armament for the strategic bombing role was the Boeing AGM-69 SRAM (short-range attack missile); two could be carried in the internal weapons bay and four more on the inner underwing pylons. Nuclear gravity bombs were also typical FB armament. Fuel tanks were often carried on the third non-swivelling pylon of each wing. The FB-111A had a total weapon load of .
EF-111A Raven
To replace the aging B-66 Destroyer, Douglas EB-66, the USAF contracted with Grumman in 1972 to convert 42 existing F-111As into electronic warfare aircraft. The EF-111A can be distinguished from the F-111A by the equipment bulge atop their tails. In May 1998, the USAF withdrew the final EF-111As from service, placing them in storage at 309th Aerospace Maintenance and Regeneration Group, Aerospace Maintenance and Regeneration Center (AMARC) at Davis–Monthan Air Force Base.Baugher, Joe"Grumman EF-111A Raven."
''USAAC/USAAF/USAF Fighters'', 20 December 1999. Retrieved: 5 October 2009.
Operators
 ;
*
;
*Royal Australian Air Force
"Through Adversity to the Stars"
, colours =
, colours_label =
, march =
, mascot =
, anniversaries = RAAF Anniversary Commemoration ...
*No. 82 Wing RAAF, No. 82 Wing – RAAF Base Amberley
**No. 1 Squadron RAAF, No. 1 Squadron F-111C
The General Dynamics F-111C (nicknamed "Pig") is a variant of the F-111 Aardvark medium-range interdictor and tactical strike aircraft, developed by General Dynamics to meet Australian requirements. The design was based on the F-111A model but ...
(1973–2009)
**No. 6 Squadron RAAF, No. 6 Squadron F-111C (1973–2010), F-111G (1993–2007)
;
United States Air Force operated F-111A/D/E/F/G, FB-111A and EF-111A. Officially retired its F-111s in 1996 and the EF-111A in 1998.
:Tactical Air Command 1968–1992
:Air Combat Command 1992–1998
*27th Special Operations Wing, 27th Tactical Fighter Wing – Cannon Air Force Base, Cannon AFB
::428th Tactical Fighter Training Squadron F-111G (1990–1993), F-111E (1993–1995)
::481st Tactical Fighter Squadron F-111A/E (1969–1973), F-111D (1973–1980)
::522d Fighter Squadron, 522d Tactical Fighter Squadron F-111A/E (1971–1972), F-111D (1973–1992), F-111F (1992–1995)
::523d Fighter Squadron, 523d Tactical Fighter Squadron F-111A/E (1971–1972), F-111D (1973–1992), F-111F (1992–1995)
::524th Special Operations Squadron, 524th Tactical Fighter Squadron F-111A/E (1971–1972), F-111D (1973–1992), F-111F (1992–1995)
*366th Fighter Wing, 366th Tactical Fighter Wing – Mountain Home Air Force Base, Mountain Home AFB
::389th Fighter Squadron, 389th Tactical Fighter Squadron F-111F (1971–1977), F-111A (1977–1991)
::390th Fighter Squadron, 390th Tactical Fighter Squadron F-111F (1971–1977), F-111A (1977–1982)
::391st Fighter Squadron, 391st Tactical Fighter Squadron F-111F (1971–1977), F-111A (1977–1990)
*474th Tactical Fighter Wing – Nellis Air Force Base, Nellis AFB
::428th Fighter Squadron, 428th Tactical Fighter Squadron F-111A (1968–1977)
::429th Electronic Combat Squadron, 429th Tactical Fighter Squadron F-111A (1969–1977)
::430th Electronic Combat Squadron, 430th Tactical Fighter Squadron F-111A (1969–1977)
::442nd Tactical Fighter Training Squadron F-111A (1969–1977)
:United States Air Forces in Europe
*20th Fighter Wing, 20th Tactical Fighter Wing – RAF Upper Heyford
::55th Fighter Squadron, 55th Tactical Fighter Squadron F-111E (1971–1993)
::77th Fighter Squadron, 77th Tactical Fighter Squadron F-111E (1971–1993)
::79th Fighter Squadron, 79th Tactical Fighter Squadron F-111E (1971–1993)
*48th Fighter Wing, 48th Tactical Fighter Wing – RAF Lakenheath
::492d Fighter Squadron, 492d Tactical Fighter Squadron F-111F (1977–1992)
::493d Fighter Squadron, 493rd Tactical Fighter Squadron F-111F (1977–1992)
::494th Fighter Squadron, 494th Tactical Fighter Squadron F-111F (1977–1992)
::495th Tactical Fighter Squadron F-111F (1977–1991)
:Strategic Air Command
*340th Bombardment Group (Medium) – Carswell Air Force Base, Carswell AFB
::4007th Combat Crew Training Squadron FB-111 (1968–1971)
*380th Air Expeditionary Wing, 380th Bombardment Wing (Medium) – Plattsburgh Air Force Base, Plattsburgh AFB
::528th Bombardment Squadron (Medium) FB-111 (1971–1995)
::529th Bombardment Squadron (Medium) FB-111 (1971–1995)
*509th Bomb Wing, 509th Bombardment Wing (Medium) – Pease Air National Guard Base, Pease AFB
::393d Bombardment Squadron (Medium) FB-111 (1970–1990)
::715th Weapons Squadron, 715th Bombardment Squadron (Medium) FB-111 (1971–1990)
*NASA
Aircraft on display

Australia
;F-111G * A8-272 – RAAF Museum, Point Cook, Victoria"F-111 Aardvark/A8-272."''RAAF Museum.'' Retrieved: 11 March 2013.
United Kingdom
;F-111E * 67-0120 – American Air Museum, Imperial War Museum Duxford, Duxford, England. The last F-111E from 20th Tactical Fighter Wing in the UK. It was directly transferred from USAF service at RAF Upper Heyford to the museum in late 1993, prior to the base closure in 1994. * 68-0011 – RAF Lakenheath, England (in front of base post office, marked as 48th TFW F-111F) ;F-111F * 74-0177 – National Cold War Exhibition, Royal Air Force Museum CosfordUnited States
;F-111A * 63-9766 – Air Force Flight Test Center Museum, Edwards AFB, Palmdale, California (first F-111) * 63-9767 – Waukegan National Airport, Waukegan, Illinois. To be put on display at the Lake County Veterans Memorial at the airport. Formerly on display at Octave Chanute Aerospace Museum (former Chanute AFB), Rantoul, Illinois. * 63-9771 – Cannon AFB, Clovis, New Mexico * 63-9773 – Sheppard AFB Air Park, Sheppard AFB, Wichita Falls, Texas * 63-9775 – United States Space and Rocket Center, Huntsville, Alabama * 63-9776 – Mountain Home AFB, Idaho (the only RF-111A, marked as 66-0022) * 63-9778 – Air Force Flight Test Center Museum, Edwards AFB, Palmdale, California (TACT/General Dynamics–Boeing AFTI/F-111A Aardvark, AFTI F-111) * 66-0012 – Battle Mountain Air Museum, Battle Mountain, Nevada * 67-0046 – Brownwood Regional Airport, Brownwood, Texas * 67-0047 – American Airpower Museum, Long Island, New York * 67-0051 – Historic Aviation Memorial Museum, Tyler Pounds Regional Airport, Tyler, Texas (marked as 67-0050) * 67-0057 – Dyess Air Force Base Linear Air Park, Abilene, Texas * 67-0058 – Carl Miller Park, Mountain Home, Idaho * 67-0067 – National Museum of the United States Air Force, Wright-Patterson AFB, Dayton, Ohio * 67-0069 – The Southern Museum of Flight, Birmingham, Alabama * 67-0100 – Nellis Air Force Base, Las Vegas, Nevada (aircraft display park) ;F-111D * 68-0140 – Clovis, New Mexico (F-111 "Vark" Memorial Park) ;F-111E * 68-0009 – Fort Worth Aviation Museum Fort Worth, Texas * 68-0020 – Hill Aerospace Museum, Hill AFB, Utah (nicknamed "My Lucky Blonde") * 68-0027 – Commemorative Air Force, Midland, Texas * 68-0033 – Pima Air and Space Museum (adjacent to Davis-Monthan AFB), Tucson, Arizona * 68-0039 – Shaw AFB, Sumter, South Carolina * 68-0055 – Museum of Aviation (Warner Robins), Museum of Aviation, Robins AFB, Warner Robins, Georgia (nicknamed "Heartbreaker")
* 68-0058 – Air Force Armament Museum, Eglin AFB, Valparaiso, Florida
;F-111F
* 70-2364 – In the median strip of U.S. Route 70 in New Mexico, U.S. Highway 70, in Portales, New Mexico
* 70-2390 – National Museum of the United States Air Force, Wright-Patterson AFB, Dayton, Ohio
* 70-2408 – Santa Fe County Municipal, Santa Fe, New Mexico
* 74-0178 – Aviation Heritage Park, Bowling Green, Kentucky
; FB-111A / F-111G
* 67-0159 – Aerospace Museum of California, McClellan AFB (formerly), Sacramento, California (FB-111A development aircraft, converted to F-111G)
* 68-0239 – K. I. Sawyer Heritage Air Museum, formerly K.I. Sawyer AFB, Marquette, Michigan (nicknamed the "Rough Night"); converted to F-111G
* 68-0245 – March Field Air Museum, March Air Reserve Base, March ARB, Riverside, California (nicknamed "Ready Teddy")
* 68-0248 – South Dakota Air and Space Museum, Ellsworth AFB, South Dakota (nicknamed "Free For All")
* 68-0267 – Strategic Air Command & Aerospace Museum in Ashland, Nebraska (nicknamed "Black Widow")
* 68-0275 – Kelly Field Heritage Museum, Lackland AFB / Kelly Field San Antonio, Texas (painted in tactical scheme)
* 68-0284 – Barksdale Global Power Museum, Barksdale AFB, Bossier City, Louisiana
* 68-0286 – Clyde Lewis Airpark (adjacent to former Plattsburgh AFB), Plattsburgh, New York (nicknamed "SAC Time")
* 68-0287 – Wings Over the Rockies Air and Space Museum (former Lowry AFB), Denver, Colorado
* 69-6507 – Castle Air Museum (former Castle AFB), Atwater, California (nicknamed "Madam Queen")
* 69-6509 – Whiteman AFB, Knob Noster, Missouri (gate guard) (Converted to F-111G; nicknamed "The Spirit of the Seacoast")
* 68-0055 – Museum of Aviation (Warner Robins), Museum of Aviation, Robins AFB, Warner Robins, Georgia (nicknamed "Heartbreaker")
* 68-0058 – Air Force Armament Museum, Eglin AFB, Valparaiso, Florida
;F-111F
* 70-2364 – In the median strip of U.S. Route 70 in New Mexico, U.S. Highway 70, in Portales, New Mexico
* 70-2390 – National Museum of the United States Air Force, Wright-Patterson AFB, Dayton, Ohio
* 70-2408 – Santa Fe County Municipal, Santa Fe, New Mexico
* 74-0178 – Aviation Heritage Park, Bowling Green, Kentucky
; FB-111A / F-111G
* 67-0159 – Aerospace Museum of California, McClellan AFB (formerly), Sacramento, California (FB-111A development aircraft, converted to F-111G)
* 68-0239 – K. I. Sawyer Heritage Air Museum, formerly K.I. Sawyer AFB, Marquette, Michigan (nicknamed the "Rough Night"); converted to F-111G
* 68-0245 – March Field Air Museum, March Air Reserve Base, March ARB, Riverside, California (nicknamed "Ready Teddy")
* 68-0248 – South Dakota Air and Space Museum, Ellsworth AFB, South Dakota (nicknamed "Free For All")
* 68-0267 – Strategic Air Command & Aerospace Museum in Ashland, Nebraska (nicknamed "Black Widow")
* 68-0275 – Kelly Field Heritage Museum, Lackland AFB / Kelly Field San Antonio, Texas (painted in tactical scheme)
* 68-0284 – Barksdale Global Power Museum, Barksdale AFB, Bossier City, Louisiana
* 68-0286 – Clyde Lewis Airpark (adjacent to former Plattsburgh AFB), Plattsburgh, New York (nicknamed "SAC Time")
* 68-0287 – Wings Over the Rockies Air and Space Museum (former Lowry AFB), Denver, Colorado
* 69-6507 – Castle Air Museum (former Castle AFB), Atwater, California (nicknamed "Madam Queen")
* 69-6509 – Whiteman AFB, Knob Noster, Missouri (gate guard) (Converted to F-111G; nicknamed "The Spirit of the Seacoast")
Specifications (F-111F)
Popular culture
American artist James Rosenquist portrayed the aircraft in his acclaimed 1965 room-sized pop art painting entitled ''F-111'' that features an early natural-finish example of the aircraft in USAF markings. The painting hangs in the Museum of Modern Art in New York City. The sound of an F-111 flyby is on the Voyager Golden Record.''NASA,'' 17 August 2008. Retrieved: 1 August 2010.
See also
References
Notes
Citations
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * Gunston, Bill. ''F-111,'' (Modern Fighting Aircraft, Vol. 3). New York: Salamander Books, 1983. . * Knaack, Marcelle Size''Encyclopedia of US Air Force Aircraft and Missile Systems: Volume 1 Post-World War II Fighters 1945-1973''.
Washington, D.C.: Office of Air Force History, 1978. . * Lax, Mark
''From Controversy to Cutting Edge: A History of the F-111 in Australian Service''.
Canberra, Australia: Air Power Development Centre, Department of Defence (Australia), 2010. . * Logan, Don. ''General Dynamics F-111 Aardvark''. Atglen, Pennsylvania: Schiffer Military History, 1998. . * * Miller, Jay. ''General Dynamics F-111 "Aardvark"''. Fallbrook, California: Aero Publishers, 1982. . *Poore, Richard. ''Premature Fielding of an Immature Weapons System?''. Air Enthusiast 115, January–February 2005, p. 74 * Spick, Mike. '' B-1B'' (Modern Fighting Aircraft). New York: Prentice Hall, 1986. . * Thomason, Tommy. ''Grumman Navy F-111B Swing Wing'' (Navy Fighters No. 41). Simi Valley, California: Steve Ginter, 1998. . * Thornborough, Anthony M. ''F-111 Aardvark''. London: Arms and Armour, 1989. . * Thornborough, Anthony M. and Peter E. Davies. ''F-111 Success in Action''. London: Arms and Armour Press Ltd., 1989. . * Wilson, Stewart. ''Lincoln, Canberra and F-111 in Australian Service''. Weston Creek, ACT, Australia: Aerospace Publications, 1989. .
Further reading
* Angelucci, Enzo. ''The American Fighter.'' New York: Haynes, 1987. . * Art, Robert J. ''The TFX Decision: McNamara and the Military.'' Boston: Little, Brown, 1968. * Neubeck, Ken. ''F-111 Aardvark Walk Around''. Carrollton, Texas: Squadron/Signal Publications, 2009. . * Winchester, Jim, ed. ''General Dynamics FB-111A''. ''Grumman/General Dynamics EF-111A Raven''. ''Military Aircraft of the Cold War'' (The Aviation Factfile). London: Grange Books plc, 2006. .External links
F-111 page on USAF National Museum web site
F-111.net
F-111 profile on Aerospaceweb.org
"The Truth About the Amazing F-111". ''Popular Science,'' May 1968
{{Authority control General Dynamics aircraft, F-111 1960s United States attack aircraft, F-111 Aardvark Variable-sweep-wing aircraft Twinjets Aircraft first flown in 1964 Shoulder-wing aircraft