Eye movement on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Eye movement includes the voluntary or involuntary movement of the eyes. Eye movements are used by a number of
Eye movement includes the voluntary or involuntary movement of the eyes. Eye movements are used by a number of
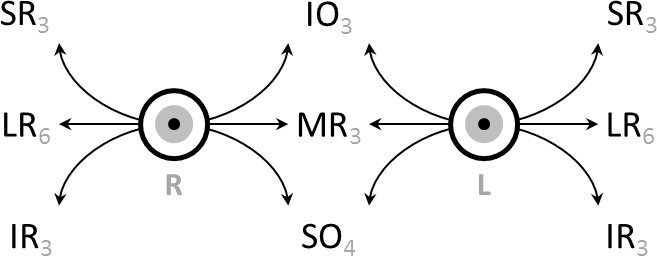 Three antagonistic pairs of muscles control eye movement: the lateral and medial recti muscles, the superior and inferior recti muscles, and the superior and inferior oblique muscles. These muscles are responsible for movement of the eye along three different axes: horizontal, either toward the nose (adduction) or away from the nose (abduction); vertical, either elevation or depression; and torsional, movements that bring the top of the eye toward the nose (intorsion) or away from the nose (extorsion). Horizontal movement is controlled entirely by the medial and lateral recti muscles; the medial rectus muscle is responsible for adduction, the lateral rectus muscle for abduction. Vertical movement requires the coordinated action of the superior and inferior recti muscles, as well as the oblique muscles. The relative contribution of the recti and oblique groups depends on the horizontal position of the eye. In the primary position (eyes straight ahead), both of these groups contribute to vertical movement. Elevation is due to the action of the superior rectus and inferior oblique muscles, while depression is due to the action of the inferior rectus and superior oblique muscles. When the eye is abducted, the recti muscles are the prime vertical movers. Elevation is due to the action of the superior rectus, and depression is due to the action of the inferior rectus. When the eye is adducted, the oblique muscles are the prime vertical movers. Elevation is due to the action of the inferior oblique muscle, while depression is due to the action of the superior oblique muscle. The oblique muscles are also primarily responsible for torsional movement.
The muscles are supplied by the
Three antagonistic pairs of muscles control eye movement: the lateral and medial recti muscles, the superior and inferior recti muscles, and the superior and inferior oblique muscles. These muscles are responsible for movement of the eye along three different axes: horizontal, either toward the nose (adduction) or away from the nose (abduction); vertical, either elevation or depression; and torsional, movements that bring the top of the eye toward the nose (intorsion) or away from the nose (extorsion). Horizontal movement is controlled entirely by the medial and lateral recti muscles; the medial rectus muscle is responsible for adduction, the lateral rectus muscle for abduction. Vertical movement requires the coordinated action of the superior and inferior recti muscles, as well as the oblique muscles. The relative contribution of the recti and oblique groups depends on the horizontal position of the eye. In the primary position (eyes straight ahead), both of these groups contribute to vertical movement. Elevation is due to the action of the superior rectus and inferior oblique muscles, while depression is due to the action of the inferior rectus and superior oblique muscles. When the eye is abducted, the recti muscles are the prime vertical movers. Elevation is due to the action of the superior rectus, and depression is due to the action of the inferior rectus. When the eye is adducted, the oblique muscles are the prime vertical movers. Elevation is due to the action of the inferior oblique muscle, while depression is due to the action of the superior oblique muscle. The oblique muscles are also primarily responsible for torsional movement.
The muscles are supplied by the
eMedicine – Extraocular Muscles, Actions
''Oculomotor Control – Nystagmus and Dizziness''
Department of Otolaryngology – Queen's University at Kingston, Canada
Software system for simulating eye motility disorders and their surgical correction
which shows changes in eye movements for any given muscle or nerve impairment. {{DEFAULTSORT:Eye Movement (Sensory) Eye
 Eye movement includes the voluntary or involuntary movement of the eyes. Eye movements are used by a number of
Eye movement includes the voluntary or involuntary movement of the eyes. Eye movements are used by a number of organisms
In biology, an organism () is any living system that functions as an individual entity. All organisms are composed of cells ( cell theory). Organisms are classified by taxonomy into groups such as multicellular animals, plants, and fu ...
(e.g. primates
Primates are a diverse order of mammals. They are divided into the strepsirrhines, which include the lemurs, galagos, and lorisids, and the haplorhines, which include the tarsiers and the simians ( monkeys and apes, the latter including ...
, rodents
Rodents (from Latin , 'to gnaw') are mammals of the order Rodentia (), which are characterized by a single pair of continuously growing incisors in each of the upper and lower jaws. About 40% of all mammal species are rodents. They are na ...
, flies
Flies are insects of the order Diptera, the name being derived from the Greek δι- ''di-'' "two", and πτερόν ''pteron'' "wing". Insects of this order use only a single pair of wings to fly, the hindwings having evolved into advanced m ...
, birds
Birds are a group of warm-blooded vertebrates constituting the class Aves (), characterised by feathers, toothless beaked jaws, the laying of hard-shelled eggs, a high metabolic rate, a four-chambered heart, and a strong yet lightweigh ...
, fish
Fish are Aquatic animal, aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack Limb (anatomy), limbs with Digit (anatomy), digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and Chondrichthyes, cartilaginous and bony fish as we ...
, cats
The cat (''Felis catus'') is a domestic species of small carnivorous mammal. It is the only domesticated species in the family Felidae and is commonly referred to as the domestic cat or house cat to distinguish it from the wild members o ...
, crabs
Crabs are decapod crustaceans of the infraorder Brachyura, which typically have a very short projecting "tail" (abdomen) ( el, βραχύς , translit=brachys = short, / = tail), usually hidden entirely under the thorax. They live in all the ...
, octopus
An octopus ( : octopuses or octopodes, see below for variants) is a soft-bodied, eight- limbed mollusc of the order Octopoda (, ). The order consists of some 300 species and is grouped within the class Cephalopoda with squids, cuttlefish, ...
) to fixate, inspect and track
Track or Tracks may refer to:
Routes or imprints
* Ancient trackway, any track or trail whose origin is lost in antiquity
* Animal track, imprints left on surfaces that an animal walks across
* Desire path, a line worn by people taking the shorte ...
visual objects of interests. A special type of eye movement, rapid eye movement, occurs during REM sleep
Rapid eye movement sleep (REM sleep or REMS) is a unique phase of sleep in mammals and birds, characterized by random rapid movement of the eyes, accompanied by low muscle tone throughout the body, and the propensity of the sleeper to dream ...
.
The eyes are the visual organs of the human body, and move using a system of six muscles. The retina
The retina (from la, rete "net") is the innermost, light-sensitive layer of tissue of the eye of most vertebrates and some molluscs. The optics of the eye create a focused two-dimensional image of the visual world on the retina, which the ...
, a specialised type of tissue containing photoreceptors, senses light. These specialised cells convert light into electrochemical
Electrochemistry is the branch of physical chemistry concerned with the relationship between electrical potential difference, as a measurable and quantitative phenomenon, and identifiable chemical change, with the potential difference as an outc ...
signals. These signals travel along the optic nerve
In neuroanatomy, the optic nerve, also known as the second cranial nerve, cranial nerve II, or simply CN II, is a paired cranial nerve that transmits visual information from the retina to the brain. In humans, the optic nerve is derived fro ...
fibers to the brain, where they are interpreted as vision in the visual cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Sensory input originating from the eyes travels through the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalamus ...
.
Primates and many other vertebrates use three types of voluntary eye movement to track objects of interest: smooth pursuit
In the scientific study of vision, smooth pursuit describes a type of eye movement in which the eyes remain fixated on a moving object. It is one of two ways that visual animals can voluntarily shift gaze, the other being saccadic eye movemen ...
, vergence shifts and saccade
A saccade ( , French for ''jerk'') is a quick, simultaneous movement of both eyes between two or more phases of fixation in the same direction.Cassin, B. and Solomon, S. ''Dictionary of Eye Terminology''. Gainesville, Florida: Triad Publishi ...
s. These types of movements appear to be initiated by a small cortical region in the brain's frontal lobe
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a groove be ...
. This is corroborated by removal of the frontal lobe. In this case, the reflexes (such as reflex shifting the eyes to a moving light) are intact, though the voluntary control is obliterated."Sensory Reception: Human Vision: Structure and function of the Human Eye" Encyclopædia Britannica, 1987
Anatomy
Muscles
Sixextraocular muscles
The extraocular muscles (extrinsic ocular muscles), are the seven extrinsic muscles of the human eye. Six of the extraocular muscles, the four recti muscles, and the superior and inferior oblique muscles, control movement of the eye and the oth ...
facilitate eye movement. These muscles arise from the common tendinous ring
The common tendinous ring, also known as the annulus of Zinn, or annular tendon, is a ring of fibrous tissue surrounding the optic nerve at its entrance at the apex of the orbit. It is the common origin of the four recti muscles of the group of ex ...
(annulus of Zinn) in the orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as ...
(eye cavity), and attach to the eyeball
Eyes are organs of the visual system. They provide living organisms with vision, the ability to receive and process visual detail, as well as enabling several photo response functions that are independent of vision. Eyes detect light and con ...
. The six muscles are the lateral
Lateral is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
Healthcare
*Lateral (anatomy), an anatomical direction
* Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle
* Lateral release (surgery), a surgical procedure on the side of a kneecap
Phonetics
*Lateral co ...
, medial, inferior and superior
Superior may refer to:
*Superior (hierarchy), something which is higher in a hierarchical structure of any kind
Places
*Superior (proposed U.S. state), an unsuccessful proposal for the Upper Peninsula of Michigan to form a separate state
*Lake ...
recti muscles
The extraocular muscles (extrinsic ocular muscles), are the seven extrinsic muscles of the human eye. Six of the extraocular muscles, the four recti muscles, and the superior and inferior oblique muscles, control movement of the eye and the oth ...
, and the inferior and superior oblique muscles. The muscles, when contracting, cause movement of the eyeball, by pulling the eyeball towards the muscle. For example, the lateral rectus
Lateral is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
Healthcare
* Lateral (anatomy), an anatomical direction
* Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle
* Lateral release (surgery), a surgical procedure on the side of a kneecap
Phonetics
* Lateral ...
is on the lateral
Lateral is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
Healthcare
*Lateral (anatomy), an anatomical direction
* Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle
* Lateral release (surgery), a surgical procedure on the side of a kneecap
Phonetics
*Lateral co ...
side of the eyeball. When it contracts, the eyeball moves so that the pupil looks outwards. The medial rectus causes the eyeball to look inwards; the inferior rectus downwards and the superior rectus upwards. The superior oblique muscle
The superior oblique muscle, or obliquus oculi superior, is a fusiform muscle originating in the upper, medial side of the orbit (i.e. from beside the nose) which abducts, depresses and internally rotates the eye. It is the only extraocular mu ...
and inferior oblique muscle
The inferior oblique muscle or obliquus oculi inferior is a thin, narrow muscle placed near the anterior margin of the floor of the orbit. The inferior oblique is one of the extraocular muscles, and is attached to the maxillary bone (origin) an ...
attach at angles to the eyeball.
 Three antagonistic pairs of muscles control eye movement: the lateral and medial recti muscles, the superior and inferior recti muscles, and the superior and inferior oblique muscles. These muscles are responsible for movement of the eye along three different axes: horizontal, either toward the nose (adduction) or away from the nose (abduction); vertical, either elevation or depression; and torsional, movements that bring the top of the eye toward the nose (intorsion) or away from the nose (extorsion). Horizontal movement is controlled entirely by the medial and lateral recti muscles; the medial rectus muscle is responsible for adduction, the lateral rectus muscle for abduction. Vertical movement requires the coordinated action of the superior and inferior recti muscles, as well as the oblique muscles. The relative contribution of the recti and oblique groups depends on the horizontal position of the eye. In the primary position (eyes straight ahead), both of these groups contribute to vertical movement. Elevation is due to the action of the superior rectus and inferior oblique muscles, while depression is due to the action of the inferior rectus and superior oblique muscles. When the eye is abducted, the recti muscles are the prime vertical movers. Elevation is due to the action of the superior rectus, and depression is due to the action of the inferior rectus. When the eye is adducted, the oblique muscles are the prime vertical movers. Elevation is due to the action of the inferior oblique muscle, while depression is due to the action of the superior oblique muscle. The oblique muscles are also primarily responsible for torsional movement.
The muscles are supplied by the
Three antagonistic pairs of muscles control eye movement: the lateral and medial recti muscles, the superior and inferior recti muscles, and the superior and inferior oblique muscles. These muscles are responsible for movement of the eye along three different axes: horizontal, either toward the nose (adduction) or away from the nose (abduction); vertical, either elevation or depression; and torsional, movements that bring the top of the eye toward the nose (intorsion) or away from the nose (extorsion). Horizontal movement is controlled entirely by the medial and lateral recti muscles; the medial rectus muscle is responsible for adduction, the lateral rectus muscle for abduction. Vertical movement requires the coordinated action of the superior and inferior recti muscles, as well as the oblique muscles. The relative contribution of the recti and oblique groups depends on the horizontal position of the eye. In the primary position (eyes straight ahead), both of these groups contribute to vertical movement. Elevation is due to the action of the superior rectus and inferior oblique muscles, while depression is due to the action of the inferior rectus and superior oblique muscles. When the eye is abducted, the recti muscles are the prime vertical movers. Elevation is due to the action of the superior rectus, and depression is due to the action of the inferior rectus. When the eye is adducted, the oblique muscles are the prime vertical movers. Elevation is due to the action of the inferior oblique muscle, while depression is due to the action of the superior oblique muscle. The oblique muscles are also primarily responsible for torsional movement.
The muscles are supplied by the oculomotor nerve
The oculomotor nerve, also known as the third cranial nerve, cranial nerve III, or simply CN III, is a cranial nerve that enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure and innervates extraocular muscles that enable most movements of ...
, with the exception of the superior oblique, which is supplied by the trochlear nerve
The trochlear nerve (), ( lit. ''pulley-like'' nerve) also known as the fourth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IV, or CN IV, is a cranial nerve that innervates just one muscle: the superior oblique muscle of the eye, which operates through the pu ...
, and the lateral rectus, supplied by the abducens nerve
The abducens nerve or abducent nerve, also known as the sixth cranial nerve, cranial nerve VI, or simply CN VI, is a cranial nerve in humans and various other animals that controls the movement of the lateral rectus muscle, one of the extraocu ...
.
Neuroanatomy
The brain exerts ultimate control over both voluntary and involuntary eye movement. Threecranial nerve
Cranial nerves are the nerves that emerge directly from the brain (including the brainstem), of which there are conventionally considered twelve pairs. Cranial nerves relay information between the brain and parts of the body, primarily to and ...
s carry signals from the brain to control the extraocular muscles. These are the oculomotor nerve
The oculomotor nerve, also known as the third cranial nerve, cranial nerve III, or simply CN III, is a cranial nerve that enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure and innervates extraocular muscles that enable most movements of ...
, which controls the majority of the muscles, the trochlear nerve
The trochlear nerve (), ( lit. ''pulley-like'' nerve) also known as the fourth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IV, or CN IV, is a cranial nerve that innervates just one muscle: the superior oblique muscle of the eye, which operates through the pu ...
, which controls the superior oblique muscle
The superior oblique muscle, or obliquus oculi superior, is a fusiform muscle originating in the upper, medial side of the orbit (i.e. from beside the nose) which abducts, depresses and internally rotates the eye. It is the only extraocular mu ...
, and the abducens nerve
The abducens nerve or abducent nerve, also known as the sixth cranial nerve, cranial nerve VI, or simply CN VI, is a cranial nerve in humans and various other animals that controls the movement of the lateral rectus muscle, one of the extraocu ...
, which controls the lateral rectus
Lateral is a geometric term of location which may refer to:
Healthcare
* Lateral (anatomy), an anatomical direction
* Lateral cricoarytenoid muscle
* Lateral release (surgery), a surgical procedure on the side of a kneecap
Phonetics
* Lateral ...
muscle.
In addition to the movement of muscles, numerous areas in the brain contribute to involuntary and voluntary eye movement. These include providing the conscious perception of vision
Vision, Visions, or The Vision may refer to:
Perception Optical perception
* Visual perception, the sense of sight
* Visual system, the physical mechanism of eyesight
* Computer vision, a field dealing with how computers can be made to gain und ...
, as well as areas that facilitate tracking.
* Brain
** Cerebral cortex
The cerebral cortex, also known as the cerebral mantle, is the outer layer of neural tissue of the cerebrum of the brain in humans and other mammals. The cerebral cortex mostly consists of the six-layered neocortex, with just 10% consisting o ...
*** Frontal lobe
The frontal lobe is the largest of the four major lobes of the brain in mammals, and is located at the front of each cerebral hemisphere (in front of the parietal lobe and the temporal lobe). It is parted from the parietal lobe by a groove be ...
– frontal eye fields (FEF), medial eye fields (MEF), supplementary eye fields
Supplementary eye field (SEF) is the name for the anatomical area of the dorsal medial frontal lobe of the primate cerebral cortex that is indirectly involved in the control of saccadic eye movements. Evidence for a supplementary eye field was f ...
(SEF), dorsomedial frontal cortex (DMFC)
*** Parietal lobe
The parietal lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The parietal lobe is positioned above the temporal lobe and behind the frontal lobe and central sulcus.
The parietal lobe integrates sensory informa ...
– Lateral intraparietal cortex
The lateral intraparietal cortex (area LIP) is found in the intraparietal sulcus of the brain. This area is most likely involved in eye movement, as electrical stimulation evokes saccades (quick movements) of the eyes. It is also thought to contri ...
(LIP), middle temporal area (MT), medial superior temporal area The medial superior temporal (MST) area is a part of the cerebral cortex, which lies in the dorsal stream of the visual area of the primate brain. The MST receives most of its inputs from the middle temporal (MT) area, which is involved primarily in ...
(MST)
*** Occipital lobe
The occipital lobe is one of the four major lobes of the cerebral cortex in the brain of mammals. The name derives from its position at the back of the head, from the Latin ''ob'', "behind", and ''caput'', "head".
The occipital lobe is the vi ...
**** Visual cortex
The visual cortex of the brain is the area of the cerebral cortex that processes visual information. It is located in the occipital lobe. Sensory input originating from the eyes travels through the lateral geniculate nucleus in the thalamus ...
** Cerebellum
The cerebellum (Latin for "little brain") is a major feature of the hindbrain of all vertebrates. Although usually smaller than the cerebrum, in some animals such as the mormyrid fishes it may be as large as or even larger. In humans, the cerebe ...
* Midbrain
The midbrain or mesencephalon is the forward-most portion of the brainstem and is associated with vision, hearing, motor control, sleep and wakefulness, arousal ( alertness), and temperature regulation. The name comes from the Greek ''mesos'', ...
** Pretectal area
In neuroanatomy, the pretectal area, or pretectum, is a midbrain structure composed of seven nuclei and comprises part of the subcortical visual system. Through reciprocal bilateral projections from the retina, it is involved primarily in mediati ...
– Pretectal nuclei
** Superior colliculus
In neuroanatomy, the superior colliculus () is a structure lying on the roof of the mammalian midbrain. In non-mammalian vertebrates, the homologous structure is known as the optic tectum, or optic lobe. The adjective form '' tectal'' is common ...
(SC)
** Premotor nuclei in the reticular formation
The reticular formation is a set of interconnected nuclei that are located throughout the brainstem. It is not anatomically well defined, because it includes neurons located in different parts of the brain. The neurons of the reticular formatio ...
(PMN)
*** riMLF
** III, IV cranial nerve nuclei
* Pons
The pons (from Latin , "bridge") is part of the brainstem that in humans and other bipeds lies inferior to the midbrain, superior to the medulla oblongata and anterior to the cerebellum.
The pons is also called the pons Varolii ("bridge of Va ...
** Paramedian pontine reticular formation
The paramedian pontine reticular formation, also known as PPRF or paraabducens nucleus, is part of the pontine reticular formation, a brain region without clearly defined borders in the center of the pons. It is involved in the coordination of eye ...
(PMRF)
** Nucleus prepositus hypoglossi
** Vestibular nuclei
The vestibular nuclei (VN) are the cranial nuclei for the vestibular nerve located in the brainstem.
In Terminologia Anatomica they are grouped in both the pons and the medulla in the brainstem.
Structure Path
The fibers of the vestibular n ...
** VI cranial nerve nuclei
* Medial longitudinal fasciculus
The medial longitudinal fasciculus (MLF) is an area of crossed over tracts, on each side of the brainstem. These bundles of axons are situated near the midline of the brainstem. They are made up of both ascending and descending fibers that ...
Physiology
Eye movement can be classified according to two systems: * the involvement of one or both eyes; involving one eye they may be classified asduction A duction is an eye movement involving only one eye. There are generally six possible movements depending upon the eye's axis of rotation:
# Abduction refers to the outward movement of an eye.
#Adduction refers to the inward movement of an eye
#Supr ...
, and both eyes either version, if moving in the same direction, or vergence
A vergence is the simultaneous movement of both eyes in opposite directions to obtain or maintain single binocular vision.
When a creature with binocular vision looks at an object, the eyes must rotate around a vertical axis so that the proje ...
, if moving in opposite directions.Kanski, JJ. ''Clinical Ophthalmology: A Systematic Approach.'' Boston:Butterworth-Heinemann;1989.
* fixational, ''gaze-stabilizing'', or ''gaze-shifting''. Gaze-stabilising movement may include the vestibulo-ocular reflex and optokinetic reflex
The optokinetic response is a combination of a slow-phase and fast-phase eye movements. It is seen when an individual tracks (pursuit movement) a moving object with their eyes, which then moves out of the field of vision, a point at which their ...
, and gaze-shifting mechanisms as saccade
A saccade ( , French for ''jerk'') is a quick, simultaneous movement of both eyes between two or more phases of fixation in the same direction.Cassin, B. and Solomon, S. ''Dictionary of Eye Terminology''. Gainesville, Florida: Triad Publishi ...
s and pursuit movements.
''Vergence movement'' or convergence
Convergence may refer to:
Arts and media Literature
*''Convergence'' (book series), edited by Ruth Nanda Anshen
*Convergence (comics), "Convergence" (comics), two separate story lines published by DC Comics:
**A four-part crossover storyline that ...
is the movement of both eyes to make sure that the image of the object being looked at falls on the corresponding spot on both retinas. This type of movement helps in the depth perception
Depth perception is the ability to perceive distance to objects in the world using the visual system and visual perception. It is a major factor in perceiving the world in three dimensions. Depth perception happens primarily due to stereopsis ...
of objectsCarlson and Heth (2010). Psychology the Science of Behaviour 4e. Pearson Education Canada. Page 140
''Pursuit movement'' or smooth pursuit
In the scientific study of vision, smooth pursuit describes a type of eye movement in which the eyes remain fixated on a moving object. It is one of two ways that visual animals can voluntarily shift gaze, the other being saccadic eye movemen ...
is the movement the eyes make while tracking an object's movement, so that its moving image can remain maintained on fovea
Fovea () (Latin for "pit"; plural foveae ) is a term in anatomy. It refers to a pit or depression in a structure.
Human anatomy
*Fovea centralis of the retina
* Fovea buccalis or Dimple
* Fovea of the femoral head
* Trochlear fovea of the fr ...
.
Saccades
The eyes are never completely at rest: they make frequent fixational eye movement even when fixated at one point. The reason for this movement is related to the photoreceptors and the ganglion cells. It appears that a constant visual stimulus can make the photoreceptors or the ganglion cells become unresponsive; on the other hand a changing stimulus will not. So the eye movement constantly changes the stimuli that fall on the photoreceptors and the ganglion cells, making the image clearer.Saccade
A saccade ( , French for ''jerk'') is a quick, simultaneous movement of both eyes between two or more phases of fixation in the same direction.Cassin, B. and Solomon, S. ''Dictionary of Eye Terminology''. Gainesville, Florida: Triad Publishi ...
s are the rapid movement of eyes that is used while scanning a visual scene. In our subjective impression, the eyes do not move smoothly across the printed page during reading. Instead, they make short and rapid movements called saccades. During each saccade the eyes move as fast as they can and the speed cannot be consciously controlled in between the fixations. Each movement is worth a few minutes of arc, at regular intervals about three to four per second. One of the main uses for saccades is to scan a greater area with the high-resolution fovea
Fovea () (Latin for "pit"; plural foveae ) is a term in anatomy. It refers to a pit or depression in a structure.
Human anatomy
*Fovea centralis of the retina
* Fovea buccalis or Dimple
* Fovea of the femoral head
* Trochlear fovea of the fr ...
of the eye. Research conducted by the University of South Australia
The University of South Australia (UniSA) is a public research university in the Australian state of South Australia. It is a founding member of the Australian Technology Network of universities, and is the largest university in South Australi ...
in partnership with the University of Stuttgart
The University of Stuttgart (german: Universität Stuttgart) is a leading research university located in Stuttgart, Germany. It was founded in 1829 and is organized into 10 faculties. It is one of the oldest technical universities in Germany wi ...
has revealed the relationship between eye moment and personality traits
In psychology, trait theory (also called dispositional theory) is an approach to the study of human personality. Trait theorists are primarily interested in the measurement of ''traits'', which can be defined as habitual patterns of behaviour, ...
that AI can read.
Vestibulo-ocular system
The visual system in the brain is too slow to process that information if the images are slipping across the retina at more than a few degrees per second. Thus, to be able to see while we are moving, the brain must compensate for the motion of the head by turning the eyes. Another specialisation of visual system in many vertebrate animals is the development of a small area of the retina with a very highvisual acuity
Visual acuity (VA) commonly refers to the clarity of vision, but technically rates an examinee's ability to recognize small details with precision. Visual acuity is dependent on optical and neural factors, i.e. (1) the sharpness of the retinal ...
. This area is called the fovea
Fovea () (Latin for "pit"; plural foveae ) is a term in anatomy. It refers to a pit or depression in a structure.
Human anatomy
*Fovea centralis of the retina
* Fovea buccalis or Dimple
* Fovea of the femoral head
* Trochlear fovea of the fr ...
, and covers about 2 degrees of visual angle in people. To get a clear view of the world, the brain must turn the eyes so that the image of the object of regard falls on the fovea. Eye movement is thus very important for visual perception, and any failure can lead to serious visual disabilities. To see a quick demonstration of this fact, try the following experiment: hold your hand up, about one foot (30 cm) in front of your nose. Keep your head still, and shake your hand from side to side, slowly at first, and then faster and faster. At first you will be able to see your fingers quite clearly. But as the frequency of shaking passes about 1 Hz, the fingers will become a blur. Now, keep your hand still, and shake your head (up and down or left and right). No matter how fast you shake your head, the image of your fingers remains clear. This demonstrates that the brain can move the eyes opposite to head motion much better than it can follow, or pursue, a hand movement. When your pursuit system fails to keep up with the moving hand, images slip on the retina and you see a blurred hand.
The brain must point both eyes accurately enough that the object of regard falls on corresponding points of the two retinas to avoid the perception of double vision
Diplopia is the simultaneous perception of two images of a single object that may be displaced horizontally or vertically in relation to each other. Also called double vision, it is a loss of visual focus under regular conditions, and is often v ...
. In most vertebrates
Vertebrates () comprise all animal taxa within the subphylum Vertebrata () (chordates with backbones), including all mammals, birds, reptiles, amphibians, and fish. Vertebrates represent the overwhelming majority of the phylum Chordata, with ...
(humans, mammals, reptiles, birds), the movement of different body parts is controlled by striated muscles
Striations means a series of ridges, furrows or linear marks, and is used in several ways:
* Glacial striation
* Striation (fatigue), in material
* Striation (geology), a ''striation'' as a result of a geological fault
* Striation Valley, in Anta ...
acting around joints. The movement of the eye is slightly different in that the eyes are not rigidly attached to anything, but are held in the orbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as ...
by six extraocular muscles
The extraocular muscles (extrinsic ocular muscles), are the seven extrinsic muscles of the human eye. Six of the extraocular muscles, the four recti muscles, and the superior and inferior oblique muscles, control movement of the eye and the oth ...
.
* Hering's law of equal innervation
* Sherrington's law of reciprocal innervation
Reading
When reading, the eye moves continuously along a line of text, but makes short rapid movements (saccades) intermingled with short stops (fixations). There is considerable variability in fixations (the point at which a saccade jumps to) and saccades between readers and even for the same person reading a single passage of text.Music reading
Eye movement in music reading is the scanning of a musical score by a musician's eyes. This usually occurs as the music is read during performance, although musicians sometimes scan music silently to study it, and sometimes perform from memory without score. Eye movement in music reading may at first appear to be similar to that in language reading, since in both activities the eyes move over the page in fixations and saccades, picking up and processing coded meanings. However, music is nonlinguistic and involves a strict and continuous time constraint on an output that is generated by a continuous stream of coded instructions.Scene viewing
Eye movement in scene viewing refers to the visual processing of information presented in scenes. A core aspect of studies in this area is the division of eye movements into the rapid movement of the eyes (saccades
A saccade ( , French language, French for ''jerk'') is a quick, simultaneous movement of both Eye movement (sensory), eyes between two or more phases of Fixation (visual), fixation in the same direction.Cassin, B. and Solomon, S. ''Dictionary ...
), and the focus of the eyes on a point (fixations). Several factors can influence eye movement in scene viewing, including the task and knowledge of the viewer (top-down factors), and the properties of the image being viewed (bottom-up factors).
Typically, when presented with a scene, viewers demonstrate short fixation durations and long saccade amplitudes in the earlier phases of viewing an image. This is followed by longer fixations and shorter saccades in the latter phases of scene viewing processing. It has also been found that eye movement behaviour in scene viewing differs with levels of cognitive development
Cognitive development is a field of study in neuroscience and psychology focusing on a child's development in terms of information processing, conceptual resources, perceptual skill, language learning, and other aspects of the developed adult bra ...
- fixation durations are thought to shorten and saccade amplitudes lengthen with an increase in age.
Spatial variation
Where eye movements fixate is affected by both bottom-up and top-down factors. Even an initial glimpse of a scene has an influence on subsequent eye movements. In bottom-up factors, the local contrast or prominence of features in an image, such as a large contrast in luminance or a greater density of edges, can affect the guidance of eye movements. However, the top-down factors of scenes have a greater impact in where eyes fixate. Areas containing more meaningful features, or areas where colour aids the discrimination of objects, can influence eye movements. Images which are related to previous images shown can also have an effect. Eye movements can also be guided towards items when they are heard verbally at the same time as seeing them. Cross-culturally, it has been found that Westerners have an inclination to concentrate on focal objects in a scene, whereas East Asians attend more to contextual information.Temporal variation
Average fixation durations last for about 330 ms, although there is a large variability in this approximation. This variability is mostly due to the properties of an image and in the task being carried out, which impact both bottom-up and top-down processing. The masking of an image and other degradations, such as a decrease inluminance
Luminance is a photometric measure of the luminous intensity per unit area of light travelling in a given direction. It describes the amount of light that passes through, is emitted from, or is reflected from a particular area, and falls with ...
, during fixations (factors which affect bottom-up processing), have been found to increase the length of fixation durations. However, an enhancement of the image with these factors also increases fixation durations.
Factors which affect top-down processing (e.g. blurring) have been found to both increase and decrease fixation durations.
Disorders
Symptoms
* Patients with eye movement disorders may reportdiplopia
Diplopia is the simultaneous perception of two images of a single object that may be displaced horizontally or vertically in relation to each other. Also called double vision, it is a loss of visual focus under regular conditions, and is often v ...
, nystagmus
Nystagmus is a condition of involuntary (or voluntary, in some cases) eye movement. Infants can be born with it but more commonly acquire it in infancy or later in life. In many cases it may result in reduced or limited vision. Due to the invol ...
, poor visual acuity
Visual acuity (VA) commonly refers to the clarity of vision, but technically rates an examinee's ability to recognize small details with precision. Visual acuity is dependent on optical and neural factors, i.e. (1) the sharpness of the retinal ...
or cosmetic blemish from squint of the eyes.
Cause
* Innervational ** Supranuclear ** Nuclear ** Nerve ** Synapse * Muscle anomalies ** Maldevelopment (e.g. Hypertrophy, atrophy/dystrophy) ** Malinsertion ** Scarring secondary to alignment surgery ** Muscle diseases (e.g.Myasthenia gravis
Myasthenia gravis (MG) is a long-term neuromuscular junction disease that leads to varying degrees of skeletal muscle weakness. The most commonly affected muscles are those of the eyes, face, and swallowing. It can result in double vision, ...
)
* Orbital anomalies
** Tumor (e.g. rhabdomyosarcoma
Rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is a highly aggressive form of cancer that develops from mesenchymal cells that have failed to fully differentiate into myocytes of skeletal muscle. Cells of the tumor are identified as rhabdomyoblasts.
There are four subt ...
)
** Excess fat behind globe (e.g. thyroid conditions)
** Bone fracture
** Check ligament (e.g. Brown's syndrome, or Superior tendon sheath syndrome)
Selected disorders
* Congenital fourth nerve palsy * Duane syndrome * Internuclear ophthalmoplegia *Nystagmus
Nystagmus is a condition of involuntary (or voluntary, in some cases) eye movement. Infants can be born with it but more commonly acquire it in infancy or later in life. In many cases it may result in reduced or limited vision. Due to the invol ...
* Ophthalmoparesis
Ophthalmoparesis refers to weakness (-paresis) or paralysis (-plegia) of one or more extraocular muscles which are responsible for eye movements. It is a physical finding in certain neurologic, ophthalmologic, and endocrine disease.
Internal ...
* Opsoclonus
Opsoclonus refers to uncontrolled, irregular, and nonrhythmic eye movement. Opsoclonus consists of rapid, involuntary, multivectorial (horizontal and vertical), unpredictable, conjugate fast eye movements without inter-saccadic intervals. It is a ...
* Sixth (abducent) nerve palsy
Vision therapy
In psychotherapy
Terminology
The following terms may be used to describe eye movement: * ''Incyclotorsion'' is a term applied to the inward, torsional (rotational) movement of the eye, mediated by the superior oblique muscle of the eye. The superior oblique muscle is innervated by cranial nerve IV (trochlear nerve
The trochlear nerve (), ( lit. ''pulley-like'' nerve) also known as the fourth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IV, or CN IV, is a cranial nerve that innervates just one muscle: the superior oblique muscle of the eye, which operates through the pu ...
). Incyclotorsion may also be used to describe one part of the condition of the eye when a patient has an oculomotor nerve palsy. The oculomotor nerve
The oculomotor nerve, also known as the third cranial nerve, cranial nerve III, or simply CN III, is a cranial nerve that enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure and innervates extraocular muscles that enable most movements of ...
(cranial nerve III) supplies the inferior oblique
The inferior oblique muscle or obliquus oculi inferior is a thin, narrow muscle placed near the anterior margin of the floor of the orbit. The inferior oblique is one of the extraocular muscles, and is attached to the maxillary bone (origin) and ...
muscle (along with four other eye muscles – superior rectus, medial rectus, inferior rectus and the striated muscle of levator palpebrae superioris), and when this muscle is non-functional (as in oculomotor palsy) the eye ''incyclotorts''; i.e. twists/rotates inward.
* ''Excyclotorsion'' is a term applied to the outward, torsional (rotational) movement of the eye, mediated by the inferior oblique
The inferior oblique muscle or obliquus oculi inferior is a thin, narrow muscle placed near the anterior margin of the floor of the orbit. The inferior oblique is one of the extraocular muscles, and is attached to the maxillary bone (origin) and ...
muscle of the eye. The inferior oblique muscle is innervated by cranial nerve III (oculomotor nerve
The oculomotor nerve, also known as the third cranial nerve, cranial nerve III, or simply CN III, is a cranial nerve that enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure and innervates extraocular muscles that enable most movements of ...
). Excyclotorsion may also be used to describe the condition or state of the eye when a patient has a cranial nerve IV (trochlear nerve
The trochlear nerve (), ( lit. ''pulley-like'' nerve) also known as the fourth cranial nerve, cranial nerve IV, or CN IV, is a cranial nerve that innervates just one muscle: the superior oblique muscle of the eye, which operates through the pu ...
) palsy Palsy is a medical term which refers to various types of paralysisDan Agin, ''More Than Genes: What Science Can Tell Us About Toxic Chemicals, Development, and the Risk to Our Children;; (2009), p. 172. or paresis, often accompanied by weakness a ...
. The trochlear nerve supplies the superior oblique muscle
The superior oblique muscle, or obliquus oculi superior, is a fusiform muscle originating in the upper, medial side of the orbit (i.e. from beside the nose) which abducts, depresses and internally rotates the eye. It is the only extraocular mu ...
, and when this muscle is non-functional (as in trochlear palsy) the eye ''excyclotorts''; i.e. twists/rotates outward. This excyclotorsion may be corrected through surgery using the Harada-Ito procedure.1. http://www.utdol.com/online/content/topic.do?topicKey=neuro_op/2892&selectedTitle=1~150&source=search_result
* A ''version'' is an eye movement involving both eyes moving synchronously and symmetrically in the same direction. Examples include:
# Dextroversion / right gaze
# Laevoversion / left gaze
# Sursumversion / elevation / up gaze
# Deorsumversion / depression / down gaze
# Dextroelevation / gaze up and right
# Dextrodepression / gaze down and right
# Laevoelevation / gaze up and left
# Laevodepression / gaze down and left
# Dextrocycloversion – top of the eye rotates to the right
# Laevocycloversion – top of the eye rotates to the left
See also
*Accommodation (eye)
Accommodation is the process by which the vertebrate eye changes optical power to maintain a clear image or focus on an object as its distance varies. In this, distances vary for individuals from the far point—the maximum distance from the ...
* Convergence micropsia Convergence micropsia is a type of micropsia characterized by the reduction in apparent size of objects viewed when the eyes are more converged than they need to be for the distance of the object from the eyes.
It occurs mainly during stereoscopy ...
* Dissociated vertical deviation
* Eye tracking
Eye tracking is the process of measuring either the point of gaze (where one is looking) or the motion of an eye relative to the head. An eye tracker is a device for measuring eye positions and eye movement. Eye trackers are used in research ...
* Gaze-contingency paradigm
* Listing's law Listing's law, named after German mathematician Johann Benedict Listing (1808–1882), describes the three-dimensional orientation of the eye and its axes of rotation. Listing's law has been shown to hold when the head is stationary and upright a ...
* Microsaccade
Microsaccades are a kind of fixational eye movement. They are small, jerk-like, involuntary eye movements, similar to miniature versions of voluntary saccades. They typically occur during prolonged visual fixation (of at least several seconds), ...
* Ocular tremor
Ocular tremor (ocular microtremor) is a constant, involuntary eye tremor of a low amplitude and high frequency. It is a type of fixational eye movement that occurs in all normal people, even when the eye appears still. The frequency of ocular m ...
* Orthoptist
Orthoptics is a profession allied to the eye care profession. Orthoptists are the experts in diagnosing and treating defects in eye movements and problems with how the eyes work together, called binocular vision. These can be caused by issues with ...
* Oculesics
Oculesics, a subcategory of kinesics, is the study of eye movement, behavior, gaze, and eye-related nonverbal communication. The specific definition varies depending on whether it applies to the fields of medicine or social science.
Nonverbal ...
* Strabismus
Strabismus is a vision disorder in which the eyes do not properly align with each other when looking at an object. The eye that is focused on an object can alternate. The condition may be present occasionally or constantly. If present during a ...
* Progressive supranuclear palsy
Progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) is a late-onset degenerative disease involving the gradual deterioration and death of specific volumes of the brain. The condition leads to symptoms including loss of balance, slowing of movement, difficulty ...
* Computer processing of body language
References
*External links
eMedicine – Extraocular Muscles, Actions
''Oculomotor Control – Nystagmus and Dizziness''
Department of Otolaryngology – Queen's University at Kingston, Canada
Software system for simulating eye motility disorders and their surgical correction
which shows changes in eye movements for any given muscle or nerve impairment. {{DEFAULTSORT:Eye Movement (Sensory) Eye