Equal channel angular extrusion on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Equal channel angular extrusion (ECAE) called also equal channel angular pressing (ECAP) is one technique from the Severe Plastic Deformation (SPD) group, aimed at producing Ultra Fine Grained (UFG) material. Developed in the Soviet Union in 1973 by Segal. However, the dates are not always consistent. In industrial metalworking, it is an 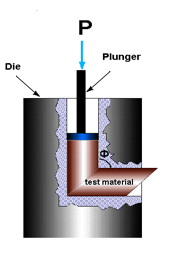 ECAE is unique because significant cold work can be accomplished without reduction in the cross sectional area of the deformed workpiece. In conventional deformation processes like
ECAE is unique because significant cold work can be accomplished without reduction in the cross sectional area of the deformed workpiece. In conventional deformation processes like
patent information
Metalworking {{Metalworking-stub
extrusion
Extrusion is a process used to create objects of a fixed cross-sectional profile by pushing material through a die of the desired cross-section. Its two main advantages over other manufacturing processes are its ability to create very complex ...
process, The technique is able to refine the microstructure
Microstructure is the very small scale structure of a material, defined as the structure of a prepared surface of material as revealed by an optical microscope above 25× magnification. The microstructure of a material (such as metals, polymers ...
of metals and alloys, thereby improving their strength according to the Hall-Petch relationship
In materials science, grain-boundary strengthening (or Hall–Petch strengthening) is a method of strengthening materials by changing their average crystallite (grain) size. It is based on the observation that grain boundaries are insurmountable ...
. This process improves not only the strength but also other properties such as corrosion and wear resistance of alloys and compounds.
 ECAE is unique because significant cold work can be accomplished without reduction in the cross sectional area of the deformed workpiece. In conventional deformation processes like
ECAE is unique because significant cold work can be accomplished without reduction in the cross sectional area of the deformed workpiece. In conventional deformation processes like rolling
Rolling is a type of motion that combines rotation (commonly, of an axially symmetric object) and translation of that object with respect to a surface (either one or the other moves), such that, if ideal conditions exist, the two are in contact ...
, forging, extrusion
Extrusion is a process used to create objects of a fixed cross-sectional profile by pushing material through a die of the desired cross-section. Its two main advantages over other manufacturing processes are its ability to create very complex ...
, and drawing, strain is introduced by reduction in the cross sectional area. ECAE produces significant deformation strain without reducing the cross sectional area. This is accomplished by extruding the work piece around a corner. For example, a square cross section bar of metal is forced through a channel with a 90° degree angle. The cross section of the channel is equal on entry and exit. The complex deformation of the metal as it flows around the corner produces very high strain. Because the cross section remains the same, a work piece can be extruded multiple times with each pass introducing additional strain.
Die design is critical because of the large forces required.
To reduce the friction of the pushed sample is lubricated with grease for example mixture of graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on lar ...
and oil, and to reduce the forces, the process is sometimes carried out at elevated temperatures but then recrystallization can occur which can also leads to excessive grain growth at elevated temperature.
There are some modifications of the process e.g. incremental ECAP (I-ECAP) for the production of continuous products.
Process routes
The process can be carried out in multiple passes. According to the rotation angle and direction between next passes, there can be four fundamental process routes named A, Ba, Bc, and C: * A - The sample in not rotated, * Ba - the sample is rotated by 90° clockwise and counterclockwise around its longitudinal axis alternatively, * Bc - the sample is rotated by 90° clockwise around its longitudinal axis, * C - the sample is rotated by 180° around its longitudinal axis.Finite element method in the ECAE process
The behave during deformation and flow of the material, are analyzed by scientists and there are many articles on computer simulation, finite element method is one of the important approaches to understand the deformation occurring in the ECAE process.See also
Severe plastic deformationStrengthening mechanisms of materials
Methods have been devised to modify the yield strength, ductility, and toughness of both crystalline and amorphous materials. These strengthening mechanisms give engineers the ability to tailor the mechanical properties of materials to suit a vari ...
References
External links
patent information
Metalworking {{Metalworking-stub