Engine order telegraph on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
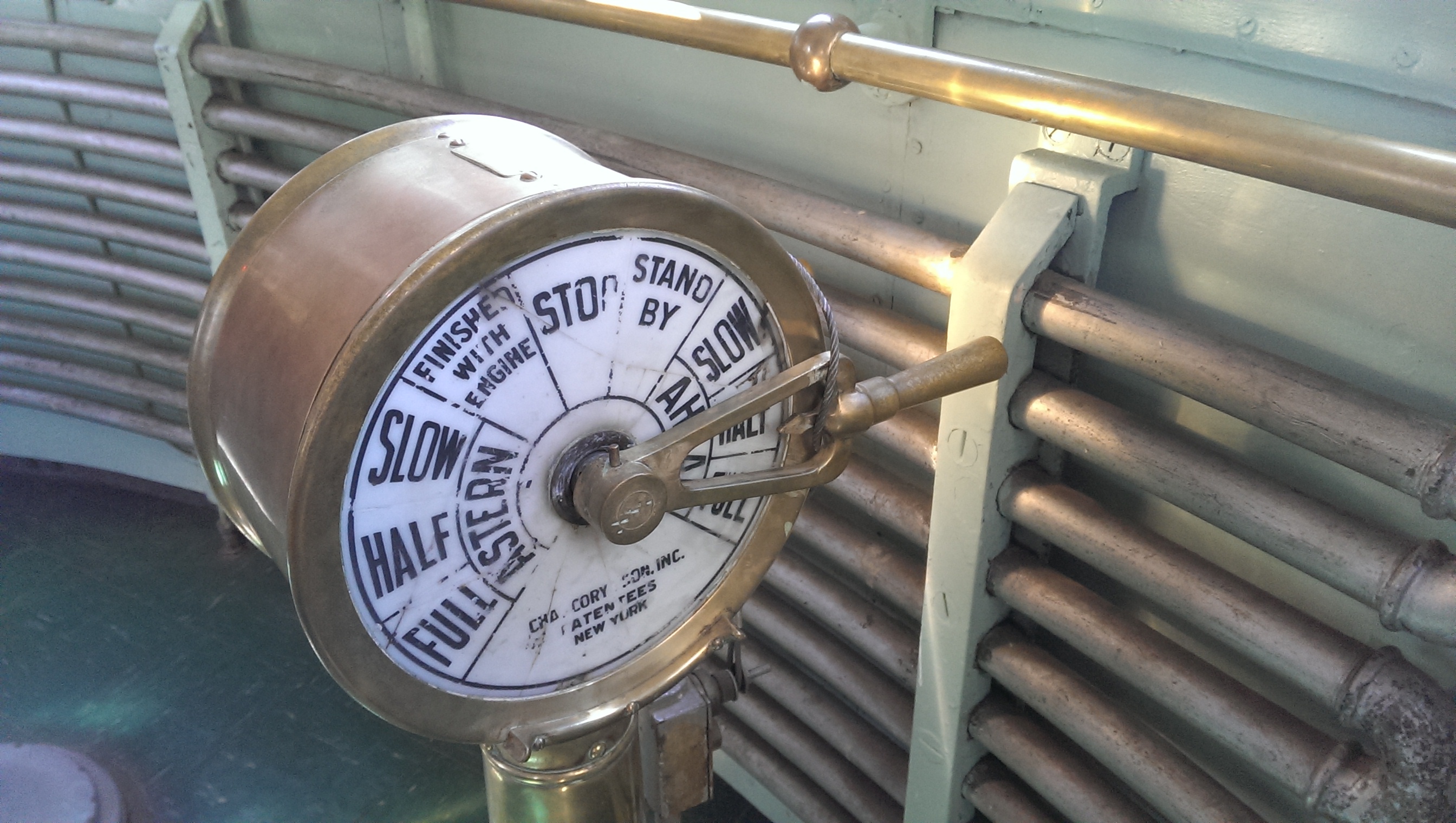 An engine order telegraph or E.O.T., also referred to as a Chadburn, is a communications device used on a
An engine order telegraph or E.O.T., also referred to as a Chadburn, is a communications device used on a
 On most modern vessels with direct combustion engines or electric propulsors, the main control handle on the bridge acts as a direct
On most modern vessels with direct combustion engines or electric propulsors, the main control handle on the bridge acts as a direct
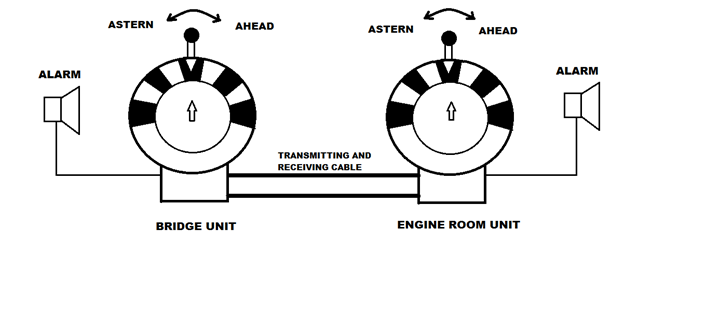 At least two telegraph units and alarms must be installed, one on the bridge and one in the engine room.
The order is given by moving the bridge unit's handle to the desired position on the dial face. This sends an
At least two telegraph units and alarms must be installed, one on the bridge and one in the engine room.
The order is given by moving the bridge unit's handle to the desired position on the dial face. This sends an
 Many past ships have the following dial indications:
* Flank ahead (1940–present) (US only)
* Full ahead
* Half ahead
* Slow ahead
* Dead slow ahead
* Standby
* Stop
* Finished with main engines
* Dead slow astern
* Slow astern
* Half astern
* Full astern
* Emergency astern (1940–present)
Any orders could also be accompanied by an RPM order, giving the precise engine speed desired.
Many modern ships have the following dial indications:
* Full ahead navigation (on notice to increase or reduce)
* Full ahead
* Half ahead
* Slow ahead
* Dead slow ahead
* Stop
* Dead slow astern
* Slow astern
* Half astern
* Full astern
"Finished with engines" and "standby" conveyed via separate control panel.
Many past ships have the following dial indications:
* Flank ahead (1940–present) (US only)
* Full ahead
* Half ahead
* Slow ahead
* Dead slow ahead
* Standby
* Stop
* Finished with main engines
* Dead slow astern
* Slow astern
* Half astern
* Full astern
* Emergency astern (1940–present)
Any orders could also be accompanied by an RPM order, giving the precise engine speed desired.
Many modern ships have the following dial indications:
* Full ahead navigation (on notice to increase or reduce)
* Full ahead
* Half ahead
* Slow ahead
* Dead slow ahead
* Stop
* Dead slow astern
* Slow astern
* Half astern
* Full astern
"Finished with engines" and "standby" conveyed via separate control panel.
 An engine order telegraph or E.O.T., also referred to as a Chadburn, is a communications device used on a
An engine order telegraph or E.O.T., also referred to as a Chadburn, is a communications device used on a ship
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research, and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished ...
(or submarine
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely op ...
) for the pilot on the bridge
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually someth ...
to order engineers in the engine room
On a ship, the engine room (ER) is the compartment where the machinery for marine propulsion is located. To increase a vessel's safety and chances of surviving damage, the machinery necessary for the ship's operation may be segregated into var ...
to power the vessel at a certain desired speed.
Construction
In early vessels, from the 19th century until about 1950, the device usually consisted of a round dial about in diameter with a knob at the center attached to one or more handles, and an indicator pointer on the face of the dial. There would also be arevolutions per minute
Revolutions per minute (abbreviated rpm, RPM, rev/min, r/min, or with the notation min−1) is a unit of rotational speed or rotational frequency for rotating machines.
Standards
ISO 80000-3:2019 defines a unit of rotation as the dimensio ...
indicator, worked by a hand crank. Modern EOTs on vessels which still use them use electronic light and sound signals.
Operation
Traditional E.O.T.s required a pilot wanting to change speed to "ring" the telegraph on the bridge, moving the handle to a different position on the dial. This would ring a bell in the engine room and move their pointer to the position on the dial selected by the bridge. The engineers hear the bell and move their handle to the same position to signal their acknowledgment of the order, and adjust the engine speed accordingly. Such an order is called a "bell", for example the order for a ship's maximum speed,flank speed
Flank speed is an American nautical term referring to a ship's true maximum speed but it is not equivalent to the term ''full speed ahead''. Usually, flank speed is reserved for situations in which a ship finds itself in imminent danger, such as ...
, is called a "flank bell".
For urgent orders requiring rapid acceleration, the handle is moved three times so that the engine room bell is rung three times. This is called a "cavitate bell" because the rapid acceleration of the ship's propeller will cause the water around it to cavitate
Cavitation is a phenomenon in which the static pressure of a liquid reduces to below the liquid's vapour pressure, leading to the formation of small vapor-filled cavities in the liquid. When subjected to higher pressure, these cavities, ca ...
, causing a lot of noise and wear on the propellers. Such noise is undesirable during conflicts because it can give away a vessel's position.
Compared to remote control throttle
 On most modern vessels with direct combustion engines or electric propulsors, the main control handle on the bridge acts as a direct
On most modern vessels with direct combustion engines or electric propulsors, the main control handle on the bridge acts as a direct throttle
A throttle is the mechanism by which fluid flow is managed by constriction or obstruction.
An engine's power can be increased or decreased by the restriction of inlet gases (by the use of a throttle), but usually decreased. The term ''throttle' ...
with no intervening engine room personnel. As such, it is regarded under the rules of marine classification societies as a remote control device rather than an EOT, though it is still often referred to by the traditional name. This is somewhat confusing, as the classification society rules for merchant ships still in fact require an EOT to be provided, to allow orders to be transmitted to the local control position in the engine room in the event that the remote control system should fail. The EOT is required to be electrically isolated from the remote control system. However, it may be mechanically linked to the main control handle, allowing telegraph orders to be given using the same user interface as for remote control orders. Traditional EOTs (though in a more modern form) can still be found on all nuclear powered ships and submarines
A submarine (or sub) is a watercraft capable of independent operation underwater. It differs from a submersible, which has more limited underwater capability. The term is also sometimes used historically or colloquially to refer to remotely op ...
as they still require an engineering crew member to operate the throttles for the steam turbines that drive the propellers. EOTs can also be found on older vessels that lack remote control technology, particularly those with conventional steam engines.
Remote control systems on modern ships usually have a control transfer system allowing control to be transferred between locations. Remote control is usually possible from two locations: the bridge and the Engine Control Room (ECR). Some ships lack a remote control handle in the ECR. When in bridge control mode, the bridge handle directly controls the engine set point. When in Engine Control Room mode the bridge handle sends a telegraph signal to the ECR and the ECR handle controls the set point of the control system. In local control, the remote control system is inactive and the bridge handle sends a telegraph signal to the local control position and the engine is operated by its manual controls in the engine room.
Order transmission
 At least two telegraph units and alarms must be installed, one on the bridge and one in the engine room.
The order is given by moving the bridge unit's handle to the desired position on the dial face. This sends an
At least two telegraph units and alarms must be installed, one on the bridge and one in the engine room.
The order is given by moving the bridge unit's handle to the desired position on the dial face. This sends an electrical signal
In signal processing, a signal is a function that conveys information about a phenomenon. Any quantity that can vary over space or time can be used as a signal to share messages between observers. The '' IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing ...
to the EOT placed in the engine room whose pointer acquires a position according to the signal given from the bridge.
An audible alarm
An alarm device is a mechanism that gives an audible, visual or other kind of alarm signal to alert someone to a problem or condition that requires urgent attention.
Alphabetical musical instruments
Etymology
The word ''alarm'' comes from t ...
sounds at both ends. Accordingly, the watch-keeping engineer acknowledges the order by moving the handle of the engine room EOT to the required position and takes necessary action. This sends an electrical signal to the bridge EOT unit, causing its pointer to acquire the respective position. The alarm stops ringing to acknowledge that the order has been carried out.
Typical dial positions
 Many past ships have the following dial indications:
* Flank ahead (1940–present) (US only)
* Full ahead
* Half ahead
* Slow ahead
* Dead slow ahead
* Standby
* Stop
* Finished with main engines
* Dead slow astern
* Slow astern
* Half astern
* Full astern
* Emergency astern (1940–present)
Any orders could also be accompanied by an RPM order, giving the precise engine speed desired.
Many modern ships have the following dial indications:
* Full ahead navigation (on notice to increase or reduce)
* Full ahead
* Half ahead
* Slow ahead
* Dead slow ahead
* Stop
* Dead slow astern
* Slow astern
* Half astern
* Full astern
"Finished with engines" and "standby" conveyed via separate control panel.
Many past ships have the following dial indications:
* Flank ahead (1940–present) (US only)
* Full ahead
* Half ahead
* Slow ahead
* Dead slow ahead
* Standby
* Stop
* Finished with main engines
* Dead slow astern
* Slow astern
* Half astern
* Full astern
* Emergency astern (1940–present)
Any orders could also be accompanied by an RPM order, giving the precise engine speed desired.
Many modern ships have the following dial indications:
* Full ahead navigation (on notice to increase or reduce)
* Full ahead
* Half ahead
* Slow ahead
* Dead slow ahead
* Stop
* Dead slow astern
* Slow astern
* Half astern
* Full astern
"Finished with engines" and "standby" conveyed via separate control panel.
See also
*Flank speed
Flank speed is an American nautical term referring to a ship's true maximum speed but it is not equivalent to the term ''full speed ahead''. Usually, flank speed is reserved for situations in which a ship finds itself in imminent danger, such as ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Engine Order Telegraph Watercraft components Control devices