Energy in Egypt on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 This article describes the
This article describes the
 Egypt has the sixth-largest proved oil reserves in Africa. Over half of these reserves are offshore reserves. Although Egypt is not a member of OPEC, it is a member of the
Egypt has the sixth-largest proved oil reserves in Africa. Over half of these reserves are offshore reserves. Although Egypt is not a member of OPEC, it is a member of the
 , Egypt's reserves of natural gas are estimated at , which are the third largest in Africa.WEC, p. 176 Egypt's production of natural gas was estimated at in 2013, of which almost was domestically consumed.
Natural gas is exported by the
, Egypt's reserves of natural gas are estimated at , which are the third largest in Africa.WEC, p. 176 Egypt's production of natural gas was estimated at in 2013, of which almost was domestically consumed.
Natural gas is exported by the
''The New York Times'' 7 March 2015 In March 2015, BP signed a $12 billion deal to develop natural gas in Egypt intended for sale in the domestic market starting in 2017. BP said it would develop a large quantity of offshore gas, equivalent to about one-quarter of Egypt's output, and bring it onshore for domestic consumers. Gas from the project, called West Nile Delta, was expected to begin flowing in 2017. BP said that additional exploration might double the amount of gas available. In September 2015,
 The majority of Egypt's electricity supply is generated from thermal and hydropower stations. The four main hydroelectric generating stations currently operating in Egypt are the
The majority of Egypt's electricity supply is generated from thermal and hydropower stations. The four main hydroelectric generating stations currently operating in Egypt are the
2011
2010
2009
2006
IEA October, crude oil p.11, coal p. 13 gas p. 15 The only remaining significant hydropower site that is currently undeveloped is the
 Egypt has a high potential for wind energy, especially in the Red Sea coast area. As of 2021, 1640 MW of wind energy was installed.
Egypt has a high potential for wind energy, especially in the Red Sea coast area. As of 2021, 1640 MW of wind energy was installed.

energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of ...
and electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as describe ...
production, consumption and import in Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
.
Overview
Electrical power
Egypt is classified as having a “high power system size (24,700 MW installed generation capacity in 2010 with more than 40 grid-connected plants).” As of 2010, 100% of the Egyptian population has access to electricity.History
When electricity was first introduced in Egypt in 1893, the generation and distribution of electricity was practiced exclusively by private companies. In 1962, the generation, transmission, and distribution of electricity were nationalized under three authorities (the Electricity Production Authority, the Electricity Distribution Authority, and the Electricity Projects Implementation Authority) leaving the government as the sole owner and operator of all electrical companies. These three authorities were replaced in 1965 by the public Egyptian Corporation for Electricity which remained active until 1976 when it was converted into the Egypt Electricity Authority as decreed by electricity sector Law no. 12. In 1978 the Egypt Electricity Authority supervised the establishment of seven geographically divided electricity distribution companies. An additional electrical power distribution authority was established in 1983 as a means of supervising distribution companies which had become independent of the Egypt Electricity Authority. Between 1996 and 2000 a series of laws and presidential decrees were passed to reorganize and regulate the growing electrical industry. *1996: Electricity sector Law no. 100 was issued, opening up the industry by allowing for the construction, operation, and maintenance of electric generation stations by both local and foreign investors. *1997: The Electric Utility and Consumer Protection Regulatory Agency was established under presidential decree no. 326 to regulate, supervise, and monitor the relation between the associated electric utility parties. *1998: Electricity sector Law no. 18 was issued declaring that all generation stations and the high voltage network were to be affiliated to the distribution companies which, in turn, were to be affiliated to the Egyptian Electricity Authority rather than the business sector. *2000: presidential decree no. 339 and electricity sector Law no. 164 were issued. Presidential decree no. 339 reorganized the Electric Utility and Consumer Protection Regulatory Agency while electricity sector Law no. 164 enacted the conversion of The Egyptian Electricity Authority to a contribution company called the Egyptian Electric Holding Company (EEHC). Between 2000 and 2001, the EEHC implemented a division in the organization of Egypt's electrical management framework. Generation (production) activity was separated from distribution activity along with the separation of control and transmission between ultra-high-voltage and high-voltage networks. This division rearranged the industry to consist of 13 companies: one company for electricity transmission, one company for hydroelectric power production, four companies for thermal power production, and seven companies for electricity distribution. In 2002 the Delta Company for electricity distribution divided into North Delta and South Delta increasing the number of companies to 14. In 2004 the Cairo company for electricity distribution divided into North Cairo and South Cairo in addition to the Delta company for electricity production dividing into three companies: East Delta, Middle Delta and West Delta. Currently, there are 16 companies affiliated with the EEHC that make up the Egyptian electric utility system. The production companies are made up of Cairo, East Delta, Middle Delta, West Delta, Upper Egypt, and Hydro Plants Electricity Production Companies. Transmission company: Egyptian Electricity Transmission Company. Distribution companies: North Cairo, South Cairo, Alexandria, Canal, North Delta, South Delta, El- Behera, Middle Egypt, and Upper Egypt Electricity Distribution Companies.Power system issues
Since the early 2000s, power outage rates and durations, as well as distribution system losses, have trended downwards indicating that distribution companies have improved their overall customer service quality over the past decade; however, Egypt has seen a great weakening in its supply security. The power system's generation reserve capacity declined from 20% in the early 2000s to 10% by the 2010s. The Egyptian power system is now significantly less able to avoid power shortages during annual peak demand periods, which are typically the afternoons on the hottest days of the year. The weakening of Egypt's supply security has caused widespread social issues in the 2010s. To deal with the extremely high demand for electricity, rolling blackouts and power cuts were implemented throughout the summer of 2012 causing great tension between the government and the people of Egypt. Angry residents from many villages protested the rolling blackouts by threatening to not pay their electricity bills and to sue their electricity provider. A campaign entitled “We Will Not Pay” was organized to encourage people to not pay their bills until the electrical service was stable once again. Residents from the Bardeen village in Zagazig also protested the unstable supply of electricity by blocking the Belbeis-Zagazig road. The government released statements encouraging people to ration their electricity consumption and announced that work was being done to generate an additional 1800 MW of power. Minister of Petroleum Abdullah Ghorab reiterated the importance of conserving electricity to avoid a state implemented policy of load shedding.Petroleum
Crude oil
 Egypt has the sixth-largest proved oil reserves in Africa. Over half of these reserves are offshore reserves. Although Egypt is not a member of OPEC, it is a member of the
Egypt has the sixth-largest proved oil reserves in Africa. Over half of these reserves are offshore reserves. Although Egypt is not a member of OPEC, it is a member of the Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries
The Organization of Arab Petroleum Exporting Countries (OAPEC) is a multi-governmental organization headquartered in Kuwait which coordinates energy policies among oil-producing Arab nations. OAPEC's primary objective is safeguarding the cooperati ...
.WEC, p.76
, Egypt's proven oil reserves were estimated at , of which was crude oil and were natural gas liquids
Natural-gas condensate, also called natural gas liquids, is a low-density mixture of hydrocarbon liquids that are present as gaseous components in the raw natural gas produced from many natural gas fields. Some gas species within the raw natu ...
. Oil production in 2005 was , (down from in 1996), of which crude oil accounted for .
The National oil company is the Egyptian General Petroleum Corporation
The Egyptian General Petroleum Corporation (EGPC) ( ar, الهيئة المصرية العامة للبترول) is a national oil company of Egypt. EGPC's business includes crude oil exploration, refining, and storage. The company also produces l ...
.
Egypt is estimated to hold initial recoverable liquid reserves. After decades of production, it is estimated that the country has approximately recoverable oil remaining, as of January 2011. These figures indicate that 83% of Egypt's recoverable oil reserves have been depleted.
Shale oil
The Safaga-Quseir area of theEastern Desert
The Eastern Desert (Archaically known as Arabia or the Arabian Desert) is the part of the Sahara desert that is located east of the Nile river. It spans of North-Eastern Africa and is bordered by the Nile river to the west and the Red Sea an ...
is estimated to have reserves equivalent about of in-place shale oil
Shale oil is an unconventional oil produced from oil shale rock fragments by pyrolysis, hydrogenation, or thermal dissolution. These processes convert the organic matter within the rock ( kerogen) into synthetic oil and gas. The resulting ...
and the Abu Tartour area of the Western Desert is estimated to have about of in-place shale oil. The 1000 to 2000 foot thick and organically rich, total organic content of about 4%, Khatatba Formation in the Western Desert is the source rock for wells there and is a potential source for shale oil and shale gas. Apache Corporation
APA Corporation is the holding company for Apache Corporation, an American company engaged in hydrocarbon exploration. It is organized in Delaware and headquartered in Houston. The company is ranked 431st on the Fortune 500.
Current operations ...
, using substantial assets acquired in 2010 from BP after the Deepwater Horizon disaster, is the major operator in the Western Desert, often in joint ventures with Egyptian General Petroleum Corporation
The Egyptian General Petroleum Corporation (EGPC) ( ar, الهيئة المصرية العامة للبترول) is a national oil company of Egypt. EGPC's business includes crude oil exploration, refining, and storage. The company also produces l ...
(EGPC) such as Khalda Petroleum Company and Qarun Petroleum Company. In 1996 Apache merged with Phoenix Resources, which had made the Qarun discovery in 1994, and took over operations of the Qarun Concession in Egypt. Apache has developed about 18% of the 10 million acres it controls, in 2012 running a score of rigs; drilling about 200 development and injection wells; and about 50 exploration wells with a success rate of about 55%. Plans for 2013 included an investment of about $1 billion in development and exploration. On 29 August 2013 Apache announced sale of a 1/3 share of its Egyptian assets to Sinopec
China Petroleum & Chemical Corporation (中国石油化工股份有限公司) or Sinopec (), is a Chinese oil and gas enterprise based in Beijing. It is listed in Hong Kong and also trades in Shanghai.
Sinopec Limited's parent, Sinopec ...
for $3.1 billion effective 1 January 2014; Apache would continue to be the operator.
Oil shale
Oil shale
Oil shale is an organic-rich fine-grained sedimentary rock containing kerogen (a solid mixture of organic chemical compounds) from which liquid hydrocarbons can be produced. In addition to kerogen, general composition of oil shales constitut ...
resources were red in the Safaga-Quseir area of the Eastern Desert
The Eastern Desert (Archaically known as Arabia or the Arabian Desert) is the part of the Sahara desert that is located east of the Nile river. It spans of North-Eastern Africa and is bordered by the Nile river to the west and the Red Sea an ...
in the 1940s. The oil shale in the Red Sea area could be extracted by underground mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the economic v ...
. In the Abu Tartour are, oil shale be mined as byproduct whilst mining for phosphate
In chemistry, a phosphate is an anion, salt, functional group or ester derived from a phosphoric acid. It most commonly means orthophosphate, a derivative of orthophosphoric acid .
The phosphate or orthophosphate ion is derived from phosph ...
s. Oil shale in Egypt is foreseen as a potential fuel for the power generation.WEC, p. 107
Natural gas
 , Egypt's reserves of natural gas are estimated at , which are the third largest in Africa.WEC, p. 176 Egypt's production of natural gas was estimated at in 2013, of which almost was domestically consumed.
Natural gas is exported by the
, Egypt's reserves of natural gas are estimated at , which are the third largest in Africa.WEC, p. 176 Egypt's production of natural gas was estimated at in 2013, of which almost was domestically consumed.
Natural gas is exported by the Arab Gas Pipeline
The Arab Gas Pipeline is a natural gas pipeline in the Middle East. It originates near Arish in the Sinai Peninsula and was built to export Egyptian natural gas to Jordan, Syria, and Lebanon, with branch underwater and overland pipelines to and ...
to the Middle East
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabian Peninsula, Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Anatolia, Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Pro ...
and in the future potentially to Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
. When completed, it will have a total length of .
Natural gas is also exported as liquefied natural gas
Liquefied natural gas (LNG) is natural gas (predominantly methane, CH4, with some mixture of ethane, C2H6) that has been cooled down to liquid form for ease and safety of non-pressurized storage or transport. It takes up about 1/600th the vol ...
(LNG), produced at the plants of Egyptian LNG
Egyptian describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to:
Nations and ethnic groups
* Egyptians, a national group in North Africa
** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of years o ...
and SEGAS LNG
The Hellenic Athletics Federation (Greek: ; abbreviated SEGAS) is Greece's governing body for amateur sport.
SEGAS was created in 1897 and has been the principal organiser of many international sporting competitions held in Greece. The associatio ...
.
BP and Eni
Eni S.p.A. () is an Italian multinational energy company headquartered in Rome. Considered one of the seven "supermajor" oil companies in the world, it has operations in 69 countries with a market capitalization of US$54.08 billion, as of 11 Ap ...
, the Italian oil and gas company, together with Gas Natural Fenosa
Naturgy Energy Group S.A''.'', formerly ''Gas Natural Fenosa'' (), is a Spanish multinational natural gas and electrical energy utilities company, which operates primarily in Spain. The company's administrative headquarters are in Barcelona, whil ...
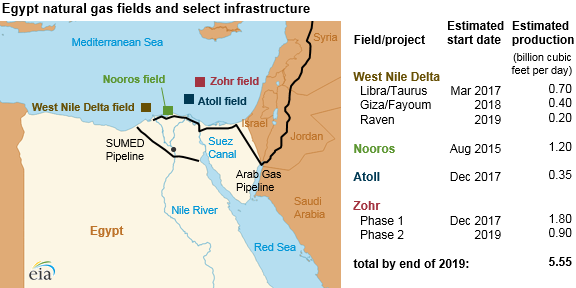
of Spain, built major liquefied natural gas facilities in Egypt for the export market, but the plants were largely idled as domestic gas consumption has soared."BP Signs 12 Billion Deal to Develop Natural Gas in Egypt"''The New York Times'' 7 March 2015 In March 2015, BP signed a $12 billion deal to develop natural gas in Egypt intended for sale in the domestic market starting in 2017. BP said it would develop a large quantity of offshore gas, equivalent to about one-quarter of Egypt's output, and bring it onshore for domestic consumers. Gas from the project, called West Nile Delta, was expected to begin flowing in 2017. BP said that additional exploration might double the amount of gas available. In September 2015,
Eni
Eni S.p.A. () is an Italian multinational energy company headquartered in Rome. Considered one of the seven "supermajor" oil companies in the world, it has operations in 69 countries with a market capitalization of US$54.08 billion, as of 11 Ap ...
announced the discovery of the Zohr gas field, largest in the Mediterranean. The field was estimated at around 30 trillion cubic feet (850×109 m³) of total gas in place.
Dolphinus Holdings Ltd provides gas from Israeli fields to Egypt. In November 2019, Egypt signed a number of energy deals at a conference, including a $430-million deal for Texas-based Noble Energy to pump natural gas through the East Mediterranean Gas Co’s pipeline.
Nuclear power
Egypt has been considering the use of nuclear energy for decades: in 1964, a 150 MWe and in 1974 a 600 MWe, nuclear power stations were proposed. The Nuclear Power Plants Authority (NPPA) was established in 1976, and in 1983 the El Dabaa site on the Mediterranean coast was selected. Egypt's nuclear plans, however, were shelved after theChernobyl accident
The Chernobyl disaster was a nuclear accident that occurred on 26 April 1986 at the No. 4 reactor in the Chernobyl Nuclear Power Plant, near the city of Pripyat in the north of the Ukrainian SSR in the Soviet Union. It is one of only two nucl ...
. In 2006, Egypt announced it would revive its civilian nuclear power programme, and build a 1,000 MW nuclear power station at El Dabaa. Its estimated cost at the time was US$1.5bn, and the plans were to do the construction with the help of foreign investors.
In March 2008, Egypt signed an agreement with Russia on the peaceful uses of nuclear energy.
In 2015, contracts were signed with a Russian company to begin the building of the plant at El Dabaa.
Renewable energy
The energy strategy in Egypt adopted by the Supreme Council of Energy in February 2008 is to increaserenewable energy
Renewable energy is energy that is collected from renewable resources that are naturally replenished on a human timescale. It includes sources such as sunlight, wind, the movement of water, and geothermal heat. Although most renewable energy ...
generation up to 20% of the total mix by 2020.
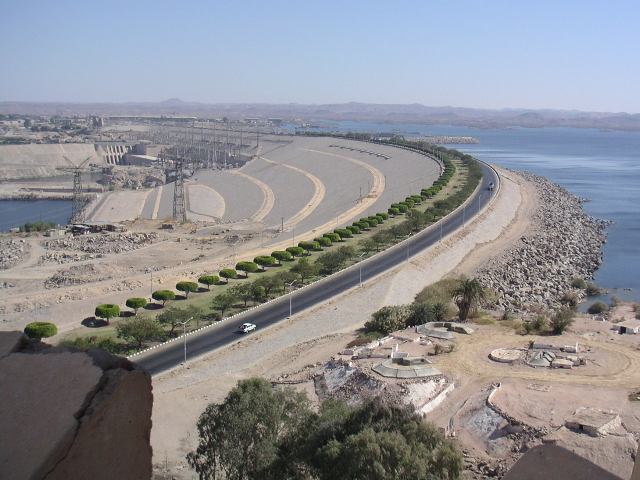
Hydropower
 The majority of Egypt's electricity supply is generated from thermal and hydropower stations. The four main hydroelectric generating stations currently operating in Egypt are the
The majority of Egypt's electricity supply is generated from thermal and hydropower stations. The four main hydroelectric generating stations currently operating in Egypt are the Aswan Low Dam
The Aswan Low Dam or Old Aswan Dam is a gravity masonry buttress dam on the Nile River in Aswan, Egypt. The dam was built at the former first cataract of the Nile, and is located about 1000 km up-river and 690 km (direct distance) sou ...
, the Esna Dam, the Aswan High Dam
The Aswan Dam, or more specifically since the 1960s, the Aswan High Dam, is one of the world's largest embankment dams, which was built across the Nile in Aswan, Egypt, between 1960 and 1970. Its significance largely eclipsed the previous Aswan Lo ...
, and the Naga Hamady Barrages. The Asyut Barrage hydropower plant is scheduled to be commissioned and added as a fifth station in 2016.
Almost all hydroelectric generation in Egypt comes from the Aswan High Dam. The Aswan High Dam has a theoretical generating capacity of 2.1GW; however, the dam is rarely able to operate at full design capacity due to low water levels. An ongoing refurbishment program is being enacted to not only increase the generating capacity of the dam to 2.4GW, but also extend the operational life of the turbines by about 40 years.
In 2011, Egypt produced 156.6 TWh gross, of which 12.9 TWh came from hydroelectric generation. The per capita consumption of electricity at the end of 2012 was 1910 kWh/yr, while Egypt's hydropower potential in 2012 was about 3,664 MW. As of 2009-2013, hydropower made up about 12% of Egypt's total installed power generation capacity – a small decline from 2006-2007 when hydropower made up about 12.8%. The percentage of hydropower energy is steadily declining due to all major conventional hydropower sites already having been developed with a limited potential for further increase in generating capacity. Outside of the Aswan High Dam, the other hydropower sites are considered very modest and most new generation plants being built in Egypt are based on fossil fuels.
Even with the addition of the Asyut Barrage hydropower plant in 2016, hydropower development in Egypt is still lagging as the existing and developed hydropower plants are no longer being constructed at a rate that can support the increasing electricity consumption in Egypt. The population of Egypt has increased by 14.3% in the five-year period from 2004 to 2009 (OECD/World Bank). Every six months there are 1 million more Egyptians. Energy production grew by 36% between 2004 and 2009.IEA Key World Energy Statistic2011
2010
2009
2006
IEA October, crude oil p.11, coal p. 13 gas p. 15 The only remaining significant hydropower site that is currently undeveloped is the
Qattara Depression
The Qattara Depression ( ar, منخفض القطارة, Munḫafaḍ al-Qaṭṭārah) is a depression in northwestern Egypt, specifically in the Matruh Governorate. The depression is part of the Western Desert of Egypt.
The Qattara Depressi ...
. Several schemes have been proposed through the years to implement a Qattara Depression Project
The Qattara Depression Project, or Qattara Project for short, is a macro-engineering project concept in Egypt. Rivalling the Aswan High Dam in scope, the intention is to develop the hydroelectric potential of the Qattara Depression by creating a ...
. None of which have been executed due to prohibitive capital costs and technical difficulties. Depending on the generating scheme chosen the Qattara Depression could potentially generate anywhere from 670MW to 6800MW.
Solar
Egypt has a high solar availability as a result of itshot desert climate
The desert climate or arid climate (in the Köppen climate classification ''BWh'' and ''BWk''), is a dry climate sub-type in which there is a severe excess of evaporation over precipitation. The typically bald, rocky, or sandy surfaces in desert ...
. The total capacity of installed photovoltaic system
A photovoltaic system, also PV system or solar power system, is an electric power system designed to supply usable solar power by means of photovoltaics. It consists of an arrangement of several components, including solar panels to absorb and ...
s is about 4.5 MWp. They are used in remote areas for water pumping, desalination, rural clinics, telecommunications, rural village electrification, etc.WEC, pp.403–404 The proposed large-scale solar power project Desertec also involves Egypt.
In some areas, the country receives over 4,000 hours of sunshine per year, which is among the highest quantities registered in the world. Due to the sharp population growth and a series of blackouts during the summer caused by a supply shortage, Egyptian demand for solar energy is increasing. However, only 1% of the electricity is produced by solar energy. The majority of solar energy available in the country derives from small-scale projects. Modestly-sized projects, up to 10 MW, are constituted by hybrid solar/diesel solutions, which are developed by the Emirati company Masdar.
In 2019 Egypt completed one of the biggest solar installations in the world, Benban Solar Park, which generates 1.8 GW to power 1 million homes.
In 2021, Egypt signed contracts worth $700 million with the Kom Ombo Solar Energy Complex which would create 10,000 jobs. The contracts include 32 solar energy projects.
Wind
See also
* Ministry of Electricity and Energy (Egypt) *Renewable energy by country
This is a list of renewable energy topics by country and territory. These links can be used to compare developments in renewable energy in different countries and territories and to help and encourage new writers to participate in writing about ...
* Waste management in Egypt
References
Citations
* {{Middle East topic, Energy policy of