Energy in Belarus on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Energy in Belarus describes
Energy in Belarus describes
Page: Country specific indicator numbers from page 48 Primary energy use per capita in Belarus in 2009 (34 MWh) was slightly more than in
 Belarus is a large oil refiner, listed 36th in the world, at 19 Mt of oil products in 2018 by the IEA. It has two refineries and oil pipelines built during the Soviet era including the Mozyr Oil Refinery.
Belarus is a large oil refiner, listed 36th in the world, at 19 Mt of oil products in 2018 by the IEA. It has two refineries and oil pipelines built during the Soviet era including the Mozyr Oil Refinery.
Map of Belarusian power grids
* Druzhba pipeline * 2004 Russia–Belarus gas dispute *

 Energy in Belarus describes
Energy in Belarus describes energy
In physics, energy (from Ancient Greek: ἐνέργεια, ''enérgeia'', “activity”) is the quantitative property that is transferred to a body or to a physical system, recognizable in the performance of work and in the form of hea ...
and electricity
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as describ ...
production, consumption and import in Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
. Belarus is a net energy importer. According to IEA, the energy import vastly exceeded the energy production in 2015, describing Belarus as one of the world's least energy sufficient countries in the world. Belarus is very dependent on Russia.
Total energy consumption (measured by total primary energy supply) in Belarus was 27.0 Mtoe in 2018, similar to consumption in Norway and Hungary. Primary energy use in Belarus was 327 TWh or 34 TWh per million persons in 2008.IEA Key energy statistics 2010Page: Country specific indicator numbers from page 48 Primary energy use per capita in Belarus in 2009 (34 MWh) was slightly more than in
Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
(26 MWh) and about half of the use in Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to th ...
(64 MWh) or Sweden (62 MWh).
Overview
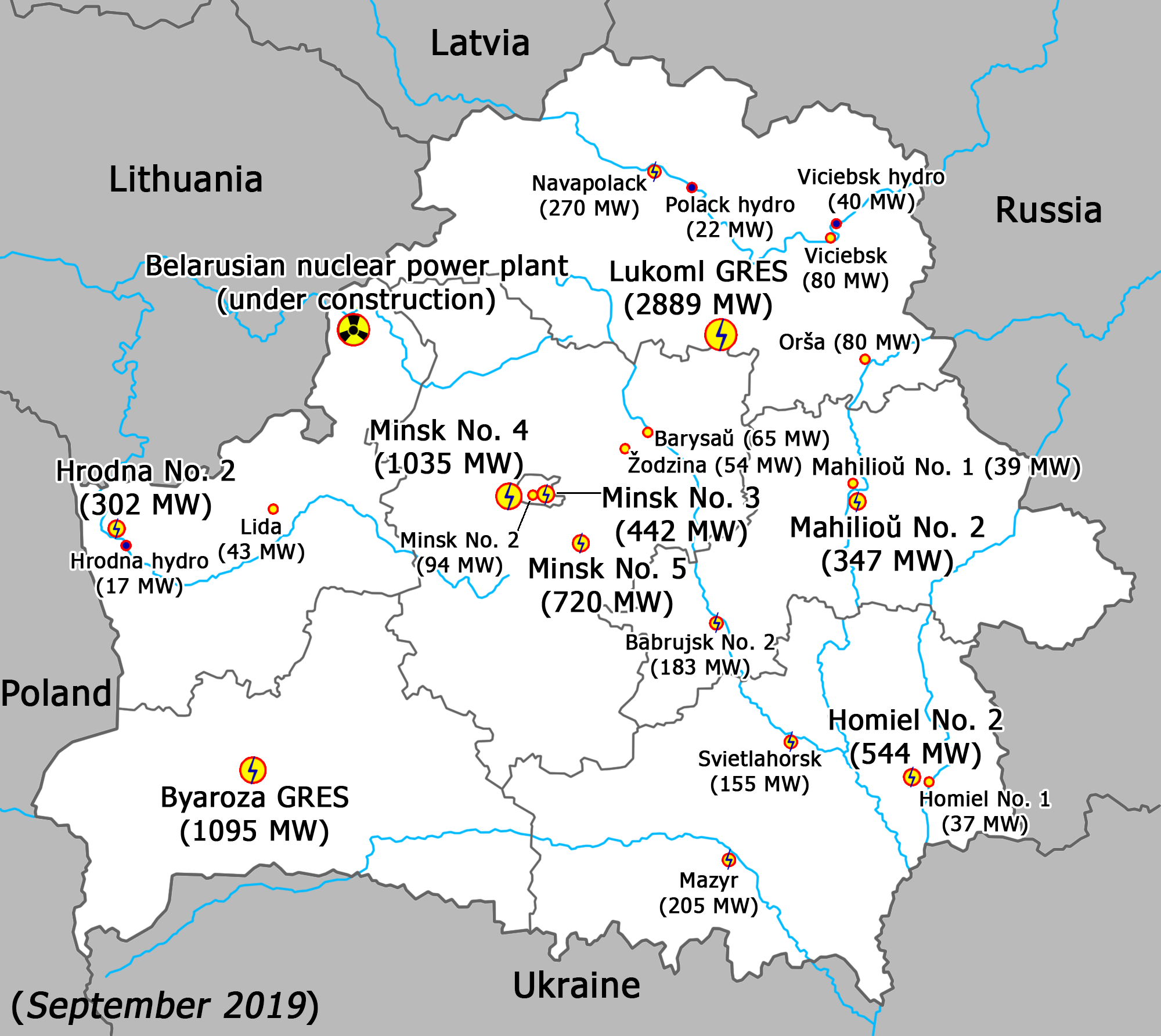
Power plants
The Astravets Nuclear Power Plant is under construction, with the first unit of two expected to come online in 2020.Natural gas
The country is one of the world’s largest importers of natural gas with estimates for 2018 being about 17 Mtoe (20 billion cubic metres cm of natural gas, making it the leading importer among the so-called EU4Energy countries:Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ' ...
, Azerbaijan
Azerbaijan (, ; az, Azərbaycan ), officially the Republic of Azerbaijan, , also sometimes officially called the Azerbaijan Republic is a transcontinental country located at the boundary of Eastern Europe and Western Asia. It is a part of t ...
, Belarus, Georgia
Georgia most commonly refers to:
* Georgia (country), a country in the Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Georgia (U.S. state), a state in the Southeast United States
Georgia may also refer to:
Places
Historical states and entities
* Related to the ...
, Kazakhstan
Kazakhstan, officially the Republic of Kazakhstan, is a transcontinental country located mainly in Central Asia and partly in Eastern Europe. It borders Russia to the north and west, China to the east, Kyrgyzstan to the southeast, Uzbeki ...
, Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan,, pronounced or the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and the People's Republic of China to the ea ...
, Moldova
Moldova ( , ; ), officially the Republic of Moldova ( ro, Republica Moldova), is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by Romania to the west and Ukraine to the north, east, and south. The unrecognised state of Transnistr ...
, Tajikistan
Tajikistan (, ; tg, Тоҷикистон, Tojikiston; russian: Таджикистан, Tadzhikistan), officially the Republic of Tajikistan ( tg, Ҷумҳурии Тоҷикистон, Jumhurii Tojikiston), is a landlocked country in Centr ...
, Turkmenistan
Turkmenistan ( or ; tk, Türkmenistan / Түркменистан, ) is a country located in Central Asia, bordered by Kazakhstan to the northwest, Uzbekistan to the north, east and northeast, Afghanistan to the southeast, Iran to the sout ...
, Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
and Uzbekistan
Uzbekistan (, ; uz, Ozbekiston, italic=yes / , ; russian: Узбекистан), officially the Republic of Uzbekistan ( uz, Ozbekiston Respublikasi, italic=yes / ; russian: Республика Узбекистан), is a doubly landlocked co ...
. In 2018 almost all generated electricity came from natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
(97%, or 39 terawatt hours Wh. In 1990, the IEA reported natural gas as constituting 52% of electricity generation, with oil generating 48%.
There are two large gas pipes running through Belarus, the Yamal–Europe pipeline
The Yamal–Europe natural gas pipeline is a pipeline connecting Russian natural gas fields in the Yamal Peninsula and Western Siberia with Poland and Germany, through Belarus.
In Gazprom's development project nomenclature the pipeline consist ...
and Northern Lights. In addition there is the Minsk–Kaliningrad Interconnection that connects to Kaliningrad
Kaliningrad ( ; rus, Калининград, p=kəlʲɪnʲɪnˈɡrat, links=y), until 1946 known as Königsberg (; rus, Кёнигсберг, Kyonigsberg, ˈkʲɵnʲɪɡzbɛrk; rus, Короле́вец, Korolevets), is the largest city and ...
.
Oil
 Belarus is a large oil refiner, listed 36th in the world, at 19 Mt of oil products in 2018 by the IEA. It has two refineries and oil pipelines built during the Soviet era including the Mozyr Oil Refinery.
Belarus is a large oil refiner, listed 36th in the world, at 19 Mt of oil products in 2018 by the IEA. It has two refineries and oil pipelines built during the Soviet era including the Mozyr Oil Refinery.
Renewable energy
Renewable energy generation accounted for 6% of Belarus’s energy in 2018, mostly from biofuels and waste. Renewables share in electricity generation was 2% in 2018 (0.8 TWh).Storage
Because non-nuclear thermal power plants are ramped up and down depending on heat requirements, and nuclear is not very flexible, increased battery storage has been suggested.Subsidies
Fossil fuelled heat is heavily subsidized.See also
Map of Belarusian power grids
* Druzhba pipeline * 2004 Russia–Belarus gas dispute *
2007 Russia–Belarus energy dispute
The Russia–Belarus energy dispute began when Russian state-owned gas supplier Gazprom demanded an increase in gas prices paid by Belarus, a country which has been closely allied with Moscow and forms a loose union state with Russia. It escalat ...
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Belarus, Energy In