Endurance (aeronautics) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 In
In aviation
Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. ''Aircraft'' includes airplane, fixed-wing and helicopter, rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as aerostat, lighter- ...
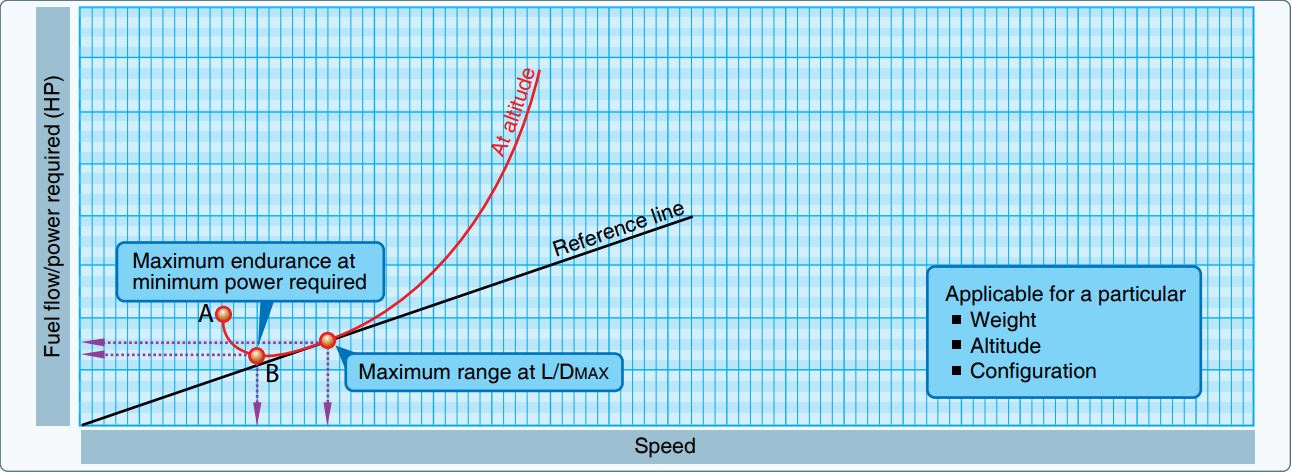
, endurance is the maximum length of time that an aircraft can spend in cruising flight. In other words, it is the amount of time an aircraft can stay in the air with one load of fuel. Endurance is different from range, which is a measure of distance flown. For example, a typical sailplane exhibits high endurance characteristics but poor range characteristics.
Endurance can be defined as:
:
where W stands for fuel weight, F for fuel flow, and t for time.
Endurance can factor into aviation design in a number of ways. Some aircraft, such as the P-3 Orion
The Lockheed P-3 Orion is a four-engined, turboprop Anti-submarine warfare, anti-submarine and maritime patrol aircraft, maritime surveillance aircraft developed for the United States Navy and introduced in the 1960s. Lockheed Corporation, Lockh ...
or U-2 spy plane, require high endurance characteristics as part of their mission profile (often referred to as loiter
Loitering is the act of remaining in a particular public place for a prolonged amount of time without any apparent purpose.
While the laws regarding loitering have been challenged and changed over time, loitering is still illegal in various j ...
time (on target)). Endurance plays a prime factor in finding out the fuel fraction for an aircraft.
Endurance, like range, is also related to fuel efficiency
Fuel efficiency is a form of thermal efficiency, meaning the ratio of effort to result of a process that converts chemical potential energy contained in a carrier (fuel) into kinetic energy or work. Overall fuel efficiency may vary per device ...
; fuel-efficient aircraft will tend to exhibit good endurance characteristics.
References
Aeronautics {{Aviation-stub