Emergency nursing on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
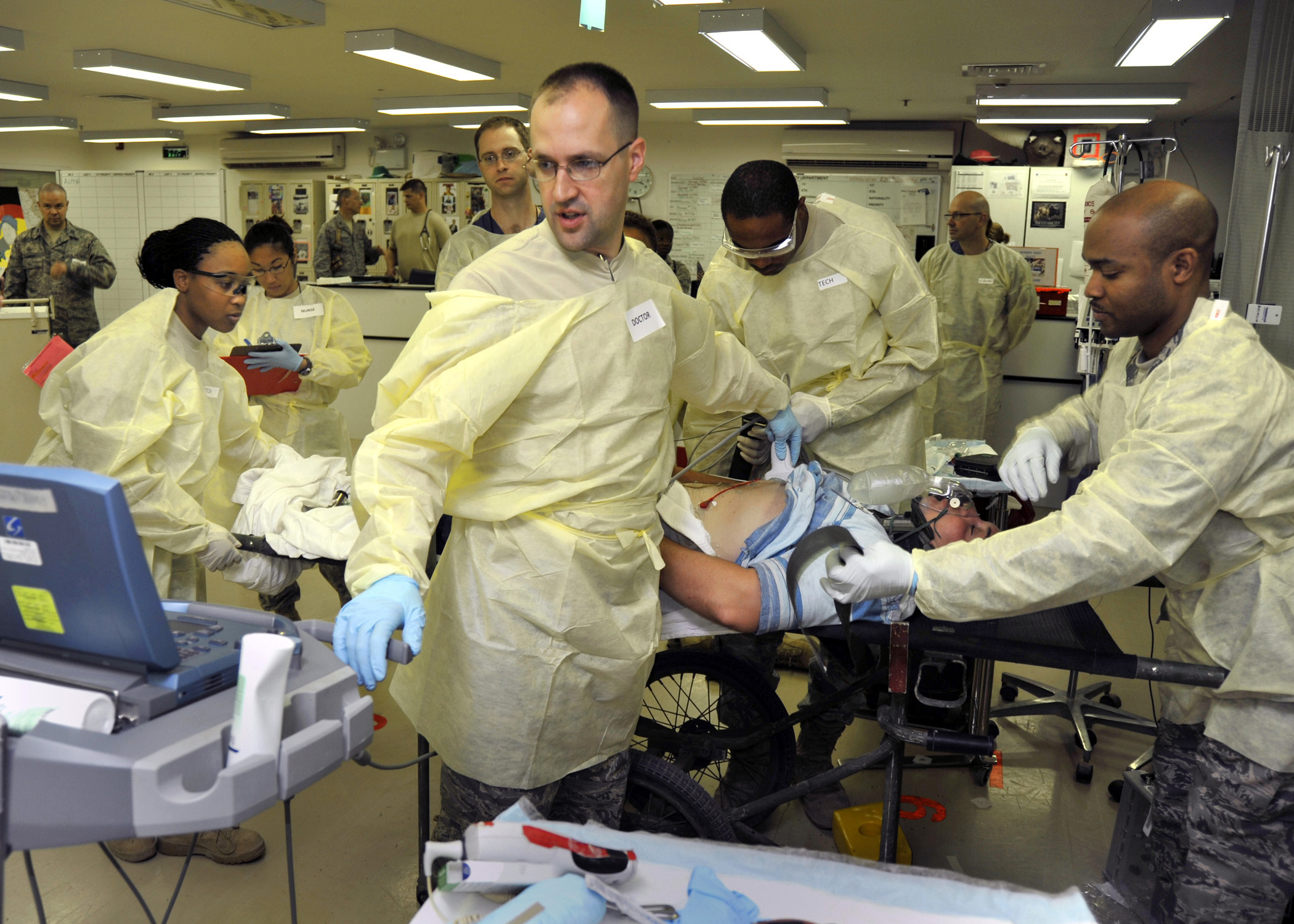 Emergency nursing is a specialty within the field of professional
Emergency nursing is a specialty within the field of professional

Emergency Nurses Association
Board of Certification of Emergency Nursing
{{Emergency medicine Hospital nursing
 Emergency nursing is a specialty within the field of professional
Emergency nursing is a specialty within the field of professional nursing
Nursing is a profession within the health care sector focused on the care of individuals, families, and communities so they may attain, maintain, or recover optimal health and quality of life. Nurses may be differentiated from other health ...
focusing on the care of patients who require prompt medical attention to avoid long-term disability or death. In addition to addressing "true emergencies," emergency nurses increasingly care for people who are unwilling or unable to get primary medical care elsewhere and come to emergency departments for help. In fact, only a small percentage of emergency department
An emergency department (ED), also known as an accident and emergency department (A&E), emergency room (ER), emergency ward (EW) or casualty department, is a medical treatment facility specializing in emergency medicine, the acute care of pati ...
(ED) patients have emergency conditions such as a stroke
A stroke is a disease, medical condition in which poor cerebral circulation, blood flow to the brain causes cell death. There are two main types of stroke: brain ischemia, ischemic, due to lack of blood flow, and intracranial hemorrhage, hemorr ...
, heart attack
A myocardial infarction (MI), commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to the coronary artery of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The most common symptom is chest pain or discomfort which ma ...
or major trauma
Major trauma is any injury that has the potential to cause prolonged disability or death. There are many causes of major trauma, blunt and penetrating, including falls, motor vehicle collisions, stabbing wounds, and gunshot wounds. Dependi ...
. Emergency nurses also tend to patients with acute alcohol and/or drug intoxication
Intoxication — or poisoning, especially by an alcoholic or narcotic substance — may refer to:
* Substance intoxication:
** Alcohol intoxication
** LSD intoxication
** Toxidrome
** Tobacco intoxication
** Cannabis intoxication
** Cocaine in ...
, psychiatric and behavioral problems and those who have been rape
Rape is a type of sexual assault usually involving sexual intercourse or other forms of sexual penetration carried out against a person without their consent. The act may be carried out by physical force, coercion, abuse of authority, or ...
d.
Emergency nurses are most frequently employed in hospital
A hospital is a health care institution providing patient treatment with specialized health science and auxiliary healthcare staff and medical equipment. The best-known type of hospital is the general hospital, which typically has an emergen ...
emergency departments, although they may also work in urgent care centers, sports arenas, and on medical transport aircraft and ground ambulances.
The history of emergency nursing
Around the 1800s hospitals became more popular and there was a growth in emergency care. The first development of an emergency room was originally called the "First Aid Room." Originally, nurses only dressed wounds, applied eye ointments, treated minor burns with salves and bandages, and attended patients with minor illnesses like colds and sore throats. The rule of thumb was first in, first served, but there were many cases where some people were in more need of emergency care than others, and as the situation became more intolerable, one of the greatest medical developments came into perspective:triage
In medicine, triage () is a practice invoked when acute care cannot be provided for lack of resources. The process rations care towards those who are most in need of immediate care, and who benefit most from it. More generally it refers to prio ...
.
For centuries triage had been used in war but was not yet established in the emergency department. The first time triage was referred to during a non-disaster situation was at Yale New Haven Hospital
Yale New Haven Hospital (YNHH) is a 1,541-bed hospital located in New Haven, Connecticut. It is owned and operated by the Yale New Haven Health System. YNHH includes the 168-bed Smilow Cancer Hospital at Yale New Haven, the 201-bed Yale New Haven ...
, Connecticut, United States in 1963, and since then has become developed and more defined.
Emergency nurse skills, knowledge and qualities
Emergency nurses must be able to sit, stand, walk, reach, squat and lift throughout their eight- or twelve-hour shift. They must have goodmanual dexterity
Fine motor skill (or dexterity) is the coordination of small muscles in movement with the eyes, hands and fingers. The complex levels of manual dexterity that humans exhibit can be related to the nervous system. Fine motor skills aid in the growt ...
, hearing and vision. They must understand principles of human development Human development may refer to:
* Development of the human body
* Developmental psychology
* Human development (economics)
* Human Development Index, an index used to rank countries by level of human development
* Human evolution
Human evoluti ...
, anatomy
Anatomy () is the branch of biology concerned with the study of the structure of organisms and their parts. Anatomy is a branch of natural science that deals with the structural organization of living things. It is an old science, having i ...
, physiology
Physiology (; ) is the scientific study of functions and mechanisms in a living system. As a sub-discipline of biology, physiology focuses on how organisms, organ systems, individual organs, cells, and biomolecules carry out the chemic ...
, pharmacology
Pharmacology is a branch of medicine, biology and pharmaceutical sciences concerned with drug or medication action, where a drug may be defined as any artificial, natural, or endogenous (from within the body) molecule which exerts a biochemica ...
, They must also have a working knowledge of the many legal issues impacting health care such as consent
Consent occurs when one person voluntarily agrees to the proposal or desires of another. It is a term of common speech, with specific definitions as used in such fields as the law, medicine, research, and sexual relationships. Consent as und ...
, handling of evidence, mandatory reporting
In many parts of the western world, a mandated reporter is a person who has regular contact with vulnerable people and is therefore legally required to ensure a report is made when abuse is observed or suspected. Specific details vary across jurisd ...
of child
A child ( : children) is a human being between the stages of birth and puberty, or between the developmental period of infancy and puberty. The legal definition of ''child'' generally refers to a minor, otherwise known as a person young ...
and elder abuse
Elder abuse (also called "elder mistreatment", "senior abuse", "abuse in later life", "abuse of older adults", "abuse of older women", and "abuse of older men") is "a single, or repeated act, or lack of appropriate action, occurring within any rela ...
, and involuntary psychiatric holds. They must be adept and comfortable working with patients of many different backgrounds, cultures, religions, ages and types of disabilities
Disability is the experience of any condition that makes it more difficult for a person to do certain activities or have equitable access within a given society. Disabilities may be cognitive, developmental, intellectual, mental, physical, ...
. They must be calm and professional at all times, especially when dealing with situations which are difficult, emotional or disgusting. Emergency nurses must also know how to care for themselves physically and emotionally.
The role of the emergency nurse
The role of the emergency nurse is to evaluate and monitor patients and to manage their care in the emergency department. They may also superviselicensed practical nurses
A licensed practical nurse (LPN), in much of the United States and Canada, is a nurse who cares for people who are sick, injured, convalescent, or disabled. In the United States, LPNs work under the direction of physicians, mid-level practitio ...
and unlicensed assistive personnel
Unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) are paraprofessionals who assist individuals with physical disabilities, mental impairments, and other health care needs with their activities of daily living (ADLs). UAPs also provide bedside care—includ ...
("nurse aides" or "care partners"). It can be a challenge to get everything done quickly and correctly in an ever-changing environment. Some ED nurse functions are common to other nursing specialties, while others are specific to emergency nursing. These can be divided into 1.) assessment, 2.) planning and managing care, 3.) tasks, 4.) communication, and 5.) teaching.
# Assessment. Emergency nurses interview a patient to get a health history
The medical history, case history, or anamnesis (from Greek: ἀνά, ''aná'', "open", and μνήσις, ''mnesis'', "memory") of a patient is information gained by a physician by asking specific questions, either to the patient or to other p ...
, a list of current medications being taken and allergies and perform a physical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the pati ...
. This is often a limited exam based on the patient's chief complaint and only infrequently a complete head-to-toe examination. The ED nurse periodically reassesses the patient to detect any changes, either improvement, decompensation or no change. This may be done after a treatment is given to evaluate its effectiveness or at certain time intervals as appropriate for the patient's condition.
# Planning and managing care. The ED nurse must have a plan of what to do for the patient, when and in what order. Managing an ED patient's care includes decisions such as whether the patient can go to X-ray before getting blood drawn, what tasks to delegate to unlicensed assistive personnel (UAPs), and how many visitors are allowed in the patient's room, among others.
# Tasks. There are procedures only the physician can perform, but many others are done by the emergency nurse. These include inserting intravenous ("IV") lines, urinary catheters
In urinary catheterization a latex, polyurethane, or silicone tube known as a urinary catheter is inserted into the bladder through the urethra to allow urine to drain from the bladder for collection. It may also be used to inject liquids used ...
and nasogastric ("NG") tubes; drawing blood samples from veins and arteries; dressing wounds; applying splints, administering medications, and in certain jurisdictions RNs are trained to suture
Suture, literally meaning "seam", may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Suture'' (album), a 2000 album by American Industrial rock band Chemlab
* ''Suture'' (film), a 1993 film directed by Scott McGehee and David Siegel
* Suture (ban ...
wounds. In some cases, emergency nurses may order certain tests and medications following "collaborative practice guidelines" or "standing orders" set out by the hospital's emergency physician staff.
# Communication. All the emergency nurse's observations are recorded in the patient's medical record
The terms medical record, health record and medical chart are used somewhat interchangeably to describe the systematic documentation of a single patient's medical history and care across time within one particular health care provider's jurisd ...
. These are used by other members of the healthcare team caring for the patient. ED nurses must keep the emergency physician
An emergency physician (often called an "ER doctor" in the United States) is a physician who works at an emergency department to care for ill patients. The emergency physician is a specialist in advanced cardiac life support (advanced life suppor ...
apprised of a patient's condition; if it suddenly worsens, the doctor must be notified immediately. If the patient is admitted to a room in the hospital or transferred to another facility, the emergency nurse must "give report" to the nurse at the patient's destination.
# Teaching. The emergency nurse keeps the patient and their family up-to-date throughout the visit and conducts teaching sessions with them. Topics often include how to take prescribed medication, how to prevent complications, when to return to the ED, and a patient's diagnosis
Diagnosis is the identification of the nature and cause of a certain phenomenon. Diagnosis is used in many different disciplines, with variations in the use of logic, analytics, and experience, to determine "cause and effect". In systems engin ...
. These are often short interactions and the nurse must evaluate what information the patient needs, how in detail to explain a topic, and the patient's readiness to learn. To do this, nurses must consider the patient's level of education, level of pain, education level, cultural influences, age, deficiencies in vision or hearing, and other factors.
Special emergency nurse roles

Triage Nurse
An emergency nurse is assigned totriage
In medicine, triage () is a practice invoked when acute care cannot be provided for lack of resources. The process rations care towards those who are most in need of immediate care, and who benefit most from it. More generally it refers to prio ...
patients as they arrive in the emergency department
An emergency department (ED), also known as an accident and emergency department (A&E), emergency room (ER), emergency ward (EW) or casualty department, is a medical treatment facility specializing in emergency medicine, the acute care of pati ...
, and as such, is the first professional patients will see. Therefore, this emergency nurse must be skilled at rapid, accurate physical examination
In a physical examination, medical examination, or clinical examination, a medical practitioner examines a patient for any possible medical signs or symptoms of a medical condition. It generally consists of a series of questions about the pati ...
and early recognition of life-threatening conditions. Based on the triage nurse's findings, a triage category is assigned. The Emergency Severity Index (ESI) triages patients into five groups from 1 (most urgent) to 5 (least urgent).
ED Charge Nurse
An experienced emergency nurse is put in the role of charge nurse or team leader. This nurse is responsible for the overall "flow" of the department. He or she assigns nurses to patients, assures patients are being transported to and from tests outside the ED, addresses patient complaints and concerns, communicates with the house supervisor, takes phone calls, and assures nurses get their breaks.Emergency Nurse Practitioner (ENP)
In the United Kingdom
A specialist nurse will independently assess, diagnose, investigate, and treat a wide range of common accidents and injuries working autonomously without supervision by medical staff. They primarily treat a wide range ofmusculoskeletal
The human musculoskeletal system (also known as the human locomotor system, and previously the activity system) is an organ system that gives humans the ability to move using their muscular and skeletal systems. The musculoskeletal system prov ...
problems, skin problems and minor illnesses. They are trained in advanced nursing skills. Under the National Health Service
The National Health Service (NHS) is the umbrella term for the publicly funded healthcare systems of the United Kingdom (UK). Since 1948, they have been funded out of general taxation. There are three systems which are referred to using the " ...
grading system, ENPs are typically graded Band 6 or 7.
Additionally, some specialized nurses perform as emergency care practitioners. They generally work in the pre-hospital setting dealing with a wide range of medical or emergency problems. Their primary function is to assess, diagnose and treat a patient in the home in an emergency setting.
In the United States
An advanced practice nurse assesses, diagnoses, and treats a variety of common illnesses, injuries and disease processes in emergency care settings. ENPs are trained in advanced nursing and medical skills such asx-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
interpretation, ophthalmic slit lamp
A slit lamp is an instrument consisting of a high-intensity light source that can be focused to shine a thin sheet of light into the eye. It is used in conjunction with a biomicroscope. The lamp facilitates an examination of the anterior segme ...
examination, suturing
A surgical suture, also known as a stitch or stitches, is a medical device used to hold body tissues together and approximate wound edges after an injury or surgery. Application generally involves using a needle with an attached length of thre ...
, local and regional anesthesia
Anesthesia is a state of controlled, temporary loss of sensation or awareness that is induced for medical or veterinary purposes. It may include some or all of analgesia (relief from or prevention of pain), paralysis (muscle relaxation), ...
, abscess
An abscess is a collection of pus that has built up within the tissue of the body. Signs and symptoms of abscesses include redness, pain, warmth, and swelling. The swelling may feel fluid-filled when pressed. The area of redness often extends ...
incision and drainage, advanced airway techniques, fracture reduction, and casting
Casting is a manufacturing process in which a liquid material is usually poured into a mold, which contains a hollow cavity of the desired shape, and then allowed to solidify. The solidified part is also known as a ''casting'', which is ejecte ...
and splinting.
In Australia
Australian nurse practitioners follow the clinical practice guidelines developed by the Victorian Emergency Nurse Practitioner Collaborative (VENPC), which has supported nurse practitioner development in Victoria. These guidelines include attending to minorhead injuries
A head injury is any injury that results in trauma to the skull or brain. The terms ''traumatic brain injury'' and ''head injury'' are often used interchangeably in the medical literature. Because head injuries cover such a broad scope of inju ...
, burns, open wounds, joint pain, haemophilia
Haemophilia, or hemophilia (), is a mostly inherited genetic disorder that impairs the body's ability to make blood clots, a process needed to stop bleeding. This results in people bleeding for a longer time after an injury, easy bruisin ...
, blood and fluid exposure, PV bleeding, urinary tract infections
A urinary tract infection (UTI) is an infection that affects part of the urinary tract. When it affects the lower urinary tract it is known as a bladder infection (cystitis) and when it affects the upper urinary tract it is known as a kidne ...
(UTIs), abdominal pain, cellulitis
Cellulitis is usually a bacterial infection involving the inner layers of the skin. It specifically affects the dermis and subcutaneous fat. Signs and symptoms include an area of redness which increases in size over a few days. The borders of ...
, and more.
Emergency nurses in Africa
Emergency nurses work in various places, many of which are understaffed as there are nursing shortages acrossAfrica
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
. There is also a shortage of doctors, leaving many tasks for nurses with limited guidelines or standards to deal with, and the scope of practice is quite undefined for many emergency nurses. Nurses may be required to work outside their scope, causing frustration and increasing the opportunities for occupational health hazards. It can be speculated that triage protocols are either lacking or not being followed. The limited basic knowledge and skill of emergency nursing included in undergraduate nurse training programs, and the limited number of nurse trainers, provides difficulty for many pending nurses to acquire the skills needed to work in emergency settings.
Challenges of emergency nursing
Emergency nursing is a demanding job and can be unpredictable. Emergency nurses need to have basic knowledge of most specialty areas, to be able to work under pressure, communicate effectively with many types of patients, collaborate with a variety of health care providers and prioritize the tasks that must be performed. It can be quite draining both physically and mentally for many nurses. Australian emergency departments treat over eight million patients each year as of 2018. They spend much of their time on their feet and must be ready for unexpected changes in patients' conditions as well as sudden influxes of patients to the emergency department. Emergency department nurses may be exposed to traumatic situations such as heavy bleeding, dismemberment and even death. Violence is a growing challenge for many nurses in the emergency department. Emergency nurses often receive bothphysical
Physical may refer to:
* Physical examination, a regular overall check-up with a doctor
* ''Physical'' (Olivia Newton-John album), 1981
** "Physical" (Olivia Newton-John song)
* ''Physical'' (Gabe Gurnsey album)
* "Physical" (Alcazar song) (2004)
* ...
and verbal abuse
Verbal abuse (also known as verbal aggression, verbal attack, verbal violence, verbal assault, psychic aggression, or psychic violence) is a type of psychological/mental abuse that involves the use of oral, gestured, and written language direct ...
from patients and visitors.
Board certification in emergency nursing
Certified Emergency Nurse - CEN
The Certified Emergency Nurse (CEN) designation is granted to aregistered nurse
A registered nurse (RN) is a nurse who has graduated or successfully passed a nursing program from a recognized nursing school and met the requirements outlined by a country, state, province or similar government-authorized licensing body to o ...
who has demonstrated expertise in emergency nursing by passing a computer-administered examination given by the Board of Certification for Emergency Nursing (BCEN). The certification exam first became available in July 1980, was accredited by the Accreditation Board for Specialty Nursing Certification (ABSNC) in February 2002, and was re-accredited in 2007, 2012, and 2016. The certification is valid for four years, and can be renewed either by passing another examination, or by attesting that the nurse has completed 100 continuing education units (CEUs) in the specialty.
As of 2019, the BCEN has designated over 38,000 active CENs in the United States and Canada. The CEN exam has 175 questions; 150 are used for testing purposes (25 are sample questions). The passing score is 70% and the candidate has three hours to take the exam. The test is administered in Pearson Vue testing centers internationally.
Certified Pediatric Emergency Nurse - CPEN
The Certified Pediatric Emergency Nurse (CPEN) designation is applied to a registered nurse who has demonstrated expertise in pediatric emergency nursing by passing a computer-administered examination given jointly by the Board of Certification for Emergency Nursing (BCEN) and the Pediatric Nursing Certification Board (PNCB). The certification exam first became available on January 21, 2009, and was accredited by ABSNC in May 2015. The certification is valid for four years, and can be renewed either by passing another examination, by completing 100 contact hours (continuing education) in the specialty, or by completing 1,000 clinical practice hours and 40 contact hours in the specialty. As of 2020, the BCEN and the PNCB have designated over 5,200 active CPENs. The CPEN exam has 175 questions; 150 are used for testing purposes (25 are sample questions). The passing score is 87% and the candidate has three hours to take the exam. The test is administered in AMP testing centers internationally.Additional emergency nursing education/certification
* Advanced Burn Life Support (ABLS) *Advanced Cardiac Life Support
Advanced cardiac life support, advanced cardiovascular life support (ACLS) refers to a set of clinical guidelines for the urgent and emergent treatment of life-threatening cardiovascular conditions that will cause or have caused cardiac arrest, ...
(ACLS)
* Advanced Medical Life Support (AMLS)
* Advanced Trauma Care for Nurses (ATCN)
* Basic Life Support
Basic life support (BLS) is a level of medical care which is used for patients with life-threatening illnesses or injuries until they can be given full medical care by advanced life support providers (paramedics, nurses, physicians). It can be p ...
(BLS)
* Certified Flight Registered Nurse (CFRN)
*Certified Transport Registered Nurse (CTRN)
* Course in Advanced Trauma (CATN)
* Emergency Nursing Pediatric Course (ENPC)
* Geriatric Emergency Nursing Education (GENE)
* Mobile Intensive Care Nurse
A Critical Care Transport Nurse is a Registered Nurse specialized in care in the pre-hospital setting. These are mostly air-medical personnel or critical care transport providers with specialized training and experience in pre-hospital care. Such ...
(MICN)
* National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale Certification (NIHSS)
* Neonatal Resuscitation Program
The Neonatal Resuscitation Program is an educational program in neonatal resuscitation that was developed and is maintained by the American Academy of Pediatrics. This program focuses on basic resuscitation skills for newly born infants.
With the ...
(NRP)
* Pediatric Advanced Life Support Pediatric advanced life support (PALS) is a course offered by the American Heart Association (AHA) for health care providers who take care of children and infants in the emergency room, critical care and intensive care units in the hospital, and ou ...
(PALS)
* Pre-Hospital Emergency Care (PHEC)
* Trauma Certified Registered Nurse (TCRN)
* Trauma Nurse Specialist (TNS)
*Trauma Nursing Core Course (TNCC)
References
External links
Emergency Nurses Association
Board of Certification of Emergency Nursing
{{Emergency medicine Hospital nursing