Electrical muscle stimulation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Electrical muscle stimulation (EMS), also known as neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) or electromyostimulation, is the elicitation of
standard indications for use, page 4; contraindications, p. 7; warnings and precautions, p. 8. Product code
NGX
/ref> A number of reviews have looked at the devices.
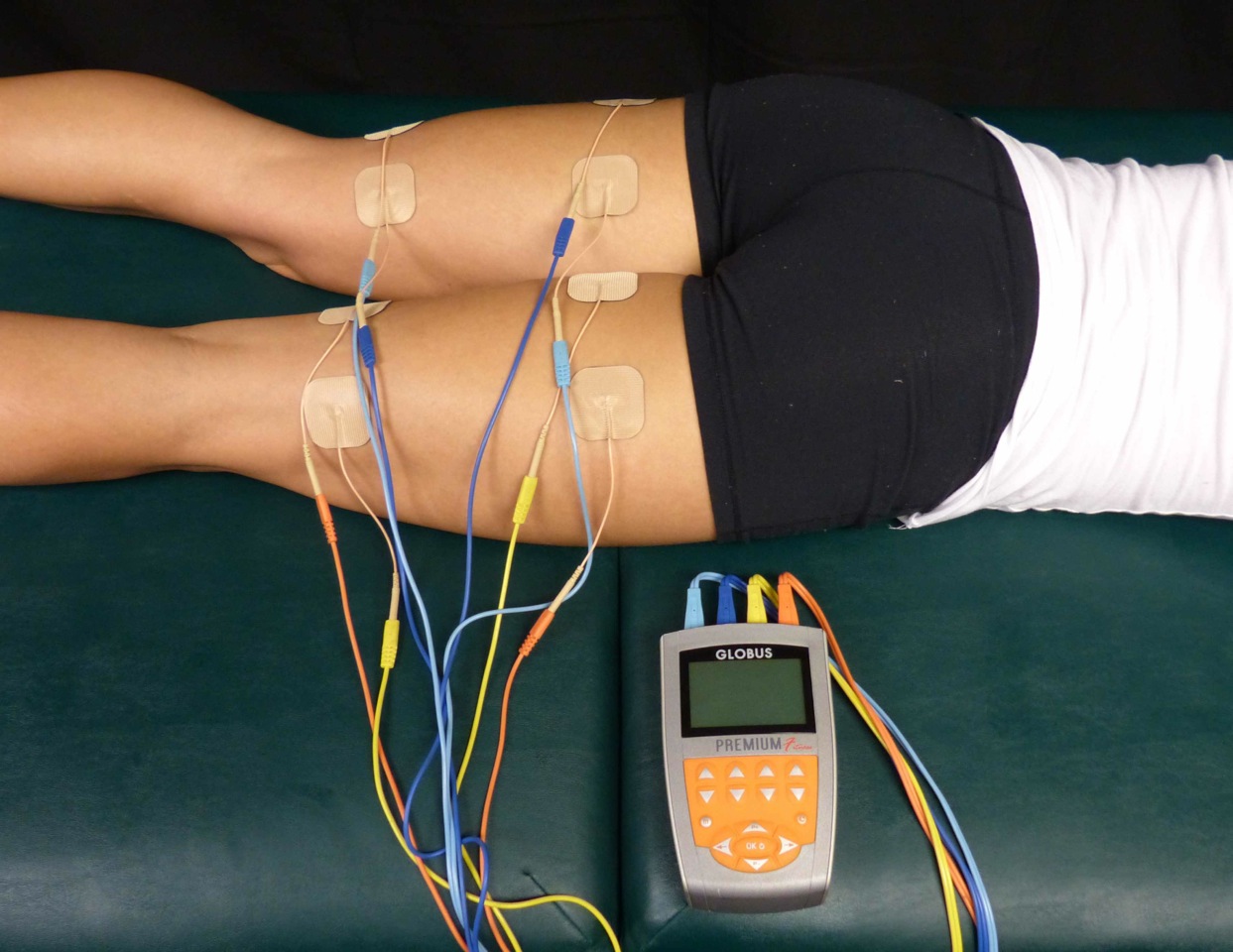 Electrical muscle stimulation can be used as a training, therapeutic, or
Electrical muscle stimulation can be used as a training, therapeutic, or
/ref> The FTC has cracked down on consumer EMS devices that made unsubstantiated claims; many have been removed from the market, some have obtained FDA certification.
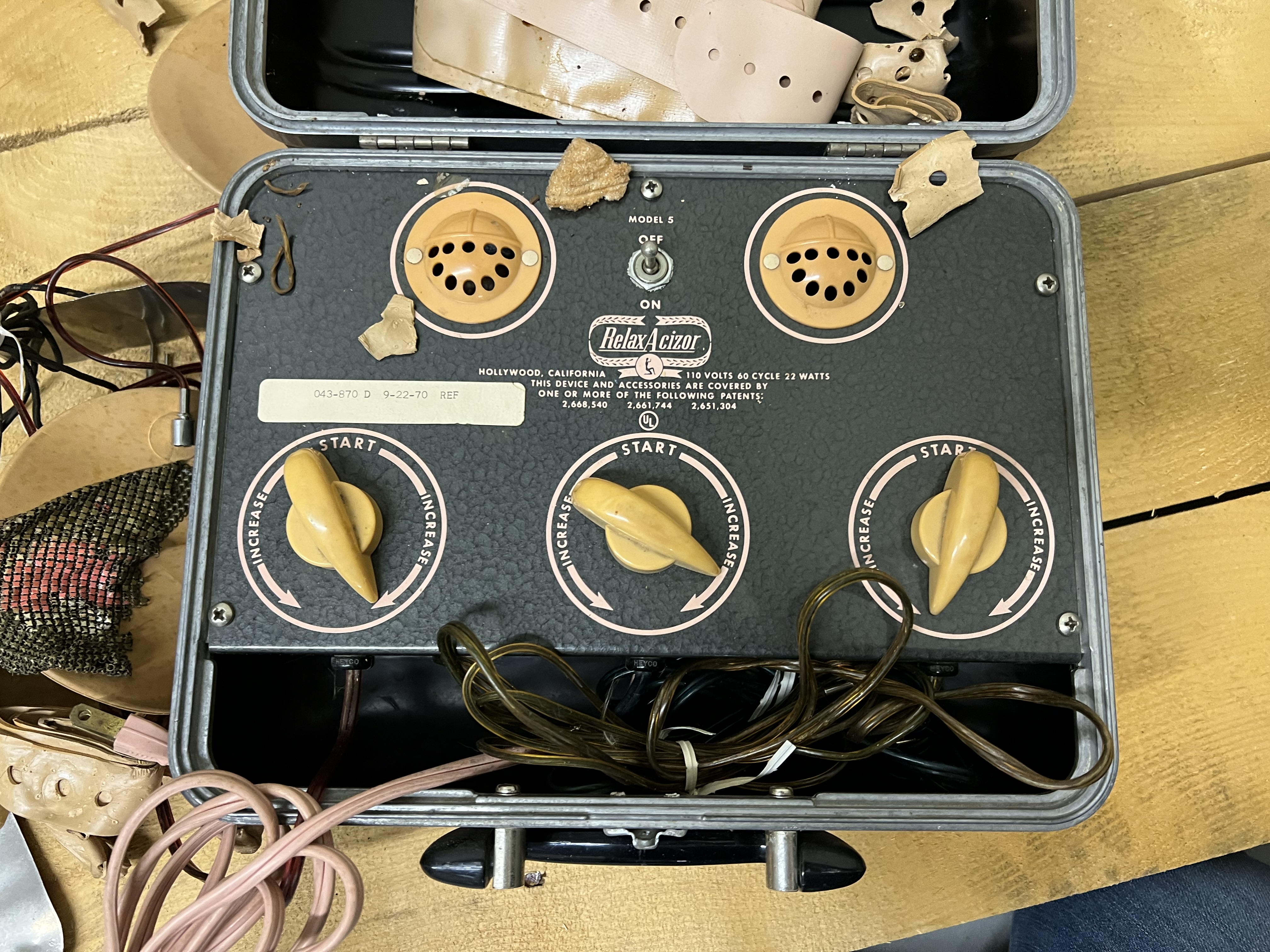 Non-professional devices target home-market consumers with wearable units in which EMS circuitry is contained in belt-like garments (ab toning belts) or other clothing items.
The Relax-A-Cizor was one brand of device manufactured by the U.S. company Relaxacizor, Inc.
From the 1950s, the company marketed the device for use in weight loss and fitness.
Non-professional devices target home-market consumers with wearable units in which EMS circuitry is contained in belt-like garments (ab toning belts) or other clothing items.
The Relax-A-Cizor was one brand of device manufactured by the U.S. company Relaxacizor, Inc.
From the 1950s, the company marketed the device for use in weight loss and fitness.
muscle contraction
Muscle contraction is the activation of tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length, such a ...
using electric impulses. EMS has received an increasing amount of attention in the last few years for many reasons: it can be utilized as a strength training tool for healthy subjects and athletes; it could be used as a rehabilitation and preventive tool for people who are partially or totally immobilized; it could be utilized as a testing tool for evaluating the neural and/or muscular function in vivo; it could be used as a post-exercise recovery tool for athletes. The impulses are generated by a device and are delivered through electrodes on the skin near to the muscles being stimulated. The electrodes are generally pads that adhere to the skin. The impulses mimic the action potential
An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls. This depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells ...
that comes from the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
, causing the muscles to contract. The use of EMS has been cited by sports scientists as a complementary technique for sports training, and published research is available on the results obtained. In the United States, EMS devices are regulated by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA).FDA Guidance Document for Powered Muscle Stimulatorstandard indications for use, page 4; contraindications, p. 7; warnings and precautions, p. 8. Product code
NGX
/ref> A number of reviews have looked at the devices.
Uses
 Electrical muscle stimulation can be used as a training, therapeutic, or
Electrical muscle stimulation can be used as a training, therapeutic, or cosmetic
Cosmetic may refer to:
*Cosmetics, or make-up, substances to enhance the beauty of the human body, apart from simple cleaning
*Cosmetic, an adjective describing beauty, aesthetics, or appearance, especially concerning the human body
*Cosmetic, a t ...
tool.Physical rehabilitation
In medicine, EMS is used for rehabilitation purposes, for instance inphysical therapy
Physical therapy (PT), also known as physiotherapy, is one of the allied health professions. It is provided by physical therapists who promote, maintain, or restore health through physical examination, diagnosis, management, prognosis, pat ...
in the prevention muscle atrophy
Muscle atrophy is the loss of skeletal muscle mass. It can be caused by immobility, aging, malnutrition, medications, or a wide range of injuries or diseases that impact the musculoskeletal or nervous system. Muscle atrophy leads to muscle weakness ...
due to inactivity or neuromuscular imbalance, which can occur for example after musculoskeletal injuries
Musculoskeletal injury refers to damage of muscular or skeletal systems, which is usually due to a strenuous activity and includes damage to skeletal muscles, bones, tendons, joints, ligaments, and other affected soft tissues. In one study, r ...
(damage to bones, joints
A joint or articulation (or articular surface) is the connection made between bones, ossicles, or other hard structures in the body which link an animal's skeletal system into a functional whole.Saladin, Ken. Anatomy & Physiology. 7th ed. McGraw- ...
, muscles, ligaments
A ligament is the fibrous connective tissue that connects bones to other bones. It is also known as ''articular ligament'', ''articular larua'', ''fibrous ligament'', or ''true ligament''. Other ligaments in the body include the:
* Peritoneal ...
and tendons
A tendon or sinew is a tough, high-tensile-strength band of dense fibrous connective tissue that connects muscle to bone. It is able to transmit the mechanical forces of muscle contraction to the skeletal system without sacrificing its abilit ...
). This is distinct from transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), in which an electric current is used for pain therapy. In the case of TENS, the current is usually sub-threshold, meaning that a muscle contraction is not observed.
For people who have progressive diseases such as cancer or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, EMS is used to improve muscle weakness for those unable or unwilling to undertake whole-body exercise. EMS may lead to statistically significant improvement in quadriceps muscle strength, however, further research is needed as this evidence is graded as low certainty. The same study also indicates that EMS may lead to increased muscle mass. Low certainty evidence indicates that adding EMS to an existing exercise programme may help people who are unwell spend fewer days confined to their beds.
During EMS training, a set of complementary muscle groups (e.g., biceps and triceps) are often targeted in alternating fashion, for specific training goals, such as improving the ability to reach for an item.
Weight loss
The FDA rejects certification of devices that claim weight reduction. EMS devices cause a calorie burning that is marginal at best: calories are burnt in significant amount only when most of the body is involved in physical exercise: several muscles, the heart and the respiratory system are all engaged at once. However, some authors imply that EMS can lead to exercise, since people toning their muscles with electrical stimulation are more likely afterwards to participate in sporting activities as the body becomes ready, fit, willing and able to take on physical activity.Effects
"Strength training by NMES does promote neural and muscular adaptations that are complementary to the well-known effects of voluntary resistance training". This statement is part of the editorial summary of a 2010 world congress of researchers on the subject. Additional studies on practical applications, which came after that congress, pointed out important factors that make the difference between effective and ineffective EMS. This in retrospect explains why in the past some researchers and practitioners obtained results that others could not reproduce. Also, as published by reputable universities, EMS causes adaptation, i.e. training, of muscle fibers. Because of the characteristics ofskeletal muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of m ...
fibers, different types of fibers can be activated to differing degrees by different types of EMS, and the modifications induced depend on the pattern of EMS activity. These patterns, referred to as protocols or programs, will cause a different response from contraction of different fiber types. Some programs will improve fatigue resistance, i.e. endurance, others will increase force production.
History
Luigi Galvani
Luigi Galvani (, also ; ; la, Aloysius Galvanus; 9 September 1737 – 4 December 1798) was an Italian physician, physicist, biologist and philosopher, who studied animal electricity. In 1780, he discovered that the muscles of dead frogs' legs ...
(1761) provided the first scientific evidence that current can activate muscle. During the 19th and 20th centuries, researchers studied and documented the exact electrical properties that generate muscle movement. It was discovered that the body functions induced by electrical stimulation caused long-term changes in the muscles. In the 1960s, Soviet sport scientists applied EMS in the training of elite athletes, claiming 40% force gains. In the 1970s, these studies were shared during conferences with the Western sport establishments. However, results were conflicting, perhaps because the mechanisms in which EMS acted were poorly understood. Medical physiology research pinpointed the mechanisms by which electrical stimulation causes adaptation of cells of muscles, blood vessels and nerves.
Society and culture
United States regulation
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) certifies and releases EMS devices into two broad categories: over-the counter devices (OTC), and prescription devices. OTC devices are marketable only for muscle toning; prescription devices can be purchased only with a medical prescription for therapy. Prescription devices should be used under supervision of an authorized practitioner, for the following uses: * Relaxation of muscle spasms; * Prevention or retardation of disuse atrophy; * Increasing local blood circulation; * Muscle re-education; * Immediate post-surgical stimulation of calf muscles to preventvenous thrombosis
Venous thrombosis is blockage of a vein caused by a thrombus (blood clot). A common form of venous thrombosis is deep vein thrombosis (DVT), when a blood clot forms in the deep veins. If a thrombus breaks off (embolizes) and flows to the lungs t ...
;
* Maintaining or increasing range of motion.
The FDA mandates that manuals prominently display contraindication, warnings, precautions and adverse reactions, including: no use for wearer of pacemaker; no use on vital parts, such as carotid sinus nerves, across the chest, or across the brain; caution in the use during pregnancy, menstruation, and other particular conditions that may be affected by muscle contractions; potential adverse effects include skin irritations and burns
Only FDA-certified devices can be lawfully sold in the US without medical prescription. These can be found at the corresponding FDA webpage for certified devices.FDA-Certified Devices/ref> The FTC has cracked down on consumer EMS devices that made unsubstantiated claims; many have been removed from the market, some have obtained FDA certification.
Devices
 Non-professional devices target home-market consumers with wearable units in which EMS circuitry is contained in belt-like garments (ab toning belts) or other clothing items.
The Relax-A-Cizor was one brand of device manufactured by the U.S. company Relaxacizor, Inc.
From the 1950s, the company marketed the device for use in weight loss and fitness.
Non-professional devices target home-market consumers with wearable units in which EMS circuitry is contained in belt-like garments (ab toning belts) or other clothing items.
The Relax-A-Cizor was one brand of device manufactured by the U.S. company Relaxacizor, Inc.
From the 1950s, the company marketed the device for use in weight loss and fitness. Electrode
An electrode is an electrical conductor used to make contact with a nonmetallic part of a circuit (e.g. a semiconductor, an electrolyte, a vacuum or air). Electrodes are essential parts of batteries that can consist of a variety of materials ...
s from the device were attached to the skin and caused muscle contraction
Muscle contraction is the activation of tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length, such a ...
s by way of electrical currents. The device caused 40 muscular contractions per minute in the muscles affected by the motor nerve points in the area of each pad. The directions for use recommended use of the device at least 30 minutes daily for each figure placement area, and suggested that the user might use it for longer periods if they wished. The device was offered in a number of different models which were powered either by battery or household current.
Relax-A-Cizors had from 1 to 6 channels. Two pads (or electrodes) were connected by wires to each channel. The user applied from 2 to 12 pads to various parts of their body. For each channel there was a dial which purported to control the intensity of the electrical current flowing into the user's body between the two pads connected to that channel.
As of 1970, the device was manufactured in Chicago, Illinois, by Eastwood Industries, Inc., a wholly owned subsidiary of Relaxacizor, Inc., and was then distributed throughout the country at the direction of Relaxacizor, Inc., or Relaxacizor Sales, Inc.
The device was banned by the United States Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
in 1970 as it was deemed to be potentially unhealthy and dangerous to the users. The case went to court, and the United States District Court for the Central District of California
The United States District Court for the Central District of California (in case citations, C.D. Cal.; commonly referred to as the CDCA or CACD) is a Federal trial court that serves over 19 million people in Southern and Central California, ...
held that the Relax-A-Cizor was a "device" within the meaning of 21 U.S.C. § 321 (h) because it was intended to affect the structure and functions of the body as a girth reducer and exerciser, and upheld the FDA's assertions that the device was potentially hazardous to health.
The FDA informed owners of Relax-A-Cizors that second-hand sale of Relax-A-Cizors was illegal, and recommended that they should destroy the devices or render them inoperable.
Slendertone is another brand name. the company's Slendertone Flex product had been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for over-the-counter sale for toning, strengthening and firming abdominal muscles.
See also
*Electroacupuncture
Electroacupuncture is a form of acupuncture where a small electric current is passed between pairs of acupuncture needles.
According to some acupuncturists, this practice augments the use of regular acupuncture, can restore health and well-bei ...
* Functional electrical stimulation
* Microcurrent electrical neuromuscular stimulator
* Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation
References
Further reading
* * Google document inspired by a workshop by author It is compiled to serve as a practical guide to understanding electrical muscle stimulation for sport training, and is supplemented by material taught by the author during workshops, and by appendices written by professional trainers. {{DEFAULTSORT:Electrical Muscle Stimulation Athletic training Electrotherapy Medical treatments Physical exercise