Eilean Siar on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Outer Hebrides () or Western Isles ( gd, Na h-Eileanan Siar or or ("islands of the strangers"); sco, Waster Isles), sometimes known as the Long Isle/Long Island ( gd, An t-Eilean Fada, links=no), is an island chain off the west coast of mainland
The Outer Hebrides () or Western Isles ( gd, Na h-Eileanan Siar or or ("islands of the strangers"); sco, Waster Isles), sometimes known as the Long Isle/Long Island ( gd, An t-Eilean Fada, links=no), is an island chain off the west coast of mainland
 The islands form an archipelago whose major islands are
The islands form an archipelago whose major islands are
SNH Information and Advisory Note Number 4. Retrieved 1 January 2010. North and South Uist and Lewis, in particular, have landscapes with a high percentage of fresh water and a maze and complexity of loch shapes. Harris has fewer large bodies of water but has innumerable small lochans. Loch Langavat on Lewis is long, and has several large islands in its midst, including Eilean Mòr. Although Loch Suaineabhal has only 25% of Loch Langavat's surface area, it has a mean depth of and is the most voluminous on the island. Of

 Much of the archipelago is a protected habitat, including both the islands and the surrounding waters. There are 53
Much of the archipelago is a protected habitat, including both the islands and the surrounding waters. There are 53
 The islands' total population was 26,502 at the 2001 census, and the 2011 figure was 27,684. During the same period
The islands' total population was 26,502 at the 2001 census, and the 2011 figure was 27,684. During the same period
. . Retrieved 20 July 2013. which has a population of about 8,100. The population estimate for 2019 was 26,720 according to a Comhairle nan Eilean Siar report which added that "the population of the Outer Hebrides is ageing" and that "young adults ..leave the islands for further education or employment purposes". Of the total population, 6,953 people reside in the "Stornoway settlement Laxdale (Lacasdal), Sandwick (Sanndabhaig) and Newmarket" with the balance distributed over 280 townships. In addition to the major North Ford (') and South Ford causeways that connect North Uist to Benbecula via the northern of the Grimsays, and another causeway from Benbecula to South Uist, several other islands are linked by smaller causeways or bridges. Great Bernera and Scalpay have bridge connections to Lewis and Harris respectively, with causeways linking Baleshare and Berneray to North Uist; Eriskay to South Uist; , and the southern Grimsay to Benbecula; and

 There are more than fifty uninhabited islands greater in size than in the Outer Hebrides, including the
There are more than fifty uninhabited islands greater in size than in the Outer Hebrides, including the
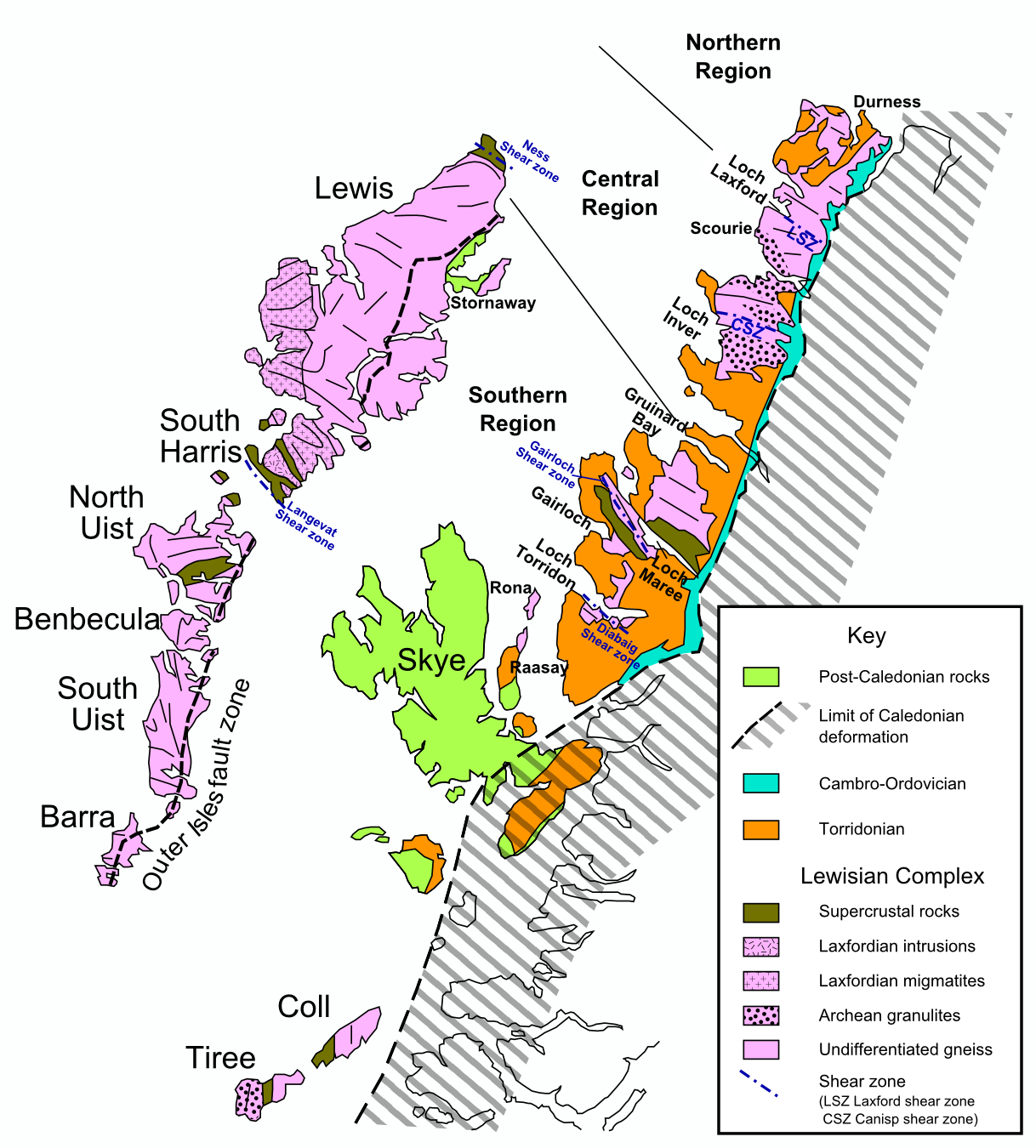 Most of the islands have a bedrock formed from
Most of the islands have a bedrock formed from
 The Hebrides were originally settled in the
The Hebrides were originally settled in the
 The earliest written references that have survived relating to the islands were made by
The earliest written references that have survived relating to the islands were made by

 As the Norse era drew to a close the Norse-speaking princes were gradually replaced by Gaelic-speaking
As the Norse era drew to a close the Norse-speaking princes were gradually replaced by Gaelic-speaking
 With the implementation of the Treaty of Union in 1707 the Hebrides became part of the new
With the implementation of the Treaty of Union in 1707 the Hebrides became part of the new
Undiscovered Scotland. Retrieved 8 July 2010. The work of the
 Modern commercial activities centre on tourism,
Modern commercial activities centre on tourism,
Comhairle nan Eilean Siar. Retrieved 4 July 2010. There is some optimism about the possibility of future developments in, for example, renewable energy generation, tourism, and education, and after declines in the 20th century the population has stabilised since 2003, although it is ageing. A 2019 report, using key assumptions, (mortality, fertility and migration) was less optimistic. It predicted that the population is "projected to fall to 22,709 by 2043"; that translates to a 16% decline, or 4,021 people, between 2018 and 2043. The UK’s largest community-owned wind farm, the 9MW Beinn Ghrideag, a "3 turbine, 9MW scheme" is located outside Stornoway and is operated by Point and Sandwick Trust (PST). The Isle of Lewis web site states that Stornoway's sheltered harbour has been important for centuries; it was named Steering Bay by
 From the passing of the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1889 to 1975 Lewis formed part of the
From the passing of the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1889 to 1975 Lewis formed part of the
''1901–2001 Gaelic in the Census''
(PowerPoint) Linguae Celticae. Retrieved 1 June 2008 In the 2001 census, each island overall was over 50% Gaelic speaking –
 Scheduled
Scheduled 
 The archipelago is exposed to wind and tide, and
The archipelago is exposed to wind and tide, and
''Adventure Guide to Scotland''
Hunter Publishing. Retrieved 19 May 2010. * Miers, Mary (2008) ''The Western Seaboard: An Illustrated Architectural Guide.'' The Rutland Press. * * Murray, W.H. (1966) ''The Hebrides''. London. Heinemann. * Murray, W.H. (1973) ''The Islands of Western Scotland: the Inner and Outer Hebrides.'' London. Eyre Methuen. * Ross, David (2005) ''Scotland – History of a Nation''. Lomond. * Rotary Club of Stornoway (1995) ''The Outer Hebrides Handbook and Guide''. Machynlleth. Kittiwake. * Thompson, Francis (1968) ''Harris and Lewis, Outer Hebrides''. Newton Abbot. David & Charles. * Watson, W. J. (1994) ''The Celtic Place-Names of Scotland''. Edinburgh; Birlinn. . First published 1926.
Stornoway Port Authority
Comhairle nan Eilean Siar
2001 Census Results for the Outer Hebrides
MacTV
Reefnet
Hebrides.com
Photographic website from ex-Eolas Sam Maynard
www.visithebrides.com
Western Isles Tourist Board site from Reefnet
Virtual Hebrides.com
Content from the VH, which went its own way and became Virtual Scotland.
hebrides.ca
Home of the Quebec-Hebridean Scots who were cleared from Lewis to Quebec 1838–1920s {{Authority control . Archipelagoes of Scotland Archipelagoes of the Atlantic Ocean Council areas of Scotland Lieutenancy areas of Scotland Regions of Scotland Former Norwegian colonies Gaelic culture
Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to ...
. The islands are geographically coextensive with , one of the 32 unitary council areas of Scotland. They form part of the archipelago of the Hebrides
The Hebrides (; gd, Innse Gall, ; non, Suðreyjar, "southern isles") are an archipelago off the west coast of the Scottish mainland. The islands fall into two main groups, based on their proximity to the mainland: the Inner and Outer Hebri ...
, separated from the Scottish mainland and from the Inner Hebrides
The Inner Hebrides (; Scottish Gaelic: ''Na h-Eileanan a-staigh'', "the inner isles") is an archipelago off the west coast of mainland Scotland, to the south east of the Outer Hebrides. Together these two island chains form the Hebrides, whi ...
by the waters of the Minch
The Minch ( gd, An Cuan Sgitheanach, ', ', '), also called North Minch, is a strait in north-west Scotland, separating the north-west Highlands and the northern Inner Hebrides from Lewis and Harris in the Outer Hebrides. It was known as ("S ...
, the Little Minch, and the Sea of the Hebrides. Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic ( gd, Gàidhlig ), also known as Scots Gaelic and Gaelic, is a Goidelic language (in the Celtic branch of the Indo-European language family) native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a Goidelic language, Scottish Gaelic, as well as ...
is the predominant spoken language, although in a few areas English speakers form a majority.
Most of the islands have a bedrock formed from ancient metamorphic
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock (protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, causi ...
rocks, and the climate is mild and oceanic. The 15 inhabited islands have a total population of and there are more than 50 substantial uninhabited islands. The distance from Barra Head
Barra Head, also known as Berneray ( gd, Beàrnaraigh; sco, Barra Heid), is the southernmost island of the Outer Hebrides in Scotland. Within the Outer Hebrides, it forms part of the Barra Isles archipelago. Originally, Barra Head only ...
to the Butt of Lewis is roughly .
There are various important prehistoric structures, many of which pre-date the first written references to the islands by Roman and Greek authors. The Western Isles became part of the Norse kingdom of the ', which lasted for over 400 years, until sovereignty over the Outer Hebrides was transferred to Scotland by the Treaty of Perth in 1266. Control of the islands was then held by clan
A clan is a group of people united by actual or perceived kinship
and descent. Even if lineage details are unknown, clans may claim descent from founding member or apical ancestor. Clans, in indigenous societies, tend to be endogamous, mea ...
chiefs, principal amongst whom were the MacLeods, MacDonalds, Mackenzies and MacNeils. The Highland Clearances
The Highland Clearances ( gd, Fuadaichean nan Gàidheal , the "eviction of the Gaels") were the evictions of a significant number of tenants in the Scottish Highlands and Islands, mostly in two phases from 1750 to 1860.
The first phase result ...
of the 19th century had a devastating effect on many communities, and it is only in recent years that population levels have ceased to decline. Much of the land is now under local control, and commercial activity is based on tourism, crofting
Crofting is a form of land tenure and small-scale food production particular to the Scottish Highlands, the islands of Scotland, and formerly on the Isle of Man.
Within the 19th century townships, individual crofts were established on the bett ...
, fishing, and weaving.
Sea transport is crucial, and a variety of ferry services operate between the islands and to mainland Scotland. Modern navigation systems now minimise the dangers, but in the past the stormy seas have claimed many ships. Religion, music and sport are important aspects of local culture, and there are numerous designated conservation areas to protect the natural environment.
Geography
 The islands form an archipelago whose major islands are
The islands form an archipelago whose major islands are Lewis and Harris
Lewis and Harris ( gd, Leòdhas agus na Hearadh, sco, Lewis an Harris), or Lewis with Harris, is a single Scottish island in the Outer Hebrides, divided by mountains. It is the largest island in Scotland and the third largest in the British ...
, North Uist
North Uist ( gd, Uibhist a Tuath; sco, North Uise) is an island and community in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland.
Etymology
In Donald Munro's ''A Description of the Western Isles of Scotland Called Hybrides'' of 1549, North Uist, Benbecula a ...
, Benbecula
Benbecula (; gd, Beinn nam Fadhla or ) is an island of the Outer Hebrides in the Atlantic Ocean off the west coast of Scotland. In the 2011 census, it had a resident population of 1,283 with a sizable percentage of Roman Catholics. It is in a ...
, South Uist
South Uist ( gd, Uibhist a Deas, ; sco, Sooth Uist) is the second-largest island of the Outer Hebrides in Scotland. At the 2011 census, it had a usually resident population of 1,754: a decrease of 64 since 2001. The island, in common with the ...
, and Barra. Lewis and Harris has an area of Haswell-Smith (2004) p. 289 and is the largest island in Scotland and the third-largest in the British Isles
The British Isles are a group of islands in the North Atlantic Ocean off the north-western coast of continental Europe, consisting of the islands of Great Britain, Ireland, the Isle of Man, the Inner and Outer Hebrides, the Northern Isl ...
, after Great Britain and Ireland. It incorporates Lewis
Lewis may refer to:
Names
* Lewis (given name), including a list of people with the given name
* Lewis (surname), including a list of people with the surname
Music
* Lewis (musician), Canadian singer
* "Lewis (Mistreated)", a song by Radiohead ...
in the north and Harris in the south, both of which are frequently referred to as individual islands, although they are connected by land. The island does not have a single name in either English or Gaelic, and is referred to as "Lewis and Harris", "Lewis with Harris", "Harris with Lewis" etc.Thompson (1968) p. 13
The largest islands are deeply indented by arms of the sea such as Loch Ròg, Loch Seaforth and Loch nam Madadh. There are also more than 7,500 freshwater lochs in the Outer Hebrides, about 24% of the total for the whole of Scotland."Botanical survey of Scottish freshwater lochs"SNH Information and Advisory Note Number 4. Retrieved 1 January 2010. North and South Uist and Lewis, in particular, have landscapes with a high percentage of fresh water and a maze and complexity of loch shapes. Harris has fewer large bodies of water but has innumerable small lochans. Loch Langavat on Lewis is long, and has several large islands in its midst, including Eilean Mòr. Although Loch Suaineabhal has only 25% of Loch Langavat's surface area, it has a mean depth of and is the most voluminous on the island. Of
Loch Sgadabhagh
Loch Sgadabhagh or Loch Scadavay is a body of water on the island of North Uist, Scotland. The name may be of Old Norse derivation meaning "lake of tax bay" although if so, the reason is obscure. Loch Sgadabhagh is the largest loch by area on No ...
on North Uist
North Uist ( gd, Uibhist a Tuath; sco, North Uise) is an island and community in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland.
Etymology
In Donald Munro's ''A Description of the Western Isles of Scotland Called Hybrides'' of 1549, North Uist, Benbecula a ...
it has been said that "there is probably no other loch in Britain which approaches Loch Scadavay in irregularity and complexity of outline." Loch Bì is South Uist's largest loch and at long it all but cuts the island in two.
Much of the western coastline of the islands is machair, a fertile low-lying dune pastureland. Lewis is comparatively flat, and largely consists of treeless moors of blanket peat
Peat (), also known as turf (), is an accumulation of partially Decomposition, decayed vegetation or organic matter. It is unique to natural areas called peatlands, bogs, mires, Moorland, moors, or muskegs. The peatland ecosystem covers and ...
. The highest eminence is Mealisval at in the south west. Most of Harris is mountainous, with large areas of exposed rock and Clisham, the archipelago's only Corbett Corbett may refer to:
* List of Corbetts (mountains), 222 mountains in Scotland between , with prominence over
* Corbett, Oregon, a community in the United States
* Corbett Award, US award for athletics administrators
* Corbett (surname), people ...
, reaches in height. North and South Uist and Benbecula (sometimes collectively referred to as The Uists) have sandy beaches and wide cultivated areas of machair to the west and virtually uninhabited mountainous areas to the east. The highest peak here is Beinn Mhòr at . The Uists and their immediate outliers have a combined area of . This includes the Uists themselves and the islands linked to them by causeways and bridges. Barra is in extent and has a rugged interior, surrounded by machair and extensive beaches.
The scenic qualities of the islands are reflected in the fact that three of Scotland's forty national scenic areas
National may refer to:
Common uses
* Nation or country
** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen
Places in the United States
* National, Maryland, ...
(NSAs) are located here. The national scenic areas are defined so as to identify areas of exceptional scenery and to ensure its protection from inappropriate development, and are considered to represent the type of scenic beauty "popularly associated with Scotland and for which it is renowned". The three NSA within the Outer Hebrides are:
*South Lewis, Harris and North Uist National Scenic Area
South Lewis, Harris and North Uist is a large national scenic area (NSA) in the Western Isles of Scotland. It is one of 40 such areas in Scotland, which are defined so as to identify areas of exceptional scenery and to ensure its protection fr ...
covers the mountainous south west of Lewis
Lewis may refer to:
Names
* Lewis (given name), including a list of people with the given name
* Lewis (surname), including a list of people with the surname
Music
* Lewis (musician), Canadian singer
* "Lewis (Mistreated)", a song by Radiohead ...
, all of Harris, the Sound of Harris
The Sound of Harris ( gd, Caolas na Hearadh) is a channel between the islands of Harris and North Uist in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland.
Geography
Approximately in width, the Sound of Harris provides the main sea passage through the Hebridean ...
and the northern part of North Uist
North Uist ( gd, Uibhist a Tuath; sco, North Uise) is an island and community in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland.
Etymology
In Donald Munro's ''A Description of the Western Isles of Scotland Called Hybrides'' of 1549, North Uist, Benbecula a ...
.
*An area of the south west coast of South Uist
South Uist ( gd, Uibhist a Deas, ; sco, Sooth Uist) is the second-largest island of the Outer Hebrides in Scotland. At the 2011 census, it had a usually resident population of 1,754: a decrease of 64 since 2001. The island, in common with the ...
is designated as the ''South Uist Machair National Scenic Area''.
*The archipelago of St Kilda is also listed as an NSA, alongside many other conservation designations.
Flora and fauna

 Much of the archipelago is a protected habitat, including both the islands and the surrounding waters. There are 53
Much of the archipelago is a protected habitat, including both the islands and the surrounding waters. There are 53 Sites of Special Scientific Interest
A Site of Special Scientific Interest (SSSI) in Great Britain or an Area of Special Scientific Interest (ASSI) in the Isle of Man and Northern Ireland is a conservation designation denoting a protected area in the United Kingdom and Isle of ...
of which the largest are Loch an Duin, North Uist () and North Harris (). South Uist
South Uist ( gd, Uibhist a Deas, ; sco, Sooth Uist) is the second-largest island of the Outer Hebrides in Scotland. At the 2011 census, it had a usually resident population of 1,754: a decrease of 64 since 2001. The island, in common with the ...
is considered the best place in the UK for the aquatic plant Slender Naiad, which is a European Protected Species European Protected Species (EPS) are species of plants and animals (other than birds) protected by law throughout the European Union. They are listed in Annexes II and IV of the European Habitats Directive.
The lists include several hundred species ...
.
There has been considerable controversy over hedgehog
A hedgehog is a spiny mammal of the subfamily Erinaceinae, in the eulipotyphlan family Erinaceidae. There are seventeen species of hedgehog in five genera found throughout parts of Europe, Asia, and Africa, and in New Zealand by introductio ...
s on the Uists. Hedgehogs are not native to the islands but were introduced in the 1970s to reduce garden pests. Their spread posed a threat to the eggs of ground-nesting wading birds. In 2003 Scottish Natural Heritage undertook culls of hedgehogs in the area, but these were halted in 2007; trapped animals are now relocated to the mainland.
Nationally important populations of breeding waders are present in the Outer Hebrides, including common redshank
The common redshank or simply redshank (''Tringa totanus'') is a Eurasian wader in the large family Scolopacidae.
Taxonomy
The common redshank was formally described by the Swedish naturalist Carl Linnaeus in 1758 in the tenth edition of his ...
, dunlin
The dunlin (''Calidris alpina'') is a small wader, formerly sometimes separated with the other "stints" in the genus ''Erolia''. The English name is a dialect form of "dunling", first recorded in 1531–1532. It derives from ''dun'', "dull brow ...
, lapwing and ringed plover
The common ringed plover or ringed plover (''Charadrius hiaticula'') is a small plover that breeds in Arctic Eurasia. The genus name ''Charadrius'' is a Late Latin word for a yellowish bird mentioned in the fourth-century Vulgate. It derives fr ...
. The islands also provide a habitat for other important species such as corncrake
The corn crake, corncrake or landrail (''Crex crex'') is a bird in the rail family. It breeds in Europe and Asia as far east as western China, and migrates to Africa for the Northern Hemisphere's winter. It is a medium-sized crake with buff- ...
, hen harrier
The hen harrier (''Circus cyaneus'') is a bird of prey. It breeds in Eurasia. The term "hen harrier" refers to its former habit of preying on free-ranging fowl.
It migrates to more southerly areas in winter. Eurasian birds move to southern Eur ...
, golden eagle
The golden eagle (''Aquila chrysaetos'') is a bird of prey living in the Northern Hemisphere. It is the most widely distributed species of eagle. Like all eagles, it belongs to the family Accipitridae. They are one of the best-known bird ...
and otter
Otters are carnivorous mammals in the subfamily Lutrinae. The 13 extant otter species are all semiaquatic, aquatic, or marine, with diets based on fish and invertebrates. Lutrinae is a branch of the Mustelidae family, which also includes we ...
. Offshore, basking shark and various species of whale and dolphin can often be seen, and the remoter islands' seabird populations are of international significance. St Kilda has 60,000 northern gannet
The northern gannet (''Morus bassanus'') is a seabird, the largest species of the gannet family, Sulidae. It is native to the coasts of the Atlantic Ocean, breeding in Western Europe and Northeastern North America. It is the largest seabird in t ...
s, amounting to 24% of the world population; 49,000 breeding pairs of Leach's petrel, up to 90% of the European population; and 136,000 pairs of puffin
Puffins are any of three species of small alcids (auks) in the bird genus ''Fratercula''. These are pelagic seabirds that feed primarily by diving in the water. They breed in large colonies on coastal cliffs or offshore islands, nesting in crev ...
and 67,000 northern fulmar
The northern fulmar (''Fulmarus glacialis''), fulmar, or Arctic fulmar is a highly abundant seabird found primarily in subarctic regions of the North Atlantic and North Pacific oceans. There has been one confirmed sighting in the Southern Hem ...
pairs, about 30% and 13% of the respective UK totals. Mingulay is an important breeding ground for razorbill
The razorbill, razor-billed auk, or lesser auk (''Alca torda'') is a colonial seabird and the only extant member of the genus '' Alca'' of the family Alcidae, the auks. It is the closest living relative of the extinct great auk (''Pinguinis im ...
s, with 9,514 pairs, 6.3% of the European population.
The bumblebee
A bumblebee (or bumble bee, bumble-bee, or humble-bee) is any of over 250 species in the genus ''Bombus'', part of Apidae, one of the bee families. This genus is the only Extant taxon, extant group in the tribe Bombini, though a few extinct r ...
''Bombus jonellus'' var. ''hebridensis'' is endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found else ...
to the Hebrides and there are local variants of the dark green fritillary and green-veined white butterflies. The St Kilda wren is a subspecies of wren
Wrens are a family of brown passerine birds in the predominantly New World family Troglodytidae. The family includes 88 species divided into 19 genera. Only the Eurasian wren occurs in the Old World, where, in Anglophone regions, it is commonl ...
whose range is confined to the islands whose name it bears.
Population
 The islands' total population was 26,502 at the 2001 census, and the 2011 figure was 27,684. During the same period
The islands' total population was 26,502 at the 2001 census, and the 2011 figure was 27,684. During the same period Scottish island
This is a list of islands of Scotland, the mainland of which is part of the island of Great Britain. Also included are various other related tables and lists. The definition of an offshore island used in this list is "land that is surrounded by ...
populations as a whole grew by 4% to 103,702. The largest settlement in the Outer Hebrides is Stornoway
Stornoway (; gd, Steòrnabhagh; sco, Stornowa) is the main town of the Western Isles and the capital of Lewis and Harris in Scotland.
The town's population is around 6,953, making it by far the largest town in the Outer Hebrides, as well ...
on Lewis,"Factfile:Population". . Retrieved 20 July 2013. which has a population of about 8,100. The population estimate for 2019 was 26,720 according to a Comhairle nan Eilean Siar report which added that "the population of the Outer Hebrides is ageing" and that "young adults ..leave the islands for further education or employment purposes". Of the total population, 6,953 people reside in the "Stornoway settlement Laxdale (Lacasdal), Sandwick (Sanndabhaig) and Newmarket" with the balance distributed over 280 townships. In addition to the major North Ford (') and South Ford causeways that connect North Uist to Benbecula via the northern of the Grimsays, and another causeway from Benbecula to South Uist, several other islands are linked by smaller causeways or bridges. Great Bernera and Scalpay have bridge connections to Lewis and Harris respectively, with causeways linking Baleshare and Berneray to North Uist; Eriskay to South Uist; , and the southern Grimsay to Benbecula; and
Vatersay
The island of Vatersay (; gd, Bhatarsaigh) is the southernmost and westernmost inhabited island in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland, and the settlement of Caolas on the north coast of the island is the westernmost permanently inhabited place in ...
to Barra."Get-a-map"Ordnance Survey
Ordnance Survey (OS) is the national mapping agency for Great Britain. The agency's name indicates its original military purpose (see ordnance and surveying), which was to map Scotland in the wake of the Jacobite rising of 1745. There was a ...
. Retrieved 1–15 August 2009."Fleet Histories"Caledonian MacBrayne
Caledonian MacBrayne ( gd, Caledonian Mac a' Bhriuthainn), usually shortened to CalMac, is the major operator of passenger and vehicle ferries, and ferry services, between the mainland of Scotland and 22 of the major islands on Scotland's west ...
. Retrieved 3 August 2009. This means that all the inhabited islands are now connected to at least one other island by a land transport route.

Uninhabited islands
 There are more than fifty uninhabited islands greater in size than in the Outer Hebrides, including the
There are more than fifty uninhabited islands greater in size than in the Outer Hebrides, including the Barra Isles
The Barra Isles, also known as the Bishop's Isles, are a small archipelago in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland. They lie south of the island of Barra, for which they are named. The group consists of nine islands and numerous rocky islets, skerri ...
, Flannan Isles
The Flannan Isles ( gd, Na h-Eileanan Flannach) or alternatively, the Seven Hunters are a small island group in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland, approximately west of the Isle of Lewis. They may take their name from Saint Flannan, the 7th centur ...
, Monach Islands, the Shiant Islands and the islands of . In common with the other main island chains of Scotland, many of the more remote islands were abandoned during the 19th and 20th centuries, in some cases after continuous habitation since the prehistoric period. More than 35 such islands have been identified in the Outer Hebrides alone. On Barra Head, for example, Historic Scotland
Historic Scotland ( gd, Alba Aosmhor) was an executive agency of the Scottish Office and later the Scottish Government from 1991 to 2015, responsible for safeguarding Scotland's built heritage, and promoting its understanding and enjoyment ...
have identified eighty-three archaeological sites on the island, the majority being of a pre-medieval date. In the 18th century, the population was over fifty, but the last native islanders had left by 1931. The island became completely uninhabited by 1980 with the automation of the lighthouse.
Some of the smaller islands continue to contribute to modern culture. The "Mingulay Boat Song
The "Mingulay Boat Song" is a song written by Sir Hugh S. Roberton (1874–1952) in the 1930s. The melody is described in Roberton's ''Songs of the Isles'' as a traditional Gaelic tune, probably titled "Lochaber". The tune was part of an old Gaeli ...
", although evocative of island life, was written after the abandonment of the island in 1938 and Taransay hosted the BBC television series '' Castaway 2000''. Others have played a part in Scottish history. On 4 May 1746, the "Young Pretender" Charles Edward Stuart
Charles Edward Louis John Sylvester Maria Casimir Stuart (20 December 1720 – 30 January 1788) was the elder son of James Francis Edward Stuart, grandson of James II and VII, and the Stuart claimant to the thrones of England, Scotland and ...
hid on with some of his men for four days whilst Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Fr ...
vessels patrolled the Minch.
Smaller isles and skerries and other island groups pepper the North Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe a ...
surrounding the main islands. Some are not geologically part of the Outer Hebrides, but are administratively and in most cases culturally, part of . to the west of Lewis lies St Kilda, now uninhabited except for a small military base. A similar distance to the north of Lewis are North Rona
Rona ( gd, Rònaigh) is a remote, uninhabited Scottish island in the North Atlantic. Rona is often referred to as North Rona to distinguish it from South Rona (another small island, in the Inner Hebrides). It has an area of and a maximum elevat ...
and , two small and remote islands. While Rona used to support a small population who grew grain and raised cattle, is an inhospitable rock. Thousands of northern gannet
The northern gannet (''Morus bassanus'') is a seabird, the largest species of the gannet family, Sulidae. It is native to the coasts of the Atlantic Ocean, breeding in Western Europe and Northeastern North America. It is the largest seabird in t ...
s nest here, and by special arrangement some of their young, known as ', are harvested annually by the men of Ness
Ness or NESS may refer to:
Places Australia
* Ness, Wapengo, a heritage-listed natural coastal area in New South Wales
United Kingdom
* Ness, Cheshire, England, a village
* Ness, Lewis, the most northerly area on Lewis, Scotland, UK
* Cuspat ...
. The status of Rockall
Rockall () is an uninhabitable granite islet situated in the North Atlantic Ocean. The United Kingdom claims that Rockall lies within its exclusive economic zone (EEZ) and is part of its territory, but this claim is not recognised by Ireland ...
, which is to the west of North Uist and which the Island of Rockall Act 1972
The Island of Rockall Act 1972 (c. 2) is a British Act of Parliament formally incorporating the island of Rockall into the United Kingdom to protect it from Irish and Icelandic claims. The Act as originally passed declared that the Island of Roc ...
decreed to be a part of the Western Isles, remains a matter of international dispute.
Geology
 Most of the islands have a bedrock formed from
Most of the islands have a bedrock formed from Lewisian gneiss
The Lewisian complex or Lewisian gneiss is a suite of Precambrian metamorphic rocks that outcrop in the northwestern part of Scotland, forming part of the Hebridean Terrane and the North Atlantic Craton. These rocks are of Archaean and Pale ...
. These are amongst the oldest rocks in Europe, having been formed in the Precambrian
The Precambrian (or Pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pꞒ, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of th ...
period up to three billion years ago. In addition to the Outer Hebrides, they form basement deposits on the Scottish mainland west of the Moine Thrust
The Moine Thrust Belt or Moine Thrust Zone is a linear tectonic feature in the Scottish Highlands which runs from Loch Eriboll on the north coast south-west to the Sleat peninsula on the Isle of Skye. The thrust belt consists of a series of ...
and on the islands of Coll
Coll (; gd, Cola; sco, Coll)Mac an Tàilleir (2003) p. 31 is an island located west of the Isle of Mull in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. Coll is known for its sandy beaches, which rise to form large sand dunes, for its corncrakes, and for ...
and Tiree
Tiree (; gd, Tiriodh, ) is the most westerly island in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. The low-lying island, southwest of Coll, has an area of and a population of around 650.
The land is highly fertile, and crofting, alongside tourism, ...
. These rocks are largely igneous in origin, mixed with metamorphosed marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or dolomite. Marble is typically not foliated (layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the term ''marble'' refers to metamorphose ...
, quartzite
Quartzite is a hard, non- foliated metamorphic rock which was originally pure quartz sandstone.Essentials of Geology, 3rd Edition, Stephen Marshak, p 182 Sandstone is converted into quartzite through heating and pressure usually related to tec ...
and mica schist and intruded by later basaltic dykes and granite magma. The gneiss's delicate pink colours are exposed throughout the islands and it is sometimes referred to by geologists as "The Old Boy".Murray (1966) p. 2
Granite intrusions are found in the parish of Barvas
Barvas (Scottish Gaelic: ''Barabhas'' or ''Barbhas'', ) is a settlement, community and civil parish on the Isle of Lewis in Scotland. It developed around a road junction. The A857 and A858 meet at the southern end of Barvas. North is the road ...
in west Lewis, and another forms the summit plateau of the mountain Roineabhal in Harris. The granite here is anorthosite
Anorthosite () is a phaneritic, intrusive igneous rock characterized by its composition: mostly plagioclase feldspar (90–100%), with a minimal mafic component (0–10%). Pyroxene, ilmenite, magnetite, and olivine are the mafic minerals most ...
, and is similar in composition to rocks found in the mountains of the Moon
The Moon is Earth's only natural satellite. It is the fifth largest satellite in the Solar System and the largest and most massive relative to its parent planet, with a diameter about one-quarter that of Earth (comparable to the width of ...
. There are relatively small outcrops of Triassic
The Triassic ( ) is a geologic period and system which spans 50.6 million years from the end of the Permian Period 251.902 million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Jurassic Period 201.36 Mya. The Triassic is the first and shortest per ...
sandstone at Broad Bay near Stornoway. The Shiant Islands and St Kilda are formed from much later tertiary basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90 ...
and basalt and gabbro
Gabbro () is a phaneritic (coarse-grained), mafic intrusive igneous rock formed from the slow cooling of magnesium-rich and iron-rich magma into a holocrystalline mass deep beneath the Earth's surface. Slow-cooling, coarse-grained gabbro is ...
s respectively. The sandstone at Broad Bay was once thought to be Torridonian or Old Red Sandstone
The Old Red Sandstone is an assemblage of rocks in the North Atlantic region largely of Devonian age. It extends in the east across Great Britain, Ireland and Norway, and in the west along the northeastern seaboard of North America. It also exte ...
.
Climate
The Outer Hebrides have a cool temperate climate that is remarkably mild and steady for such a northerlylatitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north ...
, due to the influence of the North Atlantic Current
The North Atlantic Current (NAC), also known as North Atlantic Drift and North Atlantic Sea Movement, is a powerful warm western boundary current within the Atlantic Ocean that extends the Gulf Stream northeastward.
The NAC originates from where ...
. The average temperature for the year is 6 °C (44 °F) in January and 14 °C (57 °F) in summer. The average annual rainfall in Lewis is and sunshine hours range from 1,100 to 1,200 per year. The summer days are relatively long and May to August is the driest period. Winds are a key feature of the climate and even in summer there are almost constant breezes. According to the writer W. H. Murray
William Hutchison Murray (18 March 1913 – 19 March 1996) was a Scottish mountaineer and writer, one of a group of active mountain climbers, mainly from Clydeside, before and just after World War II.
Life
Murray was born in Liverpool, the son ...
if a visitor asks an islander for a weather forecast "he will not, like a mainlander answer dry, wet or sunny, but quote you a figure from the Beaufort Scale
The Beaufort scale is an empirical measure that relates wind speed to observed conditions at sea or on land. Its full name is the Beaufort wind force scale.
History
The scale was devised in 1805 by the Irish hydrographer Francis Beaufort ...
." There are gales one day in six at the Butt of Lewis and small fish are blown onto the grass on top of 190 metre (620 ft) high cliffs at Barra Head
Barra Head, also known as Berneray ( gd, Beàrnaraigh; sco, Barra Heid), is the southernmost island of the Outer Hebrides in Scotland. Within the Outer Hebrides, it forms part of the Barra Isles archipelago. Originally, Barra Head only ...
during winter storms.
Prehistory
 The Hebrides were originally settled in the
The Hebrides were originally settled in the Mesolithic era
The Mesolithic (Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymousl ...
and have a diversity of important prehistoric
Prehistory, also known as pre-literary history, is the period of human history between the use of the first stone tools by hominins 3.3 million years ago and the beginning of recorded history with the invention of writing systems. The us ...
sites. in on North Uist
North Uist ( gd, Uibhist a Tuath; sco, North Uise) is an island and community in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland.
Etymology
In Donald Munro's ''A Description of the Western Isles of Scotland Called Hybrides'' of 1549, North Uist, Benbecula a ...
was constructed around 3200–2800 BC and may be Scotland's earliest crannog (a type of artificial island). The Callanish Stones
The Callanish Stones (or "Callanish I": gd, Clachan Chalanais or ) are an arrangement of standing stones placed in a cruciform pattern with a central stone circle. They were erected in the late Neolithic era, and were a focus for ritual activ ...
, dating from about 2900 BC, are the finest example of a stone circle
A stone circle is a ring of standing stones. Most are found in Northwestern Europe – especially in Britain, Ireland, and Brittany – and typically date from the Late Neolithic and Early Bronze Age, with most being built from 3000 BC. The ...
in Scotland, the 13 primary monolith
A monolith is a geological feature consisting of a single massive stone or rock, such as some mountains. For instance, Savandurga mountain is a monolith mountain in India. Erosion usually exposes the geological formations, which are often ma ...
s of between one and five metres high creating a circle about in diameter. on South Uist
South Uist ( gd, Uibhist a Deas, ; sco, Sooth Uist) is the second-largest island of the Outer Hebrides in Scotland. At the 2011 census, it had a usually resident population of 1,754: a decrease of 64 since 2001. The island, in common with the ...
, the only site in the UK where prehistoric mummies
A mummy is a dead human or an animal whose soft tissues and organs have been preserved by either intentional or accidental exposure to chemicals, extreme cold, very low humidity, or lack of air, so that the recovered body does not decay furt ...
have been found, and the impressive ruins of Dun Carloway on Lewis both date from the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly ...
.
Etymology
 The earliest written references that have survived relating to the islands were made by
The earliest written references that have survived relating to the islands were made by Pliny the Elder
Gaius Plinius Secundus (AD 23/2479), called Pliny the Elder (), was a Roman author, naturalist and natural philosopher, and naval and army commander of the early Roman Empire, and a friend of the emperor Vespasian. He wrote the encyclopedic ' ...
in his ''Natural History'', where he states that there are 30 ', and makes a separate reference to ''Dumna'', which Watson (1926) concludes is unequivocally the Outer Hebrides. Writing about 80 years later, in 140–150 AD, Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
, drawing on the earlier naval expeditions of , also distinguished between the ', of which he writes there were only five (and thus possibly meaning the Inner Hebrides
The Inner Hebrides (; Scottish Gaelic: ''Na h-Eileanan a-staigh'', "the inner isles") is an archipelago off the west coast of mainland Scotland, to the south east of the Outer Hebrides. Together these two island chains form the Hebrides, whi ...
) and .Breeze, David J. "The ancient geography of Scotland" in Smith and Banks (2002) pp. 11–13Watson (1926) pp. 40–41 ' is cognate with the Early Celtic ''dumnos'' and means the "deep-sea isle". Pliny probably took his information from Pytheas
Pytheas of Massalia (; Ancient Greek: Πυθέας ὁ Μασσαλιώτης ''Pythéas ho Massaliōtēs''; Latin: ''Pytheas Massiliensis''; born 350 BC, 320–306 BC) was a Greek geographer, explorer and astronomer from the Greek colony ...
of Massilia who visited Britain sometime between 322 and 285 BC. It is possible that Ptolemy did as well, as Agricola's information about the west coast of Scotland was of poor quality. Breeze also suggests that might be Lewis and Harris
Lewis and Harris ( gd, Leòdhas agus na Hearadh, sco, Lewis an Harris), or Lewis with Harris, is a single Scottish island in the Outer Hebrides, divided by mountains. It is the largest island in Scotland and the third largest in the British ...
, the largest island of the Outer Hebrides although he conflates this single island with the name "Long Island". Watson (1926) states that the meaning of Ptolemy's ' is unknown and that the root may be pre-Celtic. Murray (1966) claims that Ptolemy's ' was originally derived from the Old Norse
Old Norse, Old Nordic, or Old Scandinavian, is a stage of development of North Germanic dialects before their final divergence into separate Nordic languages. Old Norse was spoken by inhabitants of Scandinavia and their overseas settlement ...
', meaning "isles on the edge of the sea". This idea is often repeated but no firm evidence of this derivation has emerged.
Other early written references include the flight of the Nemed people from Ireland to ''Domon'', which is mentioned in the 12th-century ' and a 13th-century poem concerning , then the heir to the throne of Mann and the Isles, who is said to have "broken the gate of '". ' means "the plain of Domhna (or Domon)", but the precise meaning of the text is not clear.
In Irish mythology
Irish mythology is the body of myths native to the island of Ireland. It was originally oral tradition, passed down orally in the Prehistoric Ireland, prehistoric era, being part of ancient Celtic religion. Many myths were later Early Irish ...
the islands were the home of the Fomorians, described as "huge and ugly" and "ship men of the sea". They were pirates, extracting tribute from the coasts of Ireland and one of their kings was (i.e. Indech, son of the goddess Domnu, who ruled over the deep seas).
In modern Gaelic the islands are sometimes referred to collectively as ' (the Long Island) or ' (the Outer Isles). ' (islands of the foreigners or strangers) is also heard occasionally, a name that was originally used by mainland Highlanders when the islands were ruled by the Norse.
The individual island and place names in the Outer Hebrides have mixed Gaelic and Norse origins. Various Gaelic terms are used repeatedly:Mac an Tàilleir (2003) various pages.
There are also several islands called ' from the Norse ' meaning "tidal" or "ebb island".
History
In Scotland, the CelticIron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly ...
way of life, often troubled but never extinguished by Rome, re-asserted itself when the legions abandoned any permanent occupation in 211 AD. Hanson (2003) writes: "For many years it has been almost axiomatic in studies of the period that the Roman conquest must have had some major medium or long-term impact on Scotland. On present evidence that cannot be substantiated either in terms of environment, economy, or, indeed, society. The impact appears to have been very limited. The general picture remains one of broad continuity, not of disruption ... The Roman presence in Scotland was little more than a series of brief interludes within a longer continuum of indigenous development." The Romans' direct impact on the Highlands and Islands was scant and there is no evidence that they ever actually landed in the Outer Hebrides.
The later Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly ...
inhabitants of the northern and western Hebrides were probably Pictish, although the historical record is sparse. Hunter (2000) states that in relation to King Bridei I of the Picts in the sixth century AD: "As for Shetland, Orkney, Skye and the Western Isles, their inhabitants, most of whom appear to have been Pictish in culture and speech at this time, are likely to have regarded Bridei as a fairly distant presence." The island of Pabbay is the site of the Pabbay Stone, the only extant Pictish symbol stone
A Pictish stone is a type of monumental stele, generally carved or incised with symbols or designs. A few have ogham inscriptions. Located in Scotland, mostly north of the Clyde-Forth line and on the Eastern side of the country, these stones a ...
in the Outer Hebrides. This 6th century stele
A stele ( ),Anglicized plural steles ( ); Greek plural stelai ( ), from Greek language, Greek , ''stēlē''. The Greek plural is written , ''stēlai'', but this is only rarely encountered in English. or occasionally stela (plural ''stelas'' or ...
shows a flower, V-rod and lunar crescent to which has been added a later and somewhat crude cross.
Norse control
Viking
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
raids began on Scottish shores towards the end of the 8th century AD and the Hebrides came under Norse control and settlement during the ensuing decades, especially following the success of Harald Fairhair
Harald Fairhair no, Harald hårfagre Modern Icelandic: ( – ) was a Norwegian king. According to traditions current in Norway and Iceland in the eleventh and twelfth centuries, he reigned from 872 to 930 and was the first King of No ...
at the Battle of Hafrsfjord
The Battle of Hafrsfjord ( no, Slaget i Hafrsfjord) was a great naval battle fought in Hafrsfjord sometime between 872 and 900 that resulted in the unification of Norway, later known as the Kingdom of Norway. After the battle, the victorious Vikin ...
in 872. In the Western Isles Ketill Flatnose was the dominant figure of the mid 9th century, by which time he had amassed a substantial island realm and made a variety of alliances with other Norse leaders. These princelings nominally owed allegiance to the Norwegian crown, although in practice the latter's control was fairly limited. Norse control of the Hebrides was formalised in 1098 when Edgar, King of Scotland formally signed the islands over to Magnus III of Norway
Magnus Olafsson (Old Norse: ''Magnús Óláfsson'', Norwegian: ''Magnus Olavsson''; 1073 – 24 August 1103), better known as Magnus Barefoot (Old Norse: ''Magnús berfœttr'', Norwegian: ''Magnus Berrføtt''), was King of Norway (being Ma ...
.Hunter (2000) p. 102 The Scottish acceptance of Magnus III as King of the Isles came after the Norwegian king had conquered Orkney
Orkney (; sco, Orkney; on, Orkneyjar; nrn, Orknøjar), also known as the Orkney Islands, is an archipelago in the Northern Isles of Scotland, situated off the north coast of the island of Great Britain. Orkney is 10 miles (16 km) north ...
, the Hebrides and the Isle of Man
)
, anthem = " O Land of Our Birth"
, image = Isle of Man by Sentinel-2.jpg
, image_map = Europe-Isle_of_Man.svg
, mapsize =
, map_alt = Location of the Isle of Man in Europe
, map_caption = Location of the Isle of Man (green)
in Europ ...
in a swift campaign earlier the same year, directed against the local Norwegian leaders of the various islands‘ petty kingdoms. By capturing the islands Magnus imposed a more direct royal control, although at a price. His skald
A skald, or skáld (Old Norse: , later ; , meaning "poet"), is one of the often named poets who composed skaldic poetry, one of the two kinds of Old Norse poetry, the other being Eddic poetry, which is anonymous. Skaldic poems were traditional ...
Bjorn Cripplehand recorded that in Lewis "fire played high in the heaven" as "flame spouted from the houses" and that in the Uists "the king dyed his sword red in blood". Thompson (1968) provides a more literal translation: "Fire played in the fig-trees of Liodhus; it mounted up to heaven. Far and wide the people were driven to flight. The fire gushed out of the houses".Thompson (1968) p 39
The Hebrides were now part of Kingdom of the Isles, whose rulers were themselves vassals of the Kings of Norway. The Kingdom had two parts: the ' or South Isles encompassing the Hebrides
The Hebrides (; gd, Innse Gall, ; non, Suðreyjar, "southern isles") are an archipelago off the west coast of the Scottish mainland. The islands fall into two main groups, based on their proximity to the mainland: the Inner and Outer Hebri ...
and the Isle of Man
)
, anthem = " O Land of Our Birth"
, image = Isle of Man by Sentinel-2.jpg
, image_map = Europe-Isle_of_Man.svg
, mapsize =
, map_alt = Location of the Isle of Man in Europe
, map_caption = Location of the Isle of Man (green)
in Europ ...
; and the ' or North Isles of Orkney and Shetland
Shetland, also called the Shetland Islands and formerly Zetland, is a subarctic archipelago in Scotland lying between Orkney, the Faroe Islands and Norway. It is the northernmost region of the United Kingdom.
The islands lie about to the n ...
. This situation lasted until the partitioning of the Western Isles in 1156, at which time the Outer Hebrides remained under Norwegian control while the Inner Hebrides broke out under Somerled
Somerled (died 1164), known in Middle Irish as Somairle, Somhairle, and Somhairlidh, and in Old Norse as Sumarliði , was a mid-12th-century Norse-Gaelic lord who, through marital alliance and military conquest, rose in prominence to create the ...
, the Norse-Celtic kinsman of the Manx royal house.
Following the ill-fated 1263 expedition of Haakon IV of Norway
Haakon IV Haakonsson ( – 16 December 1263; Old Norse: ''Hákon Hákonarson'' ; Norwegian: ''Håkon Håkonsson''), sometimes called Haakon the Old in contrast to his namesake son, was King of Norway from 1217 to 1263. His reign lasted for 46 ...
, the Outer Hebrides along with the Isle of Man, were yielded to the Kingdom of Scotland a result of the 1266 Treaty of Perth. Although their contribution to the islands can still be found in personal and placenames, the archaeological record of the Norse period is very limited. The best known find from this time is the Lewis chessmen
The Lewis chessmen ( no, Lewisbrikkene; gd, Fir-Tàilisg; sco, Lewis chesmen) or Uig chessmen, named after the island or the bay where they were found, are a group of distinctive 12th-century chess pieces, along with other game pieces, most of ...
, which date from the mid 12th century.
Scots rule
 As the Norse era drew to a close the Norse-speaking princes were gradually replaced by Gaelic-speaking
As the Norse era drew to a close the Norse-speaking princes were gradually replaced by Gaelic-speaking clan
A clan is a group of people united by actual or perceived kinship
and descent. Even if lineage details are unknown, clans may claim descent from founding member or apical ancestor. Clans, in indigenous societies, tend to be endogamous, mea ...
chiefs including the MacLeods of Lewis and Harris, the MacDonalds of the Uist
"Uist" is a group of six islands and are part of the Outer Hebridean Archipelago, part of the Outer Hebrides of Scotland.
North Uist and South Uist ( or ; gd, Uibhist ) are two of the islands and are linked by causeways running via the isles ...
s and MacNeil of Barra. This transition did little to relieve the islands of internecine strife although by the early 14th century the MacDonald Lords of the Isles
The Lord of the Isles or King of the Isles
( gd, Triath nan Eilean or ) is a title of Scottish nobility with historical roots that go back beyond the Kingdom of Scotland. It began with Somerled in the 12th century and thereafter the title w ...
, based on Islay
Islay ( ; gd, Ìle, sco, Ila) is the southernmost island of the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. Known as "The Queen of the Hebrides", it lies in Argyll just south west of Jura and around north of the Northern Irish coast. The island's capital ...
, were in theory these chiefs' feudal superiors and managed to exert some control.
The growing threat that Clan Donald posed to the Scottish crown led to the forcible dissolution of the Lordship of the Isles by James IV
James IV (17 March 1473 – 9 September 1513) was King of Scotland from 11 June 1488 until his death at the Battle of Flodden in 1513. He inherited the throne at the age of fifteen on the death of his father, James III, at the Battle of Sauch ...
in 1493, but although the king had the power to subdue the organised military might of the Hebrides, he and his immediate successors lacked the will or ability to provide an alternative form of governance. The House of Stuart
The House of Stuart, originally spelt Stewart, was a royal house of Scotland, England, Ireland and later Great Britain. The family name comes from the office of High Steward of Scotland, which had been held by the family progenitor Walter fi ...
's attempts to control the Outer Hebrides were then at first desultory and little more than punitive expeditions. In 1506 the Earl of Huntly besieged and captured Stornoway Castle using cannon. In 1540 James V
James V (10 April 1512 – 14 December 1542) was King of Scotland from 9 September 1513 until his death in 1542. He was crowned on 21 September 1513 at the age of seventeen months. James was the son of King James IV and Margaret Tudor, and du ...
himself conducted a royal tour, forcing the clan chiefs to accompany him. There followed a period of peace, but all too soon the clans were at loggerheads again.
In 1598 King James VI
James is a common English language surname and given name:
*James (name), the typically masculine first name James
* James (surname), various people with the last name James
James or James City may also refer to:
People
* King James (disambiguat ...
authorised some " Gentleman Adventurers" from Fife to civilise the "most barbarous Isle of Lewis". Initially successful, the colonists were driven out by local forces commanded by Murdoch and Neil MacLeod, who based their forces on in . The colonists tried again in 1605 with the same result but a third attempt in 1607 was more successful, and in due course Stornoway became a Burgh of Barony
A burgh of barony was a type of Scottish town ( burgh).
Burghs of barony were distinct from royal burghs, as the title was granted to a landowner who, as a tenant-in-chief, held his estates directly from the crown. (In some cases, they might also ...
. By this time Lewis was held by the Mackenzies of Kintail, (later the Earls of Seaforth
Earl of Seaforth was a title in the Peerage of Scotland and the Peerage of Ireland. It was held by the family of Mackenzie from 1623 to 1716, and again from 1771 to 1781.
History
The Mackenzies trace their descent to Colin of Kintail (died 1278) ...
), who pursued a more enlightened approach, investing in fishing in particular. The historian W. C. MacKenzie was moved to write:
The Seaforth's royalist inclinations led to Lewis becoming garrisoned during the Wars of the Three Kingdoms
The Wars of the Three Kingdoms were a series of related conflicts fought between 1639 and 1653 in the kingdoms of England, Scotland and Ireland, then separate entities united in a personal union under Charles I. They include the 1639 to 1640 Bi ...
by Cromwell's troops, who destroyed the old castle in Stornoway and in 1645 Lewismen fought on the royalist side at the Battle of Auldearn.Thompson (1968) pp. 41–42 A new era of Hebridean involvement in the affairs of the wider world was about to commence.
British era
 With the implementation of the Treaty of Union in 1707 the Hebrides became part of the new
With the implementation of the Treaty of Union in 1707 the Hebrides became part of the new Kingdom of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, wh ...
, but the clans' loyalties to a distant monarch were not strong. A considerable number of islandmen "came out" in support of the Jacobite Earl of Mar
There are currently two earldoms of Mar in the Peerage of Scotland, and the title has been created seven times. The first creation of the earldom is currently held by Margaret of Mar, 31st Countess of Mar, who is also clan chief of Clan Mar. T ...
in the "15" although the response to the 1745 rising was muted. Nonetheless the aftermath of the decisive Battle of Culloden
The Battle of Culloden (; gd, Blàr Chùil Lodair) was the final confrontation of the Jacobite rising of 1745. On 16 April 1746, the Jacobite army of Charles Edward Stuart was decisively defeated by a British government force under Prince Wi ...
, which effectively ended Jacobite hopes of a Stuart restoration, was widely felt. The British government's strategy was to estrange the clan chiefs from their kinsmen and turn their descendants into English-speaking landlords whose main concern was the revenues their estates brought rather than the welfare of those who lived on them. This may have brought peace to the islands, but in the following century it came at a terrible price.
The Highland Clearances
The Highland Clearances ( gd, Fuadaichean nan Gàidheal , the "eviction of the Gaels") were the evictions of a significant number of tenants in the Scottish Highlands and Islands, mostly in two phases from 1750 to 1860.
The first phase result ...
of the 19th century destroyed communities throughout the Highlands and Islands
The Highlands and Islands is an area of Scotland broadly covering the Scottish Highlands, plus Orkney, Shetland and Outer Hebrides (Western Isles).
The Highlands and Islands are sometimes defined as the area to which the Crofters' Act of 1 ...
as the human populations were evicted and replaced with sheep farms. For example, Colonel Gordon of Cluny
Cluny () is a commune in the eastern French department of Saône-et-Loire, in the region of Bourgogne-Franche-Comté. It is northwest of Mâcon.
The town grew up around the Benedictine Abbey of Cluny, founded by Duke William I of Aquitaine in ...
, owner of Barra, South Uist and Benbecula, evicted thousands of islanders using trickery and cruelty and even offered to sell Barra to the government as a penal colony. Islands such as were completely cleared of their populations and even today the subject is recalled with bitterness and resentment in some areas. The position was exacerbated by the failure of the islands' kelp
Kelps are large brown algae seaweeds that make up the order Laminariales. There are about 30 different genera. Despite its appearance, kelp is not a plant - it is a heterokont, a completely unrelated group of organisms.
Kelp grows in "underwa ...
industry, which thrived from the 18th century until the end of the Napoleonic Wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fre ...
in 1815 and large scale emigration became endemic. For example, hundreds left North Uist for Cape Breton, Nova Scotia
Nova Scotia ( ; ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is one of the three Maritime provinces and one of the four Atlantic provinces. Nova Scotia is Latin for "New Scotland".
Most of the population are native Eng ...
. The pre-clearance population of the island had been almost 5,000, although by 1841 it had fallen to 3,870 and was only 2,349 by 1931.
The Highland potato famine (Gaiseadh a’ bhuntàta, in Scottish Gaelic), caused by a blight, started in 1846 and had a serious impact, because many islanders were crofters; potatoes were a staple of their diet. Violent riots became common. Charities, encouraged by George Pole and others in the Commissariat (a military agency) encouraged charities to come to the rescue. The Free Church was particularly helpful, "delivering oatmeal to famine-affected families all across the West Highlands and Islands", according to one report. Another report states that the Church "was prompt in organising an efficient system of private charity across the Hebrides and on the Western seaboard. It cooperated with the Edinburgh and Glasgow Relief Committees".
An interdenominational charity was in place by early 1847 and took the most significant role in famine relief. Some landowners also provided a great deal of assistance, according to one history of the region: "MacLeod of Dunvegan bought in food for his people, some eight thousand of them" ... MacLean of Ardgour provided food, and introduced new crops into the area - peas, cabbages and carrots ... Sir James Matheson on Lewis spent £329,000 on improving his lands, hoping to provide a more secure future for his people". The government of Britain provided some assistance, thanks to Sir Charles Trevelyan, who arranged for food distribution at Portree and Tobermory. The ''British Association for the Relief of Distress in Ireland and the Highlands and Islands of Scotland'' also helped as did donations received from North America. The blight struck again over the next two years, requiring an extra tax on landowners to help feed the population. The British government began encouraging mass emigration.
For those who remained new economic opportunities emerged through the export of cattle, commercial fishing and tourism. During the summer season in the 1860s and 1870s five thousand inhabitants of Lewis could be found in Wick
Wick most often refers to:
* Capillary action ("wicking")
** Candle wick, the cord used in a candle or oil lamp
** Solder wick, a copper-braided wire used to desolder electronic contacts
Wick or WICK may also refer to:
Places and placename ...
on the mainland of Scotland, employed on the fishing boats and at the quaysides. Nonetheless emigration and military service became the choice of many and the archipelago's populations continued to dwindle throughout the late 19th and 20th centuries. By 2001 the population of North Uist was only 1,271."North Uist ()"Undiscovered Scotland. Retrieved 8 July 2010. The work of the
Napier Commission
The Napier Commission, officially the Royal Commission of Inquiry into the Condition of Crofters and Cottars in the Highlands and Islands was a royal commission and public inquiry into the condition of crofters and cottars in the Highlands and I ...
and the Congested Districts Board, and the passing of the Crofting Act of 1886 helped, but social unrest continued. In July 1906 grazing land on Vatersay
The island of Vatersay (; gd, Bhatarsaigh) is the southernmost and westernmost inhabited island in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland, and the settlement of Caolas on the north coast of the island is the westernmost permanently inhabited place in ...
was raided by landless men from Barra and its isles. Lady Gordon Cathcart took legal action against the "raiders" but the visiting judge took the view that she had neglected her duties as a landowner and that "long indifference to the necessities of the cottars had gone far to drive them to exasperation". Millennia of continuous occupation notwithstanding, many of the remoter islands were abandoned — Mingulay in 1912, Hirta
Hirta ( gd, Hiort) is the largest island in the St Kilda archipelago, on the western edge of Scotland. The names (in Scottish Gaelic) and ''Hirta'' (historically in English) have also been applied to the entire archipelago. Now without a perman ...
in 1930, and in 1942 among them. This process involved a transition from these places being perceived as relatively self-sufficient agricultural economies to a view becoming held by both island residents and outsiders alike that they lacked the essential services of a modern industrial economy.
There were gradual economic improvements, among the most visible of which was the replacement of the traditional thatched blackhouse
A blackhouse ( ga, teach dubh ; gd, t(a)igh-dubh ) is a traditional type of house which used to be common in Ireland, the Hebrides, and the Scottish Highlands.
Origin of the name
The origin of the name blackhouse is of some debate. On the Is ...
with accommodation of a more modern design. The creation of the Highlands and Islands Development Board and the discovery of substantial deposits of North Sea oil
North Sea oil is a mixture of hydrocarbons, comprising liquid petroleum and natural gas, produced from petroleum reservoirs beneath the North Sea.
In the petroleum industry, the term "North Sea" often includes areas such as the Norwegian Se ...
in 1965, the establishment of a unitary local authority for the islands in 1975 and more recently the renewables sector have all contributed to a degree of economic stability in recent decades. The Arnish yard
Stornoway (; gd, Steòrnabhagh; sco, Stornowa) is the main town of the Western Isles and the capital of Lewis and Harris in Scotland.
The town's population is around 6,953, making it by far the largest town in the Outer Hebrides, as we ...
has had a chequered history but has been a significant employer in both the oil and renewables industries. , the local authority, employs 2,000 people, making it the largest employer in the Outer Hebrides. See also the " area plan 2010" and the 's "Factfile – Economy".
Economy
 Modern commercial activities centre on tourism,
Modern commercial activities centre on tourism, crofting
Crofting is a form of land tenure and small-scale food production particular to the Scottish Highlands, the islands of Scotland, and formerly on the Isle of Man.
Within the 19th century townships, individual crofts were established on the bett ...
, fishing, and weaving including the manufacture of Harris tweed
Harris Tweed, (''Clò Mór'' or ''Clò Hearach'' in Gaelic) is a tweed cloth that is handwoven by islanders at their homes in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland, finished in the Outer Hebrides, and made from pure virgin wool dyed and spun in th ...
. Crofting remains popular especially on Lewis and Harris
Lewis and Harris ( gd, Leòdhas agus na Hearadh, sco, Lewis an Harris), or Lewis with Harris, is a single Scottish island in the Outer Hebrides, divided by mountains. It is the largest island in Scotland and the third largest in the British ...
(population 21,000) with over 920 active crofters according to a 2020 report: "with crofts ranging in size from as small as a single hectare to having access to thousands of hectares through the medium of community grazing". Crofters can apply for subsidy grants; some of these are intended to help them find other avenues to supplement their incomes. Some of the funding schemes available to crofters in the Hebrides include the "Basic Payment Scheme, the suckler beef support scheme, the upland sheep support scheme and the Less Favoured Area support scheme and the Crofting Agricultural Grant Scheme (CAGS), as of March 2020.
According to the Scottish Government, "tourism is by far and away the mainstay industry" of the Outer Hebrides, "generating £65m in economic value for the islands, sustaining around 1000 jobs" The report adds that the "islands receive 219,000 visitors per year".
Some of the larger islands have development trust
Development trusts are organisations operating in the United Kingdom that are:
*community based, owned and led
*engaged in the economic, environmental and social regeneration of a defined area or community
*independent but seek to work in partners ...
s that support the local economy and, in striking contrast to the 19th and 20th century domination by absentee landlords, more than two thirds of the Western Isles population now lives on community-owned estates. However the economic position of the islands remains relatively precarious. The Western Isles, including Stornoway, are defined by Highlands and Islands Enterprise as an economically "Fragile Area" and they have an estimated trade deficit of some £163.4 million. Overall, the area is relatively reliant on primary industries and the public sector, and fishing and fish farming in particular are vulnerable to environmental impacts, changing market pressures, and European legislation."Factfile - Economy"Comhairle nan Eilean Siar. Retrieved 4 July 2010. There is some optimism about the possibility of future developments in, for example, renewable energy generation, tourism, and education, and after declines in the 20th century the population has stabilised since 2003, although it is ageing. A 2019 report, using key assumptions, (mortality, fertility and migration) was less optimistic. It predicted that the population is "projected to fall to 22,709 by 2043"; that translates to a 16% decline, or 4,021 people, between 2018 and 2043. The UK’s largest community-owned wind farm, the 9MW Beinn Ghrideag, a "3 turbine, 9MW scheme" is located outside Stornoway and is operated by Point and Sandwick Trust (PST). The Isle of Lewis web site states that Stornoway's sheltered harbour has been important for centuries; it was named Steering Bay by
Vikings
Vikings ; non, víkingr is the modern name given to seafaring people originally from Scandinavia (present-day Denmark, Norway and Sweden),
who from the late 8th to the late 11th centuries raided, pirated, traded and se ...
who often visited. A December 2020 report stated that a new deep water terminal was to be developed, the Stornoway Deep Water Terminal, using a £49 million investment. The plan included berths for cruise ships as long as 360 meters, berths for large cargo vessels, and a freight ferry berth.
Politics and local government
 From the passing of the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1889 to 1975 Lewis formed part of the
From the passing of the Local Government (Scotland) Act 1889 to 1975 Lewis formed part of the county
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposes Chambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
of Ross and Cromarty
Ross and Cromarty ( gd, Ros agus Cromba), sometimes referred to as Ross-shire and Cromartyshire, is a variously defined area in the Highlands and Islands of Scotland. There is a registration county and a lieutenancy area in current use, the lat ...
and the rest of the archipelago, including Harris, was part of Inverness-shire
Inverness-shire ( gd, Siorrachd Inbhir Nis) is a historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area of Scotland. Covering much of the Highlands and Outer Hebrides, it is Scotland's largest county, though one of the smallest in popula ...
.
The Outer Hebrides became a unitary council
A unitary authority is a local authority responsible for all local government functions within its area or performing additional functions that elsewhere are usually performed by a higher level of sub-national government or the national governme ...
area in 1975, although in most of the rest of Scotland similar unitary councils were not established until 1996. Since then, the islands have formed one of the 32 unitary council areas that now cover the whole country, with the council officially known by its Gaelic name, ' under the terms of the Local Government (Gaelic Names) (Scotland) Act 1997. The council has its base in Stornoway on Lewis and is often known locally simply as "the " or '. The is one of only three Councils in Scotland with a majority of elected members who are independents. The other independent-run councils are Shetland
Shetland, also called the Shetland Islands and formerly Zetland, is a subarctic archipelago in Scotland lying between Orkney, the Faroe Islands and Norway. It is the northernmost region of the United Kingdom.
The islands lie about to the n ...
and Orkney
Orkney (; sco, Orkney; on, Orkneyjar; nrn, Orknøjar), also known as the Orkney Islands, is an archipelago in the Northern Isles of Scotland, situated off the north coast of the island of Great Britain. Orkney is 10 miles (16 km) north ...
. Moray
Moray () gd, Moireibh or ') is one of the 32 local government council areas of Scotland. It lies in the north-east of the country, with a coastline on the Moray Firth, and borders the council areas of Aberdeenshire and Highland (council area), ...
is run by a Conservative/Independent coalition.
The name for the British Parliament constituency covering this area is , the seat being held by Angus MacNeil MP since 2005, while the Scottish Parliament constituency for the area is , the incumbent being Alasdair Allan
Alasdair James Allan (born 6 May 1971) is a Scottish politician serving as the Member of the Scottish Parliament (MSP) for the Na h-Eileanan an Iar constituency since 2007. A member of the Scottish National Party (SNP), he served as a Scottish ...
MSP.
During the 2014 Scottish independence referendum
A independence referendum, referendum on Scottish independence from the United Kingdom was held in Scotland on 18 September 2014. The referendum question was, "Should Scotland be an independent country?", which voters answered with "Yes" ...
the area voted against independence by a margin of 53.42% (10,544) to 46.58% (9,195) in favour on a turnout of 86.2%
In 2022, as part of the Levelling Up White Paper, an "Island Forum" was proposed, which would allow local policymakers and residents in the Outer Hebrides to work alongside their counterparts in Shetland
Shetland, also called the Shetland Islands and formerly Zetland, is a subarctic archipelago in Scotland lying between Orkney, the Faroe Islands and Norway. It is the northernmost region of the United Kingdom.
The islands lie about to the n ...
, Orkney
Orkney (; sco, Orkney; on, Orkneyjar; nrn, Orknøjar), also known as the Orkney Islands, is an archipelago in the Northern Isles of Scotland, situated off the north coast of the island of Great Britain. Orkney is 10 miles (16 km) north ...
, Anglesey
Anglesey (; cy, (Ynys) Môn ) is an island off the north-west coast of Wales. It forms a principal area known as the Isle of Anglesey, that includes Holy Island across the narrow Cymyran Strait and some islets and skerries. Anglesey island ...
and the Isle of Wight
The Isle of Wight ( ) is a county in the English Channel, off the coast of Hampshire, from which it is separated by the Solent. It is the largest and second-most populous island of England. Referred to as 'The Island' by residents, the Is ...
on common issues, such as broadband connectivity, and provide a platform for them to communicate directly with the government on the challenges island communities face in terms of levelling up.
Scottish Gaelic language
The Outer Hebrides have historically been a very strongScottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic ( gd, Gàidhlig ), also known as Scots Gaelic and Gaelic, is a Goidelic language (in the Celtic branch of the Indo-European language family) native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a Goidelic language, Scottish Gaelic, as well as ...
(''Gàidhlig'') speaking area. Both the 1901 and 1921 census reported that all parishes were over 75% Gaelic speaking, including areas of high population density such as Stornoway. However, the Education (Scotland) Act 1872
The Education (Scotland) Act 1872 (35 & 36 Vict. c. 62) made elementary education for all children between the ages of 5 and 13 mandatory in Scotland.
The Act achieved a more thorough transfer of existing schools to a public system than the 1 ...
mandated English-only education, and is now recognised as having dealt a major blow to the language. People still living can recall being beaten for speaking Gaelic in school. Nonetheless, by 1971 most areas were still more than 75% Gaelic speaking – with the exception of Stornoway
Stornoway (; gd, Steòrnabhagh; sco, Stornowa) is the main town of the Western Isles and the capital of Lewis and Harris in Scotland.
The town's population is around 6,953, making it by far the largest town in the Outer Hebrides, as well ...
, Benbecula
Benbecula (; gd, Beinn nam Fadhla or ) is an island of the Outer Hebrides in the Atlantic Ocean off the west coast of Scotland. In the 2011 census, it had a resident population of 1,283 with a sizable percentage of Roman Catholics. It is in a ...
and South Uist
South Uist ( gd, Uibhist a Deas, ; sco, Sooth Uist) is the second-largest island of the Outer Hebrides in Scotland. At the 2011 census, it had a usually resident population of 1,754: a decrease of 64 since 2001. The island, in common with the ...
at 50–74%.Mac an Tàilleir, Iain (2004''1901–2001 Gaelic in the Census''
(PowerPoint) Linguae Celticae. Retrieved 1 June 2008 In the 2001 census, each island overall was over 50% Gaelic speaking –
South Uist
South Uist ( gd, Uibhist a Deas, ; sco, Sooth Uist) is the second-largest island of the Outer Hebrides in Scotland. At the 2011 census, it had a usually resident population of 1,754: a decrease of 64 since 2001. The island, in common with the ...
(71%), Harris (69%), Barra (68%), North Uist
North Uist ( gd, Uibhist a Tuath; sco, North Uise) is an island and community in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland.
Etymology
In Donald Munro's ''A Description of the Western Isles of Scotland Called Hybrides'' of 1549, North Uist, Benbecula a ...
(67%), Lewis
Lewis may refer to:
Names
* Lewis (given name), including a list of people with the given name
* Lewis (surname), including a list of people with the surname
Music
* Lewis (musician), Canadian singer
* "Lewis (Mistreated)", a song by Radiohead ...
(56%) and Benbecula
Benbecula (; gd, Beinn nam Fadhla or ) is an island of the Outer Hebrides in the Atlantic Ocean off the west coast of Scotland. In the 2011 census, it had a resident population of 1,283 with a sizable percentage of Roman Catholics. It is in a ...
(56%). With 59.3% of Gaelic speakers or a total of 15,723 speakers, this made the Outer Hebrides the most strongly coherent Gaelic speaking area in Scotland.
Most areas were between 60-74% Gaelic speaking and the areas with the highest density of over 80% are Scalpay near Harris, Newtonferry and Kildonan, whilst Daliburgh
Daliburgh ( gd, Dalabrog) is a crofting township on South Uist, in the Outer Hebrides, Scotland. Daliburgh is situated west from Lochboisdale, has the second largest population of any township in South Uist, and is also in the parish of South Ui ...
, Linshader, Eriskay, Brue
Brue ( gd, Brù) is a village on the Isle of Lewis in the West Side district, in the Outer Hebrides, Scotland. It is a crofting township and it is composed of two areas: Am Baile Staigh, which is nearer the coast, and Pàirc Bhrù, which runs t ...
, Boisdale, West Harris, Ardveenish
Ardveenish ( gd, Àird Mhèanais) is a village on Barra
Barra (; gd, Barraigh or ; sco, Barra) is an island in the Outer Hebrides, Scotland, and the second southernmost inhabited island there, after the adjacent island of Vatersay to w ...
, Soval, Ness
Ness or NESS may refer to:
Places Australia
* Ness, Wapengo, a heritage-listed natural coastal area in New South Wales
United Kingdom
* Ness, Cheshire, England, a village
* Ness, Lewis, the most northerly area on Lewis, Scotland, UK
* Cuspat ...
, and Bragar
Bragar ( gd, Bràgar, ) is a village on the west side of the Isle of Lewis in the Outer Hebrides, Scotland, from the island's only town, Stornoway. Bragar is within the parish of Barvas, and is situated on the A858 between Carloway and Barvas.
...
all have more than 75%. The areas with the lowest density of speakers are Stornoway (44%), Braigh (41%), Melbost
Melbost ( gd, Mealabost) is a traditionally Gaelic-speaking village in Point on the east coast of the Isle of Lewis, in Scotland's north-west. It is largely a crofting township and is about east of Stornoway at the head of an isthmus connec ...
(41%), and Balivanich (37%).
The Gaelic Language (Scotland) Act
The Gaelic Language (Scotland) Act 2005 ( gd, Achd na Gàidhlig (Alba) 2005) is an Act of the Scottish Parliament passed in 2005. It was the first piece of legislation dedicated to the Scottish Gaelic language and was seen as the first hesitan ...
was enacted by the Scottish Parliament
The Scottish Parliament ( gd, Pàrlamaid na h-Alba ; sco, Scots Pairlament) is the devolved, unicameral legislature of Scotland. Located in the Holyrood area of the capital city, Edinburgh, it is frequently referred to by the metonym Holyr ...
in 2005 to provide continuing support for the language. However, by 2011 the overall percentage of Gaelic speakers in the Outer Hebrides had fallen to 52%.
Transport
 Scheduled
Scheduled ferry
A ferry is a ship, watercraft or amphibious vehicle used to carry passengers, and sometimes vehicles and cargo, across a body of water. A passenger ferry with many stops, such as in Venice, Italy, is sometimes called a water bus or water ta ...
services between the Outer Hebrides and the Scottish Mainland and Inner Hebrides operate on the following routes:
* Oban
Oban ( ; ' in Scottish Gaelic meaning ''The Little Bay'') is a resort town within the Argyll and Bute council area of Scotland. Despite its small size, it is the largest town between Helensburgh and Fort William. During the tourist season, ...
to Castlebay
Castlebay ( gd, Bàgh a' Chaisteil) is the main village and a community council area on the island of Barra in the Outer Hebrides, Scotland. The village is located on the south coast of the island, and overlooks a bay in the Atlantic Ocean domi ...
on Barra
*Oban
Oban ( ; ' in Scottish Gaelic meaning ''The Little Bay'') is a resort town within the Argyll and Bute council area of Scotland. Despite its small size, it is the largest town between Helensburgh and Fort William. During the tourist season, ...
to Lochboisdale on South Uist
South Uist ( gd, Uibhist a Deas, ; sco, Sooth Uist) is the second-largest island of the Outer Hebrides in Scotland. At the 2011 census, it had a usually resident population of 1,754: a decrease of 64 since 2001. The island, in common with the ...
(Winter Only)
* Mallaig to Lochboisdale on South Uist
South Uist ( gd, Uibhist a Deas, ; sco, Sooth Uist) is the second-largest island of the Outer Hebrides in Scotland. At the 2011 census, it had a usually resident population of 1,754: a decrease of 64 since 2001. The island, in common with the ...
* Uig on Skye
The Isle of Skye, or simply Skye (; gd, An t-Eilean Sgitheanach or ; sco, Isle o Skye), is the largest and northernmost of the major islands in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. The island's peninsulas radiate from a mountainous hub dominated ...
to Tarbert on Harris
* Uig on Skye
The Isle of Skye, or simply Skye (; gd, An t-Eilean Sgitheanach or ; sco, Isle o Skye), is the largest and northernmost of the major islands in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. The island's peninsulas radiate from a mountainous hub dominated ...
to Lochmaddy
Lochmaddy ( gd, Loch nam Madadh, "Loch of the Hounds") is the administrative centre of North Uist in the Outer Hebrides, Scotland. ''Na Madaidhean'' (the wolves/hounds) are rocks in the bay after which the loch, and subsequently the village, are ...
on North Uist
North Uist ( gd, Uibhist a Tuath; sco, North Uise) is an island and community in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland.
Etymology
In Donald Munro's ''A Description of the Western Isles of Scotland Called Hybrides'' of 1549, North Uist, Benbecula a ...
* Ullapool to Stornoway
Stornoway (; gd, Steòrnabhagh; sco, Stornowa) is the main town of the Western Isles and the capital of Lewis and Harris in Scotland.
The town's population is around 6,953, making it by far the largest town in the Outer Hebrides, as well ...
on Lewis
Lewis may refer to:
Names
* Lewis (given name), including a list of people with the given name
* Lewis (surname), including a list of people with the surname
Music
* Lewis (musician), Canadian singer
* "Lewis (Mistreated)", a song by Radiohead ...
* Tiree
Tiree (; gd, Tiriodh, ) is the most westerly island in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. The low-lying island, southwest of Coll, has an area of and a population of around 650.
The land is highly fertile, and crofting, alongside tourism, ...
to Castlebay
Castlebay ( gd, Bàgh a' Chaisteil) is the main village and a community council area on the island of Barra in the Outer Hebrides, Scotland. The village is located on the south coast of the island, and overlooks a bay in the Atlantic Ocean domi ...
, Barra (summer only).
Other ferries operate between some of the islands.
National Rail services are available for onward journeys, from stations at Oban
Oban ( ; ' in Scottish Gaelic meaning ''The Little Bay'') is a resort town within the Argyll and Bute council area of Scotland. Despite its small size, it is the largest town between Helensburgh and Fort William. During the tourist season, ...
and Mallaig, which has direct services to Glasgow. However, parliamentary approval notwithstanding, plans in the 1890s to lay a railway connection to Ullapool were unable to obtain sufficient funding.
There are scheduled flights from Stornoway
Stornoway (; gd, Steòrnabhagh; sco, Stornowa) is the main town of the Western Isles and the capital of Lewis and Harris in Scotland.
The town's population is around 6,953, making it by far the largest town in the Outer Hebrides, as well ...
, Benbecula
Benbecula (; gd, Beinn nam Fadhla or ) is an island of the Outer Hebrides in the Atlantic Ocean off the west coast of Scotland. In the 2011 census, it had a resident population of 1,283 with a sizable percentage of Roman Catholics. It is in a ...
and Barra airports both inter-island and to the mainland. Barra's airport is claimed to be the only one in the world to have scheduled flights landing on a beach. At high water the runways are under the sea so flight times vary with the tide.

Bus na Comhairle
Bus na Comhairle (meaning "Bus of the Council") is the council-owned local bus company of theWestern Isles
The Outer Hebrides () or Western Isles ( gd, Na h-Eileanan Siar or or ("islands of the strangers"); sco, Waster Isles), sometimes known as the Long Isle/Long Island ( gd, An t-Eilean Fada, links=no), is an island chain off the west coast ...
of Scotland. The company serves the Broadbay area of Lewis with 7 buses - 6 Optare Solos and 1 ADL Enviro 200.
Shipwrecks
 The archipelago is exposed to wind and tide, and
The archipelago is exposed to wind and tide, and lighthouse
A lighthouse is a tower, building, or other type of physical structure designed to emit light from a system of lamps and lenses and to serve as a beacon for navigational aid, for maritime pilots at sea or on inland waterways.
Lighthouses m ...
s are sited as an aid to navigation at locations from Barra Head in the south to the Butt of Lewis in the north. There are numerous sites of wrecked ships, and the Flannan Isles
The Flannan Isles ( gd, Na h-Eileanan Flannach) or alternatively, the Seven Hunters are a small island group in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland, approximately west of the Isle of Lewis. They may take their name from Saint Flannan, the 7th centur ...
are the location of an enduring mystery that occurred in December 1900, when all three lighthouse keepers vanished without trace.
''Annie Jane'', a three-masted immigrant ship out of Liverpool
Liverpool is a City status in the United Kingdom, city and metropolitan borough in Merseyside, England. With a population of in 2019, it is the List of English districts by population, 10th largest English district by population and its E ...
bound for Montreal, Canada
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple-pe ...
, struck rocks off the West Beach of Vatersay during a storm on Tuesday 28 September 1853. Within ten minutes the ship began to founder and break up casting 450 people into the raging sea. In spite of the conditions, islanders tried to rescue the passengers and crew. The remains of 350 men, women and children were buried in the dunes behind the beach and a small cairn and monument marks the site.
The tiny Beasts of Holm off the east coast of Lewis were the site of the sinking of during the first few hours of 1919, one of the worst maritime disasters in United Kingdom waters during the 20th century. Calvay
Calvay ( gd, Calbhaigh), is a currently uninhabited island situated in the Sound of Eriskay in the Outer Hebrides, at . It is one of ten islands in the Sound of Barra, a Site of Community Importance for conservation.
It was here that the ship ...
in the Sound of Barra provided the inspiration for Compton Mackenzie
Sir Edward Montague Compton Mackenzie, (17 January 1883 – 30 November 1972) was a Scottish writer of fiction, biography, histories and a memoir, as well as a cultural commentator, raconteur and lifelong Scottish nationalist. He was one of th ...
's novel '' Whisky Galore'' after the ran aground there with a cargo of single malt in 1941.
Culture
Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global popula ...
has deep roots in the Western Isles, but owing mainly to the different allegiances of the clans in the past, the people in the northern islands (Lewis, Harris, North Uist) have historically been predominantly Presbyterian
Presbyterianism is a part of the Reformed tradition within Protestantism that broke from the Roman Catholic Church in Scotland by John Knox, who was a priest at St. Giles Cathedral (Church of Scotland). Presbyterian churches derive their n ...
, and those of the southern islands (Benbecula, South Uist, Barra) predominantly Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
*Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
.
At the time of the 2001 Census, 42% of the population identified themselves as being affiliated with the Church of Scotland
The Church of Scotland ( sco, The Kirk o Scotland; gd, Eaglais na h-Alba) is the national church in Scotland.
The Church of Scotland was principally shaped by John Knox, in the Reformation of 1560, when it split from the Catholic Church ...
, with 13% Roman Catholic and 28% with other Christian churches. Many of this last group belong to the Free Church of Scotland, known for its strict observance of the Sabbath
In Abrahamic religions, the Sabbath () or Shabbat (from Hebrew ) is a day set aside for rest and worship. According to the Book of Exodus, the Sabbath is a day of rest on the seventh day, commanded by God to be kept as a holy day of rest, as ...
. 11% stated that they had no religion. This made the Western Isles the Scottish council area with the smallest percentage of non-religious in the population. There are also small Episcopalian
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of the ...
congregations in Lewis and Harris and the Outer Hebrides are part of the Diocese of Argyll and The Isles in both the Episcopalian and Catholic traditions.
Gaelic music is popular in the islands and the Lewis and Harris Traditional Music Society plays an active role in promoting the genre.Rotary Club (1995) p. 39 Fèis Bharraigh began in 1981 with the aim of developing the practice and study of the Gaelic language, literature, music, drama and culture on the islands of Barra and Vatersay. A two-week festival, it has inspired 43 other ''feisean'' throughout Scotland. The Lewis Pipe Band was founded in 1904 and the Lewis and Harris Piping Society in 1977.
Outdoor activities including rugby
Rugby may refer to:
Sport
* Rugby football in many forms:
** Rugby league: 13 players per side
*** Masters Rugby League
*** Mod league
*** Rugby league nines
*** Rugby league sevens
*** Touch (sport)
*** Wheelchair rugby league
** Rugby union: 1 ...
, football, golf
Golf is a club-and-ball sport in which players use various clubs to hit balls into a series of holes on a course in as few strokes as possible.
Golf, unlike most ball games, cannot and does not use a standardized playing area, and coping wi ...
, shinty
Shinty ( gd, camanachd, iomain) is a team game played with sticks and a ball. Shinty is now played mainly in the Scottish Highlands and amongst Highland migrants to the big cities of Scotland, but it was formerly more widespread in Scotland, and ...
, fishing, riding, canoeing, athletics, and multi-sports are popular in the Western Isles. The Hebridean Challenge is an adventure race run in five daily stages, which takes place along the length of the islands and includes hill and road running, road and mountain biking
Mountain biking is a sport of riding bicycles off-road, often over rough terrain, usually using specially designed mountain bikes. Mountain bikes share similarities with other bikes but incorporate features designed to enhance durability and pe ...
, short sea swims and demanding sea kayaking sections. There are four main sports centres: ''Ionad Spors Leodhais'' in Stornoway, which has a 25 m swimming pool; Harris Sports Centre; Lionacleit Sports Centre on Benbecula; and Castlebay
Castlebay ( gd, Bàgh a' Chaisteil) is the main village and a community council area on the island of Barra in the Outer Hebrides, Scotland. The village is located on the south coast of the island, and overlooks a bay in the Atlantic Ocean domi ...
Sports Centre on Barra. The Western Isles is a member of the International Island Games Association.
South Uist
South Uist ( gd, Uibhist a Deas, ; sco, Sooth Uist) is the second-largest island of the Outer Hebrides in Scotland. At the 2011 census, it had a usually resident population of 1,754: a decrease of 64 since 2001. The island, in common with the ...
is home to the Askernish Golf Course
Askernish ( gd, Àisgearnais, Aisgernis) is a crofting community on South Uist, in the Outer Hebrides, Scotland. Askernish is in the parish of South Uist, and is situated on the A865 north of Daliburgh. The Askernish golf course, designed by Ol ...
. The oldest links in the Outer Hebrides, it was designed by Old Tom Morris
Thomas Mitchell Morris (16 June 1821 – 24 May 1908), otherwise known as Old Tom Morris, and The Grand Old Man of Golf, was a Scottish golfer. He was born in St Andrews, Fife, the "home of golf" and location of the St Andrews Links, and died ...
. Although it was in use until the 1930s, its existence was largely forgotten until 2005 and it is now being restored to Morris's original design.
See also
* Constitutional status of Orkney, Shetland and the Western Isles *Hebridean Myths and Legends
The Inner and Outer Hebrides off the western coast of Scotland are made up of a great number of large and small islands. These isolated islands are the source of a number of Hebridean myths and legends. The Hebridean Islands are a part of Scotl ...
* Leod
* List of Category A listed buildings in the Western Isles
This is a list of Category A listed buildings in the Western Isles of Scotland ( gd, Na h-Eileanan Siar).
In Scotland, the term listed building refers to a building or other structure officially designated as being of "special architectural o ...
* List of places in the Western Isles
* List of rulers of the Kingdom of the Isles
The Kingdom of the Isles comprised the Hebrides, the islands of the Firth of Clyde and the Isle of Man from the 9th to the 13th centuries AD. The islands were known to the Norse as the , or "Southern Isles" as distinct from the or Northern Isl ...
* List of islands of Scotland
This is a list of islands of Scotland, the mainland of which is part of the island of Great Britain. Also included are various other related tables and lists. The definition of an offshore island used in this list is "land that is surrounded by ...
* Ljótólfr
* Solar eclipse of 1 May 1185
The solar eclipse of 1 May 1185 was a total solar eclipse visible in Central America, Northern Europe, Eastern Europe, and Kazakhstan. The eclipse is number 30 in the Solar Saros 115 series. The eclipse shadow on the Earth's surface was at its gr ...
* 2012 Comhairle nan Eilean Siar election
* Virtual Hebrides
The Virtual Hebrides was an influential website which was set up in the Outer Hebrides of Scotland and was in operation from late 1993 until 2000.
The Virtual Hebrides was founded by photographer and film maker Sam Maynar who had set up Eòlas ...
Notes
References
Sources
* Armit, Ian (1998) ''Scotland's Hidden History''. Tempus (in association with Historic Scotland). * Ballin Smith, B. and Banks, I. (eds) (2002) ''In the Shadow of the Brochs, the Iron Age in Scotland''. Stroud. Tempus. * Ballin Smith, Beverley; Taylor, Simon; Williams, Gareth (eds) (2007) ''West Over Sea: Studies in Scandinavian Sea-Borne Expansion and Settlement Before 1300''. Leiden. Koninklijke Brill. * Benvie, Neil (2004) ''Scotland's Wildlife''. London. Aurum Press. * Buxton, Ben (1995) ''Mingulay: An Island and Its People''. Edinburgh. Birlinn. * Downham, Clare (2007) ''Viking Kings of Britain and Ireland: The Dynasty of Ívarr to A.D. 1014''. Edinburgh. Dunedin Academic Press. * Gillen, Con (2003) ''Geology and landscapes of Scotland''. Harpenden. Terra Publishing. * Gregory, Donald (1881) ''The History of the Western Highlands and Isles of Scotland 1493–1625.'' Edinburgh. Birlinn. 2008 reprint – originally published by Thomas D. Morrison. * Hanson, William S. "The Roman Presence: Brief Interludes", in Edwards, Kevin J. & Ralston, Ian B.M. (Eds) (2003) ''Scotland After the Ice Age: Environment, Archaeology and History, 8000 BC – AD 1000''. Edinburgh. Edinburgh University Press. * Haswell-Smith, Hamish. (2004) ''The Scottish Islands''. Edinburgh. Canongate. * Hunter, James (2000) ''Last of the Free: A History of the Highlands and Islands of Scotland''. Edinburgh. Mainstream. * Keay, J. & Keay, J. (1994) ''Collins Encyclopaedia of Scotland
''Collins Encyclopaedia of Scotland'' is a reference work published by HarperCollins, edited by the husband and wife team, John and Julia Keay.
History
Scots had provided the impetus for a number of well-known references works, ''Chambers Dic ...
''. London. HarperCollins.
*
* McKirdy, Alan Gordon, John & Crofts, Roger (2007) ''Land of Mountain and Flood: The Geology and Landforms of Scotland''. Edinburgh. Birlinn.
* Maclean, Charles (1977) ''Island on the Edge of the World: the Story of St. Kilda''. Edinburgh. Canongate.
* Malhotra, R. (1992) ''Anthropology of Development: Commemoration Volume in Honour of Professor I.P. Singh''. New Delhi. Mittal.
* Li, Martin (2005''Adventure Guide to Scotland''
Hunter Publishing. Retrieved 19 May 2010. * Miers, Mary (2008) ''The Western Seaboard: An Illustrated Architectural Guide.'' The Rutland Press. * * Murray, W.H. (1966) ''The Hebrides''. London. Heinemann. * Murray, W.H. (1973) ''The Islands of Western Scotland: the Inner and Outer Hebrides.'' London. Eyre Methuen. * Ross, David (2005) ''Scotland – History of a Nation''. Lomond. * Rotary Club of Stornoway (1995) ''The Outer Hebrides Handbook and Guide''. Machynlleth. Kittiwake. * Thompson, Francis (1968) ''Harris and Lewis, Outer Hebrides''. Newton Abbot. David & Charles. * Watson, W. J. (1994) ''The Celtic Place-Names of Scotland''. Edinburgh; Birlinn. . First published 1926.
External links
*Stornoway Port Authority
Comhairle nan Eilean Siar
2001 Census Results for the Outer Hebrides
MacTV
Reefnet
Hebrides.com
Photographic website from ex-Eolas Sam Maynard
www.visithebrides.com
Western Isles Tourist Board site from Reefnet
Virtual Hebrides.com
Content from the VH, which went its own way and became Virtual Scotland.
hebrides.ca
Home of the Quebec-Hebridean Scots who were cleared from Lewis to Quebec 1838–1920s {{Authority control . Archipelagoes of Scotland Archipelagoes of the Atlantic Ocean Council areas of Scotland Lieutenancy areas of Scotland Regions of Scotland Former Norwegian colonies Gaelic culture