Economy of Chile on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Economy of
 After Spanish arrival in the 15th century Chilean economy came to revolve around autarchy estates called fundos and around the army that was engaged in the
After Spanish arrival in the 15th century Chilean economy came to revolve around autarchy estates called fundos and around the army that was engaged in the
''
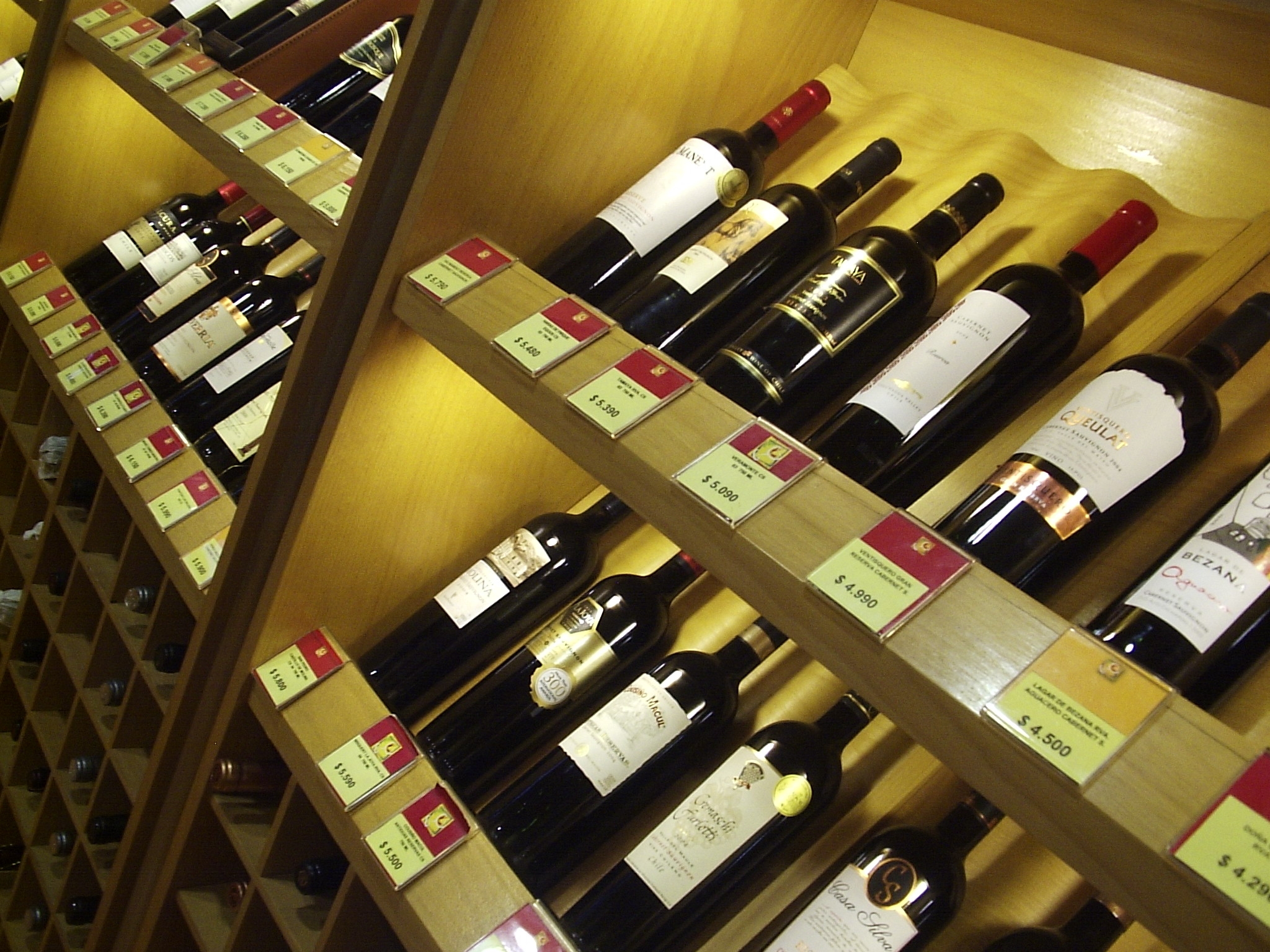 Chile's unique geography and climate make it ideal for winegrowing and the country has made the top ten list of wine producers many times in the last few decades.
The popularity of Chilean wine has been attributed not just to the quantity produced but also to increasing levels of quality. The combination of quantity and quality allows Chile to export excellent wines at reasonable prices to the international market.
Chile's unique geography and climate make it ideal for winegrowing and the country has made the top ten list of wine producers many times in the last few decades.
The popularity of Chilean wine has been attributed not just to the quantity produced but also to increasing levels of quality. The combination of quantity and quality allows Chile to export excellent wines at reasonable prices to the international market.
 The mining sector in Chile is one of the pillars of Chilean economy. The Chilean government strongly supports foreign investment in the sector and has modified its mining industry laws and regulations to create a favorable investing environment for foreigners. Thanks to a large amount of copper resources, complaisant legislation and an unregulated investment environment, Chile has become one of the main
The mining sector in Chile is one of the pillars of Chilean economy. The Chilean government strongly supports foreign investment in the sector and has modified its mining industry laws and regulations to create a favorable investing environment for foreigners. Thanks to a large amount of copper resources, complaisant legislation and an unregulated investment environment, Chile has become one of the main
 Tourism in Chile has experienced sustained growth over the last decades. Chile received about 2.25 million foreign visitors in 2006, up to 2.50 million in 2007
The percentages of foreign tourists arrivals by land, air and sea were, respectively, 55.3%, 40.5% and 4.2% for that year. The two main gateways for international tourists visiting Chile are
Tourism in Chile has experienced sustained growth over the last decades. Chile received about 2.25 million foreign visitors in 2006, up to 2.50 million in 2007
The percentages of foreign tourists arrivals by land, air and sea were, respectively, 55.3%, 40.5% and 4.2% for that year. The two main gateways for international tourists visiting Chile are
 According to the CIA World Factbook, Chile's "sound economic policies", maintained consistently since the 1980s, "have contributed to steady economic growth in Chile and have more than halved poverty rates." The 1973–90 military government sold many state-owned companies, and the three democratic governments since 1990 have implemented export promotion policies and continued privatization, though at a slower pace. The government's role in the economy is mostly limited to regulation, although the state continues to operate copper giant
According to the CIA World Factbook, Chile's "sound economic policies", maintained consistently since the 1980s, "have contributed to steady economic growth in Chile and have more than halved poverty rates." The 1973–90 military government sold many state-owned companies, and the three democratic governments since 1990 have implemented export promotion policies and continued privatization, though at a slower pace. The government's role in the economy is mostly limited to regulation, although the state continues to operate copper giant
OECD Journal on Budgeting 7(2), pp. 59–92. The target was of 1% of GDP between 2001 and 2007, it was reduced to 0.5% in 2008 and then to 0% in 2009 in the wake of the global financial crisis.Corbo, Vittorio. La política fiscal chilena.
Blogs from El Mercurio Newspaper. 25 August 2013. In 2005, key elements of this voluntary policy were incorporated into legislation through the Fiscal Responsibility Law (Law 20,128). The Fiscal Responsibility Law also allowed for the creation of two
OECD Publishing. Gross financial debt amounted to 12.2% of GDP, while in net terms it was −6.9% of GDP, both well below OECD averages.
Central Bank of Chile, January 2007. Inflation has followed a relatively stable trajectory since the year 2000, remaining under 10%, despite the temporary surge of some inflationary pressures in the year 2008. The Chilean peso's rapid appreciation against the U.S. dollar in recent years has helped dampen inflation. Most wage settlements and loans are indexed, reducing inflation's volatility. The CBoC is granted autonomous status by Chile's National Constitution, providing credibility and stability beyond the political cycle. According to the Basic Constitutional Act of the Central Bank of Chile (Law 18,840), its main objectives are to safeguard "the stability of the currency and the normal functioning of internal and external payments".
, Title I, Section 3. To meet these objectives, the CBoC is enabled to use monetary and foreign exchange policy instruments, along with some discretion on financial regulation. In practice, the CBoC monetary policy is guided by an inflation targeting regime, while the foreign exchange policy is led by a floating exchange rate and, although unusual, the bank reserves the right to intervene in the foreign exchange markets.
2009, World Trade Organization. More recently, Chile has also been an active participant of deeper plurilateral trade agreement negotiations. Notably, Chile is currently in talks with eleven other economies in the

 2006 was a record year for Chilean trade. Total trade registered a 31% increase over 2005. During 2006, exports of goods and services totaled US$58 billion, an increase of 41%. This figure was somewhat distorted by the skyrocketing price of copper. In 2006, copper exports reached a historical high of US$33.3 billion. Imports totaled US$35 billion, an increase of 17% compared to the previous year. Chile thus recorded a positive trade balance of US$2.3 billion in 2006.
The main destinations for Chilean exports were the Americas (US$39 billion), Asia (US$27.8 billion) and Europe (US$22.2 billion). Seen as shares of Chile's export markets, 42% of exports went to the Americas, 30% to Asia and 24% to Europe. Within Chile's diversified network of trade relationships, its most important partner remained the United States. Total trade with the U.S. was US$14.8 billion in 2006. Since the U.S.–Chile Free Trade Agreement went into effect on 1 January 2004, U.S.–Chilean trade has increased by 154%. Internal Government of Chile figures show that even when factoring out inflation and the recent high price of copper, bilateral trade between the U.S. and Chile has grown over 60% since then.
Total trade with Europe also grew in 2006, expanding by 42%. The Netherlands and Italy were Chile's main European trading partners. Total trade with Asia also grew significantly at nearly 31%. Trade with Korea and Japan grew significantly, but China remained Chile's most important trading partner in Asia. Chile's total trade with China reached U.S. $8.8 billion in 2006, representing nearly 66% of the value of its trade relationship with Asia.=
The growth of exports in 2006 was mainly caused by a strong increase in sales to the United States, the Netherlands, and Japan. These three markets alone accounted for an additional US$5.5 billion worth of Chilean exports. Chilean exports to the United States totaled US$9.3 billion, representing a 37.7% increase compared to 2005 (US$6.7 billion). Exports to the European Union were US$15.4 billion, a 63.7% increase compared to 2005 (US$9.4 billion). Exports to Asia increased from US$15.2 billion in 2005 to US$19.7 billion in 2006, a 29.9% increase.
During 2006, Chile imported US$26 billion from the Americas, representing 54% of total imports, followed by Asia at 22%, and Europe at 16%. Mercosur members were the main suppliers of imports to Chile at US$9.1 billion, followed by the United States with US$5.5 billion and the European Union with US$5.2 billion. From Asia, China was the most important exporter to Chile, with goods valued at US$3.6 billion. Year-on-year growth in imports was especially strong from a number of countries – Ecuador (123.9%), Thailand (72.1%), Korea (52.6%), and China (36.9%).
Chile's overall trade profile has traditionally been dependent upon copper exports. The state-owned firm CODELCO is the world's largest copper-producing company, with recorded copper reserves of 200 years. Chile has made an effort to expand nontraditional exports. The most important non-mineral exports are forestry and wood products, fresh fruit and processed food, fishmeal and seafood, and
2006 was a record year for Chilean trade. Total trade registered a 31% increase over 2005. During 2006, exports of goods and services totaled US$58 billion, an increase of 41%. This figure was somewhat distorted by the skyrocketing price of copper. In 2006, copper exports reached a historical high of US$33.3 billion. Imports totaled US$35 billion, an increase of 17% compared to the previous year. Chile thus recorded a positive trade balance of US$2.3 billion in 2006.
The main destinations for Chilean exports were the Americas (US$39 billion), Asia (US$27.8 billion) and Europe (US$22.2 billion). Seen as shares of Chile's export markets, 42% of exports went to the Americas, 30% to Asia and 24% to Europe. Within Chile's diversified network of trade relationships, its most important partner remained the United States. Total trade with the U.S. was US$14.8 billion in 2006. Since the U.S.–Chile Free Trade Agreement went into effect on 1 January 2004, U.S.–Chilean trade has increased by 154%. Internal Government of Chile figures show that even when factoring out inflation and the recent high price of copper, bilateral trade between the U.S. and Chile has grown over 60% since then.
Total trade with Europe also grew in 2006, expanding by 42%. The Netherlands and Italy were Chile's main European trading partners. Total trade with Asia also grew significantly at nearly 31%. Trade with Korea and Japan grew significantly, but China remained Chile's most important trading partner in Asia. Chile's total trade with China reached U.S. $8.8 billion in 2006, representing nearly 66% of the value of its trade relationship with Asia.=
The growth of exports in 2006 was mainly caused by a strong increase in sales to the United States, the Netherlands, and Japan. These three markets alone accounted for an additional US$5.5 billion worth of Chilean exports. Chilean exports to the United States totaled US$9.3 billion, representing a 37.7% increase compared to 2005 (US$6.7 billion). Exports to the European Union were US$15.4 billion, a 63.7% increase compared to 2005 (US$9.4 billion). Exports to Asia increased from US$15.2 billion in 2005 to US$19.7 billion in 2006, a 29.9% increase.
During 2006, Chile imported US$26 billion from the Americas, representing 54% of total imports, followed by Asia at 22%, and Europe at 16%. Mercosur members were the main suppliers of imports to Chile at US$9.1 billion, followed by the United States with US$5.5 billion and the European Union with US$5.2 billion. From Asia, China was the most important exporter to Chile, with goods valued at US$3.6 billion. Year-on-year growth in imports was especially strong from a number of countries – Ecuador (123.9%), Thailand (72.1%), Korea (52.6%), and China (36.9%).
Chile's overall trade profile has traditionally been dependent upon copper exports. The state-owned firm CODELCO is the world's largest copper-producing company, with recorded copper reserves of 200 years. Chile has made an effort to expand nontraditional exports. The most important non-mineral exports are forestry and wood products, fresh fruit and processed food, fishmeal and seafood, and
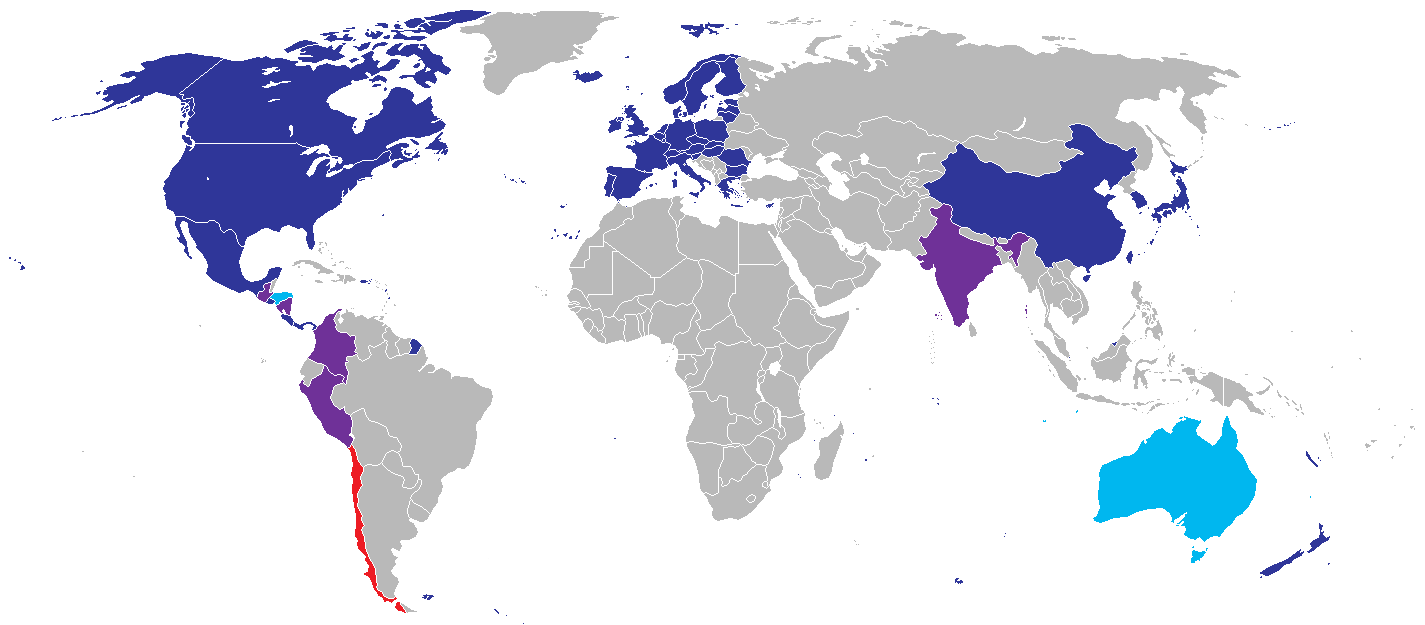 Over the last several years, Chile has signed FTAs with the European Union, South Korea, New Zealand, Singapore, Brunei, China, and Japan. It reached a partial trade agreement with India in 2005 and began negotiations for a full-fledged FTA with India in 2006. Chile conducted trade negotiations in 2007 with Australia, Malaysia, and Thailand, as well as with China to expand an existing agreement beyond just trade in goods. Chile concluded FTA negotiations with Australia and an expanded agreement with China in 2008. The members of the P4 (Chile, Singapore, New Zealand, and Brunei) also plan to conclude a chapter on finance and investment in 2008.
Successive Chilean governments have actively pursued trade-liberalizing agreements. During the 1990s, Chile signed
Over the last several years, Chile has signed FTAs with the European Union, South Korea, New Zealand, Singapore, Brunei, China, and Japan. It reached a partial trade agreement with India in 2005 and began negotiations for a full-fledged FTA with India in 2006. Chile conducted trade negotiations in 2007 with Australia, Malaysia, and Thailand, as well as with China to expand an existing agreement beyond just trade in goods. Chile concluded FTA negotiations with Australia and an expanded agreement with China in 2008. The members of the P4 (Chile, Singapore, New Zealand, and Brunei) also plan to conclude a chapter on finance and investment in 2008.
Successive Chilean governments have actively pursued trade-liberalizing agreements. During the 1990s, Chile signed
 Chile's top exports in 2013.
Source: Central Bank of Chile's statistics database.
Chile's top exports in 2013.
Source: Central Bank of Chile's statistics database.
WINN, Peter (editor).''Victims of the Chilean Miracle: Workers and Neoliberalism in the Pinochet Era, 1973–2002''. Durham, NC: Duke University Press, 2004.
Chile; A Top Stock market Performer
The Economic Transformation of Chile: A Model of Progress – HACER
Invest in Chile
World Reviews on Chile – this is Chile
Chile Export, Import, Trade Balance
Chile Trade
* Tariffs applied by Chile as provided by ITC'
ITC Market Access Map
an online database of customs tariffs and market requirements {{South America in topic, Economy of
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
is a market economy and high-income economy
A high-income economy is defined by the World Bank as a nation with a gross national income per capita of US$12,696 or more in 2020, calculated using the Atlas method. While the term "high-income" is often used interchangeably with " First Worl ...
as ranked by the World Bank
The World Bank is an international financial institution that provides loans and grants to the governments of low- and middle-income countries for the purpose of pursuing capital projects. The World Bank is the collective name for the Inte ...
. The country is considered one of South America's most prosperous nation
A nation is a community of people formed on the basis of a combination of shared features such as language, history, ethnicity, culture and/or society. A nation is thus the collective Identity (social science), identity of a group of people unde ...
s, leading the region in competitiveness
In economics, competition is a scenario where different economic firmsThis article follows the general economic convention of referring to all actors as firms; examples in include individuals and brands or divisions within the same (legal) firm ...
, income per capita
The median income is the income amount that divides a population into two equal groups, half having an income above that amount, and half having an income below that amount. It may differ from the mean (or average) income. Both of these are ways of ...
, globalization
Globalization, or globalisation (English in the Commonwealth of Nations, Commonwealth English; American and British English spelling differences#-ise, -ize (-isation, -ization), see spelling differences), is the process of foreign relation ...
, economic freedom
Economic freedom, or economic liberty, is the ability of people of a society to take economic actions. This is a term used in economic and policy debates as well as in the philosophy of economics. One approach to economic freedom comes from the l ...
, and low perception of corruption. Although Chile has high economic inequality
There are wide varieties of economic inequality, most notably income inequality measured using the distribution of income (the amount of money people are paid) and wealth inequality measured using the distribution of wealth (the amount of ...
, as measured by the Gini index, it is close to the regional mean.
In 2006, Chile became the country with the highest nominal GDP per capita in Latin America. In May 2010 Chile became the first South American country to join the OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate e ...
. Tax revenues, all together 20.2069% of GDP in 2013, were the second lowest among the 34 OECD
The Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD; french: Organisation de coopération et de développement économiques, ''OCDE'') is an intergovernmental organisation with 38 member countries, founded in 1961 to stimulate e ...
countries, and the lowest in 2010. Chile has an inequality-adjusted human development index
This is a list of countries by inequality-adjusted Human Development Index (IHDI), as published by the UNDP in its 2022 Human Development Report. According to the 2016 Report, "The IHDI can be interpreted as the level of human development when i ...
of 0.722, compared to 0.720, 0.710 and 0.576 for neighboring Argentina, Uruguay and Brazil, respectively. In 2017, only 0.7% of the population lived on less than US$1.90 a day.
The Global Competitiveness Report
The ''Global Competitiveness Report'' (GCR) is a yearly report published by the World Economic Forum. Since 2004, the ''Global Competitiveness Report'' ranks countries based on the Global Competitiveness Index, developed by Xavier Sala-i-Martin an ...
for 2009–2010 ranked Chile as being the 30th most competitive country in the world and the first in Latin America, well above Brazil (56th), Mexico (60th), and Argentina which ranks (85th); it has since fallen out of the top 30. The ease of doing business index
The ease of doing business index was an index created jointly by Simeon Djankov, Michael Klein, and Caralee McLiesh, three leading economists at the World Bank Group. The academic research for the report was done jointly with professors Edward ...
, created by the World Bank, listed Chile as 34th in the world as of 2014, 41st for 2015, and 48th as of 2016. The privatized national pension system (AFP) has an estimated total domestic savings rate of approximately 21% of GDP.
History
Arauco War
The Arauco War was a long-running conflict between colonial Spaniards and the Mapuche people, mostly fought in the Araucanía. The conflict began at first as a reaction to the Spanish conquerors attempting to establish cities and force Mapuche ...
. During early colonial times there were gold exports to Perú from placer deposit
In geology, a placer deposit or placer is an accumulation of valuable minerals formed by gravity separation from a specific source rock during sedimentary processes. The name is from the Spanish word ''placer'', meaning "alluvial sand". Placer mi ...
s which soon depleted. Trade restrictions and monopolies established by the Spanish crown are credited for having held back economic development for much of the colonial times. As effect of these restrictions the country incorporated very few new crops and animal breeds after initial conquest. Other sectors that were held back by restrictions were the wine and mining industries. The Bourbon reforms
The Bourbon Reforms ( es, Reformas Borbónicas) consisted of political and economic changes promulgated by the Spanish Monarchy, Spanish Crown under various kings of the House of Bourbon, since 1700, mainly in the 18th century. The beginning of ...
in the 18th century eased many monopolies and trade restrictions.
In the 1830s Chile consolidated under the ideas of Diego Portales
Diego José Pedro Víctor Portales y Palazuelos (; June 16, 1793 – June 6, 1837) was a Chilean statesman and entrepreneur. As a minister of president José Joaquín Prieto's government, he played a pivotal role in shaping the state and po ...
as a stable state open to foreign trade. Foreign investment in Chile grew over the 19th century. After the War of the Pacific
The War of the Pacific ( es, link=no, Guerra del Pacífico), also known as the Saltpeter War ( es, link=no, Guerra del salitre) and by multiple other names, was a war between Chile and a Bolivian–Peruvian alliance from 1879 to 1884. Fought ...
the Chilean treasury grew by 900%. The League of Nations
The League of Nations (french: link=no, Société des Nations ) was the first worldwide intergovernmental organisation whose principal mission was to maintain world peace. It was founded on 10 January 1920 by the Paris Peace Conference that ...
labeled Chile the country hardest hit by the Great Depression because 80% of government revenue came from exports of copper and nitrates, which were in low demand. After the Great Depression Chilean economic policies changed toward import substitution industrialization
Import substitution industrialization (ISI) is a trade and economic policy that advocates replacing foreign imports with domestic production.''A Comprehensive Dictionary of Economics'' p.88, ed. Nelson Brian 2009. It is based on the premise that ...
and the Production Development Corporation was established.
Under the influence of the Chicago Boys the Pinochet regime
Augusto José Ramón Pinochet Ugarte (, , , ; 25 November 1915 – 10 December 2006) was a Chilean general who ruled Chile from 1973 to 1990, first as the leader of the Military Junta of Chile from 1973 to 1981, being declared President of ...
made of Chile a leading country in establishing neoliberal policies. These policies allowed large corporations to consolidate their power over the Chilean economy, leading to long-term economic growth.
The crisis of 1982 caused the appointment of Hernán Büchi
Hernán Alberto Büchi Buc (; born March 6, 1949) is a Chilean economist who served as minister of finance of the Pinochet government. In 1989 he ran unsuccessfully for president with support of Chilean right-wing parties.
Early life
Büchi wa ...
as minister of finance and a sharp revision of economic policy. Despite a general selling of state property and contrary to neoliberal prescriptions, the regime retained the lucrative state owned mining company Codelco
Codelco (''Corporación Nacional'' ''del'' ''Cobre de Chile'' or, in English, the National Copper Corporation of Chile) is a Chilean state-owned copper mining company. It was formed in 1976 from foreign-owned copper companies that were nationalise ...
which stands for about 30% of government income.
According to the CIA World Factbook, during the early 1990s, Chile's reputation as a role model for economic reform was strengthened when the democratic government of Patricio Aylwin
Patricio Aylwin Azócar (; 26 November 1918 – 19 April 2016) was a Chilean politician from the Christian Democratic Party, lawyer, author, professor and former senator. He was the first president of Chile after dictator Augusto Pinochet, a ...
, who took over from the military in 1990, deepened the economic reform initiated by the military government. The Aylwin government departed significantly from the neoliberal doctrine of the Chicago boys, as evidenced by higher government expenditure on social programs to tackle poverty and poor quality housing. Growth in real GDP averaged 8% from 1991 to 1997, but fell to half that level in 1998 because of tight monetary policies (implemented to keep the current account deficit in check) and lower exports due to the Asian financial crisis
The Asian financial crisis was a period of financial crisis that gripped much of East Asia and Southeast Asia beginning in July 1997 and raised fears of a worldwide economic meltdown due to financial contagion. However, the recovery in 1998– ...
. Chile's economy has since recovered and has seen growth rates of 5–7% over the past several years.
After a decade of impressive growth rates, Chile began to experience a moderate economic downturn in 1999, brought on by unfavorable global economic conditions related to the Asian financial crisis
The Asian financial crisis was a period of financial crisis that gripped much of East Asia and Southeast Asia beginning in July 1997 and raised fears of a worldwide economic meltdown due to financial contagion. However, the recovery in 1998– ...
, which began in 1997. The economy remained sluggish until 2003, when it began to show clear signs of recovery, achieving 4.0% real GDP growth. The Chilean economy finished 2004 with growth of 6.0%. Real GDP growth reached 5.7% in 2005 before falling back to 4.0% in 2006. GDP expanded by 5.1% in 2007.
Sectors
During 2012, the largest sectors by GDP were mining (mainly copper), business services, personal services, manufacturing and wholesale and retail trade. Mining also represented 59.5% of exports in the period, while the manufacturing sector accounted for 34% of exports, concentrated mainly in food products, chemicals and pulp, paper and others.Agriculture
Chile is one of the 5 largest world producers of cherry andcranberry
Cranberries are a group of evergreen dwarf shrubs or trailing vines in the subgenus ''Oxycoccus'' of the genus '' Vaccinium''. In Britain, cranberry may refer to the native species '' Vaccinium oxycoccos'', while in North America, cranberry ...
, and one of the 10 largest world producers of grape
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus '' Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.
The cultivation of grapes began perhaps 8,000 years a ...
, apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple trees are cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus ''Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ancestor, ' ...
, kiwi
Kiwi most commonly refers to:
* Kiwi (bird), a flightless bird native to New Zealand
* Kiwi (nickname), a nickname for New Zealanders
* Kiwifruit, an edible berry
* Kiwi dollar or New Zealand dollar, a unit of currency
Kiwi or KIWI may also ref ...
, peach
The peach (''Prunus persica'') is a deciduous tree first domesticated and cultivated in Zhejiang province of Eastern China. It bears edible juicy fruits with various characteristics, most called peaches and others (the glossy-skinned, non-f ...
, plum and hazelnut, focusing on exporting high-value fruits.
In 2018, Chile was the 9th largest producer of grape
A grape is a fruit, botanically a berry, of the deciduous woody vines of the flowering plant genus '' Vitis''. Grapes are a non- climacteric type of fruit, generally occurring in clusters.
The cultivation of grapes began perhaps 8,000 years a ...
in the world, with 2 million tons produced; the 10th largest producer of apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple trees are cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus ''Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ancestor, ' ...
in the world, with 1.7 million tons produced; and the 6th largest producer of kiwi
Kiwi most commonly refers to:
* Kiwi (bird), a flightless bird native to New Zealand
* Kiwi (nickname), a nickname for New Zealanders
* Kiwifruit, an edible berry
* Kiwi dollar or New Zealand dollar, a unit of currency
Kiwi or KIWI may also ref ...
in the world, with 230 thousand tons produced, in addition to producing 1.4 million tons of wheat
Wheat is a grass widely cultivated for its seed, a cereal grain that is a worldwide staple food. The many species of wheat together make up the genus ''Triticum'' ; the most widely grown is common wheat (''T. aestivum''). The archaeologi ...
, 1.1 million tons of maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. The ...
, 1.1 million tons of potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern Unit ...
, 951 thousand tons of tomato
The tomato is the edible berry of the plant ''Solanum lycopersicum'', commonly known as the tomato plant. The species originated in western South America, Mexico, and Central America. The Mexican Nahuatl word gave rise to the Spanish word ...
, 571 thousand tons of oats
The oat (''Avena sativa''), sometimes called the common oat, is a species of cereal grain grown for its seed, which is known by the same name (usually in the plural, unlike other cereals and pseudocereals). While oats are suitable for human co ...
, 368 thousand tons of onion
An onion (''Allium cepa'' L., from Latin ''cepa'' meaning "onion"), also known as the bulb onion or common onion, is a vegetable that is the most widely cultivated species of the genus ''Allium''. The shallot is a botanical variety of the onio ...
, 319 thousand tons of peach
The peach (''Prunus persica'') is a deciduous tree first domesticated and cultivated in Zhejiang province of Eastern China. It bears edible juicy fruits with various characteristics, most called peaches and others (the glossy-skinned, non-f ...
, 280 thousand tons of pear
Pears are fruits produced and consumed around the world, growing on a tree and harvested in the Northern Hemisphere in late summer into October. The pear tree and shrub are a species of genus ''Pyrus'' , in the family Rosaceae, bearing the po ...
, 192 thousand tons of rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and '' Porteresia'', both wild and domesticat ...
, 170 thousand tons of barley
Barley (''Hordeum vulgare''), a member of the grass family, is a major cereal grain grown in temperate climates globally. It was one of the first cultivated grains, particularly in Eurasia as early as 10,000 years ago. Globally 70% of barley p ...
, 155 thousand tons of cherry, 151 thousand tons of lemon
The lemon (''Citrus limon'') is a species of small evergreen trees in the flowering plant family Rutaceae, native to Asia, primarily Northeast India (Assam), Northern Myanmar or China.
The tree's ellipsoidal yellow fruit is used for culin ...
, 118 thousand tons of tangerine
The tangerine is a type of citrus fruit that is orange in color. Its scientific name varies. It has been treated as a separate species under the name ''Citrus tangerina'' or ''Citrus'' × ''tangerina'', or treated as a variety of ''Citrus retic ...
, 113 thousand tons of orange
Orange most often refers to:
*Orange (fruit), the fruit of the tree species '' Citrus'' × ''sinensis''
** Orange blossom, its fragrant flower
*Orange (colour), from the color of an orange, occurs between red and yellow in the visible spectrum
* ...
, 110 thousand tons of olives
The olive, botanical name ''Olea europaea'', meaning 'European olive' in Latin, is a species of small tree or shrub in the family Oleaceae, found traditionally in the Mediterranean Basin. When in shrub form, it is known as ''Olea europaea'' 'M ...
, 106 thousand tons of cranberry
Cranberries are a group of evergreen dwarf shrubs or trailing vines in the subgenus ''Oxycoccus'' of the genus '' Vaccinium''. In Britain, cranberry may refer to the native species '' Vaccinium oxycoccos'', while in North America, cranberry ...
, in addition to smaller productions of other agricultural products.
Agriculture and allied sectors like forestry, logging and fishing accounts only for 4.9% of the GDP as of 2007 and employed 13.6% of the country's labor force
The workforce or labour force is a concept referring to the pool of human beings either in employment or in unemployment. It is generally used to describe those working for a single company or industry, but can also apply to a geographic reg ...
. Some major agriculture products of Chile includes grapes, apples, pears, onions, wheat, corn, oats, peaches, garlic, asparagus, beans, beef, poultry, wool, fish and timber.Chile''
The World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print version is availabl ...
''. Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
.
Chile's position in the Southern Hemisphere leads to an agricultural season cycle opposite to those of the principal consumer markets, primarily located in the Northern Hemisphere. Chile's extreme north–south orientation produces seven different macro-regions distinguished by climate and geographical features, which allows the country itself to stagger harvests and results in extended harvesting seasons. However, the mountainous landscape of Chile limits the extent and intensity of agriculture so that arable land corresponds only to 2.62% of the total territory. Through Chile's trade agreements, its agricultural products have gained access to a market controlling 77% of the world's GDP and by approximately 2012, 74% of Chilean agribusiness exports will be duty-free.
Chile's principal growing region
A growing region is an area suited by climate and soil conditions to the cultivation of a certain type of crop or plant group.
Most crops are cultivated not in one place only, but in several distinct regions in diverse parts of the world. Culti ...
and agricultural heartland is the Central Valley delimited by the Chilean Coast Range
The Chilean Coastal Range ( es, Cordillera de la Costa) is a mountain range that runs from north to south along the Pacific coast of South America parallel to the Andean Mountains, extending from Morro de Arica in the north to Taitao Peninsula, ...
in the west, the Andes
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long, wide (widest between 18°S – 20°S ...
in the east Aconcagua River
The Aconcagua River is a river in Chile that rises from the conflux of two minor tributary rivers at above sea level in the Andes, Juncal River from the east (which rise in the Nevado Juncal) and Blanco River from the south east. The Aconcag ...
by the north and Bío-Bío River by the south. In the northern half of Chile cultivation is highly dependent on irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been devel ...
. South of the Central Valley cultivation is gradually replaced by aquaculture, silviculture
Silviculture is the practice of controlling the growth, composition/structure, and quality of forests to meet values and needs, specifically timber production.
The name comes from the Latin ('forest') and ('growing'). The study of forests and wo ...
, sheep and cattle farming.
Salmon
Chile is the second largest producer ofsalmon
Salmon () is the common name for several commercially important species of euryhaline ray-finned fish from the family Salmonidae, which are native to tributaries of the North Atlantic (genus ''Salmo'') and North Pacific (genus '' Oncorhy ...
in the world. As of August 2007, Chile's share of worldwide salmon industry sales was 38.2%, rising from just 10% in 1990. The average growth rate of the industry for the 20 years between 1984 and 2004 was 42% per year. The presence of large foreign firms in the salmon industry has brought what probably most contributes to Chile's burgeoning salmon production, technology. Technology transfer has allowed Chile to build its global competitiveness and innovation and has led to the expansion of production as well as to an increase in average firm size in the industry. In November 2018, the Chinese company Joyvio Group ( Legend Holdings) bought the Chilean salmon producer Australis Seafoods for $880 million, thus gaining control over 30% of all Chilean salmon exports.
Forestry
The Chilean forestry industry grew to comprise 13% of the country's total exports in 2005, making it one of the largest export sectors for Chile.Radiata Pine
''Pinus radiata'' ( syn. ''Pinus insignis''), the Monterey pine, insignis pine or radiata pine, is a species of pine native to the Central Coast of California and Mexico ( Guadalupe Island and Cedros island). It is an evergreen conifer in the ...
and Eucalyptus
''Eucalyptus'' () is a genus of over seven hundred species of flowering trees, shrubs or mallees in the myrtle family, Myrtaceae. Along with several other genera in the tribe Eucalypteae, including '' Corymbia'', they are commonly known as e ...
comprise the vast majority of Chile's forestry exports. Within the forestry sector, the largest contributor to total production is pulp
Pulp may refer to:
* Pulp (fruit), the inner flesh of fruit
Engineering
* Dissolving pulp, highly purified cellulose used in fibre and film manufacture
* Pulp (paper), the fibrous material used to make paper
* Molded pulp, a packaging material
...
, followed by wood-based panels and lumber
Lumber is wood that has been processed into dimensional lumber, including beams and planks or boards, a stage in the process of wood production. Lumber is mainly used for construction framing, as well as finishing (floors, wall panels, wi ...
. Due to popular and increasing demands for Chile's forestry products, the government is currently focusing on increasing the already vast acreage of Chile's Pine and Eucalyptus plantations as well as opening new industrial plants.
Wine
 Chile's unique geography and climate make it ideal for winegrowing and the country has made the top ten list of wine producers many times in the last few decades.
The popularity of Chilean wine has been attributed not just to the quantity produced but also to increasing levels of quality. The combination of quantity and quality allows Chile to export excellent wines at reasonable prices to the international market.
Chile's unique geography and climate make it ideal for winegrowing and the country has made the top ten list of wine producers many times in the last few decades.
The popularity of Chilean wine has been attributed not just to the quantity produced but also to increasing levels of quality. The combination of quantity and quality allows Chile to export excellent wines at reasonable prices to the international market.
Mining
 The mining sector in Chile is one of the pillars of Chilean economy. The Chilean government strongly supports foreign investment in the sector and has modified its mining industry laws and regulations to create a favorable investing environment for foreigners. Thanks to a large amount of copper resources, complaisant legislation and an unregulated investment environment, Chile has become one of the main
The mining sector in Chile is one of the pillars of Chilean economy. The Chilean government strongly supports foreign investment in the sector and has modified its mining industry laws and regulations to create a favorable investing environment for foreigners. Thanks to a large amount of copper resources, complaisant legislation and an unregulated investment environment, Chile has become one of the main copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
producer, with almost 30% of the global annual copper output.
In addition to copper, Chile was, in 2019, the world's largest producer of iodine and rhenium
Rhenium is a chemical element with the symbol Re and atomic number 75. It is a silvery-gray, heavy, third-row transition metal in group 7 of the periodic table. With an estimated average concentration of 1 part per billion (ppb), rhenium is one ...
, the second largest producer of lithium
Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid ...
and molybdenum, the sixth largest producer of silver
Silver is a chemical element with the symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical ...
, the seventh largest producer of salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quant ...
, the eighth largest producer of potash
Potash () includes various mined and manufactured salts that contain potassium in water-soluble form.
, the thirteenth producer of sulfur and the thirteenth producer of iron ore in the world. The country also has considerable gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile me ...
production: between 2006 and 2017, the country produced annual amounts ranging from 35.9 tonnes in 2017 to 51.3 tonnes in 2013.
Services
The service sector in Chile has grown fast and consistently in recent decades, reinforced by the rapid development of communication and information technology, access to education and an increase in specialist skills and knowledge among the workforce. Chilean foreign policy has recognized the importance of thetertiary sector
The tertiary sector of the economy, generally known as the service sector, is the third of the three economic sectors in the three-sector model (also known as the economic cycle). The others are the primary sector (raw materials) and the second ...
or service sector to the economy, boosting its international liberalization and leading to the signing of several free trade area
A free-trade area is the region encompassing a trade bloc whose member countries have signed a free trade agreement (FTA). Such agreements involve cooperation between at least two countries to reduce trade barriers, import quotas and tariffs, and ...
agreements.
Chilean service exportation consists mainly of maritime and aeronautical services, tourism, retail (department stores, supermarkets, and shopping centers), engineering and construction services, informatics, health and education.
Chile ranked first among Latin American countries (and No. 32 worldwide) in Adecco
The Adecco Group, is a Swiss-French company based in Zurich, Switzerland, and is the world's second largest Human Resources provider and temporary staffing firm, and a Fortune Global 500 company.
They directly employ 700,000 people a day ...
's 2019 Global Talent Competitiveness Index (GTCI).
Finance
Chile's financial sector has grown quickly in recent years, with a banking reform law approved in 1997 that broadened the scope of permissible foreign activity for Chilean banks. The Chilean Government implemented a further liberalization of capital markets in 2001, and there is further pending legislation proposing further liberalization. Over the last ten years, people who live in Chile have enjoyed the introduction of new financial tools such as home equity loans, currency futures and options, factoring, leasing, and debit cards. The introduction of these new products has also been accompanied by an increased use of traditional instruments such as loans and credit cards. Chile's private pension system, with assets worth roughly $70 billion at the end of 2006, has been an important source of investment capital for the capital market. However, by 2009, it has been reported that $21 billion had been lost from the pension system to the global financial crisis.Tourism
Comodoro Arturo Merino Benítez International Airport
Comodoro is a municipality in the state of Mato Grosso in the Central-West Region of Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin Amer ...
and Paso Los Libertadores.
Chile has a great diversity of natural landscapes, from the Mars-like landscapes of the hyperarid Atacama Desert
The Atacama Desert ( es, Desierto de Atacama) is a desert plateau in South America covering a 1,600 km (990 mi) strip of land on the Pacific coast, west of the Andes Mountains. The Atacama Desert is the driest nonpolar desert in th ...
to the glacier-fed fjords of the Chilean Patagonia
Patagonia () refers to a geographical region that encompasses the southern end of South America, governed by Argentina and Chile. The region comprises the southern section of the Andes Mountains with lakes, fjords, temperate rainforests, and g ...
, passing by the winelands backdropped by the Andes
The Andes, Andes Mountains or Andean Mountains (; ) are the longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long, wide (widest between 18°S – 20°S ...
of the Central Valley and the old-growth forests of the Lakes District. Easter Island
Easter Island ( rap, Rapa Nui; es, Isla de Pascua) is an island and special territory of Chile in the southeastern Pacific Ocean, at the southeasternmost point of the Polynesian Triangle in Oceania. The island is most famous for its ne ...
and Juan Fernández Archipelago
''Juan'' is a given name, the Spanish and Manx versions of ''John''. It is very common in Spain and in other Spanish-speaking communities around the world and in the Philippines, and also (pronounced differently) in the Isle of Man. In Spanish, t ...
, including Robinson Crusoe Island
Robinson Crusoe Island ( es, Isla Róbinson Crusoe, ), formerly known as Más a Tierra (), is the second largest of the Juan Fernández Islands, situated 670 km (362 nmi; 416 mi) west of San Antonio, Chile, in the South Pacific Oc ...
, are also major attractions.
Many of the most visited attractions in Chile are protected areas. The extensive Chilean protected areas system includes 32 protected parks, 48 natural reserves and 15 natural monuments.
Economic policies
 According to the CIA World Factbook, Chile's "sound economic policies", maintained consistently since the 1980s, "have contributed to steady economic growth in Chile and have more than halved poverty rates." The 1973–90 military government sold many state-owned companies, and the three democratic governments since 1990 have implemented export promotion policies and continued privatization, though at a slower pace. The government's role in the economy is mostly limited to regulation, although the state continues to operate copper giant
According to the CIA World Factbook, Chile's "sound economic policies", maintained consistently since the 1980s, "have contributed to steady economic growth in Chile and have more than halved poverty rates." The 1973–90 military government sold many state-owned companies, and the three democratic governments since 1990 have implemented export promotion policies and continued privatization, though at a slower pace. The government's role in the economy is mostly limited to regulation, although the state continues to operate copper giant CODELCO
Codelco (''Corporación Nacional'' ''del'' ''Cobre de Chile'' or, in English, the National Copper Corporation of Chile) is a Chilean state-owned copper mining company. It was formed in 1976 from foreign-owned copper companies that were nationalise ...
and a few other enterprises (there is one state-run bank).
Under the compulsory private pension system, most formal sector employees pay 10% of their salaries into privately managed funds.
As of 2006, Chile invested 0.6% of its annual GDP in research and development (R&D). Even then, two-thirds of that was government spending. Beyond its general economic and political stability, the government has also encouraged the use of Chile as an "investment platform" for multinational corporations planning to operate in the region. Chile's approach to foreign direct investment is codified in the country's Foreign Investment Law, which gives foreign investors the same treatment as Chileans. Registration is reported to be simple and transparent, and foreign investors are guaranteed access to the official foreign exchange market to repatriate their profits and capital.
Faced with the financial crisis of 2007–2008
Finance is the study and discipline of money, currency and capital assets. It is related to, but not synonymous with economics, the study of production, distribution, and consumption of money, assets, goods and services (the discipline of fi ...
, the government announced a $4 billion economic stimulus plan to spur employment and growth, and despite the global financial crisis, aimed for an expansion of between 2 percent and 3 percent of GDP for 2009. Nonetheless, economic analysts disagreed with government estimates and predicted economic growth at a median of 1.5 percent. According to the CIA World FactBook, the GDP contracted an estimated −1.7% in 2009.
The Chilean Government has formed a Council on Innovation and Competition, which is tasked with identifying new sectors and industries to promote. It is hoped that this, combined with some tax reforms to encourage domestic and foreign investment in research and development, will bring in additional FDI to new parts of the economy.
According to The Heritage Foundation
The Heritage Foundation (abbreviated to Heritage) is an American conservative think tank based in Washington, D.C. that is primarily geared toward public policy. The foundation took a leading role in the conservative movement during the presiden ...
's '' Index of Economic Freedom'' in 2012, Chile has the strongest private property rights in Latin America, scoring 90 on a scale of 100.
Chile's AA- S&P credit rating is the highest in Latin America, while Fitch Ratings places the country one step below, in A+.
There are three main ways for Chilean firms to raise funds abroad: bank loans, issuance of bonds, and the selling of stocks on U.S. markets through American Depository Receipts (ADRs). Nearly all of the funds raised through these means go to finance domestic Chilean investment. In 2006, the Government of Chile ran a surplus of $11.3 billion, equal to almost 8% of GDP. The Government of Chile continues to pay down its foreign debt, with public debt only 3.9% of GDP at the end of 2006.
Fiscal policy
One of Chile's fiscal policy central features has been its counter-cyclical nature. This has been facilitated by the voluntary application since 2001 of a structural balance policy based on the commitment to an announced goal of a medium-term structural balance as a percentage of GDP. The structural balance nets out the effect of the economic cycle (including copper price volatility) on fiscal revenues and constrains expenditures to a correspondingly consistent level. In practice, this means that expenditures rise when activity is low and decrease in boomsRodríguez, J., C. Tokman and A. Vega (2007). "Structural balance policy in Chile".OECD Journal on Budgeting 7(2), pp. 59–92. The target was of 1% of GDP between 2001 and 2007, it was reduced to 0.5% in 2008 and then to 0% in 2009 in the wake of the global financial crisis.Corbo, Vittorio. La política fiscal chilena.
Blogs from El Mercurio Newspaper. 25 August 2013. In 2005, key elements of this voluntary policy were incorporated into legislation through the Fiscal Responsibility Law (Law 20,128). The Fiscal Responsibility Law also allowed for the creation of two
sovereign wealth funds
A sovereign wealth fund (SWF), sovereign investment fund, or social wealth fund is a state-owned investment fund that invests in real and financial assets such as stocks, bonds, real estate, precious metals, or in alternative investments such as ...
: the Pension Reserve Fund (PRF), to face increased expected old-age benefits liabilities, and the Economic and Social Stabilization Fund (ESSF), to stabilize fiscal spending by providing funds to finance fiscal deficits and debt amortization. By the end of 2012, they had respective market values of US$5.883 million and US$14.998 million.
The main taxes in Chile in terms of revenue collection are the value added tax (45.8% of total revenues in 2012) and the income tax (41.8% of total revenues in 2012). The value added tax is levied on sales of goods and services (including imports) at a rate of 19%, with a few exemptions. The income tax revenue comprises different taxes. While there is a corporate income tax of 20% over profits from companies (called First Category Tax), the system is ultimately designed to tax individuals. Therefore, corporate income taxes paid constitute a credit towards two personal income taxes: the Global Complementary Tax (in the case of residents) or the Additional Tax (in the case of non-residents). The Global Complementary Tax is payable by those that have different sources of income, while those receiving income solely from dependent work are subject to the Second Category Tax. Both taxes are equally progressive in statutory terms, with a top marginal rate of 40%. Income arising from corporate activity under the Global Complementary Tax only becomes payable when effectively distributed to the individual. There are also special sales taxes on alcohol and luxury goods, as well as specific taxes on tobacco and fuel. Other taxes include the inheritance tax and custom duties.
In 2012, general government expenditure reached 21.5% of GDP, while revenues were equivalent to 22% of GDP.OECD (2013), OECD Economic Surveys: Chile 2013.OECD Publishing. Gross financial debt amounted to 12.2% of GDP, while in net terms it was −6.9% of GDP, both well below OECD averages.
Monetary policy
Chile's monetary authority is the Central Bank of Chile (CBoC). The CBoC pursues an inflation target of 3%, with a tolerance range of 1% (below or above)."Central Bank of Chile: Monetary Policy in an Inflation Targeting Framework".Central Bank of Chile, January 2007. Inflation has followed a relatively stable trajectory since the year 2000, remaining under 10%, despite the temporary surge of some inflationary pressures in the year 2008. The Chilean peso's rapid appreciation against the U.S. dollar in recent years has helped dampen inflation. Most wage settlements and loans are indexed, reducing inflation's volatility. The CBoC is granted autonomous status by Chile's National Constitution, providing credibility and stability beyond the political cycle. According to the Basic Constitutional Act of the Central Bank of Chile (Law 18,840), its main objectives are to safeguard "the stability of the currency and the normal functioning of internal and external payments".
, Title I, Section 3. To meet these objectives, the CBoC is enabled to use monetary and foreign exchange policy instruments, along with some discretion on financial regulation. In practice, the CBoC monetary policy is guided by an inflation targeting regime, while the foreign exchange policy is led by a floating exchange rate and, although unusual, the bank reserves the right to intervene in the foreign exchange markets.
Trade policy
Chile is strongly committed to free trade and has welcomed large amounts of foreign investment. Chile has signed free trade agreements (FTAs) with a whole network of countries, including an FTA with the United States that was signed in 2003 and implemented in January 2004. Chile unilaterally lowered its across-the-board import tariff for all countries with which it does not have a trade agreement to 6% in 2003. Higher effective tariffs are charged only on imports of wheat, wheat flour, and sugar as a result of a system of import price bands. The price bands were ruled inconsistent with Chile'sWorld Trade Organization
The World Trade Organization (WTO) is an intergovernmental organization that regulates and facilitates international trade. With effective cooperation
in the United Nations System, governments use the organization to establish, revise, and ...
(WTO) obligations in 2002, and the government has introduced legislation to modify them. Under the terms of the U.S.–Chile FTA, the price bands will be completely phased out for U.S. imports of wheat, wheat flour, and sugar within 12 years.
Chile is a strong proponent of pressing ahead on negotiations for a Free Trade Area of the Americas
The Free Trade Area of the Americas (FTAA) was a proposed agreement to eliminate or reduce the trade barriers among all countries in the Americas, excluding Cuba. Negotiations to establish the FTAA ended in failure, however, with all parties unab ...
(FTAA) and is active in the WTO's Doha round of negotiations, principally through its membership in the G-20
The G20 or Group of Twenty is an intergovernmental forum comprising 19 countries and the European Union (EU). It works to address major issues related to the global economy, such as international financial stability, climate change mitigation, ...
and Cairns Group.
Most imports are not subject to the full statutory tariff, due to the extensive preferences negotiated outside the multilateral system through Regional Trade Agreements (RTAs). By the last version of the World Trade Organization's Trade Policy Review (October 2009), Chile had signed 21 RTAs with 57 countries and the number has continued to rise in recent yearsTrade Policy Review Chile2009, World Trade Organization. More recently, Chile has also been an active participant of deeper plurilateral trade agreement negotiations. Notably, Chile is currently in talks with eleven other economies in the
Trans-Pacific Partnership
The Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP), or Trans-Pacific Partnership Agreement, was a highly contested proposed trade agreement between 12 Pacific Rim economies, Australia, Brunei, Canada, Chile, Japan, Malaysia, Mexico, New Zealand, Peru, Sin ...
(TPP), a proposed agreement that would stem from the existing P-4 Agreement between Brunei, Chile, New Zealand and Singapore. Chile has signed some form of bilateral or plurilateral agreement with each of the parties at TPP, although with different degrees of integration.
Chile is also a party in conversations to establish the Pacific Alliance
The Pacific Alliance ( es, link=no, Alianza del Pacífico) is a Latin American trade bloc, formed by Chile, Colombia, Mexico and Peru, which all border the Pacific Ocean. The alliance was formed with the express purpose of improving regional in ...
along with Peru, Mexico and Colombia.
Foreign trade
 2006 was a record year for Chilean trade. Total trade registered a 31% increase over 2005. During 2006, exports of goods and services totaled US$58 billion, an increase of 41%. This figure was somewhat distorted by the skyrocketing price of copper. In 2006, copper exports reached a historical high of US$33.3 billion. Imports totaled US$35 billion, an increase of 17% compared to the previous year. Chile thus recorded a positive trade balance of US$2.3 billion in 2006.
The main destinations for Chilean exports were the Americas (US$39 billion), Asia (US$27.8 billion) and Europe (US$22.2 billion). Seen as shares of Chile's export markets, 42% of exports went to the Americas, 30% to Asia and 24% to Europe. Within Chile's diversified network of trade relationships, its most important partner remained the United States. Total trade with the U.S. was US$14.8 billion in 2006. Since the U.S.–Chile Free Trade Agreement went into effect on 1 January 2004, U.S.–Chilean trade has increased by 154%. Internal Government of Chile figures show that even when factoring out inflation and the recent high price of copper, bilateral trade between the U.S. and Chile has grown over 60% since then.
Total trade with Europe also grew in 2006, expanding by 42%. The Netherlands and Italy were Chile's main European trading partners. Total trade with Asia also grew significantly at nearly 31%. Trade with Korea and Japan grew significantly, but China remained Chile's most important trading partner in Asia. Chile's total trade with China reached U.S. $8.8 billion in 2006, representing nearly 66% of the value of its trade relationship with Asia.=
The growth of exports in 2006 was mainly caused by a strong increase in sales to the United States, the Netherlands, and Japan. These three markets alone accounted for an additional US$5.5 billion worth of Chilean exports. Chilean exports to the United States totaled US$9.3 billion, representing a 37.7% increase compared to 2005 (US$6.7 billion). Exports to the European Union were US$15.4 billion, a 63.7% increase compared to 2005 (US$9.4 billion). Exports to Asia increased from US$15.2 billion in 2005 to US$19.7 billion in 2006, a 29.9% increase.
During 2006, Chile imported US$26 billion from the Americas, representing 54% of total imports, followed by Asia at 22%, and Europe at 16%. Mercosur members were the main suppliers of imports to Chile at US$9.1 billion, followed by the United States with US$5.5 billion and the European Union with US$5.2 billion. From Asia, China was the most important exporter to Chile, with goods valued at US$3.6 billion. Year-on-year growth in imports was especially strong from a number of countries – Ecuador (123.9%), Thailand (72.1%), Korea (52.6%), and China (36.9%).
Chile's overall trade profile has traditionally been dependent upon copper exports. The state-owned firm CODELCO is the world's largest copper-producing company, with recorded copper reserves of 200 years. Chile has made an effort to expand nontraditional exports. The most important non-mineral exports are forestry and wood products, fresh fruit and processed food, fishmeal and seafood, and
2006 was a record year for Chilean trade. Total trade registered a 31% increase over 2005. During 2006, exports of goods and services totaled US$58 billion, an increase of 41%. This figure was somewhat distorted by the skyrocketing price of copper. In 2006, copper exports reached a historical high of US$33.3 billion. Imports totaled US$35 billion, an increase of 17% compared to the previous year. Chile thus recorded a positive trade balance of US$2.3 billion in 2006.
The main destinations for Chilean exports were the Americas (US$39 billion), Asia (US$27.8 billion) and Europe (US$22.2 billion). Seen as shares of Chile's export markets, 42% of exports went to the Americas, 30% to Asia and 24% to Europe. Within Chile's diversified network of trade relationships, its most important partner remained the United States. Total trade with the U.S. was US$14.8 billion in 2006. Since the U.S.–Chile Free Trade Agreement went into effect on 1 January 2004, U.S.–Chilean trade has increased by 154%. Internal Government of Chile figures show that even when factoring out inflation and the recent high price of copper, bilateral trade between the U.S. and Chile has grown over 60% since then.
Total trade with Europe also grew in 2006, expanding by 42%. The Netherlands and Italy were Chile's main European trading partners. Total trade with Asia also grew significantly at nearly 31%. Trade with Korea and Japan grew significantly, but China remained Chile's most important trading partner in Asia. Chile's total trade with China reached U.S. $8.8 billion in 2006, representing nearly 66% of the value of its trade relationship with Asia.=
The growth of exports in 2006 was mainly caused by a strong increase in sales to the United States, the Netherlands, and Japan. These three markets alone accounted for an additional US$5.5 billion worth of Chilean exports. Chilean exports to the United States totaled US$9.3 billion, representing a 37.7% increase compared to 2005 (US$6.7 billion). Exports to the European Union were US$15.4 billion, a 63.7% increase compared to 2005 (US$9.4 billion). Exports to Asia increased from US$15.2 billion in 2005 to US$19.7 billion in 2006, a 29.9% increase.
During 2006, Chile imported US$26 billion from the Americas, representing 54% of total imports, followed by Asia at 22%, and Europe at 16%. Mercosur members were the main suppliers of imports to Chile at US$9.1 billion, followed by the United States with US$5.5 billion and the European Union with US$5.2 billion. From Asia, China was the most important exporter to Chile, with goods valued at US$3.6 billion. Year-on-year growth in imports was especially strong from a number of countries – Ecuador (123.9%), Thailand (72.1%), Korea (52.6%), and China (36.9%).
Chile's overall trade profile has traditionally been dependent upon copper exports. The state-owned firm CODELCO is the world's largest copper-producing company, with recorded copper reserves of 200 years. Chile has made an effort to expand nontraditional exports. The most important non-mineral exports are forestry and wood products, fresh fruit and processed food, fishmeal and seafood, and wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from fermented grapes. Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different varieties of grapes and strains of yeasts are m ...
.
Trade agreements
 Over the last several years, Chile has signed FTAs with the European Union, South Korea, New Zealand, Singapore, Brunei, China, and Japan. It reached a partial trade agreement with India in 2005 and began negotiations for a full-fledged FTA with India in 2006. Chile conducted trade negotiations in 2007 with Australia, Malaysia, and Thailand, as well as with China to expand an existing agreement beyond just trade in goods. Chile concluded FTA negotiations with Australia and an expanded agreement with China in 2008. The members of the P4 (Chile, Singapore, New Zealand, and Brunei) also plan to conclude a chapter on finance and investment in 2008.
Successive Chilean governments have actively pursued trade-liberalizing agreements. During the 1990s, Chile signed
Over the last several years, Chile has signed FTAs with the European Union, South Korea, New Zealand, Singapore, Brunei, China, and Japan. It reached a partial trade agreement with India in 2005 and began negotiations for a full-fledged FTA with India in 2006. Chile conducted trade negotiations in 2007 with Australia, Malaysia, and Thailand, as well as with China to expand an existing agreement beyond just trade in goods. Chile concluded FTA negotiations with Australia and an expanded agreement with China in 2008. The members of the P4 (Chile, Singapore, New Zealand, and Brunei) also plan to conclude a chapter on finance and investment in 2008.
Successive Chilean governments have actively pursued trade-liberalizing agreements. During the 1990s, Chile signed free trade agreement
A free-trade agreement (FTA) or treaty is an agreement according to international law to form a free-trade area between the cooperating states. There are two types of trade agreements: bilateral and multilateral. Bilateral trade agreements occ ...
s (FTA) with Canada, Mexico, and Central America. Chile also concluded preferential trade agreements with Venezuela, Colombia, and Ecuador. An association agreement with Mercosur-Argentina, Brazil, Paraguay, and Uruguay-went into effect in October 1996. Continuing its export-oriented development strategy, Chile completed landmark free trade agreements in 2002 with the European Union and South Korea. Chile, as a member of the Asia-Pacific Economic Cooperation (APEC) organization, is seeking to boost commercial ties to Asian markets. To that end, it has signed trade agreements in recent years with New Zealand, Singapore, Brunei, India, China, and most recently Japan. In 2007, Chile held trade negotiations with Australia, Thailand, Malaysia, and China. In 2008, Chile hopes to conclude an FTA with Australia, and finalize an expanded agreement (covering trade in services and investment) with China. The P4 (Chile, Singapore, New Zealand, and Brunei) also plan to expand ties through adding a finance and investment chapter to the existing P4 agreement. Chile's trade talks with Malaysia and Thailand are also scheduled to continue in 2008.
After two years of negotiations, the United States and Chile signed an agreement in June 2003 that will lead to completely duty-free bilateral trade within 12 years. The U.S.-Chile FTA entered into force 1 January 2004, following approval by the U.S. and Chilean congresses. The FTA has greatly expanded U.S.-Chilean trade ties, with total bilateral trade jumping by 154% during the FTA's first three years. On 1 January 2014, Chile-Vietnam Free Trade Agreement officially took effect.
Issues
Unemployment hovered at 8–10% after the start of the economic slowdown in 1999, above the 7% average for the 1990s. Unemployment finally dipped to 7.8% in 2006, and continued to fall in 2007, averaging 6.8% monthly (up to August). Wages have risen faster than inflation as a result of higher productivity, boosting national living standards. The percentage of Chileans with household incomes below the poverty line – defined as twice the cost of satisfying a person's minimal nutritional needs – fell from 45.1% in 1987 to 11.7% in 2015, according to government polls. Critics in Chile, however, argue that poverty figures are considerably higher than those officially published; until 2016, the government defined the poverty line based on an outdated 1987 household consumption poll, instead of more recent polls from 1997 or 2007. According to critics who use data from the 1997 poll, the poverty rate goes up to 29%; a study published in 2017 claims that it reaches 26%. Using the relative yardstick favoured in many European countries, 27% of Chileans would be poor, according to Juan Carlos Feres of theECLAC
The United Nations Economic Commission for Latin America and the Caribbean, known as ECLAC, UNECLAC or in Spanish and Portuguese CEPAL, is a United Nations regional commission to encourage economic cooperation. ECLAC includes 46 member States (2 ...
. Starting in 2016, a new Multidimensional Poverty Index is also used, which reached 20.9% using 2015 data.
The percent of total income earned by the richest 20% of the Chilean population in 2000 was 61.0% of GDP, while the percent of total income earned by the poorest 20% of the Chilean population was 3.3% of GDP. Chile's Gini Coefficient in 2003 (53.8) has slightly changed in comparison with the value in 1995 (56.4). In 2005 the 10% poorest among the Chileans received 1.2% of GNP
The gross national income (GNI), previously known as gross national product (GNP), is the total domestic and foreign output claimed by residents of a country, consisting of gross domestic product (GDP), plus factor incomes earned by foreign ...
(2000 = 1.4%), while the 10% richest received 47% of GNP
The gross national income (GNI), previously known as gross national product (GNP), is the total domestic and foreign output claimed by residents of a country, consisting of gross domestic product (GDP), plus factor incomes earned by foreign ...
(2000 = 46%).
Regarding the census, assessments have exhibited mixed results. An initial evaluation by a domestic independent experts panel released in August 2013 placed the omission rate in 9.3%, three times as much as other census in the region, and recommended annulling the census to hold a new version in 2015. The government sought an assessment by international experts before making a final decision. The team, which included three experts that represented the World Bank and the E.U. Statistics Commission, found "no basis for doubting the usability of the census data for most, if perhaps not all, of the customary uses" and recommended its release subject to the elimination of the imputation of housing units not observed on the ground during the enumeration and the concurrent publication of a methodological and administrative report.
Statistics
Main economic indicators
The following table shows the main economic indicators in 1980–2021 (with IMF staff estimates in 2022–2027). Inflation below 5% is in green.GDP composition
Main macroeconomic aggregates of GDP. Note: Data are preliminary. Source: Cuentas Nacionales de Chile – Evolución de la actividad económica en el año 2015 (p. 29), Central Bank of Chile, accessed on 23 March 2016.GDP by sector
Gross domestic product by sector of the economy. Note: 2011 data are preliminary. Source: Cuentas Nacionales – Evolución de la actividad económica en el año 2011 (p. 34). Central Bank of Chile. accessed on 22 March 2012.Top exports
 Chile's top exports in 2013.
Source: Central Bank of Chile's statistics database.
Chile's top exports in 2013.
Source: Central Bank of Chile's statistics database.
See also
*List of Latin American and Caribbean countries by GDP growth
This is a list of estimates of the real gross domestic product growth rate (not rebased GDP) in Latin American and the Caribbean nations for the latest years recorded in the CIA World Factbook. Nations are not included if their latest growth est ...
* List of Latin American and Caribbean countries by GDP (nominal)
This is a list of Latin American and Caribbean countries by gross domestic product (nominal) in USD according to the International Monetary Fund's estimates in the October 2018 World Economic Outlook database.
Cuba is not included in the list d ...
* List of Latin American and Caribbean countries by GDP (PPP)
This is a list of Latin American and the Caribbean countries by gross domestic product at purchasing power parity in international dollars according to the International Monetary Fund's estimates in the April 2022 World Economic Outlook database. ...
Bibliography
* COLLIER, Simon and Sater, William F. ''A History of Chile, 1808–2002'', New York and London, Cambridge University Press, 2004. * CONSTABLE, Pamela and Valenzuela, Arturo. ''A Nation of Enemies: Chile Under Pinochet.'' New York, W. W. Norton & Company, 1993. * PALEY, Julia. ''Marketing Democracy: Power and Social Movements in Post-Dictatorship Chile''. University of California Press, 2001WINN, Peter (editor).''Victims of the Chilean Miracle: Workers and Neoliberalism in the Pinochet Era, 1973–2002''. Durham, NC: Duke University Press, 2004.
References
External links
*Chile; A Top Stock market Performer
The Economic Transformation of Chile: A Model of Progress – HACER
Invest in Chile
World Reviews on Chile – this is Chile
Chile Export, Import, Trade Balance
Chile Trade
* Tariffs applied by Chile as provided by ITC'
ITC Market Access Map
an online database of customs tariffs and market requirements {{South America in topic, Economy of
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...
Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the east a ...