Easter Aquhorthies on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Easter Aquhorthies stone circle, located near  The placename ''Aquhorthies'' derives from a
The placename ''Aquhorthies'' derives from a 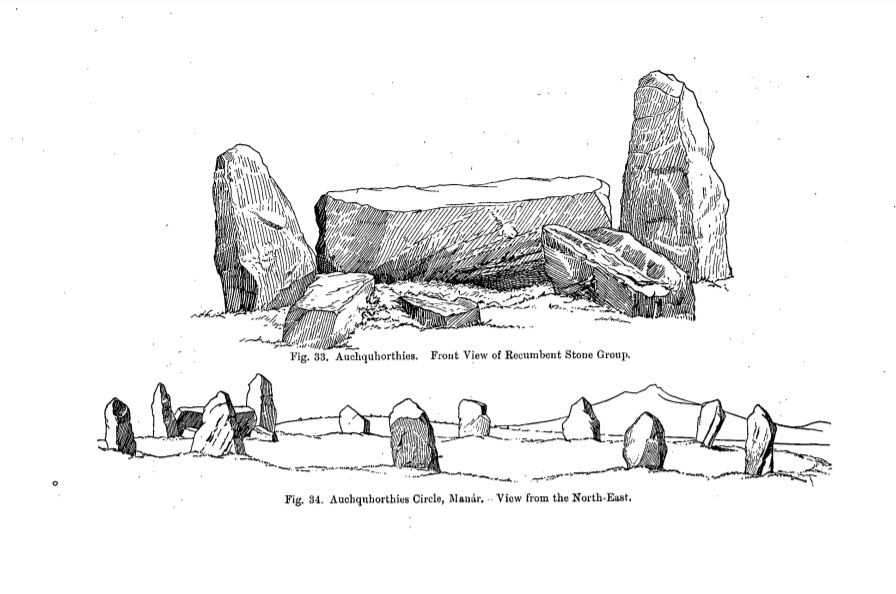 In 1900 Coles found the circle "in an excellent state of preservation", protected from damage by cattle and without shrubbery growing around. He carried out a very careful survey. The circle became badly overgrown in the first quarter of the 20th century; George Browne recorded that when he visited in 1920 it was "filled with a forest of whin bushes as high as our heads". It was scheduled as an ancient monument by the Ministry of Works in 1925, and was taken into guardianship by the State in 1963. The stones were cleaned in 1985 so that casts could be taken of them for an exhibition in
In 1900 Coles found the circle "in an excellent state of preservation", protected from damage by cattle and without shrubbery growing around. He carried out a very careful survey. The circle became badly overgrown in the first quarter of the 20th century; George Browne recorded that when he visited in 1920 it was "filled with a forest of whin bushes as high as our heads". It was scheduled as an ancient monument by the Ministry of Works in 1925, and was taken into guardianship by the State in 1963. The stones were cleaned in 1985 so that casts could be taken of them for an exhibition in
Inverurie
Inverurie (Scottish Gaelic: ''Inbhir Uraidh'' or ''Inbhir Uaraidh'', 'mouth of the River Ury') is a town in Aberdeenshire, Scotland at the confluence of the rivers Ury and Don, about north-west of Aberdeen.
Geography
Inverurie is in the vall ...
in north-east Scotland, is one of the best-preserved examples of a recumbent stone circle
A recumbent stone circle is a type of stone circle that incorporates a large monolith, known as a ''recumbent'', lying on its side. They are found in only two regions: in Aberdeenshire in the north-east of Scotland and in the far south-west of Irel ...
, and one of the few that still have their full complement of stones and the only one that has all its stones still standing without having been re-erected. It stands on a gentle hill slope about west of Inverurie, and consists of a ring of nine stones, eight of which are grey granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies undergro ...
and one red jasper
Jasper, an aggregate of microgranular quartz and/or cryptocrystalline chalcedony and other mineral phases,Kostov, R. I. 2010. Review on the mineralogical systematics of jasper and related rocks. – Archaeometry Workshop, 7, 3, 209-213PDF/ref> ...
. Two more grey granite stones flank a recumbent of red granite flecked with crystals
A crystal or crystalline solid is a solid material whose constituents (such as atoms, molecules, or ions) are arranged in a highly ordered microscopic structure, forming a crystal lattice that extends in all directions. In addition, macrosc ...
and lines of quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical form ...
. The circle is particularly notable for its builders' use of polychromy
Polychrome is the "practice of decorating architectural elements, sculpture, etc., in a variety of colors." The term is used to refer to certain styles of architecture, pottery or sculpture in multiple colors.
Ancient Egypt
Colossal statu ...
in the stones, with the reddish ones situated on the SSW side and the grey ones opposite. The discovery of a possible cist
A cist ( or ; also kist ;
from grc-gre, κίστη, Middle Welsh ''Kist'' or Germanic ''Kiste'') is a small stone-built coffin-like box or ossuary used to hold the bodies of the dead. Examples can be found across Europe and in the Middle East ...
covered by a capstone at the centre of the circle indicates that there may once have been a cairn
A cairn is a man-made pile (or stack) of stones raised for a purpose, usually as a marker or as a burial mound. The word ''cairn'' comes from the gd, càrn (plural ).
Cairns have been and are used for a broad variety of purposes. In prehis ...
there, but only a conspicuous bump now remains.
The ring of stones is not quite circular and has a somewhat "squashed" aspect, measuring along a WNW–ESE axis by . As is the case with other recumbent stone circles in the region, opposing pairs of stones have been erected on either side, increasing in height from a single low stone on the NNE side with the tallest stones, the flankers, opposite on the SSW side. The flankers are each about high, while the recumbent is long by high. It is aligned so that its level top lines up with the southern moonset in the direction of the nearby Hill of Fare. Two other large stones support the recumbent at right angles, projecting into the circle.
 The placename ''Aquhorthies'' derives from a
The placename ''Aquhorthies'' derives from a Scottish Gaelic
Scottish Gaelic ( gd, Gàidhlig ), also known as Scots Gaelic and Gaelic, is a Goidelic language (in the Celtic branch of the Indo-European language family) native to the Gaels of Scotland. As a Goidelic language, Scottish Gaelic, as well as ...
word meaning "field of prayer", and may indicate a "long continuity of sanctity" between the Stone
In geology, rock (or stone) is any naturally occurring solid mass or aggregate of minerals or mineraloid matter. It is categorized by the minerals included, its Chemical compound, chemical composition, and the way in which it is formed. Rocks ...
or Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
circle builders and their much later Gaelic successors millennia later. The circle's surroundings were landscaped in the late 19th century, and it sits within a small fenced and walled enclosure. A stone dyke, known as a roundel, was built around the circle some time between 1847 and 1866–7. The circle was subsequently brought to wider public attention in the 1870s and 1880s by a series of paintings, drawings and descriptions, though some were far-fetched, such as Christian Maclagan
Christian Maclagan (1811–10 May 1901) was a Scottish antiquarian and early archaeologist. She is known for her collection of rubbings of Celtic crosses and Pictish stones from across Scotland, and was a pioneer of stratigraphic excavat ...
's reconstruction of the circle as a kind of broch
A broch is an Iron Age drystone hollow-walled structure found in Scotland. Brochs belong to the classification "complex Atlantic roundhouse" devised by Scottish archaeologists in the 1980s. Their origin is a matter of some controversy.
Origin ...
. In 1884 it attracted the attention of the archaeologist Augustus Pitt Rivers
Lieutenant General Augustus Henry Lane Fox Pitt Rivers (14 April 18274 May 1900) was an English officer in the British Army, ethnologist, and archaeologist. He was noted for innovations in archaeological methodology, and in the museum display o ...
, and five years later his assistants William Tomkin and Claude Gray visited the site to measure, document and photograph it in order to build a scale model (which is now part of the collection of The Salisbury Museum
The Salisbury Museum (previously The Salisbury and South Wiltshire Museum) is a museum in Salisbury, Wiltshire, England. It houses one of the best collections relating to Stonehenge and local archaeology.
The museum is housed in The King's Ho ...
in Wiltshire
Wiltshire (; abbreviated Wilts) is a historic and ceremonial county in South West England with an area of . It is landlocked and borders the counties of Dorset to the southwest, Somerset to the west, Hampshire to the southeast, Gloucestershire ...
).
 In 1900 Coles found the circle "in an excellent state of preservation", protected from damage by cattle and without shrubbery growing around. He carried out a very careful survey. The circle became badly overgrown in the first quarter of the 20th century; George Browne recorded that when he visited in 1920 it was "filled with a forest of whin bushes as high as our heads". It was scheduled as an ancient monument by the Ministry of Works in 1925, and was taken into guardianship by the State in 1963. The stones were cleaned in 1985 so that casts could be taken of them for an exhibition in
In 1900 Coles found the circle "in an excellent state of preservation", protected from damage by cattle and without shrubbery growing around. He carried out a very careful survey. The circle became badly overgrown in the first quarter of the 20th century; George Browne recorded that when he visited in 1920 it was "filled with a forest of whin bushes as high as our heads". It was scheduled as an ancient monument by the Ministry of Works in 1925, and was taken into guardianship by the State in 1963. The stones were cleaned in 1985 so that casts could be taken of them for an exhibition in Edinburgh
Edinburgh ( ; gd, Dùn Èideann ) is the capital city of Scotland and one of its 32 Council areas of Scotland, council areas. Historically part of the county of Midlothian (interchangeably Edinburghshire before 1921), it is located in Lothian ...
, revealing previously undetected subtleties in their colouring. Further investigations also revealed that the ring had noteworthy acoustic properties, though it is unclear whether this was the case before the demolition of the central cairn and the construction of the roundel (which may have re-used the cairn's stones).
Notes
References
External links
*{{Historic Environment Scotland, num=SM90126, desc=East Aquhorthies, stone circle Archaeological sites in Aberdeenshire Buildings and structures in Aberdeenshire History of Aberdeenshire Stone Age sites in Scotland Stone circles in Aberdeenshire Scheduled Ancient Monuments in Aberdeenshire Inverurie