East India Squadron on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The East India Squadron, or East Indies Squadron, was a squadron of American ships which existed in the nineteenth century, it focused on protecting American interests in the
 Shortly before Senator
Shortly before Senator
 In July 1855, Chinese pirates in the
In July 1855, Chinese pirates in the

Kemp Tolley, Yangtze Patrol: The U.S. Navy in China, pg 317
/ref> * Edmund P. Kennedy, 3 March 1835 – 10 October 1837 *
Far East
The ''Far East'' was a European term to refer to the geographical regions that includes East and Southeast Asia as well as the Russian Far East to a lesser extent. South Asia is sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.
The ter ...
while the Pacific Squadron
The Pacific Squadron was part of the United States Navy squadron stationed in the Pacific Ocean in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Initially with no United States ports in the Pacific, they operated out of storeships which provided naval s ...
concentrated on the western coasts of the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World.
Along with th ...
and in the South Pacific Ocean
South is one of the cardinal directions or compass points. The direction is the opposite of north and is perpendicular to both east and west.
Etymology
The word ''south'' comes from Old English ''sūþ'', from earlier Proto-Germanic ''*sunþaz ...
. Part of the duties of this squadron was serving with the Yangtze River Patrol
The Yangtze Patrol, also known as the Yangtze River Patrol Force, Yangtze River Patrol, YangPat and ComYangPat, was a prolonged naval operation from 1854–1949 to protect American interests in the Yangtze River's treaty ports. The Yangtze P ...
in China. The East India Squadron was established in 1835 and existed until it became part of the Asiatic Squadron
The Asiatic Squadron was a squadron of United States Navy warships stationed in East Asia during the latter half of the 19th century. It was created in 1868 when the East India Squadron was disbanded. Vessels of the squadron were primarily inv ...
in 1868.
History
 Shortly before Senator
Shortly before Senator Levi Woodbury
Levi Woodbury (December 22, 1789September 4, 1851) was an American attorney, jurist, and Democratic politician from New Hampshire. During a four-decade career in public office, Woodbury served as Associate Justice of the Supreme Court of the U ...
of New Hampshire became secretary of the Navy
The secretary of the Navy (or SECNAV) is a statutory officer () and the head (chief executive officer) of the Department of the Navy, a military department (component organization) within the United States Department of Defense.
By law, the se ...
in 1831, Edmund Roberts had sent him a letter detailing the neglected state of Far Eastern commerce and whaling
Whaling is the process of hunting of whales for their usable products such as meat and blubber, which can be turned into a type of oil that became increasingly important in the Industrial Revolution.
It was practiced as an organized industry ...
. Near the end of that year, American pepper trader ''Friendship'' returned to her home port of Salem, to report that Sumatran pirates had killed the first officer and two crewmen, and plundered the cargo. In response to public outcry, President Andrew Jackson
Andrew Jackson (March 15, 1767 – June 8, 1845) was an American lawyer, planter, general, and statesman who served as the seventh president of the United States from 1829 to 1837. Before being elected to the presidency, he gained fame as ...
dispatched the ''Potomac'' on the first of what were to be two punitive expeditions to Sumatra. The sloop-of-war
In the 18th century and most of the 19th, a sloop-of-war in the Royal Navy was a warship with a single gun deck that carried up to eighteen guns. The rating system covered all vessels with 20 guns and above; thus, the term ''sloop-of-war'' enc ...
''Peacock'' was also dispatched, and, on the recommendation of Woodbury, carried Roberts as envoy to Cochin-China
Cochinchina or Cochin-China (, ; vi, Đàng Trong (17th century - 18th century, Việt Nam (1802-1831), Đại Nam (1831-1862), Nam Kỳ (1862-1945); km, កូសាំងស៊ីន, Kosăngsin; french: Cochinchine; ) is a historical exony ...
, Siam
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Mainland Southeast Asia, Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 mi ...
and Muscat
Muscat ( ar, مَسْقَط, ) is the capital and most populated city in Oman
Oman ( ; ar, عُمَان ' ), officially the Sultanate of Oman ( ar, سلْطنةُ عُمان ), is an Arabian country located in southwestern Asia. It is s ...
, to negotiate treaties to place American commerce on a surer basis, and on an equality with that of the most favored nations. Roberts succeeded with Siam and Muscat. ''Peacock'' returned in 1835–37 with Dr. W. S. W. Ruschenberger bearing ratifications of those treaties. ''Peacock'', which in 1828 had been broken down and rebuilt as an exploration vessel, joined the United States Exploring Expedition
The United States Exploring Expedition of 1838–1842 was an exploring and surveying expedition of the Pacific Ocean and surrounding lands conducted by the United States. The original appointed commanding officer was Commodore Thomas ap Catesby ...
in 1838. East India Squadron ''Columbia'' and ''John Adams'' had also joined the circumnavigating Expedition, and, without having to detour, executed the Second Sumatran Expedition.
Formation
Except for whaling and pepper, U.S. trade with the Far East was limited, but for those who risked long voyage to trade fur, sandalwood, and cotton goods for Chinese silks and tea, the results were very profitable. Indeed, stories about the riches of Far East created the national myth about the vast potential of the China market. In an effort to turn the myth into reality, the US sent envoy Roberts to Cochin-China in 1835 aboard the ''Peacock'', escorted by theschooner
A schooner () is a type of sailing vessel defined by its rig: fore-and-aft rigged on all of two or more masts and, in the case of a two-masted schooner, the foremast generally being shorter than the mainmast. A common variant, the topsail schoon ...
''Enterprise'' under the command of Commodore
Commodore may refer to:
Ranks
* Commodore (rank), a naval rank
** Commodore (Royal Navy), in the United Kingdom
** Commodore (United States)
** Commodore (Canada)
** Commodore (Finland)
** Commodore (Germany) or ''Kommodore''
* Air commodore ...
Edmund P. Kennedy. They called first at the port of Canton, and Roberts' account gives a vivid description of the state of affairs there. Kennedy subsequently established the East India Squadron.
First Opium War
Several American citizens living in China suffered personal attacks during theFirst Opium War
The First Opium War (), also known as the Opium War or the Anglo-Sino War was a series of military engagements fought between Britain and the Qing dynasty of China between 1839 and 1842. The immediate issue was the Chinese enforcement of the ...
from xenophobic
Xenophobia () is the fear or dislike of anything which is perceived as being foreign or strange. It is an expression of perceived conflict between an in-group and out-group and may manifest in suspicion by the one of the other's activities, a ...
locals. Commodore Kearny was given command of a squadron consisting of the 42-year-old frigate USS ''Constellation'' and the sloop USS ''Boston'' to protect American citizens in China. Kearny arrived in China in March 1842, a few months before the end of the conflict. Kearny first learned of the Treaty of Nanking
The Treaty of Nanjing was the peace treaty which ended the First Opium War (1839–1842) between Great Britain and the Qing dynasty of China on 29 August 1842. It was the first of what the Chinese later termed the Unequal Treaties.
In the ...
when he arrived in Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China ( abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China on the eastern Pearl River Delt ...
. Kearny observed the treaty's provisions opening five Chinese ports to British trade, and sought equal trading opportunity for Americans merchants. The Viceroy
A viceroy () is an official who reigns over a polity in the name of and as the representative of the monarch of the territory. The term derives from the Latin prefix ''vice-'', meaning "in the place of" and the French word ''roy'', meaning "k ...
of Canton offered Kearny a treaty giving Americans equal treatment. Kearny did not have authority to sign such a treaty, but tactfully informed Ke agreement would be forthcoming as soon as authorized negotiators arrived. Caleb Cushing
Caleb Cushing (January 17, 1800 – January 2, 1879) was an American Democratic politician and diplomat who served as a Congressman from Massachusetts and Attorney General under President Franklin Pierce. He was an eager proponent of territor ...
reached China in 1844, and the Treaty of Wanghia
The Treaty of Wanghia (also known as the Treaty of Wangxia; Treaty of peace, amity, and commerce, between the United States of America and the Chinese Empire; ) was the first of the unequal treaties imposed by the United States on China. As per ...
was signed on 2 July.
Opening of Japan
In December 1845, CommodoreJames Biddle
James Biddle (February 18, 1783 – October 1, 1848), of the Biddle family, brother of financier Nicholas Biddle and nephew of Capt. Nicholas Biddle, was an American commodore. His flagship was .
Education and early career
Biddle was born in Ph ...
exchanged ratifications of the Treaty of Wanghia
The Treaty of Wanghia (also known as the Treaty of Wangxia; Treaty of peace, amity, and commerce, between the United States of America and the Chinese Empire; ) was the first of the unequal treaties imposed by the United States on China. As per ...
at Poon Tong (泮塘), a village outside Guangzhou
Guangzhou (, ; ; or ; ), also known as Canton () and alternatively romanized as Kwongchow or Kwangchow, is the capital and largest city of Guangdong province in southern China. Located on the Pearl River about north-northwest of Hong Kon ...
. The treaty was the first treaty between China and the United States.
On July 20, 1846, he anchored with the two warships USS ''Columbus'' and USS ''Vincennes'' in Uraga Channel
The is a waterway connecting Tokyo Bay to the Sagami Gulf. It is an important channel for ships headed from Tokyo, Yokohama, and Chiba to the Pacific Ocean and beyond.
Geography
The Uraga channel is at the southern end of Tokyo Bay (formerly ...
at the mouth to Edo Bay in an attempt to open
Open or OPEN may refer to:
Music
* Open (band), Australian pop/rock band
* The Open (band), English indie rock band
* ''Open'' (Blues Image album), 1969
* ''Open'' (Gotthard album), 1999
* ''Open'' (Cowboy Junkies album), 2001
* ''Open'' (YF ...
up Japan to trade with the United States, but was ultimately unsuccessful. Biddle delivered his request that Japan agree to a similar treaty to that which he had just negotiated with China. Biddle eventually received the shogunate's response and was told that Japan forbade all commerce and communication with foreign nations besides that of the Dutch; also, he was informed that all foreign affairs were conducted through Nagasaki
is the capital and the largest city of Nagasaki Prefecture on the island of Kyushu in Japan.
It became the sole port used for trade with the Portuguese and Dutch during the 16th through 19th centuries. The Hidden Christian Sites in the ...
and that his ships should leave Uraga immediately.
In 1852, Commodore Matthew C. Perry
Matthew Calbraith Perry (April 10, 1794 – March 4, 1858) was a commodore of the United States Navy who commanded ships in several wars, including the War of 1812 and the Mexican–American War (1846–1848). He played a leading role in the o ...
embarked from Norfolk, Virginia
Norfolk ( ) is an independent city in the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States. Incorporated in 1705, it had a population of 238,005 at the 2020 census, making it the third-most populous city in Virginia after neighboring Virginia Be ...
for Japan, in command of a squadron in search of a Japanese trade treaty. Aboard a black-hulled steam frigate, he ported
''Mississippi'',
''Plymouth'',
''Saratoga'',
and
USS ''Susquehanna''
at Uraga Harbor
is a subdivision of the city of Yokosuka, Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan. It is located on the south eastern side of the Miura Peninsula, at the northern end of the Uraga Channel, at the entrance of Tokyo Bay.
History
With the establishment of th ...
near Edo (modern Tokyo
Tokyo (; ja, 東京, , ), officially the Tokyo Metropolis ( ja, 東京都, label=none, ), is the capital and largest city of Japan. Formerly known as Edo, its metropolitan area () is the most populous in the world, with an estimated 37.468 ...
) on July 8, 1853. His actions at this crucial juncture were informed by a careful study of Japan's previous contacts with Western ships and what could be known about the Japanese hierarchical culture. He was met by representatives of the Tokugawa Shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate (, Japanese 徳川幕府 ''Tokugawa bakufu''), also known as the , was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Tokugawa-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia ...
who told him to proceed to Nagasaki
is the capital and the largest city of Nagasaki Prefecture on the island of Kyushu in Japan.
It became the sole port used for trade with the Portuguese and Dutch during the 16th through 19th centuries. The Hidden Christian Sites in the ...
, where there was limited trade with the Netherlands and which was the only Japanese port open to foreigners at that time (see Sakoku
was the Isolationism, isolationist Foreign policy of Japan, foreign policy of the Japanese Tokugawa shogunate under which, for a period of 265 years during the Edo period (from 1603 to 1868), relations and trade between Japan and other countri ...
).
Perry returned in February 1854 with twice as many ships, finding that the delegates had prepared a treaty embodying virtually all the demands in Fillmore's letter. Perry signed the Convention of Kanagawa
The Convention of Kanagawa, also known as the Kanagawa Treaty (, ''Kanagawa Jōyaku'') or the Japan–US Treaty of Peace and Amity (, ''Nichibei Washin Jōyaku''), was a treaty signed between the United States and the Tokugawa Shogunate on March ...
on March 31, 1854, and departed, mistakenly believing the agreement had been made with imperial
Imperial is that which relates to an empire, emperor, or imperialism.
Imperial or The Imperial may also refer to:
Places
United States
* Imperial, California
* Imperial, Missouri
* Imperial, Nebraska
* Imperial, Pennsylvania
* Imperial, Texa ...
representatives. The agreement was made with the Shogun, the de facto ruler of Japan.
Johanna Expedition
The Johanna Expedition was a naval operation that occurred in August 1851 during the American anti-slavery patrols in theIndian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by th ...
. It began in response the seizure of the merchant ship ''Maria'' and her captain
Captain is a title, an appellative for the commanding officer of a military unit; the supreme leader of a navy ship, merchant ship, aeroplane, spacecraft, or other vessel; or the commander of a port, fire or police department, election precinct, e ...
, a man named Moores, in the small Sultanate of Johanna. The United States Navy sent the sloop-of-war USS ''Dale'', under Captain William Pearson, to free Moores and to demand compensation for the incident. When the sultan
Sultan (; ar, سلطان ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it ...
refused, the Americans briefly bombarded a fort
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
and blockhouse
A blockhouse is a small fortification, usually consisting of one or more rooms with loopholes, allowing its defenders to fire in various directions. It is usually an isolated fort in the form of a single building, serving as a defensive stro ...
protecting the harbor of Matsamudu.
Anti-piracy operations
 In July 1855, Chinese pirates in the
In July 1855, Chinese pirates in the Hong Kong
Hong Kong ( (US) or (UK); , ), officially the Hong Kong Special Administrative Region of the People's Republic of China ( abbr. Hong Kong SAR or HKSAR), is a city and special administrative region of China on the eastern Pearl River Delt ...
area captured four merchant ships owned by British subjects. In response, on 4 August 1855, armed boats from the East India Squadron frigate USS ''Powhatan'' and the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against F ...
sloop-of-war HMS ''Rattler'' confronted the pirates at the Battle of Ty-ho Bay
The Battle of Ty-ho Bay was a significant naval engagement in 1855 involving the United Kingdom and United States against Chinese pirates. The action off Tai O, Hong Kong was to rescue captured merchant vessels, held by a fleet of armed war-ju ...
. HMS ''Eaglet'' towed the boats into position which then proceeded to destroy twenty of thirty-six junks. Seven merchant ships were also rescued. An estimated 500 pirates were killed or wounded and over 1,000 taken prisoner compared to an allied loss of nine dead and about a dozen wounded.
Second Opium War
The United States would see action again during theSecond Opium War
The Second Opium War (), also known as the Second Anglo-Sino War, the Second China War, the Arrow War, or the Anglo-French expedition to China, was a colonial war lasting from 1856 to 1860, which pitted the British Empire and the French Emp ...
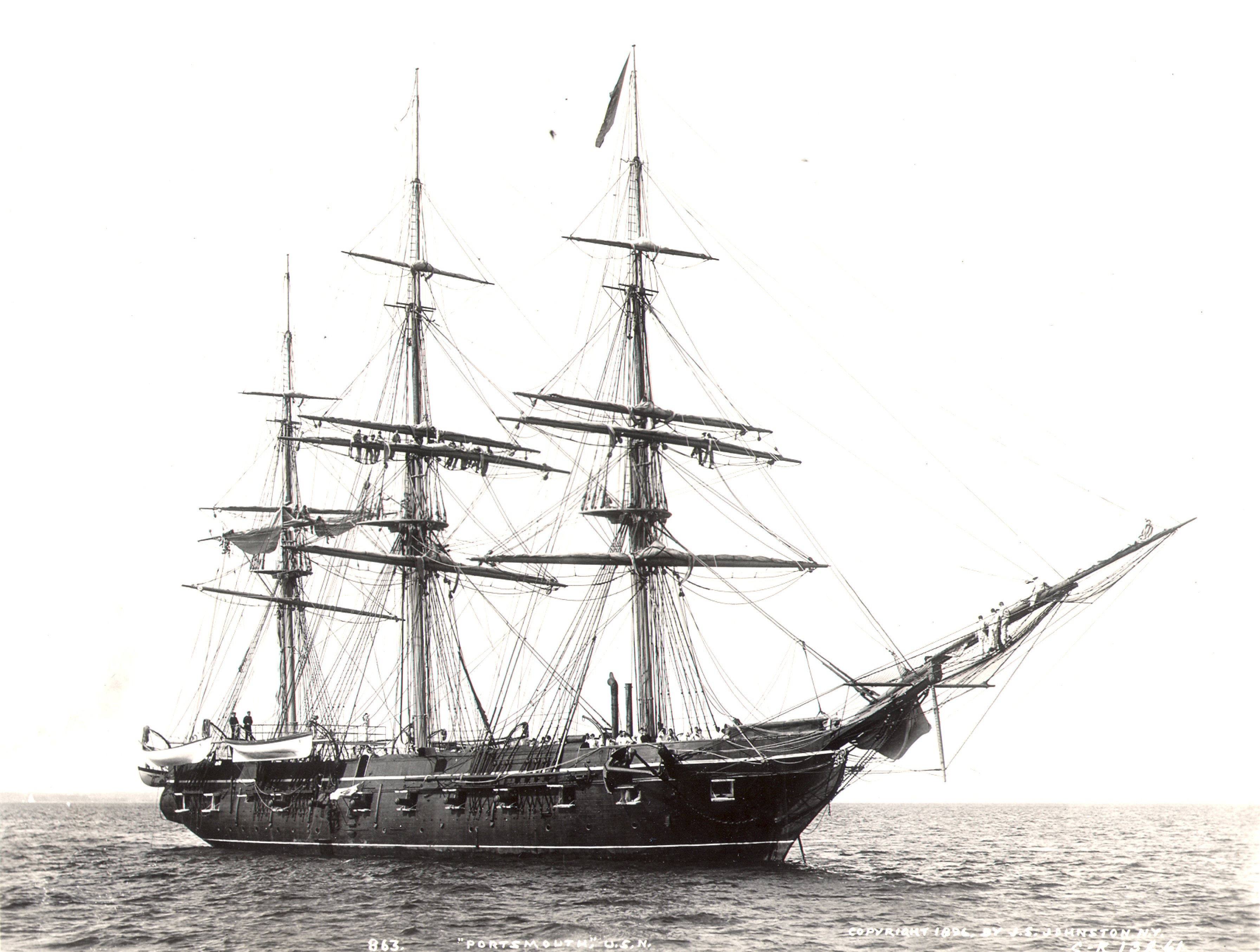
from 1856 to 1860. Four of the squadron's ships were involved in at least two battles. At the beginning of the war, the United States Navy frigate, USS ''San Jacinto'' and two sloops-of-war
In the 18th century and most of the 19th, a sloop-of-war in the Royal Navy was a warship with a single gun deck that carried up to eighteen guns. The rating system covered all vessels with 20 guns and above; thus, the term ''sloop-of-war'' enc ...
, USS ''Portsmouth'' and USS ''Levant'', launched an attack against a series of Chinese
Chinese can refer to:
* Something related to China
* Chinese people, people of Chinese nationality, citizenship, and/or ethnicity
**''Zhonghua minzu'', the supra-ethnic concept of the Chinese nation
** List of ethnic groups in China, people of ...
fort
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
s along Pearl River
The Pearl River, also known by its Chinese name Zhujiang or Zhu Jiang in Mandarin pinyin or Chu Kiang and formerly often known as the , is an extensive river system in southern China. The name "Pearl River" is also often used as a catch-a ...
. The engagement became known as the Battle of the Pearl River Forts
The Battle of the Barrier Forts (also known as the Battle of the Pearl River Forts) was fought between American and Chinese forces in the Pearl River, Guangdong, China in November 1856 during the Second Opium War. The United States Navy launched a ...
and was fought in 1856. The second involvement of an East India Squadron ship was during the Second Battle of Taku Forts in 1859. The American warship, USS ''Powhatan'', assisted an Anglo
Anglo is a prefix indicating a relation to, or descent from, the Angles, England, English culture, the English people or the English language, such as in the term '' Anglosphere''. It is often used alone, somewhat loosely, to refer to people ...
- French attack by bombarding the Taku Forts
The Taku Forts or Dagu Forts, also called the Peiho Forts are forts located by the Hai River (Peiho River) estuary in the Binhai New Area, Tianjin, in northeastern China. They are located southeast of the Tianjin urban center.
History
The ...
. No further engagements between Chinese and American forces during the war are known to have happened though American citizens living in Canton fought as militia
A militia () is generally an army or some other fighting organization of non-professional soldiers, citizens of a country, or subjects of a state, who may perform military service during a time of need, as opposed to a professional force of r ...
at the 1856 battle
A battle is an occurrence of combat in warfare between opposing military units of any number or size. A war usually consists of multiple battles. In general, a battle is a military engagement that is well defined in duration, area, and force ...
at Canton.

Bombardment of Qui Nhon
On June 30, 1861, USS ''Saginaw'', under James F. Schenck, silenced a fort at the entrance to Qui Nhon Bay,Cochinchina
Cochinchina or Cochin-China (, ; vi, Đàng Trong (17th century - 18th century, Việt Nam (1802-1831), Đại Nam (1831-1862), Nam Kỳ (1862-1945); km, កូសាំងស៊ីន, Kosăngsin; french: Cochinchine; ) is a historical exony ...
. This was after a Vietnam
Vietnam or Viet Nam ( vi, Việt Nam, ), officially the Socialist Republic of Vietnam,., group="n" is a country in Southeast Asia, at the eastern edge of mainland Southeast Asia, with an area of and population of 96 million, making i ...
ese artillery battery had fired upon her while she was searching for the missing boat and crew of an American merchant bark named ''Myrtle''. After an engagement lasting just under an hour, the Chinese fort was destroyed and a large explosion was observed by the Americans. It became the only battle of the Cochinchina Campaign involving the United States which deployed the East India Squadron to protect American interests in the region.
Formosan Expedition
Following theRover Incident
The ''Rover'' Incident ( or ) occurred on 12 March 1867 when the American merchant ship ''Rover'', captained by Joseph Hunt who was accompanied by his wife Mercy G. ''Beerman'' Hunt, and en route from Swatow to Newchwang, was wrecked off the c ...
of March 1867 in which the American bark ''Rover'' was wrecked and massacred by the Paiwan people
The Paiwan () are an indigenous people of Taiwan. They speak the Paiwan language. In 2014, the Paiwan numbered 96,334. This was approximately 17.8% of Taiwan's total indigenous population, making them the second-largest indigenous group.
The m ...
of southern Formosa
Taiwan, officially the Republic of China (ROC), is an island country located in East Asia. The main island of Taiwan, formerly known in the Western political circles, press and literature as Formosa, makes up 99% of the land area of the territorie ...
; the East India Squadron under Rear Admiral Henry H. Bell launched a punitive
Punishment, commonly, is the imposition of an undesirable or unpleasant outcome upon a group or individual, meted out by an authority—in contexts ranging from child discipline to criminal law—as a response and deterrent to a particular acti ...
expedition in retaliation. On June 18, 1867, 181 officers, sailors and marines from two screw sloops-of-war landed with the intention of destroying the hostile threat. After six hours of marching through the hot tropical Formosan mountains and after several skirmishes, the Americans turned back to their ships. The expedition failed after the death of an American commander and the loss of several men due to the humid
Humidity is the concentration of water vapor present in the air. Water vapor, the gaseous state of water, is generally invisible to the human eye. Humidity indicates the likelihood for precipitation, dew, or fog to be present.
Humidity depen ...
climate. They boarded USS ''Wyoming'' and USS ''Hartford'' and then set sail for Shanghai. A year later the squadron was merged into the new Asiatic Squadron.
Ships
USS ''Powhatan'', underCommander
Commander (commonly abbreviated as Cmdr.) is a common naval officer rank. Commander is also used as a rank or title in other formal organizations, including several police forces. In several countries this naval rank is termed frigate captain.
...
William J. McCluney, was assigned to the East India Squadron and arrived on station via Cape of Good Hope 15 June 1853. Her arrival in Chinese waters coincided with an important phase of Commodore Matthew C. Perry's negotiations for commercial relations with the Japanese and the opening of two ports. She was Perry's flagship during his November visit to Whampoa. On 14 February 1854 she entered Yedo Bay with the rest of the squadron and the Treaty of Kanagawa
The Convention of Kanagawa, also known as the Kanagawa Treaty (, ''Kanagawa Jōyaku'') or the Japan–US Treaty of Peace and Amity (, ''Nichibei Washin Jōyaku''), was a treaty signed between the United States and the Tokugawa Shogunate on March ...
was signed on her deck on 31 March 1854.
Assigned to the East India Squadron under Commodore Matthew Perry, the USS ''Macedonian'' with Capt. Joel Abbot in command, was one of the six American ships arrayed off Uraga, Japan, 13 February 1854 during Perry's second visit to negotiate the opening of Japan to foreign trade.
After completing her trials, which she began in January 1851, the side-wheel steamer USS ''Susquehanna'' sailed on 8 June for the Far East to become flagship of the East India Squadron.
The USS ''Dolphin'' got underway 6 May 1848 to join the East India Squadron, protecting American citizens in Asiatic waters.
Recommissioned on 12 August 1850, USS ''Saratoga'' got underway on 15 September and proceeded to the western Pacific for service in the East India Squadron.
USS ''Levant'' sailed 13 November for Rio de Janeiro, the Cape of Good Hope, and Hong Kong, where she arrived to join the East India Squadron 12 May 1856. On 1 July she embarked the U.S. Commissioner to China for transportation to Shanghai, arriving 1 August.
Departing Norfolk 4 August, the USS ''Germantown'' sailed via the Cape of Good Hope to Ceylon, where on 22 December she joined Flag Officer Josiah Tattnall's East India Squadron off Point de Gala. For 2 years she cruised Far Eastern waters and visited the principal ports of China and Japan, where she found "uniform friendly reception" as the squadron guarded American interests in the Orient. Sailing via the Cape of Good Hope, she returned to Norfolk in April 1860
After a four-day stop at Singapore, where Commodore Armstrong relieved Commodore Joel Abbot in command of the East India Squadron, the frigate USS ''San Jacinto'' reached the bar off the mouth of the Me Nam (later the Chao Phraya
The Chao Phraya ( or ; th, แม่น้ำเจ้าพระยา, , or ) is the major river in Thailand, with its low alluvial plain forming the centre of the country. It flows through Bangkok and then into the Gulf of Thailand.
E ...
) River.
The new side-wheel steamer USS ''Saginaw'' sailed from San Francisco Bay on 8 March 1860, headed for the western Pacific, and reached Shanghai, China, on 12 May. She then served in the East India Squadron, for the most part cruising along the Chinese coast to protect American citizens and to suppress pirates. She visited Japan in November but soon returned to Chinese waters. On 30 June 1861, she silenced a battery at the entrance to Qui Nhon Bay, Cochin China
Cochinchina or Cochin-China (, ; vi, Đàng Trong (17th century - 18th century, Việt Nam (1802-1831), Đại Nam (1831-1862), Nam Kỳ (1862-1945); km, កូសាំងស៊ីន, Kosăngsin; french: Cochinchine; ) is a historical exon ...
, which had fired upon her while she was searching for the missing boat and crew of American bark, ''Myrtle''. On 3 January 1862, ''Saginaw'' was decommissioned at Hong Kong. On 3 July 1862, she returned to Mare Island
Mare Island (Spanish: ''Isla de la Yegua'') is a peninsula in the United States in the city of Vallejo, California, about northeast of San Francisco. The Napa River forms its eastern side as it enters the Carquinez Strait juncture with the eas ...
for repairs.
Commanders
Successive Commanders-in-Chief of the East India Squadron were as follows./ref> * Edmund P. Kennedy, 3 March 1835 – 10 October 1837 *
George C. Read
George Campbell Read (January 9, 1788August 22, 1862) was a United States Naval officer who served on Old Ironsides during the War of 1812 and commanded vessels in actions off the Barbary Coast and India. Read eventually rose to the rank of r ...
, 14 December 1837 – 13 June 1840
*Lawrence Kearny
Commodore Lawrence Kearny (30 November 1789 – 29 November 1868) was an officer in the United States Navy during the early nineteenth century. In the early 1840s he began negotiations with China which opened that country to U.S. trade and poin ...
, 4 February 1841 – 27 February 1843
* Foxhall A. Parker Sr., 27 February 1843 – 21 April 1845
*James Biddle
James Biddle (February 18, 1783 – October 1, 1848), of the Biddle family, brother of financier Nicholas Biddle and nephew of Capt. Nicholas Biddle, was an American commodore. His flagship was .
Education and early career
Biddle was born in Ph ...
, 21 April 1845 – 6 March 1848
*William Shubrick
William Branford Shubrick (October 31, 1790 – May 27, 1874) was an officer in the United States Navy. His active-duty career extended from 1806 to 1861, including service in the War of 1812 and the Mexican–American War; he was placed on the ret ...
, 6 March 1848 – 13 May 1848
*David Geisinger
David Geisinger (1790 – 5 March 1860) was an officer of the United States Navy, who served during the War of 1812, and was later Commodore of the East India Squadron.
Biography
Geisinger was born in Maryland in 1790 and was appointed midshipman ...
, 13 May 1848 – 1 February 1850
*Philip Voorhees
Philip Falkerson Voorhees (23 February 1792 – 23 February 1862) was an officer in the United States Navy, who served during the War of 1812, and later commanded the East India Squadron.
Biography
Voorhees was born in New Brunswick, New Jersey, t ...
, 1 February 1850 – 30 January 1851
* John H. Aulick, 31 May 1851 – 20 November 1852
*Matthew C. Perry
Matthew Calbraith Perry (April 10, 1794 – March 4, 1858) was a commodore of the United States Navy who commanded ships in several wars, including the War of 1812 and the Mexican–American War (1846–1848). He played a leading role in the o ...
, 20 November 1852 – 6 September 1854
* Joel Abbot, 6 September 1854 – 15 October 1855
* James Armstrong, 15 October 1855 – 29 January 1858
*Josiah Tattnall III
Commodore Josiah Tattnall (November 9, 1795 – June 14, 1871) was an officer in the United States Navy during the War of 1812, the Second Barbary War and the Mexican–American War. He later served in the Confederate Navy during the American C ...
, 29 January 1858 – 20 November 1859
* Cornelius Stribling, 20 November 1859 – 23 July 1861
*Frederick K. Engle
Frederick K. Engle (October 24, 1797 – February 12, 1868) was a Rear admiral (United States), rear admiral of the United States Navy.
Early life and career
Engle was born in Chester, Pennsylvania, Chester, Delaware County, Pennsylvania. He enter ...
, 23 July 1861 – 23 September 1862
* Cicero Price, 23 September 1862 – 11 August 1865
* Henry H. Bell, 11 August 1865 – 11 January 1868
Served in squadron
Also serving in the squadron at one time were: *Thomas O. Selfridge
Rear Admiral Thomas Oliver Selfridge (24 April 1804 – 15 October 1902) was an officer in the United States Navy during the Mexican–American War and the American Civil War and was the father of another rear admiral, Thomas O. Selfridge, Jr ...
* John Pope
* Edward A. Terry served in the sloop ''Germantown'', attached to the East India Squadron, from 1857 to 1859.
* William M. Wood served as fleet surgeon with the East India Squadron from 1856 to 1858
* Montgomery Sicard
*James Glynn
James Glynn (1800–1871) was a U.S. Navy officer who in 1848 distinguished himself by being the first American to negotiate successfully with the Japanese during the " Closed Country" period.
James Glynn entered the United States Navy on March 4 ...
*Andrew Hull Foote
Andrew Hull Foote (September 12, 1806 – June 26, 1863) was an American naval officer who was noted for his service in the American Civil War and also for his contributions to several naval reforms in the years prior to the war. When the war cam ...
commanded USS ''Portsmouth'' on 20–21 November 1856. Foote led a landing party that seized the barrier forts at Canton, China, in reprisal for attacks on American ships.
References
Further reading
* ** {{Authority control Ship squadrons of the United States Navy