Early computer on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The history of computing hardware covers the developments from early simple devices to aid calculation to modern day computers. Before the 20th century, most calculations were done by humans.
The first aids to computation were purely mechanical devices which required the operator to set up the initial values of an elementary arithmetic operation, then manipulate the device to obtain the result. Later, computers represented numbers in a continuous form (e.g. distance along a scale, rotation of a shaft, or a
The history of computing hardware covers the developments from early simple devices to aid calculation to modern day computers. Before the 20th century, most calculations were done by humans.
The first aids to computation were purely mechanical devices which required the operator to set up the initial values of an elementary arithmetic operation, then manipulate the device to obtain the result. Later, computers represented numbers in a continuous form (e.g. distance along a scale, rotation of a shaft, or a

 Devices have been used to aid computation for thousands of years, mostly using
Devices have been used to aid computation for thousands of years, mostly using
 Since
Since
 In 1642, while still a teenager, Blaise Pascal started some pioneering work on calculating machines and after three years of effort and 50 prototypes he invented a
In 1642, while still a teenager, Blaise Pascal started some pioneering work on calculating machines and after three years of effort and 50 prototypes he invented a 
 Around 1820, Charles Xavier Thomas de Colmar created what would over the rest of the century become the first successful, mass-produced mechanical calculator, the Thomas
Around 1820, Charles Xavier Thomas de Colmar created what would over the rest of the century become the first successful, mass-produced mechanical calculator, the Thomas
 In the late 1880s, the American
In the late 1880s, the American
 By the 20th century, earlier mechanical calculators, cash registers, accounting machines, and so on were redesigned to use electric motors, with gear position as the representation for the state of a variable. The word "computer" was a job title assigned to primarily women who used these calculators to perform mathematical calculations. By the 1920s, British scientist Lewis Fry Richardson's interest in weather prediction led him to propose
By the 20th century, earlier mechanical calculators, cash registers, accounting machines, and so on were redesigned to use electric motors, with gear position as the representation for the state of a variable. The word "computer" was a job title assigned to primarily women who used these calculators to perform mathematical calculations. By the 1920s, British scientist Lewis Fry Richardson's interest in weather prediction led him to propose
 Charles Babbage, an English mechanical engineer and
Charles Babbage, an English mechanical engineer and  The programming language to be employed by users was akin to modern day assembly languages. Loops and conditional branching were possible, and so the language as conceived would have been
The programming language to be employed by users was akin to modern day assembly languages. Loops and conditional branching were possible, and so the language as conceived would have been  Following Babbage, although at first unaware of his earlier work, was
Following Babbage, although at first unaware of his earlier work, was
 In the first half of the 20th century,
In the first half of the 20th century,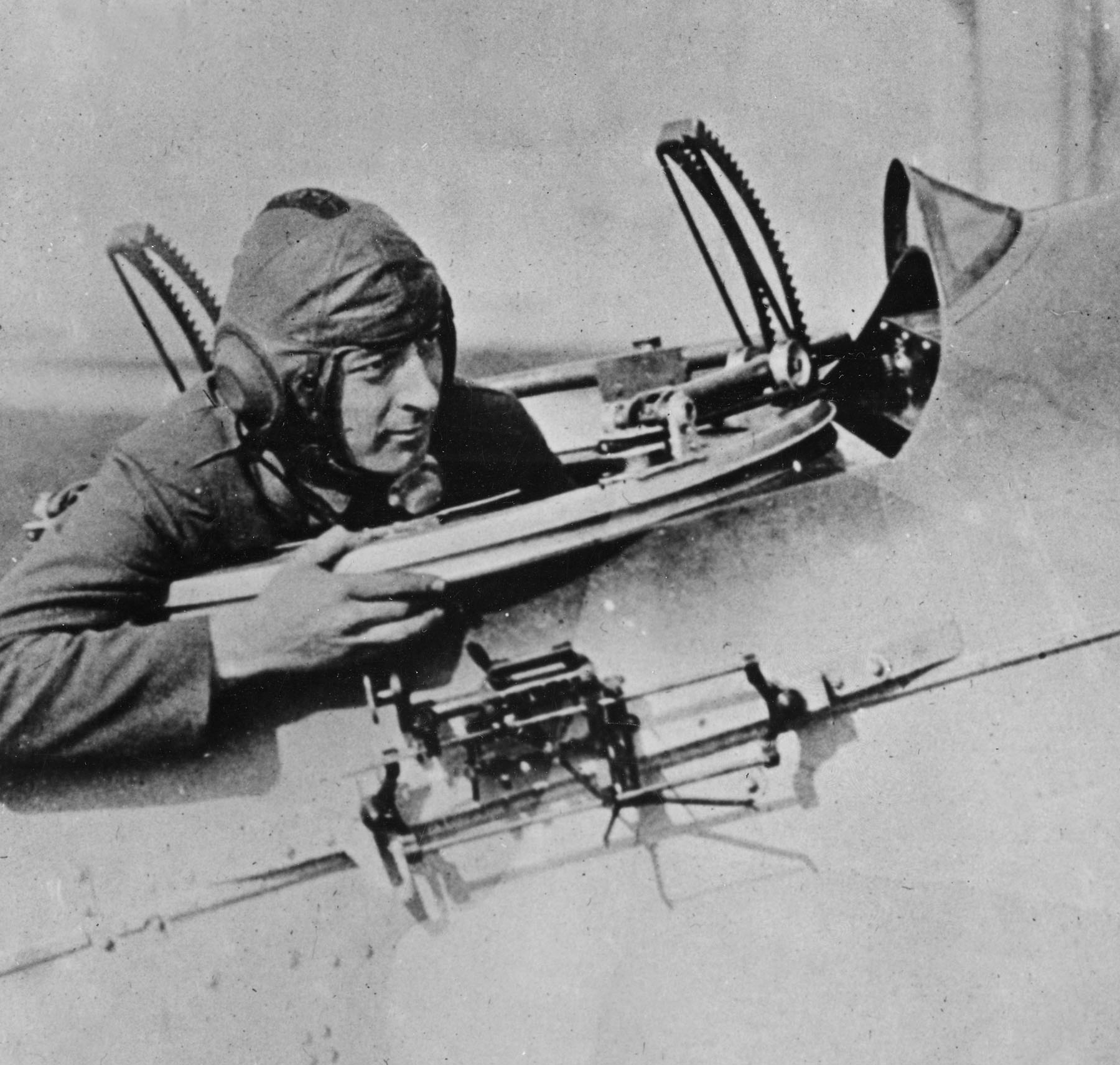  An important advance in analog computing was the development of the first fire-control systems for long range
An important advance in analog computing was the development of the first fire-control systems for long range
 In the same year, electro-mechanical devices called
In the same year, electro-mechanical devices called
 Purely electronic circuit elements soon replaced their mechanical and electromechanical equivalents, at the same time that digital calculation replaced analog. Machines such as the Z3, the AtanasoffŌĆōBerry Computer, the
Purely electronic circuit elements soon replaced their mechanical and electromechanical equivalents, at the same time that digital calculation replaced analog. Machines such as the Z3, the AtanasoffŌĆōBerry Computer, the
 During World War II, British codebreakers at
During World War II, British codebreakers at  Colossus was the world's first
Colossus was the world's first  Without the use of these machines, the Allies would have been deprived of the very valuable
Without the use of these machines, the Allies would have been deprived of the very valuable
 The theoretical basis for the stored-program computer had been proposed by
The theoretical basis for the stored-program computer had been proposed by
 The
The
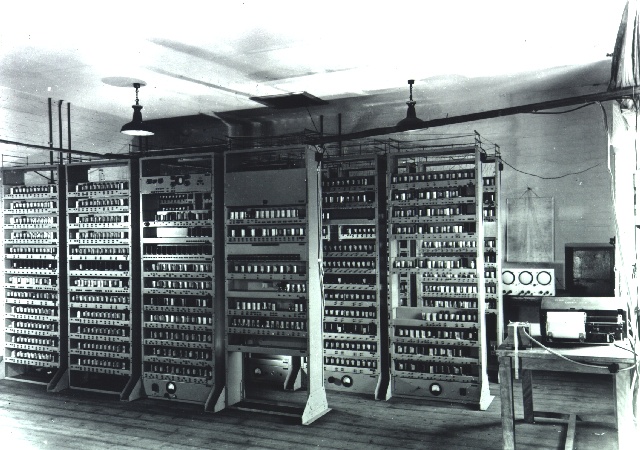 The other contender for being the first recognizably modern digital stored-program computer was the EDSAC, designed and constructed by Maurice Wilkes and his team at the
The other contender for being the first recognizably modern digital stored-program computer was the EDSAC, designed and constructed by Maurice Wilkes and his team at the

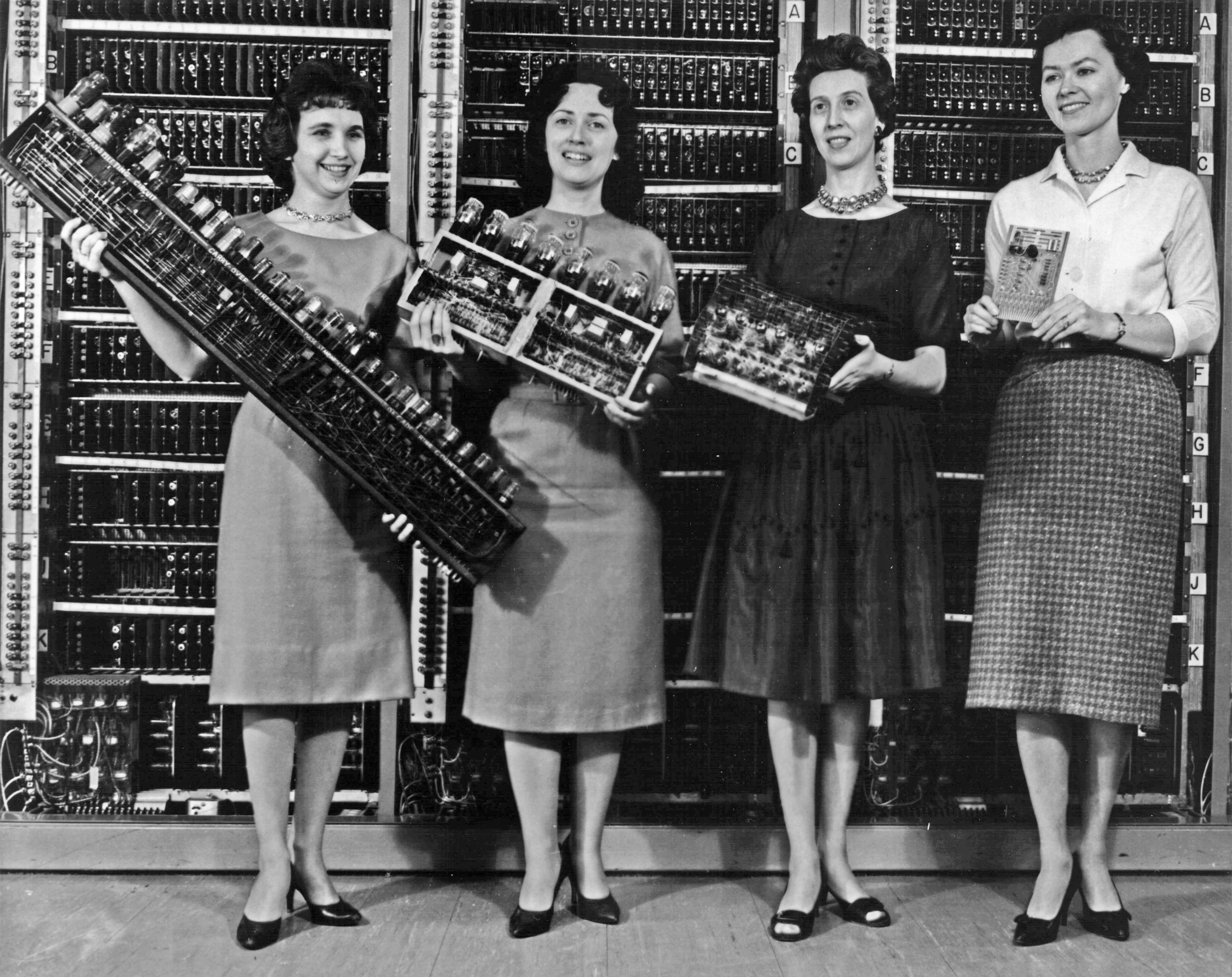
 IBM introduced a smaller, more affordable computer in 1954 that proved very popular. The IBM 650 weighed over , the attached power supply weighed around and both were held in separate cabinets of roughly 1.50.9. The system cost ($ as of ) or could be leased for a month ($ as of ). Its drum memory was originally 2,000 ten-digit words, later expanded to 4,000 words. Memory limitations such as this were to dominate programming for decades afterward. The program instructions were fetched from the spinning drum as the code ran. Efficient execution using drum memory was provided by a combination of hardware architecture ŌĆō the instruction format included the address of the next instruction ŌĆō and software: the
IBM introduced a smaller, more affordable computer in 1954 that proved very popular. The IBM 650 weighed over , the attached power supply weighed around and both were held in separate cabinets of roughly 1.50.9. The system cost ($ as of ) or could be leased for a month ($ as of ). Its drum memory was originally 2,000 ten-digit words, later expanded to 4,000 words. Memory limitations such as this were to dominate programming for decades afterward. The program instructions were fetched from the spinning drum as the code ran. Efficient execution using drum memory was provided by a combination of hardware architecture ŌĆō the instruction format included the address of the next instruction ŌĆō and software: the
 Magnetic drum memories were developed for the US Navy during WW II with the work continuing at
Magnetic drum memories were developed for the US Navy during WW II with the work continuing at
 The bipolar
The bipolar
 The early 1960s saw the advent of supercomputing. The
The early 1960s saw the advent of supercomputing. The
 The history of computing hardware covers the developments from early simple devices to aid calculation to modern day computers. Before the 20th century, most calculations were done by humans.
The first aids to computation were purely mechanical devices which required the operator to set up the initial values of an elementary arithmetic operation, then manipulate the device to obtain the result. Later, computers represented numbers in a continuous form (e.g. distance along a scale, rotation of a shaft, or a
The history of computing hardware covers the developments from early simple devices to aid calculation to modern day computers. Before the 20th century, most calculations were done by humans.
The first aids to computation were purely mechanical devices which required the operator to set up the initial values of an elementary arithmetic operation, then manipulate the device to obtain the result. Later, computers represented numbers in a continuous form (e.g. distance along a scale, rotation of a shaft, or a voltage
Voltage, also known as electric pressure, electric tension, or (electric) potential difference, is the difference in electric potential between two points. In a static electric field, it corresponds to the work needed per unit of charge to ...
). Numbers could also be represented in the form of digits, automatically manipulated by a mechanism. Although this approach generally required more complex mechanisms, it greatly increased the precision of results. The development of transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch ...
technology and then the integrated circuit chip led to a series of breakthroughs, starting with transistor computers and then integrated circuit computers, causing digital computers to largely replace analog computer
An analog computer or analogue computer is a type of computer that uses the continuous variation aspect of physical phenomena such as electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic quantities (''analog signals'') to model the problem being solved. In ...
s. Metal-oxide-semiconductor (MOS) large-scale integration
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny ...
(LSI) then enabled semiconductor memory and the microprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circ ...
, leading to another key breakthrough, the miniaturized personal computer
A personal computer (PC) is a multi-purpose microcomputer whose size, capabilities, and price make it feasible for individual use. Personal computers are intended to be operated directly by an end user, rather than by a computer expert or tec ...
(PC), in the 1970s. The cost of computers gradually became so low that personal computers by the 1990s, and then mobile computers
Mobile computing is humanŌĆōcomputer interaction in which a computer is expected to be transported during normal usage, which allows for the transmission of data, voice, and video. Mobile computing involves mobile communication, mobile hardware ...
(smartphone
A smartphone is a portable computer device that combines mobile telephone and computing functions into one unit. They are distinguished from feature phones by their stronger hardware capabilities and extensive mobile operating systems, whic ...
s and tablets) in the 2000s, became ubiquitous.
Early devices
Ancient and medieval
 Devices have been used to aid computation for thousands of years, mostly using
Devices have been used to aid computation for thousands of years, mostly using one-to-one correspondence
In mathematics, a bijection, also known as a bijective function, one-to-one correspondence, or invertible function, is a function between the elements of two sets, where each element of one set is paired with exactly one element of the other ...
with fingers
A finger is a limb of the body and a type of digit, an organ of manipulation and sensation found in the hands of most of the Tetrapods, so also with humans and other primates. Most land vertebrates have five fingers (Pentadactyly). Chambers 1 ...
. The earliest counting device was probably a form of tally stick
A tally stick (or simply tally) was an ancient memory aid device used to record and document numbers, quantities and messages. Tally sticks first appear as animal bones carved with notches during the Upper Palaeolithic; a notable example is the ...
. The Lebombo bone The Lebombo bone is a bone tool made of a baboon fibula with incised markings discovered in the Lebombo Mountains located between South Africa and Eswatini. Changes in the section of the notches indicate the use of different cutting edges, which the ...
from the mountains between Eswatini and South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the Southern Africa, southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the Atlantic Ocean, South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the ...
may be the oldest known mathematical artifact. It dates from 35,000 BCE and consists of 29 distinct notches that were deliberately cut into a baboon
Baboons are primates comprising the genus ''Papio'', one of the 23 genera of Old World monkeys. There are six species of baboon: the hamadryas baboon, the Guinea baboon, the olive baboon, the yellow baboon, the Kinda baboon and the chacma ...
's fibula
The fibula or calf bone is a leg bone on the lateral side of the tibia, to which it is connected above and below. It is the smaller of the two bones and, in proportion to its length, the most slender of all the long bones. Its upper extremity i ...
. Later record keeping aids throughout the Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent ( ar, ž¦┘ä┘ć┘䞦┘ä ž¦┘äž«žĄ┘Ŗž©) is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, spanning modern-day Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine and Jordan, together with the northern region of Kuwait, southeastern region of ...
included calculi (clay spheres, cones, etc.) which represented counts of items, probably livestock or grains, sealed in hollow unbaked clay containers. The use of counting rods
Counting rods () are small bars, typically 3ŌĆō14 cm long, that were used by mathematicians for calculation in ancient East Asia. They are placed either horizontally or vertically to represent any integer or rational number.
The written ...
is one example. The abacus
The abacus (''plural'' abaci or abacuses), also called a counting frame, is a calculating tool which has been used since ancient times. It was used in the ancient Near East, Europe, China, and Russia, centuries before the adoption of the Hi ...
was early used for arithmetic tasks. What we now call the Roman abacus
The Ancient Romans developed the Roman hand abacus, a portable, but less capable, base-10 version of earlier abacuses like those that were used by the Greeks and Babylonians.
Origin
The Roman abacus was the first portable calculating device for e ...
was used in Babylonia as early as c. 2700ŌĆō2300 BC. Since then, many other forms of reckoning boards or tables have been invented. In a medieval European counting house
A counting house, or counting room, was traditionally an office in which the financial books of a business were kept. It was also the place that the business received appointments and correspondence relating to demands for payment.
As the use of ...
, a checkered cloth would be placed on a table, and markers moved around on it according to certain rules, as an aid to calculating sums of money.
Several analog computer
An analog computer or analogue computer is a type of computer that uses the continuous variation aspect of physical phenomena such as electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic quantities (''analog signals'') to model the problem being solved. In ...
s were constructed in ancient and medieval times to perform astronomical calculations. These included the astrolabe and Antikythera mechanism
The Antikythera mechanism ( ) is an Ancient Greek hand-powered orrery, described as the oldest example of an analogue computer used to predict astronomical positions and eclipses decades in advance. It could also be used to track the four-yea ...
from the Hellenistic world
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in 3 ...
(c. 150ŌĆō100 BC). In Roman Egypt, Hero of Alexandria
Hero of Alexandria (; grc-gre, ß╝ŁŽüŽē╬Į ßĮü ß╝ł╬╗╬Ą╬Š╬▒╬Į╬┤Žü╬ĄŽŹŽé, ''Heron ho Alexandreus'', also known as Heron of Alexandria ; 60 AD) was a Greek mathematician and engineer who was active in his native city of Alexandria, Roman Egypt. He ...
(c. 10ŌĆō70 AD) made mechanical devices including automata
An automaton (; plural: automata or automatons) is a relatively self-operating machine, or control mechanism designed to automatically follow a sequence of operations, or respond to predetermined instructions.Automaton ŌĆō Definition and More ...
and a programmable cart. Other early mechanical devices used to perform one or another type of calculations include the planisphere
In astronomy, a planisphere () is a star chart analog computing instrument in the form of two adjustable disks that rotate on a common pivot. It can be adjusted to display the visible stars for any time and date. It is an instrument to assist ...
and other mechanical computing devices invented by Abu Rayhan al-Biruni (c. AD 1000); the equatorium
An equatorium (plural, equatoria) is an astronomical calculating instrument. It can be used for finding the positions of the Moon, Sun, and planets without arithmetic operations, using a geometrical model to represent the position of a given c ...
and universal latitude-independent astrolabe by Abū Ishāq Ibrāhīm al-Zarqālī (c. AD 1015); the astronomical analog computers of other medieval Muslim astronomers and engineers; and the astronomical clock tower of Su Song (1094) during the Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960ŌĆō1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest ...
. The castle clock
Clock towers are a specific type of structure which house a turret clock and have one or more clock faces on the upper exterior walls. Many clock towers are freestanding structures but they can also adjoin or be located on top of another buildi ...
, a hydropower
Hydropower (from el, ßĮĢ╬┤ŽēŽü, "water"), also known as water power, is the use of falling or fast-running water to produce electricity or to power machines. This is achieved by converting the gravitational potential or kinetic energy of a w ...
ed mechanical astronomical clock
An astronomical clock, horologium, or orloj is a clock with special mechanisms and dials to display astronomical information, such as the relative positions of the Sun, Moon, zodiacal constellations, and sometimes major planets.
Definition ...
invented by Ismail al-Jazari
Bad─½╩┐ az-Zaman Abu l-╩┐Izz ibn Ism─ü╩┐─½l ibn ar-Raz─üz al-Jazar─½ (1136ŌĆō1206, ar, ž©ž»┘Ŗž╣ ž¦┘äž▓┘ģž¦┘å žŻ┘Äž©┘Å ž¦┘Ä┘ä┘Æž╣┘Éž▓┘É žźž©┘Æ┘å┘Å žźž│┘Æ┘ģž¦ž╣┘É┘Ŗ┘ä┘É žźž©┘Æ┘å┘Å ž¦┘äž▒┘É┘æž▓ž¦ž▓ ž¦┘äž¼ž▓ž▒┘Ŗ, ) was a polymath: a scholar, ...
in 1206, was the first programmable analog computer. Ramon Llull invented the Lullian Circle: a notional machine for calculating answers to philosophical questions (in this case, to do with Christianity) via logical combinatorics. This idea was taken up by Leibniz
Gottfried Wilhelm (von) Leibniz . ( ŌĆō 14 November 1716) was a German polymath active as a mathematician, philosopher, scientist and diplomat. He is one of the most prominent figures in both the history of philosophy and the history of ma ...
centuries later, and is thus one of the founding elements in computing and information science
Information science (also known as information studies) is an academic field which is primarily concerned with analysis, collection, classification, manipulation, storage, retrieval, movement, dissemination, and protection of informatio ...
.
Renaissance calculating tools
Scottish mathematician and physicistJohn Napier
John Napier of Merchiston (; 1 February 1550 ŌĆō 4 April 1617), nicknamed Marvellous Merchiston, was a Scottish landowner known as a mathematician, physicist, and astronomer. He was the 8th Laird of Merchiston. His Latinized name was Ioan ...
discovered that the multiplication and division of numbers could be performed by the addition and subtraction, respectively, of the logarithm
In mathematics, the logarithm is the inverse function to exponentiation. That means the logarithm of a number to the base is the exponent to which must be raised, to produce . For example, since , the ''logarithm base'' 10 of ...
s of those numbers. While producing the first logarithmic tables, Napier needed to perform many tedious multiplications. It was at this point that he designed his 'Napier's bones
Napier's bones is a manually-operated calculating device created by John Napier of Merchiston, Scotland for the calculation of products and quotients of numbers. The method was based on lattice multiplication, and also called ''rabdology'', a wor ...
', an abacus-like device that greatly simplified calculations that involved multiplication and division.
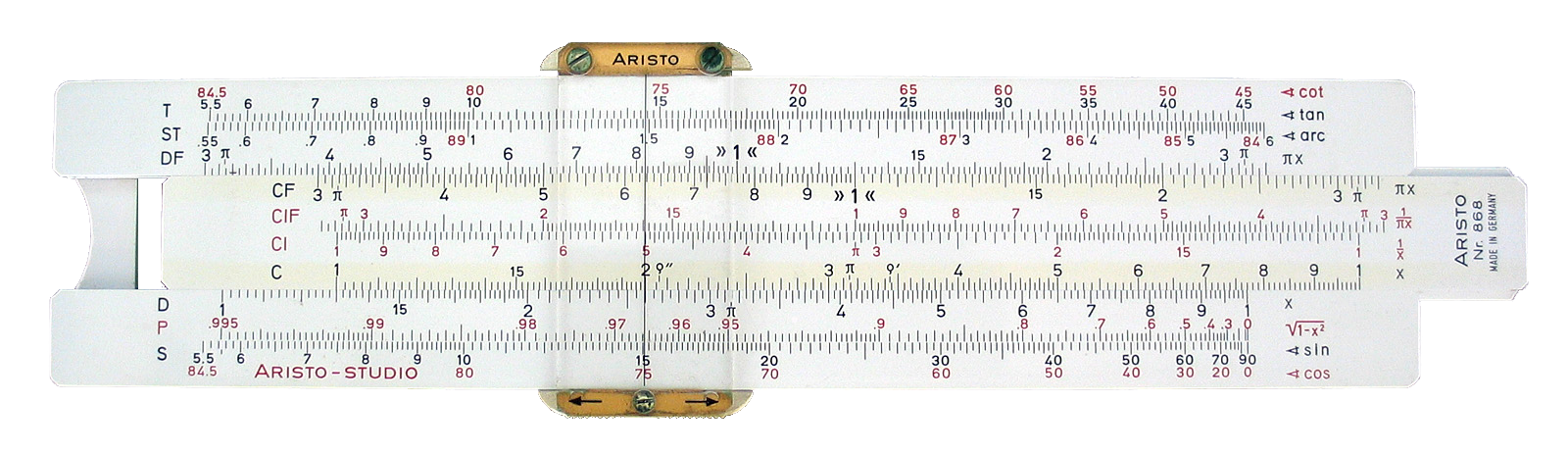
 Since
Since real number
In mathematics, a real number is a number that can be used to measure a ''continuous'' one-dimensional quantity such as a distance, duration or temperature. Here, ''continuous'' means that values can have arbitrarily small variations. Every ...
s can be represented as distances or intervals on a line, the slide rule
The slide rule is a mechanical analog computer which is used primarily for multiplication and division, and for functions such as exponents, roots, logarithms, and trigonometry. It is not typically designed for addition or subtraction, which ...
was invented in the 1620s, shortly after Napier's work, to allow multiplication and division operations to be carried out significantly faster than was previously possible. Edmund Gunter
Edmund Gunter (158110 December 1626), was an English clergyman, mathematician, geometer and astronomer of Welsh descent. He is best remembered for his mathematical contributions which include the invention of the Gunter's chain, the Gunter's qu ...
built a calculating device with a single logarithmic scale at the University of Oxford
, mottoeng = The Lord is my light
, established =
, endowment = ┬Ż6.1 billion (including colleges) (2019)
, budget = ┬Ż2.145 billion (2019ŌĆō20)
, chancellor ...
. His device greatly simplified arithmetic calculations, including multiplication and division. William Oughtred
William Oughtred ( ; 5 March 1574 ŌĆō 30 June 1660), also Owtred, Uhtred, etc., was an English mathematician and Anglican clergyman.'Oughtred (William)', in P. Bayle, translated and revised by J.P. Bernard, T. Birch and J. Lockman, ''A General ...
greatly improved this in 1630 with his circular slide rule. He followed this up with the modern slide rule in 1632, essentially a combination of two Gunter rules, held together with the hands. Slide rules were used by generations of engineers and other mathematically involved professional workers, until the invention of the pocket calculator
An electronic calculator is typically a portable electronic device used to perform calculations, ranging from basic arithmetic to complex mathematics.
The first solid-state electronic calculator was created in the early 1960s. Pocket-sized ...
.
Mechanical calculators
Wilhelm Schickard
Wilhelm Schickard (22 April 1592 – 24 October 1635) was a German professor of Hebrew and astronomy who became famous in the second part of the 20th century after Franz Hammer, a biographer (along with Max Caspar) of Johannes Kepler, claim ...
, a German polymath
A polymath ( el, ŽĆ╬┐╬╗Žģ╬╝╬▒╬Ė╬«Žé, , "having learned much"; la, homo universalis, "universal human") is an individual whose knowledge spans a substantial number of subjects, known to draw on complex bodies of knowledge to solve specific pro ...
, designed a calculating machine in 1623 which combined a mechanized form of Napier's rods with the world's first mechanical adding machine built into the base. Because it made use of a single-tooth gear there were circumstances in which its carry mechanism would jam. A fire destroyed at least one of the machines in 1624 and it is believed Schickard was too disheartened to build another.
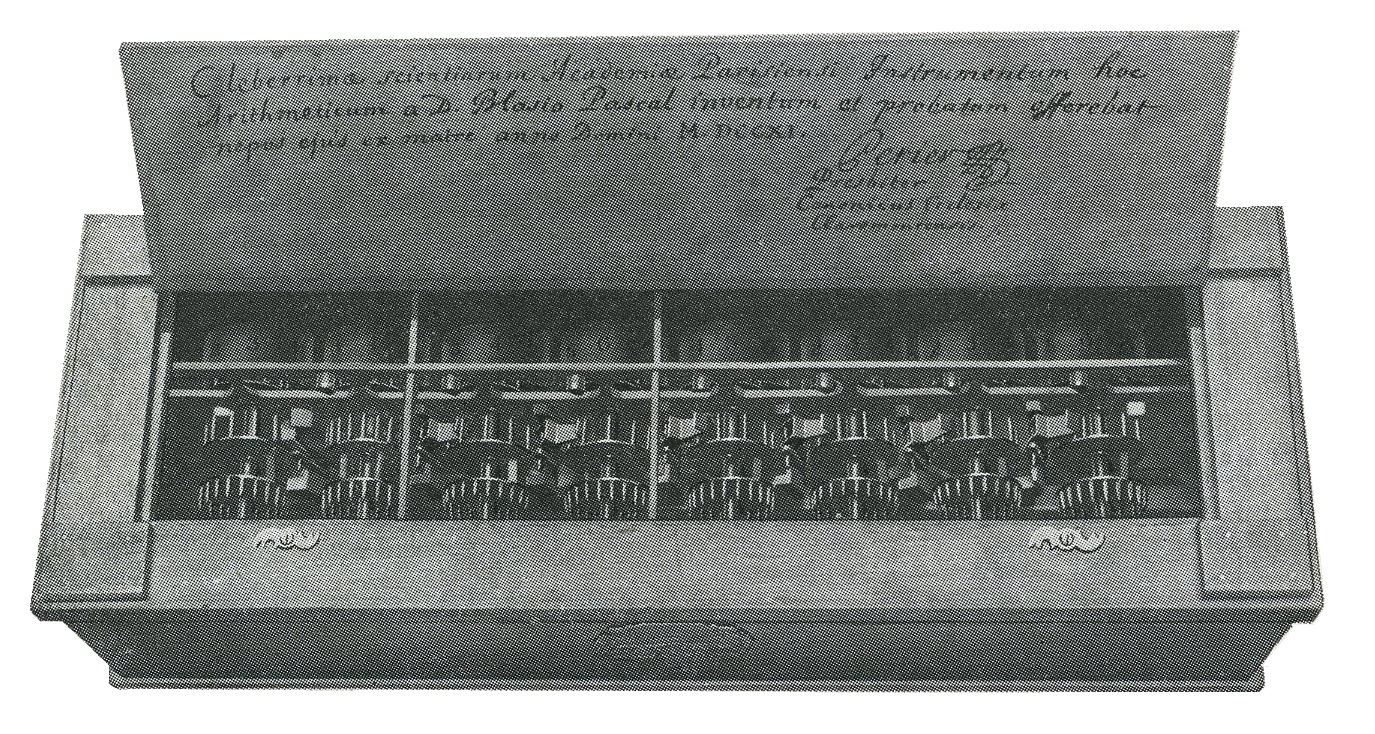
 In 1642, while still a teenager, Blaise Pascal started some pioneering work on calculating machines and after three years of effort and 50 prototypes he invented a
In 1642, while still a teenager, Blaise Pascal started some pioneering work on calculating machines and after three years of effort and 50 prototypes he invented a mechanical calculator
A mechanical calculator, or calculating machine, is a mechanical device used to perform the basic operations of arithmetic automatically, or (historically) a simulation such as an analog computer or a slide rule. Most mechanical calculators we ...
. He built twenty of these machines (called Pascal's calculator or Pascaline) in the following ten years. Nine Pascalines have survived, most of which are on display in European museums. A continuing debate exists over whether Schickard or Pascal should be regarded as the "inventor of the mechanical calculator" and the range of issues to be considered is discussed elsewhere.
Gottfried Wilhelm von Leibniz
Gottfried Wilhelm (von) Leibniz . ( ŌĆō 14 November 1716) was a German polymath active as a mathematician, philosopher, scientist and diplomat. He is one of the most prominent figures in both the history of philosophy and the history of mathem ...
invented the stepped reckoner and his famous stepped drum mechanism around 1672. He attempted to create a machine that could be used not only for addition and subtraction but would use a moveable carriage to enable multiplication and division. Leibniz once said "It is unworthy of excellent men to lose hours like slaves in the labour of calculation which could safely be relegated to anyone else if machines were used." However, Leibniz did not incorporate a fully successful carry mechanism. Leibniz also described the binary numeral system, a central ingredient of all modern computers. However, up to the 1940s, many subsequent designs (including Charles Babbage's machines of the 1822 and even ENIAC
ENIAC (; Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) was the first programmable, electronic, general-purpose digital computer, completed in 1945. There were other computers that had these features, but the ENIAC had all of them in one pac ...
of 1945) were based on the decimal system.
 Around 1820, Charles Xavier Thomas de Colmar created what would over the rest of the century become the first successful, mass-produced mechanical calculator, the Thomas
Around 1820, Charles Xavier Thomas de Colmar created what would over the rest of the century become the first successful, mass-produced mechanical calculator, the Thomas Arithmometer
The arithmometer (french: arithmom├©tre) was the first digital mechanical calculator strong enough and reliable enough to be used daily in an office environment. This calculator could add and subtract two numbers directly and could perform long ...
. It could be used to add and subtract, and with a moveable carriage the operator could also multiply, and divide by a process of long multiplication and long division. It utilised a stepped drum similar in conception to that invented by Leibniz. Mechanical calculators remained in use until the 1970s.
Punched-card data processing
In 1804, French weaver Joseph Marie Jacquard developed a loom in which the pattern being woven was controlled by a paper tape constructed frompunched cards
A punched card (also punch card or punched-card) is a piece of stiff paper that holds digital data represented by the presence or absence of holes in predefined positions. Punched cards were once common in data processing applications or to di ...
. The paper tape could be changed without changing the mechanical design of the loom. This was a landmark achievement in programmability. His machine was an improvement over similar weaving looms. Punched cards were preceded by punch bands, as in the machine proposed by Basile Bouchon. These bands would inspire information recording for automatic pianos and more recently numerical control machine tools.
 In the late 1880s, the American
In the late 1880s, the American Herman Hollerith
Herman Hollerith (February 29, 1860 ŌĆō November 17, 1929) was a German-American statistician, inventor, and businessman who developed an electromechanical tabulating machine for punched cards to assist in summarizing information and, later, i ...
invented data storage on punched card
A punched card (also punch card or punched-card) is a piece of stiff paper that holds digital data represented by the presence or absence of holes in predefined positions. Punched cards were once common in data processing applications or to di ...
s that could then be read by a machine. To process these punched cards, he invented the tabulator and the keypunch
A keypunch is a device for precisely punching holes into stiff paper cards at specific locations as determined by keys struck by a human operator. Other devices included here for that same function include the gang punch, the pantograph punch, ...
machine. His machines used electromechanical relay
A relay
Electromechanical relay schematic showing a control coil, four pairs of normally open and one pair of normally closed contacts
An automotive-style miniature relay with the dust cover taken off
A relay is an electrically operated switch ...
s and counters. Hollerith's method was used in the 1890 United States Census
The United States census of 1890 was taken beginning June 2, 1890, but most of the 1890 census materials were destroyed in 1921 when a building caught fire and in the subsequent disposal of the remaining damaged records. It determined the reside ...
. That census was processed two years faster than the prior census had been. "You may confidently look for the rapid reduction of the force of this office after the 1st of October, and the entire cessation of clerical work during the present calendar year. ... The condition of the work of the Census Division and the condition of the final reports show clearly that the work of the Eleventh Census will be completed at least two years earlier than was the work of the Tenth Census." ŌĆöŌĆēCarroll D. Wright, Commissioner of Labor in Charge Hollerith's company eventually became the core of IBM.
By 1920, electromechanical tabulating machines could add, subtract, and print accumulated totals. Machine functions were directed by inserting dozens of wire jumpers into removable control panels. When the United States instituted Social Security
Welfare, or commonly social welfare, is a type of government support intended to ensure that members of a society can meet basic human needs such as food and shelter. Social security may either be synonymous with welfare, or refer specifical ...
in 1935, IBM punched-card systems were used to process records of 26 million workers. Punched cards became ubiquitous in industry and government for accounting and administration.
Leslie Comrie's articles on punched-card methods and W. J. Eckert's publication of ''Punched Card Methods in Scientific Computation'' in 1940, described punched-card techniques sufficiently advanced to solve some differential equations or perform multiplication and division using floating-point representations, all on punched cards and unit record machines. Such machines were used during World War II for cryptographic statistical processing, as well as a vast number of administrative uses. The Astronomical Computing Bureau, Columbia University
Columbia University (also known as Columbia, and officially as Columbia University in the City of New York) is a private research university in New York City. Established in 1754 as King's College on the grounds of Trinity Church in Manhatt ...
, performed astronomical calculations representing the state of the art in computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and development of both hardware and software. Computing has scientific, ...
.
Calculators
human computer
The term "computer", in use from the early 17th century (the first known written reference dates from 1613), meant "one who computes": a person performing mathematical calculations, before electronic computers became commercially available. Ala ...
s and numerical analysis
Numerical analysis is the study of algorithms that use numerical approximation (as opposed to symbolic manipulations) for the problems of mathematical analysis (as distinguished from discrete mathematics). It is the study of numerical methods ...
to model the weather; to this day, the most powerful computers on Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's surfa ...
are needed to adequately model its weather using the NavierŌĆōStokes equations
In physics, the NavierŌĆōStokes equations ( ) are partial differential equations which describe the motion of viscous fluid substances, named after French engineer and physicist Claude-Louis Navier and Anglo-Irish physicist and mathematician Geo ...
.
Companies like Friden, Marchant Calculator
The Marchant Calculating Machine Company was founded in 1911 by Rodney and Alfred Marchant in Oakland, California.
The company built mechanical, and then electromechanical calculators which had a reputation for reliability. First models were s ...
and Monroe made desktop mechanical calculators from the 1930s that could add, subtract, multiply and divide. In 1948, the Curta
The Curta is a hand-held mechanical calculator designed by Curt Herzstark. It is known for its extremely compact design: a small cylinder that fits in the palm of the hand. It was affectionately known as the "pepper grinder" or "peppermill ...
was introduced by Austrian inventor Curt Herzstark
Curt Herzstark (January 26, 1902 ŌĆō October 27, 1988) was an Austrian engineer. During World War II, he designed plans for a mechanical pocket calculator (the ''Curta'').
Life and career
Herzstark was born in Vienna, the son of Marie and Samuel ...
. It was a small, hand-cranked mechanical calculator and as such, a descendant of Gottfried Leibniz
Gottfried Wilhelm (von) Leibniz . ( ŌĆō 14 November 1716) was a German polymath active as a mathematician, philosopher, scientist and diplomat. He is one of the most prominent figures in both the history of philosophy and the history of mathem ...
's Stepped Reckoner and Thomas
Thomas may refer to:
People
* List of people with given name Thomas
* Thomas (name)
* Thomas (surname)
* Saint Thomas (disambiguation)
* Thomas Aquinas (1225ŌĆō1274) Italian Dominican friar, philosopher, and Doctor of the Church
* Thomas the A ...
' Arithmometer
The arithmometer (french: arithmom├©tre) was the first digital mechanical calculator strong enough and reliable enough to be used daily in an office environment. This calculator could add and subtract two numbers directly and could perform long ...
.
The world's first ''all-electronic desktop'' calculator was the British Bell Punch
The Bell Punch Company was a British company manufacturing a variety of business machines, most notably several generations of public transport ticket machines and the world's first desktop electronic calculator, the Sumlock ANITA.
History
The ...
ANITA, released in 1961. It used vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied.
The type known as ...
s, cold-cathode tubes and Dekatron
In electronics, a Dekatron (or Decatron, or generically three-phase gas counting tube or glow-transfer counting tube or cold cathode tube) is a gas-filled decade counting tube. Dekatrons were used in computers, calculators, and other counti ...
s in its circuits, with 12 cold-cathode "Nixie" tubes for its display. The ANITA sold well since it was the only electronic desktop calculator available, and was silent and quick. The tube technology was superseded in June 1963 by the U.S. manufactured Friden EC-130, which had an all-transistor design, a stack of four 13-digit numbers displayed on a CRT, and introduced reverse Polish notation
Reverse Polish notation (RPN), also known as reverse Łukasiewicz notation, Polish postfix notation or simply postfix notation, is a mathematical notation in which operators ''follow'' their operands, in contrast to Polish notation (PN), in whi ...
(RPN).
First general-purpose computing device
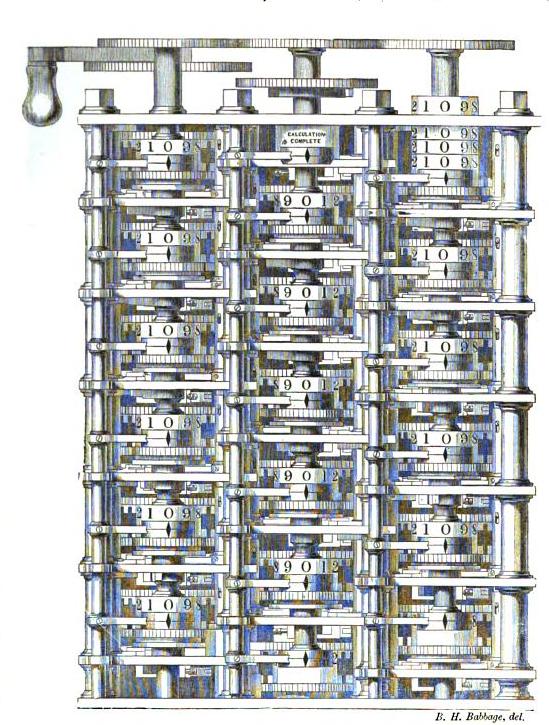
 Charles Babbage, an English mechanical engineer and
Charles Babbage, an English mechanical engineer and polymath
A polymath ( el, ŽĆ╬┐╬╗Žģ╬╝╬▒╬Ė╬«Žé, , "having learned much"; la, homo universalis, "universal human") is an individual whose knowledge spans a substantial number of subjects, known to draw on complex bodies of knowledge to solve specific pro ...
, originated the concept of a programmable computer. Considered the " father of the computer", he conceptualized and invented the first mechanical computer
A mechanical computer is a computer built from mechanical components such as levers and gears rather than electronic components. The most common examples are adding machines and mechanical counters, which use the turning of gears to increment out ...
in the early 19th century. After working on his revolutionary difference engine, designed to aid in navigational calculations, in 1833 he realized that a much more general design, an Analytical Engine, was possible. The input of programs and data was to be provided to the machine via punched card
A punched card (also punch card or punched-card) is a piece of stiff paper that holds digital data represented by the presence or absence of holes in predefined positions. Punched cards were once common in data processing applications or to di ...
s, a method being used at the time to direct mechanical looms such as the Jacquard loom. For output, the machine would have a printer, a curve plotter and a bell. The machine would also be able to punch numbers onto cards to be read in later. It employed ordinary base-10
The decimal numeral system (also called the base-ten positional numeral system and denary or decanary) is the standard system for denoting integer and non-integer numbers. It is the extension to non-integer numbers of the HinduŌĆōArabic numeral ...
fixed-point arithmetic.
The Engine incorporated an arithmetic logic unit, control flow
In computer science, control flow (or flow of control) is the order in which individual statements, instructions or function calls of an imperative program are executed or evaluated. The emphasis on explicit control flow distinguishes an ''im ...
in the form of conditional branching
In computer science, conditionals (that is, conditional statements, conditional expressions and conditional constructs,) are programming language commands for handling decisions. Specifically, conditionals perform different computations or actio ...
and loops, and integrated memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered ...
, making it the first design for a general-purpose computer that could be described in modern terms as Turing-complete
In computability theory, a system of data-manipulation rules (such as a computer's instruction set, a programming language, or a cellular automaton) is said to be Turing-complete or computationally universal if it can be used to simulate any ...
.
There was to be a store, or memory, capable of holding 1,000 numbers of 40 decimal digits each (ca. 16.7 kB). An arithmetical unit, called the "mill", would be able to perform all four arithmetic operations
Arithmetic () is an elementary part of mathematics that consists of the study of the properties of the traditional operations on numbersŌĆöaddition, subtraction, multiplication, division, exponentiation, and extraction of roots. In the 19th ce ...
, plus comparisons and optionally square root
In mathematics, a square root of a number is a number such that ; in other words, a number whose ''square'' (the result of multiplying the number by itself, or ŌĆ»⋅ŌĆ») is . For example, 4 and ŌłÆ4 are square roots of 16, because .
...
s. Initially it was conceived as a difference engine curved back upon itself, in a generally circular layout, with the long store exiting off to one side. (Later drawings depict a regularized grid layout.) Like the central processing unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just Processor (computing), processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes Instruction (computing), instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU per ...
(CPU) in a modern computer, the mill would rely on its own internal procedures, roughly equivalent to microcode in modern CPUs, to be stored in the form of pegs inserted into rotating drums called "barrels", to carry out some of the more complex instructions the user's program might specify.
 The programming language to be employed by users was akin to modern day assembly languages. Loops and conditional branching were possible, and so the language as conceived would have been
The programming language to be employed by users was akin to modern day assembly languages. Loops and conditional branching were possible, and so the language as conceived would have been Turing-complete
In computability theory, a system of data-manipulation rules (such as a computer's instruction set, a programming language, or a cellular automaton) is said to be Turing-complete or computationally universal if it can be used to simulate any ...
as later defined by Alan Turing
Alan Mathison Turing (; 23 June 1912 ŌĆō 7 June 1954) was an English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher, and theoretical biologist. Turing was highly influential in the development of theoretical co ...
. Three different types of punch cards were used: one for arithmetical operations, one for numerical constants, and one for load and store operations, transferring numbers from the store to the arithmetical unit or back. There were three separate readers for the three types of cards.
The machine was about a century ahead of its time. However, the project was slowed by various problems including disputes with the chief machinist building parts for it. All the parts for his machine had to be made by handŌĆöthis was a major problem for a machine with thousands of parts. Eventually, the project was dissolved with the decision of the British Government to cease funding. Babbage's failure to complete the analytical engine can be chiefly attributed to difficulties not only of politics and financing, but also to his desire to develop an increasingly sophisticated computer and to move ahead faster than anyone else could follow. Ada Lovelace translated and added notes to the "''Sketch of the Analytical Engine''" by Luigi Federico Menabrea
Luigi Federico Menabrea (4 September 1809 – 24 May 1896), later made 1st Count Menabrea and 1st Marquess of Valdora, was an Italian general, statesman and mathematician who served as the seventh prime minister of Italy from 1867 to 1869.
B ...
. This appears to be the first published description of programming, so Ada Lovelace is widely regarded as the first computer programmer.
 Following Babbage, although at first unaware of his earlier work, was
Following Babbage, although at first unaware of his earlier work, was Percy Ludgate
Percy Edwin Ludgate (2 August 1883 ŌĆō 16 October 1922) was an Irish amateur scientist who designed the second analytical engine (general-purpose Turing-complete computer) in history.
Life
Ludgate was born on 2 August 1883 in Skibbereen, ...
, a clerk to a corn merchant in Dublin, Ireland. He independently designed a programmable mechanical computer, which he described in a work that was published in 1909. Two other inventors, Leonardo Torres y Quevedo
Leonardo Torres y Quevedo (; 28 December 1852 ŌĆō 18 December 1936) was a Spanish civil engineer and mathematician of the late nineteenth and early twentieth centuries. Torres was a pioneer in the development of the radio control and automated ...
and Vannevar Bush
Vannevar Bush ( ; March 11, 1890 ŌĆō June 28, 1974) was an American engineer, inventor and science administrator, who during World War II headed the U.S. Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD), through which almost all warti ...
, also did follow on research based on Babbage's work. In his ''Essays on Automatics'' (1913) Torres y Quevedo designed a Babbage type of calculating machine that used electromechanical parts which included floating-point number
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic that represents real numbers approximately, using an integer with a fixed precision, called the significand, scaled by an integer exponent of a fixed base. For example, 12.345 can be r ...
representations and built an early prototype in 1920. Bush's paper ''Instrumental Analysis'' (1936) discussed using existing IBM punch card machines to implement Babbage's design. In the same year he started the Rapid Arithmetical Machine project to investigate the problems of constructing an electronic digital computer.
Analog computers
 In the first half of the 20th century,
In the first half of the 20th century, analog computer
An analog computer or analogue computer is a type of computer that uses the continuous variation aspect of physical phenomena such as electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic quantities (''analog signals'') to model the problem being solved. In ...
s were considered by many to be the future of computing. These devices used the continuously changeable aspects of physical phenomena such as electrical
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described ...
, mechanical
Mechanical may refer to:
Machine
* Machine (mechanical), a system of mechanisms that shape the actuator input to achieve a specific application of output forces and movement
* Mechanical calculator, a device used to perform the basic operations of ...
, or hydraulic
Hydraulics (from Greek: ╬ź╬┤Žü╬▒Žģ╬╗╬╣╬║╬«) is a technology and applied science using engineering, chemistry, and other sciences involving the mechanical properties and use of liquids. At a very basic level, hydraulics is the liquid counte ...
quantities to model
A model is an informative representation of an object, person or system. The term originally denoted the plans of a building in late 16th-century English, and derived via French and Italian ultimately from Latin ''modulus'', a measure.
Models c ...
the problem being solved, in contrast to digital computer
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations (computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs. These program ...
s that represented varying quantities symbolically, as their numerical values change. As an analog computer does not use discrete values, but rather continuous values, processes cannot be reliably repeated with exact equivalence, as they can with Turing machines
A Turing machine is a mathematical model of computation describing an abstract machine that manipulates symbols on a strip of tape according to a table of rules. Despite the model's simplicity, it is capable of implementing any computer algor ...
.
The first modern analog computer was a tide-predicting machine
A tide-predicting machine was a special-purpose mechanical analog computer of the late 19th and early 20th centuries, constructed and set up to predict the ebb and flow of sea tides and the irregular variations in their heights – which chan ...
, invented by Sir William Thomson
William Thomson, 1st Baron Kelvin, (26 June 182417 December 1907) was a British mathematician, mathematical physicist and engineer born in Belfast. Professor of Natural Philosophy at the University of Glasgow for 53 years, he did important ...
, later Lord Kelvin, in 1872. It used a system of pulleys and wires to automatically calculate predicted tide levels for a set period at a particular location and was of great utility to navigation in shallow waters. His device was the foundation for further developments in analog computing.
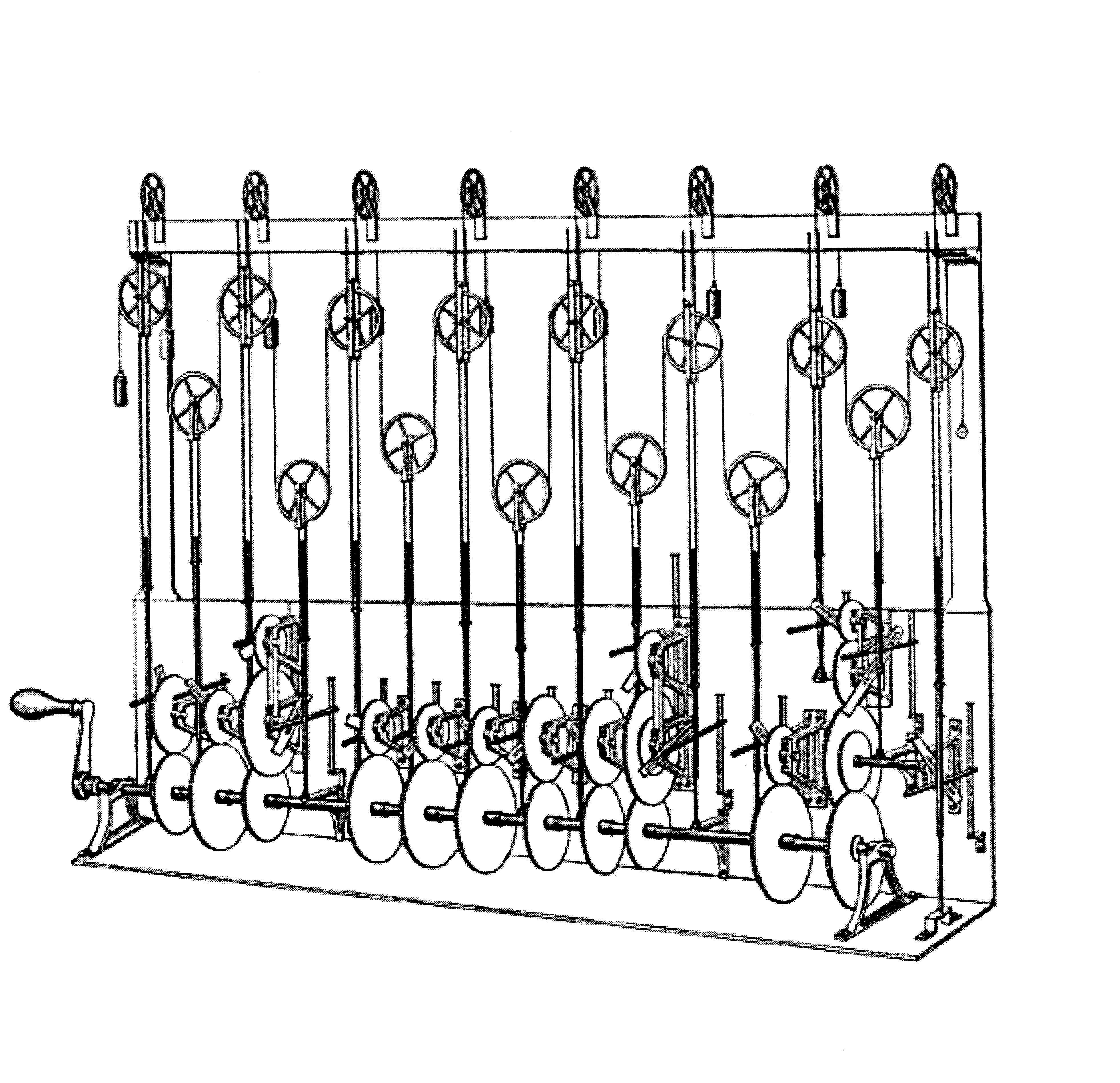
The differential analyser
The differential analyser is a mechanical analogue computer designed to solve differential equations by integration, using wheel-and-disc mechanisms to perform the integration. It was one of the first advanced computing devices to be used operat ...
, a mechanical analog computer designed to solve differential equations by integration using wheel-and-disc mechanisms, was conceptualized in 1876 by James Thomson, the brother of the more famous Lord Kelvin. He explored the possible construction of such calculators, but was stymied by the limited output torque of the ball-and-disk integrator
The ball-and-disk integrator is a key component of many advanced mechanical computers. Through simple mechanical means, it performs continual integration of the value of an input. Typical uses were the measurement of area or volume of material in ...
s. In a differential analyzer, the output of one integrator drove the input of the next integrator, or a graphing output.
 An important advance in analog computing was the development of the first fire-control systems for long range
An important advance in analog computing was the development of the first fire-control systems for long range ship
A ship is a large watercraft that travels the world's oceans and other sufficiently deep waterways, carrying cargo or passengers, or in support of specialized missions, such as defense, research, and fishing. Ships are generally distinguished ...
gunlaying. When gunnery ranges increased dramatically in the late 19th century it was no longer a simple matter of calculating the proper aim point, given the flight times of the shells. Various spotters on board the ship would relay distance measures and observations to a central plotting station. There the fire direction teams fed in the location, speed and direction of the ship and its target, as well as various adjustments for Coriolis effect
In physics, the Coriolis force is an inertial or fictitious force that acts on objects in motion within a frame of reference that rotates with respect to an inertial frame. In a reference frame with clockwise rotation, the force acts to the ...
, weather effects on the air, and other adjustments; the computer would then output a firing solution, which would be fed to the turrets for laying. In 1912, British engineer Arthur Pollen
Arthur Joseph Hungerford Pollen (13 September 1866 ŌĆō 28 January 1937) was an English journalist, businessman, and commentator on naval affairs who devised a new computerised fire-control system for use on battleships prior to the First World W ...
developed the first electrically powered mechanical analogue computer
An analog computer or analogue computer is a type of computer that uses the continuous variation aspect of physical phenomena such as electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic quantities (''analog signals'') to model the problem being solved. In ...
(called at the time the Argo Clock). It was used by the Imperial Russian Navy
The Imperial Russian Navy () operated as the navy of the Russian Tsardom and later the Russian Empire from 1696 to 1917. Formally established in 1696, it lasted until dissolved in the wake of the February Revolution of 1917. It developed from ...
in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. The alternative Dreyer Table
Admiral Sir Frederic Charles Dreyer, (8 January 1878 ŌĆō 11 December 1956) was an officer of the Royal Navy. A gunnery expert, he developed a fire control system for British warships, and served as flag captain to Admiral Sir John Jellicoe at ...
fire control system was fitted to British capital ships by mid-1916.
Mechanical devices were also used to aid the accuracy of aerial bombing. Drift Sight was the first such aid, developed by Harry Wimperis
Harry Egerton Wimperis Wh.Sch (27 August 1876 ŌĆō 16 July 1960) was a British aeronautical engineer who acted as the Director of Scientific Research at the UK's Air Ministry prior to World War II. He is best known for his role in setting up th ...
in 1916 for the Royal Naval Air Service; it measured the wind speed
In meteorology, wind speed, or wind flow speed, is a fundamental atmospheric quantity caused by air moving from high to low pressure, usually due to changes in temperature. Wind speed is now commonly measured with an anemometer.
Wind speed ...
from the air, and used that measurement to calculate the wind's effects on the trajectory of the bombs. The system was later improved with the Course Setting Bomb Sight
The Course Setting Bomb Sight (CSBS) is the canonical ''vector'' bombsight, the first practical system for properly accounting for the effects of wind when dropping bombs. It is also widely referred to as the Wimperis sight after its inventor, H ...
, and reached a climax with World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countriesŌĆöincluding all of the great powersŌĆöforming two opposing ...
bomb sights, Mark XIV bomb sight
The Mark XIV Bomb Sight was a bombsight developed by Royal Air Force (RAF) Bomber Command during the Second World War. It was also known as the Blackett sight after its primary inventor, P. M. S. Blackett. Production of a slightly modified ve ...
( RAF Bomber Command) and the Norden
Norden is a Scandinavian and German word, directly translated as "the North". It may refer to:
Places England
* Norden, Basingstoke, a ward of Basingstoke and Deane
* Norden, Dorset, a hamlet near Corfe Castle
* Norden, Greater Manchester, a vi ...
(United States Army Air Forces
The United States Army Air Forces (USAAF or AAF) was the major land-based aerial warfare service component of the United States Army and ''de facto'' aerial warfare service branch of the United States during and immediately after World War II ...
).
The art of mechanical analog computing reached its zenith with the differential analyzer
The differential analyser is a mechanical analogue computer designed to solve differential equations by integration, using wheel-and-disc mechanisms to perform the integration. It was one of the first advanced computing devices to be used operat ...
, built by H. L. Hazen and Vannevar Bush
Vannevar Bush ( ; March 11, 1890 ŌĆō June 28, 1974) was an American engineer, inventor and science administrator, who during World War II headed the U.S. Office of Scientific Research and Development (OSRD), through which almost all warti ...
at MIT
The Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) is a private land-grant research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts. Established in 1861, MIT has played a key role in the development of modern technology and science, and is one of the m ...
starting in 1927, which built on the mechanical integrators of James Thomson and the torque amplifier A torque amplifier is a mechanical device that amplifies the torque of a rotating shaft without affecting its rotational speed. It is mechanically related to the capstan seen on ships. Its most widely known use is in power steering on automobiles. ...
s invented by H. W. Nieman. A dozen of these devices were built before their obsolescence became obvious; the most powerful was constructed at the University of Pennsylvania
The University of Pennsylvania (also known as Penn or UPenn) is a private research university in Philadelphia. It is the fourth-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and is ranked among the highest-regarded universitie ...
's Moore School of Electrical Engineering
The Moore School of Electrical Engineering at the University of Pennsylvania came into existence as a result of an endowment from Alfred Fitler Moore on June 4, 1923. It was granted to Penn's School of Electrical Engineering, located in the Towne ...
, where the ENIAC
ENIAC (; Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) was the first programmable, electronic, general-purpose digital computer, completed in 1945. There were other computers that had these features, but the ENIAC had all of them in one pac ...
was built.
A fully electronic analog computer was built by Helmut H├Člzer )
, image = File:HolzerHelmut Huntsville.jpg
, image_size = 100px
, caption = Helmut H├Člzer in Huntsville, Alabama
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Bad Liebenstein, Th├╝ringen, German Empire
, death_date =
, death_place = Huntsville, Alaba ...
in 1942 at Peenem├╝nde Army Research Center
The Peenem├╝nde Army Research Center (german: Heeresversuchsanstalt Peenem├╝nde, HVP) was founded in 1937 as one of five military proving grounds under the German Army Weapons Office (''Heereswaffenamt''). Several German guided missiles an ...
.
By the 1950s the success of digital electronic computers had spelled the end for most analog computing machines, but hybrid analog computers, controlled by digital electronics, remained in substantial use into the 1950s and 1960s, and later in some specialized applications.
Advent of the digital computer
The principle of the modern computer was first described by computer scientistAlan Turing
Alan Mathison Turing (; 23 June 1912 ŌĆō 7 June 1954) was an English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher, and theoretical biologist. Turing was highly influential in the development of theoretical co ...
, who set out the idea in his seminal 1936 paper, ''On Computable Numbers''. Turing reformulated Kurt G├Čdel's 1931 results on the limits of proof and computation, replacing G├Čdel's universal arithmetic-based formal language with the formal and simple hypothetical devices that became known as Turing machine
A Turing machine is a mathematical model of computation describing an abstract machine that manipulates symbols on a strip of tape according to a table of rules. Despite the model's simplicity, it is capable of implementing any computer algori ...
s. He proved that some such machine would be capable of performing any conceivable mathematical computation if it were representable as an algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing ...
. He went on to prove that there was no solution to the ''Entscheidungsproblem
In mathematics and computer science, the ' (, ) is a challenge posed by David Hilbert and Wilhelm Ackermann in 1928. The problem asks for an algorithm that considers, as input, a statement and answers "Yes" or "No" according to whether the state ...
'' by first showing that the halting problem
In computability theory, the halting problem is the problem of determining, from a description of an arbitrary computer program and an input, whether the program will finish running, or continue to run forever. Alan Turing proved in 1936 that a ...
for Turing machines is undecidable: in general, it is not possible to decide algorithmically whether a given Turing machine will ever halt.
He also introduced the notion of a "universal machine" (now known as a universal Turing machine
In computer science, a universal Turing machine (UTM) is a Turing machine that can simulate an arbitrary Turing machine on arbitrary input. The universal machine essentially achieves this by reading both the description of the machine to be simu ...
), with the idea that such a machine could perform the tasks of any other machine, or in other words, it is provably capable of computing anything that is computable by executing a program stored on tape, allowing the machine to be programmable. Von Neumann Von Neumann may refer to:
* John von Neumann (1903ŌĆō1957), a Hungarian American mathematician
* Von Neumann family
* Von Neumann (surname), a German surname
* Von Neumann (crater), a lunar impact crater
See also
* Von Neumann algebra
* Von Ne ...
acknowledged that the central concept of the modern computer was due to this paper. Turing machines are to this day a central object of study in theory of computation
In theoretical computer science and mathematics, the theory of computation is the branch that deals with what problems can be solved on a model of computation, using an algorithm, how algorithmic efficiency, efficiently they can be solved or t ...
. Except for the limitations imposed by their finite memory stores, modern computers are said to be Turing-complete
In computability theory, a system of data-manipulation rules (such as a computer's instruction set, a programming language, or a cellular automaton) is said to be Turing-complete or computationally universal if it can be used to simulate any ...
, which is to say, they have algorithm
In mathematics and computer science, an algorithm () is a finite sequence of rigorous instructions, typically used to solve a class of specific problems or to perform a computation. Algorithms are used as specifications for performing ...
execution capability equivalent to a universal Turing machine
In computer science, a universal Turing machine (UTM) is a Turing machine that can simulate an arbitrary Turing machine on arbitrary input. The universal machine essentially achieves this by reading both the description of the machine to be simu ...
.
Electromechanical computers
The era of modern computing began with a flurry of development before and during World War II. Most digital computers built in this period were electromechanical ŌĆō electric switches drove mechanical relays to perform the calculation. These devices had a low operating speed and were eventually superseded by much faster all-electric computers, originally usingvacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied.
The type known as ...
s.
The Z2 was one of the earliest examples of an electromechanical relay computer, and was created by German engineer Konrad Zuse
Konrad Ernst Otto Zuse (; 22 June 1910 ŌĆō 18 December 1995) was a German civil engineer, pioneering computer scientist, inventor and businessman. His greatest achievement was the world's first programmable computer; the functional program ...
in 1940. It was an improvement on his earlier Z1; although it used the same mechanical memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered ...
, it replaced the arithmetic and control logic with electrical relay
A relay
Electromechanical relay schematic showing a control coil, four pairs of normally open and one pair of normally closed contacts
An automotive-style miniature relay with the dust cover taken off
A relay is an electrically operated switch ...
circuits.
bombe
The bombe () was an electro-mechanical device used by British cryptologists to help decipher German Enigma-machine-encrypted secret messages during World War II. The US Navy and US Army later produced their own machines to the same functi ...
s were built by British cryptologist
This is a list of cryptographers. Cryptography is the practice and study of techniques for secure communication in the presence of third parties called adversaries.
Pre twentieth century
* Al-Khalil ibn Ahmad al-Farahidi: wrote a (now lost) bo ...
s to help decipher German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
Enigma-machine-encrypted secret messages during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countriesŌĆöincluding all of the great powersŌĆöforming two opposing ...
. The bombe's initial design was created in 1939 at the UK Government Code and Cypher School (GC&CS)
Government Communications Headquarters, commonly known as GCHQ, is an intelligence and security organisation responsible for providing signals intelligence (SIGINT) and information assurance (IA) to the government and armed forces of the Uni ...
at Bletchley Park
Bletchley Park is an English country house and estate in Bletchley, Milton Keynes ( Buckinghamshire) that became the principal centre of Allied code-breaking during the Second World War. The mansion was constructed during the years followin ...
by Alan Turing
Alan Mathison Turing (; 23 June 1912 ŌĆō 7 June 1954) was an English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher, and theoretical biologist. Turing was highly influential in the development of theoretical co ...
, with an important refinement devised in 1940 by Gordon Welchman
William Gordon Welchman (15 June 1906 ŌĆō 8 October 1985) was a British mathematician. During World War II, he worked at Britain's secret codebreaking centre, "Station X" at Bletchley Park, where he was one of the most important contributors. ...
. The engineering design and construction was the work of Harold Keen
Harold Hall "Doc" Keen (1894ŌĆō1973) was a British engineer who produced the engineering design, and oversaw the construction of, the British bombe, a codebreaking machine used in World War II to read German messages sent using the Enigma machi ...
of the British Tabulating Machine Company
__NOTOC__
The British Tabulating Machine Company (BTM) was a firm which manufactured and sold Hollerith unit record equipment and other data-processing equipment. During World War II, BTM constructed some 200 "bombes", machines used at Bletchley ...
. It was a substantial development from a device that had been designed in 1938 by Polish Cipher Bureau cryptologist Marian Rejewski, and known as the " cryptologic bomb" (Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, w ...
: ''"bomba kryptologiczna"'').
In 1941, Zuse followed his earlier machine up with the Z3, the world's first working electromechanical
In engineering, electromechanics combines processes and procedures drawn from electrical engineering and mechanical engineering. Electromechanics focuses on the interaction of electrical and mechanical systems as a whole and how the two systems ...
programmable, fully automatic digital computer. The Z3 was built with 2000 relay
A relay
Electromechanical relay schematic showing a control coil, four pairs of normally open and one pair of normally closed contacts
An automotive-style miniature relay with the dust cover taken off
A relay is an electrically operated switch ...
s, implementing a 22-bit
The bit is the most basic unit of information in computing and digital communications. The name is a portmanteau of binary digit. The bit represents a logical state with one of two possible values. These values are most commonly represente ...
word length
In computing, a word is the natural unit of data used by a particular processor design. A word is a fixed-sized datum handled as a unit by the instruction set or the hardware of the processor. The number of bits or digits in a word (the ''word s ...
that operated at a clock frequency
In computing, the clock rate or clock speed typically refers to the frequency at which the clock generator of a processor can generate pulses, which are used to synchronize the operations of its components, and is used as an indicator of the pr ...
of about 5ŌĆō10 Hz. Program code and data were stored on punched film. It was quite similar to modern machines in some respects, pioneering numerous advances such as floating-point numbers
In computing, floating-point arithmetic (FP) is arithmetic that represents real numbers approximately, using an integer with a fixed precision, called the significand, scaled by an integer exponent of a fixed base. For example, 12.345 can ...
. Replacement of the hard-to-implement decimal system (used in Charles Babbage's earlier design) by the simpler binary
Binary may refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics
* Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two digits (0 and 1)
* Binary function, a function that takes two arguments
* Binary operation, a mathematical operation that ta ...
system meant that Zuse's machines were easier to build and potentially more reliable, given the technologies available at that time. The Z3 was proven to have been a Turing-complete machine in 1998 by Ra├║l Rojas
Ra├║l Rojas Gonz├Īlez (born 1955, in Mexico City) is an emeritus professor of Computer Science and Mathematics at the Free University of Berlin, and a renowned specialist in artificial neural networks. The FU-Fighters, football-playing robots ...
. In two 1936 patent
A patent is a type of intellectual property that gives its owner the legal right to exclude others from making, using, or selling an invention for a limited period of time in exchange for publishing an enabling disclosure of the invention."A ...
applications, Zuse also anticipated that machine instructions could be stored in the same storage used for dataŌĆöthe key insight of what became known as the von Neumann architecture
The von Neumann architecture ŌĆö also known as the von Neumann model or Princeton architecture ŌĆö is a computer architecture based on a 1945 description by John von Neumann, and by others, in the '' First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC''. T ...
, first implemented in 1948 in America in the electromechanical
In engineering, electromechanics combines processes and procedures drawn from electrical engineering and mechanical engineering. Electromechanics focuses on the interaction of electrical and mechanical systems as a whole and how the two systems ...
IBM SSEC
The IBM Selective Sequence Electronic Calculator (SSEC) was an electromechanical computer built by IBM. Its design was started in late 1944 and it operated from January 1948 to August 1952. It had many of the features of a stored-program computer, ...
and in Britain in the fully electronic Manchester Baby
The Manchester Baby, also called the Small-Scale Experimental Machine (SSEM), was the first electronic stored-program computer. It was built at the University of Manchester by Frederic C. Williams, Tom Kilburn, and Geoff Tootill, and ran its ...
.
Zuse suffered setbacks during World War II when some of his machines were destroyed in the course of Allied bombing campaigns. Apparently his work remained largely unknown to engineers in the UK and US until much later, although at least IBM was aware of it as it financed his post-war startup company in 1946 in return for an option on Zuse's patents.
In 1944, the Harvard Mark I was constructed at IBM's Endicott laboratories. It was a similar general purpose electro-mechanical computer to the Z3, but was not quite Turing-complete.
Digital computation
The term digital was first suggested by George Robert Stibitz and refers to where a signal, such as a voltage, is not used to directly represent a value (as it would be in ananalog computer
An analog computer or analogue computer is a type of computer that uses the continuous variation aspect of physical phenomena such as electrical, mechanical, or hydraulic quantities (''analog signals'') to model the problem being solved. In ...
), but to encode it. In November 1937, Stibitz, then working at Bell Labs (1930ŌĆō1941), completed a relay-based calculator he later dubbed the " Model K" (for "kitchen table", on which he had assembled it), which became the first binary adder
Binary may refer to:
Science and technology Mathematics
* Binary number, a representation of numbers using only two digits (0 and 1)
* Binary function, a function that takes two arguments
* Binary operation, a mathematical operation that ta ...
. Typically signals have two states ŌĆō low (usually representing 0) and high (usually representing 1), but sometimes three-valued logic
In logic, a three-valued logic (also trinary logic, trivalent, ternary, or trilean, sometimes abbreviated 3VL) is any of several many-valued logic systems in which there are three truth values indicating ''true'', ''false'' and some indeterminate ...
is used, especially in high-density memory. Modern computers generally use binary logic, but many early machines were decimal computer
Decimal computers are computers which can represent numbers and addresses in decimal as well as providing instructions to operate on those numbers and addresses directly in decimal, without conversion to a pure binary representation. Some also h ...
s. In these machines, the basic unit of data was the decimal digit, encoded in one of several schemes, including binary-coded decimal or BCD, bi-quinary, excess-3
Excess-3, 3-excess or 10-excess-3 binary code (often abbreviated as XS-3, 3XS or X3), shifted binary or Stibitz code (after George Stibitz, who built a relay-based adding machine in 1937) is a self-complementary binary-coded decimal (BCD) cod ...
, and two-out-of-five code
A two-out-of-five code is a constant-weight code that provides exactly ten possible combinations of two bits, and is thus used for representing the decimal digits using five bits. Each bit is assigned a weight, such that the set bits sum to th ...
.
The mathematical basis of digital computing is Boolean algebra
In mathematics and mathematical logic, Boolean algebra is a branch of algebra. It differs from elementary algebra in two ways. First, the values of the variables are the truth values ''true'' and ''false'', usually denoted 1 and 0, whereas i ...
, developed by the British mathematician George Boole
George Boole (; 2 November 1815 ŌĆō 8 December 1864) was a largely self-taught English mathematician, philosopher, and logician, most of whose short career was spent as the first professor of mathematics at Queen's College, Cork in ...
in his work ''The Laws of Thought
''An Investigation of the Laws of Thought on Which are Founded the Mathematical Theories of Logic and Probabilities'' by George Boole, published in 1854, is the second of Boole's two monographs on algebraic logic. Boole was a professor of mathem ...
'', published in 1854. His Boolean algebra was further refined in the 1860s by William Jevons
William Stanley Jevons (; 1 September 183513 August 1882) was an English economist and logician.
Irving Fisher described Jevons's book ''A General Mathematical Theory of Political Economy'' (1862) as the start of the mathematical method in eco ...
and Charles Sanders Peirce
Charles Sanders Peirce ( ; September 10, 1839 ŌĆō April 19, 1914) was an American philosopher, logician, mathematician and scientist who is sometimes known as "the father of pragmatism".
Educated as a chemist and employed as a scientist for t ...
, and was first presented systematically by Ernst Schr├Čder and A. N. Whitehead. In 1879 Gottlob Frege develops the formal approach to logic and proposes the first logic language for logical equations.
In the 1930s and working independently, American electronic engineer
Electronics engineering is a sub-discipline of electrical engineering which emerged in the early 20th century and is distinguished by the additional use of active components such as semiconductor devices to amplify and control electric current ...
Claude Shannon
Claude Elwood Shannon (April 30, 1916 ŌĆō February 24, 2001) was an American mathematician, electrical engineer, and cryptographer known as a "father of information theory".
As a 21-year-old master's degree student at the Massachusetts Inst ...
and Soviet logician
Logic is the study of correct reasoning. It includes both formal and informal logic. Formal logic is the science of deductively valid inferences or of logical truths. It is a formal science investigating how conclusions follow from premises ...
Victor Shestakov
Victor Ivanovich Shestakov (Russian: ) (1907ŌĆō1987) was a Russian/Soviet logician and theoretician of electrical engineering. In 1935 he discovered the possible interpretation of Boolean algebra of logic in electro-mechanical relay circuits. He ...
both showed a one-to-one correspondence
In mathematics, a bijection, also known as a bijective function, one-to-one correspondence, or invertible function, is a function between the elements of two sets, where each element of one set is paired with exactly one element of the other ...
between the concepts of Boolean logic and certain electrical circuits, now called logic gates, which are now ubiquitous in digital computers. They showed that electronic relays and switches can realize the expression
Expression may refer to:
Linguistics
* Expression (linguistics), a word, phrase, or sentence
* Fixed expression, a form of words with a specific meaning
* Idiom, a type of fixed expression
* Metaphorical expression, a particular word, phrase, o ...
s of Boolean algebra
In mathematics and mathematical logic, Boolean algebra is a branch of algebra. It differs from elementary algebra in two ways. First, the values of the variables are the truth values ''true'' and ''false'', usually denoted 1 and 0, whereas i ...
. This thesis essentially founded practical digital circuit design. In addition Shannon's paper gives a correct circuit diagram for a 4 bit digital binary adder.
Electronic data processing
 Purely electronic circuit elements soon replaced their mechanical and electromechanical equivalents, at the same time that digital calculation replaced analog. Machines such as the Z3, the AtanasoffŌĆōBerry Computer, the
Purely electronic circuit elements soon replaced their mechanical and electromechanical equivalents, at the same time that digital calculation replaced analog. Machines such as the Z3, the AtanasoffŌĆōBerry Computer, the Colossus computer
Colossus was a set of computers developed by British codebreakers in the years 1943ŌĆō1945 to help in the cryptanalysis of the Lorenz cipher. Colossus used thermionic valves (vacuum tubes) to perform Boolean and counting operations. Colossus ...
s, and the ENIAC
ENIAC (; Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) was the first programmable, electronic, general-purpose digital computer, completed in 1945. There were other computers that had these features, but the ENIAC had all of them in one pac ...
were built by hand, using circuits containing relays or valves (vacuum tubes), and often used punched card
A punched card (also punch card or punched-card) is a piece of stiff paper that holds digital data represented by the presence or absence of holes in predefined positions. Punched cards were once common in data processing applications or to di ...
s or punched paper tape for input and as the main (non-volatile) storage medium.
Engineer Tommy Flowers
Thomas Harold Flowers MBE (22 December 1905 ŌĆō 28 October 1998) was an English engineer with the British General Post Office. During World War II, Flowers designed and built Colossus, the world's first programmable electronic computer, to help ...
joined the telecommunications branch of the General Post Office in 1926. While working at the research station
Research stations are facilities where scientific investigation, collection, analysis and experimentation occurs. A research station is a facility that is built for the purpose of conducting scientific research. There are also many types of resea ...
in Dollis Hill
Dollis Hill is an area in northwest London, which consists of the streets surrounding the 35 hectares (86 acres) Gladstone Park. It is served by a London Underground station, Dollis Hill, on the Jubilee line, providing good links to central Lo ...
in the 1930s, he began to explore the possible use of electronics for the telephone exchange. Experimental equipment that he built in 1934 went into operation 5 years later, converting a portion of the telephone exchange network into an electronic data processing system, using thousands of vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied.
The type known as ...
s.
In the US, in 1940 Arthur Dickinson (IBM) invented the first digital electronic computer. This calculating device was fully electronic ŌĆō control, calculations and output (the first electronic display). John Vincent Atanasoff and Clifford E. Berry of Iowa State University developed the AtanasoffŌĆōBerry Computer (ABC) in 1942, the first binary electronic digital calculating device. This design was semi-electronic (electro-mechanical control and electronic calculations), and used about 300 vacuum tubes, with capacitors fixed in a mechanically rotating drum for memory. However, its paper card writer/reader was unreliable and the regenerative drum contact system was mechanical. The machine's special-purpose nature and lack of changeable, stored program
A stored-program computer is a computer that stores program instructions in electronically or optically accessible memory. This contrasts with systems that stored the program instructions with plugboards or similar mechanisms.
The definition ...
distinguish it from modern computers.
Computers whose logic was primarily built using vacuum tubes are now known as first generation computers.
The electronic programmable computer
 During World War II, British codebreakers at
During World War II, British codebreakers at Bletchley Park
Bletchley Park is an English country house and estate in Bletchley, Milton Keynes ( Buckinghamshire) that became the principal centre of Allied code-breaking during the Second World War. The mansion was constructed during the years followin ...
, north of London, achieved a number of successes at breaking encrypted enemy military communications. The German encryption machine, Enigma
Enigma may refer to:
*Riddle, someone or something that is mysterious or puzzling
Biology
*ENIGMA, a class of gene in the LIM domain
Computing and technology
* Enigma (company), a New York-based data-technology startup
* Enigma machine, a family ...
, was first attacked with the help of the electro-mechanical bombe
The bombe () was an electro-mechanical device used by British cryptologists to help decipher German Enigma-machine-encrypted secret messages during World War II. The US Navy and US Army later produced their own machines to the same functi ...
s. Women often operated these bombe machines. They ruled out possible Enigma settings by performing chains of logical deductions implemented electrically. Most possibilities led to a contradiction, and the few remaining could be tested by hand.
The Germans also developed a series of teleprinter encryption systems, quite different from Enigma. The Lorenz SZ 40/42 machine was used for high-level Army communications, code-named "Tunny" by the British. The first intercepts of Lorenz messages began in 1941. As part of an attack on Tunny, Max Newman
Maxwell Herman Alexander Newman, FRS, (7 February 1897 ŌĆō 22 February 1984), generally known as Max Newman, was a British mathematician and codebreaker. His work in World War II led to the construction of Colossus, the world's first operatio ...
and his colleagues developed the Heath Robinson
William Heath Robinson (31 May 1872 ŌĆō 13 September 1944) was an English cartoonist, illustrator and artist, best known for drawings of whimsically elaborate machines to achieve simple objectives.
In the UK, the term "Heath Robinson cont ...
, a fixed-function machine to aid in code breaking. Tommy Flowers
Thomas Harold Flowers MBE (22 December 1905 ŌĆō 28 October 1998) was an English engineer with the British General Post Office. During World War II, Flowers designed and built Colossus, the world's first programmable electronic computer, to help ...
, a senior engineer at the Post Office Research Station
The Post Office Research Station was first established as a separate section of the General Post Office in 1909.
In 1921, the Research Station moved to Dollis Hill, north west London, initially in ex-army huts.
The main permanent buildings at ...
was recommended to Max Newman by Alan Turing and spent eleven months from early February 1943 designing and building the more flexible Colossus computer
Colossus was a set of computers developed by British codebreakers in the years 1943ŌĆō1945 to help in the cryptanalysis of the Lorenz cipher. Colossus used thermionic valves (vacuum tubes) to perform Boolean and counting operations. Colossus ...
(which superseded the Heath Robinson
William Heath Robinson (31 May 1872 ŌĆō 13 September 1944) was an English cartoonist, illustrator and artist, best known for drawings of whimsically elaborate machines to achieve simple objectives.
In the UK, the term "Heath Robinson cont ...
). After a functional test in December 1943, Colossus was shipped to Bletchley Park, where it was delivered on 18 January 1944 and attacked its first message on 5 February.
 Colossus was the world's first
Colossus was the world's first electronic
Electronic may refer to:
*Electronics, the science of how to control electric energy in semiconductor
* ''Electronics'' (magazine), a defunct American trade journal
*Electronic storage, the storage of data using an electronic device
*Electronic co ...
digital programmable computer. It used a large number of valves (vacuum tubes). It had paper-tape input and was capable of being configured to perform a variety of boolean logical operations on its data, but it was not Turing-complete
In computability theory, a system of data-manipulation rules (such as a computer's instruction set, a programming language, or a cellular automaton) is said to be Turing-complete or computationally universal if it can be used to simulate any ...
. Data input to Colossus was by photoelectric
The photoelectric effect is the emission of electrons when electromagnetic radiation, such as light, hits a material. Electrons emitted in this manner are called photoelectrons. The phenomenon is studied in condensed matter physics, and solid sta ...
reading of a paper tape transcription of the enciphered intercepted message. This was arranged in a continuous loop so that it could be read and re-read multiple times ŌĆō there being no internal store for the data. The reading mechanism ran at 5,000 characters per second with the paper tape moving at . Colossus Mark 1 contained 1500 thermionic valves (tubes), but Mark 2 with 2400 valves and five processors in parallel, was both 5 times faster and simpler to operate than Mark 1, greatly speeding the decoding process. Mark 2 was designed while Mark 1 was being constructed. Allen Coombs took over leadership of the Colossus Mark 2 project when Tommy Flowers
Thomas Harold Flowers MBE (22 December 1905 ŌĆō 28 October 1998) was an English engineer with the British General Post Office. During World War II, Flowers designed and built Colossus, the world's first programmable electronic computer, to help ...
moved on to other projects. The first Mark 2 Colossus became operational on 1 June 1944, just in time for the Allied Invasion of Normandy on D-Day.
Most of the use of Colossus was in determining the start positions of the Tunny rotors for a message, which was called "wheel setting". Colossus included the first-ever use of shift register
A shift register is a type of digital circuit using a cascade of flip-flops where the output of one flip-flop is connected to the input of the next. They share a single clock signal, which causes the data stored in the system to shift from one loc ...
s and systolic array
In parallel computer architectures, a systolic array is a homogeneous network of tightly coupled data processing units (DPUs) called cells or nodes. Each node or DPU independently computes a partial result as a function of the data received from i ...
s, enabling five simultaneous tests, each involving up to 100 Boolean calculations. This enabled five different possible start positions to be examined for one transit of the paper tape. As well as wheel setting some later Colossi included mechanisms intended to help determine pin patterns known as "wheel breaking". Both models were programmable using switches and plug panels in a way their predecessors had not been. Ten Mk 2 Colossi were operational by the end of the war.
 Without the use of these machines, the Allies would have been deprived of the very valuable
Without the use of these machines, the Allies would have been deprived of the very valuable intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. More generally, it can be des ...
that was obtained from reading the vast quantity of enciphered high-level telegraphic
Telegraphy is the long-distance transmission of messages where the sender uses symbolic codes, known to the recipient, rather than a physical exchange of an object bearing the message. Thus flag semaphore is a method of telegraphy, whereas p ...
messages between the German High Command (OKW) and their army
An army (from Old French ''armee'', itself derived from the Latin verb ''arm─üre'', meaning "to arm", and related to the Latin noun ''arma'', meaning "arms" or "weapons"), ground force or land force is a fighting force that fights primarily on ...
commands throughout occupied Europe. Details of their existence, design, and use were kept secret well into the 1970s. Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from ...
personally issued an order for their destruction into pieces no larger than a man's hand, to keep secret that the British were capable of cracking Lorenz SZ cyphers (from German rotor stream cipher machines) during the oncoming Cold War. Two of the machines were transferred to the newly formed GCHQ
Government Communications Headquarters, commonly known as GCHQ, is an intelligence and security organisation responsible for providing signals intelligence (SIGINT) and information assurance (IA) to the government and armed forces of the Uni ...
and the others were destroyed. As a result, the machines were not included in many histories of computing. A reconstructed working copy of one of the Colossus machines is now on display at Bletchley Park.
The US-built ENIAC
ENIAC (; Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) was the first programmable, electronic, general-purpose digital computer, completed in 1945. There were other computers that had these features, but the ENIAC had all of them in one pac ...
(Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) was the first electronic programmable computer built in the US. Although the ENIAC was similar to the Colossus it was much faster and more flexible. It was unambiguously a Turing-complete device and could compute any problem that would fit into its memory. Like the Colossus, a "program" on the ENIAC was defined by the states of its patch cables and switches, a far cry from the stored program
A stored-program computer is a computer that stores program instructions in electronically or optically accessible memory. This contrasts with systems that stored the program instructions with plugboards or similar mechanisms.
The definition ...
electronic machines that came later. Once a program was written, it had to be mechanically set into the machine with manual resetting of plugs and switches. The programmers of the ENIAC were women who had been trained as mathematicians.
It combined the high speed of electronics with the ability to be programmed for many complex problems. It could add or subtract 5000 times a second, a thousand times faster than any other machine. It also had modules to multiply, divide, and square root. High-speed memory was limited to 20 words (equivalent to about 80 bytes). Built under the direction of John Mauchly
John William Mauchly (August 30, 1907 ŌĆō January 8, 1980) was an American physicist who, along with J. Presper Eckert, designed ENIAC, the first general-purpose electronic digital computer, as well as EDVAC, BINAC and UNIVAC I, the first ...
and J. Presper Eckert
John Adam Presper Eckert Jr. (April 9, 1919 ŌĆō June 3, 1995) was an American electrical engineer and computer pioneer. With John Mauchly, he designed the first general-purpose electronic digital computer (ENIAC), presented the first course in c ...
at the University of Pennsylvania, ENIAC's development and construction lasted from 1943 to full operation at the end of 1945. The machine was huge, weighing 30 tons, using 200 kilowatts of electric power and contained over 18,000 vacuum tubes, 1,500 relays, and hundreds of thousands of resistors, capacitors, and inductors. One of its major engineering feats was to minimize the effects of tube burnout, which was a common problem in machine reliability at that time. The machine was in almost constant use for the next ten years.
Stored-program computer
Early computing machines were programmable in the sense that they could follow the sequence of steps they had been set up to execute, but the "program", or steps that the machine was to execute, were set up usually by changing how the wires were plugged into apatch panel
A patch panel is a device or unit featuring a number of jacks, usually of the same or similar type, for the use of connecting and routing circuits for monitoring, interconnecting, and testing circuits in a convenient, flexible manner. Patch ...
or plugboard
A plugboard or control panel (the term used depends on the application area) is an array of jacks or sockets (often called hubs) into which patch cords can be inserted to complete an electrical circuit. Control panels are sometimes used to di ...
. "Reprogramming", when it was possible at all, was a laborious process, starting with engineers working out flowcharts, designing the new set up, and then the often-exacting process of physically re-wiring patch panels. Stored-program computers, by contrast, were designed to store a set of instructions (a program), in memory ŌĆō typically the same memory as stored data.
Theory
Alan Turing
Alan Mathison Turing (; 23 June 1912 ŌĆō 7 June 1954) was an English mathematician, computer scientist, logician, cryptanalyst, philosopher, and theoretical biologist. Turing was highly influential in the development of theoretical co ...
in his 1936 paper. In 1945 Turing joined the National Physical Laboratory and began his work on developing an electronic stored-program digital computer. His 1945 report 'Proposed Electronic Calculator' was the first specification for such a device.
Meanwhile, John von Neumann
John von Neumann (; hu, Neumann J├Īnos Lajos, ; December 28, 1903 ŌĆō February 8, 1957) was a Hungarian-American mathematician, physicist, computer scientist, engineer and polymath. He was regarded as having perhaps the widest cove ...
at the Moore School of Electrical Engineering
The Moore School of Electrical Engineering at the University of Pennsylvania came into existence as a result of an endowment from Alfred Fitler Moore on June 4, 1923. It was granted to Penn's School of Electrical Engineering, located in the Towne ...
, University of Pennsylvania
The University of Pennsylvania (also known as Penn or UPenn) is a private research university in Philadelphia. It is the fourth-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and is ranked among the highest-regarded universitie ...
, circulated his ''First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC
The ''First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC'' (commonly shortened to ''First Draft'') is an incomplete 101-page document written by John von Neumann and distributed on June 30, 1945 by Herman Goldstine, security officer on the classified ENIAC pro ...
'' in 1945. Although substantially similar to Turing's design and containing comparatively little engineering detail, the computer architecture it outlined became known as the "von Neumann architecture
The von Neumann architecture ŌĆö also known as the von Neumann model or Princeton architecture ŌĆö is a computer architecture based on a 1945 description by John von Neumann, and by others, in the '' First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC''. T ...
". Turing presented a more detailed paper to the National Physical Laboratory (NPL) Executive Committee in 1946, giving the first reasonably complete design of a stored-program computer, a device he called the Automatic Computing Engine
The Automatic Computing Engine (ACE) was a British early Electronic storage, electronic Serial computer, serial stored-program computer designed by Alan Turing. It was based on the earlier Pilot ACE. It led to the MOSAIC computer, the Bendi ...
(ACE). However, the better-known EDVAC design of John von Neumann
John von Neumann (; hu, Neumann J├Īnos Lajos, ; December 28, 1903 ŌĆō February 8, 1957) was a Hungarian-American mathematician, physicist, computer scientist, engineer and polymath. He was regarded as having perhaps the widest cove ...
, who knew of Turing's theoretical work, received more publicity, despite its incomplete nature and questionable lack of attribution of the sources of some of the ideas.
Turing thought that the speed and the size of computer memory
In computing, memory is a device or system that is used to store information for immediate use in a computer or related computer hardware and digital electronic devices. The term ''memory'' is often synonymous with the term '' primary storag ...
were crucial elements, so he proposed a high-speed memory of what would today be called 25 KB, accessed at a speed of 1 MHz
The hertz (symbol: Hz) is the unit of frequency in the International System of Units (SI), equivalent to one event (or cycle) per second. The hertz is an SI derived unit whose expression in terms of SI base units is sŌłÆ1, meaning that one he ...
. The ACE implemented subroutine calls, whereas the EDVAC did not, and the ACE also used ''Abbreviated Computer Instructions,'' an early form of programming language
A programming language is a system of notation for writing computer programs. Most programming languages are text-based formal languages, but they may also be graphical. They are a kind of computer language.
The description of a programming ...
.
Manchester Baby
 The
The Manchester Baby
The Manchester Baby, also called the Small-Scale Experimental Machine (SSEM), was the first electronic stored-program computer. It was built at the University of Manchester by Frederic C. Williams, Tom Kilburn, and Geoff Tootill, and ran its ...
(Small Scale Experimental Machine, SSEM) was the world's first electronic stored-program computer. It was built at the Victoria University of Manchester
The Victoria University of Manchester, usually referred to as simply the University of Manchester, was a university in Manchester, England. It was founded in 1851 as Owens College. In 1880, the college joined the federal Victoria University. Afte ...
by Frederic C. Williams
Sir Frederic Calland Williams, (26 June 1911 – 11 August 1977), known as F.C. Williams or Freddie Williams, was an English engineer, a pioneer in radar and computer technology.
Education
Williams was born in Romiley, Stockport, and ed ...
, Tom Kilburn
Tom Kilburn (11 August 1921 ŌĆō 17 January 2001) was an English mathematician and computer scientist. Over the course of a productive 30-year career, he was involved in the development of five computers of great historical significance. With ...
and Geoff Tootill, and ran its first program on 21 June 1948.
The machine was not intended to be a practical computer but was instead designed as a testbed
A testbed (also spelled test bed) is a platform for conducting rigorous, transparent, and replicable testing of scientific theories, computational tools, and new technologies.
The term is used across many disciplines to describe experimental rese ...
for the Williams tube
The Williams tube, or the WilliamsŌĆōKilburn tube named after inventors Freddie Williams and Tom Kilburn, is an early form of computer memory. It was the first random-access digital storage device, and was used successfully in several early co ...
, the first random-access
Random access (more precisely and more generally called direct access) is the ability to access an arbitrary element of a sequence in equal time or any datum from a population of addressable elements roughly as easily and efficiently as any othe ...
digital storage device. Invented by Freddie Williams and Tom Kilburn
Tom Kilburn (11 August 1921 ŌĆō 17 January 2001) was an English mathematician and computer scientist. Over the course of a productive 30-year career, he was involved in the development of five computers of great historical significance. With ...
at the University of Manchester in 1946 and 1947, it was a cathode-ray tube that used an effect called secondary emission to temporarily store electronic binary data
Binary data is data whose unit can take on only two possible states. These are often labelled as 0 and 1 in accordance with the binary numeral system and Boolean algebra.
Binary data occurs in many different technical and scientific fields, wher ...
, and was used successfully in several early computers.
Described as small and primitive in a 1998 retrospective, the Baby was the first working machine to contain all of the elements essential to a modern electronic computer. As soon as it had demonstrated the feasibility of its design, a project was initiated at the university to develop the design into a more usable computer, the Manchester Mark 1
The Manchester Mark 1 was one of the earliest stored-program computers, developed at the Victoria University of Manchester, England from the Manchester Baby (operational in June 1948). Work began in August 1948, and the first version was oper ...
. The Mark 1 in turn quickly became the prototype for the Ferranti Mark 1
The Ferranti Mark 1, also known as the Manchester Electronic Computer in its sales literature, and thus sometimes called the Manchester Ferranti, was produced by British electrical engineering firm Ferranti Ltd. It was the world's first commer ...
, the world's first commercially available general-purpose computer.
The Baby had a 32-bit
The bit is the most basic unit of information in computing and digital communications. The name is a portmanteau of binary digit. The bit represents a logical state with one of two possible values. These values are most commonly represente ...
word
A word is a basic element of language that carries an objective or practical meaning, can be used on its own, and is uninterruptible. Despite the fact that language speakers often have an intuitive grasp of what a word is, there is no conse ...
length and a memory
Memory is the faculty of the mind by which data or information is encoded, stored, and retrieved when needed. It is the retention of information over time for the purpose of influencing future action. If past events could not be remembered ...
of 32 words. As it was designed to be the simplest possible stored-program computer, the only arithmetic operations implemented in hardware were subtraction and negation; other arithmetic operations were implemented in software. The first of three programs written for the machine found the highest proper divisor
In mathematics, a divisor of an integer n, also called a factor of n, is an integer m that may be multiplied by some integer to produce n. In this case, one also says that n is a multiple of m. An integer n is divisible or evenly divisible by ...
of 218 (262,144), a calculation that was known would take a long time to runŌĆöand so prove the computer's reliabilityŌĆöby testing every integer from 218 ŌłÆ 1 downwards, as division was implemented by repeated subtraction of the divisor. The program consisted of 17 instructions and ran for 52 minutes before reaching the correct answer of 131,072, after the Baby had performed 3.5 million operations (for an effective CPU speed of 1.1 kIPS). The successive approximations to the answer were displayed as a pattern of dots on the output CRT which mirrored the pattern held on the Williams tube used for storage.
Manchester Mark 1
The SSEM led to the development of theManchester Mark 1
The Manchester Mark 1 was one of the earliest stored-program computers, developed at the Victoria University of Manchester, England from the Manchester Baby (operational in June 1948). Work began in August 1948, and the first version was oper ...
at the University of Manchester. Work began in August 1948, and the first version was operational by April 1949; a program written to search for Mersenne prime
In mathematics, a Mersenne prime is a prime number that is one less than a power of two. That is, it is a prime number of the form for some integer . They are named after Marin Mersenne, a French Minim friar, who studied them in the early 17th ...
s ran error-free for nine hours on the night of 16/17 June 1949.
The machine's successful operation was widely reported in the British press, which used the phrase "electronic brain" in describing it to their readers.
The computer is especially historically significant because of its pioneering inclusion of index register
An index register in a computer's CPU is a processor register (or an assigned memory location) used for pointing to operand addresses during the run of a program. It is useful for stepping through strings and arrays. It can also be used for hol ...
s, an innovation which made it easier for a program to read sequentially through an array of words
A word is a basic element of language that carries an objective or practical meaning, can be used on its own, and is uninterruptible. Despite the fact that language speakers often have an intuitive grasp of what a word is, there is no conse ...
in memory. Thirty-four patents resulted from the machine's development, and many of the ideas behind its design were incorporated in subsequent commercial products such as the and 702
__NOTOC__
Year 702 ( DCCII) was a common year starting on Sunday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar. The denomination 702 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era b ...
as well as the Ferranti Mark 1. The chief designers, Frederic C. Williams
Sir Frederic Calland Williams, (26 June 1911 – 11 August 1977), known as F.C. Williams or Freddie Williams, was an English engineer, a pioneer in radar and computer technology.
Education
Williams was born in Romiley, Stockport, and ed ...
and Tom Kilburn
Tom Kilburn (11 August 1921 ŌĆō 17 January 2001) was an English mathematician and computer scientist. Over the course of a productive 30-year career, he was involved in the development of five computers of great historical significance. With ...
, concluded from their experiences with the Mark 1 that computers would be used more in scientific roles than in pure mathematics. In 1951 they started development work on Meg, the Mark 1's successor, which would include a floating-point unit.
EDSAC
 The other contender for being the first recognizably modern digital stored-program computer was the EDSAC, designed and constructed by Maurice Wilkes and his team at the
The other contender for being the first recognizably modern digital stored-program computer was the EDSAC, designed and constructed by Maurice Wilkes and his team at the University of Cambridge Mathematical Laboratory
The Department of Computer Science and Technology, formerly the Computer Laboratory, is the computer science department of the University of Cambridge. it employed 35 academic staff, 25 support staff, 35 affiliated research staff, and about 15 ...
in England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe b ...
at the University of Cambridge
The University of Cambridge is a public collegiate research university in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1209 and granted a royal charter by Henry III in 1231, Cambridge is the world's third oldest surviving university and one of its most pr ...
in 1949. The machine was inspired by John von Neumann
John von Neumann (; hu, Neumann J├Īnos Lajos, ; December 28, 1903 ŌĆō February 8, 1957) was a Hungarian-American mathematician, physicist, computer scientist, engineer and polymath. He was regarded as having perhaps the widest cove ...
's seminal ''First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC
The ''First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC'' (commonly shortened to ''First Draft'') is an incomplete 101-page document written by John von Neumann and distributed on June 30, 1945 by Herman Goldstine, security officer on the classified ENIAC pro ...
'' and was one of the first usefully operational electronic digital stored-program computer.
EDSAC ran its first programs on 6 May 1949, when it calculated a table of squares and a list of prime number
A prime number (or a prime) is a natural number greater than 1 that is not a product of two smaller natural numbers. A natural number greater than 1 that is not prime is called a composite number. For example, 5 is prime because the only ways ...
s.The EDSAC also served as the basis for the first commercially applied computer, the LEO I
The LEO I (Lyons Electronic Office I) was the first computer used for commercial business applications.
The prototype LEO I was modelled closely on the Cambridge EDSAC. Its construction was overseen by Oliver Standingford, Raymond Thompson and ...
, used by food manufacturing company J. Lyons & Co. Ltd. EDSAC 1 was finally shut down on 11 July 1958, having been superseded by EDSAC 2 which stayed in use until 1965.
EDVAC

ENIAC
ENIAC (; Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) was the first programmable, electronic, general-purpose digital computer, completed in 1945. There were other computers that had these features, but the ENIAC had all of them in one pac ...
inventors John Mauchly
John William Mauchly (August 30, 1907 ŌĆō January 8, 1980) was an American physicist who, along with J. Presper Eckert, designed ENIAC, the first general-purpose electronic digital computer, as well as EDVAC, BINAC and UNIVAC I, the first ...
and J. Presper Eckert
John Adam Presper Eckert Jr. (April 9, 1919 ŌĆō June 3, 1995) was an American electrical engineer and computer pioneer. With John Mauchly, he designed the first general-purpose electronic digital computer (ENIAC), presented the first course in c ...
proposed the EDVAC's construction in August 1944, and design work for the EDVAC commenced at the University of Pennsylvania
The University of Pennsylvania (also known as Penn or UPenn) is a private research university in Philadelphia. It is the fourth-oldest institution of higher education in the United States and is ranked among the highest-regarded universitie ...
's Moore School of Electrical Engineering
The Moore School of Electrical Engineering at the University of Pennsylvania came into existence as a result of an endowment from Alfred Fitler Moore on June 4, 1923. It was granted to Penn's School of Electrical Engineering, located in the Towne ...
, before the ENIAC
ENIAC (; Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer) was the first programmable, electronic, general-purpose digital computer, completed in 1945. There were other computers that had these features, but the ENIAC had all of them in one pac ...
was fully operational. The design implemented a number of important architectural and logical improvements conceived during the ENIAC's construction, and a high-speed serial-access memory. However, Eckert and Mauchly left the project and its construction floundered.
It was finally delivered to the U.S. Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, cl ...
's Ballistics Research Laboratory at the Aberdeen Proving Ground
Aberdeen Proving Ground (APG) (sometimes erroneously called Aberdeen Proving ''Grounds'') is a U.S. Army facility located adjacent to Aberdeen, Harford County, Maryland, United States. More than 7,500 civilians and 5,000 military personnel work a ...
in August 1949, but due to a number of problems, the computer only began operation in 1951, and then only on a limited basis.
Commercial computers
The first commercial computer was theFerranti Mark 1
The Ferranti Mark 1, also known as the Manchester Electronic Computer in its sales literature, and thus sometimes called the Manchester Ferranti, was produced by British electrical engineering firm Ferranti Ltd. It was the world's first commer ...
, built by Ferranti
Ferranti or Ferranti International plc was a UK electrical engineering and equipment firm that operated for over a century from 1885 until it went bankrupt in 1993. The company was once a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index.
The firm was known ...
and delivered to the University of Manchester
, mottoeng = Knowledge, Wisdom, Humanity
, established = 2004 ŌĆō University of Manchester Predecessor institutions: 1956 ŌĆō UMIST (as university college; university 1994) 1904 ŌĆō Victoria University of Manchester 1880 ŌĆō Victoria Univ ...
in February 1951. It was based on the Manchester Mark 1
The Manchester Mark 1 was one of the earliest stored-program computers, developed at the Victoria University of Manchester, England from the Manchester Baby (operational in June 1948). Work began in August 1948, and the first version was oper ...
. The main improvements over the Manchester Mark 1 were in the size of the primary storage
Computer data storage is a technology consisting of computer components and recording media that are used to retain digital data. It is a core function and fundamental component of computers.
The central processing unit (CPU) of a compute ...
(using random access Williams tubes), secondary storage (using a magnetic drum
Drum memory was a magnetic data storage device invented by Gustav Tauschek in 1932 in Austria. Drums were widely used in the 1950s and into the 1960s as computer memory.
For many early computers, drum memory formed the main working memory of ...
), a faster multiplier, and additional instructions. The basic cycle time was 1.2 milliseconds, and a multiplication could be completed in about 2.16 milliseconds. The multiplier used almost a quarter of the machine's 4,050 vacuum tubes (valves). A second machine was purchased by the University of Toronto
The University of Toronto (UToronto or U of T) is a public university, public research university in Toronto, Ontario, Canada, located on the grounds that surround Queen's Park (Toronto), Queen's Park. It was founded by royal charter in 1827 ...
, before the design was revised into the Mark 1 Star. At least seven of these later machines were delivered between 1953 and 1957, one of them to Shell
Shell may refer to:
Architecture and design
* Shell (structure), a thin structure
** Concrete shell, a thin shell of concrete, usually with no interior columns or exterior buttresses
** Thin-shell structure
Science Biology
* Seashell, a hard o ...
labs in Amsterdam.
In October 1947, the directors of J. Lyons & Company, a British catering company famous for its teashops but with strong interests in new office management techniques, decided to take an active role in promoting the commercial development of computers. The LEO I
The LEO I (Lyons Electronic Office I) was the first computer used for commercial business applications.
The prototype LEO I was modelled closely on the Cambridge EDSAC. Its construction was overseen by Oliver Standingford, Raymond Thompson and ...
computer (Lyons Electronic Office) became operational in April 1951 and ran the world's first regular routine office computer job
Work or labor (or labour in British English) is intentional activity people perform to support the needs and wants of themselves, others, or a wider community. In the context of economics, work can be viewed as the human activity that contr ...
. On 17 November 1951, the J. Lyons company began weekly operation of a bakery valuations job on the LEO ŌĆō the first business application to go live on a stored program computer.
In June 1951, the UNIVAC I
The UNIVAC I (Universal Automatic Computer I) was the first general-purpose electronic digital computer design for business application produced in the United States. It was designed principally by J. Presper Eckert and John Mauchly, the inven ...
(Universal Automatic Computer) was delivered to the U.S. Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of the ...
. Remington Rand eventually sold 46 machines at more than each ($ as of ). UNIVAC was the first "mass produced" computer. It used 5,200 vacuum tubes and consumed of power. Its primary storage was serial-access mercury delay lines capable of storing 1,000 words of 11 decimal digits plus sign (72-bit words).
 IBM introduced a smaller, more affordable computer in 1954 that proved very popular. The IBM 650 weighed over , the attached power supply weighed around and both were held in separate cabinets of roughly 1.50.9. The system cost ($ as of ) or could be leased for a month ($ as of ). Its drum memory was originally 2,000 ten-digit words, later expanded to 4,000 words. Memory limitations such as this were to dominate programming for decades afterward. The program instructions were fetched from the spinning drum as the code ran. Efficient execution using drum memory was provided by a combination of hardware architecture ŌĆō the instruction format included the address of the next instruction ŌĆō and software: the
IBM introduced a smaller, more affordable computer in 1954 that proved very popular. The IBM 650 weighed over , the attached power supply weighed around and both were held in separate cabinets of roughly 1.50.9. The system cost ($ as of ) or could be leased for a month ($ as of ). Its drum memory was originally 2,000 ten-digit words, later expanded to 4,000 words. Memory limitations such as this were to dominate programming for decades afterward. The program instructions were fetched from the spinning drum as the code ran. Efficient execution using drum memory was provided by a combination of hardware architecture ŌĆō the instruction format included the address of the next instruction ŌĆō and software: the Symbolic Optimal Assembly Program
The Symbolic Optimal Assembly Program (SOAP) is an Assembler (computing), assembler for the IBM 650 Magnetic Drum Data-Processing Machine, an early computer first used in 1954. It was developed by Stan Poley at the IBM Thomas J. Watson Research Ce ...
, SOAP, assigned instructions to the optimal addresses (to the extent possible by static analysis of the source program). Thus many instructions were, when needed, located in the next row of the drum to be read and additional wait time for drum rotation was reduced.
Microprogramming
In 1951, British scientist Maurice Wilkes developed the concept ofmicroprogramming
In processor design, microcode (╬╝code) is a technique that interposes a layer of computer organization between the central processing unit (CPU) hardware and the programmer-visible instruction set architecture of a computer. Microcode is a la ...
from the realisation that the central processing unit
A central processing unit (CPU), also called a central processor, main processor or just Processor (computing), processor, is the electronic circuitry that executes Instruction (computing), instructions comprising a computer program. The CPU per ...
of a computer could be controlled by a miniature, highly specialized computer program
A computer program is a sequence or set of instructions in a programming language for a computer to execute. Computer programs are one component of software, which also includes documentation and other intangible components.
A computer program ...
in high-speed ROM
Rom, or ROM may refer to:
Biomechanics and medicine
* Risk of mortality, a medical classification to estimate the likelihood of death for a patient
* Rupture of membranes, a term used during pregnancy to describe a rupture of the amniotic sac
* ...
. Microprogramming allows the base instruction set to be defined or extended by built-in programs (now called firmware or microcode). This concept greatly simplified CPU development. He first described this at the University of Manchester
, mottoeng = Knowledge, Wisdom, Humanity
, established = 2004 ŌĆō University of Manchester Predecessor institutions: 1956 ŌĆō UMIST (as university college; university 1994) 1904 ŌĆō Victoria University of Manchester 1880 ŌĆō Victoria Univ ...
Computer Inaugural Conference in 1951, then published in expanded form in ''IEEE Spectrum
''IEEE Spectrum'' is a magazine edited by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers.
The first issue of ''IEEE Spectrum'' was published in January 1964 as a successor to ''Electrical Engineering''. The magazine contains peer-reviewe ...
'' in 1955.
It was widely used in the CPUs and floating-point units of mainframe and other computers; it was implemented for the first time in EDSAC 2, which also used multiple identical "bit slices" to simplify design. Interchangeable, replaceable tube assemblies were used for each bit of the processor.
Magnetic memory
Engineering Research Associates
Engineering Research Associates, commonly known as ERA, was a pioneering computer firm from the 1950s. ERA became famous for their numerical computers, but as the market expanded they became better known for their drum memory systems. They were ev ...
(ERA) in 1946 and 1947. ERA, then a part of Univac included a drum memory in its 1103
Year 1103 (Roman numerals, MCIII) was a common year starting on Thursday (link will display the full calendar) of the Julian calendar.
Events
By place
Levant
* Spring – Bohemond I of Antioch, Bohemond I, Norman prince of Antioc ...
, announced in February 1953. The first mass-produced computer, the IBM 650, also announced in 1953 had about 8.5 kilobytes of drum memory.
Magnetic core memory patented in 1949 with its first usage demonstrated for the Whirlwind computer in August 1953. Commercialization followed quickly. Magnetic core was used in peripherals of the IBM 702 delivered in July 1955, and later in the 702 itself. The IBM 704 (1955) and the Ferranti Mercury (1957) used magnetic-core memory. It went on to dominate the field into the 1970s, when it was replaced with semiconductor memory. Magnetic core peaked in volume about 1975 and declined in usage and market share thereafter.
As late as 1980, PDP-11/45 machines using magnetic-core main memory and drums for swapping were still in use at many of the original UNIX sites.
Early digital computer characteristics
Transistor computers
 The bipolar
The bipolar transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch ...
was invented in 1947. From 1955 onward transistors replaced vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, valve (British usage), or tube (North America), is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric potential difference has been applied.
The type known as ...
s in computer designs, giving rise to the "second generation" of computers. Compared to vacuum tubes, transistors have many advantages: they are smaller, and require less power than vacuum tubes, so give off less heat. Silicon junction transistors were much more reliable than vacuum tubes and had longer service life. Transistorized computers could contain tens of thousands of binary logic circuits in a relatively compact space. Transistors greatly reduced computers' size, initial cost, and operating cost
Operating costs or operational costs, are the expenses which are related to the operation of a business, or to the operation of a device, component, piece of equipment or facility. They are the cost of resources used by an organization just to main ...
. Typically, second-generation computers were composed of large numbers of printed circuit boards such as the IBM Standard Modular System
The Standard Modular System (SMS) is a system of standard transistorized circuit boards and mounting racks developed by IBM in the late 1950s, originally for the IBM 7030 Stretch. They were used throughout IBM's second-generation computers, per ...
, each carrying one to four logic gates or flip-flops
Flip-flops are a type of light sandal, typically worn as a form of casual footwear. They consist of a flat sole held loosely on the foot by a Y-shaped strap known as a toe thong that passes between the first and second toes and around both side ...
.
At the University of Manchester
, mottoeng = Knowledge, Wisdom, Humanity
, established = 2004 ŌĆō University of Manchester Predecessor institutions: 1956 ŌĆō UMIST (as university college; university 1994) 1904 ŌĆō Victoria University of Manchester 1880 ŌĆō Victoria Univ ...
, a team under the leadership of Tom Kilburn
Tom Kilburn (11 August 1921 ŌĆō 17 January 2001) was an English mathematician and computer scientist. Over the course of a productive 30-year career, he was involved in the development of five computers of great historical significance. With ...
designed and built a machine using the newly developed transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch ...
s instead of valves. Initially the only devices available were germanium point-contact transistors, less reliable than the valves they replaced but which consumed far less power. Their first transistorized computer, and the first in the world, was operational by 1953, and a second version was completed there in April 1955. The 1955 version used 200 transistors, 1,300 solid-state
Solid state, or solid matter, is one of the four fundamental states of matter.
Solid state may also refer to:
Electronics
* Solid-state electronics, circuits built of solid materials
* Solid state ionics, study of ionic conductors and their use ...
diodes, and had a power consumption of 150 watts. However, the machine did make use of valves to generate its 125 kHz clock waveforms and in the circuitry to read and write on its magnetic drum memory, so it was not the first completely transistorized computer.
That distinction goes to the Harwell CADET
The Harwell CADET was the first fully transistorised computer in Europe, and may have been the first fully transistorised computer in the world.
The electronics division of the Atomic Energy Research Establishment at Harwell, UK built the H ...
of 1955, built by the electronics division of the Atomic Energy Research Establishment at Harwell. The design featured a 64-kilobyte magnetic drum memory store with multiple moving heads that had been designed at the National Physical Laboratory, UK
The National Physical Laboratory (NPL) is the national measurement standards laboratory of the United Kingdom. It is one of the most extensive government laboratories in the UK and has a prestigious reputation for its role in setting and mainta ...
. By 1953 this team had transistor circuits operating to read and write on a smaller magnetic drum from the Royal Radar Establishment
The Royal Radar Establishment was a research centre in Malvern, Worcestershire in the United Kingdom. It was formed in 1953 as the Radar Research Establishment by the merger of the Air Ministry's Telecommunications Research Establishment (TRE) a ...
. The machine used a low clock speed of only 58 kHz to avoid having to use any valves to generate the clock waveforms.
CADET used 324-point-contact transistors provided by the UK company Standard Telephones and Cables
Standard Telephones and Cables Ltd (later STC plc) was a British manufacturer of telephone, telegraph, radio, telecommunications, and related equipment. During its history, STC invented and developed several groundbreaking new technologies incl ...
; 76 junction transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor, uses only one kind of charge carrier. A bipolar ...
s were used for the first stage amplifiers for data read from the drum, since point-contact transistors were too noisy. From August 1956 CADET was offering a regular computing service, during which it often executed continuous computing runs of 80 hours or more. Problems with the reliability of early batches of point contact and alloyed junction transistors meant that the machine's mean time between failures
Mean time between failures (MTBF) is the predicted elapsed time between inherent failures of a mechanical or electronic system during normal system operation. MTBF can be calculated as the arithmetic mean (average) time between failures of a system ...
was about 90 minutes, but this improved once the more reliable bipolar junction transistor
A bipolar junction transistor (BJT) is a type of transistor that uses both electrons and electron holes as charge carriers. In contrast, a unipolar transistor, such as a field-effect transistor, uses only one kind of charge carrier. A bipola ...
s became available.
The Manchester University Transistor Computer's design was adopted by the local engineering firm of Metropolitan-Vickers
Metropolitan-Vickers, Metrovick, or Metrovicks, was a British heavy electrical engineering company of the early-to-mid 20th century formerly known as British Westinghouse. Highly diversified, it was particularly well known for its industrial el ...
in their Metrovick 950
The Metrovick 950 was a transistorized computer, built from 1956 onwards by British company Metropolitan-Vickers, to the extent of sixDavid P. Anderson, ''Tom Kilburn: A Pioneer of Computer Design'', IEEE Annals of the History of Computing - Vo ...
, the first commercial transistor computer anywhere. Six Metrovick 950s were built, the first completed in 1956. They were successfully deployed within various departments of the company and were in use for about five years. A second generation computer, the IBM 1401
The IBM 1401 is a variable-wordlength decimal computer that was announced by IBM on October 5, 1959. The first member of the highly successful IBM 1400 series, it was aimed at replacing unit record equipment for processing data stored on pu ...
, captured about one third of the world market. IBM installed more than ten thousand 1401s between 1960 and 1964.
Transistor peripherals
Transistorized electronics improved not only the CPU (Central Processing Unit), but also theperipheral devices
A peripheral or peripheral device is an auxiliary device used to put information into and get information out of a computer. The term ''peripheral device'' refers to all hardware components that are attached to a computer and are controlled by the ...
. The second generation disk data storage units were able to store tens of millions of letters and digits. Next to the fixed disk storage units, connected to the CPU via high-speed data transmission, were removable disk data storage units. A removable disk pack
Disk packs and disk cartridges were early forms of removable media for computer data storage, introduced in the 1960s.
Disk pack
A disk pack is a layered grouping of hard disk platters (circular, rigid discs coated with a magnetic data storage ...
can be easily exchanged with another pack in a few seconds. Even if the removable disks' capacity is smaller than fixed disks, their interchangeability guarantees a nearly unlimited quantity of data close at hand. Magnetic tape provided archival capability for this data, at a lower cost than disk.
Many second-generation CPUs delegated peripheral device communications to a secondary processor. For example, while the communication processor controlled card reading and punching, the main CPU executed calculations and binary branch instructions. One databus would bear data between the main CPU and core memory at the CPU's fetch-execute cycle
The instruction cycle (also known as the fetchŌĆōdecodeŌĆōexecute cycle, or simply the fetch-execute cycle) is the cycle that the central processing unit (CPU) follows from boot-up until the computer has shut down in order to process instruction ...
rate, and other databusses would typically serve the peripheral devices. On the PDP-1
The PDP-1 (''Programmed Data Processor-1'') is the first computer in Digital Equipment Corporation's PDP series and was first produced in 1959. It is famous for being the computer most important in the creation of hacker culture at Massachusett ...
, the core memory's cycle time was 5 microseconds; consequently most arithmetic instructions took 10 microseconds (100,000 operations per second) because most operations took at least two memory cycles; one for the instruction, one for the operand
In mathematics, an operand is the object of a mathematical operation, i.e., it is the object or quantity that is operated on.
Example
The following arithmetic expression shows an example of operators and operands:
:3 + 6 = 9
In the above exam ...
data fetch.
During the second generation remote terminal units (often in the form of Teleprinter
A teleprinter (teletypewriter, teletype or TTY) is an electromechanical device that can be used to send and receive typed messages through various communications channels, in both point-to-point and point-to-multipoint configurations. Init ...
s like a Friden Flexowriter
The Friden Flexowriter produced by the Friden Calculating Machine Company, was a teleprinter, a heavy-duty electric typewriter capable of being driven not only by a human typing, but also automatically by several methods, including direct atta ...
) saw greatly increased use. Telephone connections provided sufficient speed for early remote terminals and allowed hundreds of kilometers separation between remote-terminals and the computing center. Eventually these stand-alone computer networks would be generalized into an interconnected '' network of networks''ŌĆöthe Internet.
Transistor supercomputers
Atlas
An atlas is a collection of maps; it is typically a bundle of maps of Earth or of a region of Earth.
Atlases have traditionally been bound into book form, but today many atlases are in multimedia formats. In addition to presenting geograp ...
was a joint development between the University of Manchester
, mottoeng = Knowledge, Wisdom, Humanity
, established = 2004 ŌĆō University of Manchester Predecessor institutions: 1956 ŌĆō UMIST (as university college; university 1994) 1904 ŌĆō Victoria University of Manchester 1880 ŌĆō Victoria Univ ...
, Ferranti
Ferranti or Ferranti International plc was a UK electrical engineering and equipment firm that operated for over a century from 1885 until it went bankrupt in 1993. The company was once a constituent of the FTSE 100 Index.
The firm was known ...
, and Plessey
The Plessey Company plc was a British electronics, defence and telecommunications company. It originated in 1917, growing and diversifying into electronics. It expanded after World War II by acquisition of companies and formed overseas compani ...
, and was first installed at Manchester University and officially commissioned in 1962 as one of the world's first supercomputers
A supercomputer is a computer with a high level of performance as compared to a general-purpose computer. The performance of a supercomputer is commonly measured in floating-point operations per second (FLOPS) instead of million instructions p ...
ŌĆō considered to be the most powerful computer in the world at that time. It was said that whenever Atlas went offline half of the United Kingdom's computer capacity was lost. It was a second-generation machine, using discrete
Discrete may refer to:
*Discrete particle or quantum in physics, for example in quantum theory
*Discrete device, an electronic component with just one circuit element, either passive or active, other than an integrated circuit
*Discrete group, a g ...
germanium transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch ...
s. Atlas also pioneered the Atlas Supervisor
The Atlas Supervisor was the program which managed the allocation of processing resources of Manchester University's Atlas Computer so that the machine was able to act on many tasks and user programs concurrently.
Its various functions includ ...
, "considered by many to be the first recognisable modern operating system
An operating system (OS) is system software that manages computer hardware, software resources, and provides common services for computer programs.
Time-sharing operating systems schedule tasks for efficient use of the system and may also i ...
".
In the US, a series of computers at Control Data Corporation (CDC) were designed by Seymour Cray
Seymour Roger Cray (September 28, 1925 ŌĆō October 5, 1996
) was an American
(c. 2008), (HTML), Texas Instruments, Retrieved 29 May 2008. Kilby's invention was a
Sasaki credits the idea for a 4 bit-slice PMOS chip to a woman researcher's idea at Sharp Corporation, which was not accepted by the other members of the Sharp brainstorming group. A 40-million yen infusion from Busicom to Intel was made at Sasaki's behest, to exploit the 4 bit-slice PMOS chip. While the earliest microprocessor ICs literally contained only the processor, i.e. the central processing unit, of a computer, their progressive development naturally led to chips containing most or all of the internal electronic parts of a computer. The integrated circuit in the image on the right, for example, an
While the earliest microprocessor ICs literally contained only the processor, i.e. the central processing unit, of a computer, their progressive development naturally led to chips containing most or all of the internal electronic parts of a computer. The integrated circuit in the image on the right, for example, an  While which specific product is considered the first microcomputer system is a matter of debate, one of the earliest is R2E's Micral N (
While which specific product is considered the first microcomputer system is a matter of debate, one of the earliest is R2E's Micral N (
as cited in ''Science magazine'
Physicists Move Closer To Defeating Errors In Quantum Computation
/ref> ''Physical Review X'' reported a technique for 'single-gate sensing as a viable readout method for spin qubits' (a singlet-triplet spin state in silicon) on 26 November 2018. A Google team has succeeded in operating their RF pulse modulator chip at 3 Kelvin, simplifying the cryogenics of their 72-qubit computer, which is set up to operate at 0.3 Kelvin; but the readout circuitry and another driver remain to be brought into the cryogenics. ''See: Quantum supremacy'' Silicon qubit systems have demonstrated entanglement at non-local distances. Computing hardware and its software have even become a metaphor for the operation of the universe.
''Annals of the History of Computing''
year by year, back to 1995, so far.
Proceedings of the London Mathematical SocietyAnother link online.
* * * * Wang, An * * * * * *
Computers and Automation
Magazine ŌĆō Pictorial Report on the Computer Field: ** ''A PICTORIAL INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS'' ŌĆ
06/1957
** ''A PICTORIAL MANUAL ON COMPUTERS'' ŌĆ
12/1957
** ''A PICTORIAL MANUAL ON COMPUTERS, Part 2'' ŌĆ
01/1958
** 1958ŌĆō1967 Pictorial Report on the Computer Field ŌĆō December issues
195812.pdf, ..., 196712.pdf
* ''Bit by Bit: An Illustrated History of Computers'', Stan Augarten, 1984
OCR with permission of the author
Obsolete Technology ŌĆō Old Computers
History of calculating technology
Computer History
ŌĆö a collection of articles by
25 Microchips that shook the world
(archived) ŌĆō a collection of articles by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
Columbia University Computing History
Computer Histories
ŌĆō An introductory course on the history of computing
Revolution ŌĆō The First 2000 Years Of Computing
Computer History Museum {{Basic computer components *01 History of computing
) was an American
CDC 6600
The CDC 6600 was the flagship of the 6000 series of mainframe computer systems manufactured by Control Data Corporation. Generally considered to be the first successful supercomputer, it outperformed the industry's prior recordholder, the IBM ...
, released in 1964, is generally considered the first supercomputer. The CDC 6600 outperformed its predecessor, the IBM 7030 Stretch
The IBM 7030, also known as Stretch, was IBM's first transistorized supercomputer. It was the fastest computer in the world from 1961 until the first CDC 6600 became operational in 1964."Designed by Seymour Cray, the CDC 6600 was almost three t ...
, by about a factor of 3. With performance of about 1 megaFLOPS, the CDC 6600 was the world's fastest computer from 1964 to 1969, when it relinquished that status to its successor, the CDC 7600
The CDC 7600 was the Seymour Cray-designed successor to the CDC 6600, extending Control Data's dominance of the supercomputer field into the 1970s. The 7600 ran at 36.4 MHz (27.5 ns clock cycle) and had a 65 Kword primary memory (with a 6 ...
.
Integrated circuit computers
The "third-generation" of digital electronic computers used integrated circuit (IC) chips as the basis of their logic. The idea of an integrated circuit was conceived by a radar scientist working for theRoyal Radar Establishment
The Royal Radar Establishment was a research centre in Malvern, Worcestershire in the United Kingdom. It was formed in 1953 as the Radar Research Establishment by the merger of the Air Ministry's Telecommunications Research Establishment (TRE) a ...
of the Ministry of Defence, Geoffrey W.A. Dummer.
The first working integrated circuits were invented by Jack Kilby
Jack St. Clair Kilby (November 8, 1923 ŌĆō June 20, 2005) was an American electrical engineer who took part (along with Robert Noyce of Fairchild) in the realization of the first integrated circuit while working at Texas Instruments (TI) in 1 ...
at Texas Instruments
Texas Instruments Incorporated (TI) is an American technology company headquartered in Dallas, Texas, that designs and manufactures semiconductors and various integrated circuits, which it sells to electronics designers and manufacturers globa ...
and Robert Noyce at Fairchild Semiconductor. Kilby recorded his initial ideas concerning the integrated circuit in July 1958, successfully demonstrating the first working integrated example on 12 September 1958.''The Chip that Jack Built''(c. 2008), (HTML), Texas Instruments, Retrieved 29 May 2008. Kilby's invention was a
hybrid integrated circuit
A hybrid integrated circuit (HIC), hybrid microcircuit, hybrid circuit or simply hybrid is a miniaturized electronic circuit constructed of individual devices, such as semiconductor devices (e.g. transistors, diodes or monolithic ICs) and pa ...
(hybrid IC). It had external wire connections, which made it difficult to mass-produce.
Noyce came up with his own idea of an integrated circuit half a year after Kilby. Noyce's invention was a monolithic integrated circuit
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny M ...
(IC) chip. His chip solved many practical problems that Kilby's had not. Produced at Fairchild Semiconductor, it was made of silicon
Silicon is a chemical element with the symbol Si and atomic number 14. It is a hard, brittle crystalline solid with a blue-grey metallic luster, and is a tetravalent metalloid and semiconductor. It is a member of group 14 in the periodic ta ...
, whereas Kilby's chip was made of germanium. The basis for Noyce's monolithic IC was Fairchild's planar process, which allowed integrated circuits to be laid out using the same principles as those of printed circuit
A printed circuit board (PCB; also printed wiring board or PWB) is a medium used in electrical and electronic engineering to connect electronic components to one another in a controlled manner. It takes the form of a laminated sandwich struct ...
s. The planar process was developed by Noyce's colleague Jean Hoerni
Jean Am├®d├®e Hoerni (September 26, 1924 ŌĆō January 12, 1997) was a Swiss-American engineer. He was a silicon transistor pioneer, and a member of the " traitorous eight". He developed the planar process, an important technology for reliably fab ...
in early 1959, based on Mohamed M. Atalla
Mohamed M. Atalla ( ar, ┘ģžŁ┘ģž» ž╣žĘž¦ž¦┘ä┘ä┘ć; August 4, 1924 – December 30, 2009) was an Egyptian-American engineer, physicist, cryptographer, inventor and entrepreneur. He was a semiconductor pioneer who made important contributions to ...
's work on semiconductor surface passivation by silicon dioxide at Bell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, originally named Bell Telephone Laboratories (1925ŌĆō1984),
then AT&T Bell Laboratories (1984ŌĆō1996)
and Bell Labs Innovations (1996ŌĆō2007),
is an American industrial Research and development, research and scientific developm ...
in the late 1950s.
Third generation (integrated circuit) computers first appeared in the early 1960s in computers developed for government purposes, and then in commercial computers beginning in the mid-1960s. The first silicon IC computer was the Apollo Guidance Computer or AGC. Although not the most powerful computer of its time, the extreme constraints on size, mass, and power of the Apollo spacecraft required the AGC to be much smaller and denser than any prior computer, weighing in at only . Each lunar landing mission carried two AGCs, one each in the command and lunar ascent modules.
Semiconductor memory
The MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor, or MOS transistor) was invented byMohamed M. Atalla
Mohamed M. Atalla ( ar, ┘ģžŁ┘ģž» ž╣žĘž¦ž¦┘ä┘ä┘ć; August 4, 1924 – December 30, 2009) was an Egyptian-American engineer, physicist, cryptographer, inventor and entrepreneur. He was a semiconductor pioneer who made important contributions to ...
and Dawon Kahng
Dawon Kahng ( ko, Ļ░ĢļīĆņøÉ; May 4, 1931 ŌĆō May 13, 1992) was a Korean-American electrical engineer and inventor, known for his work in solid-state electronics. He is best known for inventing the MOSFET (metalŌĆōoxideŌĆōsemiconductor field-effe ...
at Bell Labs
Nokia Bell Labs, originally named Bell Telephone Laboratories (1925ŌĆō1984),
then AT&T Bell Laboratories (1984ŌĆō1996)
and Bell Labs Innovations (1996ŌĆō2007),
is an American industrial Research and development, research and scientific developm ...
in 1959. In addition to data processing, the MOSFET enabled the practical use of MOS transistors as memory cell storage elements, a function previously served by magnetic cores. Semiconductor memory, also known as MOS memory
Semiconductor memory is a digital electronic semiconductor device used for digital data storage, such as computer memory. It typically refers to devices in which data is stored within metalŌĆōoxideŌĆōsemiconductor (MOS) memory cells on a sili ...
, was cheaper and consumed less power than magnetic-core memory
Magnetic-core memory was the predominant form of random-access computer memory for 20 years between about 1955 and 1975.
Such memory is often just called core memory, or, informally, core.
Core memory uses toroids (rings) of a hard magneti ...
. MOS random-access memory
Random-access memory (RAM; ) is a form of computer memory that can be read and changed in any order, typically used to store working data and machine code. A random-access memory device allows data items to be read or written in almost the ...
(RAM), in the form of static RAM (SRAM), was developed by John Schmidt at Fairchild Semiconductor in 1964. In 1966, Robert Dennard
Robert Heath Dennard (born September 5, 1932) is an American electrical engineer and inventor.
Biography
Dennard was born in Terrell, Texas, U.S. He received his B.S. and M.S. degrees in Electrical Engineering from Southern Methodist University, ...
at the IBM Thomas J. Watson Research Center
The Thomas J. Watson Research Center is the headquarters for IBM Research. The center comprises three sites, with its main laboratory in Yorktown Heights, New York, U.S., 38 miles (61 km) north of New York City, Albany, New York and wit ...
developed MOS dynamic RAM
Dynamic random-access memory (dynamic RAM or DRAM) is a type of random-access semiconductor memory that stores each bit of data in a memory cell, usually consisting of a tiny capacitor and a transistor, both typically based on metal-oxid ...
(DRAM). In 1967, Dawon Kahng and Simon Sze
Simon Min Sze, or Shi Min (; born 1936), is a Chinese-American electrical engineer. He is best known for inventing the floating-gate MOSFET with Korean electrical engineer Dawon Kahng in 1967.
Biography
Sze was born in Nanjing, Jiangsu, and grew ...
at Bell Labs developed the floating-gate MOSFET
The floating-gate MOSFET (FGMOS), also known as a floating-gate MOS transistor or floating-gate transistor, is a type of metalŌĆōoxideŌĆōsemiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET) where the gate is electrically isolated, creating a floating no ...
, the basis for MOS non-volatile memory
Non-volatile memory (NVM) or non-volatile storage is a type of computer memory that can retain stored information even after power is removed. In contrast, volatile memory needs constant power in order to retain data.
Non-volatile memory typi ...
such as EPROM
An EPROM (rarely EROM), or erasable programmable read-only memory, is a type of programmable read-only memory (PROM) chip that retains its data when its power supply is switched off. Computer memory that can retrieve stored data after a power s ...
, EEPROM and flash memory.
Microprocessor computers
The "fourth-generation" of digital electronic computers usedmicroprocessor
A microprocessor is a computer processor where the data processing logic and control is included on a single integrated circuit, or a small number of integrated circuits. The microprocessor contains the arithmetic, logic, and control circ ...
s as the basis of their logic. The microprocessor has origins in the MOS integrated circuit
upright=1.6, gate (G), body (B), source (S), and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an gate oxide">insulating layer (pink).
The metalŌĆōoxideŌĆōsemiconductor field-effect transistor (MOSFET, MOS-FET, or MOS FET), also ...
(MOS IC) chip. Due to rapid MOSFET scaling, MOS IC chips rapidly increased in complexity at a rate predicted by Moore's law, leading to large-scale integration
An integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon. Large numbers of tiny ...
(LSI) with hundreds of transistors on a single MOS chip by the late 1960s. The application of MOS LSI chips to computing
Computing is any goal-oriented activity requiring, benefiting from, or creating computing machinery. It includes the study and experimentation of algorithmic processes, and development of both hardware and software. Computing has scientific, ...
was the basis for the first microprocessors, as engineers began recognizing that a complete computer processor
In computing and computer science, a processor or processing unit is an electrical component (digital circuit) that performs operations on an external data source, usually memory or some other data stream. It typically takes the form of a micropr ...
could be contained on a single MOS LSI chip.
The subject of exactly which device was the first microprocessor is contentious, partly due to lack of agreement on the exact definition of the term "microprocessor". The earliest multi-chip microprocessors were the Four-Phase Systems
Four-Phase Systems was a computer company, founded by Lee Boysel and others, which built one of the earliest computers using semiconductor main memory and MOS LSI logic. The company was incorporated in February 1969 and had moderate commercial ...
AL-1 in 1969 and Garrett AiResearch
Garrett AiResearch was a manufacturer of turboprop engines and turbochargers, and a pioneer in numerous aerospace technologies. It was previously known as Aircraft Tool and Supply Company, Garrett Supply Company, AiResearch Manufacturing Compa ...
MP944
The F-14's Central Air Data Computer, also abbreviated as CADC, computes altitude, vertical speed, air speed, and mach number from sensor inputs such as Pitot-static_system#Pitot_pressure, pitot and Pitot-static_system#Static_pressure, static press ...
in 1970, developed with multiple MOS LSI chips. The first single-chip microprocessor was the Intel 4004
The Intel 4004 is a 4-bit central processing unit (CPU) released by Intel Corporation in 1971. Sold for US$60, it was the first commercially produced microprocessor, and the first in a long line of Intel CPUs.
The 4004 was the first significa ...
, developed on a single PMOS LSI chip. It was designed and realized by Ted Hoff
Marcian Edward "Ted" Hoff Jr. (born October 28, 1937 in Rochester, New York) is one of the inventors of the microprocessor.
Education and work history
Hoff received a bachelor's degree in electrical engineering from the Rensselaer Polytechnic Inst ...
, Federico Faggin
Federico Faggin (, ; born 1 December 1941) is an Italian physicist, engineer, inventor and entrepreneur. He is best known for designing the first commercial microprocessor, the Intel 4004. He led the 4004 (MCS-4) project and the design group d ...
, Masatoshi Shima
is a Japanese electronics engineer. He was one of the architects of the world's first microprocessor, the Intel 4004. In 1968, Shima worked for Busicom in Japan, and did the logic design for a specialized CPU to be translated into three-chip c ...
and Stanley Mazor at Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 seri ...
, and released in 1971. Tadashi Sasaki and Masatoshi Shima
is a Japanese electronics engineer. He was one of the architects of the world's first microprocessor, the Intel 4004. In 1968, Shima worked for Busicom in Japan, and did the logic design for a specialized CPU to be translated into three-chip c ...
at Busicom, a calculator manufacturer, had the initial insight that the CPU could be a single MOS LSI chip, supplied by Intel.William Aspray (May 25, 1994) Oral-History: Tadashi SasakiSasaki credits the idea for a 4 bit-slice PMOS chip to a woman researcher's idea at Sharp Corporation, which was not accepted by the other members of the Sharp brainstorming group. A 40-million yen infusion from Busicom to Intel was made at Sasaki's behest, to exploit the 4 bit-slice PMOS chip.
 While the earliest microprocessor ICs literally contained only the processor, i.e. the central processing unit, of a computer, their progressive development naturally led to chips containing most or all of the internal electronic parts of a computer. The integrated circuit in the image on the right, for example, an
While the earliest microprocessor ICs literally contained only the processor, i.e. the central processing unit, of a computer, their progressive development naturally led to chips containing most or all of the internal electronic parts of a computer. The integrated circuit in the image on the right, for example, an Intel
Intel Corporation is an American multinational corporation and technology company headquartered in Santa Clara, California. It is the world's largest semiconductor chip manufacturer by revenue, and is one of the developers of the x86 seri ...
8742, is an 8-bit microcontroller that includes a CPU running at 12 MHz, 128 bytes of RAM
Ram, ram, or RAM may refer to:
Animals
* A male sheep
* Ram cichlid, a freshwater tropical fish
People
* Ram (given name)
* Ram (surname)
* Ram (director) (Ramsubramaniam), an Indian Tamil film director
* RAM (musician) (born 1974), Dutch
* ...
, 2048 bytes of EPROM
An EPROM (rarely EROM), or erasable programmable read-only memory, is a type of programmable read-only memory (PROM) chip that retains its data when its power supply is switched off. Computer memory that can retrieve stored data after a power s ...
, and I/O in the same chip.
During the 1960s there was considerable overlap between second and third generation technologies. IBM implemented its IBM Solid Logic Technology
Solid Logic Technology (SLT) was IBM's method for hybrid packaging of electronic circuitry introduced in 1964 with the IBM System/360 series of computers and related machines. IBM chose to design custom hybrid circuits using discrete, flip ch ...
modules in hybrid circuit
A hybrid integrated circuit (HIC), hybrid microcircuit, hybrid circuit or simply hybrid is a miniaturized electronic circuit constructed of individual devices, such as semiconductor devices (e.g. transistors, diodes or monolithic ICs) and ...
s for the IBM System/360 in 1964. As late as 1975, Sperry Univac continued the manufacture of second-generation machines such as the UNIVAC 494. The Burroughs large systems
The Burroughs Large Systems Group produced a family of large 48-bit mainframes using stack machine instruction sets with dense syllables.E.g., 12-bit syllables for B5000, 8-bit syllables for B6500 The first machine in the family was the B5000 in ...
such as the B5000 were stack machines, which allowed for simpler programming. These pushdown automaton
In the theory of computation, a branch of theoretical computer science, a pushdown automaton (PDA) is
a type of automaton that employs a stack.
Pushdown automata are used in theories about what can be computed by machines. They are more capab ...
s were also implemented in minicomputers and microprocessors later, which influenced programming language design. Minicomputers served as low-cost computer centers for industry, business and universities. It became possible to simulate analog circuits with the ''simulation program with integrated circuit emphasis'', or SPICE
A spice is a seed, fruit, root, bark, or other plant substance primarily used for flavoring or coloring food. Spices are distinguished from herbs, which are the leaves, flowers, or stems of plants used for flavoring or as a garnish. Spice ...
(1971) on minicomputers, one of the programs for electronic design automation (EDA EDA or Eda may refer to:
Computing
* Electronic design automation
* Enterprise Desktop Alliance, a computer technology consortium
* Enterprise digital assistant
* Estimation of distribution algorithm
* Event-driven architecture
* Exploratory ...
). The microprocessor led to the development of microcomputers, small, low-cost computers that could be owned by individuals and small businesses. Microcomputers, the first of which appeared in the 1970s, became ubiquitous in the 1980s and beyond.
 While which specific product is considered the first microcomputer system is a matter of debate, one of the earliest is R2E's Micral N (
While which specific product is considered the first microcomputer system is a matter of debate, one of the earliest is R2E's Micral N (Fran├¦ois Gernelle
Fran├¦ois Gernelle (born December 20, 1944) is a French engineer, computer scientist and entrepreneur famous for inventing the first micro-computer using a micro-processor, the Micral N.
Education
In the late 1960s, Gernelle earned an engineeri ...
, Andr├® Truong) launched "early 1973" using the Intel 8008. The first commercially available microcomputer kit was the Intel 8080
The Intel 8080 (''"eighty-eighty"'') is the second 8-bit microprocessor designed and manufactured by Intel. It first appeared in April 1974 and is an extended and enhanced variant of the earlier 8008 design, although without binary compatibil ...
-based Altair 8800, which was announced in the January 1975 cover article of ''Popular Electronics
''Popular Electronics'' was an American magazine published by John August Media, LLC, and hosted at TechnicaCuriosa.com. The magazine was started by Ziff-Davis Publishing Company in October 1954 for electronics hobbyists and experimenters. It soo ...
''. However, the Altair 8800 was an extremely limited system in its initial stages, having only 256 bytes of DRAM in its initial package and no input-output except its toggle switches and LED register display. Despite this, it was initially surprisingly popular, with several hundred sales in the first year, and demand rapidly outstripped supply. Several early third-party vendors such as Cromemco
Cromemco was a Mountain View, California microcomputer company known for its high-end Z80-based S-100 bus computers and peripherals in the early days of the personal computer revolution.
The company began as a partnership in 1974 between Harry ...
and Processor Technology
Processor Technology Corporation was a personal computer company founded in April 1975 by Gary Ingram and Bob Marsh in Berkeley, California. Their first product was a 4K byte RAM board that was compatible with the MITS Altair 8800 computer but mo ...
soon began supplying additional S-100 bus
The S-100 bus or Altair bus, IEEE 696-1983 ''(withdrawn)'', is an early computer bus designed in 1974 as a part of the Altair 8800. The bus was the first industry standard expansion bus for the microcomputer industry. computers, consisting of p ...
hardware for the Altair 8800.
In April 1975 at the Hannover Fair, Olivetti
Olivetti S.p.A. is an Italian manufacturer of computers, tablets, smartphones, printers and other such business products as calculators and fax machines. Headquartered in Ivrea, in the Metropolitan City of Turin, the company has been par ...
presented the P6060, the world's first complete, pre-assembled personal computer system. The central processing unit consisted of two cards, code named PUCE1 and PUCE2, and unlike most other personal computers was built with TTL
TTL may refer to:
Photography
* Through-the-lens metering, a camera feature
* Zenit TTL, an SLR film camera named for its TTL metering capability
Technology
* Time to live, a computer data lifespan-limiting mechanism
* TransistorŌĆōtransistor lo ...
components rather than a microprocessor. It had one or two 8" floppy disk drives, a 32-character plasma display
A plasma display panel (PDP) is a type of flat panel display that uses small cells containing plasma: ionized gas that responds to electric fields. Plasma televisions were the first large (over 32 inches diagonal) flat panel displays to be releas ...
, 80-column graphical thermal printer
Thermal printing (or direct thermal printing) is a digital printing process which produces a printed image by passing paper with a thermochromic coating, commonly known as thermal paper, over a print head consisting of tiny electrically heated ...
, 48 Kbytes of RAM
Ram, ram, or RAM may refer to:
Animals
* A male sheep
* Ram cichlid, a freshwater tropical fish
People
* Ram (given name)
* Ram (surname)
* Ram (director) (Ramsubramaniam), an Indian Tamil film director
* RAM (musician) (born 1974), Dutch
* ...
, and BASIC language. It weighed . As a complete system, this was a significant step from the Altair, though it never achieved the same success. It was in competition with a similar product by IBM that had an external floppy disk drive.
From 1975 to 1977, most microcomputers, such as the MOS Technology KIM-1, the Altair 8800, and some versions of the Apple I
The Apple Computer 1, originally released as the Apple Computer and known later as the Apple I or Apple-1, is an 8-bit desktop computer released by the Apple Computer Company (now Apple Inc.) in 1976. It was designed by Steve Wozniak. The i ...
, were sold as kits for do-it-yourselfers. Pre-assembled systems did not gain much ground until 1977, with the introduction of the Apple II, the Tandy TRS-80
The TRS-80 Micro Computer System (TRS-80, later renamed the Model I to distinguish it from successors) is a desktop microcomputer launched in 1977 and sold by Tandy Corporation through their Radio Shack stores. The name is an abbreviation of '' ...
, the first SWTPC
Southwest Technical Products Corporation, or SWTPC, was an American producer of electronic kits, and later complete computer systems. It was incorporated in 1967 in San Antonio, Texas, succeeding the Daniel E. Meyer Company. In 1990, SWTPC bec ...
computers, and the Commodore PET
The Commodore PET is a line of personal computers produced starting in 1977 by Commodore International. A single all-in-one case combines a MOS Technology 6502 microprocessor, Commodore BASIC in read-only memory, keyboard, monochrome monitor, ...
. Computing has evolved with microcomputer architectures, with features added from their larger brethren, now dominant in most market segments.
A NeXT Computer and its object-oriented
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is a programming paradigm based on the concept of " objects", which can contain data and code. The data is in the form of fields (often known as attributes or ''properties''), and the code is in the form of p ...
development tools and libraries were used by Tim Berners-Lee and Robert Cailliau
Robert Cailliau (, born 26 January 1947) is a Belgian informatics engineer, computer scientist and author who proposed the first (pre-www) hypertext system for CERN in 1987 and collaborated with Tim Berners-Lee on the World Wide Web (jointly wi ...
at CERN to develop the world's first web server software, CERN httpd, and also used to write the first web browser
A web browser is application software for accessing websites. When a user requests a web page from a particular website, the browser retrieves its files from a web server and then displays the page on the user's screen. Browsers are used o ...
, WorldWideWeb
WorldWideWeb (later renamed Nexus to avoid confusion between the software and the World Wide Web) is the first web browser and web page editor. It was discontinued in 1994. It was the first WYSIWYG HTML editor.
The source code was released in ...
.
Systems as complicated as computers require very high reliability
Reliability, reliable, or unreliable may refer to:
Science, technology, and mathematics Computing
* Data reliability (disambiguation), a property of some disk arrays in computer storage
* High availability
* Reliability (computer networking), a ...
. ENIAC remained on, in continuous operation from 1947 to 1955, for eight years before being shut down. Although a vacuum tube might fail, it would be replaced without bringing down the system. By the simple strategy of never shutting down ENIAC, the failures were dramatically reduced. The vacuum-tube SAGE
Sage or SAGE may refer to:
Plants
* ''Salvia officinalis'', common sage, a small evergreen subshrub used as a culinary herb
** Lamiaceae, a family of flowering plants commonly known as the mint or deadnettle or sage family
** ''Salvia'', a large ...
air-defense computers became remarkably reliable ŌĆō installed in pairs, one off-line, tubes likely to fail did so when the computer was intentionally run at reduced power to find them. Hot-pluggable hard disks, like the hot-pluggable vacuum tubes of yesteryear, continue the tradition of repair during continuous operation. Semiconductor memories routinely have no errors when they operate, although operating systems like Unix have employed memory tests on start-up to detect failing hardware. Today, the requirement of reliable performance is made even more stringent when server farm
A server farm or server cluster is a collection of computer servers, usually maintained by an organization to supply server functionality far beyond the capability of a single machine. They often consist of thousands of computers which require ...
s are the delivery platform. Google has managed this by using fault-tolerant software to recover from hardware failures, and is even working on the concept of replacing entire server farms on-the-fly, during a service event.
In the 21st century, multi-core CPUs became commercially available. Content-addressable memory
Content-addressable memory (CAM) is a special type of computer memory used in certain very-high-speed searching applications. It is also known as associative memory or associative storage and compares input search data against a table of stored d ...
(CAM) has become inexpensive enough to be used in networking, and is frequently used for on-chip cache memory
In computing, a cache ( ) is a hardware or software component that stores data so that future requests for that data can be served faster; the data stored in a cache might be the result of an earlier computation or a copy of data stored elsewher ...
in modern microprocessors, although no computer system has yet implemented hardware CAMs for use in programming languages. Currently, CAMs (or associative arrays) in software are programming-language-specific. Semiconductor memory cell arrays are very regular structures, and manufacturers prove their processes on them; this allows price reductions on memory products. During the 1980s, CMOS logic gates
A logic gate is an idealized or physical device implementing a Boolean function, a logical operation performed on one or more binary inputs that produces a single binary output. Depending on the context, the term may refer to an ideal logic gate ...
developed into devices that could be made as fast as other circuit types; computer power consumption could therefore be decreased dramatically. Unlike the continuous current draw of a gate based on other logic types, a CMOS gate only draws significant current during the 'transition' between logic states, except for leakage.
CMOS circuits have allowed computing to become a commodity which is now ubiquitous, embedded in many forms, from greeting cards and telephone
A telephone is a telecommunications device that permits two or more users to conduct a conversation when they are too far apart to be easily heard directly. A telephone converts sound, typically and most efficiently the human voice, into e ...
s to satellites. The thermal design power
The thermal design power (TDP), sometimes called thermal design point, is the maximum amount of heat generated by a computer chip or component (often a CPU, GPU or system on a chip) that the cooling system in a computer is designed to dissipate ...
which is dissipated during operation has become as essential as computing speed of operation. In 2006 servers consumed 1.5% of the total energy budget of the U.S. The energy consumption of computer data centers was expected to double to 3% of world consumption by 2011. The SoC (system on a chip) has compressed even more of the integrated circuitry into a single chip; SoCs are enabling phones and PCs to converge into single hand-held wireless mobile device
A mobile device (or handheld computer) is a computer small enough to hold and operate in the hand. Mobile devices typically have a flat LCD or OLED screen, a touchscreen interface, and digital or physical buttons. They may also have a physica ...
s.
Quantum computing is an emerging technology in the field of computing. ''MIT Technology Review'' reported 10 November 2017 that IBM has created a 50-qubit
In quantum computing, a qubit () or quantum bit is a basic unit of quantum informationŌĆöthe quantum version of the classic binary bit physically realized with a two-state device. A qubit is a two-state (or two-level) quantum-mechanical system, ...
computer; currently its quantum state lasts 50 microseconds. Google researchers have been able to extend the 50 microsecond time limit, as reported 14 July 2021 in ''Nature''; stability has been extended 100-fold by spreading a single logical qubit over chains of data qubits for quantum error correction.Julian Kelly, et.al. (16 July 2021) Exponential suppression of bit or phase errors with cyclic error correctionas cited in ''Science magazine'
Physicists Move Closer To Defeating Errors In Quantum Computation
/ref> ''Physical Review X'' reported a technique for 'single-gate sensing as a viable readout method for spin qubits' (a singlet-triplet spin state in silicon) on 26 November 2018. A Google team has succeeded in operating their RF pulse modulator chip at 3 Kelvin, simplifying the cryogenics of their 72-qubit computer, which is set up to operate at 0.3 Kelvin; but the readout circuitry and another driver remain to be brought into the cryogenics. ''See: Quantum supremacy'' Silicon qubit systems have demonstrated entanglement at non-local distances. Computing hardware and its software have even become a metaphor for the operation of the universe.
Epilogue
An indication of the rapidity of development of this field can be inferred from the history of the seminal 1947 article by Burks, Goldstine and von Neumann. By the time that anyone had time to write anything down, it was obsolete. After 1945, others read John von Neumann's ''First Draft of a Report on the EDVAC'', and immediately started implementing their own systems. To this day, the rapid pace of development has continued, worldwide.''DBLP
DBLP is a computer science bibliography website. Starting in 1993 at Universit├żt Trier in Germany, it grew from a small collection of HTML files and became an organization hosting a database and logic programming bibliography site. Since Novem ...
'' summarizes th''Annals of the History of Computing''
year by year, back to 1995, so far.
See also
*Antikythera mechanism
The Antikythera mechanism ( ) is an Ancient Greek hand-powered orrery, described as the oldest example of an analogue computer used to predict astronomical positions and eclipses decades in advance. It could also be used to track the four-yea ...
* History of computing
The history of computing is longer than the history of computing hardware and modern computing technology and includes the history of methods intended for pen and paper or for chalk and slate, with or without the aid of tables.
Concrete devices ...
* History of computing hardware (1960sŌĆōpresent)
* History of laptops
* History of personal computers
The history of the personal computer as a mass-market consumer electronic device began with the microcomputer revolution of the 1970s. A personal computer is one intended for interactive individual use, as opposed to a mainframe computer where ...
* History of software
Software is a set of programmed instructions stored in the memory of stored-program digital computers for execution by the processor. Software is a recent development in human history, and it is fundamental to the Information Age.
Ada Lovelace ...
* Information Age
The Information Age (also known as the Computer Age, Digital Age, Silicon Age, or New Media Age) is a historical period that began in the mid-20th century. It is characterized by a rapid shift from traditional industries, as established during ...
* IT History Society
The IT History Society (ITHS) is an organization that supports the history and scholarship of information technology by encouraging, fostering, and facilitating archival and historical research. Formerly known as the Charles Babbage Foundation, ...
* Retrocomputing
Retrocomputing is the use of older computer hardware and software in modern times. Retrocomputing is usually classed as a hobby and recreation rather than a practical application of technology; enthusiasts often collect rare and valuable hardw ...
* Timeline of computing
* List of pioneers in computer science
This is a list of people who made transformative breakthroughs in the creation, development and imagining of what computers could do.
Pioneers
: ''To arrange the list by date or person (ascending or descending), click that column's small "up-do ...
* Vacuum-tube computer
A vacuum-tube computer, now termed a first-generation computer, is a computer that uses vacuum tubes for logic circuitry. Although superseded by second-generation transistorized computers, vacuum-tube computers continued to be built into the 196 ...
Notes
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * With notes upon the Memoir by the Translator. * German to English translation, M.I.T., 1969. * * * Noyce, Robert * * * * * * * * * * * * * * Pages 220ŌĆō226 are annotated references and guide for further reading. * * * Stibitz, George * * (and ) Other online versionsProceedings of the London Mathematical Society
* * * * Wang, An * * * * * *
Further reading
* *Computers and Automation
Magazine ŌĆō Pictorial Report on the Computer Field: ** ''A PICTORIAL INTRODUCTION TO COMPUTERS'' ŌĆ
06/1957
** ''A PICTORIAL MANUAL ON COMPUTERS'' ŌĆ
12/1957
** ''A PICTORIAL MANUAL ON COMPUTERS, Part 2'' ŌĆ
01/1958
** 1958ŌĆō1967 Pictorial Report on the Computer Field ŌĆō December issues
195812.pdf, ..., 196712.pdf
* ''Bit by Bit: An Illustrated History of Computers'', Stan Augarten, 1984
OCR with permission of the author
External links
Obsolete Technology ŌĆō Old Computers
History of calculating technology
Computer History
ŌĆö a collection of articles by
Bob Bemer
Robert William Bemer (February 8, 1920 ŌĆō June 22, 2004) was a computer scientist best known for his work at IBM during the late 1950s and early 1960s.
Early life and education
Born in Sault Ste. Marie, Michigan, Bemer graduated from Cranb ...
25 Microchips that shook the world
(archived) ŌĆō a collection of articles by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
Columbia University Computing History
Computer Histories
ŌĆō An introductory course on the history of computing
Revolution ŌĆō The First 2000 Years Of Computing
Computer History Museum {{Basic computer components *01 History of computing