EQ J221734.0+001701 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
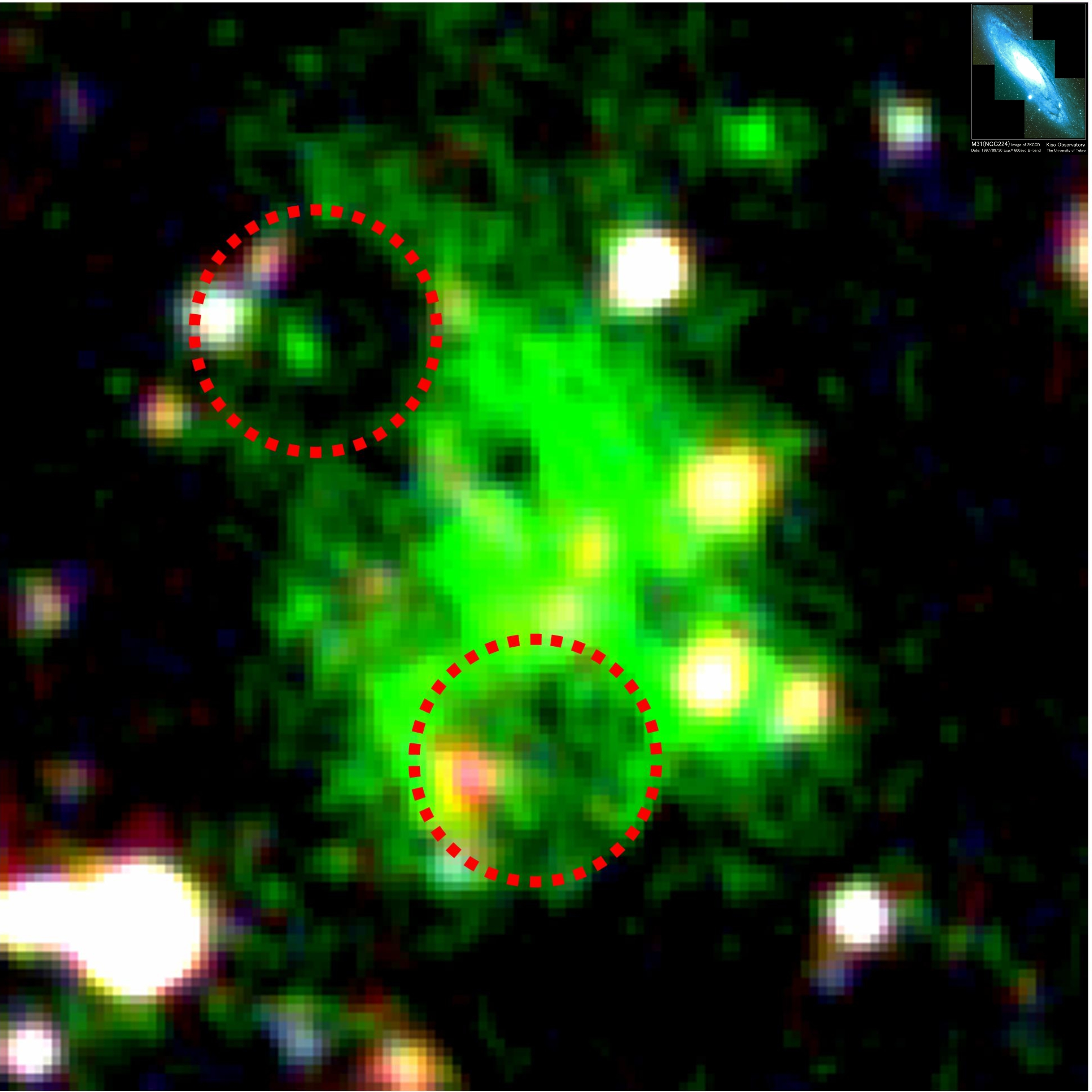 The SSA22 Protocluster, also known as EQ J221734.0+001701, is a galaxy protocluster located at z=3.1 in the SSA 22 region. It is located at and was originally discovered in 1998.Astrophysical Journal, "A Large Structure of Galaxies at Redshift Z approximately 3 and Its Cosmological Implications", Steidel, Charles C.; Adelberger, Kurt L.; Dickinson, Mark; Giavalisco, Mauro; Pettini, Max; Kellogg, Melinda, v.492, p.428, 01/1998, ,
In 2006, a multifilamentary structure measuring 200 million light-years in width was announced, coinciding with the protocluster. Discovered in 2005 by Ryosuke Yamauchi from Tohoku University in Sendai, Japan, and his colleagues, the structure was found in a region of the universe known to contain large concentrations of gas. The structure is a very distant object; the astronomers that discovered it were actually looking at something from 12 billion years ago. This object is made up of lyman-break galaxies and large gas bubbles, such as
The SSA22 Protocluster, also known as EQ J221734.0+001701, is a galaxy protocluster located at z=3.1 in the SSA 22 region. It is located at and was originally discovered in 1998.Astrophysical Journal, "A Large Structure of Galaxies at Redshift Z approximately 3 and Its Cosmological Implications", Steidel, Charles C.; Adelberger, Kurt L.; Dickinson, Mark; Giavalisco, Mauro; Pettini, Max; Kellogg, Melinda, v.492, p.428, 01/1998, ,
In 2006, a multifilamentary structure measuring 200 million light-years in width was announced, coinciding with the protocluster. Discovered in 2005 by Ryosuke Yamauchi from Tohoku University in Sendai, Japan, and his colleagues, the structure was found in a region of the universe known to contain large concentrations of gas. The structure is a very distant object; the astronomers that discovered it were actually looking at something from 12 billion years ago. This object is made up of lyman-break galaxies and large gas bubbles, such as
 The SSA22 Protocluster, also known as EQ J221734.0+001701, is a galaxy protocluster located at z=3.1 in the SSA 22 region. It is located at and was originally discovered in 1998.Astrophysical Journal, "A Large Structure of Galaxies at Redshift Z approximately 3 and Its Cosmological Implications", Steidel, Charles C.; Adelberger, Kurt L.; Dickinson, Mark; Giavalisco, Mauro; Pettini, Max; Kellogg, Melinda, v.492, p.428, 01/1998, ,
In 2006, a multifilamentary structure measuring 200 million light-years in width was announced, coinciding with the protocluster. Discovered in 2005 by Ryosuke Yamauchi from Tohoku University in Sendai, Japan, and his colleagues, the structure was found in a region of the universe known to contain large concentrations of gas. The structure is a very distant object; the astronomers that discovered it were actually looking at something from 12 billion years ago. This object is made up of lyman-break galaxies and large gas bubbles, such as
The SSA22 Protocluster, also known as EQ J221734.0+001701, is a galaxy protocluster located at z=3.1 in the SSA 22 region. It is located at and was originally discovered in 1998.Astrophysical Journal, "A Large Structure of Galaxies at Redshift Z approximately 3 and Its Cosmological Implications", Steidel, Charles C.; Adelberger, Kurt L.; Dickinson, Mark; Giavalisco, Mauro; Pettini, Max; Kellogg, Melinda, v.492, p.428, 01/1998, ,
In 2006, a multifilamentary structure measuring 200 million light-years in width was announced, coinciding with the protocluster. Discovered in 2005 by Ryosuke Yamauchi from Tohoku University in Sendai, Japan, and his colleagues, the structure was found in a region of the universe known to contain large concentrations of gas. The structure is a very distant object; the astronomers that discovered it were actually looking at something from 12 billion years ago. This object is made up of lyman-break galaxies and large gas bubbles, such as lyman-alpha blob
In astronomy, a Lyman-alpha blob (LAB) is a huge concentration of a gas emitting the Lyman-alpha emission line. LABs are some of the largest known individual objects in the Universe. Some of these gaseous structures are more than 400,000 light ...
s and lyman-alpha emitter
A Lyman-alpha emitter (LAE) is a type of distant galaxy that emits Lyman-alpha radiation from neutral hydrogen.
Most known LAEs are extremely distant, and because of the finite travel time of light they provide glimpses into the history of the un ...
s gaseous filaments.Astrophysical Journal, "Large-Scale Filamentary Structure around the Protocluster at Redshift z = 3.1", Yuichi Matsuda et al., Volume 634, Issue 2, pp. L125-L128, , , Some of the gas bubbles that make up this colossal structure are up to 400,000 light-years across, over twice the diameter of the Andromeda Galaxy
The Andromeda Galaxy (IPA: ), also known as Messier 31, M31, or NGC 224 and originally the Andromeda Nebula, is a barred spiral galaxy with the diameter of about approximately from Earth and the nearest large galaxy to the Milky Way. The gal ...
. Some scientists believe that these giant bubbles formed after massive stars born in the early universe exploded as supernovae and ejected their surrounding gases. The galaxies and gas bubbles that are part of this structure line up along three curved filaments, or arms, that formed approximately 2 billion years after the Big Bang. These filaments were observed with the help of the Subaru and Keck telescopes located on the Mauna Kea volcano in Hawaii.
This structure is not only incredibly large, but also very dense; the galaxies located in each of the filaments are four times closer to each other than the universe's average. Before its discovery, astronomers had predicted the existence of a structure like this one. According to computer models, several of the most massive galaxies originated in structures like this. These galaxies are believed to have formed as a result of blobs like those constituent to this structure collapsing under their own gravity. Since the densest areas in the universe are thought to be the places where galaxies formed first, this structure may be one of the earliest to have formed. This structure may reveal when and how the first galaxies formed and could help us better understand how our own galaxy came to be.
References
{{Reflist Galaxy clusters