Dwe'e people on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Badwe'e (also ''Bajwe'e''; French ''Badjoué'') are an ethnic group inhabiting the
rain forest
Rainforests are characterized by a closed and continuous tree canopy, moisture-dependent vegetation, the presence of epiphytes and lianas and the absence of wildfire. Rainforest can be classified as tropical rainforest or temperate rainforest ...
zone of southeastern Cameroon
Cameroon (; french: Cameroun, ff, Kamerun), officially the Republic of Cameroon (french: République du Cameroun, links=no), is a country in west-central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west and north; Chad to the northeast; the C ...
. They recognize themselves as the descendants of Edwe'e, the youngest son of Koo and the brother of Njeme and Nzime. The Badwe'e live south of Messaména
Messamena (also spelled Messaména) is a town and commune in Cameroon.
Location
The town of Messamena is the capital of the ''arrondissement'' (commune) of the same name. They are located in the Haut-Nyong Department, East Region.East Province in a region south of the Bekol and both north and west of the Nzime. Their territory includes much of the northern and western border of the Dja Biosphere Reserve. They speak a dialect of Koozime, together with the Nzime.
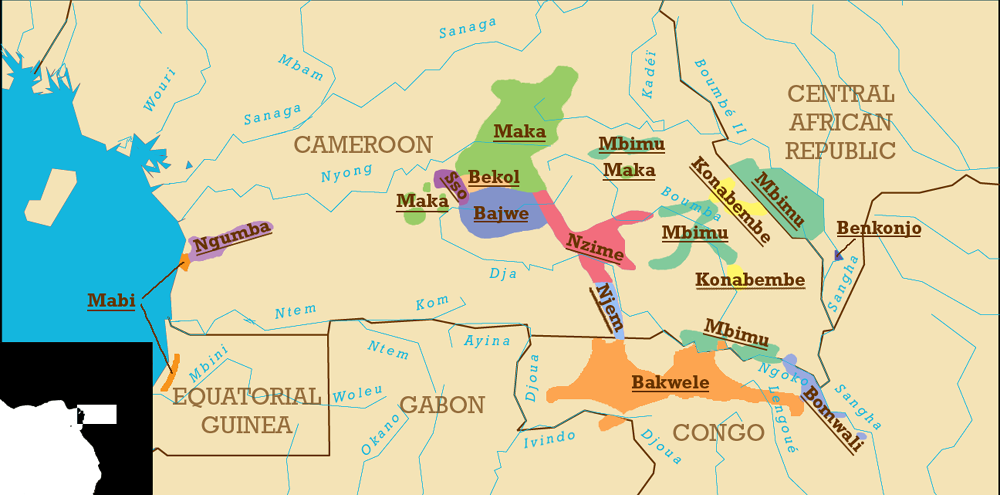 The ancestors of the Badwe'e lived in the
The ancestors of the Badwe'e lived in the
Koonzime
. ''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'', 15th ed. Dallas: SIL International. Accessed 7 June 2006. * Gordon, Raymond G., Jr. (ed.) (2005):
Makaa–Njem (A80)
. ''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'', 15th ed. Dallas: SIL International. Accessed 7 June 2006. * Neba, Aaron, Ph.D. (1999) ''Modern Geography of the Republic of Cameroon,'' 3rd ed. Bamenda: Neba Publishers. * Ngima Mawoung, Godefroy (2001) "The Relationship Between the Bakola and the Bantu Peoples of the Coastal Regions of Cameroon and their Perception of Commercial Forest Exploitation". ''African Study Monographs'', Suppl. 26: 209–235. * Ngoh, Victor Julius (1996) ''History of Cameroon Since 1800.'' Limbé: Presbook. * Seme, P. M. (August 1998).
. ''Canopée: Bulletin sur l'environnement en Afrique Centrale''. Accessed 21 June 2006. {{authority control Bantu peoples Ethnic groups in Cameroon Indigenous peoples of Central Africa Indigenous peoples of West Africa
History
 The ancestors of the Badwe'e lived in the
The ancestors of the Badwe'e lived in the Congo River basin
The Congo River ( kg, Nzâdi Kôngo, french: Fleuve Congo, pt, Rio Congo), formerly also known as the Zaire River, is the second longest river in Africa, shorter only than the Nile, as well as the second largest river in the world by discharge ...
or the present territory of Chad before moving into the present territory of Cameroon between the 14th and 17th centuries. Along with the other speakers of Makaa–Njyem languages, they lived along the northern Lom River
The Lom ( , ) is a river in northwestern Bulgaria, a right tributary of the Danube flowing into it 1 km east of the town of Lom.
The river takes its source from the foot of Midzhur (2,168 m), the highest peak of western Stara Planina, on ...
near the present-day border between the Adamawa and East provinces. Under pressure from migrating Beti-Pahuin
The Beti-Pahuin are a Bantu ethnic group located in rain forest regions of Cameroon, Republic of the Congo, Equatorial Guinea, Gabon, and São Tomé and Príncipe. Though they separate themselves into several individual clans, they all share a c ...
groups (themselves fleeing the Vute
Vute is a Mambiloid language of Cameroon and Gabon, with a thousand speakers in Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, i ...
and Mbum
Mbum Proper (also Mboum, Buna, Mboumtiba and Wuna) is a Adamawa–Ubangi language of Central Africa. It is spoken by about people in Cameroon and the Central African Republic.
History
The Mbum language is spoken by the Mbum people who inhabit ...
), the Makaa–Njem-speaking groups moved farther south. The Badwe'e eventually settled south of the Bekol and west of the Nzime. During the colonial period, they created villages to the north of the Nzime, beginning at Djaposten and extending to Mindourou. This was to assist them to receive medical treatment against sleeping sickness.
Lifestyle and settlement patterns
Most Badwe'e live as subsistence farmers and live in linear villages oriented toward the roads through their region. They grow crops such asmanioc
''Manihot esculenta'', commonly called cassava (), manioc, or yuca (among numerous regional names), is a woody shrub of the spurge family, Euphorbiaceae, native to South America. Although a perennial plant, cassava is extensively cultivated ...
, plantains
Plantain may refer to:
Plants and fruits
* Cooking banana, banana cultivars in the genus ''Musa'' whose fruits are generally used in cooking
** True plantains, a group of cultivars of the genus ''Musa''
* ''Plantaginaceae'', a family of flowerin ...
, and maize
Maize ( ; ''Zea mays'' subsp. ''mays'', from es, maíz after tnq, mahiz), also known as corn (North American and Australian English), is a cereal grain first domesticated by indigenous peoples in southern Mexico about 10,000 years ago. The ...
, as well as smaller amounts of bananas, cocoyam
Cocoyam is a common name for more than one tropical root crop and vegetable crop belonging to the Arum family (also known as Aroids and by the family name ''Araceae'') and may refer to:
* Taro
Taro () (''Colocasia esculenta)'' is a root veg ...
s, groundnuts, and fruits. Small livestock
Livestock are the domesticated animals raised in an agricultural setting to provide labor and produce diversified products for consumption such as meat, eggs, milk, fur, leather, and wool. The term is sometimes used to refer solely to animal ...
that does not require much care forms another part of the diet. Other Bajwe hunt
Hunting is the human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products (fur/ hide, bone/tusks, horn/antler, e ...
with trap
A trap is a mechanical device used to capture or restrain an animal for purposes such as hunting, pest control, or ecological research.
Trap or TRAP may also refer to:
Art and entertainment Films and television
* ''Trap'' (2015 film), Fil ...
s or, more commonly today, firearms. The resulting bushmeat has become an important source of income for some people.
Most Badwe'e profess Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global pop ...
as their faith. A New Testament in Badwe'e is in use.
Over 60 Badwe'e villages border the Dja Biosphere Reserve. Most of these are relatively small, with fewer than 113 inhabitants.Seme.
Notes
References
* Gordon, Raymond G., Jr. (ed.) (2005):Koonzime
. ''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'', 15th ed. Dallas: SIL International. Accessed 7 June 2006. * Gordon, Raymond G., Jr. (ed.) (2005):
Makaa–Njem (A80)
. ''Ethnologue: Languages of the World'', 15th ed. Dallas: SIL International. Accessed 7 June 2006. * Neba, Aaron, Ph.D. (1999) ''Modern Geography of the Republic of Cameroon,'' 3rd ed. Bamenda: Neba Publishers. * Ngima Mawoung, Godefroy (2001) "The Relationship Between the Bakola and the Bantu Peoples of the Coastal Regions of Cameroon and their Perception of Commercial Forest Exploitation". ''African Study Monographs'', Suppl. 26: 209–235. * Ngoh, Victor Julius (1996) ''History of Cameroon Since 1800.'' Limbé: Presbook. * Seme, P. M. (August 1998).
. ''Canopée: Bulletin sur l'environnement en Afrique Centrale''. Accessed 21 June 2006. {{authority control Bantu peoples Ethnic groups in Cameroon Indigenous peoples of Central Africa Indigenous peoples of West Africa