Duchy of Prussia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Duchy of Prussia (german: Herzogtum Preußen, pl, Księstwo Pruskie, lt, Prūsijos kunigaikštystė) or Ducal Prussia (german: Herzogliches Preußen, link=no; pl, Prusy Książęce, link=no) was a duchy in the region of Prussia established as a result of secularization of the Monastic Prussia, the territory that remained under the control of the
''Die Kirche in Klein Litauen''
(section: 2. Reformatorische Anfänge; ) on
''Lietuvos Evangelikų Liuteronų Bažnyčia''
retrieved on 28 August 2011. and a number of his commanders already supporting Protestant ideas, Albert began to consider a radical solution. At
 When Albert returned to Königsberg, he publicly declared his conversion and announced to a quorum of Teutonic Knights his new ducal status. The knights who disapproved of the decision were pressured into acceptance by Albert's supporters and the
When Albert returned to Königsberg, he publicly declared his conversion and announced to a quorum of Teutonic Knights his new ducal status. The knights who disapproved of the decision were pressured into acceptance by Albert's supporters and the
''Die Kirche in Klein Litauen''
(section: 5. Die Pfarrer und ihre Ausbildung; ) on
''Lietuvos Evangelikų Liuteronų Bažnyčia''
retrieved on 28 August 2011. While the composition of the nobility changed little in the transition from the monastic state to the duchy, the control of the nobility over the dependent peasantry increased. Prussia's free peasants, called Kölmer were holders of free estates according to Culm law). These Kölmer held with about a sixth of the arable land, a considerable share as compared with other nations in the feudal era. Administratively, little changed in the transition from the Teutonic Knights to ducal rule. Although he was formally a vassal of the crown of Poland, Albert retained self-government for Prussia, his own army, the minting of his currency, a
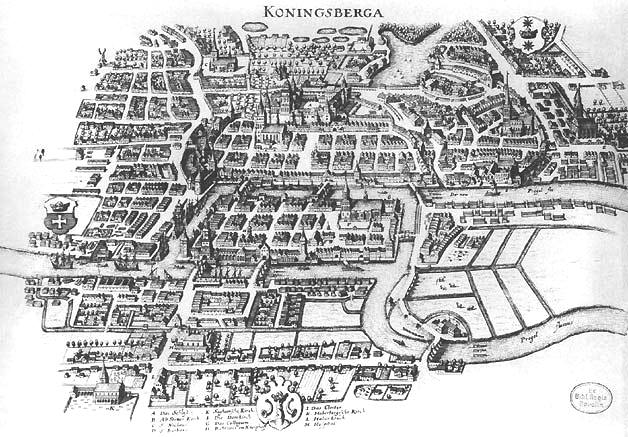 However, the end of Polish suzerainty was met with resistance of the population, regardless of ethnicity, as it was afraid of Brandenburg absolutism and wished to remain part of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland. The burghers of the capital city of Königsberg, led by
However, the end of Polish suzerainty was met with resistance of the population, regardless of ethnicity, as it was afraid of Brandenburg absolutism and wished to remain part of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland. The burghers of the capital city of Königsberg, led by
State of the Teutonic Order
The State of the Teutonic Order (german: Staat des Deutschen Ordens, ; la, Civitas Ordinis Theutonici; lt, Vokiečių ordino valstybė; pl, Państwo zakonu krzyżackiego), also called () or (), was a medieval Crusader state, located in Cent ...
until the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and ...
in 1525.
Overview
The duchy became the firstProtestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
state when Albert, Duke of Prussia
Albert of Prussia (german: Albrecht von Preussen; 17 May 149020 March 1568) was a German prince who was the 37th Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights, who after converting to Lutheranism, became the first ruler of the Duchy of Prussia, the s ...
formally adopted Lutheranism
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Catholic Church launched th ...
in 1525. It was inhabited by a German, Polish (mainly in Masuria), and Lithuanian-speaking (mainly in Lithuania Minor) population.
In 1525, during the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and ...
, in accordance to the Treaty of Kraków
The Treaty of Kraków was signed on 8 April 1525 between the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights. It officially ended the Polish–Teutonic War.John Freely Celestial Revolutionary: Copernicus, the Man and His Universe ...
, the Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights, Albert, secularized the order's prevailing Prussian territory (the Monastic Prussia), becoming Albert, Duke of Prussia
Albert of Prussia (german: Albrecht von Preussen; 17 May 149020 March 1568) was a German prince who was the 37th Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights, who after converting to Lutheranism, became the first ruler of the Duchy of Prussia, the s ...
. As the region had been a part of the Kingdom of Poland
The Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Królestwo Polskie; Latin: ''Regnum Poloniae'') was a state in Central Europe. It may refer to:
Historical political entities
* Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom existing from 1025 to 1031
* Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom exi ...
since the Second Peace of Thorn (1466)
The Peace of Thorn or Toruń of 1466, also known as the Second Peace of Thorn or Toruń ( pl, drugi pokój toruński; german: Zweiter Friede von Thorn), was a peace treaty signed in the Hanseatic city of Thorn (Toruń) on 19 October 1466 betwe ...
, King of Poland Sigismund I the Old, as its suzerain, granted the territory as a hereditary fief
A fief (; la, feudum) was a central element in medieval contracts based on feudal law. It consisted of a form of property holding or other rights granted by an overlord to a vassal, who held it in fealty or "in fee" in return for a form ...
of Poland to Duke Albert per the Treaty of Kraków, a decision that was sealed by the Prussian Homage
The Prussian Homage or Prussian Tribute (german: Preußische Huldigung; pl, hołd pruski) was the formal investment of Albert of Prussia as duke of the Polish fief of Ducal Prussia.
In the aftermath of the armistice ending the Polish-Teuton ...
in Kraków
Kraków (), or Cracow, is the second-largest and one of the oldest cities in Poland. Situated on the Vistula River in Lesser Poland Voivodeship, the city dates back to the seventh century. Kraków was the official capital of Poland until 1596 ...
in April 1525. The new duke established Lutheranism as the first Protestant state church. The capital remained in Königsberg (modern Kaliningrad). The duchy was inherited by the Hohenzollern prince-elector
The prince-electors (german: Kurfürst pl. , cz, Kurfiřt, la, Princeps Elector), or electors for short, were the members of the electoral college that elected the emperor of the Holy Roman Empire.
From the 13th century onwards, the prin ...
s of Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 sq ...
in 1618. This personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interlink ...
is referred to as Brandenburg-Prussia. Frederick William, the "Great Elector" of Brandenburg, achieved full sovereignty over the duchy under the 1657 Treaty of Wehlau
The Treaty of Bromberg (, Latin: Pacta Bydgostensia) or Treaty of Bydgoszcz was a treaty between John II Casimir of Poland and Elector Frederick William of Brandenburg-Prussia that was ratified at Bromberg (Bydgoszcz) on 6 November 1657. The tr ...
, confirmed in the 1660 Treaty of Oliva
The Treaty or Peace of Oliva of 23 April (OS)/3 May (NS) 1660Evans (2008), p.55 ( pl, Pokój Oliwski, sv, Freden i Oliva, german: Vertrag von Oliva) was one of the peace treaties ending the Second Northern War (1655-1660).Frost (2000), p.183 ...
. In the following years, attempts were made to return to Polish suzerainty, especially by the capital city of Königsberg, whose burghers rejected the treaties and viewed the region as part of Poland. The Duchy of Prussia was elevated to a kingdom
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
in 1701.
History
Background
AsProtestantism
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
spread among the laity of the Teutonic Monastic State of Prussia, dissent began to develop against the Roman Catholic
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
* Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*'' Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a let ...
rule of the Teutonic Knights, whose Grand Master, Albert, Duke of Prussia
Albert of Prussia (german: Albrecht von Preussen; 17 May 149020 March 1568) was a German prince who was the 37th Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights, who after converting to Lutheranism, became the first ruler of the Duchy of Prussia, the s ...
, a member of a cadet branch of the House of Hohenzollern
The House of Hohenzollern (, also , german: Haus Hohenzollern, , ro, Casa de Hohenzollern) is a German royal (and from 1871 to 1918, imperial) dynasty whose members were variously princes, electors, kings and emperors of Hohenzollern, Brandenbu ...
, lacked the military resources to assert the order's authority.
After losing a war against the Kingdom of Poland
The Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Królestwo Polskie; Latin: ''Regnum Poloniae'') was a state in Central Europe. It may refer to:
Historical political entities
* Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom existing from 1025 to 1031
* Kingdom of Poland, a kingdom exi ...
, and with his personal bishop, Georg von Polenz
George of Polentz (born: ; died: 1550 in Balga) was bishop of Samland and Pomesania and a lawyer. He was the first Lutheran bishop and also a Protestant reformer.
Polentz was a member of an old Saxon noble family. He studied law in Bologna ...
of Pomesania and of Samland, who had converted to Lutheranism in 1523,Albertas Juška, ''Mažosios Lietuvos Bažnyčia XVI-XX amžiuje'', Klaipėda: 1997, pp. 742–771, hereafter the German translatio''Die Kirche in Klein Litauen''
(section: 2. Reformatorische Anfänge; ) on
''Lietuvos Evangelikų Liuteronų Bažnyčia''
retrieved on 28 August 2011. and a number of his commanders already supporting Protestant ideas, Albert began to consider a radical solution. At
Wittenberg
Wittenberg ( , ; Low Saxon: ''Wittenbarg''; meaning ''White Mountain''; officially Lutherstadt Wittenberg (''Luther City Wittenberg'')), is the fourth largest town in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. Wittenberg is situated on the River Elbe, north o ...
in 1522, and at Nuremberg
Nuremberg ( ; german: link=no, Nürnberg ; in the local East Franconian dialect: ''Nämberch'' ) is the second-largest city of the German state of Bavaria after its capital Munich, and its 518,370 (2019) inhabitants make it the 14th-largest ...
in 1524, Martin Luther encouraged him to convert the order's territory into a secular principality under his personal rule, as the Teutonic Knights would not be able to survive the reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and in ...
. Christiansen, Eric. ''The Northern Crusades''. Penguin Books. London, 1997.
Establishment
On 10 April 1525 Albert resigned his position, became a Protestant, and in thePrussian Homage
The Prussian Homage or Prussian Tribute (german: Preußische Huldigung; pl, hołd pruski) was the formal investment of Albert of Prussia as duke of the Polish fief of Ducal Prussia.
In the aftermath of the armistice ending the Polish-Teuton ...
was granted the title "Duke of Prussia" by his uncle, King Sigismund I of Poland. In a deal partly brokered by Luther, Ducal Prussia became the first Protestant state, anticipating the dispensations of the Peace of Augsburg of 1555.
 When Albert returned to Königsberg, he publicly declared his conversion and announced to a quorum of Teutonic Knights his new ducal status. The knights who disapproved of the decision were pressured into acceptance by Albert's supporters and the
When Albert returned to Königsberg, he publicly declared his conversion and announced to a quorum of Teutonic Knights his new ducal status. The knights who disapproved of the decision were pressured into acceptance by Albert's supporters and the burgher
Burgher may refer to:
* Burgher (social class), a medieval, early modern European title of a citizen of a town, and a social class from which city officials could be drawn
** Burgess (title), a resident of a burgh in northern Britain
** Grand Bu ...
s of Königsberg, and only Eric of Brunswick-Wolfenbüttel, Komtur
Commander ( it, Commendatore; french: Commandeur; german: Komtur; es, Comendador; pt, Comendador), or Knight Commander, is a title of honor prevalent in chivalric orders and fraternal orders.
The title of Commander occurred in the medieval mili ...
of Memel, opposed the new duke. On 10 December 1525, at their session in Königsberg, the Prussian estates The Prussian estates (german: Preußischer Landtag, pl, Stany pruskie) were representative bodies of Prussia, first created by the Monastic state of Teutonic Prussia in the 14th century (around the 1370s)Daniel Stone, ''A History of Central Europe ...
established the Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Cathol ...
Church in Ducal Prussia by deciding the Church Order
Church order is the systematically organized set of rules drawn up by a qualified body of a local church. P. Coertzen. ''Church and Order''. Belgium: Peeters. From the point of view of civil law, the ''church order'' can be described as the inter ...
.
By the end of Albert's rule, the offices of Grand Commander and Marshal of the Order had deliberately been left vacant while the order was left with but 55 knights in Prussia. Some of the knights converted to Lutheranism in order to retain their property and then married into the Prussian nobility, while others returned to the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
, and remained Catholic
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
. Seward, Desmond. ''The Monks of War: The Military Religious Orders''. Penguin Books. London, 1995. These remaining Teutonic Knights, led by the next Grand Master, Walter von Cronberg
Walter von Cronberg (1477 or 1479 – 4 April 1543) was the 38th Grand Master of the Teutonic Order, serving from 1527 to 1543.
Biography
Von Cronberg hailed from a rather poor family of knights from Kronberg Castle near Frankfurt. He joined t ...
, continued to unsuccessfully claim Prussia, but retained much of the estates in the Teutonic bailiwicks outside of Prussia.
On 1 March 1526, Albert married Princess Dorothea, daughter of King Frederick I of Denmark
Frederick I (Danish and ; ; ; 7 October 1471 – 10 April 1533) was King of Denmark and Norway. He was the last Roman Catholic monarch to reign over Denmark and Norway, when subsequent monarchs embraced Lutheranism after the Protestant Re ...
, thereby establishing political ties between Lutheranism and Scandinavia. Albert was greatly aided by his elder brother George, Margrave of Brandenburg-Ansbach
George of Brandenburg-Ansbach (German: ''Georg''; 4 March 1484 – 27 December 1543), known as George the Pious (''Georg der Fromme''), was a Margrave of Brandenburg-Ansbach from the House of Hohenzollern.
Biography
Early life
He was bo ...
, who had earlier established the Protestant religion in his territories of Franconia and Upper Silesia
Upper Silesia ( pl, Górny Śląsk; szl, Gůrny Ślůnsk, Gōrny Ślōnsk; cs, Horní Slezsko; german: Oberschlesien; Silesian German: ; la, Silesia Superior) is the southeastern part of the historical and geographical region of Silesia, locate ...
. Albert also found himself reliant on support from his uncle Sigismund I of catholic Poland, as the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
, and the Roman Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, had banned him for his Protestantism.
The Teutonic Order had only superficially carried out its mission to Christianize the native rural population and had erected few churches within the state's territory. There was little longing for Roman Catholicism. Baltic Old Prussians
Old Prussians, Baltic Prussians or simply Prussians ( Old Prussian: ''prūsai''; german: Pruzzen or ''Prußen''; la, Pruteni; lv, prūši; lt, prūsai; pl, Prusowie; csb, Prësowié) were an indigenous tribe among the Baltic peoples that ...
and Prussian Lithuanian peasants continued to practice pagan customs in some areas, for example, adhering to beliefs in Perkūnas (Perkunos), symbolized by the goat buck, Potrimpo, and Pikullos (Patollu) while "consuming the roasted flesh of a goat". Kirby, David. ''Northern Europe in the Early Modern Period: The Baltic World, 1492–1772''. Longman. London, 1990. Bishop George of Polentz
George of Polentz (born: ; died: 1550 in Balga) was bishop of Samland and Pomesania and a lawyer. He was the first Lutheran bishop and also a Protestant reformer.
Polentz was a member of an old Saxon noble family. He studied law in Bologna a ...
had forbidden the widespread forms of pagan worship in 1524, and repeated the ban in 1540.
On 18 January 1524 Bishop George had ordered the use of native languages at baptisms, which improved the acceptance of baptism by the peasants. There was little active resistance to the new Protestant religion. The fact that the Teutonic Knights had brought Catholicism and Protestantism made the transition easier. Koch, H.W. ''A History of Prussia''. Barnes & Noble Books. New York, 1978.
The Church Order of 1525 provided for visitations of the parishioners and pastors, first carried out by Bishop George in 1538. Because Ducal Prussia was ostensibly a Lutheran
Lutheranism is one of the largest branches of Protestantism, identifying primarily with the theology of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German monk and Protestant Reformers, reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practice of the Cathol ...
land, authorities traveled throughout the duchy ensuring that Lutheran teachings were being followed and imposing penalties on pagans and dissidents. The rural population of native descent was only thoroughly christianised starting with the Reformation in Prussia.
A peasant rebellion broke out in Sambia
Sambia (russian: Самбийский полуостров, lit=Sambian Peninsula, translit=Sambiysky poluostrov) or Samland (russian: Земландский полуостров, lit=Zemlandic Peninsula, translit=Zemlandsky poluostrov) or Kalini ...
in 1525. The combination of taxation by the nobility, the contentions of the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and ...
, and the abrupt secularization of the Teutonic Order's remaining Prussian lands exacerbated peasant unrest. The relatively well-to-do rebel leaders, including a miller from Kaimen and an innkeeper from Schaaken in Prussia, were supported by sympathizers in Königsberg. The rebels demanded the elimination of newer taxes by the nobility and a return to an older tax of two marks
Marks may refer to:
Business
* Mark's, a Canadian retail chain
* Marks & Spencer, a British retail chain
* Collective trade marks, trademarks owned by an organisation for the benefit of its members
* Marks & Co, the inspiration for the novel ...
for every hide a measure of land of approximately forty acres.
They claimed to be rebelling against the harsh nobility, not against Duke Albert, who was away in the Holy Roman Empire, but they would only swear allegiance to him in person. Upon Albert's return from the Empire, he called for a meeting of the peasants in a field, whereupon he surrounded them with loyal troops and had them arrested without incident. The leaders of the rebellion were subsequently executed. There were no more large-scale rebellions. Ducal Prussia became known as a land of Protestantism and sectarianism.
In 1544 Duke Albert founded the Albertina University
The Albertina is a museum in the Innere Stadt (First District) of Vienna, Austria. It houses one of the largest and most important print rooms in the world with approximately 65,000 drawings and approximately 1 million old master prints, as well ...
in Königsberg, which became the principal educational establishment for Lutheran pastors and theologians of Prussia. In 1560, the university received a royal privilege from King Sigismund II Augustus
Sigismund II Augustus ( pl, Zygmunt II August, lt, Žygimantas Augustas; 1 August 1520 – 7 July 1572) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania, the son of Sigismund I the Old, whom Sigismund II succeeded in 1548. He was the first ruler ...
of Poland. It was granted the same rights and autonomy those enjoyed by the Kraków University, thus it became one of the leading universities in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi- confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Poland and Lithuania ru ...
. The use of the native languages in church services made Duke Albert appoint exiled Protestant Lithuanian pastors as professors, e.g. Stanislovas Rapolionis and Abraomas Kulvietis
Abraomas Kulvietis ( la, Abraham Culvensis; pl, Abraham Kulwieć; c. 1509 – 19 June 1545) was a Lithuanian Lutheran jurist and a professor at Königsberg Albertina University, as well as a reformer of the church.
Kulvietis was born in Kulva, ...
, making the Albertina also a centre of Lithuanian language and literature.Albertas Juška, ''Mažosios Lietuvos Bažnyčia XVI-XX amžiuje'', Klaipėda: 1997, pp. 742–771, here after the German translatio''Die Kirche in Klein Litauen''
(section: 5. Die Pfarrer und ihre Ausbildung; ) on
''Lietuvos Evangelikų Liuteronų Bažnyčia''
retrieved on 28 August 2011. While the composition of the nobility changed little in the transition from the monastic state to the duchy, the control of the nobility over the dependent peasantry increased. Prussia's free peasants, called Kölmer were holders of free estates according to Culm law). These Kölmer held with about a sixth of the arable land, a considerable share as compared with other nations in the feudal era. Administratively, little changed in the transition from the Teutonic Knights to ducal rule. Although he was formally a vassal of the crown of Poland, Albert retained self-government for Prussia, his own army, the minting of his currency, a
provincial assembly
Provincial may refer to:
Government & Administration
* Provincial capitals, an administrative sub-national capital of a country
* Provincial city (disambiguation)
* Provincial minister (disambiguation)
* Provincial Secretary, a position in Can ...
, (de, '' Landtag''), and had substantial autonomy in foreign affairs. Urban, William. ''The Teutonic Knights: A Military History''. Greenhill Books. London, 2003.
Lack of heirs
When Albert died in 1568, his teenage son (exact age is unknown) Albert Frederick inherited the duchy. Sigismund II was also Albert Frederick's cousin. The Elector of Brandenburg Joachim II, converted to Lutheranism in 1539. Joachim wanted to merge his lands with the Prussian dukedom, so his heirs would inherit both. Joachim petitioned his brother-in-law, king Sigismund II of Poland the co-enfeoffment of his line of the Hohenzollern with the Prussian dukedom, and finally succeeded, including the then usual expenses. On 19 July 1569, when, in Lublin, Poland, duke Albert Frederick rendered King Sigismund II homage and was in return installed as Duke of Prussia in Lublin, the King simultaneously enfeoffed Joachim II and his descendants as co-heirs. Administration in the duchy declined as Albert Frederick became increasingly feeble-minded, leading Margrave George Frederick ofBrandenburg-Ansbach
The Principality or Margraviate of (Brandenburg-)Ansbach (german: Fürstentum Ansbach or ) was a principality in the Holy Roman Empire centered on the Franconian city of Ansbach. The ruling Hohenzollern princes of the land were known as margrave ...
to become Regent
A regent (from Latin : ruling, governing) is a person appointed to govern a state '' pro tempore'' (Latin: 'for the time being') because the monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge the powers and duties of the monarchy ...
of Prussia in 1577.
Following King Sigismund III's Prussian regency contract (1605) with Joachim Frederick of Brandenburg and his Treaty of Warsaw, 1611, with John Sigismund of Brandenburg, confirming the Brandenburgian co-inheritance of Prussia, these two regents guaranteed the free practice of Catholic religion in predominantly Lutheran Prussia. Based on these contracts some Lutheran churches were reconsecrated as Catholic places of worship (e.g. St. Nicholas Church, Elbląg in 1612).
Personal union with Brandenburg
In 1618, the Prussian Hohenzollern became extinct in the male line, and so the Polish fief of Prussia was passed on to the senior Brandenburg Hohenzollern line, the ruling margraves andprince-elector
The prince-electors (german: Kurfürst pl. , cz, Kurfiřt, la, Princeps Elector), or electors for short, were the members of the electoral college that elected the emperor of the Holy Roman Empire.
From the 13th century onwards, the prin ...
s of Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 sq ...
, who thereafter ruled Brandenburg (a fief of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
), and Ducal Prussia (a Polish fief), in personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interlink ...
. This legal contradiction made a cross-border real union
Real union is a union of two or more states, which share some state institutions in contrast to personal unions; however, they are not as unified as states in a political union. It is a development from personal union and has historically be ...
impossible; however, in practice, Brandenburg and Ducal Prussia were more and more ruled as one, and colloquially referred to as '' Brandenburg-Prussia''.
In 1618, the Thirty Years' War broke out, and John Sigismund himself died the following year. His son, George William, was successfully invested with the duchy in 1623 by King of Poland Sigismund III Vasa
Sigismund III Vasa ( pl, Zygmunt III Waza, lt, Žygimantas Vaza; 20 June 1566 – 30 April 1632
N.S.) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1587 to 1632 and, as Sigismund, King of Sweden and Grand Duke of Finland from 1592 to ...
, thus the personal union Brandenburg-Prussia was confirmed. Many of the Prussian Junkers
The Junkers ( ; ) were members of the landed nobility in Prussia. They owned great estates that were maintained and worked by peasants with few rights. These estates often lay in the countryside outside of major cities or towns. They were an impor ...
were opposed to rule by the House of Hohenzollern
The House of Hohenzollern (, also , german: Haus Hohenzollern, , ro, Casa de Hohenzollern) is a German royal (and from 1871 to 1918, imperial) dynasty whose members were variously princes, electors, kings and emperors of Hohenzollern, Brandenbu ...
of Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and List of cities in Germany by population, largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European Union by population within ci ...
and appealed to Sigismund III Vasa for redress, or even incorporation of Ducal Prussia into the Polish kingdom, but without success. Eulenberg, Herbert. ''The Hohenzollerns''. Translated by M.M. Bozman. The Century Co. New York, 1929.
Due to the Polish–Swedish War, in 1635 the duchy was administered by Polish statesman Jerzy Ossoliński
Prince Jerzy Ossoliński h. Topór (15 December 1595 – 9 August 1650) was a Polish nobleman ('' szlachcic''), Crown Court Treasurer from 1632, governor (''voivode'') of Sandomierz from 1636, ''Reichsfürst'' (Imperial Prince) since 1634, Cro ...
, appointed by Polish King Władysław IV Vasa
Władysław IV Vasa; lt, Vladislovas Vaza; sv, Vladislav IV av Polen; rus, Владислав IV Ваза, r=Vladislav IV Vaza; la, Ladislaus IV Vasa or Ladislaus IV of Poland (9 June 1595 – 20 May 1648) was King of Poland, Grand Duke of ...
.
Frederick William the "Great Elector", duke of Prussia and prince-elector of Brandenburg, wished to acquire Royal Prussia
Royal Prussia ( pl, Prusy Królewskie; german: Königlich-Preußen or , csb, Królewsczé Prësë) or Polish PrussiaAnton Friedrich Büsching, Patrick Murdoch. ''A New System of Geography'', London 1762p. 588/ref> (Polish: ; German: ) was a ...
in order to territorially connect his two fiefs. Yet, during the Second Northern War, Charles X Gustav of Sweden invaded Ducal Prussia and dictated the Treaty of Königsberg (January 1656), which made the duchy a Swedish fief. In the subsequent Treaty of Marienburg (June 1656), Charles X Gustav promised to cede to Frederick William the Polish voivodships of Chełmno, Malbork, Pomerania
Pomerania ( pl, Pomorze; german: Pommern; Kashubian: ''Pòmòrskô''; sv, Pommern) is a historical region on the southern shore of the Baltic Sea in Central Europe, split between Poland and Germany. The western part of Pomerania belongs to ...
, and the Prince-Bishopric of Warmia
The Prince-Bishopric of Warmia ( pl, Biskupie Księstwo Warmińskie; german: Fürstbistum Ermland) was a semi-independent ecclesiastical state, ruled by the incumbent ordinary of the Warmia see and comprising one third of the then diocesan area ...
, if Frederick William would support Charles Gustav's effort. The proposition was somewhat risky, since Frederick William would definitely have to provide military support, while the reward could only be provided conditional on victory. When the tide of the war turned against Charles X Gustav, he concluded the Treaty of Labiau (November 1656), making Frederick William I the full sovereign in Ducal Prussia and Warmia, which, however, was part of Poland.
Emancipation
In response to the Swedish-Prussian alliance, KingJohn II Casimir of Poland
John II Casimir ( pl, Jan II Kazimierz Waza; lt, Jonas Kazimieras Vaza; 22 March 1609 – 16 December 1672) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1648 until his abdication in 1668 as well as titular King of Sweden from 1648 ...
submitted a counter-offer which Frederick William accepted. They signed the Treaty of Wehlau
The Treaty of Bromberg (, Latin: Pacta Bydgostensia) or Treaty of Bydgoszcz was a treaty between John II Casimir of Poland and Elector Frederick William of Brandenburg-Prussia that was ratified at Bromberg (Bydgoszcz) on 6 November 1657. The tr ...
on 19 September 1657 and the Treaty of Bromberg
The Treaty of Bromberg (, Latin: Pacta Bydgostensia) or Treaty of Bydgoszcz was a treaty between John II Casimir of Poland and Elector Frederick William of Brandenburg-Prussia that was ratified at Bromberg (Bydgoszcz) on 6 November 1657. The tr ...
on 6 November 1657. In return for Frederick William's renunciation of the Swedish-Prussian alliance, John Casimir recognised Frederick William's full sovereignty over the Duchy of Prussia. After almost 200 years of Polish suzerainty over the Teutonic Monastic State of Prussia and its successor Ducal Prussia, the territory passed under the full sovereignty of Brandenburg. Therefore, ''Duchy of Prussia'' then became the more adequate appellation for the state. Full sovereignty was a necessary prerequisite to upgrade Ducal Prussia to the sovereign Kingdom of Prussia
The Kingdom of Prussia (german: Königreich Preußen, ) was a German kingdom that constituted the state of Prussia between 1701 and 1918. Marriott, J. A. R., and Charles Grant Robertson. ''The Evolution of Prussia, the Making of an Empire''. ...
, in 1701. (Not to be confused with Polish Royal Prussia
Royal Prussia ( pl, Prusy Królewskie; german: Königlich-Preußen or , csb, Królewsczé Prësë) or Polish PrussiaAnton Friedrich Büsching, Patrick Murdoch. ''A New System of Geography'', London 1762p. 588/ref> (Polish: ; German: ) was a ...
.)
 However, the end of Polish suzerainty was met with resistance of the population, regardless of ethnicity, as it was afraid of Brandenburg absolutism and wished to remain part of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland. The burghers of the capital city of Königsberg, led by
However, the end of Polish suzerainty was met with resistance of the population, regardless of ethnicity, as it was afraid of Brandenburg absolutism and wished to remain part of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland. The burghers of the capital city of Königsberg, led by Hieronymus Roth
Hieronymus Roth (1606–1678) was a lawyer and alderman of Königsberg (Polish: ''Królewiec'', modern day Kaliningrad) who led the city burghers in opposition to Elector Frederick William.
In the Treaty of Oliva of 1660 the Elector had managed ...
, rejected the treaties of Wehlau and Oliva and viewed Prussia as "indisputably contained within the territory of the Polish Crown".Janusz Jasiński, ''Polska a Królewiec'', Komunikaty Mazursko-Warmińskie nr 2, 2005, p. 126 (in Polish) It was noted that the incorporation into the Polish Crown
The Crown of the Kingdom of Poland ( pl, Korona Królestwa Polskiego; Latin: ''Corona Regni Poloniae''), known also as the Polish Crown, is the common name for the historic Late Middle Ages territorial possessions of the King of Poland, incl ...
under the Treaty of Kraków
The Treaty of Kraków was signed on 8 April 1525 between the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Master of the Teutonic Knights. It officially ended the Polish–Teutonic War.John Freely Celestial Revolutionary: Copernicus, the Man and His Universe ...
was approved by the city of Königsberg, while the separation from Poland took place without the city's consent. Polish King John II Casimir Vasa
John II Casimir ( pl, Jan II Kazimierz Waza; lt, Jonas Kazimieras Vaza; 22 March 1609 – 16 December 1672) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1648 until his abdication in 1668 as well as titular King of Sweden from 1648 ...
was asked for help, masses were held in Protestant churches for the Polish King and the Polish Kingdom. In 1662, elector Frederick William entered the city with his troops and forced the city to swear allegiance to him. However, in the following decades attempts to return to Polish suzerainty were still made. In 1675, the Polish-French Treaty of Jaworów was even signed, according to which France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
was to support Polish efforts to regain control of the region, while Poland was to join the ongoing Franco-Brandenburgian war on the French side, however, it was not implemented.
The nature of the ''de facto'' collectively ruled governance of Brandenburg-Prussia became more apparent through the titles of the higher ranks of the Prussian government, seated in Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 sq ...
's capital of Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and List of cities in Germany by population, largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European Union by population within ci ...
after the return of the court from Königsberg, where they had sought refuge from the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648).
Promotion
Ducal Prussia's full sovereignty allowed Elector Frederick III of Brandenburg to become " king in Prussia" in 1701 without offending Emperor Leopold I. The government of de facto collectively ruled Brandenburg-Prussia, seated inBrandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 sq ...
's capital Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and List of cities in Germany by population, largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's List of cities in the European Union by population within ci ...
, mostly appeared under the higher ranking titles of the Prussian government.
Expansion and consolidation
After the Kingdom of Prussia's annexation of the bulk of the province ofRoyal Prussia
Royal Prussia ( pl, Prusy Królewskie; german: Königlich-Preußen or , csb, Królewsczé Prësë) or Polish PrussiaAnton Friedrich Büsching, Patrick Murdoch. ''A New System of Geography'', London 1762p. 588/ref> (Polish: ; German: ) was a ...
in the First Partition of Poland in 1772, former Ducal Prussia — including previously Polish-controlled Warmia
Warmia ( pl, Warmia; Latin: ''Varmia'', ''Warmia''; ; Warmian: ''Warńija''; lt, Varmė; Old Prussian: ''Wārmi'') is both a historical and an ethnographic region in northern Poland, forming part of historical Prussia. Its historic capital ...
within Royal Prussia — was reorganized into the Province of East Prussia, while Pomerelia and the Malbork Land became the Province of West Prussia, with the exceptions of the two principal cities of Gdańsk and Toruń, annexed into West Prussia only in 1793. The Kingdom of Prussia, then consisting of East and West Prussia, being a sovereign state, and Brandenburg, being a fief within the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 ...
, were amalgamated ''de jure
In law and government, ''de jure'' ( ; , "by law") describes practices that are legally recognized, regardless of whether the practice exists in reality. In contrast, ("in fact") describes situations that exist in reality, even if not legally ...
'' only after the latter's dissolution in 1806, though later became again partially distinct during the existence of the German Confederation (1815-1866).
See also
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Prussia, Duchy of Former duchies Duchies of Poland Duchy of Prussia Duchy of Prussia . . Duchy of Prussia Duchy of Prussia Duchy of Prussia Duchy of Prussia Fiefdoms of Poland Prussia