Down Syndrome on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Down syndrome or Down's syndrome, also known as trisomy 21, is a genetic disorder caused by the presence of all or part of a third copy of

 Those with Down syndrome nearly always have physical and intellectual disabilities. As adults, their mental abilities are typically similar to those of an 8- or 9-year-old. They also typically have poor immune function and generally reach developmental milestones at a later age. They have an increased risk of a number of other health problems, including
Those with Down syndrome nearly always have physical and intellectual disabilities. As adults, their mental abilities are typically similar to those of an 8- or 9-year-old. They also typically have poor immune function and generally reach developmental milestones at a later age. They have an increased risk of a number of other health problems, including
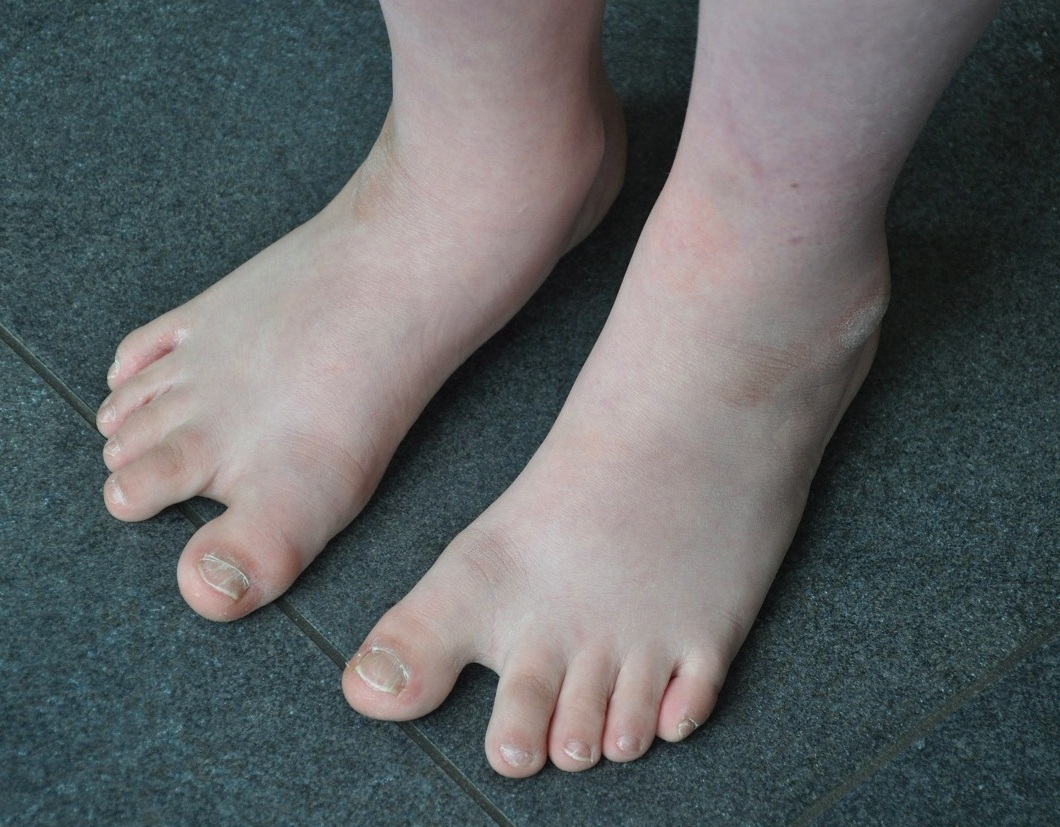 People with Down syndrome may have some or all of these physical characteristics: a small chin, slanted eyes, poor muscle tone, a flat
People with Down syndrome may have some or all of these physical characteristics: a small chin, slanted eyes, poor muscle tone, a flat
 Hearing and vision disorders occur in more than half of people with Down syndrome.
Vision problems occur in 38 to 80%. Between 20 and 50% have
Hearing and vision disorders occur in more than half of people with Down syndrome.
Vision problems occur in 38 to 80%. Between 20 and 50% have
 Down syndrome is caused by having three copies of the genes on
Down syndrome is caused by having three copies of the genes on
T21.JPG, Ultrasound of fetus with Down syndrome showing a large bladder
Nuchal edema in Down Syndrome Dr. W. Moroder.jpg, Enlarged NT and absent nasal bone in a fetus at 11 weeks with Down syndrome
 Between 5 and 15% of children with Down syndrome in Sweden attend regular school. Some graduate from high school; however, most do not. Of those with intellectual disability in the United States who attended high school about 40% graduated. Many learn to read and write and some are able to do paid work. In adulthood about 20% in the United States do paid work in some capacity. In Sweden, however, less than 1% have regular jobs. Many are able to live semi-independently, but they often require help with financial, medical, and legal matters. Those with mosaic Down syndrome usually have better outcomes.
Individuals with Down syndrome have a higher risk of early death than the general population. This is most often from heart problems or infections. Following improved medical care, particularly for heart and gastrointestinal problems, the life expectancy has increased. This increase has been from 12 years in 1912, to 25 years in the 1980s, to 50 to 60 years in the developed world in the 2000s. Currently between 4 and 12% die in the first year of life. The probability of long-term survival is partly determined by the presence of heart problems. In those with congenital heart problems, 60% survive to 10 years and 50% survive to 30 years of age. In those without heart problems, 85% survive to 10 years and 80% survive to 30 years of age. About 10% live to 70 years of age. The National Down Syndrome Society provide information regarding raising a child with Down syndrome.
Between 5 and 15% of children with Down syndrome in Sweden attend regular school. Some graduate from high school; however, most do not. Of those with intellectual disability in the United States who attended high school about 40% graduated. Many learn to read and write and some are able to do paid work. In adulthood about 20% in the United States do paid work in some capacity. In Sweden, however, less than 1% have regular jobs. Many are able to live semi-independently, but they often require help with financial, medical, and legal matters. Those with mosaic Down syndrome usually have better outcomes.
Individuals with Down syndrome have a higher risk of early death than the general population. This is most often from heart problems or infections. Following improved medical care, particularly for heart and gastrointestinal problems, the life expectancy has increased. This increase has been from 12 years in 1912, to 25 years in the 1980s, to 50 to 60 years in the developed world in the 2000s. Currently between 4 and 12% die in the first year of life. The probability of long-term survival is partly determined by the presence of heart problems. In those with congenital heart problems, 60% survive to 10 years and 50% survive to 30 years of age. In those without heart problems, 85% survive to 10 years and 80% survive to 30 years of age. About 10% live to 70 years of age. The National Down Syndrome Society provide information regarding raising a child with Down syndrome.
 Down syndrome is the most common chromosomal abnormality in humans. Globally, , Down syndrome occurs in about 1 per 1,000 births and results in about 17,000 deaths. More children are born with Down syndrome in countries where abortion is not allowed and in countries where pregnancy more commonly occurs at a later age. About 1.4 per 1,000 live births in the United States and 1.1 per 1,000 live births in Norway are affected. In the 1950s, in the United States, it occurred in 2 per 1,000 live births with the decrease since then due to prenatal screening and abortions. The number of pregnancies with Down syndrome is more than two times greater with many spontaneously aborting. It is the cause of 8% of all congenital disorders.
Maternal age effect, Maternal age affects the chances of having a pregnancy with Down syndrome. At age 20, the chance is 1 in 1,441; at age 30, it is 1 in 959; at age 40, it is 1 in 84; and at age 50 it is 1 in 44. Although the probability increases with maternal age, 70% of children with Down syndrome are born to women 35 years of age and younger, because younger people have more children. The Paternal age effect, father's older age is also a risk factor in women older than 35, but not in women younger than 35, and may partly explain the increase in risk as women age.
Down syndrome is the most common chromosomal abnormality in humans. Globally, , Down syndrome occurs in about 1 per 1,000 births and results in about 17,000 deaths. More children are born with Down syndrome in countries where abortion is not allowed and in countries where pregnancy more commonly occurs at a later age. About 1.4 per 1,000 live births in the United States and 1.1 per 1,000 live births in Norway are affected. In the 1950s, in the United States, it occurred in 2 per 1,000 live births with the decrease since then due to prenatal screening and abortions. The number of pregnancies with Down syndrome is more than two times greater with many spontaneously aborting. It is the cause of 8% of all congenital disorders.
Maternal age effect, Maternal age affects the chances of having a pregnancy with Down syndrome. At age 20, the chance is 1 in 1,441; at age 30, it is 1 in 959; at age 40, it is 1 in 84; and at age 50 it is 1 in 44. Although the probability increases with maternal age, 70% of children with Down syndrome are born to women 35 years of age and younger, because younger people have more children. The Paternal age effect, father's older age is also a risk factor in women older than 35, but not in women younger than 35, and may partly explain the increase in risk as women age.
 English physician John Langdon Down first described Down syndrome in 1862, recognizing it as a distinct type of mental disability, and again in a more widely published report in 1866. Édouard Séguin described it as separate from cretinism in 1844. By the 20th century, Down syndrome had become the most recognizable form of mental disability.
In antiquity, many infants with disabilities were either killed or abandoned.
In June 2020, the earliest incidence of Down syndrome was found in genomic evidence from an infant that was buried before 3200 BC at Poulnabrone dolmen in Ireland.
Researchers believe that a number of historical pieces of art portray Down syndrome, including pottery from the pre-Columbian Tumaco-La Tolita culture in present-day Colombia and Ecuador, and the 16th-century painting ''The Adoration of the Christ Child''.
In the 20th century, many individuals with Down syndrome were institutionalized, few of the associated medical problems were treated, and most people died in infancy or early adulthood. With the rise of the eugenics movement, 33 of the then 48 U.S. states and several countries began programs of forced sterilization of individuals with Down syndrome and comparable degrees of disability. Action T4 in Nazi Germany made public policy of a program of systematic Involuntary euthanasia, involuntary euthanization.
With the discovery of karyotype techniques in the 1950s it became possible to identify abnormalities of chromosomal number or shape. In 1959 Jérôme Lejeune reported the discovery that Down syndrome resulted from an extra chromosome. However, Lejeune's claim to the discovery has been disputed, and in 2014 the Scientific Council of the French Federation of Human Genetics unanimously awarded its Grand Prize to his colleague Marthe Gautier for her role in this discovery. The discovery took place in the laboratory of Raymond Turpin at the Hôpital Trousseau in Paris, France. Jérôme Lejeune and Marthe Gautier were both his students.
As a result of this discovery, the condition became known as trisomy 21. Even before the discovery of its cause, the presence of the syndrome in all races, its association with older maternal age, and its rarity of recurrence had been noticed. Medical texts had assumed it was caused by a combination of inheritable factors that had not been identified. Other theories had focused on injuries sustained during birth.
English physician John Langdon Down first described Down syndrome in 1862, recognizing it as a distinct type of mental disability, and again in a more widely published report in 1866. Édouard Séguin described it as separate from cretinism in 1844. By the 20th century, Down syndrome had become the most recognizable form of mental disability.
In antiquity, many infants with disabilities were either killed or abandoned.
In June 2020, the earliest incidence of Down syndrome was found in genomic evidence from an infant that was buried before 3200 BC at Poulnabrone dolmen in Ireland.
Researchers believe that a number of historical pieces of art portray Down syndrome, including pottery from the pre-Columbian Tumaco-La Tolita culture in present-day Colombia and Ecuador, and the 16th-century painting ''The Adoration of the Christ Child''.
In the 20th century, many individuals with Down syndrome were institutionalized, few of the associated medical problems were treated, and most people died in infancy or early adulthood. With the rise of the eugenics movement, 33 of the then 48 U.S. states and several countries began programs of forced sterilization of individuals with Down syndrome and comparable degrees of disability. Action T4 in Nazi Germany made public policy of a program of systematic Involuntary euthanasia, involuntary euthanization.
With the discovery of karyotype techniques in the 1950s it became possible to identify abnormalities of chromosomal number or shape. In 1959 Jérôme Lejeune reported the discovery that Down syndrome resulted from an extra chromosome. However, Lejeune's claim to the discovery has been disputed, and in 2014 the Scientific Council of the French Federation of Human Genetics unanimously awarded its Grand Prize to his colleague Marthe Gautier for her role in this discovery. The discovery took place in the laboratory of Raymond Turpin at the Hôpital Trousseau in Paris, France. Jérôme Lejeune and Marthe Gautier were both his students.
As a result of this discovery, the condition became known as trisomy 21. Even before the discovery of its cause, the presence of the syndrome in all races, its association with older maternal age, and its rarity of recurrence had been noticed. Medical texts had assumed it was caused by a combination of inheritable factors that had not been identified. Other theories had focused on injuries sustained during birth.
 Most obstetricians argue that not offering screening for Down syndrome is unethical. As it is a medically reasonable procedure, per informed consent, people should at least be given information about it. It will then be the woman's choice, based on her personal beliefs, how much or how little screening she wishes. When results from testing become available, it is also considered unethical not to give the results to the person in question.
Some bioethicists deem it reasonable for parents to select a child who would have the highest well-being. One criticism of this reasoning is that it often values those with disabilities less. Some parents argue that Down syndrome should not be prevented or cured and that eliminating Down syndrome amounts to genocide. The Disability rights, disability rights movement does not have a position on screening, although some members consider testing and abortion discriminatory. Some in the United States who are anti-abortion support abortion if the fetus is disabled, while others do not. Of a group of 40 mothers in the United States who have had one child with Down syndrome, half agreed to screening in the next pregnancy.
Within the US, some Protestant denominations see abortion as acceptable when a fetus has Down syndrome while Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox Christianity and Roman Catholics, Roman Catholicism do not. Some of those against screening refer to it as a form of eugenics. Disagreement exists within Islam regarding the acceptability of abortion in those carrying a fetus with Down syndrome. Some Islamic countries allow abortion, while others do not. Parents may be stigmatized whichever decision they make.
Most obstetricians argue that not offering screening for Down syndrome is unethical. As it is a medically reasonable procedure, per informed consent, people should at least be given information about it. It will then be the woman's choice, based on her personal beliefs, how much or how little screening she wishes. When results from testing become available, it is also considered unethical not to give the results to the person in question.
Some bioethicists deem it reasonable for parents to select a child who would have the highest well-being. One criticism of this reasoning is that it often values those with disabilities less. Some parents argue that Down syndrome should not be prevented or cured and that eliminating Down syndrome amounts to genocide. The Disability rights, disability rights movement does not have a position on screening, although some members consider testing and abortion discriminatory. Some in the United States who are anti-abortion support abortion if the fetus is disabled, while others do not. Of a group of 40 mothers in the United States who have had one child with Down syndrome, half agreed to screening in the next pregnancy.
Within the US, some Protestant denominations see abortion as acceptable when a fetus has Down syndrome while Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox Christianity and Roman Catholics, Roman Catholicism do not. Some of those against screening refer to it as a form of eugenics. Disagreement exists within Islam regarding the acceptability of abortion in those carrying a fetus with Down syndrome. Some Islamic countries allow abortion, while others do not. Parents may be stigmatized whichever decision they make.
Down's syndrome
by the UK National Health Service {{Authority control Down syndrome, Autosomal trisomies Chromosomal abnormalities Genetic diseases and disorders Genetic syndromes Intellectual disability Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate (full) Syndromes affecting the gastrointestinal tract Syndromes affecting the heart Syndromes affecting the nervous system Syndromes with craniofacial abnormalities
chromosome 21
Chromosome 21 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. Chromosome 21 is both the smallest human autosome and chromosome, with 48 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) representing about 1.5 percent of the total DNA in cells. M ...
. It is usually associated with physical growth delays, mild to moderate intellectual disability
Intellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disability in the United Kingdom and formerly mental retardation, Rosa's Law, Pub. L. 111-256124 Stat. 2643(2010). is a generalized neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by signif ...
, and characteristic facial features. The average IQ of a young adult with Down syndrome is 50, equivalent to the mental ability of an eight- or nine-year-old child, but this can vary widely.
The parents of the affected individual are usually genetically
Genetics is the study of genes, genetic variation, and heredity in organisms.Hartl D, Jones E (2005) It is an important branch in biology because heredity is vital to organisms' evolution. Gregor Mendel, a Moravian Augustinian friar working i ...
normal. The probability increases from less than 0.1% in 20-year-old mothers to 3% in those of age 45. The extra chromosome is believed to occur by chance, with no known behavioral activity or environmental factor that changes the probability. Down syndrome can be identified during pregnancy by prenatal screening followed by diagnostic testing or after birth by direct observation and genetic testing. Since the introduction of screening, Down syndrome pregnancies are often aborted
Aborted is a Belgian death metal band formed in 1995 in Waregem. The group currently consists of vocalist, founder and only constant member Sven de Caluwé, guitarist Ian Jekelis, bassist Stefano Franceschini and drummer Ken Bedene. Although t ...
.
There is no cure for Down syndrome. Education and proper care have been shown to improve quality of life. Some children with Down syndrome are educated in typical school classes, while others require more specialized education. Some individuals with Down syndrome graduate from high school, and a few attend post-secondary education
Tertiary education, also referred to as third-level, third-stage or post-secondary education, is the educational level following the completion of secondary education. The World Bank, for example, defines tertiary education as including univers ...
. In adulthood, about 20% in the United States do paid work in some capacity, with many requiring a sheltered work environment. Support in financial and legal matters is often needed. Life expectancy is around 50 to 60 years in the developed world
A developed country (or industrialized country, high-income country, more economically developed country (MEDC), advanced country) is a sovereign state that has a high quality of life, developed economy and advanced technological infrastruct ...
with proper health care. Regular screening for health problems common in Down syndrome is recommended throughout the person's life.
Down syndrome is one of the most common chromosome abnormalities
A chromosomal abnormality, chromosomal anomaly, chromosomal aberration, chromosomal mutation, or chromosomal disorder, is a missing, extra, or irregular portion of chromosomal DNA. These can occur in the form of numerical abnormalities, where ther ...
in humans. It occurs in about 1 in 1,000 babies born each year. In 2015, Down syndrome was present in 5.4 million individuals globally and resulted in 27,000 deaths, down from 43,000 deaths in 1990. It is named after British doctor John Langdon Down, who fully described the syndrome in 1866. Some aspects of the condition were described earlier by French psychiatrist Jean-Étienne Dominique Esquirol in 1838 and French physician Édouard Séguin in 1844. The genetic cause of Down syndrome was discovered in 1959.
Signs and symptoms

congenital heart defect
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital heart defect is classed as a cardiovascul ...
, epilepsy, leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia and pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ...
, thyroid diseases, and mental disorders.
Physical
nasal bridge
The nasal bridge is the upper, bony part of the human nose, which overlies the nasal bones.
Association with epicanthic folds
Low-rooted nasal bridges are closely associated with epicanthic folds. A lower nasal bridge is more likely to cause an ...
, a single crease of the palm, and a protruding tongue due to a small mouth and relatively large tongue. These airway changes lead to obstructive sleep apnea in around half of those with Down syndrome. Other common features include: a flat and wide face, a short neck, excessive joint flexibility, extra space between big toe and second toe, abnormal patterns on the fingertips and short fingers. Instability of the atlantoaxial joint occurs in about 20% and may lead to spinal cord injury in 1–2%. Hip dislocations may occur without trauma in up to a third of people with Down syndrome.
Growth in height is slower, resulting in adults who tend to have short stature
Short stature refers to a height of a human which is below typical. Whether a person is considered short depends on the context. Because of the lack of preciseness, there is often disagreement about the degree of shortness that should be called ' ...
—the average height for men is 154 cm (5 ft 1 in) and for women is 142 cm (4 ft 8 in). Individuals with Down syndrome are at increased risk for obesity
Obesity is a medical condition, sometimes considered a disease, in which excess body fat has accumulated to such an extent that it may negatively affect health. People are classified as obese when their body mass index (BMI)—a person's ...
as they age. Growth charts have been developed specifically for children with Down syndrome.
Neurological
This syndrome causes about a third of cases of intellectual disability. Many developmental milestones are delayed with the ability to crawl typically occurring around 8 months rather than 5 months and the ability to walk independently typically occurring around 21 months rather than 14 months. Most individuals with Down syndrome have mild (IQ: 50–69) or moderate (IQ: 35–50)intellectual disability
Intellectual disability (ID), also known as general learning disability in the United Kingdom and formerly mental retardation, Rosa's Law, Pub. L. 111-256124 Stat. 2643(2010). is a generalized neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by signif ...
with some cases having severe (IQ: 20–35) difficulties. Those with mosaic Down syndrome typically have IQ scores 10–30 points higher than that. As they age, people with Down syndrome typically perform worse than their same-age peers.
Commonly, individuals with Down syndrome have better language understanding than ability to speak. Between 10 and 45% have either a stutter or rapid and irregular speech, making it difficult to understand them. After reaching 30 years of age, some may lose their ability to speak.
They typically do fairly well with social skills. Behavior problems are not generally as great an issue as in other syndromes associated with intellectual disability. In children with Down syndrome, mental illness occurs in nearly 30% with autism occurring in 5–10%. People with Down syndrome experience a wide range of emotions. While people with Down syndrome are generally happy, symptoms of depression and anxiety may develop in early adulthood.
Children and adults with Down syndrome are at increased risk of epileptic seizures
An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with los ...
, which occur in 5–10% of children and up to 50% of adults. This includes an increased risk of a specific type of seizure called infantile spasms. Many (15%) who live 40 years or longer develop Alzheimer's disease. In those who reach 60 years of age, 50–70% have the disease.
Senses
 Hearing and vision disorders occur in more than half of people with Down syndrome.
Vision problems occur in 38 to 80%. Between 20 and 50% have
Hearing and vision disorders occur in more than half of people with Down syndrome.
Vision problems occur in 38 to 80%. Between 20 and 50% have strabismus
Strabismus is a vision disorder in which the eyes do not properly align with each other when looking at an object. The eye that is focused on an object can alternate. The condition may be present occasionally or constantly. If present during a ...
, in which the two eyes do not move together. Cataract
A cataract is a cloudy area in the lens of the eye that leads to a decrease in vision. Cataracts often develop slowly and can affect one or both eyes. Symptoms may include faded colors, blurry or double vision, halos around light, trouble ...
s (cloudiness of the lens
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements ...
of the eye) occur in 15%, and may be present at birth. Keratoconus (a thin, cone-shaped cornea) and glaucoma (increased eye pressure) are also more common, as are refractive errors
Refractive error, also known as refraction error, is a problem with focusing light accurately on the retina due to the shape of the eye and or cornea. The most common types of refractive error are near-sightedness, far-sightedness, astigmatism, ...
requiring glasses or contacts
Contact lenses, or simply contacts, are thin lenses placed directly on the surface of the eyes. Contact lenses are ocular prosthetic devices used by over 150 million people worldwide, and they can be worn to correct vision or for cosmetic ...
. Brushfield spots (small white or grayish/brown spots on the outer part of the iris
Iris most often refers to:
*Iris (anatomy), part of the eye
*Iris (mythology), a Greek goddess
* ''Iris'' (plant), a genus of flowering plants
* Iris (color), an ambiguous color term
Iris or IRIS may also refer to:
Arts and media
Fictional ent ...
) are present in 38 to 85% of individuals.
Hearing problems are found in 50–90% of children with Down syndrome. This is often the result of otitis media with effusion
Otitis media is a group of inflammatory diseases of the middle ear. One of the two main types is acute otitis media (AOM), an infection of rapid onset that usually presents with ear pain. In young children this may result in pulling at the ear, ...
which occurs in 50–70% and chronic ear infections which occur in 40 to 60%. Ear infections often begin in the first year of life and are partly due to poor eustachian tube function. Excessive ear wax can also cause hearing loss due to obstruction of the outer ear canal. Even a mild degree of hearing loss can have negative consequences for speech, language understanding, and academics. It is important to rule out hearing loss as a factor in social and cognitive deterioration. Age-related hearing loss of the sensorineural type occurs at a much earlier age and affects 10–70% of people with Down syndrome.
Heart
The rate ofcongenital heart disease
A congenital heart defect (CHD), also known as a congenital heart anomaly and congenital heart disease, is a defect in the structure of the heart or great vessels that is present at birth. A congenital heart defect is classed as a cardiovascular ...
in newborns with Down syndrome is around 40%. Of those with heart disease, about 80% have an atrioventricular septal defect
Atrioventricular septal defect (AVSD) or atrioventricular canal defect (AVCD), also known as "common atrioventricular canal" (CAVC) or " endocardial cushion defect" (ECD), is characterized by a deficiency of the atrioventricular septum of the hea ...
or ventricular septal defect
A ventricular septal defect (VSD) is a defect in the ventricular septum, the wall dividing the left and right ventricles of the heart. The extent of the opening may vary from pin size to complete absence of the ventricular septum, creating one ...
with the former being more common. Congenital heart disease can also put individuals at a higher risk of pulmonary hypertension, where arteries in the lungs narrow and cause inadequate blood oxygenation. Some of the genetic contributions to pulmonary hypertension in individuals with Down Syndrome are abnormal lung development, endothelial dysfunction
In vascular diseases, endothelial dysfunction is a systemic pathological state of the endothelium. Along with acting as a semi-permeable membrane, the endothelium is responsible for maintaining vascular tone and regulating oxidative stress by ...
, and proinflammatory genes. Mitral valve problems become common as people age, even in those without heart problems at birth. Other problems that may occur include tetralogy of Fallot
Tetralogy of Fallot (TOF), formerly known as Steno-Fallot tetralogy, is a congenital heart defect characterized by four specific cardiac defects. Classically, the four defects are:
*pulmonary stenosis, which is narrowing of the exit from the r ...
and patent ductus arteriosus
''Patent ductus arteriosus'' (PDA) is a medical condition in which the ''ductus arteriosus'' fails to close after birth: this allows a portion of oxygenated blood from the left heart to flow back to the lungs by flowing from the aorta, which has ...
. People with Down syndrome have a lower risk of hardening of the arteries.
Cancer
Although the overall risk ofcancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
in Down syndrome is not changed, the risk of testicular cancer and certain blood cancers, including acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL) and acute megakaryoblastic leukemia
Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (AMKL) is life-threatening leukemia in which malignant megakaryoblasts proliferate abnormally and injure various tissues. Megakaryoblasts are the most immature precursor cells in a platelet-forming lineage; they matu ...
(AMKL) is increased while the risk of other non-blood cancers is decreased. People with Down syndrome are believed to have an increased risk of developing cancers derived from germ cells whether these cancers are blood- or non-blood-related.
Blood cancers
Leukemia
Leukemia ( also spelled leukaemia and pronounced ) is a group of blood cancers that usually begin in the bone marrow and result in high numbers of abnormal blood cells. These blood cells are not fully developed and are called ''blasts'' or ...
is 10 to 15 times more common in children with Down syndrome. In particular, acute lymphoblastic leukemia is 20 times more common and the megakaryoblastic form of acute myeloid leukemia
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML) is a cancer of the myeloid line of blood cells, characterized by the rapid growth of abnormal cells that build up in the bone marrow and blood and interfere with normal blood cell production. Symptoms may inclu ...
(acute megakaryoblastic leukemia
Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (AMKL) is life-threatening leukemia in which malignant megakaryoblasts proliferate abnormally and injure various tissues. Megakaryoblasts are the most immature precursor cells in a platelet-forming lineage; they matu ...
), is 500 times more common. Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia (AMKL) is a leukemia of megakaryoblasts, the precursors cells to megakaryocyte
A megakaryocyte (''mega-'' + '' karyo-'' + '' -cyte'', "large-nucleus cell") is a large bone marrow cell with a lobated nucleus responsible for the production of blood thrombocytes (platelets), which are necessary for normal blood clotting. In ...
s which form blood platelet
Platelets, also called thrombocytes (from Greek θρόμβος, "clot" and κύτος, "cell"), are a component of blood whose function (along with the coagulation factors) is to react to bleeding from blood vessel injury by clumping, thereby i ...
s. Acute lymphoblastic leukemia in Down syndrome accounts for 1–3% of all childhood cases of ALL. It occurs most often in those older than nine years or having a white blood cell count greater than 50,000 per microliter and is rare in those younger than one year old. ALL in Down syndrome tends to have poorer outcomes than other cases of ALL in people without Down syndrome.
In Down syndrome, AMKL is typically preceded by transient myeloproliferative disease
Transient myeloproliferative disease (TMD) occurs in a significant percentage of individuals born with the congenital genetic disorder, Down syndrome. It may occur in individuals who are not diagnosed with the syndrome but have some hematological c ...
(TMD), a disorder of blood cell production in which non-cancerous megakaryoblasts with a mutation in the ''GATA1
GATA-binding factor 1 or GATA-1 (also termed Erythroid transcription factor) is the founding member of the GATA family of transcription factors. This protein is widely expressed throughout vertebrate species. In humans and mice, it is encoded by ...
'' gene rapidly divide during the later period of pregnancy. The condition affects 3–10% of babies with Down. While it often spontaneously resolves within three months of birth, it can cause serious blood, liver, or other complications. In about 10% of cases, TMD progresses to AMKL during the three months to five years following its resolution.
Non-blood cancers
People with Down syndrome have a lower risk of all major solid cancers, including those of lung, breast, and cervix, with the lowest relative rates occurring in those aged 50 years or older. This low risk is thought due to an increase in the expression of tumor suppressor genes present on chromosome 21. One exception is testicular germ cell cancer which occurs at a higher rate in Down syndrome.Endocrine
Problems of the thyroid gland occur in 20–50% of individuals with Down syndrome. Low thyroid is the most common form, occurring in almost half of all individuals. Thyroid problems can be due to a poorly or nonfunctioning thyroid at birth (known as congenital hypothyroidism) which occurs in 1% or can develop later due to an attack on the thyroid by the immune system resulting in Graves' disease or autoimmune hypothyroidism. Type 1 diabetes mellitus is also more common.Gastrointestinal
Constipation occurs in nearly half of people with Down syndrome and may result in changes in behavior. One potential cause is Hirschsprung's disease, occurring in 2–15%, which is due to a lack of nerve cells controlling the colon. Other frequent congenital problems include duodenal atresia,pyloric stenosis
Pyloric stenosis is a narrowing of the opening from the stomach to the first part of the small intestine (the pylorus). Symptoms include projectile vomiting without the presence of bile. This most often occurs after the baby is fed. The typical a ...
, Meckel diverticulum, and imperforate anus. Celiac disease
Coeliac disease (British English) or celiac disease (American English) is a long-term autoimmune disorder, primarily affecting the small intestine, where individuals develop intolerance to gluten, present in foods such as wheat, rye and barle ...
affects about 7–20% and gastroesophageal reflux disease
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) is one of the upper gastrointestinal chronic diseases where stomach content persistently and regularly flows up into the esophagus, resulting in symptoms and/ ...
is also more common.
Teeth
People with Down syndrome tend to be more susceptible to gingivitis as well as early, severeperiodontal
Periodontology or periodontics (from Ancient Greek , – 'around'; and , – 'tooth', genitive , ) is the specialty of dentistry that studies supporting structures of teeth, as well as diseases and conditions that affect them. The supporting ...
disease, necrotising ulcerative gingivitis, and early tooth loss Tooth loss is a process in which one or more teeth come loose and fall out. Tooth loss is normal for deciduous teeth (baby teeth), when they are replaced by a person's adult teeth. Otherwise, losing teeth is undesirable and is the result of inju ...
, especially in the lower front teeth. While plaque
Plaque may refer to:
Commemorations or awards
* Commemorative plaque, a plate or tablet fixed to a wall to mark an event, person, etc.
* Memorial Plaque (medallion), issued to next-of-kin of dead British military personnel after World War I
* Pl ...
and poor oral hygiene are contributing factors, the severity of these periodontal diseases cannot be explained solely by external factors. Research suggests that the severity is likely a result of a weakened immune system. The weakened immune system also contributes to increased incidence of yeast infections in the mouth (from ''Candida albicans
''Candida albicans'' is an opportunistic pathogenic yeast that is a common member of the human gut flora. It can also survive outside the human body. It is detected in the gastrointestinal tract and mouth in 40–60% of healthy adults. It is usu ...
'').
People with Down syndrome also tend to have a more alkaline saliva resulting in a greater resistance to tooth decay
Tooth decay, also known as cavities or caries, is the breakdown of teeth due to acids produced by bacteria. The cavities may be a number of different colors from yellow to black. Symptoms may include pain and difficulty with eating. Complicatio ...
, despite decreased quantities of saliva, less effective oral hygiene habits, and higher plaque indexes.
Higher rates of tooth wear and bruxism are also common. Other common oral manifestations of Down syndrome include enlarged hypotonic tongue, crusted and hypotonic lips, mouth breathing
Mouth breathing, medically known as chronic oral ventilation, is long-term breathing through the mouth. It often is caused by an obstruction to breathing through the nose, the innate breathing organ in the human body. Chronic mouth breathing ma ...
, narrow palate
The palate () is the roof of the mouth in humans and other mammals. It separates the oral cavity from the nasal cavity.
A similar structure is found in crocodilians, but in most other tetrapods, the oral and nasal cavities are not truly separ ...
with crowded teeth, class III malocclusion
In orthodontics, a malocclusion is a misalignment or incorrect relation between the teeth of the upper and lower dental arches when they approach each other as the jaws close. The English-language term dates from 1864; Edward Angle (1855-19 ...
with an underdeveloped maxilla and posterior crossbite
Crossbite is a form of malocclusion where a tooth (or teeth) has a more buccal or lingual position (that is, the tooth is either closer to the cheek or to the tongue) than its corresponding antagonist tooth in the upper or lower dental arch. In ...
, delayed exfoliation of baby teeth and delayed eruption of adult teeth, shorter roots on teeth, and often missing and malformed (usually smaller) teeth. Less common manifestations include cleft lip and palate
A cleft lip contains an opening in the upper lip that may extend into the nose. The opening may be on one side, both sides, or in the middle. A cleft palate occurs when the palate (the roof of the mouth) contains an opening into the nose. The ...
and enamel hypocalcification
Enamel hypocalcification is a defect of tooth enamel in which normal amounts of enamel are produced but are hypomineralized. In this defect the enamel is softer than normal. Some areas in enamel are hypocalcified: enamel spindles, enamel tufts, an ...
(20% prevalence).
Taurodontism, an elongation of the pulp chamber, has a high prevalence in people with DS.
Fertility
Males with Down syndrome usually do not father children, while females have lower rates of fertility relative to those who are unaffected. Fertility is estimated to be present in 30–50% of females. Menopause usually occurs at an earlier age. The poor fertility in males is thought to be due to problems with sperm development; however, it may also be related to not being sexually active. As of 2006, three instances of males with Down syndrome fathering children and 26 cases of females having children have been reported. Withoutassisted reproductive technologies
Assisted reproductive technology (ART) includes medical procedures used primarily to address infertility. This subject involves procedures such as in vitro fertilization (IVF), intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI), cryopreservation of gametes ...
, around half of the children of someone with Down syndrome will also have the syndrome.
Cause
The cause of the extra full or partial chromosome is still unknown. Most of the time, Down syndrome is caused by a random mistake in cell division during early development of the fetus, but not inherited, and no scientific research shows that environmental factors or the parents' activities contribute to Down syndrome. The only factor that has been linked to the increased chance of having a baby with Down syndrome is maternal age. Down syndrome is caused by having three copies of the genes on
Down syndrome is caused by having three copies of the genes on chromosome 21
Chromosome 21 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. Chromosome 21 is both the smallest human autosome and chromosome, with 48 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) representing about 1.5 percent of the total DNA in cells. M ...
, rather than the usual two. The parents of the affected individual are typically genetically normal. Those who have one child with Down syndrome have about a 1% possibility of having a second child with the syndrome, if both parents are found to have normal karyotypes.
The extra chromosome content can arise through several different ways. The most common cause (about 92–95% of cases) is a complete extra copy of chromosome 21, resulting in trisomy 21. In 1.0 to 2.5% of cases, some of the cells in the body are normal and others have trisomy 21, known as mosaic Down syndrome. The other common mechanisms that can give rise to Down syndrome include: a Robertsonian translocation, isochromosome, or ring chromosome
A ring chromosome is an aberrant chromosome whose ends have fused together to form a ring. Ring chromosomes were first discovered by Lilian Vaughan Morgan in 1926. A ring chromosome is denoted by the symbol ''r'' in human genetics and ''R'' in '' ...
. These contain additional material from chromosome 21 and occur in about 2.5% of cases. An isochromosome results when the two long arms of a chromosome separate together rather than the long and short arm separating together during egg or sperm development.
Trisomy 21
Trisomy 21 (also known by the karyotype 47,XX,+21 for females and 47,XY,+21 for males) is caused by a failure of the 21st chromosome to separate during egg or sperm development ( nondisjunction). As a result, a sperm or egg cell is produced with an extra copy of chromosome 21; this cell thus has 24 chromosomes. When combined with a normal cell from the other parent, the baby has 47 chromosomes, with three copies of chromosome 21. About 88% of cases of trisomy 21 result from nonseparation of the chromosomes in the mother, 8% from nonseparation in the father, and 3% after the egg and sperm have merged.Mosaicism
Mosaicism
Mosaicism or genetic mosaicism is a condition in multicellular organisms in which a single organism possesses more than one genetic line as the result of genetic mutation. This means that various genetic lines resulted from a single fertilized ...
is diagnosed when there is a mixture of two types of cells: some cells have three copies of chromosome 21 but some cells have the typical two copies of chromosome 21. Mosaicism is the least common form of Down syndrome and accounts for only about 1% of all cases of Down syndrome. Children with mosaic Down syndrome may have the same features as other children with Down syndrome. However, they may have fewer characteristics of the condition due to the presence of some (or many) cells with a typical number of chromosomes.
Translocation
The extra chromosome 21 material may also occur due to a Robertsonian translocation in 2–4% of cases. In this situation, the long arm of chromosome 21 is attached to another chromosome, oftenchromosome 14
Chromosome 14 is one of the 23 pairs of chromosomes in humans. People normally have two copies of this chromosome. Chromosome 14 spans about 107 million base pairs (the building material of DNA) and represents between 3 and 3.5% of the total DNA ...
. In a male affected with Down syndrome, it results in a karyotype of 46XY,t(14q21q). This may be a new mutation or previously present in one of the parents. The parent with such a translocation is usually normal physically and mentally; however, during production of egg or sperm cells, a higher chance of creating reproductive cells with extra chromosome 21 material exists. This results in a 15% chance of having a child with Down syndrome when the mother is affected and a less than 5% probability if the father is affected. The probability of this type of Down syndrome is not related to the mother's age. Some children without Down syndrome may inherit the translocation and have a higher probability of having children of their own with Down syndrome. In this case it is sometimes known as familial Down syndrome.
Mechanism
The extra genetic material present in Down syndrome results in overexpression of a portion of the 310 genes located on chromosome 21. This overexpression has been estimated at 50%, due to the third copy of the chromosome present. Some research has suggested the Down syndrome critical region is located at bands 21q22.1–q22.3, with this area including genes for the amyloid precursor protein, superoxide dismutase, and likely the ETS2 protooncogene
An oncogene is a gene that has the potential to cause cancer. In tumor cells, these genes are often mutated, or expressed at high levels.
. Other research, however, has not confirmed these findings. MicroRNA
MicroRNA (miRNA) are small, single-stranded, non-coding RNA molecules containing 21 to 23 nucleotides. Found in plants, animals and some viruses, miRNAs are involved in RNA silencing and post-transcriptional regulation of gene expression. mi ...
s are also proposed to be involved.
The dementia that occurs in Down syndrome is due to an excess of amyloid beta peptide produced in the brain and is similar to Alzheimer's disease, which also involves amyloid beta build-up. Amyloid beta is processed from amyloid precursor protein, the gene for which is located on chromosome 21. Senile plaques
Amyloid plaques (also known as neuritic plaques, amyloid beta plaques or senile plaques) are extracellular deposits of the amyloid beta (Aβ) protein mainly in the grey matter of the brain. Degenerative neuronal elements and an abundance of micr ...
and neurofibrillary tangles are present in nearly all by 35 years of age, though dementia may not be present. Those with Down syndrome also lack a normal number of lymphocytes and produce less antibodies which contributes to their increased risk of infection.
Epigenetics
Down syndrome is associated with an increased risk of many chronic diseases that are typically associated with older age such as Alzheimer's disease. The accelerated aging suggest that trisomy 21 increases the biological age of tissues, but molecular evidence for this hypothesis is sparse. According to a biomarker of tissue age known as epigenetic clock, trisomy 21 increases the age of blood and brain tissue (on average by 6.6 years).Diagnosis
Before birth
When screening tests predict a high possibility of Down syndrome, a more invasive diagnostic test (amniocentesis
Amniocentesis is a medical procedure used primarily in the prenatal diagnosis of genetic conditions. It has other uses such as in the assessment of infection and fetal lung maturity. Prenatal diagnostic testing, which includes amniocentesis, is n ...
or chorionic villus sampling) is needed to confirm the diagnosis. The false-positive rate with screening is about 2–5% (see section Screening below). Amniocentesis and chorionic villus sampling are more reliable tests, but they increase the risk of miscarriage by between 0.5 and 1%. The risk of limb problems may be increased in the offspring if chorionic villus sampling is performed before 10 weeks. The risk from the procedure is greater the earlier it is performed, thus amniocentesis is not recommended before 15 weeks gestational age and chorionic villus sampling before 10 weeks gestational age.
Abortion rates
About 92% of pregnancies in Europe with a diagnosis of Down syndrome are terminated. As a result, there is almost no one with Down syndrome inIceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its s ...
and Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
, where screening is commonplace. In the United States, the termination rate after diagnosis is around 75%, but varies from 61% to 93% depending on the population surveyed. Rates are lower among women who are younger and have decreased over time. When asked if they would have a termination if their fetus tested positive, 23–33% said yes, when high-risk pregnant women were asked, 46–86% said yes, and when women who screened positive are asked, 89–97% say yes.
After birth
The diagnosis can often be suspected based on the child's physical appearance at birth. An analysis of the child's chromosomes is needed to confirm the diagnosis, and to determine if a translocation is present, as this may help determine the chances of the child's parents having further children with Down syndrome. Parents generally wish to know the possible diagnosis once it is suspected and do notScreening
Guidelines recommend screening for Down syndrome to be offered to all pregnant women, regardless of age. A number of tests are used, with varying levels of accuracy. They are typically used in combination to increase the detection rate. None can be definitive, thus if screening is positive, eitheramniocentesis
Amniocentesis is a medical procedure used primarily in the prenatal diagnosis of genetic conditions. It has other uses such as in the assessment of infection and fetal lung maturity. Prenatal diagnostic testing, which includes amniocentesis, is n ...
or chorionic villus sampling is required to confirm the diagnosis. Screening in both the first and second trimesters is better than just screening in the first trimester. The different screening techniques in use are able to pick up 90–95% of cases, with a false-positive rate of 2–5%. If Down syndrome occurs in one in 500 pregnancies with a 90% detection rate and the test used has a 5% false-positive rate, this means, of 20 women who test positive on screening, only one will not have a fetus with Down syndrome confirmed. If the screening test has a 2% false-positive rate, this means, of 50 women who test positive on screening, one will have a fetus with Down syndrome.
Ultrasound
Ultrasound imaging can be used to screen for Down syndrome. Findings that indicate increased chances when seen at 14 to 24 weeks of gestation include a small or no nasal bone, large ventricles, nuchal fold thickness, and an abnormal right subclavian artery, among others. The presence or absence of many markers is more accurate. Increased fetal nuchal translucency (NT) indicates an increased possibility of Down syndrome picking up 75–80% of cases and being falsely positive in 6%.Blood tests
Several blood markers can be measured to predict the chances of Down syndrome during the first or second trimester. Testing in both trimesters is sometimes recommended and test results are often combined with ultrasound results. In the second trimester, often two or three tests are used in combination with two or three of: α-fetoprotein, unconjugated estriol, total hCG, and free βhCG detecting about 60–70% of cases. Testing of the mother's blood for fetal DNA is being studied and appears promising in the first trimester. The International Society for Prenatal Diagnosis considers it a reasonable screening option for those women whose pregnancies are at a high likelihood of trisomy 21. Accuracy has been reported at 98.6% in the first trimester of pregnancy. Confirmatory testing by invasive techniques (amniocentesis, CVS) is still required to confirm the screening result.Management
Efforts such as early childhood intervention, screening for common problems, medical treatment where indicated, a good family environment, and work-related training can improve the development of children with Down syndrome. Education and proper care can improve quality of life. Raising a child with Down syndrome is more work for parents than raising an unaffected child. Typical childhood vaccinations are recommended.Health screening
A number of health organizations have issued recommendations for screening (medicine), screening those with Down syndrome for particular diseases. This is recommended to be done systematically. At birth, all children should get an electrocardiogram and echocardiogram, ultrasound of the heart. Surgical repair of heart problems may be required as early as three months of age. Heart valve problems may occur in young adults, and further ultrasound evaluation may be needed in adolescents and in early adulthood. Due to the elevated risk of testicular cancer, some recommend checking the person's testicles yearly.Cognitive development
Hearing aids or other amplification devices can be useful for language learning in those with hearing loss. Speech-Language Pathology, Speech therapy may be useful and is recommended to be started around nine months of age. As those with Down syndrome typically have good hand-eye coordination, learning sign language may be possible. Augmentative and alternative communication methods, such as pointing, body language, objects, or pictures, are often used to help with communication. Behavioral issues and mental illness are typically managed with counseling or medications. Education programs before reaching school age may be useful. School-age children with Down syndrome may benefit from inclusive education (whereby students of differing abilities are placed in classes with their peers of the same age), provided some adjustments are made to the curriculum. Evidence to support this, however, is not very strong. In the United States, the Individuals with Disabilities Education Act of 1975 requires public schools generally to allow attendance by students with Down syndrome. Individuals with Down syndrome may learn better visually. Drawing may help with language, speech, and reading skills. Children with Down syndrome still often have difficulty with sentence structure and grammar, as well as developing the ability to speak clearly. Several types of early intervention can help with cognitive development. Efforts to develop motor skills include physical therapy, speech and language therapy, and occupational therapy. Physical therapy focuses specifically on motor development and teaching children to interact with their environment. Speech and language therapy can help prepare for later language. Lastly, occupational therapy can help with skills needed for later independence.Other
Tympanostomy tubes are often needed and often more than one set during the person's childhood. Tonsillectomy is also often done to help with sleep apnea and pharyngitis, throat infections. Surgery, however, does not always address the sleep apnea and a continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) machine may be useful. Physical therapy and participation in physical education may improve motor skills. Evidence to support this in adults, however, is not very good. Efforts to prevent respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) infection with human monoclonal antibodies should be considered, especially in those with heart problems. In those who develop dementia there is no evidence for memantine, donepezil, rivastigmine, or galantamine. Plastic surgery has been suggested as a method of improving the appearance and thus the acceptance of people with Down syndrome. It has also been proposed as a way to improve speech. Evidence, however, does not support a meaningful difference in either of these outcomes. Plastic surgery on children with Down syndrome is uncommon, and continues to be controversial. The U.S. National Down Syndrome Society views the goal as one of mutual respect and acceptance, not appearance. Many alternative medical techniques are used in Down syndrome; however, they are poorly supported by evidence. These include: dietary changes, massage, animal therapy, chiropractic and naturopathy, among others. Some proposed treatments may also be harmful.Prognosis
Epidemiology
 Down syndrome is the most common chromosomal abnormality in humans. Globally, , Down syndrome occurs in about 1 per 1,000 births and results in about 17,000 deaths. More children are born with Down syndrome in countries where abortion is not allowed and in countries where pregnancy more commonly occurs at a later age. About 1.4 per 1,000 live births in the United States and 1.1 per 1,000 live births in Norway are affected. In the 1950s, in the United States, it occurred in 2 per 1,000 live births with the decrease since then due to prenatal screening and abortions. The number of pregnancies with Down syndrome is more than two times greater with many spontaneously aborting. It is the cause of 8% of all congenital disorders.
Maternal age effect, Maternal age affects the chances of having a pregnancy with Down syndrome. At age 20, the chance is 1 in 1,441; at age 30, it is 1 in 959; at age 40, it is 1 in 84; and at age 50 it is 1 in 44. Although the probability increases with maternal age, 70% of children with Down syndrome are born to women 35 years of age and younger, because younger people have more children. The Paternal age effect, father's older age is also a risk factor in women older than 35, but not in women younger than 35, and may partly explain the increase in risk as women age.
Down syndrome is the most common chromosomal abnormality in humans. Globally, , Down syndrome occurs in about 1 per 1,000 births and results in about 17,000 deaths. More children are born with Down syndrome in countries where abortion is not allowed and in countries where pregnancy more commonly occurs at a later age. About 1.4 per 1,000 live births in the United States and 1.1 per 1,000 live births in Norway are affected. In the 1950s, in the United States, it occurred in 2 per 1,000 live births with the decrease since then due to prenatal screening and abortions. The number of pregnancies with Down syndrome is more than two times greater with many spontaneously aborting. It is the cause of 8% of all congenital disorders.
Maternal age effect, Maternal age affects the chances of having a pregnancy with Down syndrome. At age 20, the chance is 1 in 1,441; at age 30, it is 1 in 959; at age 40, it is 1 in 84; and at age 50 it is 1 in 44. Although the probability increases with maternal age, 70% of children with Down syndrome are born to women 35 years of age and younger, because younger people have more children. The Paternal age effect, father's older age is also a risk factor in women older than 35, but not in women younger than 35, and may partly explain the increase in risk as women age.
Life expectancy
According to the Mayo Clinic, the average life expectancy of a person with Down syndrome is more than 60 years.History
 English physician John Langdon Down first described Down syndrome in 1862, recognizing it as a distinct type of mental disability, and again in a more widely published report in 1866. Édouard Séguin described it as separate from cretinism in 1844. By the 20th century, Down syndrome had become the most recognizable form of mental disability.
In antiquity, many infants with disabilities were either killed or abandoned.
In June 2020, the earliest incidence of Down syndrome was found in genomic evidence from an infant that was buried before 3200 BC at Poulnabrone dolmen in Ireland.
Researchers believe that a number of historical pieces of art portray Down syndrome, including pottery from the pre-Columbian Tumaco-La Tolita culture in present-day Colombia and Ecuador, and the 16th-century painting ''The Adoration of the Christ Child''.
In the 20th century, many individuals with Down syndrome were institutionalized, few of the associated medical problems were treated, and most people died in infancy or early adulthood. With the rise of the eugenics movement, 33 of the then 48 U.S. states and several countries began programs of forced sterilization of individuals with Down syndrome and comparable degrees of disability. Action T4 in Nazi Germany made public policy of a program of systematic Involuntary euthanasia, involuntary euthanization.
With the discovery of karyotype techniques in the 1950s it became possible to identify abnormalities of chromosomal number or shape. In 1959 Jérôme Lejeune reported the discovery that Down syndrome resulted from an extra chromosome. However, Lejeune's claim to the discovery has been disputed, and in 2014 the Scientific Council of the French Federation of Human Genetics unanimously awarded its Grand Prize to his colleague Marthe Gautier for her role in this discovery. The discovery took place in the laboratory of Raymond Turpin at the Hôpital Trousseau in Paris, France. Jérôme Lejeune and Marthe Gautier were both his students.
As a result of this discovery, the condition became known as trisomy 21. Even before the discovery of its cause, the presence of the syndrome in all races, its association with older maternal age, and its rarity of recurrence had been noticed. Medical texts had assumed it was caused by a combination of inheritable factors that had not been identified. Other theories had focused on injuries sustained during birth.
English physician John Langdon Down first described Down syndrome in 1862, recognizing it as a distinct type of mental disability, and again in a more widely published report in 1866. Édouard Séguin described it as separate from cretinism in 1844. By the 20th century, Down syndrome had become the most recognizable form of mental disability.
In antiquity, many infants with disabilities were either killed or abandoned.
In June 2020, the earliest incidence of Down syndrome was found in genomic evidence from an infant that was buried before 3200 BC at Poulnabrone dolmen in Ireland.
Researchers believe that a number of historical pieces of art portray Down syndrome, including pottery from the pre-Columbian Tumaco-La Tolita culture in present-day Colombia and Ecuador, and the 16th-century painting ''The Adoration of the Christ Child''.
In the 20th century, many individuals with Down syndrome were institutionalized, few of the associated medical problems were treated, and most people died in infancy or early adulthood. With the rise of the eugenics movement, 33 of the then 48 U.S. states and several countries began programs of forced sterilization of individuals with Down syndrome and comparable degrees of disability. Action T4 in Nazi Germany made public policy of a program of systematic Involuntary euthanasia, involuntary euthanization.
With the discovery of karyotype techniques in the 1950s it became possible to identify abnormalities of chromosomal number or shape. In 1959 Jérôme Lejeune reported the discovery that Down syndrome resulted from an extra chromosome. However, Lejeune's claim to the discovery has been disputed, and in 2014 the Scientific Council of the French Federation of Human Genetics unanimously awarded its Grand Prize to his colleague Marthe Gautier for her role in this discovery. The discovery took place in the laboratory of Raymond Turpin at the Hôpital Trousseau in Paris, France. Jérôme Lejeune and Marthe Gautier were both his students.
As a result of this discovery, the condition became known as trisomy 21. Even before the discovery of its cause, the presence of the syndrome in all races, its association with older maternal age, and its rarity of recurrence had been noticed. Medical texts had assumed it was caused by a combination of inheritable factors that had not been identified. Other theories had focused on injuries sustained during birth.
Society and culture
Name
Due to his perception that children with Down syndrome shared facial similarities with those of Mongoloid, Blumenbach's Mongolian race, John Langdon Down used the term "Mongolian idiocy, mongoloid". He felt that the existence of Down syndrome confirmed that all peoples were genetically related. In the 1950s with discovery of the underlying cause as being related to chromosomes, concerns about the race-based nature of the name increased. In 1961, a group of nineteen scientists suggested that "mongolism" had "misleading connotations" and had become "an embarrassing term". The World Health Organization (WHO) dropped the term in 1965 after a request by the delegation from the Mongolian People's Republic. While the term mongoloid (also mongolism, Mongolian imbecility or idiocy) continued to be used until the early 1980s, it is now considered unacceptable and is no longer in common use. In 1975, the United States National Institutes of Health (NIH) convened a conference to standardize the naming and recommended replacing the possessive form, "Down's syndrome" with "Down syndrome". However, both the possessive and nonpossessive forms remain in use by the general population. The term "trisomy 21" is also commonly used.Ethics
 Most obstetricians argue that not offering screening for Down syndrome is unethical. As it is a medically reasonable procedure, per informed consent, people should at least be given information about it. It will then be the woman's choice, based on her personal beliefs, how much or how little screening she wishes. When results from testing become available, it is also considered unethical not to give the results to the person in question.
Some bioethicists deem it reasonable for parents to select a child who would have the highest well-being. One criticism of this reasoning is that it often values those with disabilities less. Some parents argue that Down syndrome should not be prevented or cured and that eliminating Down syndrome amounts to genocide. The Disability rights, disability rights movement does not have a position on screening, although some members consider testing and abortion discriminatory. Some in the United States who are anti-abortion support abortion if the fetus is disabled, while others do not. Of a group of 40 mothers in the United States who have had one child with Down syndrome, half agreed to screening in the next pregnancy.
Within the US, some Protestant denominations see abortion as acceptable when a fetus has Down syndrome while Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox Christianity and Roman Catholics, Roman Catholicism do not. Some of those against screening refer to it as a form of eugenics. Disagreement exists within Islam regarding the acceptability of abortion in those carrying a fetus with Down syndrome. Some Islamic countries allow abortion, while others do not. Parents may be stigmatized whichever decision they make.
Most obstetricians argue that not offering screening for Down syndrome is unethical. As it is a medically reasonable procedure, per informed consent, people should at least be given information about it. It will then be the woman's choice, based on her personal beliefs, how much or how little screening she wishes. When results from testing become available, it is also considered unethical not to give the results to the person in question.
Some bioethicists deem it reasonable for parents to select a child who would have the highest well-being. One criticism of this reasoning is that it often values those with disabilities less. Some parents argue that Down syndrome should not be prevented or cured and that eliminating Down syndrome amounts to genocide. The Disability rights, disability rights movement does not have a position on screening, although some members consider testing and abortion discriminatory. Some in the United States who are anti-abortion support abortion if the fetus is disabled, while others do not. Of a group of 40 mothers in the United States who have had one child with Down syndrome, half agreed to screening in the next pregnancy.
Within the US, some Protestant denominations see abortion as acceptable when a fetus has Down syndrome while Eastern Orthodox Church, Orthodox Christianity and Roman Catholics, Roman Catholicism do not. Some of those against screening refer to it as a form of eugenics. Disagreement exists within Islam regarding the acceptability of abortion in those carrying a fetus with Down syndrome. Some Islamic countries allow abortion, while others do not. Parents may be stigmatized whichever decision they make.
Advocacy groups
Advocacy groups for individuals with Down syndrome began to be formed after the World War II, Second World War. These were organizations advocating for the inclusion of people with Down syndrome into the general school system and for a greater understanding of the condition among the general population, as well as groups providing support for families with children living with Down syndrome. Before this individuals with Down syndrome were often placed in History of psychiatric institutions, mental hospitals or asylums. Organizations included the Mencap, Royal Society for Handicapped Children and Adults founded in the UK in 1946 by Judy Fryd, Kobato Kai founded in Japan in 1964, the National Down Syndrome Congress founded in the United States in 1973 by Kathryn McGee and others, and the National Down Syndrome Society founded in 1979 in the United States. The first Roman Catholic order of nuns for women with Down Syndrome, Little Sisters Disciples of the Lamb, was founded in 1985 in France. The first World Down Syndrome Day was held on 21 March 2006. The day and month were chosen to correspond with 21 and trisomy, respectively. It was recognized by the United Nations General Assembly in 2011.Research
Efforts are underway to determine how the extra chromosome 21 material causes Down syndrome, as currently this is unknown, and to develop treatments to improve intelligence in those with the syndrome. Two efforts being studied are the use stem cells and gene therapy. Other methods being studied include the use of antioxidants, gamma secretase inhibition, adrenergic agonists, and memantine. Research is often carried out on an animal model, the mouse models of Down syndrome, Ts65Dn mouse.Other hominids
Down syndrome may also occur in hominidae, hominids other than humans. In great apes chromosome 22 corresponds to the human chromosome 21 and thus trisomy 22 causes Down syndrome in apes. The condition was observed in a common chimpanzee in 1969 and a Bornean orangutan in 1979, but neither lived very long. The common chimpanzee Kanako (born around 1993, in Japan) has become the longest-lived known example of this condition. Kanako has some of the same symptoms that are common in human Down syndrome. It is unknown how common this condition is in chimps but it is plausible it could be roughly as common as Down syndrome is in humans.In popular culture
*Struck by Lightning (1990 film), ''Struck by Lightning'', an Australian film by Jerzy Domaradzki and starring Garry McDonald, is a comedy-drama depicting the efforts by a newly appointed physical education teacher to introduce soccer to a specialized school for youths with Down syndrome.References
External links
* Thompson, S.B.N. (2000). "The Central Executive System in people with Down's syndrome and dementia". Clinical Gerontologist. 21 (3): 3–32. Taylor & Francis (Routledge). Digital object identifier, DOI 10.1300/j018v21n03_02. eISSN 1545-2301. OCLC 1106716083. S2CID 218575706. * Thompson, S.B.N. (2000). "Investigation into Down's syndrome and dementia". ''Journal of the Association of Practitioners in Learning Disability, 17''(3): 10–14. * Thompson, S.B.N. (1999). "Examining dementia in Down's syndrome (DS): decline in social abilities in DS compared with other learning disabilities". ''Clinical Gerontologist, 20''(3): 23–44. Taylor & Francis (Routledge). Digital object identifier, DOI 10.1300/j018v20n03_04 eISSN 1545-2301 OCLC 1106716083 *External links
*Down's syndrome
by the UK National Health Service {{Authority control Down syndrome, Autosomal trisomies Chromosomal abnormalities Genetic diseases and disorders Genetic syndromes Intellectual disability Wikipedia medicine articles ready to translate (full) Syndromes affecting the gastrointestinal tract Syndromes affecting the heart Syndromes affecting the nervous system Syndromes with craniofacial abnormalities