Donetsk Region on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Donetsk Oblast ( ukr, Донецька область, Donetska oblast, ), also referred to as Donechchyna ( ukr, Донеччина, links=no), is an

 In 2013, the population of Donetsk Oblast was 4.43 million, which constituted 10% of the overall Ukrainian population, making it the most populous and most densely populated region of the country. Its large population is due to the presence of several big industrial cities and numerous villages agglomerated around them.
During the 2004 Ukrainian presidential election, 2004 presidential election, political supporters of Viktor Yanukovych threatened to demand Autonomous administrative division, autonomy for Donetsk and neighboring oblasts if the election of their candidate was not recognised. However, no official moves were ever made.
At the Ukrainian Census (2001), 2001 Ukrainian National Census, the ethnic groups within the Donetsk Oblast were: Ukrainians – 2,744,100 (56.9%), Russians – 1,844,400 (38.2%), Pontic Greeks – 77,500 (1.6%), Belarusians – 44,500 (0.9%), others (2.3%).Ukrcensus.gov.ua — Donetsk region
In 2013, the population of Donetsk Oblast was 4.43 million, which constituted 10% of the overall Ukrainian population, making it the most populous and most densely populated region of the country. Its large population is due to the presence of several big industrial cities and numerous villages agglomerated around them.
During the 2004 Ukrainian presidential election, 2004 presidential election, political supporters of Viktor Yanukovych threatened to demand Autonomous administrative division, autonomy for Donetsk and neighboring oblasts if the election of their candidate was not recognised. However, no official moves were ever made.
At the Ukrainian Census (2001), 2001 Ukrainian National Census, the ethnic groups within the Donetsk Oblast were: Ukrainians – 2,744,100 (56.9%), Russians – 1,844,400 (38.2%), Pontic Greeks – 77,500 (1.6%), Belarusians – 44,500 (0.9%), others (2.3%).Ukrcensus.gov.ua — Donetsk region
URL accessed on 13 January 2007 At the 2001 census, the languages spoken within the oblast were: Russian (spoken by 98.6% of Russians living there, 58.7% of Ukrainians, 58.7% of Greeks, and 85.5% of Belarusians) and Ukrainian language, Ukrainian (spoken by 41.2% of Ukrainians, 1.3% of Russians, 3.2% of Greeks, and 3.9% of Belarusians). The oblast also contains 21% of the country's Muslims.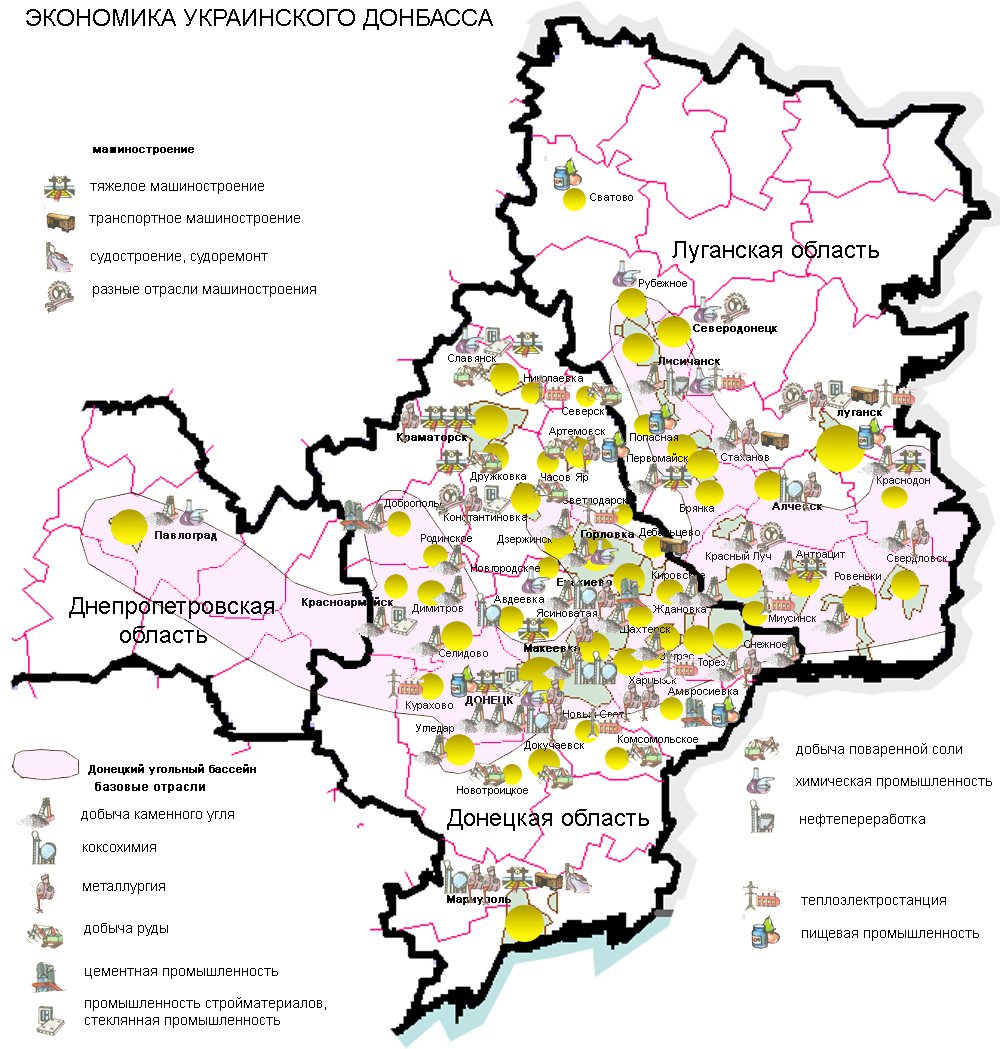
URL accessed on 13 January 2007 The oblast has a developed transport infrastructure which includes the Donetsk railway (covers 40% of national transportation), the Mariupol Port, the Donetsk International Airport, passenger airports in
Information Card of the Region
– Official site of the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine
www.citylife.donetsk.ua
– Official Donetsk city guide – English
donoda.gov.ua
– Official site of Donetsk Oblast Administration
catalogue.biz.ua
– Post codes directory of Donetsk Oblast * {{Authority control Donetsk Oblast, Oblasts of Ukraine States and territories established in 1938 1938 establishments in Ukraine Donbas De-Stalinization Ukrainian territories claimed by Russia
oblast
An oblast (; ; Cyrillic (in most languages, including Russian and Ukrainian): , Bulgarian: ) is a type of administrative division of Belarus, Bulgaria, Kazakhstan, Kyrgyzstan, Russia, and Ukraine, as well as the Soviet Union and the Kingdo ...
of eastern Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
. It is Ukraine's most populous province, with around 4.1 million residents. Its administrative centre is Donetsk
Donetsk ( , ; uk, Донецьк, translit=Donets'k ; russian: Донецк ), formerly known as Aleksandrovka, Yuzivka (or Hughesovka), Stalin and Stalino (see also: cities' alternative names), is an industrial city in eastern Ukraine loca ...
; however, its Regional State Administration has been temporarily relocated to Kramatorsk
Kramatorsk ( uk, Краматорськ, translit=Kramatorsk ) is a city and the administrative centre of Kramatorsk Raion in the northern portion of Donetsk Oblast, in eastern Ukraine. Prior to 2020, Kramatorsk was a city of oblast significan ...
because of the ongoing Russo-Ukrainian war
The Russo-Ukrainian War; uk, російсько-українська війна, rosiisko-ukrainska viina. has been ongoing between Russia (alongside Russian separatists in Ukraine) and Ukraine since February 2014. Following Ukraine's Rev ...
. Historically, the region has been an important part of the Donbas region. From its creation in 1938 until November 1961, it bore the name ''Stalino Oblast'' as Donetsk was then named "Stalino", in honour of Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secretar ...
. As part of the de-Stalinization process, it was renamed after the Siversky Donets
The Seversky Donets () or Siverskyi Donets (), usually simply called the Donets, is a river on the south of the East European Plain. It originates in the Central Russian Upland, north of Belgorod, flows south-east through Ukraine (Kharkiv, Done ...
river, the main artery of Eastern Ukraine
Eastern Ukraine or east Ukraine ( uk, Східна Україна, Skhidna Ukrayina; russian: Восточная Украина, Vostochnaya Ukraina) is primarily the territory of Ukraine east of the Dnipro (or Dnieper) river, particularly Khar ...
. Its population is estimated as
The oblast is known for its urban sprawl
Urban sprawl (also known as suburban sprawl or urban encroachment) is defined as "the spreading of urban developments (such as houses and shopping centers) on undeveloped land near a city." Urban sprawl has been described as the unrestricted growt ...
of Donetsk
Donetsk ( , ; uk, Донецьк, translit=Donets'k ; russian: Донецк ), formerly known as Aleksandrovka, Yuzivka (or Hughesovka), Stalin and Stalino (see also: cities' alternative names), is an industrial city in eastern Ukraine loca ...
–Makiivka
Makiivka ( uk, Макіївка, Makíyivka, ; russian: Макеевка, Makeyevka, ), formerly Dmytriivsk, is an industrial city in Donetsk Oblast in eastern Ukraine. Located from the capital Donetsk, the two cities are practically a conurbati ...
and Horlivka
Horlivka ( , ; uk, Го́рлівка ), or Gorlovka (russian: link=no, Горловка ), is a city of regional significance in Donetsk Oblast, Ukraine.
In 2001, the city's population was 292,000, and it was estimated as Economic activi ...
–Yenakiieve
Yenakiieve ( uk, Єна́кієве, ''Yenákiieve'', ; russian: Ена́киево, ''Yenákiyevo'') is a city in the Donetsk Oblast (province) of eastern Ukraine. It is incorporated as a city of oblast significance (a special status within t ...
and it is often associated with the coal mining industry.
The war in Donbas
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular o ...
and the subsequent 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
On 24 February 2022, in a major escalation of the Russo-Ukrainian War, which began in 2014. The invasion has resulted in tens of thousands of deaths on both sides. It has caused Europe's largest refugee crisis since World War II. ...
has seen parts of the oblast come under the control of the self-proclaimed Donetsk People's Republic and Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
, with the administrative center relocated to Mariupol
Mariupol (, ; uk, Маріу́поль ; russian: Мариу́поль) is a city in Donetsk Oblast, Ukraine. It is situated on the northern coast ( Pryazovia) of the Sea of Azov, at the mouth of the Kalmius River. Prior to the 2022 Russia ...
then to Kramatorsk
Kramatorsk ( uk, Краматорськ, translit=Kramatorsk ) is a city and the administrative centre of Kramatorsk Raion in the northern portion of Donetsk Oblast, in eastern Ukraine. Prior to 2020, Kramatorsk was a city of oblast significan ...
. The oblast is notable for heavy fighting during the Battle of Donbas (2022)
The Battle of Donbas is an ongoing military offensive that is part of the wider eastern Ukraine offensive of the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine. The battle began on 18 April 2022 between the armed forces of Russia and Ukraine for control of ...
.
On 30 September 2022 Russia annexed the Donetsk (DPR), Luhansk
Luhansk (, ; uk, Луганськ, ), also known as Lugansk (, ; russian: Луганск, ), is a city in what is internationally recognised as Ukraine, although it is administered by Russia as capital of the Luhansk People's Republic (LPR). A ...
(Luhansk People's Republic
The Luhansk or Lugansk People's Republic (russian: Луга́нская Наро́дная Респу́блика, Luganskaya Narodnaya Respublika, ; abbreviated as LPR or LNR, rus, ЛНР) is a disputed entity created by Russian-backed ...
), Zaporizhzhia
Zaporizhzhia ( uk, Запоріжжя) or Zaporozhye (russian: Запорожье) is a city in southeast Ukraine, situated on the banks of the Dnieper River. It is the administrative centre of Zaporizhzhia Oblast. Zaporizhzhia has a populat ...
, and Kherson Oblasts. However, the staged referendums
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of a ...
and subsequent annexations are internationally unrecognized, and Ukraine still controls much of the province. The United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
General Assembly
A general assembly or general meeting is a meeting of all the members of an organization or shareholders of a company.
Specific examples of general assembly include:
Churches
* General Assembly (presbyterian church), the highest court of presb ...
subsequently passed a resolution
Resolution(s) may refer to:
Common meanings
* Resolution (debate), the statement which is debated in policy debate
* Resolution (law), a written motion adopted by a deliberative body
* New Year's resolution, a commitment that an individual mak ...
calling on countries not to recognise what it described as an "attempted illegal annexation" and demanded that Russia "immediately, completely and unconditionally withdraw".
History
Before the establishment of the Donetsian Oblast, three districts ( okruhas) existed on its territory from 1923 to 1930. TheDonets Governorate
Donets Governorate ( uk, Донецька губернія, translit=Donetska huberniia) was a gubernia, governorate of the Ukrainian SSR (Ukraine) that existed between 1919 and 1925.
History
The governorate was originally created on 5 February 19 ...
was terminated in 1925. As part of Soviet Ukraine
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic ( uk, Украї́нська Радя́нська Соціалісти́чна Респу́бліка, ; russian: Украи́нская Сове́тская Социалисти́ческая Респ ...
, the Donetsian Oblast was established on 2 July 1932 out of the Kharkiv Oblast, the Dnipropetrovsk Oblast and a number of raions that were under the direct administration of Kharkiv (then-capital of Soviet Ukraine
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic ( uk, Украї́нська Радя́нська Соціалісти́чна Респу́бліка, ; russian: Украи́нская Сове́тская Социалисти́ческая Респ ...
). Artemivsk (today Bakhmut) served as the Oblast's administrative center for two weeks until 16 July 1932, when the city of Stalino (today Donetsk
Donetsk ( , ; uk, Донецьк, translit=Donets'k ; russian: Донецк ), formerly known as Aleksandrovka, Yuzivka (or Hughesovka), Stalin and Stalino (see also: cities' alternative names), is an industrial city in eastern Ukraine loca ...
) took on the role. Until 1938, the Donetsian Oblast included the territories of the modern Donetsk Oblast and the Luhansk Oblast. In June 1938 it was split into the Stalino Oblast (modern Donetsk Oblast) and the Voroshylovhrad Oblast (modern Luhansk Oblast).
During the Reichskommissariat Ukraine, Nazi German occupation from fall 1941 to fall 1943, Donetsk Oblast was known as Yuzivka Oblast (after the original name of Donetsk
Donetsk ( , ; uk, Донецьк, translit=Donets'k ; russian: Донецк ), formerly known as Aleksandrovka, Yuzivka (or Hughesovka), Stalin and Stalino (see also: cities' alternative names), is an industrial city in eastern Ukraine loca ...
).
As part of de-Stalinization in the Soviet Union, in 1961 Stalino along with Stalino Oblast were renamed into Donetsk and Donetsk Oblast, respectively.
During the dissolution of the Soviet Union, 83.9% of voters in Donetsk Oblast approved Ukraine's declaration of independence in the 1991 Ukrainian independence referendum, 1991 referendum.
In the mid-1990s, the region became known for its heightened criminal activity, including the killings of high-profile business people such as Akhat Bragin and Yevhen Shcherban. Donetsk Oblast was also a base for Ukraine's main pro-Russian political faction, Party of Regions, which became part of the Ukrainian government in 2002 and paved a way into Ukrainian politics for the powerful "Donetsk political clan".
In late 2004, the Party of Regions was involved in the creation of a political project, South-East Ukrainian Autonomous Republic, which intended to include Donetsk Oblast. Having close ties with the Russian government, the Party of Regions along with local communists and pro-Russian activists instigated the 2014 pro-Russian unrest in Ukraine, pro-Russian unrest which escalated into the war in Donbas
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular o ...
. In May 2014 Ukraine lost control over its border with Russia in Donetsk Oblast. Currently, portions of the region are controlled by the Separatist forces of the war in Donbas, Novorossiya Armed Forces and claimed by the self-proclaimed Donetsk People's Republic.
Geography
Donetsk Oblast is located in southeastern Ukraine. The area of the oblast (26,517 km2), comprises about 4.4% of the total area of the country. The oblast borders the Dnipropetrovsk Oblast, Dnipropetrovsk and Zaporizhzhia Oblasts on the southwest, the Kharkiv Oblast on the north, the Luhansk Oblast on the northeast, the Rostov Oblast in Russia on the east, and with the Sea of Azov on the south. Its longitude from north to south is 270 km, from east to west – 190 km. The extreme points of the oblast's borders are: ''Bilosarayska Kosa'' (Spit (landform), spit) on the south, Shevchenko of Velykonovosilkivskyi Raion on the west, ''Verkhnyi Kut'' of Shakhtarskyi Raion on the east, and ''Lozove'' of Lyman Raion, Donetsk Oblast, Lyman Raion on the north. The state historic-architectural preserve near the city of Sviatohirsk with the Sviatohirsk Lavra was nominated for the Seven Wonders of Ukraine.

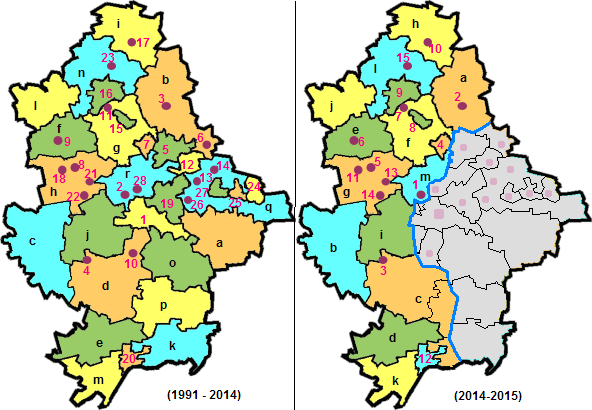
Administrative divisions
The province is primarily divided into 18 ''raions'' (districts) and 28 municipalities of equal status (22 ''miskradas'' and 6 ''mistos'' – cities of regional significance), including the provincial administrative centerDonetsk
Donetsk ( , ; uk, Донецьк, translit=Donets'k ; russian: Донецк ), formerly known as Aleksandrovka, Yuzivka (or Hughesovka), Stalin and Stalino (see also: cities' alternative names), is an industrial city in eastern Ukraine loca ...
. These are listed below with their areas and populations.State Statistics Committee of Ukraine, Kiev.
The province's secondary division consists of various municipalities that are governed by their councils. Those municipalities may consist of one or more populated places. All are administratively subordinate to the raion in which they are located.
The following data incorporates the number of each type of second-level administrative divisions of Donetsk Oblast:
* total of Settlements – 1,283, including:
** Villages – 1,124;
** Cities/Towns – 159, including:
*** Urban-type settlement – List of urban-type settlements in Ukraine by subdivision#Donetsk Oblast, 131;
*** Cities of raion subordinance – 24;
* selsoviet, Selsovets – ''N/A''.
The local administration of the oblast' is controlled by the Donetsk Oblast Rada. The governor of the oblast' is the Head of Donetsk Oblast administration, appointed by the President of Ukraine.
Cities
* regional municipalitiesDemographics
 In 2013, the population of Donetsk Oblast was 4.43 million, which constituted 10% of the overall Ukrainian population, making it the most populous and most densely populated region of the country. Its large population is due to the presence of several big industrial cities and numerous villages agglomerated around them.
During the 2004 Ukrainian presidential election, 2004 presidential election, political supporters of Viktor Yanukovych threatened to demand Autonomous administrative division, autonomy for Donetsk and neighboring oblasts if the election of their candidate was not recognised. However, no official moves were ever made.
At the Ukrainian Census (2001), 2001 Ukrainian National Census, the ethnic groups within the Donetsk Oblast were: Ukrainians – 2,744,100 (56.9%), Russians – 1,844,400 (38.2%), Pontic Greeks – 77,500 (1.6%), Belarusians – 44,500 (0.9%), others (2.3%).Ukrcensus.gov.ua — Donetsk region
In 2013, the population of Donetsk Oblast was 4.43 million, which constituted 10% of the overall Ukrainian population, making it the most populous and most densely populated region of the country. Its large population is due to the presence of several big industrial cities and numerous villages agglomerated around them.
During the 2004 Ukrainian presidential election, 2004 presidential election, political supporters of Viktor Yanukovych threatened to demand Autonomous administrative division, autonomy for Donetsk and neighboring oblasts if the election of their candidate was not recognised. However, no official moves were ever made.
At the Ukrainian Census (2001), 2001 Ukrainian National Census, the ethnic groups within the Donetsk Oblast were: Ukrainians – 2,744,100 (56.9%), Russians – 1,844,400 (38.2%), Pontic Greeks – 77,500 (1.6%), Belarusians – 44,500 (0.9%), others (2.3%).Ukrcensus.gov.ua — Donetsk regionURL accessed on 13 January 2007 At the 2001 census, the languages spoken within the oblast were: Russian (spoken by 98.6% of Russians living there, 58.7% of Ukrainians, 58.7% of Greeks, and 85.5% of Belarusians) and Ukrainian language, Ukrainian (spoken by 41.2% of Ukrainians, 1.3% of Russians, 3.2% of Greeks, and 3.9% of Belarusians). The oblast also contains 21% of the country's Muslims.

Age structure
: ''0–14 years:'' 12.6% (male 283,584/female 266,977) : ''15–64 years:'' 70.4% (male 1,453,273/female 1,619,241) : ''65 years and over:'' 17.0% (male 243,048/female 496,434) (2013 official)Median age
: ''total:'' 41.9 years : ''male:'' 38.0 years : ''female:'' 45.8 years (2013 official)Economy
Industry
The Donetsk Oblast accounts for more than one half of the coal, finished steel, coke, cast iron and steel production in Ukraine. Ferrous metallurgy, fuel industry and power industry are in demand in the structure of industry production. There are about 882 industry enterprises that are on independent balance, and 2,095 small industry enterprises in the oblast.Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine — Donetsk RegionURL accessed on 13 January 2007 The oblast has a developed transport infrastructure which includes the Donetsk railway (covers 40% of national transportation), the Mariupol Port, the Donetsk International Airport, passenger airports in
Mariupol
Mariupol (, ; uk, Маріу́поль ; russian: Мариу́поль) is a city in Donetsk Oblast, Ukraine. It is situated on the northern coast ( Pryazovia) of the Sea of Azov, at the mouth of the Kalmius River. Prior to the 2022 Russia ...
and Kramatorsk
Kramatorsk ( uk, Краматорськ, translit=Kramatorsk ) is a city and the administrative centre of Kramatorsk Raion in the northern portion of Donetsk Oblast, in eastern Ukraine. Prior to 2020, Kramatorsk was a city of oblast significan ...
, and dense road systems. In the Donetsk Oblast two special economic zones have been created, ''Donetsk'' and ''Azov'', which have a privileged tax regime.
Agriculture
In 1999, the gross grain yield in the oblast was about 999.1 thousand tons, sugar beets – 27.1 thousand tons, sunflower seeds – 309.4 thousand tons, and potatoes – 380.2 thousand tons. Also, 134.2 thousand tons of meat, 494.3 thousand tons of milk and 646.4 million eggs have been produced. At the beginning of 1999 there were 2108 farms within the oblast.Geology
The Donetsk Oblast's climate is mostly continental, which is characterised by hot summers and relatively cold winters with changeable snow surfaces. East and southeast strong winds, high temperatures and heavy rain showers are typical in the summer. The average annual rainfall is 524 mm. The basic minerals found here are: coal (reserves – 25 billion tons), Halite, rock salt, lime carbonate, potassium, mercury (element), mercury, asbestos, and graphite. The area is also rich in fertile black earth. Important resources for recreation within the area are: the mild climate, the Sea of Azov coast, curative mud, sources of minerals, and radon and table water. Due to these numerous recreation resources, many resort hotels and camps are located here. There are about 26 health centres and pensions, 52 rest homes and boarding houses, and rest camps for children in the oblast. The curative areas in the oblast include the Slovyansk salt lakes and mineral water sources. The oblast also contains many park zones, some of which are of great national value. They include the Khomutivsky steppe and the Azov sea coast. Overall, the Donetsk Oblast contains about 70 protected park and nature attractions including branches of the Ukrainian steppe park, six state reserves, ten memorials of nature, landscapes, and six park tracts.Polls
During the 1991 Ukrainian independence referendum, 1991 referendum, 83.90% of votes in Donetsk Oblast were in favour of the Declaration of Independence of Ukraine, fourth lowest in the country after Crimea, Sevastopol and Luhansk Oblast. A survey conducted in December 2014 by the Kyiv International Institute of Sociology found 18.5% of the oblast's population supported their region joining Russia, 53.8% did not support the idea, 22.5% were undecided, and 5.2% did not respond; insurgent-controlled areas (which hold over 50% of the population) were not polled.See also
* Administrative divisions of Ukraine * List of cities in Donetsk OblastReferences
External links
Information Card of the Region
– Official site of the Cabinet of Ministers of Ukraine
www.citylife.donetsk.ua
– Official Donetsk city guide – English
donoda.gov.ua
– Official site of Donetsk Oblast Administration
catalogue.biz.ua
– Post codes directory of Donetsk Oblast * {{Authority control Donetsk Oblast, Oblasts of Ukraine States and territories established in 1938 1938 establishments in Ukraine Donbas De-Stalinization Ukrainian territories claimed by Russia