Dolby AC-3 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Dolby Digital, originally synonymous with Dolby AC-3, is the name for what has now become a family of audio compression technologies developed by
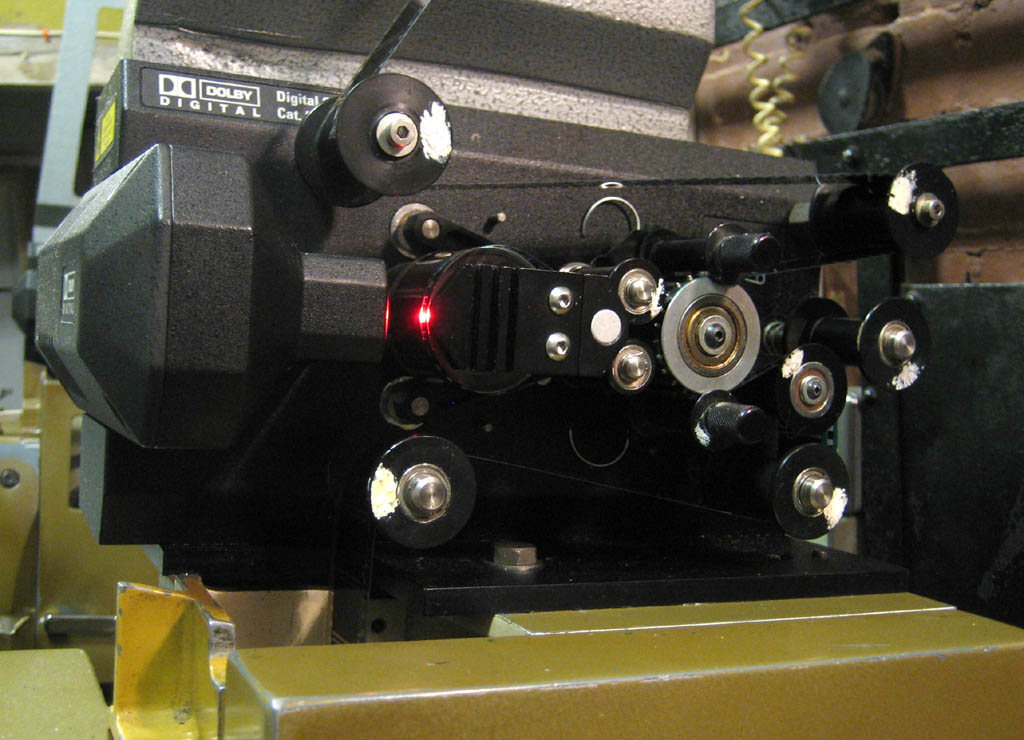
 The simplest way of converting existing projectors is to add a so-called ''penthouse'' digital soundhead above the projector head. However, for new projectors it made sense to use dual analogue/digital soundheads in the normal optical soundhead position under the projector head. To allow for the dual-soundhead arrangement the data is recorded 26 frames ahead of the picture. If a penthouse soundhead is used, the data must be delayed in the processor for the required amount of time, around 2 seconds. This delay can be adjusted in steps of the time between perforations, (approximately 10.4 ms).
, Dolby Digital in film sound mixing has mostly been replaced with Dolby Surround 7.1, with the more advanced Dolby Atmos technology also gaining in popularity. While the majority of movie theaters currently utilize Dolby Digital, virtually all films released today are mixed in Dolby Surround 7.1 and Dolby Atmos. Also more theaters are gradually upgrading to Dolby Surround 7.1, which completes by 2028, with premium formats adopting
The simplest way of converting existing projectors is to add a so-called ''penthouse'' digital soundhead above the projector head. However, for new projectors it made sense to use dual analogue/digital soundheads in the normal optical soundhead position under the projector head. To allow for the dual-soundhead arrangement the data is recorded 26 frames ahead of the picture. If a penthouse soundhead is used, the data must be delayed in the processor for the required amount of time, around 2 seconds. This delay can be adjusted in steps of the time between perforations, (approximately 10.4 ms).
, Dolby Digital in film sound mixing has mostly been replaced with Dolby Surround 7.1, with the more advanced Dolby Atmos technology also gaining in popularity. While the majority of movie theaters currently utilize Dolby Digital, virtually all films released today are mixed in Dolby Surround 7.1 and Dolby Atmos. Also more theaters are gradually upgrading to Dolby Surround 7.1, which completes by 2028, with premium formats adopting

ATSC "Digital Audio Compression (AC-3) (E-AC-3) Standard"
section 5.4.
liba52
is available under the
ATSC standardsDigital Audio Compression Standard (AC-3, E-AC-3)
at the ATSC website {{Video formats American inventions Audio codecs Consumer electronics Dolby Laboratories Film sound production High-definition television Surround sound Audiovisual introductions in 1986 Development organizations
Dolby Laboratories
Dolby Laboratories, Inc. (often shortened to Dolby Labs and known simply as Dolby) is an American company specializing in audio noise reduction, audio encoding/compression, spatial audio, and HDR imaging. Dolby licenses its technologies to ...
. Formerly named Dolby Stereo Digital until 1995, the audio compression is lossy
In information technology, lossy compression or irreversible compression is the class of data compression methods that uses inexact approximations and partial data discarding to represent the content. These techniques are used to reduce data si ...
(except for Dolby TrueHD), based on the modified discrete cosine transform
The modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT) is a transform based on the type-IV discrete cosine transform (DCT-IV), with the additional property of being lapped: it is designed to be performed on consecutive blocks of a larger dataset, where ...
(MDCT) algorithm. The first use of Dolby Digital was to provide digital sound in cinemas from 35 mm film prints; today, it is also used for applications such as TV broadcast, radio broadcast via satellite, digital video streaming, DVDs, Blu-ray
The Blu-ray Disc (BD), often known simply as Blu-ray, is a digital optical disc data storage format. It was invented and developed in 2005 and released on June 20, 2006 worldwide. It is designed to supersede the DVD format, and capable of st ...
discs and game consoles.
The main basis of the Dolby AC-3 multi-channel audio coding standard
An audio coding format (or sometimes audio compression format) is a content representation format for storage or transmission of digital audio (such as in digital television, digital radio and in audio and video files). Examples of audio coding f ...
is the modified discrete cosine transform
The modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT) is a transform based on the type-IV discrete cosine transform (DCT-IV), with the additional property of being lapped: it is designed to be performed on consecutive blocks of a larger dataset, where ...
(MDCT), a lossy
In information technology, lossy compression or irreversible compression is the class of data compression methods that uses inexact approximations and partial data discarding to represent the content. These techniques are used to reduce data si ...
audio compression algorithm. It is a modification of the discrete cosine transform (DCT) algorithm, which was first proposed by Nasir Ahmed in 1972 and was originally intended for image compression. The DCT was adapted into the modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT) by J.P. Princen, A.W. Johnson and Alan B. Bradley at the University of Surrey in 1987.
Dolby Laboratories
Dolby Laboratories, Inc. (often shortened to Dolby Labs and known simply as Dolby) is an American company specializing in audio noise reduction, audio encoding/compression, spatial audio, and HDR imaging. Dolby licenses its technologies to ...
adapted the MDCT algorithm along with perceptual coding principles to develop the AC-3 audio format for cinema needs. The AC-3 format was released as the Dolby Digital standard in February 1991. Dolby Digital was the earliest MDCT-based audio compression standard to be released, and was followed by other MDCT-based audio compression standards for home and portable usage, such as Sony
, commonly stylized as SONY, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. As a major technology company, it operates as one of the world's largest manufacturers of consumer and professional ...
's ATRAC
Adaptive Transform Acoustic Coding (ATRAC) is a family of proprietary audio compression algorithms developed by Sony. MiniDisc was the first commercial product to incorporate ATRAC in 1992. ATRAC allowed a relatively small disc like MiniDisc to h ...
(1992), the MP3 standard (1993) and AAC (1997).
Cinema
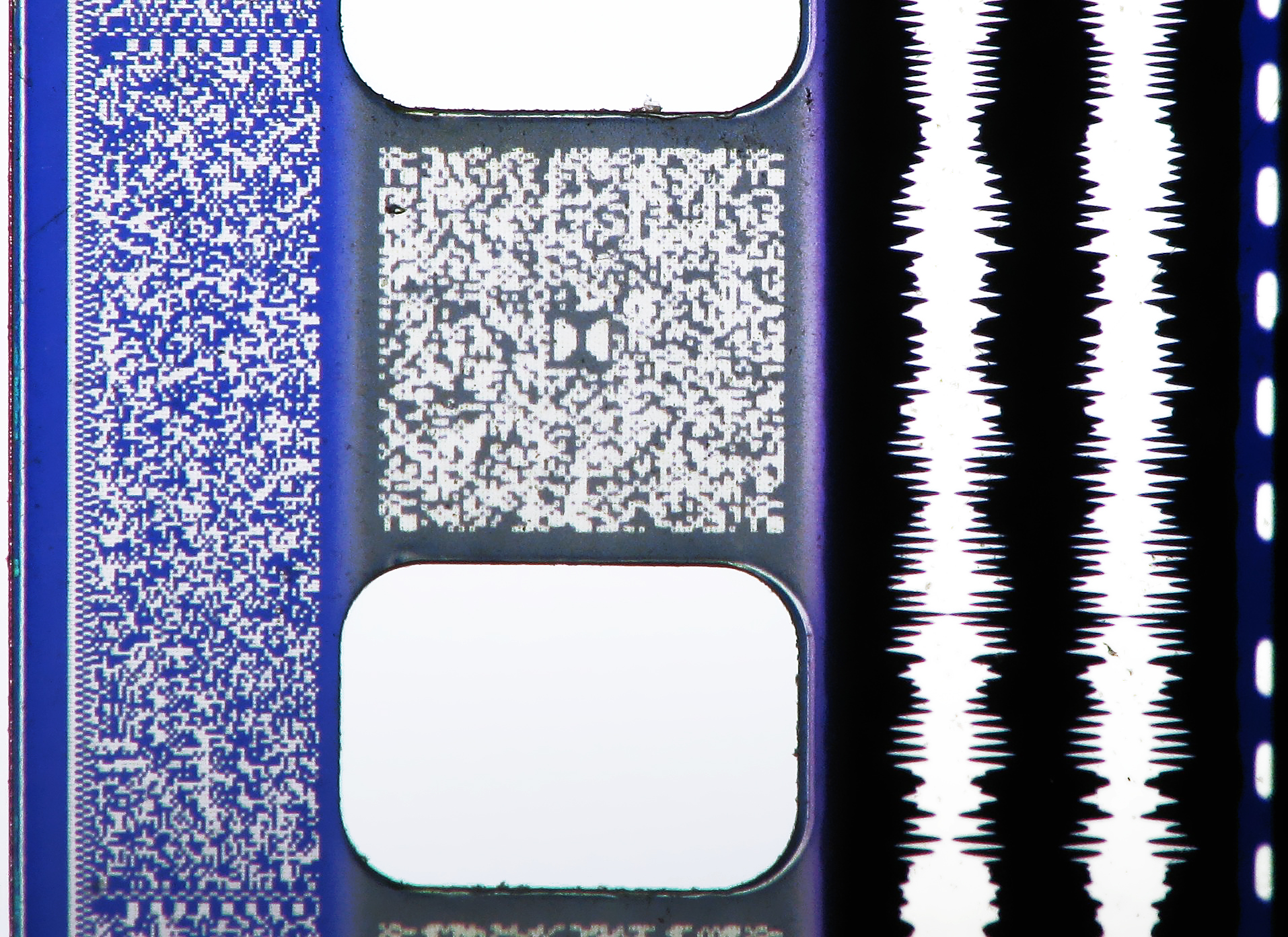
'' Batman Returns'' was the first film to be announced as using Dolby SR-D (Spectral Recording-Digital) technology when it premiered in theaters in the summer of 1992. Dolby Digital cinema soundtracks are optically recorded on a 35 mm release print using sequential data blocks placed between every perforation hole on the sound track side of the film. A constant bit rate of 320 kbit/s is used. A charge-coupled device (CCD) scanner in theimage projector
A projector or image projector is an optical device that projects an image (or moving images) onto a surface, commonly a projection screen. Most projectors create an image by shining a light through a small transparent lens, but some newer typ ...
picks up a scanned video image of this area, and a processor correlates the image area and extracts the digital data as an AC-3 bitstream
A bitstream (or bit stream), also known as binary sequence, is a sequence of bits.
A bytestream is a sequence of bytes. Typically, each byte is an 8-bit quantity, and so the term octet stream is sometimes used interchangeably. An octet may ...
. The data is then decoded into a 5.1 channel audio source. All film prints with Dolby Digital data also have Dolby Stereo analogue soundtracks using Dolby SR noise reduction and such prints are known as Dolby SR-D prints. The analogue soundtrack provides a fall-back option in case of damage to the data area or failure of the digital decoding; it also provides compatibility with projectors not equipped with digital soundheads. Almost all current release cinema prints are of this type and may also include SDDS
is a cinema sound system developed by Sony, in which compressed digital sound information is recorded on both outer edges of the 35 mm film release print. The system supports up to eight independent channels of sound: five front chann ...
data and a timecode track to synchronize CD-ROMs carrying DTS soundtracks.

 The simplest way of converting existing projectors is to add a so-called ''penthouse'' digital soundhead above the projector head. However, for new projectors it made sense to use dual analogue/digital soundheads in the normal optical soundhead position under the projector head. To allow for the dual-soundhead arrangement the data is recorded 26 frames ahead of the picture. If a penthouse soundhead is used, the data must be delayed in the processor for the required amount of time, around 2 seconds. This delay can be adjusted in steps of the time between perforations, (approximately 10.4 ms).
, Dolby Digital in film sound mixing has mostly been replaced with Dolby Surround 7.1, with the more advanced Dolby Atmos technology also gaining in popularity. While the majority of movie theaters currently utilize Dolby Digital, virtually all films released today are mixed in Dolby Surround 7.1 and Dolby Atmos. Also more theaters are gradually upgrading to Dolby Surround 7.1, which completes by 2028, with premium formats adopting
The simplest way of converting existing projectors is to add a so-called ''penthouse'' digital soundhead above the projector head. However, for new projectors it made sense to use dual analogue/digital soundheads in the normal optical soundhead position under the projector head. To allow for the dual-soundhead arrangement the data is recorded 26 frames ahead of the picture. If a penthouse soundhead is used, the data must be delayed in the processor for the required amount of time, around 2 seconds. This delay can be adjusted in steps of the time between perforations, (approximately 10.4 ms).
, Dolby Digital in film sound mixing has mostly been replaced with Dolby Surround 7.1, with the more advanced Dolby Atmos technology also gaining in popularity. While the majority of movie theaters currently utilize Dolby Digital, virtually all films released today are mixed in Dolby Surround 7.1 and Dolby Atmos. Also more theaters are gradually upgrading to Dolby Surround 7.1, which completes by 2028, with premium formats adopting Dolby Cinema
Dolby Cinema is a premium cinema created by Dolby Laboratories that combines Dolby proprietary technologies such as Dolby Vision and Dolby Atmos, as well as other signature entrance and intrinsic design features. The technology competes with ...
.
Versions
Dolby Digital has similar technologies, included in Dolby Digital EX, Dolby Digital Live, Dolby Digital Plus, Dolby Digital Surround EX, Dolby Digital Recording, Dolby Digital Cinema, Dolby Digital Stereo Creator and Dolby Digital 5.1 Creator.Dolby Digital
Dolby Digital is the common version containing up to six discrete channels of sound. The most elaborate mode in common use involves five channels for normal-range speakers () (right, center, left, right surround, left surround) and one channel ( allotted audio) for the subwoofer driven low-frequency effects.Mono
Mono may refer to:
Common meanings
* Infectious mononucleosis, "the kissing disease"
* Monaural, monophonic sound reproduction, often shortened to mono
* Mono-, a numerical prefix representing anything single
Music Performers
* Mono (Japanes ...
and stereo
Stereophonic sound, or more commonly stereo, is a method of sound reproduction that recreates a multi-directional, 3-dimensional audible perspective. This is usually achieved by using two independent audio channels through a configuration ...
modes are also supported. AC-3 supports audio sample-rates up to 48 kHz.
This format has different names:
* Dolby Digital
* DD (an abbreviation for Dolby Digital, often combined with channel count; for instance, DD 2.0, DD 5.1)
* AC-3 (Audio Codec 3, Advanced Codec 3, Acoustic Coder 3. hese_are_backronyms._ATRAC3.html" ;"title="backronym.html" ;"title="hese are backronym">hese are backronyms. ATRAC3">Adaptive Transform Acoustic Coding 3 is a separate format developed by Sony
, commonly stylized as SONY, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. As a major technology company, it operates as one of the world's largest manufacturers of consumer and professional ...
.])
* ATSC standards, ATSC A/52 (name of the standard)
* Before 1996, was marketed as Dolby Surround AC-3, Dolby Stereo Digital, and Dolby SRD.
In 1991, a limited experimental release of '' Star Trek VI: The Undiscovered Country'' in Dolby Digital played in 3 US theatres. In 1992, '' Batman Returns'' is the first movie to be released in Dolby Digital. In 1995, the LaserDisc
The LaserDisc (LD) is a home video format and the first commercial optical disc storage medium, initially licensed, sold and marketed as MCA DiscoVision (also known simply as "DiscoVision") in the United States in 1978. Its diameter typical ...
version of '' Clear and Present Danger'' featured the first home theater Dolby Digital mix, quickly followed by ''True Lies
''True Lies'' is a 1994 American spy action comedy film written and directed by James Cameron. It stars Arnold Schwarzenegger, Jamie Lee Curtis, Tom Arnold, Art Malik, Tia Carrere, Bill Paxton, Eliza Dushku, Grant Heslov and Charlton Heston. I ...
'', ''Stargate
''Stargate'' (often stylized in all caps) is a military science fiction media franchise based on the film directed by Roland Emmerich, which he co-wrote with producer Dean Devlin. The franchise is based on the idea of an alien Einstein–Rosen ...
'', ''Forrest Gump
''Forrest Gump'' is a 1994 American comedy-drama film directed by Robert Zemeckis and written by Eric Roth. It is based on the 1986 novel of the same name by Winston Groom and stars Tom Hanks, Robin Wright, Gary Sinise, Mykelti Williamson ...
'', and '' Interview with the Vampire'' among others.
Dolby Digital EX
Dolby Digital EX is similar in practice to Dolby's earlierPro Logic
Dolby Pro Logic is a surround sound processing technology developed by Dolby Laboratories, designed to decode soundtracks encoded with Dolby Surround.
Dolby Stereo (also known as ''Dolby MP'' or ''Dolby SVA'') was developed by Dolby in 1976 fo ...
format, which utilized matrix
Matrix most commonly refers to:
* ''The Matrix'' (franchise), an American media franchise
** '' The Matrix'', a 1999 science-fiction action film
** "The Matrix", a fictional setting, a virtual reality environment, within ''The Matrix'' (franchi ...
technology to add a center surround channel
Surround channels are audio channels in surround sound multichannel audio. They primarily serve to deliver ambience and diffuse sounds in a film or music soundtrack.
History
Dolby Stereo (1975) was the first standard cinema sound system usin ...
and single rear surround channel to stereo soundtracks. EX adds an extension to the standard 5.1
5.1 surround sound ("five-point one") is the common name for surround sound audio systems. 5.1 is the most commonly used layout in home theatres. It uses five full bandwidth channels and one low-frequency effects channel (the "point one"). Dolb ...
channel Dolby Digital codec in the form of matrixed rear channels, creating 6.1 or 7.1 channel output.
Dolby Digital Surround EX
It provides an economical and backwards-compatible means for 5.1 soundtracks to carry a sixth, center back surround channel for improved localization of effects. The extra surround channel is matrix encoded onto the discrete ''left surround'' and ''right surround'' channels of the 5.1 mix, much like the frontcenter channel
Center channel refers to an audio channel common to many surround sound formats. It is the channel that is mostly, or fully, dedicated to the reproduction of the dialogue of an audiovisual program. The speaker(s) connected to the center channel a ...
on Dolby Pro Logic encoded stereo soundtracks. The result can be played without loss of information on standard 5.1 systems, or played in 6.1 or 7.1 on systems with Surround EX decoding and added speakers. A number of DVDs have a Dolby Digital Surround EX audio option.
The theater version of ''Dolby Digital Surround EX'' was introduced in 1999, when Dolby and Skywalker Sound, a division of Lucasfilm Ltd., codeveloped ''Dolby Digital Surround EX''™ for the release of ''Star Wars: Episode I – The Phantom Menace
''Star Wars: Episode I – The Phantom Menace'' is a 1999 American Epic film, epic space opera film written and directed by George Lucas. It stars Liam Neeson, Ewan McGregor, Natalie Portman, Jake Lloyd, Ahmed Best, Ian McDiarmid, Anthony Dan ...
''. Dolby Digital Surround EX has since been used on the DVD releases of the ''Star Wars'' prequel and original trilogies.
Dolby Digital Live
Dolby Digital Live (DDL) is a real-time encoding technology for interactive media such as video games. It converts any audio signals on a PC or game console into a 5.1-channel 16-bit/48 kHz Dolby Digital format at 640 kbit/s and transports it via a single S/PDIF cable. A similar technology known asDTS Connect
DTS, Inc. (originally Digital Theater Systems) is an American company that makes multichannel audio technologies for film and video. Based in Calabasas, California, the company introduced its DTS technology in 1993 as a competitor to Dolby Labor ...
is available from competitor DTS. An important benefit of this technology is that it enables the use of digital multichannel sound with consumer sound cards, which are otherwise limited to digital PCM
Pulse-code modulation (PCM) is a method used to digitally represent sampled analog signals. It is the standard form of digital audio in computers, compact discs, digital telephony and other digital audio applications. In a PCM stream, the am ...
stereo or analog multichannel sound because S/PDIF over RCA, BNC, and TOSLINK can only support two-channel PCM, Dolby Digital multichannel audio, and DTS multichannel audio. HDMI
High-Definition Multimedia Interface (HDMI) is a proprietary audio/video interface for transmitting uncompressed video data and compressed or uncompressed digital audio data from an HDMI-compliant source device, such as a display controlle ...
was later introduced, and it can carry uncompressed multichannel PCM, lossless compressed multichannel audio, and lossy compressed digital audio. However, Dolby Digital Live is still useful with HDMI to allow transport of multichannel audio over HDMI to devices that are unable to handle uncompressed multichannel PCM.
Dolby Digital Live is available in sound cards using various manufacturers' audio chipsets. The SoundStorm, used for the Xbox
Xbox is a video gaming brand created and owned by Microsoft. The brand consists of five video game consoles, as well as applications (games), streaming services, an online service by the name of Xbox network, and the development arm by the ...
game console and certain nForce2 motherboards, used an early form of this technology. DDL is available on motherboards with codecs such as Realtek
Realtek Semiconductor Corp () is a fabless semiconductor company situated in the Hsinchu Science Park, Hsinchu, Taiwan. Realtek was founded in October 1987 and subsequently listed on the Taiwan Stock Exchange in 1998. Realtek currently manufa ...
's ALC882D, ALC888DD and ALC888H. Other examples include some C-Media PCI sound cards and Creative Labs' X-Fi and Z series sound cards, whose drivers have enabled support for DDL.
NVIDIA later decided to drop DDL support in their motherboards due to the cost of involved royalties, leaving an empty space in this regard in the sound cards market.
Then in June 2005 came Auzentech
Auzentech was a Korean computer hardware manufacturer that specialized in high-definition audio equipment and in particular PC sound cards.
Auzentech has its origins in March 2005, when under the company name HDA (HiTeC Digital Audio), the compan ...
, which with its X-Mystique PCI card, provided the first consumer sound card with Dolby Digital Live support.
Initially no Creative X-Fi based sound cards supported DDL (2005~2007) but a collaboration of Creative and Auzentech
Auzentech was a Korean computer hardware manufacturer that specialized in high-definition audio equipment and in particular PC sound cards.
Auzentech has its origins in March 2005, when under the company name HDA (HiTeC Digital Audio), the compan ...
resulted in the development of the Auzentech Prelude, the first X-Fi card to support DDL. Originally planned to extend DDL support to all X-Fi based sound cards (except the 'Xtreme Audio' line which is incapable of DDL hardware implementation), the plan was dropped because Dolby licensing would have required a royalty payment for all X-Fi cards and, problematically, those already sold.
In 2008, Creative released the X-Fi Titanium series of sound cards which fully supports Dolby Digital Live while leaving all PCI versions of Creative X-Fi still lacking support for DDL.
Since September 2008, all Creative X-Fi based sound cards support DDL (except the 'Xtreme Audio' and its based line such as Prodigy 7.1e, which is incapable of DDL in hardware). X-Fi's case differs.
While they forgot about the plan, programmer Daniel Kawakami made a hot issue by applying Auzentech Prelude DDL module back to Creative X-Fi cards by disguising the hardware identity as Auzentech Prelude.
Creative Labs alleged Kawakami violated their intellectual property and demanded he cease distributing his modified drivers.
Eventually Creative struck an agreement with Dolby Laboratories regarding the Dolby license royalty by arranging that the licensing cost be folded into the purchase price of the Creative X-Fi PCI cards rather than as a royalty paid by Creative themselves. Based on the agreement, in September 2008 Creative began selling the ''Dolby Digital Live'' packs enabling Dolby Digital Live on Creative's X-Fi PCI series of sound cards. It can be purchased and downloaded from Creative. Subsequently, Creative added their ''DTS Connect'' pack to the DDL pack at no added cost.
Dolby Digital Plus
E-AC-3 (Dolby Digital Plus) is an enhanced coding system based on the AC-3 codec. It offers increased bitrates (up to 6.144 Mbit/s), support for even more audio channels (up to 15.1 discrete channels in the future), and improved coding techniques (only at low data rates) to reducecompression artifacts
A compression artifact (or artefact) is a noticeable distortion of media (including images, audio, and video) caused by the application of lossy compression. Lossy data compression involves discarding some of the media's data so that it beco ...
, enabling lower data rates than those supported by AC-3 (e.g. 5.1-channel audio at 256 kbit/s). It is not backward compatible with existing AC-3 hardware, though E-AC-3 codecs generally are capable of transcoding
Transcoding is the direct digital-to-digital conversion of one encoding to another, such as for video data files, audio files (e.g., MP3, WAV), or character encoding (e.g., UTF-8, ISO/IEC 8859). This is usually done in cases where a target d ...
to AC-3 for equipment connected via S/PDIF. E-AC-3 decoders can also decode AC-3 bitstreams. The fourth generation Apple TV supports E-AC-3. The discontinued HD DVD system directly supported E-AC-3. Blu-ray Disc
The Blu-ray Disc (BD), often known simply as Blu-ray, is a digital optical disc data storage format. It was invented and developed in 2005 and released on June 20, 2006 worldwide. It is designed to supersede the DVD format, and capable of sto ...
offers E-AC-3 as an option to graft added channels onto an otherwise 5.1
5.1 surround sound ("five-point one") is the common name for surround sound audio systems. 5.1 is the most commonly used layout in home theatres. It uses five full bandwidth channels and one low-frequency effects channel (the "point one"). Dolb ...
AC-3 stream, as well as for delivery of secondary audio content (e.g. director's commentary) that is intended to be mixed with the primary audio soundtrack in the Blu-ray Disc player.
Dolby AC-4
Dolby AC-4 is an audio compression standard supporting multiple audio channels and/or audio objects. Support for 5.1 channel audio is mandatory and additional channels up to 7.1.4 are optional. AC-4 provides a 50% reduction in bit rate over AC-3/ Dolby Digital Plus.Dolby TrueHD
Dolby TrueHD, developed by Dolby Laboratories, is an advanced lossless audio codec based onMeridian Lossless Packing
Meridian Lossless Packing, also known as Packed PCM (PPCM), is a lossless compression technique for PCM audio data developed by Meridian Audio, Ltd. MLP is the standard lossless compression method for DVD-Audio content (often advertised with t ...
. Support for the codec was mandatory for HD DVD and is optional for Blu-ray Disc
The Blu-ray Disc (BD), often known simply as Blu-ray, is a digital optical disc data storage format. It was invented and developed in 2005 and released on June 20, 2006 worldwide. It is designed to supersede the DVD format, and capable of sto ...
hardware. Dolby TrueHD supports 24-bit bit depths and sample rates up to 192 kHz. Maximum bitrate is 18 Mbit/s while it supports up to 16 audio channels (HD DVD and Blu-ray Disc standards currently limit the maximum number of audio channels to eight). It supports metadata, including dialog normalization and Dynamic Range Control.
Channel configurations
Although commonly associated with the 5.1 channel configuration, Dolby Digital allows a number of different channel selections. The options are: * Dolby Digital 1/0 – Mono (center only) * Dolby Digital 2/0 – 2-channel stereo (left + right), optionally carrying matrixed Dolby Surround * Dolby Digital 3/0 – 3-channel stereo (left, center, right) * Dolby Digital 2/1 – 2-channel stereo with mono surround (left, right, surround) * Dolby Digital 3/1 – 3-channel stereo with mono surround (left, center, right, surround) * Dolby Digital 2/2 – 4-channel quadraphonic (left, right, left surround, right surround) * Dolby Digital 3/2 – 5-channel surround (left, center, right, left surround, right surround) These configurations optionally include the extra low-frequency effects (LFE) channel. The last two with stereo surrounds optionally use Dolby Digital EX matrix encoding to add an extra Rear Surround channel. Many Dolby Digital decoders are equipped withdownmixing
In sound recording and reproduction, audio mixing is the process of optimizing and combining multitrack recordings into a final mono, stereo or surround sound product. In the process of combining the separate tracks, their relative levels are ad ...
to distribute encoded channels to speakers. This includes such functions as playing surround information through the front speakers if surround speakers are unavailable, and distributing the center channel
Center channel refers to an audio channel common to many surround sound formats. It is the channel that is mostly, or fully, dedicated to the reproduction of the dialogue of an audiovisual program. The speaker(s) connected to the center channel a ...
to left and right if no center speaker is available. When outputting to separate equipment over a 2-channel connection, a Dolby Digital decoder can optionally encode the output using Dolby Surround to preserve surround information.
The '.1' in 5.1, 7.1 etc. refers to the LFE channel, which is also a discrete channel.
Applications
Dolby Digital audio is used on DVD-Video and other purely digital media, like home cinema. In this format, the AC-3 bitstream is interleaved with the video and control bitstreams. The system is used in bandwidth-limited applications other than DVD-Video, such as digital TV. The AC-3 standard allows a maximum coded bit rate of 640 kbit/s. 35 mm film prints use a fixed rate of 320 kbit/s, which is the same as the maximum bit rate for 2-channel MP3. DVD-Video discs are limited to 448 kbit/s, although many players can successfully play higher-rate bitstreams (which are non-compliant with the DVD specification). HD DVD limits AC-3 to 448 kbit/s. ATSC and digital cable standards limit AC-3 to 448 kbit/s. Blu-ray Disc, the PlayStation 3 and the Xbox game console can output an AC-3 signal at a full 640 kbit/s. Some Sony PlayStation 2 console games are able to output AC-3 standard audio as well, primarily during pre-rendered cutscenes. Dolby is part of a group of organizations involved in the development of AAC (Advanced Audio Coding), part of MPEG specifications, and considered the successor to MP3. Dolby Digital Plus (DD-Plus) and TrueHD are supported in HD-DVD, as mandatory codecs, and in Blu-ray Disc, as optional codecs.Dolby technologies in packaged media formats
AC3RF
In the LaserDisc world ''AC3RF'' is the term widely placed on connectors of players that support Dolby Digital. Specific demodulators and receivers from the LaserDisc era (1990s thru early 2000s) also include placement of this term on connectors. LaserDisc titles with Dolby Digital tracks often have THX logo on their covers.Technical details
The data layout of AC-3 is described by simplified " C-like" language in official specifications. An AC-3 stream is a series of frames; the frame size code is used along with the sample rate code to determine the number of (2-byte) words before the next syncword. Channel blocks can be either long, in which case the entire block is processed as singlemodified discrete cosine transform
The modified discrete cosine transform (MDCT) is a transform based on the type-IV discrete cosine transform (DCT-IV), with the additional property of being lapped: it is designed to be performed on consecutive blocks of a larger dataset, where ...
, or short, in which case two half length transforms are performed on the block. Below is a simplified AC-3 header. A detailed description is in thATSC "Digital Audio Compression (AC-3) (E-AC-3) Standard"
section 5.4.
License
AC3 was covered by patents (expired since March 2017). Patents were used to ask to pay a commercial license to publish an application that decodes AC3. This led some audio app developers to ban AC3 from their apps, although the open source VLC media player supported AC-3 audio without having paid for any kind of patent license fee. In Dolby's 2005 original and amended S-1 filings with the SEC, Dolby acknowledged that "Patents relating to our Dolby Digital technologies expire between 2008 and 2017." The last patent covering AC-3 expired March 20, 2017, so it is now generally free to use.Open source implementation
A free ATSC A/52 (AC3) stream decoderliba52
is available under the
GNU General Public License
The GNU General Public License (GNU GPL or simply GPL) is a series of widely used free software licenses that guarantee end users the four freedoms to run, study, share, and modify the software. The license was the first copyleft for general ...
. FFmpeg and the VLC media player each include code for handling AC-3.
See also
* C-Media – producer of DDL audio chipsets used in many sound cards and motherboards *Dialnorm
Dialnorm is the metadata parameter that controls playback gain within the Dolby Laboratories Dolby Digital (AC-3) audio compression system. Dialnorm stands for dialog normalization. Dialnorm is an integer value with range 1 to 31 corresponding to ...
– Dolby Digital metadata parameter controlling decoder gain
* Dolby Laboratories
Dolby Laboratories, Inc. (often shortened to Dolby Labs and known simply as Dolby) is an American company specializing in audio noise reduction, audio encoding/compression, spatial audio, and HDR imaging. Dolby licenses its technologies to ...
– company history and technology development
* Dolby noise-reduction system – analogue recording on magnetic tape, including compact cassette
The Compact Cassette or Musicassette (MC), also commonly called the tape cassette, cassette tape, audio cassette, or simply tape or cassette, is an analog magnetic tape recording format for audio recording and playback. Invented by Lou Otte ...
tapes
* Dolby Stereo – first active matrix analogue surround sound format
* Dolby SR – Recording process, noise reduction and expander with superior fidelity over earlier A-type system
* Dolby Surround
Dolby Pro Logic is a surround sound processing technology developed by Dolby Laboratories, designed to decode soundtracks encoded with Dolby Surround.
Dolby Stereo (also known as ''Dolby MP'' or ''Dolby SVA'') was developed by Dolby in 1976 ...
– Marketed consumer name of the theatrical Dolby Stereo analog surround format
* Dolby Pro Logic – Reference active 2:4 matrix decoding system used on Dolby Stereo soundtracks and Dolby Surround fter 1987
* Dolby TrueHD – lossless codec for HD DVD and Blu-ray Disc
* Dolby E
Dolby E is a lossy audio compression and decoding technology developed by Dolby Laboratories that allows 6 to 8 channels of audio to be compressed into an AES3 digital audio stream that can be stored as a standard stereo pair of digital audio t ...
– allows 6 to 8 channels of audio to be compressed into an AES3 digital audio stream
* DTS (sound system)
DTS, Inc. (originally Digital Theater Systems) is an American company that makes multichannel audio technologies for film and video. Based in Calabasas, California, the company introduced its DTS technology in 1993 as a competitor to Dolby L ...
– formerly Digital Theater Systems
* Home cinema
* Loudspeaker
A loudspeaker (commonly referred to as a speaker or speaker driver) is an electroacoustic transducer that converts an electrical audio signal into a corresponding sound. A ''speaker system'', also often simply referred to as a "speaker" or ...
* SoundStorm – a real-time AC-3 encoder included in certain nForce2 motherboards
* THX
References
External links
*, Dolby LaboratoriesATSC standards
at the ATSC website {{Video formats American inventions Audio codecs Consumer electronics Dolby Laboratories Film sound production High-definition television Surround sound Audiovisual introductions in 1986 Development organizations