District of Columbia Organic Act of 1871 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The District of Columbia Organic Act of 1871 is an Act of Congress that repealed the individual charters of the cities of Washington and Georgetown and established a new territorial government for the whole
 The passage of the
The passage of the
PDF version
The Seal of the District of Columbia features the date 1871, recognizing the year the District's government was incorporated. The Act did not establish a new city or city government within the District. Regarding a city of Washington, it stated that "that portion of said District included within the present limits of the city of Washington shall continue to be known as the city of Washington". In the present day, the name "Washington" is commonly used to refer to the entire District, but DC law continues to use the definition of the city of Washington as given in the 1871 Organic Act. In 1873, President Grant appointed an influential member of the board of public works, Alexander Robey Shepherd, to the post of governor. Shepherd authorized large-scale municipal projects, which greatly modernized Washington. In doing so however, the governor spent three times the money that had been budgeted for capital improvements, bankrupting the city. In 1874, Congress replaced the District's quasi-elected territorial government with an appointed three-member Board of Commissioners. Direct rule by Congress continued until the 1973 passage of the District of Columbia Home Rule Act, a century later.
"An Act to provide a Government for the District of Columbia"
Statutes at Large, Library of Congress {{Georgetown, Washington, D.C. United States federal territory and statehood legislation Legal history of the District of Columbia 1871 in law 1871 in the United States 1871 in Washington, D.C.
District of Columbia
)
, image_skyline =
, image_caption = Clockwise from top left: the Washington Monument and Lincoln Memorial on the National Mall, United States Capitol, Logan Circle (Washington, D.C.), Logan Circle, Jefferson Memoria ...
. Though Congress repealed the territorial government in 1874, the legislation was the first to create a single municipal government for the federal district
A federal district is a type of administrative division of a federation, usually under the direct control of a federal government and organized sometimes with a single municipal body. Federal districts often include capital districts, and they ...
.
History
 The passage of the
The passage of the Residence Act
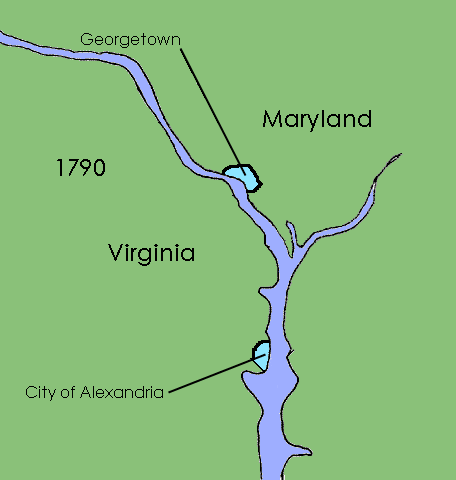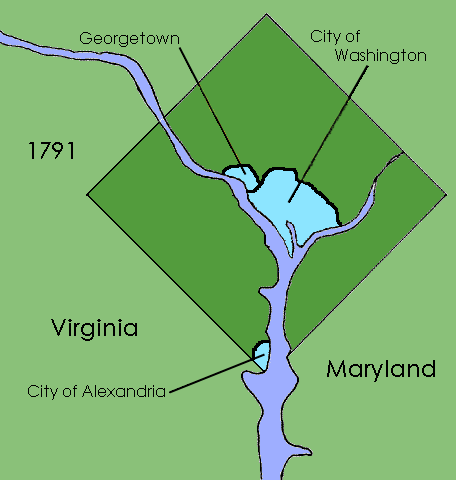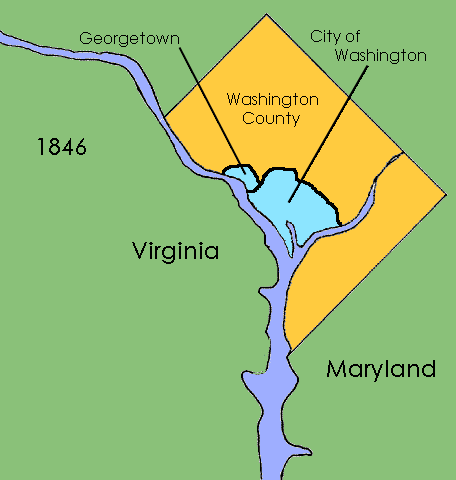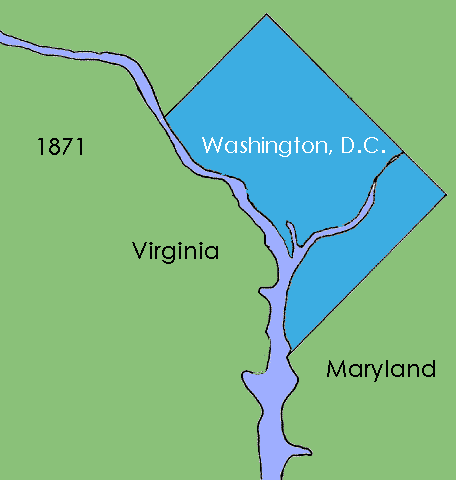
The Residence Act of 1790, officially titled An Act for establishing the temporary and permanent seat of the Government of the United States (), is a United States federal statute adopted during the second session of the First United States Co ...
in 1790 created a new federal district that would become the capital of the United States. Formed from land donated by the states of Maryland
Maryland ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States. It shares borders with Virginia, West Virginia, and the District of Columbia to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and Delaware and the Atlantic Ocean t ...
and Virginia
Virginia, officially the Commonwealth of Virginia, is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Southeastern regions of the United States, between the Atlantic Coast and the Appalachian Mountains. The geography and climate of the Commonwealth are ...
, the capital territory already included two large settlements at its creation: the port of Georgetown, Maryland
Georgetown is an unincorporated community in northeastern Kent County, Maryland, United States. The community was laid out in 1736. Georgetown was named for Prince George who later became King of the United Kingdom. Georgetown is located on the ...
and the town of Alexandria, Virginia
Alexandria is an independent city in the northern region of the Commonwealth of Virginia, United States. It lies on the western bank of the Potomac River approximately south of downtown Washington, D.C.
In 2020, the population was 159,467. ...
. A new capital city named in honor of President George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of ...
was founded to the east of Georgetown in 1791.
Shortly after establishing operations in the new capital, Congress passed the Organic Act of 1801
The District of Columbia Organic Act of 1801, officially An Act Concerning the District of Columbia (6th Congress, 2nd Sess., ch. 15, , February 27, 1801), is an organic act enacted by the United States Congress in accordance with Article 1, Sec ...
, which organized the federal territory. The territory within the federal district east of the Potomac formed the new County of Washington, which was governed by a levy court consisting of seven to eleven Justices of the Peace
A justice of the peace (JP) is a judicial officer of a lower or '' puisne'' court, elected or appointed by means of a commission (letters patent) to keep the peace. In past centuries the term commissioner of the peace was often used with the sam ...
appointed by the president, and was governed by Maryland law as of 1801. The area west of the river became Alexandria County which was governed by Virginia law. In addition, Congress allowed the cities of Washington, Alexandria and Georgetown to each maintain their own municipal governments. In 1846 Alexandria County was returned by Congress to the state of Virginia.
The outbreak of the American Civil War
The American Civil War (April 12, 1861 – May 26, 1865; also known by Names of the American Civil War, other names) was a civil war in the United States. It was fought between the Union (American Civil War), Union ("the North") and t ...
in 1861 led to notable growth in the capital's population due to the expansion of the federal government and a large influx of emancipated slaves. By 1870, the District's population had grown 75% to nearly 132,000 residents. Growth was even more dramatic within the County of Washington, where the population more than doubled as people escaped the crowded city.
The individual local governments within the District were insufficient to handle the population growth. Living conditions were poor throughout the capital, which still had dirt roads and lacked basic sanitation. The situation was so bad that some lawmakers in Congress even suggested moving the capital out further west, but President Ulysses S. Grant
Ulysses S. Grant (born Hiram Ulysses Grant ; April 27, 1822July 23, 1885) was an American military officer and politician who served as the 18th president of the United States from 1869 to 1877. As Commanding General, he led the Union A ...
refused to consider the proposals.
Effect
Instead, Congress passed the Organic Act of 1871, which revoked the individual charters of the cities of Washington and Georgetown and combined them with Washington County to create a unified territorial government for the entire District of Columbia. The new government consisted of an appointed governor and 11-member council, a locally elected 22-member assembly, and a board of public works charged with modernizing the city. (AltPDF version
The Seal of the District of Columbia features the date 1871, recognizing the year the District's government was incorporated. The Act did not establish a new city or city government within the District. Regarding a city of Washington, it stated that "that portion of said District included within the present limits of the city of Washington shall continue to be known as the city of Washington". In the present day, the name "Washington" is commonly used to refer to the entire District, but DC law continues to use the definition of the city of Washington as given in the 1871 Organic Act. In 1873, President Grant appointed an influential member of the board of public works, Alexander Robey Shepherd, to the post of governor. Shepherd authorized large-scale municipal projects, which greatly modernized Washington. In doing so however, the governor spent three times the money that had been budgeted for capital improvements, bankrupting the city. In 1874, Congress replaced the District's quasi-elected territorial government with an appointed three-member Board of Commissioners. Direct rule by Congress continued until the 1973 passage of the District of Columbia Home Rule Act, a century later.
Conspiracy theories
The Act is the basis of several claims held by the sovereign citizen movement. According to these, the Act made the District, and consequently the whole United States, into a business corporation. These claims stem from the termmunicipal corporation
A municipal corporation is the legal term for a local governing body, including (but not necessarily limited to) cities, counties, towns, townships, charter townships, villages, and boroughs. The term can also be used to describe municipally ...
used in the Act. There are many kinds of corporations; a corporation is any group authorized to legally act as a single entity; in this case, an incorporated, organized district of the United States. Most U.S. cities and counties are municipal corporations.
This was later used by QAnon supporters to falsely claim that former president Donald Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who served as the 45th president of the United States from 2017 to 2021.
Trump graduated from the Wharton School of the University of P ...
would be sworn in as the 19th president of the "original United States" on March 4, 2021. This date corresponds to the original presidential inauguration date because they claimed the Twentieth Amendment was invalid, as it was not passed by the original United States.
See also
* District of Columbia Organic Act of 1801 * History of Washington, D.C. * District of Columbia home ruleReferences
External links
"An Act to provide a Government for the District of Columbia"
Statutes at Large, Library of Congress {{Georgetown, Washington, D.C. United States federal territory and statehood legislation Legal history of the District of Columbia 1871 in law 1871 in the United States 1871 in Washington, D.C.