Disinformation on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Disinformation is false information deliberately spread to
 Ion Mihai Pacepa, former senior official from the Romanian secret police, said the word was coined by
Ion Mihai Pacepa, former senior official from the Romanian secret police, said the word was coined by
 The extent of Soviet disinformation covert operation campaigns came to light through the defections of KGB officers and officers of allied Soviet bloc services from the late 1960s to the 1980s. Stanislav Levchenko and Ilya Dzerkvilov were among the Soviet defectors. By 1990, both men had written books recounting their work on disinformation operations for the KGB. Archival documentation revealed in the disorder of the
The extent of Soviet disinformation covert operation campaigns came to light through the defections of KGB officers and officers of allied Soviet bloc services from the late 1960s to the 1980s. Stanislav Levchenko and Ilya Dzerkvilov were among the Soviet defectors. By 1990, both men had written books recounting their work on disinformation operations for the KGB. Archival documentation revealed in the disorder of the
deceive
Deception or falsehood is an act or statement that misleads, hides the truth, or promotes a belief, concept, or idea that is not true. It is often done for personal gain or advantage. Deception can involve dissimulation, propaganda and sleight ...
people. It is sometimes confused with misinformation
Misinformation is incorrect or misleading information. It differs from disinformation, which is ''deliberately'' deceptive. Rumors are information not attributed to any particular source, and so are unreliable and often unverified, but can turn ...
, which is false information but is not deliberate.
The English word ''disinformation'' comes from the application of the Latin prefix ''dis-'' to ''information'' making the meaning "reversal or removal of information". The rarely used word had appeared with this usage in print at least as far back as 1887. Some consider it a loan translation of the Russian ''dezinformatsiya'', derived from the title of a KGB
The KGB (russian: links=no, lit=Committee for State Security, Комитет государственной безопасности (КГБ), a=ru-KGB.ogg, p=kəmʲɪˈtʲet ɡəsʊˈdarstvʲɪn(ː)əj bʲɪzɐˈpasnəsʲtʲɪ, Komitet gosud ...
black propaganda department. Defector Ion Mihai Pacepa claimed Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secretar ...
coined the term, giving it a French-sounding name to claim it had a Western origin. Russian use began with a "special disinformation office" in 1923. Disinformation was defined in '' Great Soviet Encyclopedia'' (1952) as "false information with the intention to deceive public opinion". Operation INFEKTION
Operation INFEKTION was an active measure disinformation campaign run by the KGB in the 1980s to plant the idea that the United States had invented HIV/AIDS as part of a biological weapons research project at Fort Detrick, Maryland. Historian ...
was a Soviet disinformation campaign to influence opinion that the U.S. invented AIDS. The U.S. did not actively counter disinformation until 1980, when a fake document reported that the U.S. supported apartheid
Apartheid (, especially South African English: , ; , "aparthood") was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. Apartheid was ...
.
Etymology and early usage
The English word ''disinformation'' is a translation of the Russian дезинформация,transliterated
Transliteration is a type of conversion of a text from one script to another that involves swapping letters (thus ''trans-'' + '' liter-'') in predictable ways, such as Greek → , Cyrillic → , Greek → the digraph , Armenian → or L ...
as , which Soviet planners in the 1950s defined as “dissemination (in
the press, on the radio, etc.) of false reports intended to mislead public opinion.” In order to distinguish between similar terms, including misinformation and malinformation, scholars collectively agree on the definitions for each term as follows: (1) misinformation represents the unintentional spread of false information; (2) malinformation is factual information disseminated with the intention to cause harm; and (3) disinformation is the strategic dissemination of false information with the intention to cause public harm. Where misinformation
Misinformation is incorrect or misleading information. It differs from disinformation, which is ''deliberately'' deceptive. Rumors are information not attributed to any particular source, and so are unreliable and often unverified, but can turn ...
refers to inaccuracies that stem from error, disinformation is a deliberate falsehood promulgated by design. Misinformation can be used to create disinformation when known misinformation is purposefully and intentionally disseminated.
The tactic has been used throughout history, being deployed during the long Roman-Persian Wars, at the Battle of Mount Gindarus, the Battle of Telephis–Ollaria
The assault on Telephis and Ollaria occurred in 553 during the Lazic War between the Sasanian Empire and the Byzantine Empire.
As the Byzantine position was strengthened by fresh forces, the Sasanian commander Mihr-Mihroe took the initiative a ...
, and Heraclius assault on Persia, for instance.
Disinformation is primarily carried out by government intelligence agencies
An intelligence agency is a government agency responsible for the collection, analysis, and exploitation of information in support of law enforcement, national security, military, public safety, and foreign policy objectives.
Means of informatio ...
, but has also been used by non-governmental organizations and businesses. Front groups are a form of disinformation, as they mislead the public about their true objectives and who their controllers are. Most recently, disinformation has been deliberately spread through social media in the form of "fake news
Fake news is false or misleading information presented as news. Fake news often has the aim of damaging the reputation of a person or entity, or making money through advertising revenue.Schlesinger, Robert (April 14, 2017)"Fake news in reality ...
", disinformation masked as legitimate news articles and meant to mislead readers or viewers. Disinformation may include distribution of forged
Forging is a manufacturing process involving the shaping of metal using localized compressive forces. The blows are delivered with a hammer (often a power hammer) or a die. Forging is often classified according to the temperature at which it ...
document
A document is a written, drawn, presented, or memorialized representation of thought, often the manifestation of non-fictional, as well as fictional, content. The word originates from the Latin ''Documentum'', which denotes a "teaching" o ...
s, manuscripts, and photographs, or spreading dangerous rumour
A rumor (American English), or rumour (British English; see spelling differences; derived from Latin:rumorem - noise), is "a tall tale of explanations of events circulating from person to person and pertaining to an object, event, or issue in p ...
s and fabricated intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. More generally, it can be des ...
. Use of these tactics can lead to blowback, however, causing such unintended consequences such as defamation lawsuits or damage to the dis-informer's reputation.
Use of the term related to a Russian tactical weapon started in 1923, when the deputy chairman of the KGB
The KGB (russian: links=no, lit=Committee for State Security, Комитет государственной безопасности (КГБ), a=ru-KGB.ogg, p=kəmʲɪˈtʲet ɡəsʊˈdarstvʲɪn(ː)əj bʲɪzɐˈpasnəsʲtʲɪ, Komitet gosud ...
-precursor the State Political Directorate
The State Political Directorate (also translated as the State Political Administration) (GPU) was the intelligence service and secret police of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic (RSFSR) from February 6, 1922, to December 29, 1922, ...
(GPU), Józef Unszlicht, called for the foundation of "a special disinformation office to conduct active intelligence operations". The GPU was the first organization in the Soviet Union to use the term disinformation for their intelligence tactics. William Safire wrote in his 1993 book, ''Quoth the Maven'', that disinformation was used by the KGB predecessor to indicate: "manipulation of a nation's intelligence system through the injection of credible, but misleading data". From this point on, disinformation became a tactic used in the Soviet political warfare called active measures. Active measures were a crucial part of Soviet intelligence strategy involving forgery as covert operation, subversion, and media manipulation. The 2003 encyclopedia ''Propaganda and Mass Persuasion'' states that ''disinformation'' came from , a term used by the Russian black propaganda unit known as Service A that referred to active measures. The term was used in 1939, related to a "German Disinformation Service". The 1991 edition of ''The Merriam-Webster New Book of Word Histories'' defines ''disinformation'' as a probable translation of the Russian . This dictionary notes that it was possible the English version of the word and the Russian-language version developed independently in parallel to each other—out of ongoing frustration related to the spread of propaganda before World War II.
 Ion Mihai Pacepa, former senior official from the Romanian secret police, said the word was coined by
Ion Mihai Pacepa, former senior official from the Romanian secret police, said the word was coined by Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as General Secretar ...
and used during World War II. The Stalinist government then used disinformation tactics in both World War II and the Cold War. Soviet intelligence used the term ''maskirovka'' (Russian military deception
Russian military deception, sometimes known as ''maskirovka'' (russian: маскировка, lit=disguise), is a military doctrine developed from the start of the 20th century. The doctrine covers a broad range of measures for military deceptio ...
) to refer to a combination of tactics including disinformation, simulation, camouflage, and concealment. Pacepa and Ronald J. Rychlak authored a book entitled '' Disinformation'', in which Pacepa wrote that Stalin gave the tactic a French-sounding title in order to put forth the ruse that it was a technique used by the Western world
The Western world, also known as the West, primarily refers to the various nations and states in the regions of Europe, North America, and Oceania.
. Pacepa recounted reading Soviet instruction manuals while working as an intelligence officer, that characterized disinformation as a strategy used by the Russian government that had early origins in Russian history. Pacepa recalled that the Soviet manuals said the origins of disinformation stemmed from phony towns constructed by Grigory Potyomkin
Prince Grigory Aleksandrovich Potemkin-Tauricheski (, also , ;, rus, Князь Григо́рий Алекса́ндрович Потёмкин-Таври́ческий, Knjaz' Grigórij Aleksándrovich Potjómkin-Tavrícheskij, ɡrʲɪˈɡ ...
in Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
to wow Catherine the Great during her 1783 journey to the region—subsequently referred to as Potemkin village
In politics and economics, a Potemkin village (russian: link=no, потёмкинские деревни, translit=potyómkinskiye derévni}) is any construction (literal or figurative) whose sole purpose is to provide an external façade to a co ...
s.
In their book ''Propaganda and Persuasion'', authors Garth Jowett and Victoria O'Donnell characterized ''disinformation'' as a cognate from , and was developed from the same name given to a KGB black propaganda department. The black propaganda division was reported to have formed in 1955 and was referred to as the Dezinformatsiya agency. Former Central Intelligence Agency
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
(CIA) director William Colby
William Egan Colby (January 4, 1920 – May 6, 1996) was an American intelligence officer who served as Director of Central Intelligence (DCI) from September 1973 to January 1976.
During World War II Colby served with the Office of Strateg ...
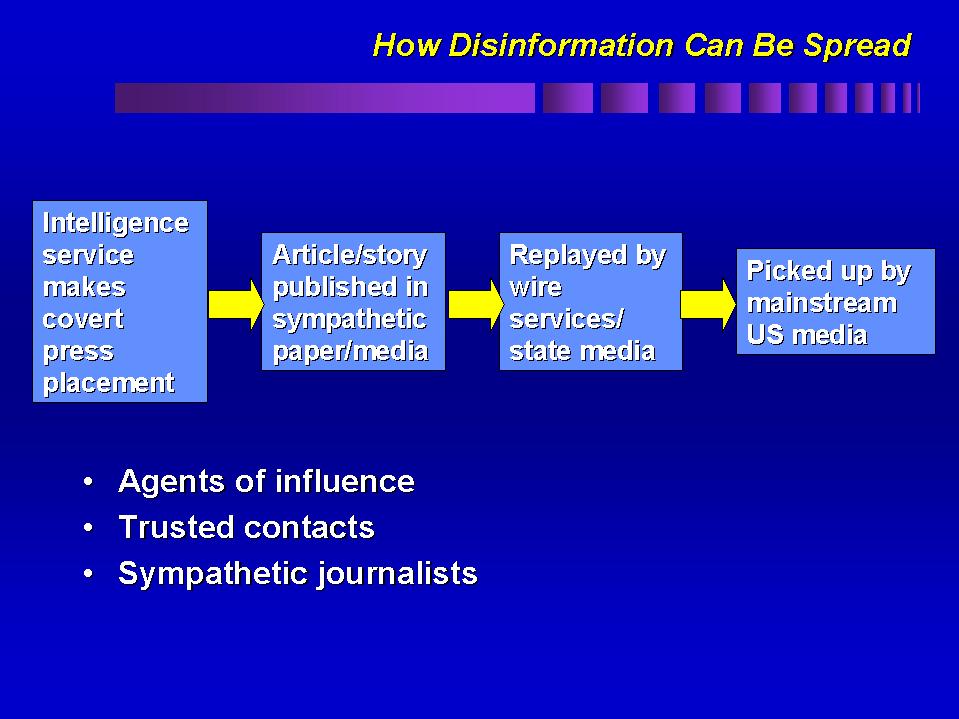
explained how the Dezinformatsiya agency operated, saying that it would place a false article in a left-leaning newspaper. The fraudulent tale would make its way to a communist periodical, before eventually being published by a Soviet newspaper, which would say its sources were undisclosed individuals. By this process a falsehood was globally proliferated as a legitimate piece of reporting.
According to ''Oxford Dictionaries Oxford dictionary may refer to any dictionary published by Oxford University Press, particularly:
Historical dictionaries
* ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'')
* ''Shorter Oxford English Dictionary'', abridgement of the ''OED''
Single-volume d ...
'' the English word ''disinformation'', as translated from the Russian , began to see use in the 1950s. The term ''disinformation'' began to see wider use as a form of Soviet tradecraft, defined in the 1952 official '' Great Soviet Encyclopedia'' as "the dissemination (in the press, radio, etc.) of false information with the intention to deceive public opinion." During the most-active period of the Cold War, from 1945 to 1989, the tactic was used by multiple intelligence agencies including the Soviet KGB, British Secret Intelligence Service, and the American CIA. The word ''disinformation'' saw increased usage in the 1960s and wider purveyance by the 1980s. A major disinformation effort in 1964, Operation Neptune, was designed by the Czechoslovak
Czechoslovak may refer to:
*A demonym or adjective pertaining to Czechoslovakia (1918–93)
**First Czechoslovak Republic (1918–38)
**Second Czechoslovak Republic (1938–39)
**Third Czechoslovak Republic (1948–60)
**Fourth Czechoslovak Repub ...
secret service, the StB, to defame West European politicians as former Nazi collaborators. Former Soviet bloc intelligence officer Ladislav Bittman, the first disinformation practitioner to publicly defect to the West, described the official definition as different from the practice: "The interpretation is slightly distorted because public opinion is only one of the potential targets. Many disinformation games are designed only to manipulate the decision-making elite, and receive no publicity." Bittman was deputy chief of the Disinformation Department of the Czechoslovak Intelligence Service, and testified before the United States Congress
The United States Congress is the legislature of the federal government of the United States. It is bicameral, composed of a lower body, the House of Representatives, and an upper body, the Senate. It meets in the U.S. Capitol in Washing ...
on his knowledge of disinformation in 1980.
Defections reveal covert operations
 The extent of Soviet disinformation covert operation campaigns came to light through the defections of KGB officers and officers of allied Soviet bloc services from the late 1960s to the 1980s. Stanislav Levchenko and Ilya Dzerkvilov were among the Soviet defectors. By 1990, both men had written books recounting their work on disinformation operations for the KGB. Archival documentation revealed in the disorder of the
The extent of Soviet disinformation covert operation campaigns came to light through the defections of KGB officers and officers of allied Soviet bloc services from the late 1960s to the 1980s. Stanislav Levchenko and Ilya Dzerkvilov were among the Soviet defectors. By 1990, both men had written books recounting their work on disinformation operations for the KGB. Archival documentation revealed in the disorder of the fall of the Soviet Union
The dissolution of the Soviet Union, also negatively connoted as rus, Разва́л Сове́тского Сою́за, r=Razvál Sovétskogo Soyúza, ''Ruining of the Soviet Union''. was the process of internal disintegration within the Sov ...
later confirmed their testimonials.
An early example of successful Soviet disinformation was the 1961 pamphlet, ''A Study of a Master Spy (Allen Dulles)''. It was published in the United Kingdom and was highly critical of U.S. CIA director Allen Dulles. The purported authors were given as Independent Labour Party
The Independent Labour Party (ILP) was a British political party of the left, established in 1893 at a conference in Bradford, after local and national dissatisfaction with the Liberals' apparent reluctance to endorse working-class candidates ...
Member of Parliament
A member of parliament (MP) is the representative in parliament of the people who live in their electoral district. In many countries with bicameral parliaments, this term refers only to members of the lower house since upper house members o ...
Bob Edwards and the reporter Kenneth Dunne, but the real author was senior disinformation officer KGB Colonel Vassily Sitnikov. in 1968, the fake '' Who's Who in the CIA'' was published, which was quoted as authoritative in the West until the early 1990s.
According to American journalist Max Holland, Soviet archives, particularly those released by Vasili Mitrokhin
Vasili Nikitich Mitrokhin (russian: link=no, Васи́лий Ники́тич Митро́хин; March 3, 1922 – January 23, 2004) was a major and senior archivist for the Soviet Union's foreign intelligence service, the First Chief Di ...
, "prove that the KGB played a central, pernicious role in fomenting the belief that the CIA was involved in Kennedy's assassination." Among other incidents, Holland stated that the KGB planted a false story in the Italian newspaper ''Paese Sera'' alleging that Clay Shaw, whom district attorney Jim Garrison
James Carothers Garrison (born Earling Carothers Garrison; November 20, 1921 – October 21, 1992) was the District Attorney of Orleans Parish, Louisiana, from 1962 to 1973. A member of the Democratic Party, he is best known for his investigat ...
indicted in connection with the assassination, was a high-level "CIA operative". The KGB disinformation influenced Garrison's subsequent arguments during the trial of Clay Shaw and was later referenced in Oliver Stone's 1991 film '' JFK'', notwithstanding Shaw's acquittal. Holland writes that "Arguably, 'JFK''is the only American feature film made during the Cold War to have, as its very axis, a lie concocted in the KGB's disinformation factories."
According to senior SVR officer Sergei Tretyakov, the KGB had been responsible for creating the entire nuclear winter story as an attempt to stop the deployment of Pershing II
The Pershing II Weapon System was a solid-fueled two-stage medium-range ballistic missile designed and built by Martin Marietta to replace the Pershing 1a Field Artillery Missile System as the United States Army's primary nuclear-capable thea ...
missiles. Tretyakov said that in 1979, the KGB started work to prevent the United States from deploying the missiles in Western Europe and that they had been directed by Yuri Andropov
Yuri Vladimirovich Andropov (– 9 February 1984) was the sixth paramount leader of the Soviet Union and the fourth General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union. After Leonid Brezhnev's 18-year rule, Andropov served in the p ...
to distribute disinformation, based on a faked "doomsday report" by the Soviet Academy of Sciences. The report contained false information on the effect of nuclear war on climate, and was distributed to peace groups, environmentalists, and the journal ''Ambio: A Journal of the Human Environment''.
During the 1970s, the U.S. intelligence apparatus made little effort to counter Soviet disinformation campaigns. That posture changed during the Carter administration, however, after the White House
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United States. It is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW in Washington, D.C., and has been the residence of every U.S. president since John Adams in ...
had been made the subject of a propaganda operation by Soviet intelligence to affect international relations between the U.S. and South Africa. On 17 September 1980, White House Press Secretary Jody Powell
Joseph Lester "Jody" Powell, Jr. (September 30, 1943 – September 14, 2009) was an American political advisor who served as a White House press secretary during the presidency of Jimmy Carter. Powell later co-founded a public relations firm.
E ...
acknowledged that a falsified ''Presidential Review Memorandum on Africa'' falsely stated that the U.S. had endorsed the apartheid
Apartheid (, especially South African English: , ; , "aparthood") was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. Apartheid was ...
government in South Africa and was actively committed to discrimination against African Americans. Prior to the revelation by Powell, an advance copy of the 18 September 1980 issue of San Francisco-based publication the ''Sun Reporter'' had been disseminated, which carried the fake claims. ''Sun Reporter'' was published by Carlton Benjamin Goodlett, a Presidential Committee member of a Soviet front group, the World Peace Council. U.S. President Jimmy Carter was appalled at the lies, and his administration then displayed increased interest in the CIA's efforts to counter Soviet disinformation.
In 1982, the CIA issued a report on active measures used by Soviet intelligence. The report documented numerous instances of disinformation campaigns against the U.S., including planting a notion that it had organized the 1979 Grand Mosque seizure
The Grand Mosque seizure lasted from 20 November 1979 to 4 December 1979, when extremist militants in Saudi Arabia calling for the overthrow of the House of Saud besieged and took over Masjid al-Haram, the holiest Islamic site, in the city of M ...
, as well as forgery of documents purporting to show the U.S. would use nuclear bombs
A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission (fission bomb) or a combination of fission and fusion reactions ( thermonuclear bomb), producing a nuclear explosion. Both bom ...
on its NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
allies.
In 1985, the Soviets launched an elaborate disinformation campaign called Operation INFEKTION
Operation INFEKTION was an active measure disinformation campaign run by the KGB in the 1980s to plant the idea that the United States had invented HIV/AIDS as part of a biological weapons research project at Fort Detrick, Maryland. Historian ...
to influence global opinion that the U.S. had invented AIDS. The campaign included allegations that the disease had been created as an "ethnic weapon" to destroy non-whites. The head of Russian foreign intelligence, Yevgeny Primakov, admitted the existence of the Operation INFEKTION in 1992.
In 1985, Aldrich Ames gave the KGB a significant amount of information on CIA informants, and the Soviet government swiftly moved to arrest those individuals. Soviet intelligence feared that the rapid action would alert the CIA that Ames was a spy, however. To conceal Ames's duplicity from the CIA, the KGB manufactured disinformation as to the reasoning behind the arrests of the intelligence agents. In the summer of 1985, a KGB officer who was a double agent
In the field of counterintelligence, a double agent is an employee of a secret intelligence service for one country, whose primary purpose is to spy on a target organization of another country, but who is now spying on their own country's organ ...
working for the CIA on a mission in Africa traveled to a dead drop in Moscow on his way home, but never reported in. The CIA heard from a European KGB source that its agent had been arrested. Simultaneously, the FBI and CIA learned from a second KGB source of its agent's arrest. Only after Ames had been outed as a spy for the KGB would it become apparent that the KGB had known all along that both men had been working for the U.S. government, and that Soviet disinformation had been successful in confounding the American intelligence agency.
Disinformation and propaganda
Whether and to what degree these terms overlap is subject to debate. Some (like U.S. Department of State) define propaganda as the use of non-rational arguments to either advance or undermine a political ideal, and use disinformation as an alternative name for undermining propaganda. While others consider them to be separate concepts altogether. One popular distinction holds that disinformation also describes politically motivated messaging designed explicitly to engender public cynicism, uncertainty, apathy, distrust, and paranoia, all of which disincentivize citizen engagement and mobilization for social or political change.Russian disinformation in the post-Soviet era
During the Cold War, the Soviet Union used propaganda and disinformation as part of its " active measures...against the populations of Western nations"." During the administration of Boris Yeltsin, the first President of Russia after the collapse of theSoviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
, "disinformation" was discussed in the Russian media and by Russian politicians in relation to the disinformation of the Soviet era, and to differentiate Boris Yeltsin
Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin ( rus, Борис Николаевич Ельцин, p=bɐˈrʲis nʲɪkɐˈla(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ ˈjelʲtsɨn, a=Ru-Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin.ogg; 1 February 1931 – 23 April 2007) was a Soviet and Russian politician wh ...
's "new Russia" from its Soviet predecessor. However, in the post-Soviet era, disinformation evolved to become a key tactic in the military doctrine of Russia
The military doctrine of the Russia is a strategic planning document of the Russia and represents a system of officially state adopted views of preparation for the armed protection of Russia. The most recent revision of the military doctrine was ap ...
. Its use has increased under the leadership of Vladimir Putin, particularly after the 2008 Russian invasion of Georgia. This style of disinformation propaganda has been described as a " firehose of falsehood" by observers due to its high number of channels and willingness to disseminate outright falsehoods, to the point of inconsistency. It differs from Soviet-era disinformation tactics in its use of the internet, claimed amateur journalism, and social media
Social media are interactive media technologies that facilitate the creation and sharing of information, ideas, interests, and other forms of expression through virtual communities and networks. While challenges to the definition of ''social medi ...
.
The European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
and NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
saw Russian disinformation in the early twenty-first century as such a problem that both set up special units to analyze and debunk fabricated falsehoods. NATO founded a modest facility in Latvia to respond to disinformation and agreement by heads of state and governments in March 2015 let the EU create the European External Action Service
The European External Action Service (EEAS) is the diplomatic service and combined foreign and defence ministry of the European Union (EU). The EEAS is led by the High Representative for Foreign Affairs and Security Policy (HR/VP), who is al ...
East Stratcom Task Force, which publishes weekly reports on its website "EU vs Disinfo." The website and its partners identified and debunked more than 3,500 pro-Kremlin disinformation cases between September 2015 and November 2017.
Russia meanwhile used its television outlet RT (formerly known as Russia Today) and the Sputnik news agency. When explaining the 2016 annual report of the Swedish Security Service
The Swedish Security Service ( sv, Säkerhetspolisen , abbreviated SÄPO ; until 1989 ''Rikspolisstyrelsens säkerhetsavdelning'', abbreviated RPS/Säk) is a Swedish government agency organised under the Ministry of Justice. It operates as a ...
on disinformation, the representative Wilhelm Unge stated: "We mean everything from Internet trolls to propaganda and misinformation spread by media companies like RT and Sputnik." RT and Sputnik were created to focus on Western audiences and function by Western standards, and RT tends to focus on how problems are the fault of Western countries.
Social media platforms and the internet
In the 2010s, as social media gained prominence, Russia then began to use platforms such asFacebook
Facebook is an online social media and social networking service owned by American company Meta Platforms. Founded in 2004 by Mark Zuckerberg with fellow Harvard College students and roommates Eduardo Saverin, Andrew McCollum, Dustin Mosk ...
, Twitter
Twitter is an online social media and social networking service owned and operated by American company Twitter, Inc., on which users post and interact with 280-character-long messages known as "tweets". Registered users can post, like, and ...
, and YouTube
YouTube is a global online video sharing and social media platform headquartered in San Bruno, California. It was launched on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim. It is owned by Google, and is the second mo ...
to spread disinformation. Russian web brigades and bots, typically operated by Russia's Internet Research Agency
The Internet Research Agency (IRA; russian: Агентство интернет-исследований, translit=Agentstvo internet-issledovaniy), also known as ''Glavset'' (russian: link=no, Главсеть) and known in Russian Internet sla ...
(IRA), were commonly used to disseminate disinformation throughout these social media channels. As of late 2017, Facebook believed that as many as 126 million of its users had seen content from Russian disinformation campaigns on its platform. Twitter stated that it had found 36,000 Russian bots spreading tweets related to the 2016 U.S. elections. Elsewhere, Russia has used social media to destabilize former Soviet states such as Ukraine and Western nations such as France and Spain.
In 2020, the US State Department identified several "proxy sites" used by Russian state actors "to create and amplify false narratives." These sites include the Strategic Culture Foundation, online journal the '' New Eastern Outlook'', Crimea-based news agency NewsFront
''Newsfront'' is a 1978 Australian drama film starring Bill Hunter, Wendy Hughes, Chris Haywood and Bryan Brown, directed by Phillip Noyce. The screenplay is written by David Elfick, Bob Ellis, Philippe Mora, and Phillip Noyce. The original mu ...
, and SouthFront
''SouthFront'' (sometimes written ''South Front'') is a multilingual website registered in Russia and based in Crimea. It has been accused by multiple sources of being an outlet for disinformation and propaganda under the control of the Russian ...
, a website targeted at "military enthusiasts, veterans, and conspiracy theorists."
Internet Research Agency
In the runup to and during the2020 U.S. presidential election
The 2020 United States presidential election was the 59th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020. The Democratic ticket of former vice president Joe Biden and the junior U.S. senator from California Kamala Ha ...
, Russia's Internet Research Agency
The Internet Research Agency (IRA; russian: Агентство интернет-исследований, translit=Agentstvo internet-issledovaniy), also known as ''Glavset'' (russian: link=no, Главсеть) and known in Russian Internet sla ...
(IRA) demonstrated evolved tactics for spreading disinformation. Probably to evade the detection mechanisms of social media platforms, the IRA co-opted activists working for a human-rights focused Ghanaian NGO to target black communities in the U.S. Russian campaigns have also evolved to become more cross-platform, with content spreading, not only on Facebook and Twitter, but also on Tumblr, Wordpress, and Medium. The IRA is also more emboldened, with evidence that they recruited U.S. journalists to write articles critical of U.S. presidential candidate Joe Biden.
Russian Institute for Strategic Studies
During both the 2016 and the 2020 elections, theRussian Institute for Strategic Studies
The Russian Institute for Strategic Studies (RISS) or (RISI) or (RISY) (russian: Российский институт стратегических исследований (РИСИ)) is a Russian research and analytical center formed by decree ...
(RISS) was integral to disinformation efforts from Putin and the Kremlin. Leonid Petrovich Reshetnikov
Leonid Petrovich Reshetnikov ( rus, Леонид Петрович Решетников}; (born 6 February 1947, Potsdam) is a Soviet and Russian secret service agent, Lieutenant-General of Foreign Intelligence Service, director of the Russian ...
headed RISS in 2016, while Mikhail Fradkov headed it in 2020. During the 2016 U.S. presidential election
The 2016 United States presidential election was the 58th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 8, 2016. The Republican ticket of businessman Donald Trump and Indiana governor Mike Pence defeated the Democratic ticket ...
, George Papadopoulos met several times with Panos Kammenos
Panagiotis "Panos" Kammenos ( el, Παναγιώτης "Πάνος" Καμμένος, ; born 12 May 1965) is a Greek politician and the founder of the right-wing party "Independent Greeks", which formed the governing coalition of the Hellenic Par ...
, who had numerous close ties to Russian intelligence, Vladimir Putin
Vladimir Vladimirovich Putin; (born 7 October 1952) is a Russian politician and former intelligence officer who holds the office of president of Russia. Putin has served continuously as president or prime minister since 1999: as prime min ...
, and the Kremlin group tasked with interfering in the 2016 U.S. elections. Kammenos formed the Athens
Athens ( ; el, Αθήνα, Athína ; grc, Ἀθῆναι, Athênai (pl.) ) is both the capital and largest city of Greece. With a population close to four million, it is also the seventh largest city in the European Union. Athens dominates ...
-based ''Institute of Geopolitical Studies'' which in November 2014 signed a "memorandum of understanding" with the former SVR officer Reshetnikov who headed RISS. In 2009, RISS, which had been an SVR operation, was placed under control of the Russian president with Reshetnikov regularly meeting with Putin and participated in Russian interference in the 2016 U.S. elections by developing plans of action; with Russian intelligence assets and using a large disinformation campaign, Putin would support Republicans and Donald Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who served as the 45th president of the United States from 2017 to 2021.
Trump graduated from the Wharton School of the University of P ...
's campaign, and disrupt Democrats and Hillary Clinton
Hillary Diane Rodham Clinton ( Rodham; born October 26, 1947) is an American politician, diplomat, and former lawyer who served as the 67th United States Secretary of State for President Barack Obama from 2009 to 2013, as a United States sen ...
's campaign, and if Trump were likely to lose the election, then Russia would shift its efforts to focus upon voter fraud in the U.S. in order to undermine the legitimacy of its electoral system and elections. Kammenos' positions followed closely with the Kremlin's talking points.
During the 2020 U.S. presidential election
The 2020 United States presidential election was the 59th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020. The Democratic ticket of former vice president Joe Biden and the junior U.S. senator from California Kamala Ha ...
campaign, Russia's numerous disinformation attacks including support for white supremacist activities and attacks of Democratic presidential candidate Joe Biden's mental fitness were utilized by Trump, senior Trump Administration officials, and his re-election campaign. Brian Murphy Brian Murphy may refer to:
Sportspeople
* Brian Murphy (Jamaican cricketer) (born 1973), Jamaican cricketer
* Brian Murphy (Zimbabwean cricketer) (born 1976), Zimbabwean cricketer
* Brian Murphy (baseball) (born 1980), American head baseball coach ...
, who was acting chief of intelligence at the Department of Homeland Security from March 2018 until August 2020, alleged that he was instructed "to cease providing intelligence assessments on the threat of Russian interference in the United States, and instead start reporting on interference activities by China and Iran." Chad Wolf, who was acting secretary of the Department of Homeland Security, alleged that Robert C. O'Brien, who was Trump's national security advisor, had the assessments of Russian interference suppressed. John Cohen, who was under secretary of intelligence at the Department of Homeland Security during Barack Obama
Barack Hussein Obama II ( ; born August 4, 1961) is an American politician who served as the 44th president of the United States from 2009 to 2017. A member of the Democratic Party, Obama was the first African-American president of the ...
's presidency, stated: "By blocking information from being released that describes threats facing the nation... undermines the ability of the public and state and local authorities to work with the federal government to counteract the threat."
Lev Parnas, Igor Fruman, Yuriy Lutsenko
Yuriy Vitaliyovych Lutsenko ( uk, Юрій Віталійович Луценко; born 14 December 1964) is a Ukrainian politician whose most recent post was Prosecutor General of Ukraine from 12 May 2016John Solomon, Dmytro Firtash, and his allies Victoria Toensing and Joe diGenova were noted in a Fox News internal report ''Ukraine, Disinformation, & the Trump Administration: a Full Timeline of Events'', which was written by Fox News senior political affairs specialist Bryan S. Murphy and made public by Marcus DiPaola, Based on a 9 December 2019 update of the document. as indispensable "in the collection and domestic publication of elements of this disinformation campaign" and numerous falsehoods.
 The
The
 Research related to disinformation studies is increasing as an applied area of inquiry. The call to formally classify disinformation as a cybersecurity threat is made by advocates due to its increase in social networking sites. Researchers working for the University of Oxford found that over a three-year period the number of governments engaging in online disinformation rose from 28 in 2017, to 40 in 2018, and 70 in 2019. Despite the proliferation of social media websites, Facebook and Twitter showed the most activity in terms of active disinformation campaigns. Techniques reported on included the use of bots to amplify hate speech, the illegal harvesting of data, and paid trolls to harass and threaten journalists.
Whereas disinformation research focuses primarily on how actors orchestrate deceptions on social media, primarily via
Research related to disinformation studies is increasing as an applied area of inquiry. The call to formally classify disinformation as a cybersecurity threat is made by advocates due to its increase in social networking sites. Researchers working for the University of Oxford found that over a three-year period the number of governments engaging in online disinformation rose from 28 in 2017, to 40 in 2018, and 70 in 2019. Despite the proliferation of social media websites, Facebook and Twitter showed the most activity in terms of active disinformation campaigns. Techniques reported on included the use of bots to amplify hate speech, the illegal harvesting of data, and paid trolls to harass and threaten journalists.
Whereas disinformation research focuses primarily on how actors orchestrate deceptions on social media, primarily via
Disinformation
– a learning resource from the British Library including an interactive movie and activities.
MediaWell
– an initiative of the nonprofit
Sean Hannity
Sean Patrick Hannity (born December 30, 1961) is an American talk show host, conservative political commentator, and author. He is the host of '' The Sean Hannity Show'', a nationally syndicated talk radio show, and has also hosted a commen ...
, Laura Ingraham
Laura Anne Ingraham (born June 19, 1963) is an American conservative television host. Gale Biography In Context. She has been the host of '' The Ingraham Angle'' on Fox News Channel since October 2017, and is the editor-in-chief of LifeZette ...
, Lou Dobbs, and Pete Sessions, who is the son of William S. Sessions, the former FBI director under Presidents Ronald Reagan and George H. W. Bush, were supportive of disinformation efforts. In September 2020, two supervisors and a quarter of the persons with Fox News ''Brain Room'', which was established by Roger Ailes
Roger Eugene Ailes (May 15, 1940 – May 18, 2017) was an American television executive and media consultant. He was the chairman and CEO of Fox News, Fox Television Stations and 20th Television. Ailes was a media consultant for Republica ...
as a fact-checking and research unit, received layoffs allegedly ordered by Joe Dorrego and organized by Porter Berry and Stefanie Wheeler Choi in order to have Fox News support Trump's information campaign; according to a Brain Room employee, "the Brain Room, in their research, came up with facts that were not used in Fox reports or were in contradiction to what Fox aired. I have to imagine that kind of tension has always existed there, between the fact-checkers and what is often reported."
In March 2021, Christopher A. Wray, who was the Director of the FBI during most of Trump's presidency, and the National Intelligence Council
The National Intelligence Council (NIC), established in 1979 and reporting to the Director of National Intelligence, bridges the United States Intelligence Community (IC) with policy makers in the United States. The NIC produces the "Global Tren ...
stated that numerous Russians, other individuals, proxies, and entitites, including Rudy Giuliani, Fox News, the One America News Network, the documentary film '' The Ukraine Hoax: Impeachment, Biden Cash, and Mass Murder'' that was created with support from Konstantin Kilimnik, Andrii Derkach, Andrii Telizhenko, Sergey Petrushin, and Michael Caputo
Michael Raymon Caputo (born March 24, 1962) is an American political strategist and lobbyist. In April 2020, Caputo was appointed as assistant secretary of public affairs in the Department of Health and Human Services in the Trump administration. ...
, and aired on 21 January 2022, two weeks before the Senate's acquittal of Trump after his first impeachment trial, supported anti-Biden, anti-Ukraine, pro-Trump, pro-Russia, pro-Kremlin, and pro-Putin disinformation efforts during the Trump presidency, including Trump's two impeachment trials and his two presidential campaigns.
Russo-Ukrainian War
Modern Russian propaganda is different from classic Soviet Cold War techniques, relying on obfuscation and using the contemporary information environment with all the channels available to it, including the Internet, social media, professional and amateur journalism, and media outlets. They use numerous channels and messages, in order to confuse and overwhelm the audience. ARAND
The RAND Corporation (from the phrase "research and development") is an American nonprofit global policy think tank created in 1948 by Douglas Aircraft Company to offer research and analysis to the United States Armed Forces. It is finan ...
report labeled their propaganda model as a " firehose of falsehood".
Russian disinformation has been used in the Russo-Ukrainian War
The Russo-Ukrainian War; uk, російсько-українська війна, rosiisko-ukrainska viina. has been ongoing between Russia (alongside Russian separatists in Ukraine) and Ukraine since February 2014. Following Ukraine's Rev ...
. In March 2022 during the Russian invasion, ProPublica reported what may be the first case of a disinformation false-flag operation
Disinformation is false information deliberately spread to deceive people. It is sometimes confused with misinformation, which is false information but is not deliberate.
The English word ''disinformation'' comes from the application of the ...
. Videos were discovered purporting to show Ukrainian-produced disinformation about strikes inside Ukraine which were then "debunked" as some other event outside Ukraine. However, the original supposed "Ukraine-produced" disinformation was never disseminated by anyone, and was in fact preventive disinformation created in order to be debunked and cause confusion and mitigate the impact on the Russian public of real footage of Russian strikes within Ukraine when it eventually got past Russian-controlled media. According to Patrick Warren, head of Clemson's Media Forensics Hub, "It's like Russians actually pretending to be Ukrainians spreading disinformation. ... The reason that it’s so effective is because you don’t actually have to convince someone that it's true. It’s sufficient to make people uncertain as to what they should trust."
English language spread
 The
The United States Intelligence Community
United may refer to:
Places
* United, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community
* United, West Virginia, an unincorporated community
Arts and entertainment Films
* ''United'' (2003 film), a Norwegian film
* ''United'' (2011 film), a BBC Two f ...
appropriated use of the term ''disinformation'' in the 1950s from the Russian ''dezinformatsiya'', and began to use similar strategies during the Cold War and in conflict with other nations. ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid d ...
'' reported in 2000 that during the CIA's effort to substitute Mohammed Reza Pahlavi
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the monoth ...
for then- Prime Minister of Iran Mohammad Mossadegh, the CIA placed fictitious stories in the local newspaper. Reuters
Reuters ( ) is a news agency owned by Thomson Reuters Corporation. It employs around 2,500 journalists and 600 photojournalists in about 200 locations worldwide. Reuters is one of the largest news agencies in the world.
The agency was esta ...
documented how, subsequent to the 1979 Soviet Union invasion of Afghanistan during the Soviet–Afghan War
The Soviet–Afghan War was a protracted armed conflict fought in the Democratic Republic of Afghanistan from 1979 to 1989. It saw extensive fighting between the Soviet Union and the Afghan mujahideen (alongside smaller groups of anti-Sovie ...
, the CIA put false articles in newspapers of Islamic-majority countries, inaccurately stating that Soviet embassies had "invasion day celebrations". Reuters noted a former U.S. intelligence officer said they would attempt to gain the confidence of reporters and use them as secret agent
Espionage, spying, or intelligence gathering is the act of obtaining secret or confidential information (intelligence) from non-disclosed sources or divulging of the same without the permission of the holder of the information for a tangib ...
s, to affect a nation's politics by way of their local media.
In October 1986, the term gained increased currency in the U.S. when it was revealed that two months previously, the Reagan Administration
Ronald Reagan's tenure as the 40th president of the United States began with his first inauguration on January 20, 1981, and ended on January 20, 1989. Reagan, a Republican from California, took office following a landslide victory over ...
had engaged in a disinformation campaign against then-leader of Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Suda ...
, Muammar Gaddafi. White House
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United States. It is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW in Washington, D.C., and has been the residence of every U.S. president since John Adams in ...
representative Larry Speakes said reports of a planned attack on Libya as first broken by ''The Wall Street Journal
''The Wall Street Journal'' is an American business-focused, international daily newspaper based in New York City, with international editions also available in Chinese and Japanese. The ''Journal'', along with its Asian editions, is published ...
'' on August 25, 1986, were "authoritative", and other newspapers including ''The Washington Post
''The Washington Post'' (also known as the ''Post'' and, informally, ''WaPo'') is an American daily newspaper published in Washington, D.C. It is the most widely circulated newspaper within the Washington metropolitan area and has a large nati ...
'' then wrote articles saying this was factual. U.S. State Department representative Bernard Kalb
Bernard Kalb (born February 4, 1922) is an American journalist, moderator, media critic, lecturer, and author.
Life and career
Born in New York City, he covered international affairs for more than three decades at CBS News, NBC News and '' The ...
resigned from his position in protest over the disinformation campaign, and said: "Faith in the word of America is the pulse beat of our democracy."
The executive branch of the Reagan administration
Ronald Reagan's tenure as the 40th president of the United States began with his first inauguration on January 20, 1981, and ended on January 20, 1989. Reagan, a Republican from California, took office following a landslide victory over ...
kept watch on disinformation campaigns through three yearly publications by the Department of State: ''Active Measures: A Report on the Substance and Process of Anti-U.S. Disinformation and Propaganda Campaigns'' (1986); ''Report on Active Measures and Propaganda, 1986–87'' (1987); and ''Report on Active Measures and Propaganda, 1987–88'' (1989).
''Disinformation'' first made an appearance in dictionaries in 1985, specifically, ''Webster's New College Dictionary'' and the ''American Heritage Dictionary''. In 1986, the term ''disinformation'' was not defined in ''Webster's New World Thesaurus'' or ''New Encyclopædia Britannica''. After the Soviet term became widely known in the 1980s, native speakers of English broadened the term as "any government communication (either overt or covert) containing intentionally false and misleading material, often combined selectively with true information, which seeks to mislead and manipulate
Manipulation may refer to:
* Manipulation (psychology) - the action of manipulating someone in a clever or unscrupulous way
*Crowd manipulation - use of crowd psychology to direct the behavior of a crowd toward a specific action
::* Internet mani ...
either elites or a mass audience."
By 1990, use of the term ''disinformation'' had fully established itself in the English language within the lexicon of politics. By 2001, the term ''disinformation'' had come to be known as simply a more civil phrase for saying someone was lying
A lie is an assertion that is believed to be false, typically used with the purpose of deception, deceiving or Deception, misleading someone. The practice of communicating lies is called lying. A person who communicates a lie may be termed a l ...
. Stanley B. Cunningham wrote in his 2002 book ''The Idea of Propaganda'' that ''disinformation'' had become pervasively used as a synonym for propaganda.
Responses from cultural leaders
Pope Francis
Pope Francis ( la, Franciscus; it, Francesco; es, link=, Francisco; born Jorge Mario Bergoglio, 17 December 1936) is the head of the Catholic Church. He has been the bishop of Rome and sovereign of the Vatican City State since 13 March 2013. ...
condemned disinformation in a 2016 interview, after being made the subject of a fake news website
Fake news websites (also referred to as hoax news websites) are websites on the Internet that deliberately publish fake news— hoaxes, propaganda, and disinformation purporting to be real news—often using social media to drive web traffic and ...
during the 2016 U.S. election cycle which falsely claimed that he supported Donald Trump
Donald John Trump (born June 14, 1946) is an American politician, media personality, and businessman who served as the 45th president of the United States from 2017 to 2021.
Trump graduated from the Wharton School of the University of P ...
. He said the worst thing the news media could do was spread disinformation. He said the act was a sin
In a religious context, sin is a transgression against divine law. Each culture has its own interpretation of what it means to commit a sin. While sins are generally considered actions, any thought, word, or act considered immoral, selfish, s ...
, comparing those who spread disinformation to individuals who engage in coprophilia
Coprophilia (from Greek κόπρος, ''kópros'' 'excrement' and φιλία, ''philía'' 'liking, fondness'), also called scatophilia or scat (Greek: σκατά, ''skatá'' 'feces'), is the paraphilia involving sexual arousal and pleasure from ...
.
Ethics in warfare
In a contribution to the 2014 book ''Military Ethics and Emerging Technologies'', writers David Danks and Joseph H. Danks discuss the ethical implications in using disinformation as a tactic during information warfare. They note there has been a significant degree of philosophical debate over the issue as related to the ethics of war and use of the technique. The writers describe a position whereby the use of disinformation is occasionally allowed, but not in all situations. Typically the ethical test to consider is whether the disinformation was performed out of a motivation of good faith and acceptable according to the rules of war. By this test, the tactic during World War II of putting fake inflatable tanks in visible locations on the Pacific Islands in order to falsely present the impression that there were larger military forces present would be considered as ethically permissible. Conversely, disguising a munitions plant as a healthcare facility in order to avoid attack would be outside the bounds of acceptable use of disinformation during war.Research
 Research related to disinformation studies is increasing as an applied area of inquiry. The call to formally classify disinformation as a cybersecurity threat is made by advocates due to its increase in social networking sites. Researchers working for the University of Oxford found that over a three-year period the number of governments engaging in online disinformation rose from 28 in 2017, to 40 in 2018, and 70 in 2019. Despite the proliferation of social media websites, Facebook and Twitter showed the most activity in terms of active disinformation campaigns. Techniques reported on included the use of bots to amplify hate speech, the illegal harvesting of data, and paid trolls to harass and threaten journalists.
Whereas disinformation research focuses primarily on how actors orchestrate deceptions on social media, primarily via
Research related to disinformation studies is increasing as an applied area of inquiry. The call to formally classify disinformation as a cybersecurity threat is made by advocates due to its increase in social networking sites. Researchers working for the University of Oxford found that over a three-year period the number of governments engaging in online disinformation rose from 28 in 2017, to 40 in 2018, and 70 in 2019. Despite the proliferation of social media websites, Facebook and Twitter showed the most activity in terms of active disinformation campaigns. Techniques reported on included the use of bots to amplify hate speech, the illegal harvesting of data, and paid trolls to harass and threaten journalists.
Whereas disinformation research focuses primarily on how actors orchestrate deceptions on social media, primarily via fake news
Fake news is false or misleading information presented as news. Fake news often has the aim of damaging the reputation of a person or entity, or making money through advertising revenue.Schlesinger, Robert (April 14, 2017)"Fake news in reality ...
, new research investigates how people take what started as deceptions and circulate them as their personal views. As a result, research shows that disinformation can be conceptualized as a program that encourages engagement in oppositional fantasies (i.e., culture war
A culture war is a cultural conflict between social groups and the struggle for dominance of their values, beliefs, and practices. It commonly refers to topics on which there is general societal disagreement and polarization in societal valu ...
s), through which disinformation circulates as rhetorical ammunition for never-ending arguments. As disinformation entangles with culture war
A culture war is a cultural conflict between social groups and the struggle for dominance of their values, beliefs, and practices. It commonly refers to topics on which there is general societal disagreement and polarization in societal valu ...
s, identity-driven controversies constitute a vehicle through which disinformation disseminates on social media
Social media are interactive media technologies that facilitate the creation and sharing of information, ideas, interests, and other forms of expression through virtual communities and networks. While challenges to the definition of ''social medi ...
. This means that disinformation thrives, not despite raucous grudges but because of them. The reason is that controversies provide fertile ground for never-ending debates that solidify points of view.
Scholars have pointed out that disinformation is not only a foreign threat as domestic purveyors of disinformation are also leveraging traditional media outlets such as newspapers, radio stations, and television news media to disseminate false information. Current research suggests right-wing online political activists
Activism (or Advocacy) consists of efforts to promote, impede, direct or intervene in social, political, economic or environmental reform with the desire to make changes in society toward a perceived greater good. Forms of activism range fro ...
in the United States may be more likely to use disinformation as a strategy and tactic. Governments have responded with a wide range of policies to address concerns about the potential threats that disinformation poses to democracy, however, there is little agreement in elite policy discourse or academic literature as to what it means for disinformation to threaten democracy, and how different policies might help to counter its negative implications.
Consequences of exposure to disinformation online
There is a broad consensus amongst scholars that there is a high degree of disinformation, misinformation, and propaganda online; however, it is unclear to what extent such disinformation has on political attitudes in the public and, therefore, political outcomes. Thisconventional wisdom
The conventional wisdom or received opinion is the body of ideas or explanations generally accepted by the public and/or by experts in a field. In religion, this is known as orthodoxy.
Etymology
The term is often credited to the economist John ...
has come mostly from investigative journalists, with a particular rise during the 2016 U.S. election: some of the earliest work came from Craig Silverman at Buzzfeed News. Cass Sunstein supported this in ''#Republic,'' arguing that the internet would become rife with echo chambers and informational cascades of misinformation leading to a highly polarized and ill-informed society.
Research after the 2016 election found: (1) for 14 percent of Americans social media was their “most important” source of election news; 2) known false news stories “favoring Trump were shared a total of 30 million times on Facebook, while those favoring Clinton were shared 8 million times”; 3) the average American adult saw fake news stories, “with just over half of those who recalled seeing them believing them”; and 4) people are more likely to “believe stories that favor their preferred candidate, especially if they have ideologically segregated social media networks.” Correspondingly, whilst there is wide agreement that the digital spread and uptake of disinformation during the 2016 election was massive and very likely facilitated by foreign agents, there is an ongoing debate on whether all this had any actual effect on the election. For example, a double blind randomized-control experiment by researchers from the London School of Economics (LSE), found that exposure to online fake news about either Trump or Clinton had no significant effect on intentions to vote for those candidates. The authors of the study argue that their findings in tandem with the documented political demographic makeup of online fake news American readerships shown in other studies, indicate that fake news at most reinforces a reader’s pre-existing partisan and ideological dispositions, but is otherwise highly unlikely to induce conversions in voter preferences. This further suggests that the sharing and believing of online political fake news posts and articles didn’t cause readers who weren’t already very likely to (i.e., already politically conservative), to then vote for Donald Trump. As such, despite its mass dissemination during the 2016 Presidential Elections, online fake news probably didn’t cost Hillary Clinton the votes needed to secure the presidency.
Research on this topic is continuing, and some evidence is less clear. For example, internet access and time spent on social media does not appear correlated with polarisation. Further, misinformation appears not to significantly change political knowledge of those exposed to it. There seems to be a higher level of diversity of news sources that users are exposed to on Facebook and Twitter than conventional wisdom would dictate, as well as a higher frequency of cross-spectrum discussion. Other evidence has found that disinformation campaigns rarely succeed in altering the foreign policies of the targeted states.
Research is also challenging because disinformation is meant to be difficult to detect and some social media companies have discouraged outside research efforts. For example, researchers found disinformation made “existing detection algorithms from traditional news media ineffective or not applicable... ecause disinformationis intentionally written to mislead readers... ndusers' social engagements with fake news produce data that is big, incomplete, unstructured, and noisy.” Facebook, the largest social media company, has been criticized by analytical journalists and scholars for preventing outside research of disinformation.
Strategies for spreading disinformation
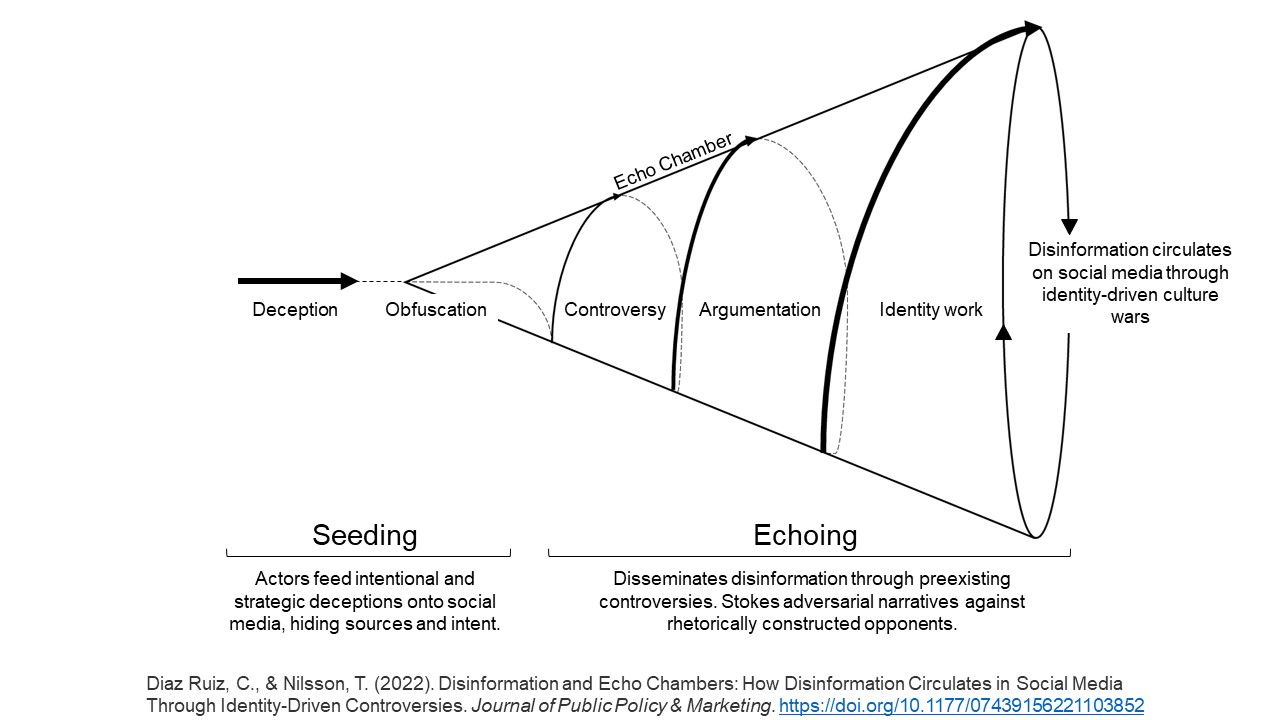
The research literature on how disinformation spreads is growing. Studies show that disinformation spread in social media can be classified into two broad stages: seeding and echoing. "Seeding," when malicious actors strategically insert deceptions, like fake news, into a social media ecosystem, and "echoing" is when the audience disseminates disinformation argumentatively as their own opinions often by incorporating disinformation into a confrontational fantasy. Studies show four main methods of seeding disinformation: # Selective censorship # Manipulation of search rankings # Hacking and releasing # Directly Sharing DisinformationSee also
*Active Measures Working Group The Interagency Active Measures Working Group was a group led by the United States Department of State and later by the United States Information Agency (USIA). The group was formed early during the Reagan administration, in 1981, as an effort to co ...
* Agitprop
Agitprop (; from rus, агитпроп, r=agitpróp, portmanteau of ''agitatsiya'', "agitation" and ''propaganda'', " propaganda") refers to an intentional, vigorous promulgation of ideas. The term originated in Soviet Russia where it referred ...
* Black propaganda
* Censorship
Censorship is the suppression of speech, public communication, or other information. This may be done on the basis that such material is considered objectionable, harmful, sensitive, or "inconvenient". Censorship can be conducted by governments ...
* Chinese information operations and information warfare
* Counter Misinformation Team
* COVID-19 misinformation
False information, including intentional disinformation and conspiracy theories, about the scale of the COVID-19 pandemic and the origin, prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of the disease has been spread through social media, text messagin ...
* Deepfakes
Deepfakes (a portmanteau of "deep learning" and "fake") are synthetic media in which a person in an existing image or video is replaced with someone else's likeness. While the act of creating fake content is not new, deepfakes leverage powerful ...
* Demoralization (warfare)
Demoralization is, in a context of warfare, national security, and law enforcement, a process in psychological warfare with the objective to erode morale among enemy combatants and/or noncombatants. That can encourage them to retreat, surrend ...
* Denial and deception
* Disinformation in the 2021–2022 Russo-Ukrainian crisis
Disinformation has been distributed by governmental agencies and web brigades of the Russian Federation, the Donetsk People's Republic (DPR), and the Luhansk People's Republic (LPR) separatist areas of Ukraine in relation to the 2021–2022 ...
* False flag
A false flag operation is an act committed with the intent of disguising the actual source of responsibility and pinning blame on another party. The term "false flag" originated in the 16th century as an expression meaning an intentional misr ...
* Fear, uncertainty and doubt
Fear, uncertainty and doubt (often shortened to FUD) is a propaganda tactic used in sales, marketing, public relations, politics, polling and cults. FUD is generally a strategy to influence perception by disseminating negative and dubious or fal ...
* Gaslighting
Gaslighting is a colloquialism, loosely defined as manipulating someone so as to make them question their own reality. The term derives from the title of the 1944 American film ''Gaslight'', which was based on the 1938 British theatre play ''Gas ...
* Internet manipulation
Internet manipulation refers to the co-optation of digital technology, such as social media algorithms and automated scripts, for commercial, social or political purposes. Such tactics may be employed with the explicit intent to manipulate public ...
* Kompromat
(russian: links=no, компромат, short for "compromising material") is damaging information about a politician, a businessperson, or other public figure, which may be used to create negative publicity, as well as for blackmail, often to ...
* Manufacturing Consent
''Manufacturing Consent: The Political Economy of the Mass Media'' is a 1988 book by Edward S. Herman and Noam Chomsky. It argues that the mass communication media of the U.S. "are effective and powerful ideological institutions that carry out ...
* Post-truth politics
Post-truth politics (also called post-factual politics and post-reality politics) is a political culture where true/false, honesty/lying have become a focal concern of public life and are viewed by popular commentators and academic researchers a ...
* Propaganda in the Soviet Union
Propaganda in the Soviet Union was the practice of state-directed communication to promote class conflict, internationalism, the goals of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, and the party itself.
The main Soviet censorship body, Glavli ...
* Sharp power Sharp power is the use of manipulative diplomatic policies by one country to influence and undermine the political system of a target country.
History
The National Endowment for Democracy (NED) popularised the term "sharp power" (in use since th ...
* Social engineering (political science)
* The Disinformation Project
Notes
References
Further reading
* * * * O'Connor, Cailin, and James Owen Weatherall, "Why We Trust Lies: The most effective misinformation starts with seeds oftruth
Truth is the property of being in accord with fact or reality.Merriam-Webster's Online Dictionarytruth 2005 In everyday language, truth is typically ascribed to things that aim to represent reality or otherwise correspond to it, such as beliefs ...
", ''Scientific American
''Scientific American'', informally abbreviated ''SciAm'' or sometimes ''SA'', is an American popular science magazine. Many famous scientists, including Albert Einstein and Nikola Tesla, have contributed articles to it. In print since 1845, it i ...
'', vol. 321, no. 3 (September 2019), pp. 54–61.
*
*
*
*
*
External links
Disinformation
– a learning resource from the British Library including an interactive movie and activities.
MediaWell
– an initiative of the nonprofit
Social Science Research Council
The Social Science Research Council (SSRC) is a US-based, independent, international nonprofit organization dedicated to advancing research in the social sciences and related disciplines. Established in Manhattan in 1923, it today maintains a he ...
seeking to track and curate disinformation, misinformation, and fake news research.
{{Authority control
Deception
Communication of falsehoods
Media manipulation
Propaganda techniques
Black propaganda
1920s neologisms
Russian words and phrases
Psychological warfare techniques
Intelligence operations by type