Deportation of the Crimean Tatars on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The deportation of the Crimean Tatars ( crh, Qırımtatar halqınıñ sürgünligi,
 The
The  After the 1917
After the 1917
 Officially due to the collaboration with the Axis Powers during World War II, the Soviet government collectively punished ten ethnic minorities, among them the Crimean Tatars. Punishment included deportation to distant regions of
Officially due to the collaboration with the Axis Powers during World War II, the Soviet government collectively punished ten ethnic minorities, among them the Crimean Tatars. Punishment included deportation to distant regions of  Officially, Crimean Tatars were eliminated from Crimea. The deportation encompassed every person considered by the government to be Crimean Tatar, including children, women, and the elderly, and even those who had been members of the
Officially, Crimean Tatars were eliminated from Crimea. The deportation encompassed every person considered by the government to be Crimean Tatar, including children, women, and the elderly, and even those who had been members of the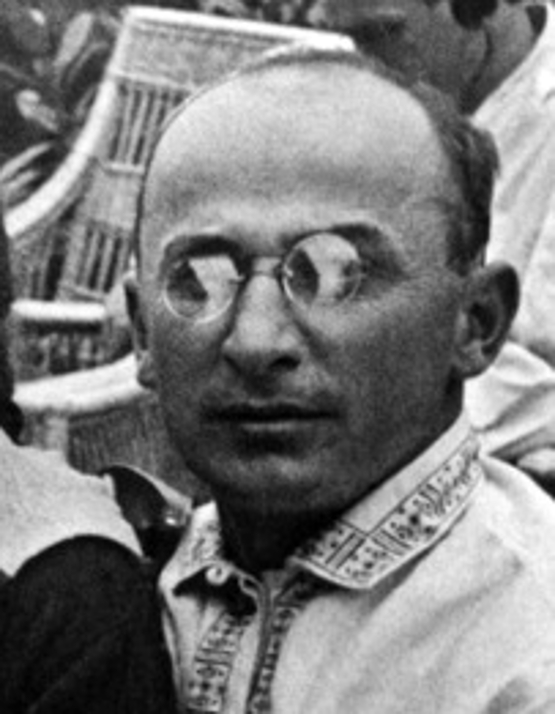  The mass Crimean deportations were organized by Lavrentiy Beria, the chief of the Soviet secret police, the NKVD, and his subordinates Bogdan Kobulov,
The mass Crimean deportations were organized by Lavrentiy Beria, the chief of the Soviet secret police, the NKVD, and his subordinates Bogdan Kobulov,


 The UN reported that of the over 10,000 people left Crimea after the annexation in 2014, most were Crimean Tatars, which caused a further decline of their fragile community. Crimean Tatars stated several reasons for their departure, among them insecurity, fear, and intimidation from the new Russian authorities. In its 2015 report, the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights warned that various
The UN reported that of the over 10,000 people left Crimea after the annexation in 2014, most were Crimean Tatars, which caused a further decline of their fragile community. Crimean Tatars stated several reasons for their departure, among them insecurity, fear, and intimidation from the new Russian authorities. In its 2015 report, the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights warned that various
 Despite the thousands of Crimean Tatars in the Red Army when it attacked Berlin, the Crimean Tatars continued to be seen and treated as a fifth column for decades. Some historians explain this as part of Stalin's plan to take complete control of Crimea. The Soviet sought access to the
Despite the thousands of Crimean Tatars in the Red Army when it attacked Berlin, the Crimean Tatars continued to be seen and treated as a fifth column for decades. Some historians explain this as part of Stalin's plan to take complete control of Crimea. The Soviet sought access to the
 In 2008, Lily Hyde, a British journalist living in Ukraine, published a novel titled ''Dreamland'' that revolves around a Crimean Tatar family return to their homeland in the 1990s. The story is told from the perspective of a 12-year-old girl who moves from Uzbekistan to a demolished village with her parents, brother, and grandfather. Her grandfather tells her stories about the heroes and victims among the Crimean Tatars.
The 2013 Ukrainian Crimean Tatar-language film '' Haytarma'' portrays the experience of Crimean Tatar flying ace and
In 2008, Lily Hyde, a British journalist living in Ukraine, published a novel titled ''Dreamland'' that revolves around a Crimean Tatar family return to their homeland in the 1990s. The story is told from the perspective of a 12-year-old girl who moves from Uzbekistan to a demolished village with her parents, brother, and grandfather. Her grandfather tells her stories about the heroes and victims among the Crimean Tatars.
The 2013 Ukrainian Crimean Tatar-language film '' Haytarma'' portrays the experience of Crimean Tatar flying ace and
Cyrillic
The Cyrillic script ( ), Slavonic script or the Slavic script, is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking co ...
: Къырымтатар халкъынынъ сюргюнлиги) or the Sürgünlik ('exile') was the ethnic cleansing
Ethnic cleansing is the systematic forced removal of ethnic, racial, and religious groups from a given area, with the intent of making a region ethnically homogeneous. Along with direct removal, extermination, deportation or population transfer ...
and cultural genocide
Cultural genocide or cultural cleansing is a concept which was proposed by lawyer Raphael Lemkin in 1944 as a component of genocide. Though the precise definition of ''cultural genocide'' remains contested, the Armenian Genocide Museum defines i ...
of at least 191,044 Crimean Tatars
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg
, flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars
, image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg
, caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace ...
carried out by the Soviet authorities from 18 to 20 May 1944, which was supervised by Lavrentiy Beria
Lavrentiy Pavlovich Beria (; rus, Лавре́нтий Па́влович Бе́рия, Lavréntiy Pávlovich Bériya, p=ˈbʲerʲiə; ka, ლავრენტი ბერია, tr, ; – 23 December 1953) was a Georgian Bolshevik ...
, head of Soviet state security and the secret police
Secret police (or political police) are intelligence, security or police agencies that engage in covert operations against a government's political, religious, or social opponents and dissidents. Secret police organizations are characteristic ...
, and which was ordered by the Soviet leader Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet Union, Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as Ge ...
. Within those three days, the NKVD
The People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs (russian: Наро́дный комиссариа́т вну́тренних дел, Naródnyy komissariát vnútrennikh del, ), abbreviated NKVD ( ), was the interior ministry of the Soviet Union.
...
used cattle trains to deport mostly women, children, and the elderly, even Communist Party
A communist party is a political party that seeks to realize the socio-economic goals of communism. The term ''communist party'' was popularized by the title of '' The Manifesto of the Communist Party'' (1848) by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engel ...
members and Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian language, Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist R ...
members, to mostly the Uzbek SSR
Uzbekistan (, ) is the common English name for the Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic (Uzbek SSR; uz, Ўзбекистон Совет Социалистик Республикаси, Oʻzbekiston Sovet Sotsialistik Respublikasi, in Russian: Уз ...
, several thousand kilometres away. They were one of the several ethnicities
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
who were subjected to Stalin's policy of population transfer in the Soviet Union
From 1930 to 1952, the government of the Soviet Union, on the orders of Soviet leader Joseph Stalin under the direction of the NKVD official Lavrentiy Beria, forcibly transferred populations of various groups. These actions may be classified ...
.
The deportation was officially presented as collective punishment for the claimed collaboration of some Crimean Tatars with Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
, but modern experts say that the deportation was part of the Soviet plan to gain access to the Dardanelles
The Dardanelles (; tr, Çanakkale Boğazı, lit=Strait of Çanakkale, el, Δαρδανέλλια, translit=Dardanéllia), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli from the Gallipoli peninsula or from Classical Antiquity as the Hellespont (; ...
and acquire territory in Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
, where the Tatars had Turkic ethnic kin, or to remove minorities from the Soviet Union's border regions.
Nearly 8,000 Crimean Tatars died during the deportation, and tens of thousands perished subsequently due to the harsh exile conditions. The Crimean Tatar deportation resulted in the abandonment of 80,000 households and 360,000 acres of land. An intense campaign of detatarization followed to try to erase the remaining traces of Crimean Tatar existence. In 1956, the new Soviet leader Nikita Khrushchev
Nikita Sergeyevich Khrushchev (– 11 September 1971) was the First Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1953 to 1964 and chairman of the country's Council of Ministers from 1958 to 1964. During his rule, Khrushchev s ...
condemned Stalin's policies, including the deportation of various ethnic groups, but did not lift the directive forbidding the return of the Crimean Tatars despite allowing most other deported peoples to return. The Crimean Tatars remained in Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
for several more decades until the perestroika
''Perestroika'' (; russian: links=no, перестройка, p=pʲɪrʲɪˈstrojkə, a=ru-perestroika.ogg) was a political movement for reform within the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU) during the late 1980s widely associated wit ...
era in the late 1980s, when 260,000 Crimean Tatars returned to Crimea. Their exile had lasted 45 years. The ban on their return was officially declared null and void when the Supreme Council of Crimea
Verkhovna Rada of Crimea or the Supreme Council of Crimea, officially the Supreme Council of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea ( uk, Верховна Рада Автономної Республіки Крим, Verkhovna Rada Avtonomnoï Respubl ...
declared on 14 November 1989 that the deportations had been a crime.
By 2004, the number of Crimean Tatars who had returned to Crimea had increased their share of the peninsula's population to 12 percent. The Soviet authorities had neither assisted their return nor compensated them for the land they lost. Neither Ukraine nor the Russian Federation
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
provided reparations
Reparation(s) may refer to:
Christianity
* Restitution (theology), the Christian doctrine calling for reparation
* Acts of reparation, prayers for repairing the damages of sin
History
*War reparations
**World War I reparations, made from ...
, compensated those deported for lost property, or filed legal proceedings against the perpetrators of the forced resettlement. The deportation and subsequent assimilation efforts in Asia represent a crucial period in the history of the Crimean Tatars. Between 2015 and 2019, the deportation was formally recognized as genocide by Ukraine, Lithuania, Latvia and Canada.
Background
Crimean Tatars
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg
, flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars
, image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg
, caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace ...
controlled the Crimean Khanate
The Crimean Khanate ( crh, , or ), officially the Great Horde and Desht-i Kipchak () and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary ( la, Tartaria Minor), was a Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to 1783, the long ...
from 1441 to 1783, when Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a p ...
was annexed by the Russian Empire as a target of Russian expansion
The borders of Russia changed through military conquests and by ideological and political unions in the course of over five centuries (1533–present).
Russian Tsardom and Empire
The name ''Russia'' for the Grand Duchy of Moscow began to ap ...
. By the 14th century, most of the Turkic-speaking population of Crimea had adopted Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
, following the conversion of Ozbeg Khan of the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragmen ...
. It was the longest surviving state of the Golden Horde. They often engaged in conflicts with Moscow—from 1468 until the 17th century, Crimean Tatars were averse to the newly-established Russian rule. Thus, Crimean Tatars began leaving Crimea in several waves of emigration. Between 1784 and 1790, out of a total population of about a million, around 300,000 Crimean Tatars left for the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
.
The Crimean War
The Crimean War, , was fought from October 1853 to February 1856 between Russia and an ultimately victorious alliance of the Ottoman Empire, France, the United Kingdom and Piedmont-Sardinia.
Geopolitical causes of the war included the ...
triggered another mass exodus
Exodus or the Exodus may refer to:
Religion
* Book of Exodus, second book of the Hebrew Torah and the Christian Bible
* The Exodus, the biblical story of the migration of the ancient Israelites from Egypt into Canaan
Historical events
* E ...
of Crimean Tatars. Between 1855 and 1866 at least 500,000 Muslims, and possibly up to 900,000, left the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
and emigrated to the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
. Out of that number, at least one third were from Crimea, while the rest were from the Caucasus
The Caucasus () or Caucasia (), is a region between the Black Sea and the Caspian Sea, mainly comprising Armenia, Azerbaijan, Georgia, and parts of Southern Russia. The Caucasus Mountains, including the Greater Caucasus range, have historica ...
. These emigrants comprised 15–23 percent of the total population of Crimea. The Russian Empire used that fact as the ideological foundation to further Russify "New Russia
Novorossiya, literally "New Russia", is a historical name, used during the era of the Russian Empire for an administrative area that would later become the southern mainland of Ukraine: the region immediately north of the Black Sea and Crime ...
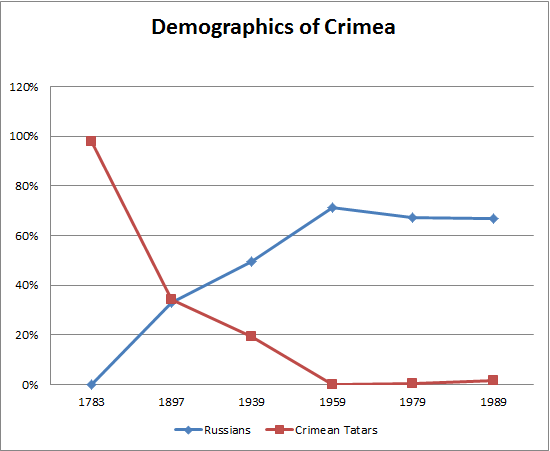
". Eventually, the Crimean Tatars became a minority in Crimea; in 1783, they comprised 98 per cent of the population, but by 1897, this was down to 34.1 per cent. While Crimean Tatars were emigrating, the Russian government encouraged Russification
Russification (russian: русификация, rusifikatsiya), or Russianization, is a form of cultural assimilation in which non-Russians, whether involuntarily or voluntarily, give up their culture and language in favor of the Russian cult ...
of the peninsula, populating it with Russians
, native_name_lang = ru
, image =
, caption =
, population =
, popplace =
118 million Russians in the Russian Federation (2002 '' Winkler Prins'' estimate)
, region1 =
, pop1 ...
, Ukrainians
Ukrainians ( uk, Українці, Ukraintsi, ) are an East Slavic ethnic group native to Ukraine. They are the seventh-largest nation in Europe. The native language of the Ukrainians is Ukrainian. The majority of Ukrainians are Eastern Ort ...
, and other Slavic ethnic groups; this Russification continued during the Soviet era. Vardys (1971), p. 101
 After the 1917
After the 1917 October Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key mom ...
, Crimea received autonomous status inside the USSR
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nati ...
on 18 October 1921, but collectivization
Collective farming and communal farming are various types of, "agricultural production in which multiple farmers run their holdings as a joint enterprise". There are two broad types of communal farms: agricultural cooperatives, in which member- ...
in the 1920s led to severe famine from which up to 100,000 Crimeans perished when their crops were transported to "more important" regions of the Soviet Union. By one estimate, three-quarters of the famine victims were Crimean Tatars. Their status deteriorated further after Joseph Stalin
Joseph Vissarionovich Stalin (born Ioseb Besarionis dze Jughashvili; – 5 March 1953) was a Georgian revolutionary and Soviet Union, Soviet political leader who led the Soviet Union from 1924 until his death in 1953. He held power as Ge ...
became the Soviet leader and implemented repressions that led to the deaths of at least 5.2 million Soviet citizens between 1927 and 1938.
World War II
In 1940, theCrimean Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic
During the existence of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, different governments existed within the Crimean Peninsula. From 1921 to 1936, the government in the Crimean Peninsula was known as the Crimean Autonomous Socialist Soviet Republic ...
had approximately 1,126,800 inhabitants, of which 218,000 people, or 19.4 percent of the population, were Crimean Tatars. In 1941, Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
invaded Eastern Europe, annexing much of the western USSR. Crimean Tatars initially viewed the Germans as liberators from Stalinism, and they had also been positively treated by the Germans in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
. Williams (2015), p. 92
Many of the captured Crimean Tatars serving in the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian language, Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist R ...
were sent to POW camps after Romanians
The Romanians ( ro, români, ; dated exonym '' Vlachs'') are a Romance-speaking ethnic group. Sharing a common Romanian culture and ancestry, and speaking the Romanian language, they live primarily in Romania and Moldova. The 2011 Romania ...
and Nazis came to occupy the bulk of Crimea. Though Nazis initially called for murder of all "Asiatic inferiors" and paraded around Crimean Tatar POW's labeled as "Mongol sub-humanity", they revised this policy in the face of determined resistance from the Red Army. Beginning in 1942, Germans recruited Soviet prisoners of war to form support armies. The Dobruja
Dobruja or Dobrudja (; bg, Добруджа, Dobrudzha or ''Dobrudža''; ro, Dobrogea, or ; tr, Dobruca) is a historical region in the Balkans that has been divided since the 19th century between the territories of Bulgaria and Romania. I ...
n Tatar nationalist Fazil Ulkusal and Lipka Tatar Edige Kirimal helped in freeing Crimean Tatars from German prisoner-of-war camp
A prisoner-of-war camp (often abbreviated as POW camp) is a site for the containment of enemy fighters captured by a belligerent power in time of war.
There are significant differences among POW camps, internment camps, and military prisons. ...
s and enlisting them in the independent Crimean support legion for the ''Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the '' Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previo ...
''. This legion eventually included eight battalions, although many members were of other nationalities. From November 1941, German authorities allowed Crimean Tatars to establish Muslim Committees in various towns as a symbolic recognition of some local government authority, though they were not given any political power.
Many Crimean Tatar communists strongly opposed the occupation and assisted the resistance movement
A resistance movement is an organized effort by some portion of the civil population of a country to withstand the legally established government or an occupying power and to disrupt civil order and stability. It may seek to achieve its objectives ...
to provide valuable strategic and political information. Other Crimean Tatars also fought on the side of the Soviet partisans, like the Tarhanov movement of 250 Crimean Tatars which fought throughout 1942 until its destruction. Six Crimean Tatars were even named the Heroes of the Soviet Union
The title Hero of the Soviet Union (russian: Герой Советского Союза, translit=Geroy Sovietskogo Soyuza) was the highest distinction in the Soviet Union, awarded together with the Order of Lenin personally or collectively for ...
, and thousands more were awarded high honors in the Red Army.
Up to 130,000 people died during the Axis occupation of Crimea. The Nazis implemented a brutal repression, destroying more than 70 villages that were together home to about 25 per cent of the Crimean Tatar population. Thousands of Crimean Tatars were forcibly transferred to work as ''Ostarbeiter
:
' (, "Eastern worker") was a Nazi German designation for foreign slave workers gathered from occupied Central and Eastern Europe to perform forced labor in Germany during World War II. The Germans started deporting civilians at the beginnin ...
'' in German factories under the supervision of the Gestapo
The (), abbreviated Gestapo (; ), was the official secret police of Nazi Germany and in German-occupied Europe.
The force was created by Hermann Göring in 1933 by combining the various political police agencies of Prussia into one orga ...
in what were described as "vast slave workshops", resulting in loss of all Crimean Tatar support. In April 1944 the Red Army managed to repel the Axis forces
The Axis powers, ; it, Potenze dell'Asse ; ja, 枢軸国 ''Sūjikukoku'', group=nb originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis, was a military coalition that initiated World War II and fought against the Allies. Its principal members were ...
from the peninsula in the Crimean Offensive
The Crimean offensive (8 April – 12 May 1944), known in German sources as the Battle of the Crimea, was a series of offensives by the Red Army directed at the German-held Crimea. The Red Army's 4th Ukrainian Front engaged the German 17th Army ...
.
A majority of the hiwis (helpers), their families and all those associated with the Muslim Committees were evacuated to Germany and Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Cr ...
or Dobruja by the Wehrmacht and Romanian Army where they joined the Eastern Turkic division. Thus, the majority of the collaborators had been evacuated from Crimea by the retreating Wehrmacht. Many Soviet officials had also recognized this and rejected claims that the Crimean Tatars had betrayed the Soviet Union ''en masse''. The presence of Muslim Committees organized from Berlin by various Turkic foreigners appeared a cause for concern in the eyes of the Soviet government, already wary of Turkey at the time. Williams (2001), pp. 382–384
Falsification of information in media
Soviet publications blatantly falsified information about Crimean Tatars in the Red Army, going so far as to describe Crimean TatarHero of the Soviet Union
The title Hero of the Soviet Union (russian: Герой Советского Союза, translit=Geroy Sovietskogo Soyuza) was the highest distinction in the Soviet Union, awarded together with the Order of Lenin personally or collectively for ...
Uzeir Abduramanov as Azeri
Azerbaijanis (; az, Azərbaycanlılar, ), Azeris ( az, Azərilər, ), or Azerbaijani Turks ( az, Azərbaycan Türkləri, ) are a Turkic people living mainly in northwestern Iran and the Republic of Azerbaijan. They are the second-most nume ...
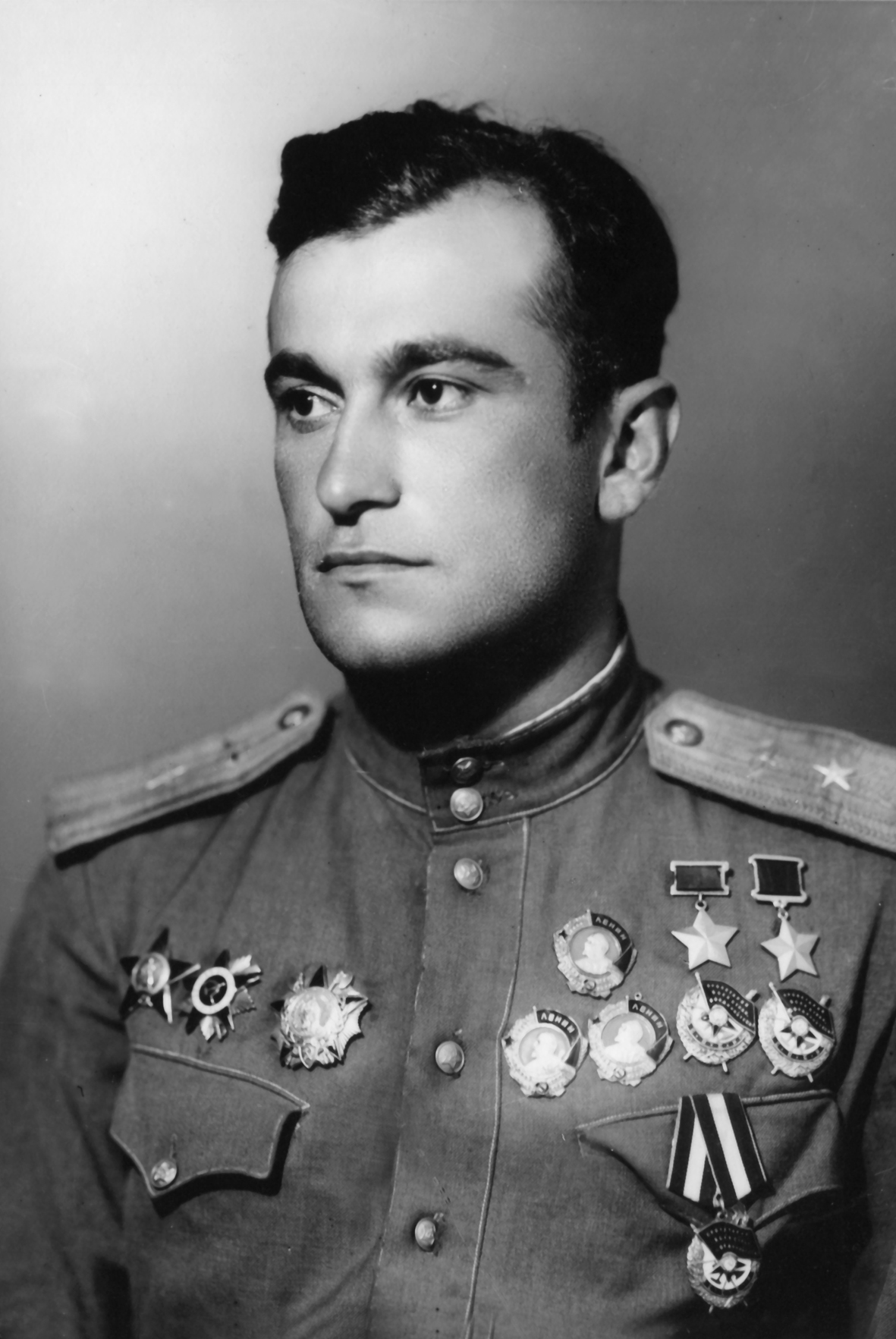
, not Crimean Tatar, on the cover of a 1944 issue of ''Ogonyok'' magazine - even though his family had been deported for being Crimean Tatar just a few months earlier. The book ''In the Mountains of Tavria'' falsely claimed that volunteer partisan scout Bekir Osmanov was a German spy and shot, although the central committee later acknowledged that he never served the Germans and survived the war, ordering later editions to have corrections after still-living Osmanov and his family noticed the obvious falsehood. Amet-khan Sultan, born to a Crimean Tatar mother and Lak father in Crimea, where he was born and raised, was often described as a Dagestani in post-deportation media, even though he always considered himself a Crimean Tatar.
Deportation
 Officially due to the collaboration with the Axis Powers during World War II, the Soviet government collectively punished ten ethnic minorities, among them the Crimean Tatars. Punishment included deportation to distant regions of
Officially due to the collaboration with the Axis Powers during World War II, the Soviet government collectively punished ten ethnic minorities, among them the Crimean Tatars. Punishment included deportation to distant regions of Central Asia
Central Asia, also known as Middle Asia, is a region of Asia that stretches from the Caspian Sea in the west to western China and Mongolia in the east, and from Afghanistan and Iran in the south to Russia in the north. It includes the fo ...
and Siberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part ...
. Soviet accounts of the late 1940s indict the Crimean Tatars as an ethnicity of traitors. Although the Crimean Tatars denied that they had committed treason, this idea was widely accepted during the Soviet period and persists in the Russian scholarly and popular literature.
On 10 May 1944, Lavrentiy Beria
Lavrentiy Pavlovich Beria (; rus, Лавре́нтий Па́влович Бе́рия, Lavréntiy Pávlovich Bériya, p=ˈbʲerʲiə; ka, ლავრენტი ბერია, tr, ; – 23 December 1953) was a Georgian Bolshevik ...
recommended to Stalin that the Crimean Tatars should be deported away from the border regions due to their "traitorous actions". Stalin subsequently issued GKO Order No. 5859ss, which envisaged the resettlement of the Crimean Tatars. Buckley, Ruble & Hoffman (2008), p. 231 The deportation lasted only three days, 18–20 May 1944, during which NKVD
The People's Commissariat for Internal Affairs (russian: Наро́дный комиссариа́т вну́тренних дел, Naródnyy komissariát vnútrennikh del, ), abbreviated NKVD ( ), was the interior ministry of the Soviet Union.
...
agents went house to house collecting Crimean Tatars at gunpoint and forcing them to enter sealed-off cattle trains that would transfer them almost to remote locations in the Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic
Uzbekistan (, ) is the common English name for the Uzbek Soviet Socialist Republic (Uzbek SSR; uz, Ўзбекистон Совет Социалистик Республикаси, Oʻzbekiston Sovet Sotsialistik Respublikasi, in Russian: Уз ...
. The Crimean Tatars were allowed to carry up to 500 kg of their property per family. The only ones who could avoid this fate were Crimean Tatar women who were married to men of non-punished ethnic groups. The exiled Crimean Tatars travelled in overcrowded wagons for several weeks and lacked food and water. It is estimated that at least 228,392 people were deported from Crimea, of which at least 191,044 were Crimean Tatars in 47,000 families. Since 7,889 people perished in the long transit in sealed-off railcars, the NKVD registered the 183,155 living Crimean Tatars who arrived at their destinations in Central Asia. The majority of the deportees were rounded up from the Crimean countryside. Only 18,983 of the exiles were from Crimean cities.
On 4 July 1944, the NKVD officially informed Stalin that the resettlement was complete. However, not long after that report, the NKVD found out that one of its units had forgotten to deport people from the Arabat Spit
The Arabat Spit ( uk, Арабатська коса; russian: Арабатская коса) or Arabat Arrow is a spit (landform), barrier spit that separates the large, shallow and very salty Syvash lagoons from the Sea of Azov. The spit runs ...
. Instead of preparing an additional transfer in trains, on 20 July the NKVD boarded hundreds of Crimean Tatars onto an old boat, took it to the middle of the Azov Sea
The Sea of Azov ( Crimean Tatar: ''Azaq deñizi''; russian: Азовское море, Azovskoye more; uk, Азовське море, Azovs'ke more) is a sea in Eastern Europe connected to the Black Sea by the narrow (about ) Strait of Kerch ...
, and sank the ship. Those who did not drown were finished off by machine-guns.
Communist Party
A communist party is a political party that seeks to realize the socio-economic goals of communism. The term ''communist party'' was popularized by the title of '' The Manifesto of the Communist Party'' (1848) by Karl Marx and Friedrich Engel ...
or the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army (Russian language, Russian: Рабо́че-крестья́нская Кра́сная армия),) often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Federative Socialist R ...
. As such, they were legally designated as special settler
Forced settlements in the Soviet Union were the result of population transfers and were performed in a series of operations organized according to social class or nationality of the deported. Resettling of "enemy classes" such as prosperous p ...
s, which meant that they were officially second-class citizens, prohibited from leaving the perimeter of their assigned area, attending prestigious universities, and had to regularly appear before the commandant's office.
During this mass eviction, the Soviet authorities confiscated around 80,000 houses, 500,000 cattle
Cattle (''Bos taurus'') are large, domesticated, cloven-hooved, herbivores. They are a prominent modern member of the subfamily Bovinae and the most widespread species of the genus '' Bos''. Adult females are referred to as cows and adult ...
, 360,000 acres
The acre is a unit of land area used in the imperial and US customary systems. It is traditionally defined as the area of one chain by one furlong (66 by 660 feet), which is exactly equal to 10 square chains, of a square mile, 4,840 square ...
of land, and 40,000 tons of agricultural provisions. Besides 191,000 deported Crimean Tatars, the Soviet authorities also evicted 9,620 Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, ''hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora ...
, 12,420 Bulgarians
Bulgarians ( bg, българи, Bǎlgari, ) are a nation and South Slavic ethnic group native to Bulgaria and the rest of Southeast Europe.
Etymology
Bulgarians derive their ethnonym from the Bulgars. Their name is not completely underst ...
, and 15,040 Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, ot ...
from the peninsula. All were collectively branded as traitors and became second-class citizens for decades in the USSR. Among the deported, there were also 283 persons of other ethnicities: Italians
, flag =
, flag_caption = The national flag of Italy
, population =
, regions = Italy 55,551,000
, region1 = Brazil
, pop1 = 25–33 million
, ref1 =
, region2 ...
, Romanians, Karaims, Kurds ug:كۇردلار
Kurds ( ku, کورد ,Kurd, italic=yes, rtl=yes) or Kurdish people are an Iranian peoples, Iranian ethnic group native to the mountainous region of Kurdistan in Western Asia, which spans southeastern Turkey, northwestern Ir ...
, Czechs
The Czechs ( cs, Češi, ; singular Czech, masculine: ''Čech'' , singular feminine: ''Češka'' ), or the Czech people (), are a West Slavic ethnic group and a nation native to the Czech Republic in Central Europe, who share a common ancestry, ...
, Hungarians
Hungarians, also known as Magyars ( ; hu, magyarok ), are a nation and ethnic group native to Hungary () and historical Hungarian lands who share a common culture, history, ancestry, and language. The Hungarian language belongs to the ...
, and Croats
The Croats (; hr, Hrvati ) are a South Slavic ethnic group who share a common Croatian ancestry, culture, history and language. They are also a recognized minority in a number of neighboring countries, namely Austria, the Czech Republic ...
. During 1947 and 1948, a further 2,012 veteran returnees were deported from Crimea by the local MVD.
In total, 151,136 Crimean Tatars were deported to the Uzbek SSR; 8,597 to the Mari Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic
The Mari Autonomous Soviet Socialist Republic (Mari ASSR) ( Mari: Марий Автоном Совет Социализм Республик, ''Mariy Avtonom Sovet Sotsializm Respublik'') was an autonomous republic of the Russian SFSR, succeeding ...
; and 4,286 to the Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic
; kk, Қазақ Советтік Социалистік Республикасы)
*1991: Republic of Kazakhstan (russian: Республика Казахстан; kk, Қазақстан Республикасы)
, linking_name = the ...
; and the remaining 29,846 were sent to various remote regions of the Russian SFSR
The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR or RSFSR ( rus, Российская Советская Федеративная Социалистическая Республика, Rossíyskaya Sovétskaya Federatívnaya Soci ...
. When the Crimean Tatars arrived at their destination in the Uzbek SSR, they were met with hostility by Uzbek locals who threw stones at them, even their children, because they heard that the Crimean Tatars were "traitors" and "fascist collaborators." The Uzbeks objected to becoming the "dumping ground for treasonous nations." In the coming years, several assaults against the Crimean Tatars population were registered, some of which were fatal.
 The mass Crimean deportations were organized by Lavrentiy Beria, the chief of the Soviet secret police, the NKVD, and his subordinates Bogdan Kobulov,
The mass Crimean deportations were organized by Lavrentiy Beria, the chief of the Soviet secret police, the NKVD, and his subordinates Bogdan Kobulov, Ivan Serov
Ivan Alexandrovich Serov (russian: Ива́н Алекса́ндрович Серóв; 13 August 1905 – 1 July 1990) was a Russian Soviet intelligence officer who served as the head of the KGB between March 1954 and December 1958, as well as ...
, B. P. Obruchnikov, M.G. Svinelupov, and A. N. Apolonov. The field operations were conducted by G. P. Dobrynin, the Deputy Head of the Gulag
The Gulag, an acronym for , , "chief administration of the camps". The original name given to the system of camps controlled by the State Political Directorate, GPU was the Main Administration of Corrective Labor Camps (, )., name=, group= ...
system; G. A. Bezhanov, the Colonel of State Security; I. I. Piiashev, Major General; S. A. Klepov, Commissar of State Security; I. S. Sheredega, Lt. General; B. I. Tekayev, Lt. Colonel of State Security; and two local leaders, P. M. Fokin, head of the Crimea NKGB, and V. T. Sergjenko, Lt. General. In order to execute this deportation, the NKVD secured 5,000 armed agents and the NKGB
The People's Commissariat for State Security (russian: Народный комиссариат государственной безопасности) or NKGB, was the name of the Soviet secret police, intelligence and counter-intelligence fo ...
allocated a further 20,000 armed men, together with a few thousand regular soldiers. Two of Stalin's directives from May 1944 reveal that many parts of the Soviet government, from financing to transit, were involved in executing the operation.
On 14 July 1944 the GKO authorized the immigration of 51,000 people, mostly Russians, to 17,000 empty collective farms on Crimea. On 30 June 1945, the Crimean ASSR
During the existence of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, different governments existed within the Crimean Peninsula. From 1921 to 1936, the government in the Crimean Peninsula was known as the Crimean Autonomous Socialist Soviet Republic; ...
was abolished.
Soviet propaganda
Propaganda in the Soviet Union was the practice of state-directed communication to promote class conflict, internationalism, the goals of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union, and the party itself.
The main Soviet censorship body, Glavlit ...
sought to hide the population transfer by claiming that the Crimean Tatars had "voluntarily resettle to Central Asia". In essence, though, according to historian Paul Robert Magocsi
Paul Robert Magocsi (born January 26, 1945 in Englewood, New Jersey) is an American professor of history, political science, and Chair of Ukrainian Studies at the University of Toronto. He has been with the university since 1980, and became ...
, Crimea was " ethnically cleansed." After this act, the term ''Crimean Tatar'' was banished from the Russian-Soviet lexicon, and all Crimean Tatar toponyms
Toponymy, toponymics, or toponomastics is the study of '' toponyms'' (proper names of places, also known as place names and geographic names), including their origins, meanings, usage and types. Toponym is the general term for a proper name of ...
(names of towns, villages, and mountains) in Crimea were changed to Russian names on all maps as part of a wide detatarization campaign. Muslim graveyards and religious objects in Crimea were demolished or converted into secular places. During Stalin's rule, nobody was allowed to mention that this ethnicity even existed in the USSR. This went so far that many individuals were even forbidden to declare themselves as Crimean Tatars during the Soviet censuses of 1959, 1970
Events
January
* January 1 – Unix time epoch reached at 00:00:00 UTC.
* January 5 – The 7.1 Tonghai earthquake shakes Tonghai County, Yunnan province, China, with a maximum Mercalli intensity of X (''Extreme''). Between 10,000 and ...
, and 1979. They could only declare themselves as Tatars. This ban was lifted during the Soviet census of 1989.
Aftermath
Mortality and death toll
The first deportees started arriving in the Uzbek SSR on 29 May 1944 and most had arrived by 8 June 1944. The consequentmortality rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically expressed in units of d ...
remains disputed; the NKVD kept incomplete records of the death rate among the resettled ethnicities living in exile. Like the other deported peoples, the Crimean Tatars were placed under the regime of special settlements. Many of those deported performed forced labor
Forced labour, or unfree labour, is any work relation, especially in modern or early modern history, in which people are employed against their will with the threat of destitution, detention, violence including death, or other forms of ex ...
: their tasks included working in coal mines
Coal mining is the process of extracting coal from the ground. Coal is valued for its energy content and since the 1880s has been widely used to generate electricity. Steel and cement industries use coal as a fuel for extraction of iron fro ...
and construction battalions, under the supervision of the NKVD. Deserters were executed. Special settlers routinely worked eleven to twelve hours a day, seven days a week. Despite this difficult physical labor, the Crimean Tatars were given only around to of bread per day. Accommodations were insufficient; some were forced to live in mud hut
A hut is a small dwelling, which may be constructed of various local materials. Huts are a type of vernacular architecture because they are built of readily available materials such as wood, snow, ice, stone, grass, palm leaves, branches, hid ...
s where "there were no doors or windows, nothing, just reeds" on the floor to sleep on.
The sole transport to these remote areas and labour colonies was equally as strenuous. Theoretically, the NKVD loaded 50 people into each railroad car, together with their property. One witness claimed that 133 people were in her wagon. They had only one hole in the floor of the wagon which was used as a toilet. Some pregnant women were forced to give birth inside these sealed-off railroad cars. The conditions in the overcrowded train wagons were exacerbated by a lack of hygiene
Hygiene is a series of practices performed to preserve health.
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), "Hygiene refers to conditions and practices that help to maintain health and prevent the spread of diseases." Personal hygiene refer ...
, leading to cases of typhus
Typhus, also known as typhus fever, is a group of infectious diseases that include epidemic typhus, scrub typhus, and murine typhus. Common symptoms include fever, headache, and a rash. Typically these begin one to two weeks after exposure. ...
. Since the trains only stopped to open the doors at rare occasions during the trip, the sick inevitably contaminated others in the wagons. It was only when they arrived at their destination in the Uzbek SSR that the Crimean Tatars were released from the sealed-off railroad cars. Still, some were redirected to other destinations in Central Asia and had to continue their journey. Some witnesses claimed that they travelled for 24 consecutive days. During this whole time, they were given very little food or water while trapped inside. There was no fresh air since the doors and windows were bolted shut. In Kazakh SSR
; kk, Қазақ Советтік Социалистік Республикасы)
*1991: Republic of Kazakhstan (russian: Республика Казахстан; kk, Қазақстан Республикасы)
, linking_name = the ...
, the transport guards unlocked the door only to toss out the corpses along the railroad. The Crimean Tatars thus called these railcars "crematoria
Cremation is a method of final disposition of a dead body through burning.
Cremation may serve as a funeral or post-funeral rite and as an alternative to burial. In some countries, including India and Nepal, cremation on an open-air pyre ...
on wheels." The records show that at least 7,889 Crimean Tatars died during this long journey, amounting to about 4 per cent of their entire ethnicity.
The high mortality rate continued for several years in exile due to malnutrition
Malnutrition occurs when an organism gets too few or too many nutrients, resulting in health problems. Specifically, it is "a deficiency, excess, or imbalance of energy, protein and other nutrients" which adversely affects the body's tissues ...
, labor exploitation, diseases, lack of medical care, and exposure to the harsh desert climate of Uzbekistan. The exiles were frequently assigned to the heaviest construction sites. The Uzbek medical facilities filled with Crimean Tatars who were susceptible to the local Asian diseases not found on the Crimean peninsula where the water was purer, including yellow fever
Yellow fever is a viral disease of typically short duration. In most cases, symptoms include fever, chills, loss of appetite, nausea, muscle pains – particularly in the back – and headaches. Symptoms typically improve within five days. ...
, dystrophy
Dystrophy is the degeneration of tissue, due to disease or malnutrition, most likely due to heredity.
Types
* Muscular dystrophy
** Duchenne muscular dystrophy
** Becker's muscular dystrophy
** Myotonic dystrophy
* Reflex neurovascular d ...
, malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. ...
, and intestinal illness. The death toll was the highest during the first five years. In 1949 the Soviet authorities counted the population of the deported ethnic groups who lived in special settlements. According to their records, there were 44,887 excess deaths in these five years, 19.6 per cent of that total group. Buckley, Ruble & Hofmann (2008), p. 207 Other sources give a figure of 44,125 deaths during that time, while a third source, using alternative NKVD archives, gives a figure of 32,107 deaths. These reports included all the people resettled from Crimea (including Armenians, Bulgarians, and Greeks), but the Crimean Tatars formed a majority in this group. It took five years until the number of births among the deported people started to surpass the number of deaths. Soviet archives reveal that between May 1944 and January 1945 a total of 13,592 Crimean Tatars perished in exile, about 7 per cent of their entire population. Almost half of all deaths (6,096) were of children under the age of 16; another 4,525 were adult women and 2,562 were adult men. During 1945, a further 13,183 people died. Thus, by the end of December 1945, at least 27,000 Crimean Tatars had already died in exile. One Crimean Tatar woman living near Tashkent recalled the events from 1944:
Estimates produced by Crimean Tatars indicate mortality figures that were far higher and amounted to 46% of their population living in exile. In 1968, when Leonid Brezhnev
Leonid Ilyich Brezhnev; uk, links= no, Леонід Ілліч Брежнєв, . (19 December 1906– 10 November 1982) was a Soviet politician who served as General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union between 1964 and 1 ...
presided over the USSR, Crimean Tatar activists were persecuted for using that high mortality figure under the guise that it was a "slander to the USSR." In order to show that Crimean Tatars were exaggerating, the KGB published figures showing that "only" 22 per cent of that ethnic group died. The Karachay demographer Dalchat Ediev estimates that 34,300 Crimean Tatars died due to the deportation, representing an 18 per cent mortality rate. Hannibal Travis estimates that overall 40,000–80,000 Crimean Tatars died in exile. Professor Michael Rywkin gives a figure of at least 42,000 Crimean Tatars who died between 1944 and 1951, including 7,900 who died during the transit Professor Brian Glyn Williams
Brian Glyn Williams is a professor of Islamic History at the University of Massachusetts Dartmouth who worked for the CIA. As an undergraduate, he attended Stetson University, graduating with a Bachelor of Arts in 1988. He received his PhD in Mi ...
gives a figure of between 40,000 and 44,000 deaths as a consequence of this deportation. The Crimean State Committee estimated that 45,000 Crimean Tatars died between 1944 and 1948. The official NKVD report estimated that 27 per cent of that ethnicity died.
Various estimates of the mortality rates of the Crimean Tatars:
Rehabilitation
Stalin's government denied the Crimean Tatars the right to education orpublication
To publish is to make content available to the general public.Berne Conve ...
in their native language. Despite the prohibition, and although they had to study in Russian or Uzbek, they maintained their cultural identity. In 1956 the new Soviet leader, Nikita Khrushchev
Nikita Sergeyevich Khrushchev (– 11 September 1971) was the First Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union from 1953 to 1964 and chairman of the country's Council of Ministers from 1958 to 1964. During his rule, Khrushchev s ...
, held a speech in which he condemned Stalin's policies, including the mass deportations of various ethnicities. Still, even though many peoples were allowed to return to their homes, three groups were forced to stay in exile: the Soviet Germans, the Meskhetian Turks
Meskhetian Turks, also referred to as Turkish Meskhetians, Ahiska Turks, and Turkish Ahiskans, ( ka, მესხეთის თურქები ''Meskhetis turk'ebi'') are an ethnic subgroup of Turks formerly inhabiting the Meskheti reg ...
, and the Crimean Tatars. In 1954, Khrushchev allowed Crimea to be included in the Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic
The Ukrainian Soviet Socialist Republic ( uk, Украї́нська Радя́нська Соціалісти́чна Респу́бліка, ; russian: Украи́нская Сове́тская Социалисти́ческая Респ ...
since Crimea is linked by land to Ukraine and not with the Russian SFSR. On 28 April 1956, the directive "On Removing Restrictions on the Special Settlement of the Crimean Tatars... Relocated during the Great Patriotic War" was issued, ordering a de-registration of the deportees and their release from administrative supervision. However, various other restrictions were still kept and the Crimean Tatars were not allowed to return to Crimea. Moreover, that same year the Ukrainian Council of Ministers banned the exiled Crimean Tatars, Greeks, Germans, Armenians and Bulgarians from relocating even to the Kherson
Kherson (, ) is a port city of Ukraine that serves as the administrative centre of Kherson Oblast. Located on the Black Sea and on the Dnieper River, Kherson is the home of a major ship-building industry and is a regional economic centre. I ...
, Zaporizhia
Zaporizhzhia ( uk, Запоріжжя) or Zaporozhye (russian: Запорожье) is a city in southeast Ukraine, situated on the banks of the Dnieper River. It is the administrative centre of Zaporizhzhia Oblast. Zaporizhzhia has a populatio ...
, Mykolaiv
Mykolaiv ( uk, Миколаїв, ) is a city and municipality in Southern Ukraine, the administrative center of the Mykolaiv Oblast. Mykolaiv city, which provides Ukraine with access to the Black Sea, is the location of the most downriver brid ...
and Odessa Oblast
Odesa Oblast ( uk, Оде́ська о́бласть, translit=Odeska oblast), also referred to as Odeshchyna ( uk, Оде́щина) is an oblast (province) of southwestern Ukraine, located along the northern coast of the Black Sea. Its admin ...
s in the Ukrainian SSR. The Crimean Tatars did not get any compensation for their lost property.
In the 1950s, the Crimean Tatars started actively advocating for the right to return. In 1957, they collected 6,000 signatures in a petition that was sent to the Supreme Soviet
The Supreme Soviet (russian: Верховный Совет, Verkhovny Sovet, Supreme Council) was the common name for the legislative bodies (parliaments) of the Soviet socialist republics (SSR) in the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USS ...
that demanded their political rehabilitation
Political rehabilitation is the process by which a disgraced member of a political party or a government is restored to public respectability and thus political acceptability. The term is usually applied to leaders or other prominent individuals ...
and return to Crimea. In 1961 25,000 signatures were collected in a petition that was sent to the Kremlin
The Kremlin ( rus, Московский Кремль, r=Moskovskiy Kreml', p=ˈmɐˈskofskʲɪj krʲemlʲ, t=Moscow Kremlin) is a fortified complex in the center of Moscow founded by the Rurik dynasty. It is the best known of the kremlins (Ru ...
.
Mustafa Dzhemilev
Mustafa Abduldzhemil Jemilev ( crh, Mustafa Abdülcemil Cemilev, Мустафа Абдюльджемиль Джемилев, ), also known widely with his adopted descriptive surname Qırımoğlu "Son of Crimea" ( Crimean Tatar Cyrillic: , ; born ...
, who was only six months old when his family was deported from Crimea, grew up in Uzbekistan and became an activist for the right of the Crimean Tatars to return. In 1966 he was arrested for the first time and spent a total of 17 years in prison during the Soviet era. This earned him the nickname of "Crimean Tatar Mandela
Nelson Rolihlahla Mandela (; ; 18 July 1918 – 5 December 2013) was a South African anti-apartheid activist who served as the first president of South Africa from 1994 to 1999. He was the country's first black head of state and the ...
." In 1984 he was sentenced for the sixth time for "anti-Soviet activity" but was given moral support by the Soviet dissident Andrei Sakharov
Andrei Dmitrievich Sakharov ( rus, Андрей Дмитриевич Сахаров, p=ɐnˈdrʲej ˈdmʲitrʲɪjevʲɪtɕ ˈsaxərəf; 21 May 192114 December 1989) was a Soviet nuclear physicist, dissident, nobel laureate and activist for n ...
, who had observed Dzhemilev's fourth trial in 1976. When older dissidents were arrested, a new, younger generation emerged that would replace them.
On 21 July 1967, representatives of the Crimean Tatars, led by the dissident Ayshe Seitmuratova, gained permission to meet with high-ranking Soviet officials in Moscow, including Yuri Andropov
Yuri Vladimirovich Andropov (– 9 February 1984) was the sixth paramount leader of the Soviet Union and the fourth General Secretary of the Communist Party of the Soviet Union. After Leonid Brezhnev's 18-year rule, Andropov served in the ...
. During the meeting, the Crimean Tatars demanded a correction of all the injustices of the USSR against their people. In September 1967, the Supreme Soviet
The Supreme Soviet (russian: Верховный Совет, Verkhovny Sovet, Supreme Council) was the common name for the legislative bodies (parliaments) of the Soviet socialist republics (SSR) in the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USS ...
issued a decree that acknowledged the charge of treason against the entire nation was "unreasonable" but that did not allow Crimean Tatars the same full rehabilitation encompassing the right of return that other deported peoples were given. The carefully worded decree referred to them not as "Crimean Tatars" but as "citizens of Tatar nationality who having formerly lived in Crimea ��have taken root in the Uzbek SSR", thereby minimizing Crimean Tatar existence and downplaying their desire for the right of return in addition to creating a premise for claims of the issue being "settled". Individuals united and formed groups that went back to Crimea in 1968 on their own, without state permission, but the Soviet authorities deported 6,000 of them once again. Williams (2001), p. 425 The most notable example of such resistance was a Crimean Tatar activist, Musa Mamut, who was deported when he was 12 and who returned to Crimea because he wanted to see his home again. When the police informed him that he would be evicted, he set himself on fire. Nevertheless, 577 families managed to obtain state permission to reside in Crimea.
In 1968 unrest erupted among the Crimean Tatar people in the Uzbek city of Chirchiq
Chirchiq, also spelled as Chirchik, ( uz, Chirchiq / Чирчиқ; russian: Чирчик) is a district-level city in Tashkent Region, Uzbekistan. It is about 32 km northeast of Tashkent, along the river Chirchiq. Chirchiq lies in the Chatk ...
. In October 1973, the Jewish poet and professor Ilya Gabay
Ilya Yankelevich Gabay (russian: Илья́ Янкеле́вич Габа́й, p=ɪˈlʲjæ jənkʲɪˈlʲevʲɪtɕ ɡɐˈbaj, a=Il'ya Yankyelyevich Gabay.ru.vorb.oga; 9 October 1935, Baku – 20 October 1973, Moscow; buried in Baku) was a key ...
committed suicide by jumping off a building in Moscow. He was one of the significant Jewish dissidents in the USSR who fought for the rights of the oppressed peoples, especially Crimean Tatars. Gabay had been arrested and sent to a labour camp
A labor camp (or labour camp, see spelling differences) or work camp is a detention facility where inmates are forced to engage in penal labor as a form of punishment. Labor camps have many common aspects with slavery and with prisons (espe ...
but still insisted on his cause because he was convinced that the treatment of the Crimean Tatars by the USSR amounted to genocide. In 1973, Dzhemilev was also arrested for his advocacy for Crimean Tatar right to return to Crimea.

Repatriation
Despitede-Stalinization
De-Stalinization (russian: десталинизация, translit=destalinizatsiya) comprised a series of political reforms in the Soviet Union after the death of long-time leader Joseph Stalin in 1953, and the thaw brought about by ascension ...
, the situation didn't change until Gorbachev
Mikhail Sergeyevich Gorbachev (2 March 1931 – 30 August 2022) was a Soviet politician who served as the 8th and final leader of the Soviet Union from 1985 to the country's dissolution in 1991. He served as General Secretary of the Comm ...
's perestroika
''Perestroika'' (; russian: links=no, перестройка, p=pʲɪrʲɪˈstrojkə, a=ru-perestroika.ogg) was a political movement for reform within the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU) during the late 1980s widely associated wit ...
in the late 1980s. A 1987 Tatar protest near the Kremlin
The Kremlin ( rus, Московский Кремль, r=Moskovskiy Kreml', p=ˈmɐˈskofskʲɪj krʲemlʲ, t=Moscow Kremlin) is a fortified complex in the center of Moscow founded by the Rurik dynasty. It is the best known of the kremlins (Ru ...
prompted Gorbachev to form the Gromyko Commission which found against Tatar claims, but a second commission recommended "renewal of autonomy" for Crimean Tatars. In 1989 the ban on the return of deported ethnicities was declared officially null and void and the Supreme Council of Crimea
Verkhovna Rada of Crimea or the Supreme Council of Crimea, officially the Supreme Council of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea ( uk, Верховна Рада Автономної Республіки Крим, Verkhovna Rada Avtonomnoï Respubl ...
further declared the deportations criminal, paving the way for the Crimean Tatars to return. Dzhemilev returned to Crimea that year, with at least 166,000 other Tatars doing the same by January 1992. The 1991 Russian law ''On the Rehabilitation of Repressed Peoples ''On the Rehabilitation of Repressed Peoples'' (russian: Закон РСФСР от 26 апреля 1991 г. N 1107-I "О реабилитации репрессированных народов") is the law N 1107-I of the Russian Soviet Federati ...
'' rehabilitated all Soviet repressed ethnicities and abolished all previous Russian laws relating to the deportations, calling for the "restoration and return of the cultural and spiritual values and archives which represent the heritage of the repressed people."
By 2004 the Crimean Tatars formed 12 per cent of the population of Crimea. The return was fraught: with Russian nationalist
Russian nationalism is a form of nationalism that promotes Russian cultural identity and unity. Russian nationalism first rose to prominence in the early 19th century, and from its origin in the Russian Empire, to its repression during early B ...
protests in Crimea and clashes between locals and Crimean Tatars near Yalta
Yalta (: Я́лта) is a resort city on the south coast of the Crimean Peninsula surrounded by the Black Sea. It serves as the administrative center of Yalta Municipality, one of the regions within Crimea. Yalta, along with the rest of Cri ...
, which needed army intervention. Local Soviet authorities were reluctant to help returnees with jobs or housing, After the dissolution of the USSR
The dissolution of the Soviet Union, also negatively connoted as rus, Разва́л Сове́тского Сою́за, r=Razvál Sovétskogo Soyúza, ''Ruining of the Soviet Union''. was the process of internal disintegration within the Sov ...
, Crimea was part of Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inva ...
, but Kyiv
Kyiv, also spelled Kiev, is the capital and most populous city of Ukraine. It is in north-central Ukraine along the Dnieper River. As of 1 January 2021, its population was 2,962,180, making Kyiv the seventh-most populous city in Europe.
Ky ...
gave limited support to Crimean Tatar settlers. Some 150,000 of the returnees were granted citizenship automatically under Ukraine's Citizenship Law
Nationality law is the law of a sovereign state, and of each of its jurisdictions, that defines the legal manner in which a national identity is acquired and how it may be lost. In international law, the legal means to acquire nationality and for ...
of 1991, but 100,000 who returned after Ukraine declared independence faced several obstacles including a costly bureaucratic process.
Annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation
In March 2014, theannexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation
In February and March 2014, Russia invaded and subsequently annexed the Crimean Peninsula from Ukraine. This event took place in the aftermath of the Revolution of Dignity and is part of the wider Russo-Ukrainian War.
The events in Kyiv t ...
unfolded, which was, in turn, declared illegal by the United Nations General Assembly
The United Nations General Assembly (UNGA or GA; french: link=no, Assemblée générale, AG) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN), serving as the main deliberative, policymaking, and representative organ of the UN. Curr ...
( United Nations General Assembly Resolution 68/262) and which led to further deterioration of the rights of the Crimean Tatars. Even though the Russian Federation
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
issued Decree No. 268 "On the Measures for the Rehabilitation of Armenian, Bulgarian, Greek, Crimean Tatar and German Peoples and the State Support of Their Revival and Development" on 21 April 2014, in practice it has treated Crimean Tatars with far less care. The Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights
The Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights, commonly known as the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) or the United Nations Human Rights Office, is a department of the Secretariat of the United Nat ...
issued a warning against the Kremlin in 2016 because it "intimidated, harassed and jailed Crimean Tatar representatives, often on dubious charges", while the representative body the Mejlis of the Crimean Tatar People
The Mejlis of the Crimean Tatar People ( crh, Къырымтатар Миллий Меджлиси - ''Qırımtatar Milliy Meclisi'') is the single highest executive-representative body of the Crimean Tatars in period between sessions of the ...
was banned.

 The UN reported that of the over 10,000 people left Crimea after the annexation in 2014, most were Crimean Tatars, which caused a further decline of their fragile community. Crimean Tatars stated several reasons for their departure, among them insecurity, fear, and intimidation from the new Russian authorities. In its 2015 report, the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights warned that various
The UN reported that of the over 10,000 people left Crimea after the annexation in 2014, most were Crimean Tatars, which caused a further decline of their fragile community. Crimean Tatars stated several reasons for their departure, among them insecurity, fear, and intimidation from the new Russian authorities. In its 2015 report, the Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights warned that various human rights violations
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hum ...
were recorded in Crimea, including the prevention of Crimean Tatars from marking the 71st anniversary of their deportation.
Modern views and legacy
HistorianEdward Allworth
Edward Christopher Allworth (July 6, 1895 – June 24, 1966) was an American officer in the United States Army during World War I.
Biography
Allworth was born in Battle Ground, Washington, Allworth graduated from Oregon State University in 1916 ...
has noted that the extent of marginalization of the Crimean Tatars was a distinct anomaly among national policy in the USSR given the party's firm commitment maintaining the status quo of not recognizing them as a distinct ethnic group in addition to assimilating and "rooting" them in exile, in sharp contrast to the rehabilitation other deported ethnic groups such as the Chechens, Ingush, Karachays, Balkars, and Kalmyks experienced in the Khrushchev era.
Between 1989 and 1994, around a quarter of a million Crimean Tatars returned to Crimea from exile in Central Asia. This was seen as a symbolic victory of their efforts to return to their native land. They returned after 45 years of exile.
Not one of the several ethnic groups who were deported during Stalin's era received any kind of financial compensation. Some Crimean Tatar groups and activists have called for the international community to put pressure on the Russian Federation, the successor state
Succession of states is a concept in international relations regarding a successor state that has become a sovereign state over a territory (and populace) that was previously under the sovereignty of another state. The theory has its roots in 19th- ...
of the USSR, to finance rehabilitation of that ethnicity and provide financial compensation
Financial compensation refers to the act of providing a person with money or other things of economic value in exchange for their goods, labor, or to provide for the costs of injuries that they have incurred.
Kinds of financial compensation inclu ...
for forcible resettlement.
Dardanelles
The Dardanelles (; tr, Çanakkale Boğazı, lit=Strait of Çanakkale, el, Δαρδανέλλια, translit=Dardanéllia), also known as the Strait of Gallipoli from the Gallipoli peninsula or from Classical Antiquity as the Hellespont (; ...
and control of territory in Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
, where the Crimean Tatars had ethnic kin. By painting the Crimean Tatars as traitors, this taint could be extended to their kin. Scholar Walter Kolarz alleges that the deportation and the attempt of liquidation of Crimean Tatars as an ethnicity in 1944 was just the final act of the centuries-long process of Russian colonization of Crimea that started in 1783. Historian Gregory Dufaud regards the Soviet accusations against Crimean Tatars as a convenient excuse for their forcible transfer through which Moscow secured an unrivalled access to the geostrategic southern Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
on one hand and eliminated hypothetical rebellious nations at the same time. Professor of Russian and Soviet history Rebecca Manley similarly concluded that the real aim of the Soviet government was to "cleanse" the border regions of "unreliable elements". Professor Brian Glyn Williams
Brian Glyn Williams is a professor of Islamic History at the University of Massachusetts Dartmouth who worked for the CIA. As an undergraduate, he attended Stetson University, graduating with a Bachelor of Arts in 1988. He received his PhD in Mi ...
states that the deportations of Meskhetian Turks
Meskhetian Turks, also referred to as Turkish Meskhetians, Ahiska Turks, and Turkish Ahiskans, ( ka, მესხეთის თურქები ''Meskhetis turk'ebi'') are an ethnic subgroup of Turks formerly inhabiting the Meskheti reg ...
, despite never being close to the scene of combat and never being charged with any crime, lends the strongest credence to the fact that the deportations of Crimeans and Caucasians was due to Soviet foreign policy rather than any real "universal mass crimes".
Modern interpretations by scholars and historians sometimes classify this mass deportation of civilians as a crime against humanity
Crimes against humanity are widespread or systemic acts committed by or on behalf of a ''de facto'' authority, usually a state, that grossly violate human rights. Unlike war crimes, crimes against humanity do not have to take place within the ...
, ethnic cleansing
Ethnic cleansing is the systematic forced removal of ethnic, racial, and religious groups from a given area, with the intent of making a region ethnically homogeneous. Along with direct removal, extermination, deportation or population transfer ...
, depopulation
A population decline (also sometimes called underpopulation, depopulation, or population collapse) in humans is a reduction in a human population size. Over the long term, stretching from prehistory to the present, Earth's total human population ...
, an act of Stalinist repression, or an " ethnocide", meaning a deliberate wiping out of an identity and culture of a nation. Crimean Tatars call this event ''Sürgünlik'' ("exile"). The perception of Crimean Tatars as "uncivilized" and deserving the deportation remains throughout the Russian and Ukrainian settlers in Crimea.
Genocide question and recognition
Some activists, politicians, scholars, countries, and historians go even further and consider the deportation a crime ofgenocide
Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word (, "race, people") with the ...
or cultural genocide
Cultural genocide or cultural cleansing is a concept which was proposed by lawyer Raphael Lemkin in 1944 as a component of genocide. Though the precise definition of ''cultural genocide'' remains contested, the Armenian Genocide Museum defines i ...
. Norman Naimark writes " e Chechens and Ingush, the Crimean Tatars, and other 'punished peoples' of the wartime period were, indeed, slated for elimination, if not physically, then as self-identifying nationalities." Professor Lyman H. Legters argued that the Soviet penal system, combined with its resettlement policies, should count as genocidal since the sentences were borne most heavily specifically on certain ethnic groups, and that a relocation of these ethnic groups, whose survival depends on ties to its particular homeland, "had a genocidal effect remediable only by restoration of the group to its homeland." Soviet dissidents Ilya Gabay
Ilya Yankelevich Gabay (russian: Илья́ Янкеле́вич Габа́й, p=ɪˈlʲjæ jənkʲɪˈlʲevʲɪtɕ ɡɐˈbaj, a=Il'ya Yankyelyevich Gabay.ru.vorb.oga; 9 October 1935, Baku – 20 October 1973, Moscow; buried in Baku) was a key ...
and Pyotr Grigorenko
Petro Grigorenko or Petro Hryhorovych Hryhorenko ( uk, Петро́ Григо́рович Григоре́нко, russian: Пётр Григо́рьевич Григоре́нко, link=no, – 21 February 1987) was a high-ranking Soviet Army ...
both classified the event as a genocide. Historian Timothy Snyder
Timothy David Snyder (born August 18, 1969) is an American historian specializing in the modern history of Central and Eastern Europe. He is the Richard C. Levin Professor of History at Yale University and a permanent fellow at the Institute ...
included it in a list of Soviet policies that “meet the standard of genocide." On 12 December 2015, the Ukrainian Parliament
The Verkhovna Rada of Ukraine ( uk, Верхо́вна Ра́да Украї́ни, translit=, Verkhovna Rada Ukrainy, translation=Supreme Council of Ukraine, Ukrainian abbreviation ''ВРУ''), often simply Verkhovna Rada or just Rada, is the ...
issued a resolution recognizing this event as genocide and established 18 May as the "Day of Remembrance for the victims of the Crimean Tatar genocide." The parliament of Latvia
The Saeima () is the parliament of the Republic of Latvia. It is a unicameral parliament consisting of 100 members who are elected by proportional representation, with seats allocated to political parties which gain at least 5% of the popular vo ...
recognized the event as an act of genocide on 9 May 2019. The Parliament of Lithuania
The Seimas of the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublikos Seimas), or simply the Seimas (), is the unicameral parliament of Lithuania. The Seimas constitutes the legislative branch of government in Lithuania, enacting laws and amendm ...
did the same on 6 June 2019. Canadian Parliament passed a motion on June 10, 2019, recognizing the Crimean Tatar deportation of 1944 (Sürgünlik) as a genocide perpetrated by Soviet dictator Stalin, designating May 18 to be a day of remembrance. On 26 April 1991 the Supreme Soviet of the Russian Socialist Federal Soviet Republic, under its chairman Boris Yeltsin
Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin ( rus, Борис Николаевич Ельцин, p=bɐˈrʲis nʲɪkɐˈla(j)ɪvʲɪtɕ ˈjelʲtsɨn, a=Ru-Boris Nikolayevich Yeltsin.ogg; 1 February 1931 – 23 April 2007) was a Soviet and Russian politician wh ...
, passed the law On the Rehabilitation of Repressed Peoples with Article 2 denouncing all mass deportations as "Stalin's policy of defamation and genocide
Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word (, "race, people") with the ...
."
A minority dispute defining the event as genocide. According to Alexander Statiev, the Soviet deportations
From 1930 to 1952, the government of the Soviet Union, on the orders of Soviet leader Joseph Stalin under the direction of the NKVD official Lavrentiy Beria, forcibly transferred populations of various groups. These actions may be classified ...
resulted in a "genocidal death rate
Mortality rate, or death rate, is a measure of the number of deaths (in general, or due to a specific cause) in a particular population, scaled to the size of that population, per unit of time. Mortality rate is typically expressed in units of d ...
", but Stalin did not have the intent
''The Intent'' is a 2016 British crime thriller film
Thriller film, also known as suspense film or suspense thriller, is a broad film genre that evokes excitement and suspense in the audience. The suspense element found in most films' plots ...
to exterminate these peoples. He considers such deportations merely an example of Soviet assimilation of "unwanted nations." According to Amir Weiner
Amir Weiner (born 17 September 1961) is an American historian and associate professor of Soviet history at Stanford University. His interests include mass violence, population politics, totalitarianism, and World War II. Weiner is the director ...
, the Soviet regime sought to eradicate "only" their "territorial identity". Such views were criticized by Jon Chang as "gentrified racism
Racism is the belief that groups of humans possess different behavioral traits corresponding to inherited attributes and can be divided based on the superiority of one race over another. It may also mean prejudice, discrimination, or antagoni ...
" and historical revisionism
In historiography, historical revisionism is the reinterpretation of a historical account. It usually involves challenging the orthodox (established, accepted or traditional) views held by professional scholars about a historical event or times ...
. He noted that the deportations had been in fact based on ethnicity of victims.
In popular culture
 In 2008, Lily Hyde, a British journalist living in Ukraine, published a novel titled ''Dreamland'' that revolves around a Crimean Tatar family return to their homeland in the 1990s. The story is told from the perspective of a 12-year-old girl who moves from Uzbekistan to a demolished village with her parents, brother, and grandfather. Her grandfather tells her stories about the heroes and victims among the Crimean Tatars.
The 2013 Ukrainian Crimean Tatar-language film '' Haytarma'' portrays the experience of Crimean Tatar flying ace and
In 2008, Lily Hyde, a British journalist living in Ukraine, published a novel titled ''Dreamland'' that revolves around a Crimean Tatar family return to their homeland in the 1990s. The story is told from the perspective of a 12-year-old girl who moves from Uzbekistan to a demolished village with her parents, brother, and grandfather. Her grandfather tells her stories about the heroes and victims among the Crimean Tatars.
The 2013 Ukrainian Crimean Tatar-language film '' Haytarma'' portrays the experience of Crimean Tatar flying ace and Hero of the Soviet Union
The title Hero of the Soviet Union (russian: Герой Советского Союза, translit=Geroy Sovietskogo Soyuza) was the highest distinction in the Soviet Union, awarded together with the Order of Lenin personally or collectively for ...
Amet-khan Sultan during the 1944 deportations.
In 2015 Christina Paschyn released the documentary film ''A Struggle for Home: The Crimean Tatars'' in a Ukrainian–Qatari co-production. It depicts the history of the Crimean Tatars from 1783 up until 2014, with a special emphasis on the 1944 mass deportation.
At the Eurovision Song Contest 2016
The Eurovision Song Contest 2016 was the 61st edition of the Eurovision Song Contest. It took place in Stockholm, Sweden, following the country's victory at the with the song " Heroes" by Måns Zelmerlöw. Organised by the European Broadcastin ...
in Stockholm
Stockholm () is the capital and largest city of Sweden as well as the largest urban area in Scandinavia. Approximately 980,000 people live in the municipality, with 1.6 million in the urban area, and 2.4 million in the metropo ...
, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic countries, Nordic c ...
, the Ukrainian Crimean Tatar singer Jamala
Susana Alimivna Jamaladinova, ; rus, Суса́на Али́мовна Джамалади́нова, Susána Alímovna Dzhamaladínova, sʊˈsanə ɐˈlʲiməvnə dʐəməlɐˈdʲinəvə, links=yes. (born 27 August 1983), known professionally ...
performed the song "1944
Events
Below, the events of World War II have the "WWII" prefix.
January
* January 2 – WWII:
** Free French General Jean de Lattre de Tassigny is appointed to command French Army B, part of the Sixth United States Army Group in ...
", which refers to the deportation of the Crimean Tatars in the eponymous year. Jamala, an ethnic Crimean Tatar born in exile in Kyrgyzstan
Kyrgyzstan,, pronounced or the Kyrgyz Republic, is a landlocked country in Central Asia. Kyrgyzstan is bordered by Kazakhstan to the north, Uzbekistan to the west, Tajikistan to the south, and the People's Republic of China to the ea ...
, dedicated the song to her deported great-grandmother. She became the first Crimean Tatar to perform at Eurovision and also the first to perform with a song with lyrics in the Crimean Tatar language. She went on to win the contest, becoming the second Ukrainian artist to win the event. John, 13 May 2016
See also
*De-Tatarization of Crimea
The de-Tatarization of Crimea ( crh, Qırımnıñ tatarsızlaştırıluvı, italics=yes; russian: Детатаризация Крыма, Detatarizatsiya Kryma) refers to the Soviet and Russian efforts to remove traces of the indigenous Crimean Tat ...
* Deportation of the Chechens and Ingush
The deportation of the Chechens and Ingush ( ce, До́хадар, Махках дахар, inh, Мехках дахар), or Ardakhar Genocide ( ce, Ардахар Махках), and also known as Operation Lentil (russian: Чечевица ...
* Deportation of the Meskhetian Turks
* List of ethnic cleansing campaigns
* List of genocides by death toll
This list of genocides by death toll includes estimates of all deaths which were directly or indirectly caused by genocide, as it is defined by the UN Convention on Genocide. It excludes other mass killings, which may be referred to as gen ...
* Population transfer in the Soviet Union
From 1930 to 1952, the government of the Soviet Union, on the orders of Soviet leader Joseph Stalin under the direction of the NKVD official Lavrentiy Beria, forcibly transferred populations of various groups. These actions may be classified ...
Comments
Citations
General and cited sources
Books
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Online news reports
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * *Journal articles
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *International and NGO sources
* * * * * *External links
* {{Crimea topics 1944 in the Soviet Union Anti-indigenous racism Crimea in World War II Crimean Tatar diaspora Crimes against humanity Deportation Ethnic cleansing in EuropeCrimean Tatars
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg
, flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars
, image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg
, caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace ...
Genocides in Europe
Joseph Stalin
Persecution of Muslims
Persecution of Turkic peoples
Political repression in the Soviet Union
Soviet ethnic policy
Soviet World War II crimes
Tatarophobia
Violence against Muslims