The Autonomous Administration of North and East Syria (AANES), also known as Rojava, is a
de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with ''de jure'' ("by la ...
autonomous region
An autonomous administrative division (also referred to as an autonomous area, entity, unit, region, subdivision, or territory) is a subnational administrative division or internal territory of a sovereign state that has a degree of autonomy� ...
in northeastern
Syria. It consists of self-governing
sub-regions in the areas of
Afrin,
Jazira
Jazira or Al-Jazira ( 'island'), or variants, may refer to:
Business
*Jazeera Airways, an airlines company based in Kuwait
Locations
* Al-Jazira, a traditional region known today as Upper Mesopotamia or the smaller region of Cizre
* Al-Jazira ( ...
,
Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers''). Originating in Turkey, the Eup ...
,
Raqqa
Raqqa ( ar, ٱلرَّقَّة, ar-Raqqah, also and ) (Kurdish: Reqa/ ڕەقە) is a city in Syria on the northeast bank of the Euphrates River, about east of Aleppo. It is located east of the Tabqa Dam, Syria's largest dam. The Hellenistic, ...
,
Tabqa,
Manbij
Manbij ( ar, مَنْبِج, Manbiǧ, ku, مەنبج, Minbic, tr, Münbiç, Menbic, or Menbiç) is a city in the northeast of Aleppo Governorate in northern Syria, 30 kilometers (19 mi) west of the Euphrates. In the 2004 census by the Cen ...
and
Deir Ez-Zor
, population_urban =
, population_density_urban_km2 =
, population_density_urban_sq_mi =
, population_blank1_title = Ethnicities
, population_blank1 =
, population_blank2_title = Religions
, population_blank2 =
...
.
Rojava conflict
The Rojava conflict, also known as the Rojava Revolution, is a political upheaval and military conflict taking place in northern Syria, known among Kurds as Western Kurdistan or Rojava.
During the Syrian civil war that began in 2011, a Kurdish ...
and the wider Syrian Civil War, in which its official military force, the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF), has taken part.
While entertaining some foreign relations, the region is not officially recognized as autonomous by the government of Syria or any state except for the Catalan Parliament
The Parliament of Catalonia ( ca, Parlament de Catalunya, ; es, Parlamento de Cataluña; oc, Parlament de Catalonha) is the unicameral legislature of the autonomous community of Catalonia, Spain. The Parliament is currently made up of 135 mem ...
.[ The AANES has widespread support for its universal democratic, sustainable, ]autonomous
In developmental psychology and moral, political, and bioethical philosophy, autonomy, from , ''autonomos'', from αὐτο- ''auto-'' "self" and νόμος ''nomos'', "law", hence when combined understood to mean "one who gives oneself one's ow ...
pluralist, equal, and feminist policies in dialogues with other parties
A party is a gathering of people who have been invited by a host for the purposes of socializing, conversation, recreation, or as part of a festival or other commemoration or celebration of a special occasion. A party will often feature ...
and organizations.polyethnic
Polyethnicity, alternatively 'polyethnics'' and also pluriethnicity or multiethnicity, (from prefixes wikt:poly-, poly-, pluri-, wikt:multi-, multi- / all designating plurality), refers to specific cultural phenomena that are characterized by so ...
and home to sizeable ethnic Kurdish
Kurdish may refer to:
*Kurds or Kurdish people
*Kurdish languages
*Kurdish alphabets
*Kurdistan, the land of the Kurdish people which includes:
**Southern Kurdistan
**Eastern Kurdistan
**Northern Kurdistan
**Western Kurdistan
See also
* Kurd (dis ...
, Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
and Assyrian populations, with smaller communities of ethnic Turkmen, Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diasp ...
, Circassians
The Circassians (also referred to as Cherkess or Adyghe; Adyghe and Kabardian: Адыгэхэр, romanized: ''Adıgəxər'') are an indigenous Northwest Caucasian ethnic group and nation native to the historical country-region of Circassia ...
, and Yazidis
Yazidis or Yezidis (; ku, ئێزیدی, translit=Êzidî) are a Kurmanji-speaking endogamous minority group who are indigenous to Kurdistan, a geographical region in Western Asia that includes parts of Iraq, Syria, Turkey and Iran. The ma ...
.
The supporters of the region's administration state that it is an officially secular
Secularity, also the secular or secularness (from Latin ''saeculum'', "worldly" or "of a generation"), is the state of being unrelated or neutral in regards to religion. Anything that does not have an explicit reference to religion, either negativ ...
polity[ with ]direct democratic
Direct democracy or pure democracy is a form of democracy in which the electorate decides on policy initiatives without elected representatives as proxies. This differs from the majority of currently established democracies, which are represe ...
ambitions based on an anarchistic, feminist, and libertarian socialist ideology promoting decentralization
Decentralization or decentralisation is the process by which the activities of an organization, particularly those regarding planning and decision making, are distributed or delegated away from a central, authoritative location or group.
Conce ...
, gender equality
Gender equality, also known as sexual equality or equality of the sexes, is the state of equal ease of access to resources and opportunities regardless of gender, including economic participation and decision-making; and the state of valuing d ...
, environmental sustainability, social ecology
Ecology () is the study of the relationships between living organisms, including humans, and their physical environment. Ecology considers organisms at the individual, population, community, ecosystem, and biosphere level. Ecology overl ...
and pluralistic tolerance for religious
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatur ...
, cultural and political diversity
Diversity, diversify, or diverse may refer to:
Business
*Diversity (business), the inclusion of people of different identities (ethnicity, gender, age) in the workforce
*Diversity marketing, marketing communication targeting diverse customers
* ...
, and that these values are mirrored in its constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princ ...
, society, and politics, stating it to be a model for a federalized Syria as a whole, rather than outright independence.[ The region's administration has also been accused by some partisan and non-partisan sources of ]authoritarianism
Authoritarianism is a political system characterized by the rejection of political plurality, the use of strong central power to preserve the political ''status quo'', and reductions in the rule of law, separation of powers, and democratic voti ...
, support of the Syrian government, Kurdification, and displacement.human rights
Human rights are moral principles or normsJames Nickel, with assistance from Thomas Pogge, M.B.E. Smith, and Leif Wenar, 13 December 2013, Stanford Encyclopedia of PhilosophyHuman Rights Retrieved 14 August 2014 for certain standards of hu ...
within the region, as well as defense of minority and religious rights
Freedom of religion or religious liberty is a principle that supports the freedom of an individual or community, in public or private, to manifest religion or belief in teaching, practice, worship, and observance. It also includes the freedom ...
within Syria.social justice
Social justice is justice in terms of the distribution of wealth, Equal opportunity, opportunities, and Social privilege, privileges within a society. In Western Civilization, Western and Culture of Asia, Asian cultures, the concept of social ...
approach which emphasizes rehabilitation, empowerment
Empowerment is the degree of autonomy and self-determination in people and in communities. This enables them to represent their interests in a responsible and self-determined way, acting on their own authority. It is the process of becoming strong ...
and social care
Social work is an academic discipline and practice-based profession concerned with meeting the basic needs of individuals, families, groups, communities, and society as a whole to enhance their individual and collective well-being. Social wor ...
over retribution. The death penalty was abolished. Prisons house mostly people charged with terrorist activity related to ISIL
An Islamic state is a state that has a form of government based on Islamic law (sharia). As a term, it has been used to describe various historical polities and theories of governance in the Islamic world. As a translation of the Arabic term ...
and other extremist groups, and are a large strain on the region's economy
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with the ...
. The autonomous region is ruled by a coalition which bases its policy ambitions to a large extent on democratic libertarian socialist
Libertarian socialism, also known by various other names, is a left-wing,Diemer, Ulli (1997)"What Is Libertarian Socialism?" The Anarchist Library. Retrieved 4 August 2019. anti-authoritarian, anti-statist and libertarianLong, Roderick T. (20 ...
ideology of democratic confederalism and have been described as pursuing a model of economy that blends co-operative and market enterprise, through a system of local councils in minority, cultural and religious representation. The AANES has by far the highest average salaries and standard of living throughout Syria, with salaries being twice as large as in regime-controlled Syria; following the collapse of the Syrian pound the AANES doubled salaries to maintain inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reduct ...
, and allow for good wages. Independent organizations providing healthcare in the region include the Kurdish Red Crescent, the Syrian American Medical Society, the Free Burma Rangers and Doctors Without Borders
Doctor or The Doctor may refer to:
Personal titles
* Doctor (title), the holder of an accredited academic degree
* A medical practitioner, including:
** Physician
** Surgeon
** Dentist
** Veterinary physician
** Optometrist
*Other roles
** ...
.
Since 2016, Turkish and Turkish-backed Syrian rebel forces have occupied parts of Rojava through a series of military operations against the SDF. AANES and its SDF have stated they will defend all regions of autonomous administration from any aggressiveness.
Polity names and translations
 Parts of northern Syria are known as Western Kurdistan ( ku, Rojavayê Kurdistanê) or simply Rojava ( ; "the West") among Kurds,
Parts of northern Syria are known as Western Kurdistan ( ku, Rojavayê Kurdistanê) or simply Rojava ( ; "the West") among Kurds,[: "On 19 July the PYD formally announced that it had written a constitution for an autonomous Syrian Kurdish region to be known as West Kurdistan."] one of the four parts of Greater Kurdistan
Kurdistan ( ku, کوردستان ,Kurdistan ; lit. "land of the Kurds") or Greater Kurdistan is a roughly defined geo-cultural territory in Western Asia wherein the Kurds form a prominent majority population and the Kurdish culture, languages, ...
. The name "Rojava" was thus associated with a Kurdish identity of the administration. As the region expanded and increasingly included areas dominated by non-Kurdish groups, mostly Arabs, "Rojava" was used less and less by the administration in hopes of deethnicising its appearance and making it more acceptable to other ethnicities. Regardless, the polity continued to be called "Rojava" by locals and international observers,Assyrian homeland
The Assyrian homeland, Assyria ( syc, ܐܬܘܪ, Āṯūr or syc, ܒܝܬ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, Bêth Nahrin) refers to the homeland of the Assyrian people within which Assyrian civilisation developed, located in their indigenous Upper Mesopotamia. T ...
, by Syriac-Assyrians. The area has also been nicknamed Federal Northern Syria, and the democratic confederalist autonomous areas of northern Syria.
The first name of the local government for the Kurdish-dominated areas in Afrin District
Afrin District ( ar, منطقة عفرين, manṭiqat Afrīn) is a district of Aleppo Governorate in northern Syria. The administrative centre is the city of Afrin. At the 2004 census, the district had a population of 172,095. Also available i ...
, Ayn al-Arab District (Kobanî), and northern al-Hasakah Governorate
Al-Hasakah Governorate ( ar, محافظة الحسكة, Muḥāfaẓat al-Ḥasakah, ku, Parêzgeha Hesekê}, syc, ܗܘܦܪܟܝܐ ܕܚܣܟܗ, Huparkiyo d'Ḥasake, also known as syc, ܓܙܪܬܐ, Gozarto) is one of the fourteen governorates (pro ...
was "Interim Transitional Administration", adopted in 2013. After the three autonomous cantons were proclaimed in 2014, PYD-governed territories were also nicknamed "the Autonomous Regions" or "Democratic Autonomous Administration".federal system
Federalism is a combined or compound mode of government that combines a general government (the central or "federal" government) with regional governments ( provincial, state, cantonal, territorial, or other sub-unit governments) in a single p ...
of government as the Democratic Federation of Rojava – Northern Syria ( ku, Federaliya Demokratîk a Rojava – Bakurê Sûriyê; ar, الفدرالية الديمقراطية لروج آفا – شمال سوريا, translit=al-Fidirāliyya al-Dīmuqrāṭiyya li-Rūj ʾĀvā – Šamāl Suriyā; syc, ܦܕܪܐܠܝܘܬ݂ܐ ܕܝܡܩܪܐܛܝܬܐ ܠܓܙܪܬܐ ܒܓܪܒܝܐ ܕܣܘܪܝܐ, translit=Federaloyotho Demoqraṭoyto l'Gozarto b'Garbyo d'Suriya; sometimes abbreviated as NSR).Syrian Democratic Council
The Syrian Democratic Council ( ku, Meclîsa Sûriya Demokratîk, MSD; ar, مجلس سوريا الديمقراطية; syc, ܡܘܬܒܐ ܕܣܘܪܝܐ ܕܝܡܩܪܛܝܬܐ, translit=Mawtbo d'Suriya Demoqraṭoyto) is the political wing of the Syri ...
has adopted a new name for the region, naming it the Autonomous Administration of North and East Syria (NES) ( ku, Rêveberiya Xweser a Bakur û Rojhilatê Sûriyeyê; ar, الإدارة الذاتية لشمال وشرق سوريا; syc, ܡܕܰܒܪܳܢܘܬ݂ܳܐ ܝܳܬ݂ܰܝܬܳܐ ܠܓܰܪܒܝܳܐ ܘܡܰܕܢܚܳܐ ܕܣܘܪܝܰܐ, translit=Mdabronuṯo Yoṯayto l-Garbyo w-Madnḥyo d-Suriya; tr, Kuzey ve Doğu Suriye Özerk Yönetimi) also sometimes translated into English as the "Self-Administration of North and East Syria", encompassing the Euphrates, Afrin, and Jazira regions as well as the local civil councils in the regions of Raqqa, Manbij, Tabqa, and Deir ez-Zor.[
]
Geography

 The region mainly lies to the west of the
The region mainly lies to the west of the Tigris
The Tigris () is the easternmost of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian and Arabian Deserts, and empties into the ...
, to the east of the Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers''). Originating in Turkey, the Eup ...
, south of the Turkish border and borders
A border is a geographical boundary.
Border, borders, The Border or The Borders may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Film and television
* ''Border'' (1997 film), an Indian Hindi-language war film
* ''Border'' (2018 Swedish film), ...
Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
to the southeast as well as the Iraqi Kurdistan Region
Kurdistan Region ( ku, هەرێمی کوردستان, translit=Herêmî Kurdistan; ar, إقليم كردستان), abbr. KRI, is an autonomous region in Iraq comprising the four Kurdish-majority governorates of Erbil, Sulaymaniyah, Duhok ...
to the northeast. The region is at latitude approximately 36°30' north and mostly consists of plains and low hills, however there are some mountains in the region such as Mount Abdulaziz as well as the western part of the Sinjar Mountain Range in the Jazira Region.
In terms of governorates of Syria
Syria is a unitary state, but for administrative purposes, it is divided into fourteen governorates, also called provinces or counties in English (Arabic ''muḥāfaẓāt'', singular '' muḥāfaẓah''). The governorates are divided into si ...
, the region is formed from parts of the al-Hasakah, Raqqa
Raqqa ( ar, ٱلرَّقَّة, ar-Raqqah, also and ) (Kurdish: Reqa/ ڕەقە) is a city in Syria on the northeast bank of the Euphrates River, about east of Aleppo. It is located east of the Tabqa Dam, Syria's largest dam. The Hellenistic, ...
, Deir ez-Zor
, population_urban =
, population_density_urban_km2 =
, population_density_urban_sq_mi =
, population_blank1_title = Ethnicities
, population_blank1 =
, population_blank2_title = Religions
, population_blank2 =
...
and the Aleppo governorates.
History
Background

 Northern Syria is part of the
Northern Syria is part of the Fertile Crescent
The Fertile Crescent ( ar, الهلال الخصيب) is a crescent-shaped region in the Middle East, spanning modern-day Iraq, Syria, Lebanon, Israel, Palestine and Jordan, together with the northern region of Kuwait, southeastern region of ...
, and includes archaeological sites dating to the Neolithic, such as Tell Halaf
Tell Halaf ( ar, تل حلف) is an archaeological site in the Al Hasakah governorate of northeastern Syria, a few kilometers from the city of Ra's al-'Ayn near the Turkish border. The site, which dates to the 6th millennium BCE, was the firs ...
. In antiquity, the area was part of the Mitanni
Mitanni (; Hittite cuneiform ; ''Mittani'' '), c. 1550–1260 BC, earlier called Ḫabigalbat in old Babylonian texts, c. 1600 BC; Hanigalbat or Hani-Rabbat (''Hanikalbat'', ''Khanigalbat'', cuneiform ') in Assyrian records, or ''Naharin'' in ...
kingdom, its centre being the Khabur river valley in modern-day Jazira Region. It was then part of Assyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the ...
, with the last surviving Assyrian imperial records, from between 604 BC and 599 BC, were found in and around the Assyrian city of Dūr-Katlimmu. Later it was ruled by different dynasties and empires – the Achaemenids
The Achaemenid Empire or Achaemenian Empire (; peo, 𐎧𐏁𐏂, , ), also called the First Persian Empire, was an ancient Iranian empire founded by Cyrus the Great in 550 BC. Based in Western Asia, it was contemporarily the largest emp ...
of Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
, the Hellenistic empires who succeeded Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
, the Artaxiads of Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ' ...
, Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
, the Iranian Parthians and Sasanians
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
, then by the Byzantines and successive Arab Islamic caliphates. In course of these regimes, different groups settled in northern Syria, often contributing to population shifts. Arabic tribes have been present in the area for millennia. Under the Hellenistic Seleucid Empire (312–63 BC), different tribal groups and mercenaries were settled in northern Syria as military colonists; these included Arabs and possibly Kurds. Jan Retso argued that Abai, an Arab settlement where the Seleucid king Antiochus VI Dionysus
Antiochus VI Dionysus (c. 148–142/1 BC), king of the Hellenistic Seleucid kingdom, was the son of Alexander Balas and Cleopatra Thea, daughter of Ptolemy VI of Egypt
Ptolemy VI Philometor ( gr, Πτολεμαῖος Φιλομήτωρ, ...
was raised, was located in northern Syria. By the 3rd century, the Arab tribe of the Fahmids lived in northern Syria.
By the 9th century, northern Syria was inhabited by a mixed population of Arabs, Assyrians, Kurds, Turkic groups, and others. Kurdish tribes in the area often operated as soldiers for hire, and were still placed in specific military settlements in the northern Syrian mountains. There existed a Kurdish elite of which Saladin
Yusuf ibn Ayyub ibn Shadi () ( – 4 March 1193), commonly known by the epithet Saladin,, ; ku, سهلاحهدین, ; was the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty. Hailing from an ethnic Kurdish family, he was the first of both Egypt and ...
, the founder of the Ayyubid dynasty and the Emir of Masyaf
Masyaf ( ar, مصياف ') is a city in northwestern Syria. It is the center of the Masyaf District in the Hama Governorate. As of 2004, Masyaf had a religiously diverse population of approximately 22,000 Ismailis, Alawites and Christians. The c ...
in the 12th century were part of.Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
(1516–1922), large Kurdish-speaking tribal groups both settled in and were deported to areas of northern Syria from Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
.Armenian
Armenian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Armenia, a country in the South Caucasus region of Eurasia
* Armenians, the national people of Armenia, or people of Armenian descent
** Armenian Diaspora, Armenian communities across the ...
and Assyrian Christians in Upper Mesopotamia
Upper Mesopotamia is the name used for the uplands and great outwash plain of northwestern Iraq, northeastern Syria and southeastern Turkey, in the northern Middle East. Since the early Muslim conquests of the mid-7th century, the region has been ...
, between 1914 and 1920, with further attacks on unarmed fleeing civilians conducted by local Arab militias.[Travis, Hannibal. ''Genocide in the Middle East: The Ottoman Empire, Iraq, and Sudan''. Durham, NC: Carolina Academic Press, 2010, 2007, pp. 237–77, 293–294.]
Syria's independence and rule of the Ba'ath Party
 Following Syria's independence, policies of
Following Syria's independence, policies of Arab nationalism
Arab nationalism ( ar, القومية العربية, al-Qawmīya al-ʿArabīya) is a nationalist ideology that asserts the Arabs are a nation and promotes the unity of Arab people, celebrating the glories of Arab civilization, the language a ...
and attempts at forced Arabization became widespread in the country's north, to a large part directed against the Kurdish population.Human Rights Council
The United Nations Human Rights Council (UNHRC), CDH is a United Nations body whose mission is to promote and protect human rights around the world. The Council has 47 members elected for staggered three-year terms on a regional group basis. ...
titled ''Persecution and Discrimination against Kurdish Citizens in Syria'', the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights
The Office of the United Nations High Commissioner for Human Rights, commonly known as the Office of the High Commissioner for Human Rights (OHCHR) or the United Nations Human Rights Office, is a department of the Secretariat of the United Nati ...
held that "Successive Syrian governments continued to adopt a policy of ethnic discrimination and national persecution against Kurds, completely depriving them of their national, democratic and human rights an integral part of human existence. The government imposed ethnically-based programs, regulations and exclusionary measures on various aspects of Kurds' lives political, economic, social and cultural." In many instances, the Syrian government arbitrarily deprived ethnic Kurdish citizens of their citizenship. The largest such instance was a consequence of a census in 1962, which was conducted for exactly this purpose. 120,000 ethnic Kurdish citizens saw their citizenship arbitrarily taken away and became stateless.
In many instances, the Syrian government arbitrarily deprived ethnic Kurdish citizens of their citizenship. The largest such instance was a consequence of a census in 1962, which was conducted for exactly this purpose. 120,000 ethnic Kurdish citizens saw their citizenship arbitrarily taken away and became stateless.Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization, headquartered in New York City, that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. The group pressures governments, policy makers, companies, and individual human r ...
(HRW) estimated the number of such "stateless" Kurdish people in Syria at 300,000.Al-Hasakah Governorate
Al-Hasakah Governorate ( ar, محافظة الحسكة, Muḥāfaẓat al-Ḥasakah, ku, Parêzgeha Hesekê}, syc, ܗܘܦܪܟܝܐ ܕܚܣܟܗ, Huparkiyo d'Ḥasake, also known as syc, ܓܙܪܬܐ, Gozarto) is one of the fourteen governorates (pro ...
, which was owned and cultivated by tens of thousands of Kurdish citizens, and gave it to Arab families brought in from other provinces.Kurdish Democratic Progressive Party
The Kurdish Democratic Progressive Party in Syria ( Kurdish: ''Partiya Dîmoqratî Pêşverû Kurd li Sûriyê''; abbreviated PDPKS, KDPP or Pêşverû) is one of the oldest Kurdish parties in Syria, having been active since seceding from the ...
and the Assyrian Democratic Party attempted to work within the system, hoping to bring about changes through soft pressure. In general, parties that openly represented certain ethnic and religious minorities were not allowed to participate in elections, but their politicians were occasionally allowed to run as Independents. Some Kurdish politicians won seats during the Syrian elections in 1990. The government also recruited Kurdish officials, in particular as mayors, to ease ethnic relations. Regardless, northern Syrian ethnic groups remained deliberately underrepresented in the bureaucracy, and many Kurdish majority areas were run by Arab officials from other parts of the country. Security and intelligence agencies worked hard to suppress dissidents, and most Kurdish parties remained underground movements. The government monitored, though generally allowed this "sub-state activity" because the northern minorities including the Kurds rarely caused unrest with the exception of the 2004 Qamishli riots. The situation improved after the death of Hafez al-Assad and the election of his son, Bashar al-Assad, under whom the number of Kurdish officials grew.
Despite the Ba'athist internal policies which officially suppressed a Kurdish identity, the Syrian government allowed the Kurdistan Workers' Party
The Kurdistan Workers' Party or PKK is a Kurdish militant political organization and armed guerrilla movement, which historically operated throughout Kurdistan, but is now primarily based in the mountainous Kurdish-majority regions of sout ...
(PKK) to set up training camps from 1980. The PKK was a militant Kurdish group led by Abdullah Öcalan which was waging an insurgency against Turkey. Syria and Turkey were hostile toward each other at the time, resulting in the use of the PKK as proxy group.al-Hasakah Governorate
Al-Hasakah Governorate ( ar, محافظة الحسكة, Muḥāfaẓat al-Ḥasakah, ku, Parêzgeha Hesekê}, syc, ܗܘܦܪܟܝܐ ܕܚܣܟܗ, Huparkiyo d'Ḥasake, also known as syc, ܓܙܪܬܐ, Gozarto) is one of the fourteen governorates (pro ...
, where other Kurdish parties maintained more influence. Many Syrian Kurds developed a long-lasting sympathy for the PKK, and a large number, possibly more than 10,000, joined its insurgency in Turkey. A rapprochement between Syria and Turkey brought an end to this phase in 1998, when Öcalan and the PKK were formally expelled from northern Syria. Regardless, the PKK maintained a clandestine presence in the region.Kurdistan Communities Union
The Kurdistan Communities Union ( ku, Koma Civakên Kurdistanê, italic=yes, KCK) is a Kurdish political organization committed to implementing Abdullah Öcalan's ideology of democratic confederalism. Öcalan, Abdullahbr>Declaration of Democratic ...
(KCK) to implement Öcalan's ideas in various Middle Eastern countries. A KCK branch was also set up in Syria, led by Sofi Nureddin and known as "KCK-Rojava". In an attempt to outwardly distance the Syrian branch from the PKK,People's Protection Units
The People's Defense Units (YPG), (YPG) ; ar, وحدات حماية الشعب, Waḥdāt Ḥimāyat aš-Šaʽb) also called People's Protection Units, is a mainly- Kurdish militia in Syria and the primary component of the Syrian Democra ...
" (YPG), a paramilitary wing of the PYD, was also founded during this time, but remained dormant.
Establishment of de facto autonomy and war against ISIL
 In 2011, a civil uprising erupted in Syria, prompting hasty government reforms. One of the issues addressed during this time was the status of Syria's stateless Kurds, as President Bashar al-Assad granted about 220,000 Kurds citizenship. In course of the next months, the crisis in Syria escalated into a civil war. The armed Syrian opposition seized control of several regions, while security forces were overstretched. In mid-2012 the government responded to this development by withdrawing its military from three mainly Kurdish areas
In 2011, a civil uprising erupted in Syria, prompting hasty government reforms. One of the issues addressed during this time was the status of Syria's stateless Kurds, as President Bashar al-Assad granted about 220,000 Kurds citizenship. In course of the next months, the crisis in Syria escalated into a civil war. The armed Syrian opposition seized control of several regions, while security forces were overstretched. In mid-2012 the government responded to this development by withdrawing its military from three mainly Kurdish areas[ and leaving control to local militias. This has been described as an attempt by the Assad regime to keep the Kurdish population out of the initial civil uprising and civil war.][
Existing underground Kurdish political parties, namely the PYD and the Kurdish National Council (KNC), joined to form the Kurdish Supreme Committee (KSC) and the People's Protection Units (YPG) militia was reestablished to defend Kurdish-inhabited areas in northern Syria. In July 2012, the YPG established control in the towns of Kobanî, Amuda and Afrin, Syria, Afrin, and the Kurdish Supreme Committee established a joint leadership council to administer the towns. Soon YPG also gained control of the cities of Al-Malikiyah, Ras al-Ayn, al-Darbasiyah, and al-Muabbada and parts of al-Hasakah, Hasakah and Qamishli.] The Kurdish Supreme Committee was dissolved in 2013, when the PYD abandoned the alliance with the KNC and established the Movement for a Democratic Society (TEV-DEM) coalition with other political parties.
The Kurdish Supreme Committee was dissolved in 2013, when the PYD abandoned the alliance with the KNC and established the Movement for a Democratic Society (TEV-DEM) coalition with other political parties.constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these princ ...
(also known as ''social contract'') was approved. The Syrian opposition and the Kurdish parties belonging to the KNC condemned this move, regarding the canton system as illegal, authoritarian, and supportive of the Syrian government. The PYD countered that the constitution was open to review and amendment, and that the KNC had been consulted on its drafting beforehand. From September 2014 to spring 2015, the YPG forces in Kobanî Canton, supported by some Free Syrian Army militias and leftist international and Kurdistan Workers' Party
The Kurdistan Workers' Party or PKK is a Kurdish militant political organization and armed guerrilla movement, which historically operated throughout Kurdistan, but is now primarily based in the mountainous Kurdish-majority regions of sout ...
(PKK) volunteers, fought and finally repelled an assault by the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) during the Siege of Kobanî, and in the YPG's Tell Abyad offensive of summer of 2015, the regions of Jazira and Kobanî were connected.
 After the YPG victory over ISIL in Kobanî in March 2015, an alliance between YPG and the United States was formed, which greatly worried Turkey, because Turkey stated the YPG was a clone of the
After the YPG victory over ISIL in Kobanî in March 2015, an alliance between YPG and the United States was formed, which greatly worried Turkey, because Turkey stated the YPG was a clone of the Kurdistan Workers' Party
The Kurdistan Workers' Party or PKK is a Kurdish militant political organization and armed guerrilla movement, which historically operated throughout Kurdistan, but is now primarily based in the mountainous Kurdish-majority regions of sout ...
(PKK) which Turkey (and the U.S. and the E.U.) designate as Terrorism, terrorists.[ In December 2015, the ]Syrian Democratic Council
The Syrian Democratic Council ( ku, Meclîsa Sûriya Demokratîk, MSD; ar, مجلس سوريا الديمقراطية; syc, ܡܘܬܒܐ ܕܣܘܪܝܐ ܕܝܡܩܪܛܝܬܐ, translit=Mawtbo d'Suriya Demoqraṭoyto) is the political wing of the Syri ...
was created. On 17 March 2016, at a TEV-DEM-organized conference in Rmelan the establishment the ''Democratic Federation of Rojava – Northern Syria'' was declared in the areas they controlled in Northern Syria. The declaration was quickly denounced by both the Syrian government and the National Coalition for Syrian Revolutionary and Opposition Forces.[
In March 2016, Hediya Yousef and Mansur Selum were elected co-chairpersons for the executive committee to organise a constitution for the region, to replace the 2014 constitution.][ Yousef said the decision to set up a federal government was in large part driven by the expansion of territories captured from Islamic State: "Now, after the liberation of many areas, it requires us to go to a wider and more comprehensive system that can embrace all the developments in the area, that will also give rights to all the groups to represent themselves and to form their own administrations". In July 2016, a draft for the new constitution was presented, based on the principles of the 2014 constitution, mentioning all ethnic groups living in Northern Syria and addressing their cultural, political and linguistic rights.]
Turkish military operations and occupation
 Since 2012, when the first YPG pockets appeared, Turkey had been alarmed by the presence of PKK-related forces at its southern border and grew concerned when the YPG entered into an alliance with the US to oppose ISIS forces in the region. The Turkish government refused to allow aid to be sent to the YPG during the Siege of Kobanî. This led to the 2014 Kurdish riots in Turkey, Kurdish riots, the breakdown of the Kurdish–Turkish peace process, 2013–2015 peace process in July 2015 and the renewal of Kurdish–Turkish conflict (2015–present), armed conflict between the PKK and Turkish forces. According to the Turkish pro-government newspaper ''Daily Sabah,'' the YPG's parent organisation, the PYD, provided the PKK with militants, explosives, arms and ammunition.
in August 2016, Turkey launched Operation Euphrates Shield to prevent the YPG-led Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) from linking Afrin Canton (now Afrin Region) with the rest of Rojava and to capture
Since 2012, when the first YPG pockets appeared, Turkey had been alarmed by the presence of PKK-related forces at its southern border and grew concerned when the YPG entered into an alliance with the US to oppose ISIS forces in the region. The Turkish government refused to allow aid to be sent to the YPG during the Siege of Kobanî. This led to the 2014 Kurdish riots in Turkey, Kurdish riots, the breakdown of the Kurdish–Turkish peace process, 2013–2015 peace process in July 2015 and the renewal of Kurdish–Turkish conflict (2015–present), armed conflict between the PKK and Turkish forces. According to the Turkish pro-government newspaper ''Daily Sabah,'' the YPG's parent organisation, the PYD, provided the PKK with militants, explosives, arms and ammunition.
in August 2016, Turkey launched Operation Euphrates Shield to prevent the YPG-led Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) from linking Afrin Canton (now Afrin Region) with the rest of Rojava and to capture Manbij
Manbij ( ar, مَنْبِج, Manbiǧ, ku, مەنبج, Minbic, tr, Münbiç, Menbic, or Menbiç) is a city in the northeast of Aleppo Governorate in northern Syria, 30 kilometers (19 mi) west of the Euphrates. In the 2004 census by the Cen ...
from the SDF. Turkish and Turkish-backed Syrian rebel forces prevented the linking of Rojava's cantons and captured all settlements in Jarabulus previously under SDF control. The SDF handed over part of the region to the Syrian government to act as a buffer zone against Turkey. Manbij remained under SDF control.
In early 2018, Turkey launched Operation Olive Branch alongside Turkish-backed Free Syrian Army to capture the Kurdish-majority Afrin, Syria, Afrin and oust the YPG/SDF from region. Afrin Canton, a subdivision of the region, was occupied and over 100,000 civilians were displaced and relocated to Afrin Region's Shahba Canton which remained under SDF, then joint SDF-Syrian Arab Army (SAA) control. The remaining SDF forces later launched an SDF insurgency in Northern Aleppo, ongoing insurgency against the Turkish and Turkish-backed Syrian rebel forces.
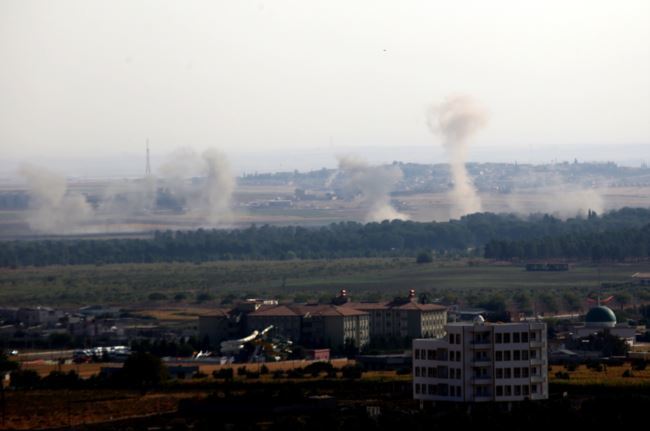 In 2019, Turkey launched 2019 Turkish offensive into north-eastern Syria, Operation Peace Spring against the SDF. On 9 October, the Turkish Air Force launched airstrikes on border towns. On 6 October President of the United States, President Donald Trump had ordered United States troops to withdraw from northeastern Syria where they had been American-led intervention in the Syrian Civil War, providing support to the SDF. Journalists called the withdrawal "a serious betrayal to the Kurds" and "a catastrophic blow to US credibility as an ally and Washington's standing on the world stage"; one journalist stated that "this was one of the worst US foreign policy disasters since the Iraq War". Turkish and Turkish-backed Syrian rebel forces captured 68 settlements, including Ras al-Ayn, Tell Abyad, Suluk, Syria, Suluk, Mabrouka and Al-Manajir, Manajir during the 9-day operation before a 120-hour ceasefire was announced. The operation was condemned by the international community, and human rights violations by Turkish forces were reported. Media outlets labelled the attack "no surprise" because Turkish president Recep Tayyip Erdoğan, Erdoğan had for months warned that the presence of the YPG on the Turkish-Syrian border despite the Northern Syria Buffer Zone was unacceptable.
In 2019, Turkey launched 2019 Turkish offensive into north-eastern Syria, Operation Peace Spring against the SDF. On 9 October, the Turkish Air Force launched airstrikes on border towns. On 6 October President of the United States, President Donald Trump had ordered United States troops to withdraw from northeastern Syria where they had been American-led intervention in the Syrian Civil War, providing support to the SDF. Journalists called the withdrawal "a serious betrayal to the Kurds" and "a catastrophic blow to US credibility as an ally and Washington's standing on the world stage"; one journalist stated that "this was one of the worst US foreign policy disasters since the Iraq War". Turkish and Turkish-backed Syrian rebel forces captured 68 settlements, including Ras al-Ayn, Tell Abyad, Suluk, Syria, Suluk, Mabrouka and Al-Manajir, Manajir during the 9-day operation before a 120-hour ceasefire was announced. The operation was condemned by the international community, and human rights violations by Turkish forces were reported. Media outlets labelled the attack "no surprise" because Turkish president Recep Tayyip Erdoğan, Erdoğan had for months warned that the presence of the YPG on the Turkish-Syrian border despite the Northern Syria Buffer Zone was unacceptable.[ An unintended consequence of the attack was that it raised the worldwide popularity and legitimacy of the northeastern Syrian administration, and several PYD and YPG representatives became internationally known to an unprecedented degree. However, these events caused tensions within the KCK, as differences emerged between the PKK and PYD leadership. The PYD was determined to maintain the regional autonomy and hoped for a continued alliance with the United States. In contrast, the PKK central command was now willing to restart negotiations with Turkey, distrusted the United States, and emphasized the international success of its leftist ideology over the survival of Rojava as administrative entity.]
Politics
 The political system of the region is based on its adopted constitution, officially titled "Charter of the Social Contract".
The political system of the region is based on its adopted constitution, officially titled "Charter of the Social Contract".gender equality
Gender equality, also known as sexual equality or equality of the sexes, is the state of equal ease of access to resources and opportunities regardless of gender, including economic participation and decision-making; and the state of valuing d ...
and freedom of religion.[ It also provides for property rights.][Andrea Glioti]
Rojava: A libertarian myth under scrutiny
Al-Jazeera (6 August 2016). The region's system of community government has direct democratic
Direct democracy or pure democracy is a form of democracy in which the electorate decides on policy initiatives without elected representatives as proxies. This differs from the majority of currently established democracies, which are represe ...
aspirations.
The Former diplomat Ross Carne observed in September 2015 in ''The New York Times'':Kurdistan Workers' Party
The Kurdistan Workers' Party or PKK is a Kurdish militant political organization and armed guerrilla movement, which historically operated throughout Kurdistan, but is now primarily based in the mountainous Kurdish-majority regions of sout ...
(PKK) leader Imprisonment of Abdullah Öcalan, imprisoned in İmralı prison, İmralı, Turkey, has become an iconic figure in the region whose libertarian socialist ideology has shaped the region's society and politics through the ruling TEV-DEM coalition, a political alliance including the PYD and a number of smaller parties. Before TEV-DEM, the region was governed by the Kurdish Supreme Committee, a coalition of the PYD and the Kurdish National Council (KNC), which was dissolved by the PYD in 2013.[ Besides the parties represented in TEV-DEM and the KNC, several other political groups operate in northern Syria. Several of these, such as the Kurdish National Alliance in Syria, the Democratic Conservative Party (Syria), Democratic Conservative Party, the Assyrian Democratic Party, and others actively participate in governing the region.
] The politics of the region has been described as having "libertarian transnational aspirations" influenced by the PKK's shift toward anarchism, but also includes various "tribal, ethno-sectarian, capitalist and patriarchal structures."
The politics of the region has been described as having "libertarian transnational aspirations" influenced by the PKK's shift toward anarchism, but also includes various "tribal, ethno-sectarian, capitalist and patriarchal structures."[ but the area's governing body later relocated to Ayn Issa.][
]
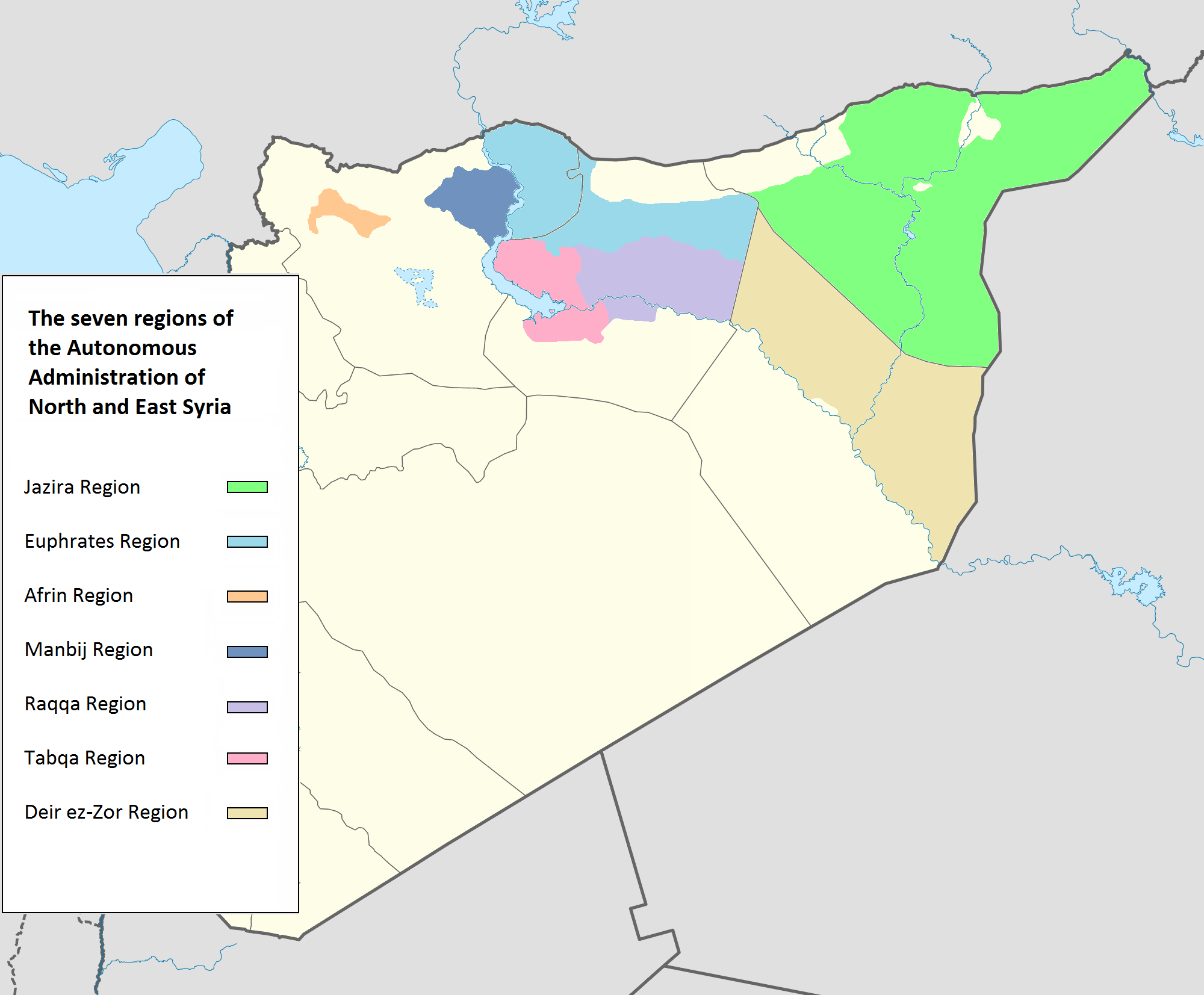
Administrative divisions
 Article 8 of the 2014 constitution stipulates that "All Cantons in the autonomous regions are founded on the principle of local self-government. Cantons may freely elect their representatives and representative bodies, and may pursue their rights insofar as it does not contravene the articles of the Charter."
Article 8 of the 2014 constitution stipulates that "All Cantons in the autonomous regions are founded on the principle of local self-government. Cantons may freely elect their representatives and representative bodies, and may pursue their rights insofar as it does not contravene the articles of the Charter."[
] The cantons were later reorganized into regions with subordinate cantons/provinces, areas, districts and communes. The first 2017 Northern Syria local elections, communal elections in the region were held on 22 September 2017. 12,421 candidates competed for around 3,700 communal positions during the elections, which were organized by the region's High Electoral Commission. Elections for the councils of the Jazira Region, Euphrates Region and Afrin Region were held in 2017 Northern Syria regional elections, December 2017.
The cantons were later reorganized into regions with subordinate cantons/provinces, areas, districts and communes. The first 2017 Northern Syria local elections, communal elections in the region were held on 22 September 2017. 12,421 candidates competed for around 3,700 communal positions during the elections, which were organized by the region's High Electoral Commission. Elections for the councils of the Jazira Region, Euphrates Region and Afrin Region were held in 2017 Northern Syria regional elections, December 2017.[
On 6 September 2018, during a meeting of the ]Syrian Democratic Council
The Syrian Democratic Council ( ku, Meclîsa Sûriya Demokratîk, MSD; ar, مجلس سوريا الديمقراطية; syc, ܡܘܬܒܐ ܕܣܘܪܝܐ ܕܝܡܩܪܛܝܬܐ, translit=Mawtbo d'Suriya Demoqraṭoyto) is the political wing of the Syri ...
in Ayn Issa, a new name for the region was adopted, the "Autonomous Administration of North and East Syria", encompassing the Euphrates, Afrin, and Jazira regions as well as the local civil councils in the regions of Raqqa, Manbij, Tabqa, and Deir ez-Zor. During the meeting, a 70-member "General Council for the Autonomous Administration of North and East Syria" was formed.
Legislature
In December 2015, during a meeting of the region's representatives in Al-Malikiyah, the Syrian Democratic Council
The Syrian Democratic Council ( ku, Meclîsa Sûriya Demokratîk, MSD; ar, مجلس سوريا الديمقراطية; syc, ܡܘܬܒܐ ܕܣܘܪܝܐ ܕܝܡܩܪܛܝܬܐ, translit=Mawtbo d'Suriya Demoqraṭoyto) is the political wing of the Syri ...
(SDC) was established to serve as the political representative of the Syrian Democratic Forces.[ General elections were planned for 2014 and 2018,][ but this was postponed due to fighting.
]
Education, media, and culture
School
 Under the rule of the Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party – Syria Region, Ba'ath Party, school education consisted of only Arabic language public schools, supplemented by Assyrian private confessional schools. In 2015, the region's administration introduced primary education in the first language, native language (either Kurdish language, Kurdish or Arabic) and mandatory Multilingualism, bilingual education (Kurdish and Arabic) for public schools, with English as a mandatory third language. There are ongoing disagreements and negotiations over curriculums with the Syrian central government,
Under the rule of the Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party – Syria Region, Ba'ath Party, school education consisted of only Arabic language public schools, supplemented by Assyrian private confessional schools. In 2015, the region's administration introduced primary education in the first language, native language (either Kurdish language, Kurdish or Arabic) and mandatory Multilingualism, bilingual education (Kurdish and Arabic) for public schools, with English as a mandatory third language. There are ongoing disagreements and negotiations over curriculums with the Syrian central government,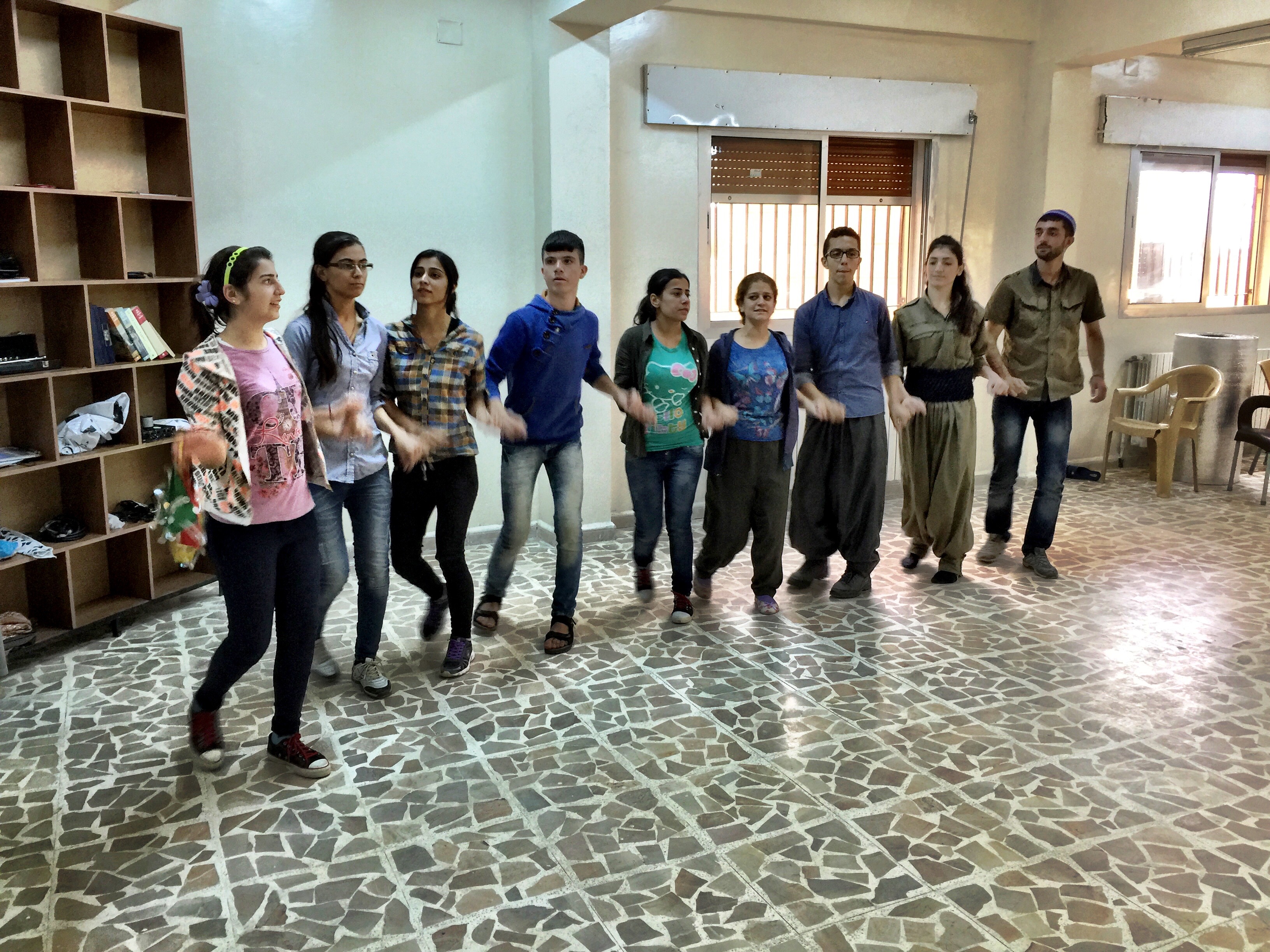 In August 2016, the Ourhi Centre was founded by the Assyrian community in the city of Qamishli, to educate teachers in order to make Syriac language, Syriac-Aramaic an additional language in public schools in Jazira Region, which then started in the 2016/17 academic year.
In August 2016, the Ourhi Centre was founded by the Assyrian community in the city of Qamishli, to educate teachers in order to make Syriac language, Syriac-Aramaic an additional language in public schools in Jazira Region, which then started in the 2016/17 academic year.
Higher education
While there was no institution of tertiary education on the territory of the region at the onset of the Syrian Civil War, an increasing number of such institutions have been established by the regional administrations in the region since.
* In September 2014, the Mesopotamian Social Sciences Academy in Qamishli started classes.[ More such academies designed under a ]libertarian socialist
Libertarian socialism, also known by various other names, is a left-wing,Diemer, Ulli (1997)"What Is Libertarian Socialism?" The Anarchist Library. Retrieved 4 August 2019. anti-authoritarian, anti-statist and libertarianLong, Roderick T. (20 ...
academic philosophy and concept are in the process of founding or planning.
* In August 2015, the traditionally-designed University of Afrin in Afrin started teaching, with initial programs in literature, engineering and economics, including institutes for medicine, topographic engineering, music and theater, business administration and the Kurdish language. After the Turkish army invaded Afrin in 2018, several of it students were transferred to the University of Rojava in Qamishli.[ There is an additional Faculty for Petroleum and Pharmacology in Rmelan.]
Media
 Incorporating the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights, as well as other internationally recognized human rights conventions, the 2014 Constitution of North and East Syria guarantees freedom of speech and freedom of the press. As a result, a diverse media landscape has developed in the region,
Incorporating the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights, as well as other internationally recognized human rights conventions, the 2014 Constitution of North and East Syria guarantees freedom of speech and freedom of the press. As a result, a diverse media landscape has developed in the region,
BBC documentary (2014): ''Rojava: Syria's Secret Revolution''
o
Sky1 documentary (2016): ''Rojava – The Fight Against ISIS''
Internet connections in the region are often slow due to inadequate infrastructure. Internet lines are operated by Syrian Telecom, which as of January 2017 is working on a major extension of the fibre optic cable network in southern Jazira Region.
The arts
 After the establishment of the de facto autonomous region, the Center of Art and Democratic Culture, located in Jazira Region, has become a venue for aspiring artists who showcase their work. Among major cultural events in the region is the annual ''Festival of Theater'' in March/April as well as the ''Rojava Short Story Festival'' in June, both in the city of Qamishli, and the ''Afrin Short Film Festival'' in April.
After the establishment of the de facto autonomous region, the Center of Art and Democratic Culture, located in Jazira Region, has become a venue for aspiring artists who showcase their work. Among major cultural events in the region is the annual ''Festival of Theater'' in March/April as well as the ''Rojava Short Story Festival'' in June, both in the city of Qamishli, and the ''Afrin Short Film Festival'' in April.
Economy
The Jazira Region is a major wheat and cotton producer and has a considerable oil industry. The Euphrates Region suffered most destruction of the three regions and has huge challenges in reconstruction, and has recently seen some greenhouse agriculture construction. The Afrin Region has had a traditional specialization on olive oil including Aleppo soap made from it, and had drawn much industrial production from the nearby city of Aleppo due to the Battle of Aleppo (2012–2016), fighting in Aleppo city from 2012 to 2016. Price controls are managed by local committees, which can set the price of basic goods such as food and medical goods.[ During the Syrian Civil War, the infrastructure of the region on average experienced less destruction than other parts of Syria. In May 2016, Ahmed Yousef, head of the Economic Body and chairman of Afrin University, stated that at the time, the economic output of the region (including agriculture, industry and oil) accounted for about 55% of Syria's gross domestic product.] At first, there were no Direct tax, direct or indirect taxes on people or businesses in the region; instead, the administration raised money mainly through tariffs and selling oil and other natural resources.
At first, there were no Direct tax, direct or indirect taxes on people or businesses in the region; instead, the administration raised money mainly through tariffs and selling oil and other natural resources.Euphrates
The Euphrates () is the longest and one of the most historically important rivers of Western Asia. Together with the Tigris, it is one of the two defining rivers of Mesopotamia ( ''the land between the rivers''). Originating in Turkey, the Eup ...
river, Syrians largest.
The main sources of revenue for the autonomous region have been presented as: 1. Public properties such as grain silos and oil and gas in the Jazira Region, 2. Local taxation and customs fees taken at the border crossings, 3. Service delivery, 4. Remittances from Iraq and Turkey, and 5. Local donations. In 2015, the autonomous administration shared information about the region's finances where its 2014 revenue was about LS 3 billion (≈US$5.8 million) of which 50% was spent on "self-defense and protection", 18% for the Jazira Canton (now Jazira Region), 8.5% for the Kobani Canton (now Euphrates Region), 8.5% for the Afrin Canton (now Afrin Region), 15% for the "Internal Committee" and any remainder was a reserve for the next year.[ The AANES has by far the highest average salaries and standard of living throughout Syria, with salaries being twice as large as in regime controlled Syira, following the collapse of the Syrian pound the AANES doubled salaries to maintain ]inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reduct ...
, and allow for good wages. The AANES still faces challenges with distribution, food security, and healthcare.
External economic relations
 Oil and food production is substantial,
Oil and food production is substantial,
Economy policy framework
 The autonomous region is ruled by a coalition which bases its policy ambitions to a large extent on the libertarian socialist ideology of Abdullah Öcalan and have been described as pursuing a model of economy that blends co-operative and private enterprise.
The autonomous region is ruled by a coalition which bases its policy ambitions to a large extent on the libertarian socialist ideology of Abdullah Öcalan and have been described as pursuing a model of economy that blends co-operative and private enterprise.
Law and security

Legal system
Syrian civil laws are valid in the region if they do not conflict with the Constitution of the autonomous region. One example for amendment is personal status law, which in Syria is based on Sharia and applied by Sharia Courts, while the Secularism, secular autonomous region proclaims absolute equality of women under the law, allowing civil marriage and banning forced marriage, polygamy
Policing and security
 Policing in the region is performed by the Asayish (Syria), Asayish armed formation. Asayish was established on 25 July 2013 to fill the gap of security when the Syrian security forces withdrew.
Policing in the region is performed by the Asayish (Syria), Asayish armed formation. Asayish was established on 25 July 2013 to fill the gap of security when the Syrian security forces withdrew.
Militias

 The main military force of the region is the Syrian Democratic Forces, an alliance of Syrian rebel groups formed in 2015. The SDF is led by the Kurdish majority
The main military force of the region is the Syrian Democratic Forces, an alliance of Syrian rebel groups formed in 2015. The SDF is led by the Kurdish majority People's Protection Units
The People's Defense Units (YPG), (YPG) ; ar, وحدات حماية الشعب, Waḥdāt Ḥimāyat aš-Šaʽb) also called People's Protection Units, is a mainly- Kurdish militia in Syria and the primary component of the Syrian Democra ...
(', YPG). The YPG was founded by the Democratic Union Party (Syria), PYD after the 2004 Qamishli riots, 2004 Qamishli clashes, but was first active in the Syrian Civil War.
Human rights
 In the course of the Syrian Civil War, including the years 2014 and 2015, reports by
In the course of the Syrian Civil War, including the years 2014 and 2015, reports by Human Rights Watch
Human Rights Watch (HRW) is an international non-governmental organization, headquartered in New York City, that conducts research and advocacy on human rights. The group pressures governments, policy makers, companies, and individual human r ...
(HRW) and Amnesty International stated that Human rights in North and East Syria#NES-associated militias, militias associated with the autonomous region were committing war crimes, in particular members of the People's Protection Units
The People's Defense Units (YPG), (YPG) ; ar, وحدات حماية الشعب, Waḥdāt Ḥimāyat aš-Šaʽb) also called People's Protection Units, is a mainly- Kurdish militia in Syria and the primary component of the Syrian Democra ...
(YPG). The reports from 2014 include reports of arbitrary arrests and torture, other reports include the use of child soldiers. The region's civil government has been hailed in international media for human rights advancement in particular Human rights in North and East Syria#Human rights development in the legal system, in the legal system, concerning Human rights in North and East Syria#Women's rights, women's rights, Human rights in North and East Syria#Ethnic minority rights, ethnic minority rights, Human rights in North and East Syria#Freedom of Speech and Press, freedom of Speech and Press and for Human rights in North and East Syria#Hosting inbound refugees, hosting inbound refugees.
The region's civil government has been hailed in international media for human rights advancement in particular Human rights in North and East Syria#Human rights development in the legal system, in the legal system, concerning Human rights in North and East Syria#Women's rights, women's rights, Human rights in North and East Syria#Ethnic minority rights, ethnic minority rights, Human rights in North and East Syria#Freedom of Speech and Press, freedom of Speech and Press and for Human rights in North and East Syria#Hosting inbound refugees, hosting inbound refugees.
Demographics
 The demographics of the region have historically been highly diverse, with several major shifts in regard to which groups form majorities or minorities in the last centuries. The
The demographics of the region have historically been highly diverse, with several major shifts in regard to which groups form majorities or minorities in the last centuries. The Al-Hasakah Governorate
Al-Hasakah Governorate ( ar, محافظة الحسكة, Muḥāfaẓat al-Ḥasakah, ku, Parêzgeha Hesekê}, syc, ܗܘܦܪܟܝܐ ܕܚܣܟܗ, Huparkiyo d'Ḥasake, also known as syc, ܓܙܪܬܐ, Gozarto) is one of the fourteen governorates (pro ...
historically been the domain of nomad and sedentary Arabs.[
Another shift in modern times was the Baath policy of settling additional Arab population in northern Syria, while displacing local Kurds.][ Most recently, during the Syrian Civil War, many refugees have fled to the north of the country. Some ethnic Arab citizens from Iraq have fled to northern Syria as well.][ As result of the civil war, estimates as to the ethnic composition of northern Syria vary widely, ranging from claims about a Kurdish majority and Arab minority to claims about Kurds being a small minority; Al Jazeera stated in October 2019 that just 10 percent of the 4.5 million inhabitants of northern and northeastern Syria were Kurds.
]
Ethnic groups
Two ethnic groups have a significant presence throughout Northern Syria:
*Kurds are an ethnic group living in northeastern and northwestern Syria, culturally and linguistically classified among the Iranian peoples. Many Kurds consider themselves descended from the ancient Iranian people of the Medes, using a calendar dating from 612 BC, when the Assyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the ...
n capital of Nineveh was conquered by the Medes. *Assyrian people, Assyrians are an ethnic group. Their presence in Syria is in the Jazira Region of the autonomous region, particularly in the urban areas (Qamishli, al-Hasakah, Ras al-Ayn, Al-Malikiyah, Al-Qahtaniyah, al-Hasakah Governorate, Al-Qahtaniyah), in the northeastern corner and in villages along the Khabur (Euphrates), Khabur River in the Tell Tamer area. They traditionally speak varieties of Northeastern Neo-Aramaic, a Semitic language. There are many Assyrians among recent refugees to Northern Syria, fleeing Islamist violence elsewhere in Syria back to their traditional lands. In the secular polyethnic political climate of the region, the Dawronoye modernization movement has a growing influence on Assyrian identity in the 21st century.
*Assyrian people, Assyrians are an ethnic group. Their presence in Syria is in the Jazira Region of the autonomous region, particularly in the urban areas (Qamishli, al-Hasakah, Ras al-Ayn, Al-Malikiyah, Al-Qahtaniyah, al-Hasakah Governorate, Al-Qahtaniyah), in the northeastern corner and in villages along the Khabur (Euphrates), Khabur River in the Tell Tamer area. They traditionally speak varieties of Northeastern Neo-Aramaic, a Semitic language. There are many Assyrians among recent refugees to Northern Syria, fleeing Islamist violence elsewhere in Syria back to their traditional lands. In the secular polyethnic political climate of the region, the Dawronoye modernization movement has a growing influence on Assyrian identity in the 21st century.[
* Turkmen are an ethnic group with a major presence in the area between Afrin Region and Euphrates Region, where they form regional majorities in the countryside from Azaz and Mare' to Jarabulus, and a minor presence in Afrin Region and Euphrates Region.
There are also smaller minorities of ]Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, '' hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diasp ...
throughout Northern Syria as well as Chechens in Ras al-Ayn.
Languages
 Regarding the status of different languages in the autonomous region, its "Social Contract" stipulates that "all languages in Northern Syria are equal in all areas of life, including social, educational, cultural, and administrative dealings. Every people shall organize its life and manage its affairs using its mother tongue." In practice, Arabic and Kurmanji are predominantly used across all areas and for most official documents, with Syriac being mainly used in the Jazira Region with some usage across all areas while Turkish and Circassian are also used in the region of Manbij.
The four main languages spoken in Northern Syria are the following, and are from three different language families:
*Kurdish languages, Kurdish (in Northern Kurdish dialect), a Western Iranian languages, Northwestern Iranian language from the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family.
*Arabic language, Arabic in the North Mesopotamian Arabic dialect (Modern Standard Arabic in education and writing), a Central Semitic language from the Semitic languages, Semitic branch of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family.
*Eastern Aramaic languages mainly in the Turoyo and Assyrian Neo-Aramaic varieties (mainly Syriac language, Syriac in education and writing), Northwest Semitic languages from the Semitic languages, Semitic branch of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family.
*Turkish language, Turkish (in Turkish dialects#Syrian Turkmen dialect, Syrian Turkmen dialect), from the Turkic languages, Turkic language family.
For these four languages, three different scripts are in use in Northern Syria:
*The Latin alphabet for Kurdish, Turkish and Turoyo
*The Arabic alphabet, Arabic alphabet (abjad) for Arabic
*The Syriac alphabet for Syriac, Turoyo and Assyrian Neo-Aramaic
Regarding the status of different languages in the autonomous region, its "Social Contract" stipulates that "all languages in Northern Syria are equal in all areas of life, including social, educational, cultural, and administrative dealings. Every people shall organize its life and manage its affairs using its mother tongue." In practice, Arabic and Kurmanji are predominantly used across all areas and for most official documents, with Syriac being mainly used in the Jazira Region with some usage across all areas while Turkish and Circassian are also used in the region of Manbij.
The four main languages spoken in Northern Syria are the following, and are from three different language families:
*Kurdish languages, Kurdish (in Northern Kurdish dialect), a Western Iranian languages, Northwestern Iranian language from the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family.
*Arabic language, Arabic in the North Mesopotamian Arabic dialect (Modern Standard Arabic in education and writing), a Central Semitic language from the Semitic languages, Semitic branch of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family.
*Eastern Aramaic languages mainly in the Turoyo and Assyrian Neo-Aramaic varieties (mainly Syriac language, Syriac in education and writing), Northwest Semitic languages from the Semitic languages, Semitic branch of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family.
*Turkish language, Turkish (in Turkish dialects#Syrian Turkmen dialect, Syrian Turkmen dialect), from the Turkic languages, Turkic language family.
For these four languages, three different scripts are in use in Northern Syria:
*The Latin alphabet for Kurdish, Turkish and Turoyo
*The Arabic alphabet, Arabic alphabet (abjad) for Arabic
*The Syriac alphabet for Syriac, Turoyo and Assyrian Neo-Aramaic
Religion
Most ethnic Kurdish and Arab people in Northern Syria adhere to Sunni Islam, while ethnic Assyrian people generally are Syriac Orthodox Church, Syriac Orthodox, Chaldean Catholic Church, Chaldean Catholic, Syriac Catholic Church, Syriac Catholic or adherents of the Assyrian Church of the East. There are also adherents to other religions, such as Yazidis
Yazidis or Yezidis (; ku, ئێزیدی, translit=Êzidî) are a Kurmanji-speaking endogamous minority group who are indigenous to Kurdistan, a geographical region in Western Asia that includes parts of Iraq, Syria, Turkey and Iran. The ma ...
m. The dominant PYD party and the political administration in the region are decidedly secular
Secularity, also the secular or secularness (from Latin ''saeculum'', "worldly" or "of a generation"), is the state of being unrelated or neutral in regards to religion. Anything that does not have an explicit reference to religion, either negativ ...
.
Population centres
This list includes all cities and towns in the region with more than 10,000 inhabitants. The population figures are given according to the 2004 Syrian census.
Cities highlighted in light grey are partially under the civil control of the Syrian government.
Health
Healthcare is organized through the region's "Health and Environment Authority" and through sub-region and canton-level Health Committees. Independent organizations providing healthcare in the region include the Kurdish Red Crescent, the Syrian American Medical Society, the Free Burma Rangers and Doctors Without Borders
Doctor or The Doctor may refer to:
Personal titles
* Doctor (title), the holder of an accredited academic degree
* A medical practitioner, including:
** Physician
** Surgeon
** Dentist
** Veterinary physician
** Optometrist
*Other roles
** ...
. The 2019 Turkish offensive into north-eastern Syria, 2019 Turkish offensive left thousands of people in the region without access to basic necessities as the majority of international aid groups withdrew during the violence.
External relations
Relations with the Syrian government
 Currently, the relations of the region to the Syrian government, Damascus government are determined by the context of the Syrian civil war. The Constitution of Syria and the Constitution of North and East Syria are legally incompatible with respect to legislative and executive authority. In the military realm, combat between the
Currently, the relations of the region to the Syrian government, Damascus government are determined by the context of the Syrian civil war. The Constitution of Syria and the Constitution of North and East Syria are legally incompatible with respect to legislative and executive authority. In the military realm, combat between the People's Protection Units
The People's Defense Units (YPG), (YPG) ; ar, وحدات حماية الشعب, Waḥdāt Ḥimāyat aš-Šaʽb) also called People's Protection Units, is a mainly- Kurdish militia in Syria and the primary component of the Syrian Democra ...
(YPG) and Syrian government forces has been rare, in the most instances some of the territory still controlled by the Syrian government in Qamishli and al-Hasakah has been lost to the YPG. In some military campaigns, in particular in northern Aleppo governate and in al-Hasakah, YPG and Syrian government forces have tacitly cooperated against Islamist forces, the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) and others.
Kurdish question
 The region's dominant political party, the Democratic Union Party (PYD), is a member organisation of the
The region's dominant political party, the Democratic Union Party (PYD), is a member organisation of the Kurdistan Communities Union
The Kurdistan Communities Union ( ku, Koma Civakên Kurdistanê, italic=yes, KCK) is a Kurdish political organization committed to implementing Abdullah Öcalan's ideology of democratic confederalism. Öcalan, Abdullahbr>Declaration of Democratic ...
(KCK) organization; however, the other KCK member organisations in the neighbouring states (Turkey, Iran and Iraq) with Kurdish minorities are either outlawed (Turkish Kurdistan, Iranian Kurdistan) or politically marginal with respect to other Kurdish parties (Iraq). Expressions of sympathy for Syrian Kurds have been numerous among Kurds in Turkey. During the Siege of Kobanî, some ethnic Kurdish citizens of Turkey crossed the border and volunteered in the defense of the town.
The region's relationship with the Kurdistan Regional Government in Iraq is complicated. One context is that the governing party there, the Kurdistan Democratic Party (KDP), views itself and its affiliated Kurdish parties in other countries as a more conservative and nationalist alternative and competitor to the KCK political agenda and blueprint in general.
International relations
 Aside of the representation offices the AANES has established in France, Sweden, Germany and Switzerland the region's role in the international arena is comprehensive military cooperation of its militias under the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) umbrella with the United States and the Military intervention against ISIL#3 December 2014, international (US-led) coalition against the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant. In a public statement in March 2016, the day after the declaration of the regions autonomy, U.S. Defense Secretary Ashton Carter praised the
Aside of the representation offices the AANES has established in France, Sweden, Germany and Switzerland the region's role in the international arena is comprehensive military cooperation of its militias under the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) umbrella with the United States and the Military intervention against ISIL#3 December 2014, international (US-led) coalition against the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant. In a public statement in March 2016, the day after the declaration of the regions autonomy, U.S. Defense Secretary Ashton Carter praised the People's Protection Units
The People's Defense Units (YPG), (YPG) ; ar, وحدات حماية الشعب, Waḥdāt Ḥimāyat aš-Šaʽb) also called People's Protection Units, is a mainly- Kurdish militia in Syria and the primary component of the Syrian Democra ...
(YPG) militia as having "proven to be excellent partners of ours on the ground in fighting ISIL. We are grateful for that, and we intend to continue to do that, recognizing the complexities of their regional role." Late October 2016, U.S. Army Lt. Gen. Stephen Townsend, the commander of the international Anti-ISIL-coalition, said that the SDF would lead the impending Raqqa offensive (2016–present), assault on Raqqa, ISIL's stronghold and capital, and that SDF commanders would plan the operation with advice from American and coalition troops. At various times, the U.S. deployed U.S. troops embedded with the SDF to the border between the region and Turkey, in order to deter Turkish aggressions against the SDF.Manbij
Manbij ( ar, مَنْبِج, Manbiǧ, ku, مەنبج, Minbic, tr, Münbiç, Menbic, or Menbiç) is a city in the northeast of Aleppo Governorate in northern Syria, 30 kilometers (19 mi) west of the Euphrates. In the 2004 census by the Cen ...
and Rmelan in a bid to assist Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) militias and in order to defuse tensions with Turkey.
 In the diplomatic field, the de facto autonomous region lacks any formal recognition. While there is comprehensive activity of reception of the region's representatives and appreciation with a broad range of countries, only Russia has on occasion openly supported the region's political ambition of federalization of Syria in the international arena,
In the diplomatic field, the de facto autonomous region lacks any formal recognition. While there is comprehensive activity of reception of the region's representatives and appreciation with a broad range of countries, only Russia has on occasion openly supported the region's political ambition of federalization of Syria in the international arena,[ International cooperation has been in the field of educational and cultural institutions, like the cooperation agreement of Paris 8 University with the newly founded University of Rojava in Qamishli, or planning for a France, French cultural centre in Amuda.
Neighbouring Turkey is consistently hostile, which has been attributed to a perceived threat from the region's emergence, in that it would encourage activism for autonomy among Kurds in Turkey in the Kurdish–Turkish conflict (1978–present), Kurdish–Turkish conflict. In this context, in particular the region's leading Democratic Union Party (PYD) and the YPG militia being members of the ]Kurdistan Communities Union
The Kurdistan Communities Union ( ku, Koma Civakên Kurdistanê, italic=yes, KCK) is a Kurdish political organization committed to implementing Abdullah Öcalan's ideology of democratic confederalism. Öcalan, Abdullahbr>Declaration of Democratic ...
(KCK) network of organisations, which also includes both political and military Kurdish organizations in Turkey itself, including the Kurdistan Workers' Party
The Kurdistan Workers' Party or PKK is a Kurdish militant political organization and armed guerrilla movement, which historically operated throughout Kurdistan, but is now primarily based in the mountainous Kurdish-majority regions of sout ...
(PKK). Turkey's policy towards the region is based on an economic blockade,[ persistent attempts of international isolation,]
Syrian Constitutional Committee
On 20 November 2019, a new Syrian Constitutional Committee began operating in order to discuss a new settlement and to draft a new constitution for Syria.[Regime continues to violate Sochi deal amid diplomatic efforts for political solution in Syria](_blank)
DAILY SABAH, ISTANBUL Published 10 December 2019. This committee comprises about 150 members. It includes representatives of the Syrian regime, opposition groups, and countries serving as guarantors of the process such as e.g. Russia. However, this committee has faced strong opposition from the Assad regime. 50 of the committee members represent the regime, and 50 members represent the opposition. The committee began its work in November 2019 in Geneva, under UN auspices. However, the Assad regime delegation left on the second day of the process.
War crimes and criticism
Accusations of human rights violations, war crimes and Kurdification, ethnic cleansing have been made against the YPG since the beginning of the Syrian civil war, such as in the take-over of the border town of Tal Abyad from the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant (ISIL) and other operations. Some of the accusations have come from Turkey and Turkish-backed Syrian militias and opposition groups in the region, while others have come from numerous human rights organizations, as well as Western and regional journalists.
“By deliberately demolishing civilian homes, in some cases razing and burning entire villages, displacing their inhabitants with no justifiable military grounds, the Autonomous Administration is abusing its authority and brazenly flouting international humanitarian law, in attacks that amount to war crimes."
and:
"In its fight against IS, the Autonomous Administration appears to be trampling all over the rights of civilians who are caught in the middle. We saw extensive displacement and destruction that did not occur as a result of fighting. This report uncovers clear evidence of a deliberate, co-ordinated campaign of collective punishment of civilians in villages previously captured by IS, or where a small minority were suspected of supporting the group.”
In March 2017 the "United Nations Independent International Commission of Inquiry on Syria" was unable to find evidence to substantiate claims about ethnic cleansing, stating:
“Though allegations of ‘ethnic cleansing’ continued to be received during the period under review, the Commission found no evidence to substantiate claims that YPG or SDF forces ever targeted Arab communities on the basis of ethnicity, nor that YPG cantonal authorities systematically sought to change the demographic composition of territories under their control through the commission of violations directed against any particular ethnic group,”
The region has also been criticized extensively by various partisan and non-partisan sides over political authoritarianism
Authoritarianism is a political system characterized by the rejection of political plurality, the use of strong central power to preserve the political ''status quo'', and reductions in the rule of law, separation of powers, and democratic voti ...
. A KDP-S politician accused the PYD of delivering him to the Assad regime.
It has also been criticized for banning journalists, media outlets and political parties that are critical of the YPG narrative in areas under its control.
See also
* Kurdistan Region
Kurdistan Region ( ku, هەرێمی کوردستان, translit=Herêmî Kurdistan; ar, إقليم كردستان), abbr. KRI, is an autonomous region in Iraq comprising the four Kurdish-majority governorates of Erbil, Sulaymaniyah, Duhok ...
* Rebel Zapatista Autonomous Municipalities
Notes
References
Works cited
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
The 2014 Constitution of the Rojava Cantons
Resources on the Rojava revolution in West Kurdistan (Syria)
'Rojava Revolution' Reading Guide
{{Authority control
Autonomous Administration of North and East Syria,
2013 establishments in Syria
Articles containing video clips
Rebel groups that actively control territory, Rojava
States and territories established in 2013
Subdivisions of Syria
Upper Mesopotamia


 Northern Syria is part of the
Northern Syria is part of the  Following Syria's independence, policies of
Following Syria's independence, policies of  In many instances, the Syrian government arbitrarily deprived ethnic Kurdish citizens of their citizenship. The largest such instance was a consequence of a census in 1962, which was conducted for exactly this purpose. 120,000 ethnic Kurdish citizens saw their citizenship arbitrarily taken away and became stateless. This status was passed to the children of a "stateless" Kurdish father. In 2010, the
In many instances, the Syrian government arbitrarily deprived ethnic Kurdish citizens of their citizenship. The largest such instance was a consequence of a census in 1962, which was conducted for exactly this purpose. 120,000 ethnic Kurdish citizens saw their citizenship arbitrarily taken away and became stateless. This status was passed to the children of a "stateless" Kurdish father. In 2010, the  In 2011, a civil uprising erupted in Syria, prompting hasty government reforms. One of the issues addressed during this time was the status of Syria's stateless Kurds, as President Bashar al-Assad granted about 220,000 Kurds citizenship. In course of the next months, the crisis in Syria escalated into a civil war. The armed Syrian opposition seized control of several regions, while security forces were overstretched. In mid-2012 the government responded to this development by withdrawing its military from three mainly Kurdish areas and leaving control to local militias. This has been described as an attempt by the Assad regime to keep the Kurdish population out of the initial civil uprising and civil war.
Existing underground Kurdish political parties, namely the PYD and the Kurdish National Council (KNC), joined to form the Kurdish Supreme Committee (KSC) and the People's Protection Units (YPG) militia was reestablished to defend Kurdish-inhabited areas in northern Syria. In July 2012, the YPG established control in the towns of Kobanî, Amuda and Afrin, Syria, Afrin, and the Kurdish Supreme Committee established a joint leadership council to administer the towns. Soon YPG also gained control of the cities of Al-Malikiyah, Ras al-Ayn, al-Darbasiyah, and al-Muabbada and parts of al-Hasakah, Hasakah and Qamishli. Doing so, the YPG and its female wing, the Women's Protection Units (YPJ), mostly battled factions of the Free Syrian Army, and Islamist militias like the al-Nusra Front and Jabhat Ghuraba al-Sham. It also eclipsed rival Kurdish militias, and absorbed some government loyalist groups. According to researcher Charles R. Lister, the government's withdrawal and concurrent rise of the PYD "raised many eyebrows", as the relationship between the two entities was "highly contentious" at the time. The PYD was known to oppose certain government policies, but had also strongly criticised the Syrian opposition.
In 2011, a civil uprising erupted in Syria, prompting hasty government reforms. One of the issues addressed during this time was the status of Syria's stateless Kurds, as President Bashar al-Assad granted about 220,000 Kurds citizenship. In course of the next months, the crisis in Syria escalated into a civil war. The armed Syrian opposition seized control of several regions, while security forces were overstretched. In mid-2012 the government responded to this development by withdrawing its military from three mainly Kurdish areas and leaving control to local militias. This has been described as an attempt by the Assad regime to keep the Kurdish population out of the initial civil uprising and civil war.
Existing underground Kurdish political parties, namely the PYD and the Kurdish National Council (KNC), joined to form the Kurdish Supreme Committee (KSC) and the People's Protection Units (YPG) militia was reestablished to defend Kurdish-inhabited areas in northern Syria. In July 2012, the YPG established control in the towns of Kobanî, Amuda and Afrin, Syria, Afrin, and the Kurdish Supreme Committee established a joint leadership council to administer the towns. Soon YPG also gained control of the cities of Al-Malikiyah, Ras al-Ayn, al-Darbasiyah, and al-Muabbada and parts of al-Hasakah, Hasakah and Qamishli. Doing so, the YPG and its female wing, the Women's Protection Units (YPJ), mostly battled factions of the Free Syrian Army, and Islamist militias like the al-Nusra Front and Jabhat Ghuraba al-Sham. It also eclipsed rival Kurdish militias, and absorbed some government loyalist groups. According to researcher Charles R. Lister, the government's withdrawal and concurrent rise of the PYD "raised many eyebrows", as the relationship between the two entities was "highly contentious" at the time. The PYD was known to oppose certain government policies, but had also strongly criticised the Syrian opposition.
 The Kurdish Supreme Committee was dissolved in 2013, when the PYD abandoned the alliance with the KNC and established the Movement for a Democratic Society (TEV-DEM) coalition with other political parties. On 19 July 2013, the PYD announced that it had written a constitution for an "autonomous Syrian Kurdish region", and planned to hold referendum to approve the constitution in October 2013. Qamishli served as first ''de facto'' capital of the PYD-led governing body, which was official called the "Interim Transitional Administration". The announcement was widely denounced by both moderate as well as Islamist factions of the Syrian opposition. In January 2014, three areas declared their autonomy as cantons (now Afrin Region, Jazira Region and Euphrates Region) and an interim
The Kurdish Supreme Committee was dissolved in 2013, when the PYD abandoned the alliance with the KNC and established the Movement for a Democratic Society (TEV-DEM) coalition with other political parties. On 19 July 2013, the PYD announced that it had written a constitution for an "autonomous Syrian Kurdish region", and planned to hold referendum to approve the constitution in October 2013. Qamishli served as first ''de facto'' capital of the PYD-led governing body, which was official called the "Interim Transitional Administration". The announcement was widely denounced by both moderate as well as Islamist factions of the Syrian opposition. In January 2014, three areas declared their autonomy as cantons (now Afrin Region, Jazira Region and Euphrates Region) and an interim  After the YPG victory over ISIL in Kobanî in March 2015, an alliance between YPG and the United States was formed, which greatly worried Turkey, because Turkey stated the YPG was a clone of the
After the YPG victory over ISIL in Kobanî in March 2015, an alliance between YPG and the United States was formed, which greatly worried Turkey, because Turkey stated the YPG was a clone of the  Since 2012, when the first YPG pockets appeared, Turkey had been alarmed by the presence of PKK-related forces at its southern border and grew concerned when the YPG entered into an alliance with the US to oppose ISIS forces in the region. The Turkish government refused to allow aid to be sent to the YPG during the Siege of Kobanî. This led to the 2014 Kurdish riots in Turkey, Kurdish riots, the breakdown of the Kurdish–Turkish peace process, 2013–2015 peace process in July 2015 and the renewal of Kurdish–Turkish conflict (2015–present), armed conflict between the PKK and Turkish forces. According to the Turkish pro-government newspaper ''Daily Sabah,'' the YPG's parent organisation, the PYD, provided the PKK with militants, explosives, arms and ammunition.
in August 2016, Turkey launched Operation Euphrates Shield to prevent the YPG-led Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) from linking Afrin Canton (now Afrin Region) with the rest of Rojava and to capture
Since 2012, when the first YPG pockets appeared, Turkey had been alarmed by the presence of PKK-related forces at its southern border and grew concerned when the YPG entered into an alliance with the US to oppose ISIS forces in the region. The Turkish government refused to allow aid to be sent to the YPG during the Siege of Kobanî. This led to the 2014 Kurdish riots in Turkey, Kurdish riots, the breakdown of the Kurdish–Turkish peace process, 2013–2015 peace process in July 2015 and the renewal of Kurdish–Turkish conflict (2015–present), armed conflict between the PKK and Turkish forces. According to the Turkish pro-government newspaper ''Daily Sabah,'' the YPG's parent organisation, the PYD, provided the PKK with militants, explosives, arms and ammunition.
in August 2016, Turkey launched Operation Euphrates Shield to prevent the YPG-led Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) from linking Afrin Canton (now Afrin Region) with the rest of Rojava and to capture  In 2019, Turkey launched 2019 Turkish offensive into north-eastern Syria, Operation Peace Spring against the SDF. On 9 October, the Turkish Air Force launched airstrikes on border towns. On 6 October President of the United States, President Donald Trump had ordered United States troops to withdraw from northeastern Syria where they had been American-led intervention in the Syrian Civil War, providing support to the SDF. Journalists called the withdrawal "a serious betrayal to the Kurds" and "a catastrophic blow to US credibility as an ally and Washington's standing on the world stage"; one journalist stated that "this was one of the worst US foreign policy disasters since the Iraq War". Turkish and Turkish-backed Syrian rebel forces captured 68 settlements, including Ras al-Ayn, Tell Abyad, Suluk, Syria, Suluk, Mabrouka and Al-Manajir, Manajir during the 9-day operation before a 120-hour ceasefire was announced. The operation was condemned by the international community, and human rights violations by Turkish forces were reported. Media outlets labelled the attack "no surprise" because Turkish president Recep Tayyip Erdoğan, Erdoğan had for months warned that the presence of the YPG on the Turkish-Syrian border despite the Northern Syria Buffer Zone was unacceptable. An unintended consequence of the attack was that it raised the worldwide popularity and legitimacy of the northeastern Syrian administration, and several PYD and YPG representatives became internationally known to an unprecedented degree. However, these events caused tensions within the KCK, as differences emerged between the PKK and PYD leadership. The PYD was determined to maintain the regional autonomy and hoped for a continued alliance with the United States. In contrast, the PKK central command was now willing to restart negotiations with Turkey, distrusted the United States, and emphasized the international success of its leftist ideology over the survival of Rojava as administrative entity.
In 2019, Turkey launched 2019 Turkish offensive into north-eastern Syria, Operation Peace Spring against the SDF. On 9 October, the Turkish Air Force launched airstrikes on border towns. On 6 October President of the United States, President Donald Trump had ordered United States troops to withdraw from northeastern Syria where they had been American-led intervention in the Syrian Civil War, providing support to the SDF. Journalists called the withdrawal "a serious betrayal to the Kurds" and "a catastrophic blow to US credibility as an ally and Washington's standing on the world stage"; one journalist stated that "this was one of the worst US foreign policy disasters since the Iraq War". Turkish and Turkish-backed Syrian rebel forces captured 68 settlements, including Ras al-Ayn, Tell Abyad, Suluk, Syria, Suluk, Mabrouka and Al-Manajir, Manajir during the 9-day operation before a 120-hour ceasefire was announced. The operation was condemned by the international community, and human rights violations by Turkish forces were reported. Media outlets labelled the attack "no surprise" because Turkish president Recep Tayyip Erdoğan, Erdoğan had for months warned that the presence of the YPG on the Turkish-Syrian border despite the Northern Syria Buffer Zone was unacceptable. An unintended consequence of the attack was that it raised the worldwide popularity and legitimacy of the northeastern Syrian administration, and several PYD and YPG representatives became internationally known to an unprecedented degree. However, these events caused tensions within the KCK, as differences emerged between the PKK and PYD leadership. The PYD was determined to maintain the regional autonomy and hoped for a continued alliance with the United States. In contrast, the PKK central command was now willing to restart negotiations with Turkey, distrusted the United States, and emphasized the international success of its leftist ideology over the survival of Rojava as administrative entity.
 The political system of the region is based on its adopted constitution, officially titled "Charter of the Social Contract". The constitution was ratified on 9 January 2014 and provides that all residents of the region shall enjoy fundamental rights such as
The political system of the region is based on its adopted constitution, officially titled "Charter of the Social Contract". The constitution was ratified on 9 January 2014 and provides that all residents of the region shall enjoy fundamental rights such as  The politics of the region has been described as having "libertarian transnational aspirations" influenced by the PKK's shift toward anarchism, but also includes various "tribal, ethno-sectarian, capitalist and patriarchal structures." The region has a "co-governance" policy in which each position at each level of government in the region includes a "female equivalent of equal authority" to a male. Similarly, there are aspirations for equal political representation of all ethno-religious components – Arabs, Kurds and Assyrians being the most sizeable ones. This has been compared this to the Lebanon, Lebanese National Pact, confessionalist system, which is based on that country's major religions.
The PYD-led rule has triggered protests in various areas since they first captured territory. In 2019, residents of tens of villages in the eastern Deir ez-Zor Governorate demonstrated for two weeks, regarding the new regional leadership as Kurdish-dominated and non-inclusive, citing arrests of suspected ISIL members, looting of oil, lack of infrastructure as well as forced conscription into the SDF as reasons. The protests resulted in deaths and injuries. It has been stated that the new political structures created in the region have been based on top-down structures, which have placed obstacles for the return of refugees, created dissent as well as a lack of trust between the SDF and the local population.
Qamishli initially served as the ''de facto'' capital of the administration, but the area's governing body later relocated to Ayn Issa.
The politics of the region has been described as having "libertarian transnational aspirations" influenced by the PKK's shift toward anarchism, but also includes various "tribal, ethno-sectarian, capitalist and patriarchal structures." The region has a "co-governance" policy in which each position at each level of government in the region includes a "female equivalent of equal authority" to a male. Similarly, there are aspirations for equal political representation of all ethno-religious components – Arabs, Kurds and Assyrians being the most sizeable ones. This has been compared this to the Lebanon, Lebanese National Pact, confessionalist system, which is based on that country's major religions.
The PYD-led rule has triggered protests in various areas since they first captured territory. In 2019, residents of tens of villages in the eastern Deir ez-Zor Governorate demonstrated for two weeks, regarding the new regional leadership as Kurdish-dominated and non-inclusive, citing arrests of suspected ISIL members, looting of oil, lack of infrastructure as well as forced conscription into the SDF as reasons. The protests resulted in deaths and injuries. It has been stated that the new political structures created in the region have been based on top-down structures, which have placed obstacles for the return of refugees, created dissent as well as a lack of trust between the SDF and the local population.
Qamishli initially served as the ''de facto'' capital of the administration, but the area's governing body later relocated to Ayn Issa.
 Article 8 of the 2014 constitution stipulates that "All Cantons in the autonomous regions are founded on the principle of local self-government. Cantons may freely elect their representatives and representative bodies, and may pursue their rights insofar as it does not contravene the articles of the Charter."
Article 8 of the 2014 constitution stipulates that "All Cantons in the autonomous regions are founded on the principle of local self-government. Cantons may freely elect their representatives and representative bodies, and may pursue their rights insofar as it does not contravene the articles of the Charter."
 The cantons were later reorganized into regions with subordinate cantons/provinces, areas, districts and communes. The first 2017 Northern Syria local elections, communal elections in the region were held on 22 September 2017. 12,421 candidates competed for around 3,700 communal positions during the elections, which were organized by the region's High Electoral Commission. Elections for the councils of the Jazira Region, Euphrates Region and Afrin Region were held in 2017 Northern Syria regional elections, December 2017. Most of Afrin Region was occupied by Turkish-led forces in early 2018, though the administrative division continued to operate from Tell Rifaat which is under joint YPG-Syrian Army control.
On 6 September 2018, during a meeting of the
The cantons were later reorganized into regions with subordinate cantons/provinces, areas, districts and communes. The first 2017 Northern Syria local elections, communal elections in the region were held on 22 September 2017. 12,421 candidates competed for around 3,700 communal positions during the elections, which were organized by the region's High Electoral Commission. Elections for the councils of the Jazira Region, Euphrates Region and Afrin Region were held in 2017 Northern Syria regional elections, December 2017. Most of Afrin Region was occupied by Turkish-led forces in early 2018, though the administrative division continued to operate from Tell Rifaat which is under joint YPG-Syrian Army control.
On 6 September 2018, during a meeting of the  Under the rule of the Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party – Syria Region, Ba'ath Party, school education consisted of only Arabic language public schools, supplemented by Assyrian private confessional schools. In 2015, the region's administration introduced primary education in the first language, native language (either Kurdish language, Kurdish or Arabic) and mandatory Multilingualism, bilingual education (Kurdish and Arabic) for public schools, with English as a mandatory third language. There are ongoing disagreements and negotiations over curriculums with the Syrian central government, which generally still pays the teachers in public schools.
Under the rule of the Arab Socialist Ba'ath Party – Syria Region, Ba'ath Party, school education consisted of only Arabic language public schools, supplemented by Assyrian private confessional schools. In 2015, the region's administration introduced primary education in the first language, native language (either Kurdish language, Kurdish or Arabic) and mandatory Multilingualism, bilingual education (Kurdish and Arabic) for public schools, with English as a mandatory third language. There are ongoing disagreements and negotiations over curriculums with the Syrian central government, which generally still pays the teachers in public schools.
 In August 2016, the Ourhi Centre was founded by the Assyrian community in the city of Qamishli, to educate teachers in order to make Syriac language, Syriac-Aramaic an additional language in public schools in Jazira Region, which then started in the 2016/17 academic year. According to the region's Education Committee, in 2016/2017 "three curriculums have replaced the old one, to include teaching in three languages: Kurdish, Arabic and Syriac." In August 2017 Galenos Yousef Issa of the Ourhi Centre announced that the Syriac curriculum would be expanded to grade 6, which earlier had been limited to grade 3, with teachers being assigned to Syriac schools in Al-Hasakah, Al-Qahtaniyah, al-Hasakah Governorate, Al-Qahtaniyah and Al-Malikiyah. At the start of the academic year 2018–2019, the curricula in Kurdish and Arabic had been expanded to grades 1–12 and Syriac to grades 1–9. "Jineology" classes had also been introduced. In general, schools are encouraged to teach the administration's "uptopian doctrine" which promotes diversity, democracy, and the ideas of Abdullah Öcalan. Local reactions to the changes to the school system and curriculum were mixed. While many praised the new system because it encouraged tolerance and allowed Kurds and other minorities to be taught in their own languages, others have criticised it as ''de facto'' compulsory indoctrination.
The federal, regional and local administrations in the region put much emphasis on promoting libraries and educational centers, to facilitate learning and social and artistic activities. Examples are the Nahawand Center for Developing Children's Talents in Amuda (est. 2015) and the Rodî û Perwîn Library in Kobani (May 2016).
For Assyrian private confessional schools there had at first been no changes. However, in August 2018 it was reported that the region's authorities was trying to implement its own Syriac curriculum in private Christian schools that have been continuing to use an Arabic curriculum with limited Syriac classes approved by the Assad regime and originally developed by Syrian Education Ministry in cooperation with Christian clergy in the 1950s. The threatening of the closure of schools not complying with this resulted in protests erupting in Qamishli. A deal was later reached in September 2018 between the region's authorities and the local Syriac Orthodox archbishopric, where the two first grades in these schools would learn the region's Syriac curriculum and grades three to six would continue to learn the Damascus approved curriculum.
In August 2016, the Ourhi Centre was founded by the Assyrian community in the city of Qamishli, to educate teachers in order to make Syriac language, Syriac-Aramaic an additional language in public schools in Jazira Region, which then started in the 2016/17 academic year. According to the region's Education Committee, in 2016/2017 "three curriculums have replaced the old one, to include teaching in three languages: Kurdish, Arabic and Syriac." In August 2017 Galenos Yousef Issa of the Ourhi Centre announced that the Syriac curriculum would be expanded to grade 6, which earlier had been limited to grade 3, with teachers being assigned to Syriac schools in Al-Hasakah, Al-Qahtaniyah, al-Hasakah Governorate, Al-Qahtaniyah and Al-Malikiyah. At the start of the academic year 2018–2019, the curricula in Kurdish and Arabic had been expanded to grades 1–12 and Syriac to grades 1–9. "Jineology" classes had also been introduced. In general, schools are encouraged to teach the administration's "uptopian doctrine" which promotes diversity, democracy, and the ideas of Abdullah Öcalan. Local reactions to the changes to the school system and curriculum were mixed. While many praised the new system because it encouraged tolerance and allowed Kurds and other minorities to be taught in their own languages, others have criticised it as ''de facto'' compulsory indoctrination.
The federal, regional and local administrations in the region put much emphasis on promoting libraries and educational centers, to facilitate learning and social and artistic activities. Examples are the Nahawand Center for Developing Children's Talents in Amuda (est. 2015) and the Rodî û Perwîn Library in Kobani (May 2016).
For Assyrian private confessional schools there had at first been no changes. However, in August 2018 it was reported that the region's authorities was trying to implement its own Syriac curriculum in private Christian schools that have been continuing to use an Arabic curriculum with limited Syriac classes approved by the Assad regime and originally developed by Syrian Education Ministry in cooperation with Christian clergy in the 1950s. The threatening of the closure of schools not complying with this resulted in protests erupting in Qamishli. A deal was later reached in September 2018 between the region's authorities and the local Syriac Orthodox archbishopric, where the two first grades in these schools would learn the region's Syriac curriculum and grades three to six would continue to learn the Damascus approved curriculum.
 Incorporating the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights, as well as other internationally recognized human rights conventions, the 2014 Constitution of North and East Syria guarantees freedom of speech and freedom of the press. As a result, a diverse media landscape has developed in the region, in each of the Kurdish languages, Kurdish, Arabic, Eastern Aramaic languages, Syriac-Aramaic and Turkish language, Turkish languages of the land, as well as in English, and media outlets frequently use more than one language. Among the most prominent media in the region are Hawar News Agency and ARA News agencies and websites as well as TV outlets Rojava Kurdistan TV, Ronahî TV, and the bimonthly magazine ''Nudem''. A landscape of local newspapers and radio stations has developed. However, media agencies often face economic pressure, as was demonstrated by the closure of news website ''Welati'' in May 2016. In addition, the autonomous regions have imposed some limits on press freedom, for example forcing the press to get work permits. These can be cancelled, thereby curtailing the ability of certain press agencies to operate. However, the extent of these restrictions differed greatly from area to area. By 2016, Kobani Canton was the least restrictive, followed by Jazira Canton which closely monitored and occasionally regulated press activity. Afrin Canton was the most restrictive, and many local reporters operated anonymously.
Political extremism in the context of the Syrian Civil War can put media outlets under pressure; for example in April 2016 the premises of Arta FM ("the first, and only, independent radio station staffed and broadcast by Syrians inside Syria") in Amuda was threatened and burned down by unidentified assailants. In December 2018 the Rojava Information Center was established. During the Turkish military operation in Afrin, the Kurdistan Democratic Party, KDP-affiliated Iraqi Kurdish Rudaw Media Network was also banned from reporting in the region. On 2 September 2019, the Iraqi Kurdistan-based Kurdistan 24 network had its license to work in the region withdrawn and had its offices confiscated by Rojava authorities.
International media and journalists operate with few restrictions in the region, one of the only regions in Syria where they can operate with some degree of freedom. This has led to several international media reports regarding the region, including major TV documentaries lik
Incorporating the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, the International Covenant on Civil and Political Rights, the International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights, as well as other internationally recognized human rights conventions, the 2014 Constitution of North and East Syria guarantees freedom of speech and freedom of the press. As a result, a diverse media landscape has developed in the region, in each of the Kurdish languages, Kurdish, Arabic, Eastern Aramaic languages, Syriac-Aramaic and Turkish language, Turkish languages of the land, as well as in English, and media outlets frequently use more than one language. Among the most prominent media in the region are Hawar News Agency and ARA News agencies and websites as well as TV outlets Rojava Kurdistan TV, Ronahî TV, and the bimonthly magazine ''Nudem''. A landscape of local newspapers and radio stations has developed. However, media agencies often face economic pressure, as was demonstrated by the closure of news website ''Welati'' in May 2016. In addition, the autonomous regions have imposed some limits on press freedom, for example forcing the press to get work permits. These can be cancelled, thereby curtailing the ability of certain press agencies to operate. However, the extent of these restrictions differed greatly from area to area. By 2016, Kobani Canton was the least restrictive, followed by Jazira Canton which closely monitored and occasionally regulated press activity. Afrin Canton was the most restrictive, and many local reporters operated anonymously.
Political extremism in the context of the Syrian Civil War can put media outlets under pressure; for example in April 2016 the premises of Arta FM ("the first, and only, independent radio station staffed and broadcast by Syrians inside Syria") in Amuda was threatened and burned down by unidentified assailants. In December 2018 the Rojava Information Center was established. During the Turkish military operation in Afrin, the Kurdistan Democratic Party, KDP-affiliated Iraqi Kurdish Rudaw Media Network was also banned from reporting in the region. On 2 September 2019, the Iraqi Kurdistan-based Kurdistan 24 network had its license to work in the region withdrawn and had its offices confiscated by Rojava authorities.
International media and journalists operate with few restrictions in the region, one of the only regions in Syria where they can operate with some degree of freedom. This has led to several international media reports regarding the region, including major TV documentaries lik After the establishment of the de facto autonomous region, the Center of Art and Democratic Culture, located in Jazira Region, has become a venue for aspiring artists who showcase their work. Among major cultural events in the region is the annual ''Festival of Theater'' in March/April as well as the ''Rojava Short Story Festival'' in June, both in the city of Qamishli, and the ''Afrin Short Film Festival'' in April.
After the establishment of the de facto autonomous region, the Center of Art and Democratic Culture, located in Jazira Region, has become a venue for aspiring artists who showcase their work. Among major cultural events in the region is the annual ''Festival of Theater'' in March/April as well as the ''Rojava Short Story Festival'' in June, both in the city of Qamishli, and the ''Afrin Short Film Festival'' in April.
 At first, there were no Direct tax, direct or indirect taxes on people or businesses in the region; instead, the administration raised money mainly through tariffs and selling oil and other natural resources. However, in July 2017, it was reported that the administration in the Jazira Region had started to collect income tax to provide for public services in the region. In May 2016, The ''The Wall Street Journal, Wall Street Journal'' reported that traders in Syria experience the region as "the one place where they aren't forced to pay bribes." The highest amount of energy is produced by the Tabqa Dam at the
At first, there were no Direct tax, direct or indirect taxes on people or businesses in the region; instead, the administration raised money mainly through tariffs and selling oil and other natural resources. However, in July 2017, it was reported that the administration in the Jazira Region had started to collect income tax to provide for public services in the region. In May 2016, The ''The Wall Street Journal, Wall Street Journal'' reported that traders in Syria experience the region as "the one place where they aren't forced to pay bribes." The highest amount of energy is produced by the Tabqa Dam at the  Oil and food production is substantial, so they are important exports. Agricultural products include sheep, grain and cotton. Important imports are consumer goods and auto parts. Trade with Turkey and access to humanitarian and military aid is difficult due to a blockade by Turkey. Turkey does not allow business people or goods to cross its border. The blockade from adjacent territories held by Turkey and ISIL, and partially also the KRG, temporarily caused heavy distortions of relative prices in Jazira Region and Euphrates Region (while separate, Afrin Region borders government-controlled territory since February 2016); for example in Jazira Region and Euphrates Region, through 2016 petrol cost only half as much as bottled water.
The Semalka Border Crossing with Iraqi Kurdistan had been intermittently closed by the Kurdistan Regional Government (KRG), but has been open permanently since June 2016, and along with the establishment of a corridor to Syrian government controlled territory in April 2017, economic exchange has increasingly normalized. Further, in May 2017 in northern Iraq, the Popular Mobilization Forces fighting ISIL cleared a corridor connecting the autonomous region and Iraqi government-controlled territory.
Oil and food production is substantial, so they are important exports. Agricultural products include sheep, grain and cotton. Important imports are consumer goods and auto parts. Trade with Turkey and access to humanitarian and military aid is difficult due to a blockade by Turkey. Turkey does not allow business people or goods to cross its border. The blockade from adjacent territories held by Turkey and ISIL, and partially also the KRG, temporarily caused heavy distortions of relative prices in Jazira Region and Euphrates Region (while separate, Afrin Region borders government-controlled territory since February 2016); for example in Jazira Region and Euphrates Region, through 2016 petrol cost only half as much as bottled water.
The Semalka Border Crossing with Iraqi Kurdistan had been intermittently closed by the Kurdistan Regional Government (KRG), but has been open permanently since June 2016, and along with the establishment of a corridor to Syrian government controlled territory in April 2017, economic exchange has increasingly normalized. Further, in May 2017 in northern Iraq, the Popular Mobilization Forces fighting ISIL cleared a corridor connecting the autonomous region and Iraqi government-controlled territory.
 The autonomous region is ruled by a coalition which bases its policy ambitions to a large extent on the libertarian socialist ideology of Abdullah Öcalan and have been described as pursuing a model of economy that blends co-operative and private enterprise. In 2012, the PYD launched what it called the "Social Economy Plan", later renamed the "People's Economy Plan" (PEP). Private property and entrepreneurship are protected under the principle of "ownership by use". Dr. Dara Kurdaxi, a regional official, has stated: "The method in Rojava is not so much against private property, but rather has the goal of putting private property in the service of all the peoples who live in Rojava." Communes and co-operatives have been established to provide essentials. Co-operatives account for a large proportion of agricultural production and are active in construction, factories, energy production, livestock, pistachio and roasted seeds, and public markets. Several hundred instances of collective farming occurred across towns and villages in the region, with communes consisting of approximately 20–35 people. According to the region's "Ministry of Economics", approximately three-quarters of all property has been placed under community ownership and a third of production has been transferred to direct management by workers' councils.
The autonomous region is ruled by a coalition which bases its policy ambitions to a large extent on the libertarian socialist ideology of Abdullah Öcalan and have been described as pursuing a model of economy that blends co-operative and private enterprise. In 2012, the PYD launched what it called the "Social Economy Plan", later renamed the "People's Economy Plan" (PEP). Private property and entrepreneurship are protected under the principle of "ownership by use". Dr. Dara Kurdaxi, a regional official, has stated: "The method in Rojava is not so much against private property, but rather has the goal of putting private property in the service of all the peoples who live in Rojava." Communes and co-operatives have been established to provide essentials. Co-operatives account for a large proportion of agricultural production and are active in construction, factories, energy production, livestock, pistachio and roasted seeds, and public markets. Several hundred instances of collective farming occurred across towns and villages in the region, with communes consisting of approximately 20–35 people. According to the region's "Ministry of Economics", approximately three-quarters of all property has been placed under community ownership and a third of production has been transferred to direct management by workers' councils.

 Policing in the region is performed by the Asayish (Syria), Asayish armed formation. Asayish was established on 25 July 2013 to fill the gap of security when the Syrian security forces withdrew. Under the Constitution of North and East Syria, policing is a competence of the regions. The Asayish forces of the regions are composed of 26 official bureaus that aim to provide security and solutions to social problems. The six main units of Asayish are Checkpoints Administration, Anti-Terror Forces Command (HAT), Intelligence Directorate, Organized Crime Directorate, Traffic Directorate and Treasury Directorate. 218 Asayish centers were established and 385 checkpoints with 10 Asayish members in each checkpoint were set up. 105 Asayish offices provide security against ISIL on the frontlines across Northern Syria. Larger cities have general directorates responsible for all aspects of security including road controls. Each region has a HAT command, and each Asayish center organizes itself autonomously.
Throughout the region, the municipal Civilian Defense Forces (HPC) and the regional Self-Defense Forces (NES regions), Self-Defense Forces (HXP) also serve local-level security. In Jazira Region, the Asayish are further complemented by the Assyrian Sutoro police force, which is organized in every area with Assyrian population, provides security and solutions to social problems in collaboration with other Asayish units. The Khabour Guards and Nattoreh, though not police units, also have a presence in the area, providing security in towns along the Khabur (Euphrates), Khabur River. The Bethnahrain Women's Protection Forces also maintain a police branch. In the areas taken from ISIL during the Raqqa campaign (2016–present), Raqqa campaign, the Raqqa Internal Security Forces and Manbij Internal Security Forces operate as police forces. Deir ez-Zor also maintain an Internal Security Forces unit.
Policing in the region is performed by the Asayish (Syria), Asayish armed formation. Asayish was established on 25 July 2013 to fill the gap of security when the Syrian security forces withdrew. Under the Constitution of North and East Syria, policing is a competence of the regions. The Asayish forces of the regions are composed of 26 official bureaus that aim to provide security and solutions to social problems. The six main units of Asayish are Checkpoints Administration, Anti-Terror Forces Command (HAT), Intelligence Directorate, Organized Crime Directorate, Traffic Directorate and Treasury Directorate. 218 Asayish centers were established and 385 checkpoints with 10 Asayish members in each checkpoint were set up. 105 Asayish offices provide security against ISIL on the frontlines across Northern Syria. Larger cities have general directorates responsible for all aspects of security including road controls. Each region has a HAT command, and each Asayish center organizes itself autonomously.
Throughout the region, the municipal Civilian Defense Forces (HPC) and the regional Self-Defense Forces (NES regions), Self-Defense Forces (HXP) also serve local-level security. In Jazira Region, the Asayish are further complemented by the Assyrian Sutoro police force, which is organized in every area with Assyrian population, provides security and solutions to social problems in collaboration with other Asayish units. The Khabour Guards and Nattoreh, though not police units, also have a presence in the area, providing security in towns along the Khabur (Euphrates), Khabur River. The Bethnahrain Women's Protection Forces also maintain a police branch. In the areas taken from ISIL during the Raqqa campaign (2016–present), Raqqa campaign, the Raqqa Internal Security Forces and Manbij Internal Security Forces operate as police forces. Deir ez-Zor also maintain an Internal Security Forces unit.

 The main military force of the region is the Syrian Democratic Forces, an alliance of Syrian rebel groups formed in 2015. The SDF is led by the Kurdish majority
The main military force of the region is the Syrian Democratic Forces, an alliance of Syrian rebel groups formed in 2015. The SDF is led by the Kurdish majority  In the course of the Syrian Civil War, including the years 2014 and 2015, reports by
In the course of the Syrian Civil War, including the years 2014 and 2015, reports by  The region's civil government has been hailed in international media for human rights advancement in particular Human rights in North and East Syria#Human rights development in the legal system, in the legal system, concerning Human rights in North and East Syria#Women's rights, women's rights, Human rights in North and East Syria#Ethnic minority rights, ethnic minority rights, Human rights in North and East Syria#Freedom of Speech and Press, freedom of Speech and Press and for Human rights in North and East Syria#Hosting inbound refugees, hosting inbound refugees. The political agenda of "trying to break the honor-based religious and tribal rules that confine women" is controversial in conservative quarters of society. Conscription into the Self-Defense Forces (NES regions), Self-Defence Forces (HXP) has been called a human rights violation by those who call the region's institutions illegitimate.
Some persistent issues in the region concern Human rights in North and East Syria#Ethnic minority rights, ethnic minority rights. One issue of contention is the consequence of Human rights in North and East Syria#Confiscation of Kurdish land and settlement by Arabs, Baathist Syrian government's exprorpiation of land from Kurdish owners and settling of tribal Arabs there in 1973 and 2007. There have been calls to expel the settlers and return the land to its previous owners, which has led the political leadership of the region to press the Syrian government for a comprehensive solution.
During the ongoing Syrian Civil War, organizations such as the Turkish government, Amnesty International and the Middle East Observer have stated that SDF was forcibly displacing inhabitants of captured areas with predominantly Arab population such as Tell Abyad. These displacements were considered attempts at ethnic cleansing. However, the head of the Syrian Observatory for Human Rights rebutted these reports and the UN Independent International Commission of Inquiry find no evidence of YPG or SDF forces committing ethnic cleansing in order to change the demographic composition of territories under their control.
The region's civil government has been hailed in international media for human rights advancement in particular Human rights in North and East Syria#Human rights development in the legal system, in the legal system, concerning Human rights in North and East Syria#Women's rights, women's rights, Human rights in North and East Syria#Ethnic minority rights, ethnic minority rights, Human rights in North and East Syria#Freedom of Speech and Press, freedom of Speech and Press and for Human rights in North and East Syria#Hosting inbound refugees, hosting inbound refugees. The political agenda of "trying to break the honor-based religious and tribal rules that confine women" is controversial in conservative quarters of society. Conscription into the Self-Defense Forces (NES regions), Self-Defence Forces (HXP) has been called a human rights violation by those who call the region's institutions illegitimate.
Some persistent issues in the region concern Human rights in North and East Syria#Ethnic minority rights, ethnic minority rights. One issue of contention is the consequence of Human rights in North and East Syria#Confiscation of Kurdish land and settlement by Arabs, Baathist Syrian government's exprorpiation of land from Kurdish owners and settling of tribal Arabs there in 1973 and 2007. There have been calls to expel the settlers and return the land to its previous owners, which has led the political leadership of the region to press the Syrian government for a comprehensive solution.
During the ongoing Syrian Civil War, organizations such as the Turkish government, Amnesty International and the Middle East Observer have stated that SDF was forcibly displacing inhabitants of captured areas with predominantly Arab population such as Tell Abyad. These displacements were considered attempts at ethnic cleansing. However, the head of the Syrian Observatory for Human Rights rebutted these reports and the UN Independent International Commission of Inquiry find no evidence of YPG or SDF forces committing ethnic cleansing in order to change the demographic composition of territories under their control.
 The demographics of the region have historically been highly diverse, with several major shifts in regard to which groups form majorities or minorities in the last centuries. The
The demographics of the region have historically been highly diverse, with several major shifts in regard to which groups form majorities or minorities in the last centuries. The  *Assyrian people, Assyrians are an ethnic group. Their presence in Syria is in the Jazira Region of the autonomous region, particularly in the urban areas (Qamishli, al-Hasakah, Ras al-Ayn, Al-Malikiyah, Al-Qahtaniyah, al-Hasakah Governorate, Al-Qahtaniyah), in the northeastern corner and in villages along the Khabur (Euphrates), Khabur River in the Tell Tamer area. They traditionally speak varieties of Northeastern Neo-Aramaic, a Semitic language. There are many Assyrians among recent refugees to Northern Syria, fleeing Islamist violence elsewhere in Syria back to their traditional lands. In the secular polyethnic political climate of the region, the Dawronoye modernization movement has a growing influence on Assyrian identity in the 21st century.
* Turkmen are an ethnic group with a major presence in the area between Afrin Region and Euphrates Region, where they form regional majorities in the countryside from Azaz and Mare' to Jarabulus, and a minor presence in Afrin Region and Euphrates Region.
There are also smaller minorities of
*Assyrian people, Assyrians are an ethnic group. Their presence in Syria is in the Jazira Region of the autonomous region, particularly in the urban areas (Qamishli, al-Hasakah, Ras al-Ayn, Al-Malikiyah, Al-Qahtaniyah, al-Hasakah Governorate, Al-Qahtaniyah), in the northeastern corner and in villages along the Khabur (Euphrates), Khabur River in the Tell Tamer area. They traditionally speak varieties of Northeastern Neo-Aramaic, a Semitic language. There are many Assyrians among recent refugees to Northern Syria, fleeing Islamist violence elsewhere in Syria back to their traditional lands. In the secular polyethnic political climate of the region, the Dawronoye modernization movement has a growing influence on Assyrian identity in the 21st century.
* Turkmen are an ethnic group with a major presence in the area between Afrin Region and Euphrates Region, where they form regional majorities in the countryside from Azaz and Mare' to Jarabulus, and a minor presence in Afrin Region and Euphrates Region.
There are also smaller minorities of  Regarding the status of different languages in the autonomous region, its "Social Contract" stipulates that "all languages in Northern Syria are equal in all areas of life, including social, educational, cultural, and administrative dealings. Every people shall organize its life and manage its affairs using its mother tongue." In practice, Arabic and Kurmanji are predominantly used across all areas and for most official documents, with Syriac being mainly used in the Jazira Region with some usage across all areas while Turkish and Circassian are also used in the region of Manbij.
The four main languages spoken in Northern Syria are the following, and are from three different language families:
*Kurdish languages, Kurdish (in Northern Kurdish dialect), a Western Iranian languages, Northwestern Iranian language from the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family.
*Arabic language, Arabic in the North Mesopotamian Arabic dialect (Modern Standard Arabic in education and writing), a Central Semitic language from the Semitic languages, Semitic branch of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family.
*Eastern Aramaic languages mainly in the Turoyo and Assyrian Neo-Aramaic varieties (mainly Syriac language, Syriac in education and writing), Northwest Semitic languages from the Semitic languages, Semitic branch of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family.
*Turkish language, Turkish (in Turkish dialects#Syrian Turkmen dialect, Syrian Turkmen dialect), from the Turkic languages, Turkic language family.
For these four languages, three different scripts are in use in Northern Syria:
*The Latin alphabet for Kurdish, Turkish and Turoyo
*The Arabic alphabet, Arabic alphabet (abjad) for Arabic
*The Syriac alphabet for Syriac, Turoyo and Assyrian Neo-Aramaic
Regarding the status of different languages in the autonomous region, its "Social Contract" stipulates that "all languages in Northern Syria are equal in all areas of life, including social, educational, cultural, and administrative dealings. Every people shall organize its life and manage its affairs using its mother tongue." In practice, Arabic and Kurmanji are predominantly used across all areas and for most official documents, with Syriac being mainly used in the Jazira Region with some usage across all areas while Turkish and Circassian are also used in the region of Manbij.
The four main languages spoken in Northern Syria are the following, and are from three different language families:
*Kurdish languages, Kurdish (in Northern Kurdish dialect), a Western Iranian languages, Northwestern Iranian language from the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family.
*Arabic language, Arabic in the North Mesopotamian Arabic dialect (Modern Standard Arabic in education and writing), a Central Semitic language from the Semitic languages, Semitic branch of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family.
*Eastern Aramaic languages mainly in the Turoyo and Assyrian Neo-Aramaic varieties (mainly Syriac language, Syriac in education and writing), Northwest Semitic languages from the Semitic languages, Semitic branch of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family.
*Turkish language, Turkish (in Turkish dialects#Syrian Turkmen dialect, Syrian Turkmen dialect), from the Turkic languages, Turkic language family.
For these four languages, three different scripts are in use in Northern Syria:
*The Latin alphabet for Kurdish, Turkish and Turoyo
*The Arabic alphabet, Arabic alphabet (abjad) for Arabic
*The Syriac alphabet for Syriac, Turoyo and Assyrian Neo-Aramaic
 The region's dominant political party, the Democratic Union Party (PYD), is a member organisation of the
The region's dominant political party, the Democratic Union Party (PYD), is a member organisation of the  Aside of the representation offices the AANES has established in France, Sweden, Germany and Switzerland the region's role in the international arena is comprehensive military cooperation of its militias under the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) umbrella with the United States and the Military intervention against ISIL#3 December 2014, international (US-led) coalition against the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant. In a public statement in March 2016, the day after the declaration of the regions autonomy, U.S. Defense Secretary Ashton Carter praised the
Aside of the representation offices the AANES has established in France, Sweden, Germany and Switzerland the region's role in the international arena is comprehensive military cooperation of its militias under the Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF) umbrella with the United States and the Military intervention against ISIL#3 December 2014, international (US-led) coalition against the Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant. In a public statement in March 2016, the day after the declaration of the regions autonomy, U.S. Defense Secretary Ashton Carter praised the  In the diplomatic field, the de facto autonomous region lacks any formal recognition. While there is comprehensive activity of reception of the region's representatives and appreciation with a broad range of countries, only Russia has on occasion openly supported the region's political ambition of federalization of Syria in the international arena, while the U.S. does not. After peace talks between Syrian civil war parties in Astana in January 2017, Russia offered a draft for a future constitution of Syria, which would, among other things, change the "Syrian Arab Republic" into the "Republic of Syria", introduce decentralized authorities as well as elements of Federalization of Syria, federalism like "association areas", strengthen the parliament at the cost of the presidency, and realize Islam and secularism, secularism by abolishing Islamic jurisprudence as a source of legislation. The region opened official representation offices in Moscow during 2016, Stockholm, Berlin, Paris, and The Hague. A broad range of public voices in the U.S. and Europe have called for more formal recognition of the region. International cooperation has been in the field of educational and cultural institutions, like the cooperation agreement of Paris 8 University with the newly founded University of Rojava in Qamishli, or planning for a France, French cultural centre in Amuda.
Neighbouring Turkey is consistently hostile, which has been attributed to a perceived threat from the region's emergence, in that it would encourage activism for autonomy among Kurds in Turkey in the Kurdish–Turkish conflict (1978–present), Kurdish–Turkish conflict. In this context, in particular the region's leading Democratic Union Party (PYD) and the YPG militia being members of the
In the diplomatic field, the de facto autonomous region lacks any formal recognition. While there is comprehensive activity of reception of the region's representatives and appreciation with a broad range of countries, only Russia has on occasion openly supported the region's political ambition of federalization of Syria in the international arena, while the U.S. does not. After peace talks between Syrian civil war parties in Astana in January 2017, Russia offered a draft for a future constitution of Syria, which would, among other things, change the "Syrian Arab Republic" into the "Republic of Syria", introduce decentralized authorities as well as elements of Federalization of Syria, federalism like "association areas", strengthen the parliament at the cost of the presidency, and realize Islam and secularism, secularism by abolishing Islamic jurisprudence as a source of legislation. The region opened official representation offices in Moscow during 2016, Stockholm, Berlin, Paris, and The Hague. A broad range of public voices in the U.S. and Europe have called for more formal recognition of the region. International cooperation has been in the field of educational and cultural institutions, like the cooperation agreement of Paris 8 University with the newly founded University of Rojava in Qamishli, or planning for a France, French cultural centre in Amuda.
Neighbouring Turkey is consistently hostile, which has been attributed to a perceived threat from the region's emergence, in that it would encourage activism for autonomy among Kurds in Turkey in the Kurdish–Turkish conflict (1978–present), Kurdish–Turkish conflict. In this context, in particular the region's leading Democratic Union Party (PYD) and the YPG militia being members of the