Democratic Federal Yugoslavia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Democratic Federal Yugoslavia, also known as Democratic Federative Yugoslavia (DF Yugoslavia or DFY), was a provisional state established during
World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
on 29 November 1943 through the Second Session of the Anti-Fascist Council for the National Liberation of Yugoslavia
The Anti-Fascist Council for the National Liberation of Yugoslavia,, mk, Антифашистичко собрание за народно ослободување на Југославија commonly abbreviated as the AVNOJ, was a deliberat ...
(AVNOJ). The National Committee for the Liberation of Yugoslavia
The National Committee for the Liberation of Yugoslavia ( sh, Nacionalni komitet oslobođenja Jugoslavije, sl, Nacionalni komite osvoboditve Jugoslavije, NKOJ), also known as the Yugoslav Committee of National Liberation, was the World War II pr ...
(NKOJ) was its original executive body. Throughout its existence it was governed by Marshal Josip Broz Tito as prime minister.
It was recognized by the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
at the Tehran Conference
The Tehran Conference ( codenamed Eureka) was a strategy meeting of Joseph Stalin, Franklin Roosevelt, and Winston Churchill from 28 November to 1 December 1943, after the Anglo-Soviet invasion of Iran. It was held in the Soviet Union's embass ...
, along with the AVNOJ as its deliberative body
A deliberative assembly is a meeting of members who use parliamentary procedure.
Etymology
In a speech to the electorate at Bristol in 1774, Edmund Burke described the British Parliament as a "deliberative assembly," and the expression became the ...
. The Yugoslav government-in-exile
The Government of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia in Exile ( sh, Vlada Kraljevine Jugoslavije u egzilu / Влада Краљевине Југославије у егзилу) was an official government of Yugoslavia, headed by King Peter II. It evacu ...
of King Peter II in London, partly due to pressure from the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
,Walter R. Roberts. ''Tito, Mihailović, and the allies, 1941-1945''. Duke University Press, 1987. Pp. 288. recognized the AVNOJ government with the Treaty of Vis
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal pers ...
, signed on 16 June 1944 between the prime minister of the government-in-exile, Ivan Šubašić
Ivan Šubašić (; 7 May 1892 – 22 March 1955) was a Yugoslav Croat politician, best known as the last Ban of Croatia and prime minister of the royalist Yugoslav Government in exile during the Second World War.
Early life
He was born in Vuk ...
, and Tito. With the Treaty of Vis, the government-in-exile and the NKOJ agreed to merge into a provisional government
A provisional government, also called an interim government, an emergency government, or a transitional government, is an emergency governmental authority set up to manage a political transition generally in the cases of a newly formed state or ...
as soon as possible. The form of the new government was agreed upon in a second Tito–Šubašić agreement signed on 1 November 1944 in the recently liberated Yugoslav capital of Belgrade. DF Yugoslavia became one of the founding members of the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
upon the signing of the United Nations Charter
The Charter of the United Nations (UN) is the foundational treaty of the UN, an intergovernmental organization. It establishes the purposes, governing structure, and overall framework of the UN system, including its six principal organs: the ...
in October 1945.
The state was formed to unite the Yugoslav resistance movement to the occupation of Yugoslavia
World War II in the Kingdom of Yugoslavia began on 6 April 1941, when the country was Invasion of Yugoslavia, swiftly conquered by Axis powers, Axis forces and partitioned between Nazi Germany, Germany, Kingdom of Italy, Italy, Kingdom of Hung ...
by the Axis powers
The Axis powers, ; it, Potenze dell'Asse ; ja, 枢軸国 ''Sūjikukoku'', group=nb originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis, was a military coalition that initiated World War II and fought against the Allies. Its principal members were ...
. The agreement left the issue of whether the state would be a monarchy or a republic intentionally undecided until after the war had ended so the position of head of state was vacant. After the merger of the governments, the state was reformed as a one-party
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government ...
Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, commonly referred to as SFR Yugoslavia or simply as Yugoslavia, was a country in Central and Southeast Europe. It emerged in 1945, following World War II, and lasted until 1992, with the breakup of Yu ...
with Josip Broz Tito as Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister i ...
and Ivan Šubašić as minister of foreign affairs
A foreign affairs minister or minister of foreign affairs (less commonly minister for foreign affairs) is generally a cabinet minister in charge of a state's foreign policy and relations. The formal title of the top official varies between co ...
.
History
The Second Session of the AVNOJ, held in Jajce in November 1943, opened with a declaration that read in part: #That the Anti-Fascist Council of National Liberation of Yugoslavia be constituted as the supreme legislative and executive representative body of Yugoslavia as the supreme representative of the sovereignty of the peoples and of the State of Yugoslavia as a whole, and that a National Committee of Liberation of Yugoslavia be established as an organ with all of the features of a national government, through which the Anti-Fascist Council of National Liberation of Yugoslavia will realize its executive function. #That the traitorous "government" in exile be deprived of all rights as the legal government of Yugoslavia, particularly of the right to represent the peoples of Yugoslavia anywhere or before anyone. #That all international treaties and obligations concluded abroad in the name of Yugoslavia by the "government" in exile be reviewed with a view to their invalidation or renewal or approval, and that all international treaties and obligations which the so-called "government" in exile may eventually conclude abroad in the future receive no recognition. #That Yugoslavia be established on a democratic federal principle as a state of equal peoples.Michael Boro Petrovich, "The Central Government of Yugoslavia", ''Political Science Quarterly'', Vol. 62, No. 4 (1947), pp. 504–30. The AVNOJ then issued six decrees and the Presidium of the AVNOJ, which continued its functions when it was not in session, followed with four decisions. Together these comprised the constitution of the new state taking shape in Yugoslavia. On 30 November the Presidium gave Tito the rank of Marshal of Yugoslavia and appointed him president of the government (or acting prime minister) and Minister of National Defence. Three vice presidents and thirteen other ministers were appointed to the NKOJ. The name "Democratic Federative Yugoslavia" was officially adopted on 17 February 1944. On the same day they adopted the five-torchemblem of Yugoslavia
The emblem of Yugoslavia featured six torches, surrounded by wheat with a red star at its top, and burning together in one flame; this represented the brotherhood and unity of the six federal republics forming Yugoslavia: Bosnia and Herzegovina, ...
.
After the deposition of King Peter II, the Federal People's Republic of Yugoslavia
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, commonly referred to as SFR Yugoslavia or simply as Yugoslavia, was a country in Central and Southeast Europe. It emerged in 1945, following World War II, and lasted until 1992, with the breakup of Yu ...
was proclaimed on 29 November 1945.
Government
Its legislature, after November 1944, was the Provisional Assembly.Vojislav Koštunica, Kosta Čavoški. ''Party pluralism or monism: social movements and the political system in Yugoslavia, 1944-1949''. East European Monographs, 1985. Pp. 22. The Tito-Šubašić agreement of 1944 declared that the state was a pluralistdemocracy
Democracy (From grc, δημοκρατία, dēmokratía, ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which people, the people have the authority to deliberate and decide legislation ("direct democracy"), or to choo ...
that guaranteed: democratic liberties; personal freedom; freedom of speech, assembly
Assembly may refer to:
Organisations and meetings
* Deliberative assembly, a gathering of members who use parliamentary procedure for making decisions
* General assembly, an official meeting of the members of an organization or of their representa ...
, and religion
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatural, ...
; and a free press.Sabrina P. Ramet. The three Yugoslavias: state-building and legitimation, 1918-2005. Bloomington, Indiana, USA: Indiana University Press. Pp. 167-168. However, by January 1945 Tito had shifted the emphasis of his government away from emphasis on pluralist democracy, claiming that though he accepted democracy, he claimed there was no "need" for multiple parties, as he claimed that multiple parties were unnecessarily divisive in the midst of Yugoslavia's war effort and that the People's Front represented all the Yugoslav people. The People's Front coalition, headed by the Communist Party of Yugoslavia and its general secretary Marshal Josip Broz Tito, was a major movement within the government. Other political movements that joined the government included the "Napred" movement represented by Milivoje Marković Milivoje ( sr, Миливоје) is a masculine given name. Notable people with the name include:
* Milivoje Blaznavac (1824–1873), Serbian soldier and politician
* Milivoje Božović (born 1985), Serbian professional basketball player
* Milivoje ...
.
Democratic Federal Yugoslavia was ruled by Temporary Government consisting mostly of Unitary National Liberation Front
The Unitary National Liberation Front ( sh, Jedinstveni narodnooslobodilački front, JNOF) or simply the National Liberation Front (sometimes referred to as the People's Liberation Front), was a World War II political organization and Anti-fascis ...
members and small number of other political parties from former Kingdom of Yugoslavia. President of the Government was Josip Broz Tito. Communists held 22 minister positions, including Finances, Internal Affairs, Justice, Transport and others. Ivan Šubašić
Ivan Šubašić (; 7 May 1892 – 22 March 1955) was a Yugoslav Croat politician, best known as the last Ban of Croatia and prime minister of the royalist Yugoslav Government in exile during the Second World War.
Early life
He was born in Vuk ...
, from Croatian Peasant Party and former ban of Croatian Banovina, was minister of Foreign Affairs, while Milan Grol
Milan Grol (12 September 1876 – 3 December 1952) was a Serbian literary critic, historian and politician. He was also director of the National Theatre of Serbia.
Biography
Milan Grol was born in Belgrade on 12 September 1876. He completed hi ...
, from Democratic Party Democratic Party most often refers to:
*Democratic Party (United States)
Democratic Party and similar terms may also refer to:
Active parties Africa
*Botswana Democratic Party
*Democratic Party of Equatorial Guinea
*Gabonese Democratic Party
*Demo ...
, was Deputy Prime Minister. Many non-communist government members resigned due to disagreement with the new policy.http://adattar.vmmi.org/fejezetek/2078/09_prva_decenija_titove_jugoslavije.pdf
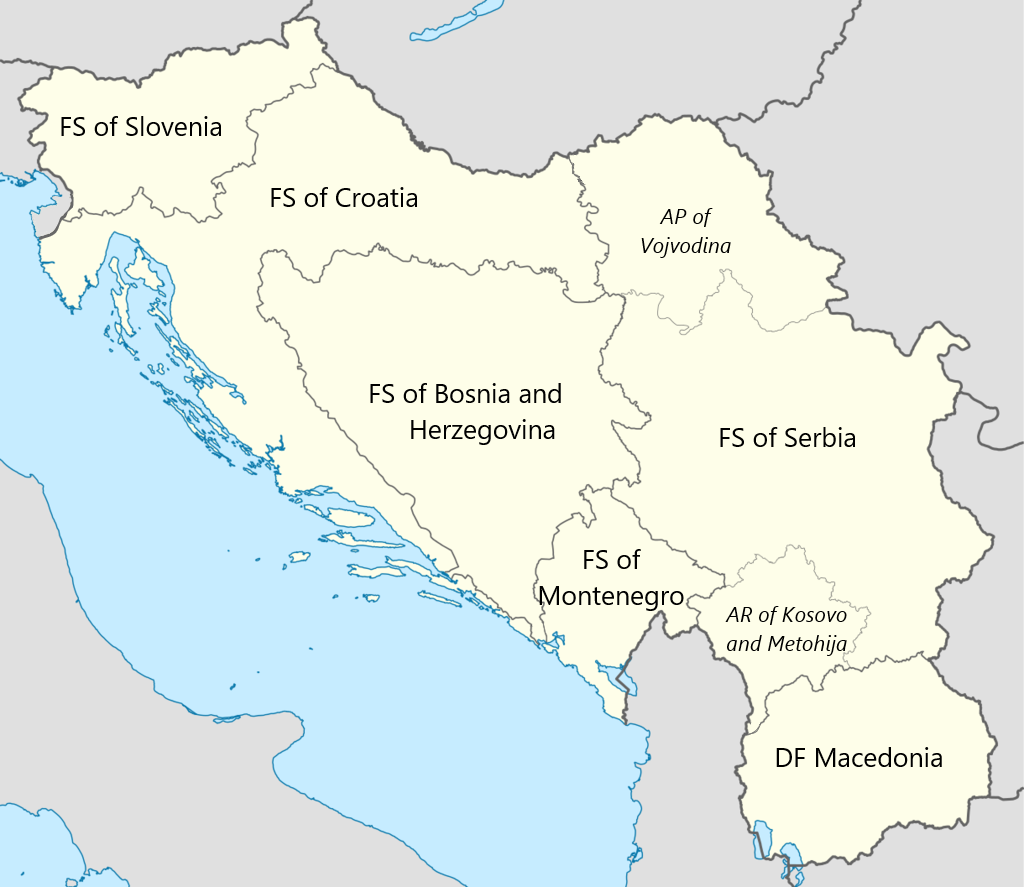
Administrative divisions
Democratic Federal Yugoslavia consisted of 6federal state
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government ( federalism). In a federation, the self-gover ...
s and 2 autonomous units:
* Federated State of Serbia
, life_span = 1944–1992
, status = Constituent state of Yugoslavia
, p1 = Territory of the Military Commander in Serbia
, flag_p1 = Flag of German Reich (1935–1945).svg
, p2 ...
** Autonomous Province of Vojvodina
Vojvodina ( sr-Cyrl, Војводина}), officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia. It lies within the Pannonian Basin, bordered to the south by the national capit ...
** Kosovo and Metohija Autonomous Region
* Federated State of Croatia
The Socialist Republic of Croatia ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Socijalistička Republika Hrvatska, Социјалистичка Република Хрватска), or SR Croatia, was a constituent republic and federated state of the Social ...
* Federated State of Bosnia and Herzegovina
The Socialist Republic of Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Socijalistička Republika Bosna i Hercegovina, Социјалистичка Pепублика Босна и Херцеговина), commonly referred to as Socia ...
* Federated State of Slovenia
* Federated State of Montenegro
* Federated State of Macedonia

References
Sources
* * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:YugoslaviaSocialist Yugoslavia
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, commonly referred to as SFR Yugoslavia or simply as Yugoslavia, was a country in Central and Southeast Europe. It emerged in 1945, following World War II, and lasted until 1992, with the breakup of Yugo ...
Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia
The Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia, commonly referred to as SFR Yugoslavia or simply as Yugoslavia, was a country in Central and Southeast Europe. It emerged in 1945, following World War II, and lasted until 1992, with the breakup of Yu ...
Socialist Yugoslavia
States and territories established in 1943
*
1940s in Kosovo
1940s in Montenegro
1940s in Slovenia
.
States and territories disestablished in 1945
1940s in Serbia