Demchok sector on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Demchok sector is a disputed area named after the villages of Demchok in Ladakh and Demchok in Tibet, situated near the confluence of the
 At the bottom of the valley, the
At the bottom of the valley, the
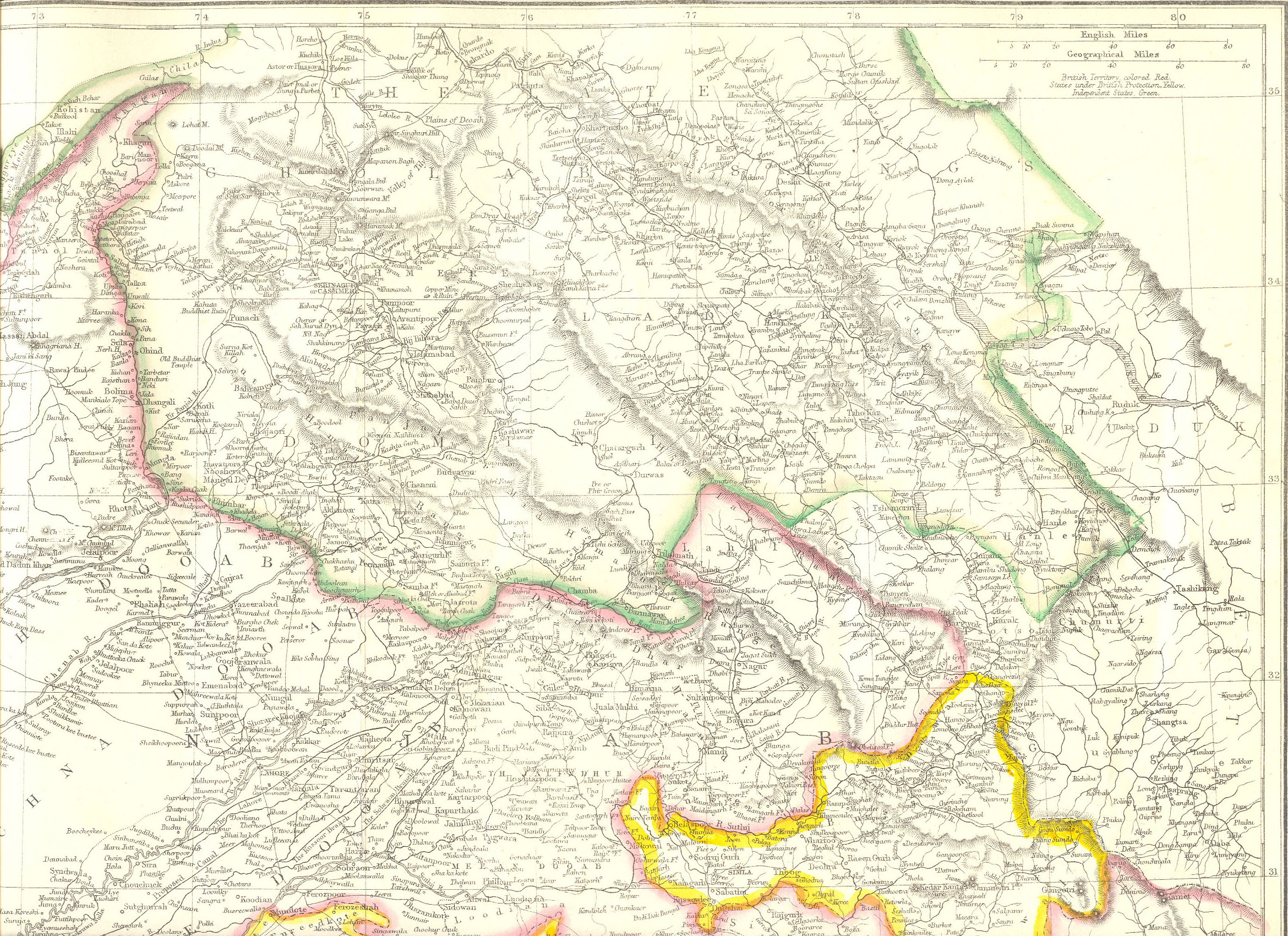 After the Dogras joined the British suzerainty as the state of Jammu and Kashmir, the British government dispatched a boundary commission consisting of P. A. Vans Agnew and Alexander Cunningham to define the borders of the state with Tibet in 1846–1847. The Chinese government was invited to join the effort for a mutually agreed border. However the Chinese declined, stating that the frontier was well-known and it did not need a new definition. The British boundary commission nevertheless surveyed the area. Its report stated:
The "rivulet" is evidently the Charding nullah. The Tibetan frontier guards prohibited the commission from proceeding beyond the rivulet. The commission placed the border on the Indus at Demchok, and followed the mountain watershed of the Indus river on its east, passing through the Jara La and Chang La passes. This appears to be the first time that the watershed principle was used in the Indian subcontinent for defining a boundary.
After the Dogras joined the British suzerainty as the state of Jammu and Kashmir, the British government dispatched a boundary commission consisting of P. A. Vans Agnew and Alexander Cunningham to define the borders of the state with Tibet in 1846–1847. The Chinese government was invited to join the effort for a mutually agreed border. However the Chinese declined, stating that the frontier was well-known and it did not need a new definition. The British boundary commission nevertheless surveyed the area. Its report stated:
The "rivulet" is evidently the Charding nullah. The Tibetan frontier guards prohibited the commission from proceeding beyond the rivulet. The commission placed the border on the Indus at Demchok, and followed the mountain watershed of the Indus river on its east, passing through the Jara La and Chang La passes. This appears to be the first time that the watershed principle was used in the Indian subcontinent for defining a boundary.
 Between 1847 and November 1864, the British Indian government conducted the Kashmir Survey (''Survey of Kashmir, Ladak, and Baltistan or Little Tibet''), whose results were published in a reduced form in the ''Kashmir Atlas'' of 1868 by the Great Trigonometrical Survey of India. Even though this was not an official boundary delimitation, the atlas made several adjustments to the boundary, including in the Demchok sector. Lamb states:
It is unclear who decided the altered boundary and on what grounds, given that the survey team leader T. G. Montgomerie was of the view that Demchok was in Ladakh. Indian commentators blame it on the rudimentary knowledge of the British surveyors about Ladakh — they were ignorant of past treaties as well as revenue records, and mistook pasture disputes as boundary disputes.:
*p.24: "But such an evaluation was seldom done and although most officials traced the boundary correctly along the watershed range running parallel to the river Indus, gross blunders were committed regarding the alignment in the Pangong and Demchok areas. This was apparently due to the unfamiliarity of some of the British officials with the traditional and treaty basis of the boundary and to their mistaking local disputes such as pasture disputes with boundary disputes."
*p.29: "The Kashmir Atlas boundary conflicts also with the first-hand evidence provided by the 1847 Commission. In regard to Demchok, it conflicts with well-established facts of history and with revenue records for the very period that the survey was conducted." In contrast, Lamb interprets this as a "compromise" wherein the British gave up territory in Demchok to include other territory near the
Between 1847 and November 1864, the British Indian government conducted the Kashmir Survey (''Survey of Kashmir, Ladak, and Baltistan or Little Tibet''), whose results were published in a reduced form in the ''Kashmir Atlas'' of 1868 by the Great Trigonometrical Survey of India. Even though this was not an official boundary delimitation, the atlas made several adjustments to the boundary, including in the Demchok sector. Lamb states:
It is unclear who decided the altered boundary and on what grounds, given that the survey team leader T. G. Montgomerie was of the view that Demchok was in Ladakh. Indian commentators blame it on the rudimentary knowledge of the British surveyors about Ladakh — they were ignorant of past treaties as well as revenue records, and mistook pasture disputes as boundary disputes.:
*p.24: "But such an evaluation was seldom done and although most officials traced the boundary correctly along the watershed range running parallel to the river Indus, gross blunders were committed regarding the alignment in the Pangong and Demchok areas. This was apparently due to the unfamiliarity of some of the British officials with the traditional and treaty basis of the boundary and to their mistaking local disputes such as pasture disputes with boundary disputes."
*p.29: "The Kashmir Atlas boundary conflicts also with the first-hand evidence provided by the 1847 Commission. In regard to Demchok, it conflicts with well-established facts of history and with revenue records for the very period that the survey was conducted." In contrast, Lamb interprets this as a "compromise" wherein the British gave up territory in Demchok to include other territory near the
The Case of Demchok
Indian Defence Review, 19 May 2017. It has also been referred to as "Lari Karpo" ("white lhari") and "Demchok Lari Karpo" in Tibetan documents. After the
Demchok Eastern Sector
on OpenStreetMap (Chinese-controlled)
Demchok Western Sector
on OpenStreetMap (Indian-controlled) Geography of Ladakh Geography of Tibet History of Ladakh History of Tibet Territorial disputes of China Territorial disputes of India Divided regions China–India border Demchok sector
Charding Nullah
The Charding Nullah, traditionally known as the Lhari stream and called Demchok River by China,{{efn, name="White Paper XII" is a small river that originates near the Charding La pass that is also on the border between the two countries and flows n ...
and Indus River. It is a part of the greater Sino-Indian border dispute between China and India. Both China and India claim the disputed region, with a Line of Actual Control
The Line of Actual Control (LAC), in the context of the Sino-Indian border dispute, is a notional demarcation lineAnanth KrishnanLine of Actual Control , India-China: the line of actual contest, 13 June 2020: "In contrast, the alignment of ...
between the two nations situated along the Charding Nullah
The Charding Nullah, traditionally known as the Lhari stream and called Demchok River by China,{{efn, name="White Paper XII" is a small river that originates near the Charding La pass that is also on the border between the two countries and flows n ...
.
The Charding Nullah was mentioned by the name "Lhari stream" in a treaty between the Kingdom of Ladakh
Maryul (also called ''Mar-yul'' of ''mNgah-ris''), later the Kingdom of Ladakh, was a west Tibetan kingdom based in modern-day Ladakh and Tibet. The kingdom had its capital at Shey.
The kingdom was founded by Lhachen Palgyigon, during the rul ...
and the Ganden Phodrang
The Ganden Phodrang or Ganden Podrang (; ) was the Tibetan system of government established by the 5th Dalai Lama in 1642; it operated in Tibet until the 1950s. Lhasa became the capital of Tibet again early in this period, after the Oirat lo ...
government of Tibet
Tibet (; ''Böd''; ) is a region in East Asia, covering much of the Tibetan Plateau and spanning about . It is the traditional homeland of the Tibetan people. Also resident on the plateau are some other ethnic groups such as Monpa, Taman ...
in 1684 and stated as the boundary between the two regions. British surveys placed the border in 1847 between the princely state of Jammu and Kashmir
Jammu and Kashmir, officially known as the Princely State of Kashmir and Jammu, was a princely state during the Company rule in India from 1757 to 1858 as well as the British Raj in India from 1846 to 1952. The princely state was created afte ...
and Qing Tibet on the stream, while British maps from 1868 onwards placed the border downstream and west of Demchok. After independence in 1947, India claimed the southern watershed of the river (roughly 3 miles southeast of Demchok) as its boundary, which has been contested by the People's Republic of China whose claims coincide with the British maps. The two countries fought a brief war in 1962, after which the Demchok region has remained divided between the two nations across a Line of Actual Control
The Line of Actual Control (LAC), in the context of the Sino-Indian border dispute, is a notional demarcation lineAnanth KrishnanLine of Actual Control , India-China: the line of actual contest, 13 June 2020: "In contrast, the alignment of ...
.
Geography
 At the bottom of the valley, the
At the bottom of the valley, the Charding Nullah
The Charding Nullah, traditionally known as the Lhari stream and called Demchok River by China,{{efn, name="White Paper XII" is a small river that originates near the Charding La pass that is also on the border between the two countries and flows n ...
branches into a 2 km-wide delta as it joins the Indus River. During the British colonial period
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts esta ...
, there was a village on both the sides of the delta, going by the name Demchok. The southern village appears to have been the main one, frequently referred to by travellers.: According to a report by the governor of Ladakh in 1904–05, "I visited Demchok on the boundary with Lhasa. ... A nullah falls into the Indus river from the south-west and it (Demchok) is situated at the junction of the river. Across is the boundary of Lhasa, where there are 8 to 9 huts of the Lhasa zamindars. On this side there are only two zamindars." The Chinese spell the name of the village as Dêmqog. Travel writer Romesh Bhattacharji stated in 2012 that they expected to set up a trading village, but India never renewed trade after the war. He stated that the southern Dêmqog village has only commercial buildings whereas the northern village has security-related buildings. Both the Indians and the Chinese have track roads going up the valley on the two sides of the Charding Nullah, reaching up to the Charding–Nilung Nullah Junction (CNNJ). Occasional stand-offs between the two forces at CNNJ are reported in the newspapers.
The watershed east of the Koyul Lungpa river, near the village of Koyul
Koyul is a village in the Leh district of Ladakh, India. It is located in the Nyoma tehsil, on the banks of the Koyul Lungpa river just before it joins the Indus River.
Geography
The village of Koyul is in the Koyul Lungpa valley, which hous ...
, is at the western boundary of the disputed sector, with China's claim line running along the crest of the ridge.
Modern Chinese sources refer to the disputed area around Demchok as Parigas () or the Parigas region (). It is apparently named after the Tibetan name Palicasi () of an insignificant camping site that is known to Ladakhis as Silungle. Chinese sources describe the disputed territory as having a total area of with India controlling of its southwest corner, west of DĂŞmqog and the Indus River.
History
Early history
The Demchok region was mentioned as being part of the modern kingdom of Ladakh, when it was founded in the 10th century under the name Maryul. King Nyimagon, who founded the West Tibetan kingdom of Ngari Khorsum, divided his kingdom among his three sons upon his death. The eldest son Palgyigon, who is believed to have been the organiser of the Ladakh part of the kingdom, received Ladakh, and the other two sons received Guge– Purang andZanskar
Zanskar, Zahar (locally) or Zangskar, is a tehsil of Kargil district, in the Indian union territory of Ladakh. The administrative centre is Padum (former Capital of Zanskar). Zanskar, together with the neighboring region of Ladakh, was brie ...
. The description of Maryul in the Ladakh Chronicles mentions Demchok Karpo, the pyramidal white peak behind the Ladakhi Demchok village as one of the landmarks, possibly on its frontier. Other neighbouring landmarks like the Imis Pass ("Yimig rock") and an unidentified place called ''Raba Dmarpo'' were also mentioned.
In addition to modern Ladakh, Rudok was also part of Maryul at the time of its formation. Whether it remained affiliated to Ladakh in later times is not unknown, but during the reigns of Tsewang Namgyal () and Sengge Namgyal
Sengge Namgyal (''Sen-ge-rnam-rgyal'', c. 1570–1642) was a 17th-century Namgyal dynasty King of Ladakh, India from 1616 to his death in 1642. A Buddhist, he was noted for his immense work in building monasteries, palaces and shrines in Ladakh ...
(), all the regions of Ngari Khorsum are known to have paid tribute to Ladakh. Sengge Namgyal is credited with building a Drukpa monastery at Tashigang, southeast of Demchok. He also built the present monasteries of Hemis
Hemis, also spelled Hamis, is a village in the Leh district of Ladakh, India. It is located in the Kharu tehsil, 40 km southeast of Leh town on the Leh-Manali Highway and under-construction Bilaspur–Leh line.
Hemis is well known for ...
and Hanle, and the sacred site of Demchok was apparently been placed under the former's jurisdiction.
Treaty of Tingmosgang (1684)
The '' Ladakh Chronicles'' (''La-dvags-rgyal-rabs'') mention that, at the conclusion of theTibet–Ladakh–Mughal War
The Tibet–Ladakh–Mughal War of 1679–1684 was fought between the Central Tibetan Ganden Phodrang government, with the assistance of Mongol khanates, and the Namgyal dynasty of Ladakh with assistance from the Mughal Empire in Kashmir.
Back ...
in 1684, Tibet and Ladakh agreed on the Treaty of Tingmosgang, by which the extensive territories in West Tibet (Ngari
Ngari Prefecture () or Ali Prefecture () is a prefecture of China's Tibet Autonomous Region covering Western Tibet, whose traditional name is Ngari Khorsum. Its administrative centre and largest settlement is the town of Shiquanhe.
History
Ngar ...
) previously controlled by Ladakh were removed from its control and the frontier was fixed at the "Lha-ri stream at Demchok". The original text of the Treaty of Tingmosgang is not available to us.
The traditional border between the two regions prior to these conflicts is not clearly known.
According to Alexander Cunningham, "A large stone was then set up as a permanent boundary between the two countries, the line of demarcation drawn from the village of ''Dechhog'' emchokto the hill of ''Karbonas'' nidentified"
Roughly 160 years after the Treaty of Tingmosgang, Ladakh came under the rule of the Dogras
The Dogras or Dogra people, are an Indo-Aryan ethno-linguistic group in India and Pakistan consisting of the Dogri language speakers. They live predominantly in the Jammu region of Jammu and Kashmir, and in adjoining areas of Punjab, Himacha ...
, who launched an invasion into the West Tibet leading to the Dogra–Tibetan War
The Dogra–Tibetan War or Sino-Sikh War was fought from May 1841 to August 1842, between the forces of the Dogra nobleman Gulab Singh of Jammu, under the suzerainty of the Sikh Empire, and those of Tibet. Gulab Singh's commander was the able ...
. The war ended in a stalemate. The resulting Treaty of Chushul in 1842 bound the parties to the "old, established frontiers".
British boundary commission (1846–1847)
 After the Dogras joined the British suzerainty as the state of Jammu and Kashmir, the British government dispatched a boundary commission consisting of P. A. Vans Agnew and Alexander Cunningham to define the borders of the state with Tibet in 1846–1847. The Chinese government was invited to join the effort for a mutually agreed border. However the Chinese declined, stating that the frontier was well-known and it did not need a new definition. The British boundary commission nevertheless surveyed the area. Its report stated:
The "rivulet" is evidently the Charding nullah. The Tibetan frontier guards prohibited the commission from proceeding beyond the rivulet. The commission placed the border on the Indus at Demchok, and followed the mountain watershed of the Indus river on its east, passing through the Jara La and Chang La passes. This appears to be the first time that the watershed principle was used in the Indian subcontinent for defining a boundary.
After the Dogras joined the British suzerainty as the state of Jammu and Kashmir, the British government dispatched a boundary commission consisting of P. A. Vans Agnew and Alexander Cunningham to define the borders of the state with Tibet in 1846–1847. The Chinese government was invited to join the effort for a mutually agreed border. However the Chinese declined, stating that the frontier was well-known and it did not need a new definition. The British boundary commission nevertheless surveyed the area. Its report stated:
The "rivulet" is evidently the Charding nullah. The Tibetan frontier guards prohibited the commission from proceeding beyond the rivulet. The commission placed the border on the Indus at Demchok, and followed the mountain watershed of the Indus river on its east, passing through the Jara La and Chang La passes. This appears to be the first time that the watershed principle was used in the Indian subcontinent for defining a boundary.
Kashmir Atlas (1868)
 Between 1847 and November 1864, the British Indian government conducted the Kashmir Survey (''Survey of Kashmir, Ladak, and Baltistan or Little Tibet''), whose results were published in a reduced form in the ''Kashmir Atlas'' of 1868 by the Great Trigonometrical Survey of India. Even though this was not an official boundary delimitation, the atlas made several adjustments to the boundary, including in the Demchok sector. Lamb states:
It is unclear who decided the altered boundary and on what grounds, given that the survey team leader T. G. Montgomerie was of the view that Demchok was in Ladakh. Indian commentators blame it on the rudimentary knowledge of the British surveyors about Ladakh — they were ignorant of past treaties as well as revenue records, and mistook pasture disputes as boundary disputes.:
*p.24: "But such an evaluation was seldom done and although most officials traced the boundary correctly along the watershed range running parallel to the river Indus, gross blunders were committed regarding the alignment in the Pangong and Demchok areas. This was apparently due to the unfamiliarity of some of the British officials with the traditional and treaty basis of the boundary and to their mistaking local disputes such as pasture disputes with boundary disputes."
*p.29: "The Kashmir Atlas boundary conflicts also with the first-hand evidence provided by the 1847 Commission. In regard to Demchok, it conflicts with well-established facts of history and with revenue records for the very period that the survey was conducted." In contrast, Lamb interprets this as a "compromise" wherein the British gave up territory in Demchok to include other territory near the
Between 1847 and November 1864, the British Indian government conducted the Kashmir Survey (''Survey of Kashmir, Ladak, and Baltistan or Little Tibet''), whose results were published in a reduced form in the ''Kashmir Atlas'' of 1868 by the Great Trigonometrical Survey of India. Even though this was not an official boundary delimitation, the atlas made several adjustments to the boundary, including in the Demchok sector. Lamb states:
It is unclear who decided the altered boundary and on what grounds, given that the survey team leader T. G. Montgomerie was of the view that Demchok was in Ladakh. Indian commentators blame it on the rudimentary knowledge of the British surveyors about Ladakh — they were ignorant of past treaties as well as revenue records, and mistook pasture disputes as boundary disputes.:
*p.24: "But such an evaluation was seldom done and although most officials traced the boundary correctly along the watershed range running parallel to the river Indus, gross blunders were committed regarding the alignment in the Pangong and Demchok areas. This was apparently due to the unfamiliarity of some of the British officials with the traditional and treaty basis of the boundary and to their mistaking local disputes such as pasture disputes with boundary disputes."
*p.29: "The Kashmir Atlas boundary conflicts also with the first-hand evidence provided by the 1847 Commission. In regard to Demchok, it conflicts with well-established facts of history and with revenue records for the very period that the survey was conducted." In contrast, Lamb interprets this as a "compromise" wherein the British gave up territory in Demchok to include other territory near the Spanggur Lake
Spanggur Tso, also called Maindong Tso, Mendong Tso, is a saltwater lake in Rutog County in the Tibet Autonomous Region of China, close to the border with Ladakh. India claims a major portion of the lake as its own territory, as part of Ladakh. ...
.
Later colonial period (1868–1947)
Subsequent to the ''Kashmir Atlas'' of 1868, there was a flood of British publications on Ladakh. Despite this, no revisions were made to the border at Demchok. According to Lamb, the majority of British maps published between 1918 and 1947 reproduced the Kashmir Atlas, slotting Demchok within Tibet. During the two World Wars, some maps from world powers (including China) showed the same borders. Independent of the colonial cartography, the traditional boundaries continued to be followed on the ground. The Kashmir government disregarded the British maps and the Tibetan claims to Demchok seem to have persisted. Lamb states, "by the time of the Transfer of Power in 1947 nothing had been settled."Modern claims
Since the 1950s, Indian maps do not agree entirely with either the 1846–1847 survey or the 1868 ''Kashmir Atlas'': the Indian claims lie east of Demchok, whereas the 1846–1847 British boundary commission placed the border through the middle of Demchok, and British maps from the 1860s onwards showed the border to be west of Demchok. The Chinese claims coincide with British maps that placed the border west of Demchok. The Chinese claims also coincided with the borders used by the 1945 National Geographic and 1955 United States Army Map Service maps. Prior to theSino-Indian War
The Sino-Indian War took place between China and India from October to November 1962, as a major flare-up of the Sino-Indian border dispute. There had been a series of violent border skirmishes between the two countries after the 1959 Tibet ...
of 1962, India had established a border post to the south of the delta (the "New Demchok post"). As the war progressed, the post was evacuated and the Chinese forces occupied it.
Claude ArpiThe Case of Demchok
Indian Defence Review, 19 May 2017. It has also been referred to as "Lari Karpo" ("white lhari") and "Demchok Lari Karpo" in Tibetan documents. After the
1962 Sino-Indian War
The Sino-Indian War took place between China and India from October to November 1962, as a major flare-up of the Sino-Indian border dispute. There had been a series of violent border skirmishes between the two countries after the 1959 Tibet ...
, the village of Demchok was divided in two parts, with Demchok, Ladakh
Demchok (),
KNAB Place Name Databse, retrieved 27 July 2021. previously called New Demchok, and called Parigas () by the ...
administered by India and DĂŞmqog, KNAB Place Name Databse, retrieved 27 July 2021. previously called New Demchok, and called Parigas () by the ...
Tibet Autonomous Region
The Tibet Autonomous Region or Xizang Autonomous Region, often shortened to Tibet or Xizang, is a province-level autonomous region of the People's Republic of China in Southwest China. It was overlayed on the traditional Tibetan regions of Ă ...
administered by China. The split did not divide any of the resident families.
Sources vary on whether the larger sector is administered by China or India.A selection of sources that state that the Demchok sector is administered by China:A selection of sources that state that the Demchok sector is administered by India:
See also
* Skakjung *Chumar
Chumar or Chumur () is a village and the centre of nomadic grazing region located in south-eastern Ladakh, India. It is in Rupshu block, south of the Tso Moriri lake, on the bank of the Parang River (or ''Pare Chu''), close to Ladakh's border w ...
*Aksai Chin
Aksai Chin is a region administered by China as part of Hotan County, Hotan Prefecture, Xinjiang and Rutog County, Ngari Prefecture, Tibet. It is claimed by India to be a part of its Leh District, Ladakh Union Territory. It is a part of t ...
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * ** Indian Report: ; ; ; ** Chinese report: ; ; ; * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{refendExternal links
Demchok Eastern Sector
on OpenStreetMap (Chinese-controlled)
Demchok Western Sector
on OpenStreetMap (Indian-controlled) Geography of Ladakh Geography of Tibet History of Ladakh History of Tibet Territorial disputes of China Territorial disputes of India Divided regions China–India border Demchok sector