Dark slope streak on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Dark slope streaks are narrow,
Dark slope streaks are narrow,
 Albedo features cover the
Albedo features cover the
PIA03170 fig1duststroms.jpg, Mars without a dust storm in June 2001 (on left) and with a global dust storm in July 2001 (on right), as seen by Mars Global Surveyor
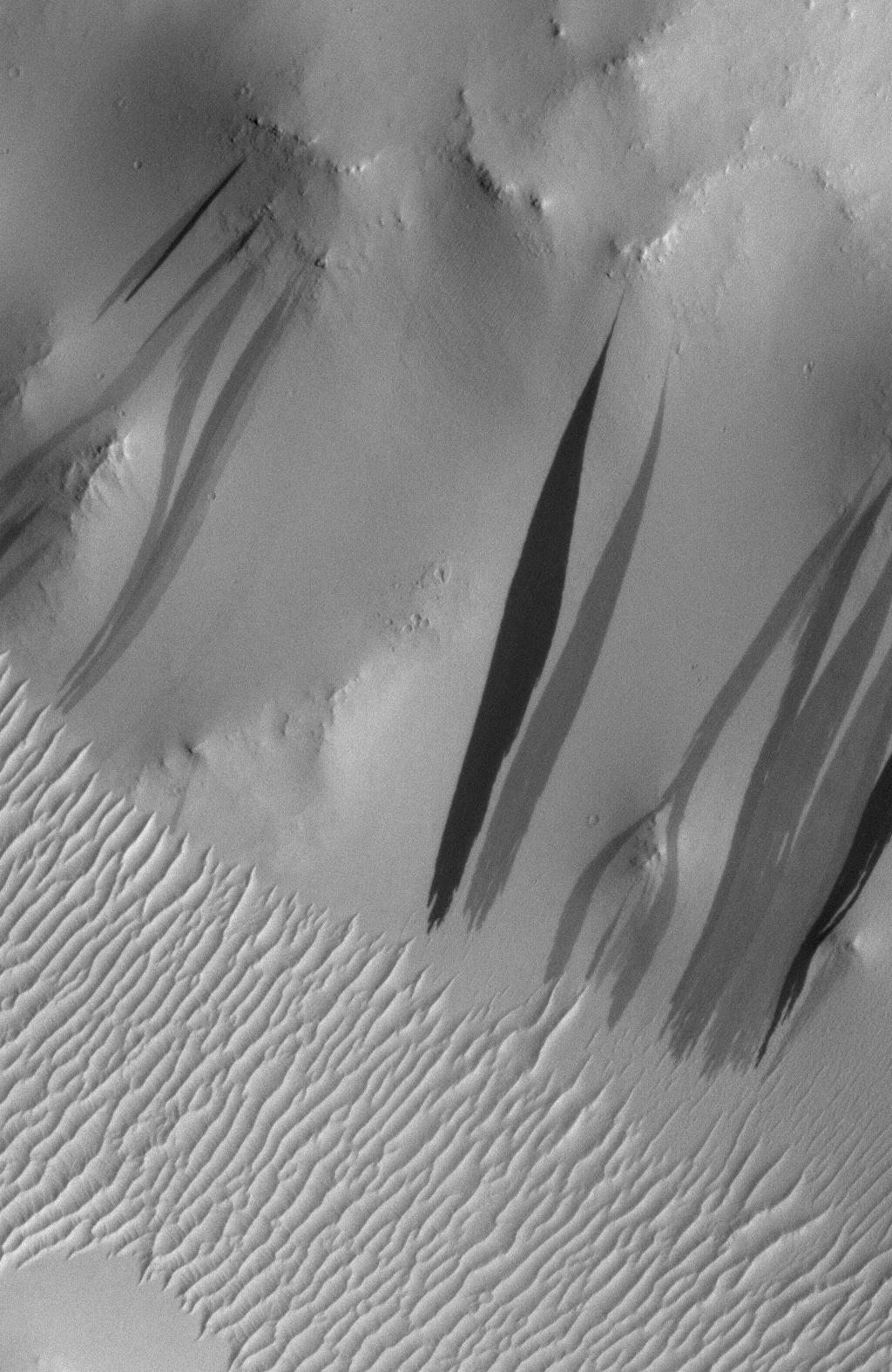
 At moderate resolutions (20–50 m/pixel), dark slope streaks appear as thin, parallel filaments aligned downslope along crater rims and escarpments. They are often straight but may also be curved or
At moderate resolutions (20–50 m/pixel), dark slope streaks appear as thin, parallel filaments aligned downslope along crater rims and escarpments. They are often straight but may also be curved or  Images from the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (
Images from the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (
 Researchers have proposed a number of mechanisms for dark slope streak formation. The most widely held view is that the streaks are the result of dust
Researchers have proposed a number of mechanisms for dark slope streak formation. The most widely held view is that the streaks are the result of dust
File:ESP 054066 1920newstreak.jpg, New streak that was caused by a recent impact that created a small crater, as seen by HiRISE. Location is the
Research, published in January 2012 in Icarus, found that dark streaks were initiated by airblasts from meteorites traveling at supersonic speeds. The team of scientists was led by Kaylan Burleigh, an undergraduate at the University of Arizona. After counting some 65,000 dark streaks around the impact site of a group of 5 new craters, patterns emerged. The number of streaks was greatest closer to the impact site. So, the impact somehow probably caused the streaks. Also, the distribution of the streaks formed a pattern with two wings extending from the impact site. The curved wings resembled scimitars, curved knives. This pattern suggests that an interaction of airblasts from the group of meteorites shook dust loose enough to start dust avalanches that formed the many dark streaks. At first it was thought that the shaking of the ground from the impact caused the dust avalanches, but if that was the case the dark streaks would have been arranged symmetrically around the impacts, rather than being concentrated into curved shapes.
The crater cluster lies near the equator 510 miles) south of Olympus Mons, on a type of terrain called the Medusae Fossae formation. The formation is coated with dust and contains wind-carved ridges called yardangs. These yardangs have steep slopes thickly covered with dust, so when the sonic boom of the airblast arrived from the impacts dust started to move down the slope.
Using photos from Mars Global Surveyor and HiRISE camera on NASA's Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, scientists have found about 20 new impacts each year on Mars. Because the spacecraft have been imaging Mars almost continuously for a span of 14 years, newer images with suspected recent craters can be compared to older images to determine when the craters were formed. Since the craters were spotted in a HiRISE image from February 2006, but were not present in a Mars Global Surveyor image taken in May 2004, the impact occurred in that time frame.
The largest crater in the cluster is about 22 meters (72 feet) in diameter with close to the area of a basketball court. As the meteorite traveled through the Martian atmosphere it probably broke up; hence a tight group of impact craters resulted.
Dark slope streaks have been seen for some time, and many ideas have been advanced to explain them. This research may have finally solved this mystery.
Image:2764streaks.jpg, Image indicates crater cluster and curved lines formed by airblast from meteorites. Meteorites caused airblast which caused dust avalanches on steep slopes. Image is from HiRISE.
Image:2764streaksclose.jpg, Close up of previous image along light/dark boundary. Dark line in middle of image shows border between light and dark area of curved lines. Green arrows show high areas of ridges. Loose dust moved down steep slopes when it felt the airblast from meteorite strikes. Image is from HiRISE.
 Slope streaks are one of the few
Slope streaks are one of the few
Image:Slope Streaks Crater PIA11312.jpg, A. Dark slope streaks are the tiny, linear albedo features along the SE wall of the crater. Compare with the far larger, wind-related albedo feature (oval patch at center top of image). This image is a

 Dark slope streaks are narrow,
Dark slope streaks are narrow, avalanche
An avalanche is a rapid flow of snow down a slope, such as a hill or mountain.
Avalanches can be set off spontaneously, by such factors as increased precipitation or snowpack weakening, or by external means such as humans, animals, and eart ...
-like features common on dust-covered slopes in the equatorial regions of Mars
Mars is the fourth planet from the Sun and the second-smallest planet in the Solar System, only being larger than Mercury. In the English language, Mars is named for the Roman god of war. Mars is a terrestrial planet with a thin at ...
.Chuang, F.C.; Beyer, R.A.; Bridges, N.T. (2010). Modification of Martian Slope Streaks by Eolian Processes. ''Icarus,'' 205 154–164. They form in relatively steep terrain
Terrain or relief (also topographical relief) involves the vertical and horizontal dimensions of land surface. The term bathymetry is used to describe underwater relief, while hypsometry studies terrain relative to sea level. The Latin wo ...
, such as along escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations.
The terms ''scarp'' and ''scarp face'' are often used interchangeably with ''esca ...
s and crater walls.Schorghofer, N.; Aharonson, O.; Khatiwala, S. (2002). Slope Streaks on Mars: Correlations with Surface Properties and the Potential Role of Water. ''Geophys. Res. Lett.,'' 29(23), 2126, . Although first recognized in Viking Orbiter
The ''Viking'' program consisted of a pair of identical American space probes, ''Viking 1'' and ''Viking 2'', which landed on Mars in 1976. Each spacecraft was composed of two main parts: an orbiter designed to photograph the surface of Mars f ...
images from the late 1970s,Morris, E.C. (1982). Aureole Deposits of the Martian Volcano Olympus Mons. ''J. Geophys. Res.,'' 87(B2), 1164–1178.Ferguson, H.M.; Lucchitta, B.K. (1984). Dark Streaks on Talus Slopes, Mars in ''Reports of the Planetary Geology Program 1983, NASA Tech. Memo., TM-86246,'' pp. 188–190. https://ntrs.nasa.gov/archive/nasa/casi.ntrs.nasa.gov/19840015363_1984015363.pdf. dark slope streaks were not studied in detail until higher-resolution images from the Mars Global Surveyor
''Mars Global Surveyor'' (MGS) was an American robotic space probe developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and launched November 1996. MGS was a global mapping mission that examined the entire planet, from the ionosphere down through t ...
(MGS) and Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' (MRO) is a spacecraft designed to study the geology and climate of Mars, provide reconnaissance of future landing sites, and relay data from surface missions back to Earth. It was launched on August 12, 2005, an ...
(MRO) spacecraft became available in the late 1990s and 2000s.Chuang, F.C. ''et al.'' (2007). HiRISE Observations of Slope Streaks on Mars. ''Geophys. Res. Lett.,'' 34 L20204, .
The physical process that produces dark slope streaks is still uncertain. They are most likely caused by the mass movement of loose, fine-grained material on oversteepened slopes (i.e., dust avalanches).Sullivan, R.; Daubar, I.; Fenton, L.; Malin, M.; Veverka, J. (1999). Mass-Movement Considerations for Dark Slope Streaks Imaged by the Mars Orbiter Camera. 30th Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Abstract #1809. http://www.lpi.usra.edu/meetings/LPSC99/pdf/1809.pdf. The avalanching disturbs and removes a bright surface layer of dust to expose a darker substrate. The role that water and other volatiles plays, if any, in streak formation is still debated. Slope streaks are particularly intriguing because they are one of the few geological phenomena that can be observed occurring on Mars in the present day.Kreslavsky, M.A.; Head, J.W. (2009). Slope Streaks on Mars: A New "Wet" Mechanism. ''Icarus,'' 201 517–527.Aharonson, O.; Schorghofer, N.; Gerstell, M.F. (2003). Slope Streak Formation and Dust Deposition Rates on Mars. ''J. Geophys. Res.,'' 108(E12), 5138, .
Nature of streaks on Mars
Dark slope streaks arealbedo
Albedo (; ) is the measure of the diffuse reflection of solar radiation out of the total solar radiation and measured on a scale from 0, corresponding to a black body that absorbs all incident radiation, to 1, corresponding to a body that refl ...
features. They appear to the eye as a brightness difference between the streak and the lighter-toned background slope. Usually no topographic relief
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term '' relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that th ...
is visible to distinguish the streak from its surroundings, except in the very highest resolution (<1 m/pixel) images. In many cases, the original surface texture of the slope is preserved and continuous across the streak, as though unaffected by events involved in dark streak formation (pictured left). The overall effect is equivalent in appearance to a partial shadow cast down the sloping surface. These observations indicate that whatever process forms the streaks, it affects only the very thinnest layer at the surface. Slope streaks are only about 10% darker than their surroundings but often appear black in images because the contrast has been enhanced ( stretched).Baratoux, D. et al. (2006). The Role of the Wind-Transported Dust in Slope Streaks Activity: Evidence from the HRSC Data. ''Icarus,'' 183 30–45.
 Albedo features cover the
Albedo features cover the Martian surface
The study of surface characteristics (or surface properties and processes) is a broad category of Mars science that examines the nature of the materials making up the Martian surface. The study evolved from telescopic and remote-sensing techniques ...
at a wide variety of scales. They make up the classical light and dark marking seen on Mars through telescopes. (See Classical albedo features on Mars.) The markings are caused by differing proportions of dust covering the surface. Martian dust is bright reddish ochre in color, while the bedrock and soil (regolith
Regolith () is a blanket of unconsolidated, loose, heterogeneous superficial deposits covering solid rock. It includes dust, broken rocks, and other related materials and is present on Earth, the Moon, Mars, some asteroids, and other terrestr ...
) is dark gray (the color of unaltered basalt
Basalt (; ) is an aphanitic (fine-grained) extrusive igneous rock formed from the rapid cooling of low-viscosity lava rich in magnesium and iron (mafic lava) exposed at or very near the surface of a rocky planet or moon. More than 90 ...
). Thus, dusty areas on Mars appear bright (high albedo), and surfaces with a high percentage of rocks and rock fragments are generally dark (low albedo). Most albedo features on Mars are caused by winds, which clear some areas of dust, leaving behind a darker lag. In other areas, dust is deposited to produce a bright surface. The selective removal and deposition of dust is most conspicuous around impact crater
An impact crater is a circular depression in the surface of a solid astronomical object formed by the hypervelocity impact of a smaller object. In contrast to volcanic craters, which result from explosion or internal collapse, impact crater ...
s and other obstacles where a variety of streaks (wind tails) and blotches are formed.
Dark slope streaks are relatively small features. (See A in Photo Gallery.) They differ from larger albedo features in being produced by gravity rather than wind, although wind may contribute to their initial formation.Schorghofer, Aharonson, O.; Gerstell, M.F.; Tatsumi, L. (2007). Three Decades of Slope Streak Activity on Mars. ''Icarus,'' 191 132–140, . (See B in Photo Gallery.) The cause of the darkening is uncertain. The particle sizes involved are believed to be very small (sand
Sand is a granular material composed of finely divided mineral particles. Sand has various compositions but is defined by its grain size. Sand grains are smaller than gravel and coarser than silt. Sand can also refer to a textural class o ...
, silt
Silt is granular material of a size between sand and clay and composed mostly of broken grains of quartz. Silt may occur as a soil (often mixed with sand or clay) or as sediment mixed in suspension with water. Silt usually has a floury feel ...
, and clay
Clay is a type of fine-grained natural soil material containing clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4).
Clays develop plasticity when wet, due to a molecular film of water surrounding the clay par ...
-sized particles). No clasts
Clastic rocks are composed of fragments, or clasts, of pre-existing minerals and rock. A clast is a fragment of geological detritus,Essentials of Geology, 3rd Ed, Stephen Marshak, p. G-3 chunks, and smaller grains of rock broken off other rocks ...
large enough to be imaged are present, and the underlying bedrock slope is never exposed ( i.e., dust is avalanching on a surface of dust).Malin, M.C.; Edgett, K.S. (2001). Mars Global Surveyor Mars Orbiter Camera: Interplanetary cruise through primary mission. ''J. Geophys. Res.,'' 106(E10), 23,429–23,570. Apparently, other optical, mechanical, or chemical properties are involved in producing the darker tone.
Dark slope streaks commonly share the same slope with other slope streaks of varying tones. The darkest streaks are presumed to be youngest; they have margins that are more sharply defined than streaks that are not as dark.Williams, S.H. (1991). Dark Talus Streaks on Mars are Similar to Aeolian Dark Streaks. 22nd Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Abstract #1750. http://www.lpi.usra.edu/meetings/lpsc1991/pdf/1750.pdf. This relationship suggests that streaks lighten and become more diffuse with age, probably because they become covered with fresh dust falling from the atmosphere. Faded dark slope streaks should not be confused with bright slope streaks (discussed below). Dust storms are common on Mars. At times the whole planet is enveloped in a dust storm, as shown in the pictures below.
Morphology and occurrence
 At moderate resolutions (20–50 m/pixel), dark slope streaks appear as thin, parallel filaments aligned downslope along crater rims and escarpments. They are often straight but may also be curved or
At moderate resolutions (20–50 m/pixel), dark slope streaks appear as thin, parallel filaments aligned downslope along crater rims and escarpments. They are often straight but may also be curved or sigmoid
Sigmoid means resembling the lower-case Greek letter sigma (uppercase Σ, lowercase σ, lowercase in word-final position ς) or the Latin letter S. Specific uses include:
* Sigmoid function, a mathematical function
* Sigmoid colon, part of the l ...
in shape. (See C in Photo Gallery.) Closer up, dark slope streaks typically have elongated, fan-like shapes (pictured right). They range from about 20 to 200 meters in width and are generally several hundred meters to over 1,000 meters long. Dark slope streaks exceeding 2 kilometers in length are uncommon; most terminate on slope and do not extend further out on to level terrain.
A streak commonly starts at a single point (apex
The apex is the highest point of something. The word may also refer to:
Arts and media Fictional entities
* Apex (comics), a teenaged super villainess in the Marvel Universe
* Ape-X, a super-intelligent ape in the Squadron Supreme universe
*Apex, ...
) high on the slope. The apex is often associated with an isolated small ridge, knob, or other area of local steepening. In high-resolution images, a tiny impact crater is sometimes visible at the apex. Slope streaks widen downslope from the apex in a triangular fashion, usually reaching their maximum widths short of the halfway point of their lengths. A single slope streak can split into two separate streaks around an obstacle or form an anastamosing (braided) pattern. (See D and E in Photo Gallery.) Slope streaks commonly develop multiple fingers (digitation) at their downslope ends.
 Images from the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (
Images from the High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment (HiRISE
High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment is a camera on board the '' Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' which has been orbiting and studying Mars since 2006. The 65 kg (143 lb), US$40 million instrument was built under the direction ...
) on MRO have shown that many slope streaks have relief
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term '' relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that th ...
, contrary to earlier descriptions in which no topographic distinction could be seen between the streaked and adjacent, non-streaked surface. The streaked surface is typically about 1 m lower than the non-streaked surface. This relief is only visible in maximum resolution images under optimal viewing conditions.
Dark slope streaks are most common in the equatorial regions of Mars, particularly in Tharsis, Arabia Terra
Arabia Terra is a large upland region in the north of Mars that lies mostly in the Arabia quadrangle, but a small part is in the Mare Acidalium quadrangle. It is densely cratered and heavily eroded. This battered topography indicates great age ...
, and Amazonis Planitia (pictured left). They occur between latitudes 39°N and 28°S. At their northern limits, they appear preferentially on warmer, south facing slopes. Curiously, slope streaks are also associated with areas that reach peak temperatures of 275K (2 °C), a temperature close to the triple point
In thermodynamics, the triple point of a substance is the temperature and pressure at which the three phases (gas, liquid, and solid) of that substance coexist in thermodynamic equilibrium.. It is that temperature and pressure at which the sub ...
of water on Mars. This relationship has led some researchers to suggest that liquid water is involved in dark slope streak formation.
Dark slope streaks do not appear to correlate with elevation or areas of specific bedrock geology. They occur on a wide range of slope textures, including surfaces that are smooth, featureless, and presumably young, as well as older, heavily cratered slopes. However, they are always associated with areas of high surface roughness, high albedo, and low thermal inertia
In thermodynamics, a material's thermal effusivity, thermal inertia or thermal responsivity is a measure of its ability to exchange thermal energy with its surroundings. It is defined as the square root of the product of the material's thermal co ...
, properties that indicate steep slopes covered with a lot of dust.
It has been suggested that streaks could form when accumulations of dry ice start subliming right after sunrise. Nighttime CO2 frost is widespread in low latitudes.
Formation mechanism
avalanche
An avalanche is a rapid flow of snow down a slope, such as a hill or mountain.
Avalanches can be set off spontaneously, by such factors as increased precipitation or snowpack weakening, or by external means such as humans, animals, and eart ...
s produced by dry granular flow on oversteepened slopes. Dust avalanches resemble loose snow avalanches on Earth. Loose snow avalanches occur when snow accumulates under cold, nearly windless conditions, producing a dry, powdery snow with little cohesion between individual snow crystals. The process produces a very shallow trough (slough) on the surface of the snow, which from a distance appears slightly darker in tone than the rest of the slope.
Other models involve water, either in the form of spring discharges, wet debris flows, or seasonal percolation
Percolation (from Latin ''percolare'', "to filter" or "trickle through"), in physics, chemistry and materials science, refers to the movement and filtering of fluids through porous materials.
It is described by Darcy's law.
Broader applicatio ...
of chloride
The chloride ion is the anion (negatively charged ion) Cl−. It is formed when the element chlorine (a halogen) gains an electron or when a compound such as hydrogen chloride is dissolved in water or other polar solvents. Chloride sa ...
-rich brines. Using data from the Mars Odyssey
''2001 Mars Odyssey'' is a robotic spacecraft orbiting the planet Mars. The project was developed by NASA, and contracted out to Lockheed Martin, with an expected cost for the entire mission of US$297 million. Its mission is to use spectro ...
Neutron Spectrometer, researchers found that slope streaks in the Schiaparelli basin occur in areas predicted to yield between 7.0 and 9.0 weight percent Water Equivalent Hydrogen (WEH) in contrast to typical background values of less than 4% WEH. This relationship suggests a connection between high WEH percentages and the occurrence of dark slope streaks. However, any process that requires voluminous amounts of water (e.g., spring discharges) seems unlikely because of the overall thermodynamic instability of liquid water on Mars.
Another model proposes that dark slope streaks are produced by ground-hugging density currents of dry dust lubricated by carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is trans ...
(CO2) gas. In this scenario, a small initial slump at the surface releases CO2 gas adsorbed
Adsorption is the adhesion of atoms, ions or molecules from a gas, liquid or dissolved solid to a surface. This process creates a film of the ''adsorbate'' on the surface of the ''adsorbent''. This process differs from absorption, in which a ...
onto subsurface grains. This release produces a gas-supported dust flow that moves as a tenuous density current downslope. This mechanism may help explain slope streaks that are unusually long.
Some observations suggest that dark slope streaks can be triggered by impacts. Pictures acquired by CTX in 2007 and 2010 showed a new streak appeared in the aureole of Olympus Mons. A follow up image from HiRISE showed that a new crater at the top of the streak. The researchers concluded that the impact triggered the new slope streak. Another streak connected with an impact was found in the Arabia quadrangle.
Arabia quadrangle
The Arabia quadrangle is one of a series of 30 quadrangle maps of Mars used by the United States Geological Survey (USGS) Astrogeology Research Program. The Arabia quadrangle is also referred to as MC-12 (Mars Chart-12).
The quadrangle contai ...
.
Formation rate
 Slope streaks are one of the few
Slope streaks are one of the few geomorphic
Geomorphology (from Ancient Greek: , ', "earth"; , ', "form"; and , ', "study") is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of topographic and bathymetric features created by physical, chemical or biological processes operating at or ...
features forming on the surface of present-day Mars. New streaks were first identified by comparing images from the Viking Orbiters of the 1970s to images of the same locations taken by the MGS Mars Orbiter Camera
The Mars Orbiter Camera and Mars Observer Camera (MOC) were scientific instruments on board the Mars Observer and Mars Global Surveyor spacecraft. The camera was built by Malin Space Science Systems (MSSS) for NASA and the cost of the whole MOC s ...
(MOC) in the late 1990s. The presence of new streaks showed that slope streaks are actively forming on Mars, on at least annual to decade-long timescales.Edgett, K.S.; Malin, M.C.; Sullivan, R.J.; Thomas, P.; Veverka, J. (2000). Dynamic Mars: New Dark Slope Streaks Observed on Annual and Decadal Time Scales. 31st Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Abstract #1058. http://www.lpi.usra.edu/meetings/lpsc2000/pdf/1058.pdf. A later, statistical treatment using overlapping MOC images spaced days to several years apart showed that slope streaks may form on Mars at a rate of about 70 per day. If accurate, this rate suggests that slope streaks are the most dynamic geologic features observed on the surface of Mars.
Dark slope streaks fade and disappear at a much slower rate than new ones appear. Most streaks identified in Viking images are still visible after decades, although a few have vanished. Researchers infer that streaks appear at a rate 10 times faster than they disappear, and that the number of slope streaks on Mars has increased in the last three decades. This imbalance is unlikely to have persisted for geologically significant periods of time. One possible solution to the imbalance is that streaks last for centuries, but are wiped clean ''en masse'' after extremely rare but fierce dust storms (storms of a magnitude not observed on Mars since Viking). After the storm subsides, a thick layer of fresh dust is deposited to begin a new cycle of streak formation. A recent study published in Icarus found that they last about 40 years. The researchers looked at a region in Lycus Sulci with Viking images and with CTX images from the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter. The ones first observed with Viking have all gone, but have been replaced with new ones.
Similar and related features
Dark slope streaks occur in association with or superficially resemble a number of other small-scale, slope-related features on Mars. These include bright slope streaks, avalanche scars, and recurring slope lineae. Water tracks are features that occur in the polar regions of Earth. They resemble dark slope streaks and recurring slope lineae, but have not yet been described on Mars. Many of the slope features on Mars may originate through a continuum of processes with drymass wasting
Mass wasting, also known as mass movement, is a general term for the movement of rock or soil down slopes under the force of gravity. It differs from other processes of erosion in that the debris transported by mass wasting is not entrained in ...
and minor fluvial (water-related) activity occupying opposite endpoints. Gullies
A gully is a landform created by running water, mass movement, or commonly a combination of both eroding sharply into soil or other relatively erodible material, typically on a hillside or in river floodplains or terraces. Gullies resemble lar ...
are another feature common on slopes in the mid-latitude southern hemisphere of Mars They have received much attention in the literature but are not discussed here.
Bright slope streaks
Bright slope streaks are streaks that have a lighter tone (about 2%) than their surroundings. (See F in Photo Gallery.) They are much rarer than dark slope streaks, but both types of streaks have similar morphologies and occur in the same regions of Mars. Evidence suggests that bright slope streaks are older than dark slope streaks. New bright slope streaks have never been observed, and dark slope streaks can be seen overlying bright slope streaks in some images, indicating that the former are younger than the latter. It is likely that bright slope streaks form from old dark slope streaks that have transitioned past a partially faded stage. This supposition is supported by geographical evidence indicating that bright slope streaks are slightly more common in regions where the formation rate of new dark slope streaks is low. In other words, areas with relatively many bright streaks tend to be less active and contain a higher population of old dark streaks.Avalanche scars
Areas with abundant slope streaks also contain an apparently distinct class of avalanche scars. The scars resemble slope streaks in morphology and size. (See G in Photo Gallery) They are typically several meters deep and hundreds of meters long. They begin at a single point (sometimes a small, barely resolved impact crater) high on a slope. The edges radiate downslope in a triangular fashion. In about half of the documented examples, a low-lying mound of debris is visible at the downslope end. Originally called "meters-thick avalanche scars," these features were thought to be distinct from slope streaks. However, higher-resolution images from theHiRISE
High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment is a camera on board the '' Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' which has been orbiting and studying Mars since 2006. The 65 kg (143 lb), US$40 million instrument was built under the direction ...
instrument on MRO suggest that meters-thick avalanche scars and slope streaks are related and part of a continuum of active mass wasting
Mass wasting, also known as mass movement, is a general term for the movement of rock or soil down slopes under the force of gravity. It differs from other processes of erosion in that the debris transported by mass wasting is not entrained in ...
features formed by dust avalanches.Gerstell, M.F.; Aharonson, O; Schorghofer, N. (2004). A Distinct Class of Avalanche Scars on Mars. ''Icarus,'' 168 122–130.
Recurring slope lineae (warm-season flows)
In the summer of 2011, a paper appeared in ''Science'' describing a new class of slope features with characteristics that suggest formation by seasonal releases of liquid water. (See H and I in Photo Gallery.) Called "recurring slope lineae" (RSL), the features received a considerable amount of media attention. RSLs are narrow (0.5 to 5 meters) dark markings that preferentially occur on steep, equator-facing slopes in the southern hemisphere between latitudes 48°S to 32°S. RepeatHiRISE
High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment is a camera on board the '' Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' which has been orbiting and studying Mars since 2006. The 65 kg (143 lb), US$40 million instrument was built under the direction ...
images show that the markings appear and grow incrementally during warm seasons and fade in cold seasons. RSLs bear only a superficial resemblance to dark slope streaks. They are much smaller in width and have a different pattern of geographic occurrence and slope properties than dark slope streaks.McEwen, A. Ojha L.; Dundas C.; Mattson, S.; Byrne S.; Wray J.; Cull S.; Murchie S. (2011). Transient Slope Lineae: Evidence for Summertime Briny Flows on Mars? 42nd Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Abstract #2314. http://www.lpi.usra.edu/meetings/lpsc2011/pdf/2314.pdf. RSLs seem to occur on bedrock slopes with seasonally high surface temperatures of 250–300K (-23–27 °C). These location may favor the flow of briney fluids emerging from seeps at certain times of the Martian year. Unlike RSLs, dark slope streaks appear to occur sporadically throughout the Martian year, and their triggering seems unrelated to season or large regional events.Schorghofer, N.; King, C.M. (2011). Sporadic Formation of Slope Streaks on Mars. ''Icarus,'' 216(1), 159-168.
Water tracks
Water tracks are little-studied slope features common in permafrost-dominated terrains in thearctic
The Arctic ( or ) is a polar region located at the northernmost part of Earth. The Arctic consists of the Arctic Ocean, adjacent seas, and parts of Canada (Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut), Danish Realm (Greenland), Finland, Iceland, N ...
and Antarctic regions of Earth. They are zones of enhanced soil moisture that route water downslope over the top of the permanently frozen ground just below the surface ( ice table). Although water tracks have not been specifically identified on Mars, several researchers have noted their morphological and spectroscopic similarity to Martian slope streaks.Levy, J. S.; Fountain, A. G. (2011). "Water Tracks" in the McMurdo Dry Valleys, Antarctica: A Permafrost-Based Hydrological System Supporting Complex Biological and Geochemical Processes in a Mars-Analog Environment. 42nd Lunar and Planetary Science Conference, Abstract #1210. http://www.lpi.usra.edu/meetings/lpsc2011/pdf/1210.pdf. Like dark slope streaks, water tracks are narrow, sublinear features elongated in the downslope direction. They typically display a slight darkness relative to their surroundings and show little or no detectable relief. During peak flow conditions, they appear as damp, darkened, patches of soil that are generally less than 60 m wide and several hundred meters long. The dark surface discoloration vanishes in frozen water tracks during winter, rendering them nearly undetectable.
Photo gallery
Dark streaks and related features appear in the images below. To see the features described in the caption and text, it may be necessary to enlarge the image by clicking on it.THEMIS
In Greek mythology and religion, Themis (; grc, Θέμις, Themis, justice, law, custom) is one of the twelve Titan children of Gaia and Uranus, and the second wife of Zeus. She is the goddess and personification of justice, divine order, fai ...
VIS from the Mars Odyssey
''2001 Mars Odyssey'' is a robotic spacecraft orbiting the planet Mars. The project was developed by NASA, and contracted out to Lockheed Martin, with an expected cost for the entire mission of US$297 million. Its mission is to use spectro ...
spacecraft. It is about 25 km wide. North is at top.
Image:Slope Streak Dust Devil.jpg, B. This dark slope streak may have been initiated by winds from dust devil. A thin dust devil track is visible across the apex of the slope streak. This Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter
''Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' (MRO) is a spacecraft designed to study the geology and climate of Mars, provide reconnaissance of future landing sites, and relay data from surface missions back to Earth. It was launched on August 12, 2005, an ...
(MRO) HiRISE
High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment is a camera on board the '' Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' which has been orbiting and studying Mars since 2006. The 65 kg (143 lb), US$40 million instrument was built under the direction ...
image is 1.8 km across and based on Schorghofer ''et al.,'' 2007, p. 136, Fig. 5.
Image:Dark streaks in Diacria.JPG, C. Dark streaks in Diacria quadrangle, as seen by the Mars Orbiter Camera
The Mars Orbiter Camera and Mars Observer Camera (MOC) were scientific instruments on board the Mars Observer and Mars Global Surveyor spacecraft. The camera was built by Malin Space Science Systems (MSSS) for NASA and the cost of the whole MOC s ...
(MOC) on Mars Global Surveyor
''Mars Global Surveyor'' (MGS) was an American robotic space probe developed by NASA's Jet Propulsion Laboratory and launched November 1996. MGS was a global mapping mission that examined the entire planet, from the ionosphere down through t ...
(MGS).
Image:Slope Streak Diverting PIA08672.jpg, D. Dark slope streaks in Phlegra Dorsa region as seen by MOC. The streak near the center of image has been diverted around a small hill. The image is about 3 km (1.9 mi) across.
Image:Braided_Slope_Streak.jpg, E. Braided (anastomosing) slope streak in Lycus Sulci region as seen by MOC. The morphology resembles features produced by fuidized flow. The image is about 3 km (1.9 mi) across.
Image:Bright Slope Streaks PIA03587.jpg, F. Both dark and bright slope sreaks occur together on the wall of this impact crater in Arabia Terra
Arabia Terra is a large upland region in the north of Mars that lies mostly in the Arabia quadrangle, but a small part is in the Mare Acidalium quadrangle. It is densely cratered and heavily eroded. This battered topography indicates great age ...
as seen by MOC. Photometric analysis shows that the brightness of the streaks is inherent and not due to lighting conditions or viewing geometry.
Image:Avalanche Scars PSP 003239 1870.jpg, G. Shallow avalanche scars associated with dark slope streak. The slope streak has the same sharp apex and triangular-faceted morphology as the scars, suggesting that both types of features have a similar origin. Image is from HiRISE
High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment is a camera on board the '' Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' which has been orbiting and studying Mars since 2006. The 65 kg (143 lb), US$40 million instrument was built under the direction ...
.
Image:Slope Lineae PIA14479-43 946-710.jpg, H. Recurring slope lineae as seen by HiRISE
High Resolution Imaging Science Experiment is a camera on board the '' Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter'' which has been orbiting and studying Mars since 2006. The 65 kg (143 lb), US$40 million instrument was built under the direction ...
.
Image:PIA17934-MartianSlope-SeasonalDarkFlows-20140210.jpg, I. Seasonal Dark Flows, "Recurring Slope Linae" (RSL), on Martian slopes (2 November 2007).
Image:Pedestaltop22919.jpg, Dark slope streaks near the top of a pedestal crater, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program HiWish is a program created by NASA so that anyone can suggest a place for the HiRISE camera on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter to photograph. It was started in January 2010. In the first few months of the program 3000 people signed up to use HiRIS ...
.
Image:Streaks22919.jpg, Dark slope streaks and layers near a pedestal crater, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program.
Image:23677streaks.jpg, Young and old dark streaks, as seen by HiRISE under HiWish program HiWish is a program created by NASA so that anyone can suggest a place for the HiRISE camera on the Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter to photograph. It was started in January 2010. In the first few months of the program 3000 people signed up to use HiRIS ...
. Location is Diacria quadrangle.
File:55107 1930streaks.jpg, Dark slope streaks, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program Arrows show how boulders affected the shape of the streaks.
File:55107 1930streaksclose.jpg, Dark slope streaks, as seen by HiRISE under the HiWish program Arrows show how boulders affected the shape of the streaks.
References
Further reading
*Barlow, N.G. (2008). ''Mars: An Introduction to Its Interior, Surface, and Atmosphere;'' Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, . *Hartmann, William, K. (2003). ''A Traveler’s Guide to Mars: The Mysterious Landscapes of the Red Planet;'' Workman: New York, . {{Portal bar, Solar System Geology of Mars Surface features of Mars