Darfur War on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The War in Darfur, also nicknamed the Land Cruiser War, is a major armed conflict in the Darfur region of Sudan that began in February 2003 when the
Estimates of the number of human casualties range up to several hundred thousand dead, from either combat or starvation and disease. Mass displacements and coercive migrations forced millions into refugee camps or across the border, creating a
 At 5:30 am on 25 April 2003, the
At 5:30 am on 25 April 2003, the
 In August, the African Union sent 150 Rwandan troops to protect the ceasefire monitors. However, it soon became apparent that 150 troops would not be enough, and they were subsequently joined by 150
In August, the African Union sent 150 Rwandan troops to protect the ceasefire monitors. However, it soon became apparent that 150 troops would not be enough, and they were subsequently joined by 150
(BBC) 24 May 2004 On 10 July 2005, Ex-SPLA leader
On 10 July 2005, Ex-SPLA leader
(BBC) 10 July 2005 However, on 30 July, Garang died in a helicopter crash.Sudan VP Garang killed in crash
(BBC) 1 August 2005 Despite improved security, talks between the various rebels in the Darfur region progressed slowly. An attack on the Chadian town of
(BBC) 20 December 2005 Escalating tensions led the
By Stephanie Hancock, BBC News,
 On 5 May 2006, the Sudanese government signed the
On 5 May 2006, the Sudanese government signed the
, '' On 12 October, Nigerian Foreign Minister
On 12 October, Nigerian Foreign Minister
Chaos in Darfur on rise as Arabs fight with Arabs
", news article, ''The New York Times'', 3 September 2007, pp 1, A7
 Some 93 soldiers and 13 policemen were killed along with 30 civilians in the attack on Khartoum and Omdurman. Sudanese forces confirmed that they found the bodies of 90 rebels and had spotted dozens more strewn outside the city limits. While Sudanese authorities claimed that up to 400 rebels could have been killed, the rebels stated that they lost 45 fighters dead or wounded. Sudanese authorities also claimed to have destroyed 40 rebel vehicles and captured 17.
Some 93 soldiers and 13 policemen were killed along with 30 civilians in the attack on Khartoum and Omdurman. Sudanese forces confirmed that they found the bodies of 90 rebels and had spotted dozens more strewn outside the city limits. While Sudanese authorities claimed that up to 400 rebels could have been killed, the rebels stated that they lost 45 fighters dead or wounded. Sudanese authorities also claimed to have destroyed 40 rebel vehicles and captured 17.
 Martin Luther Agwai, General Martin Agwai, head of the joint African Union-United Nations mission in Darfur, said the war was over in the region, although low-level disputes remained. There was still "Banditry, localised issues, people trying to resolve issues over water and land at a local level. But real war as such, I think we are over that," he said.
Martin Luther Agwai, General Martin Agwai, head of the joint African Union-United Nations mission in Darfur, said the war was over in the region, although low-level disputes remained. There was still "Banditry, localised issues, people trying to resolve issues over water and land at a local level. But real war as such, I think we are over that," he said.
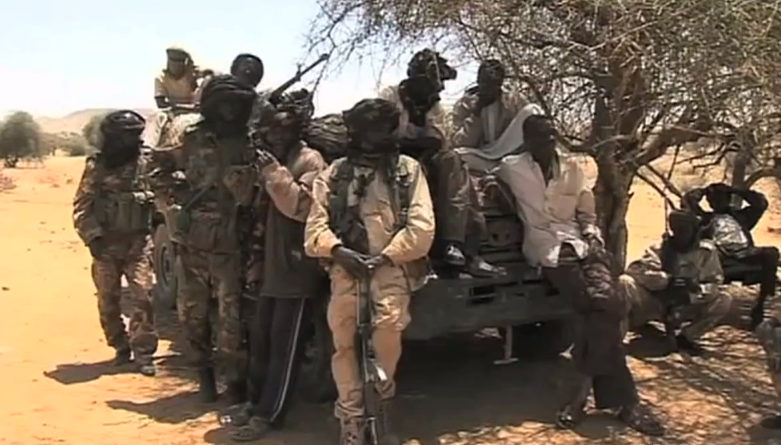 A donors conference in Doha pledged US$3.6 billion to help rebuild Darfur. The conference was criticised in the region that the Sudan Liberation Army (Minni Minnawi) rebels had taken. According to the group's Hussein Minnawi, Ashma, Sudan, Ashma village and another town close to the
A donors conference in Doha pledged US$3.6 billion to help rebuild Darfur. The conference was criticised in the region that the Sudan Liberation Army (Minni Minnawi) rebels had taken. According to the group's Hussein Minnawi, Ashma, Sudan, Ashma village and another town close to the
 The well-armed Janjaweed quickly gained an advantage over rebel factions. By the spring of 2004, several thousand people – mostly from the non-Arab population – had been killed and as many as a million more had been driven from their homes, causing a major humanitarian crisis. The crisis took on an international dimension when over 100,000 refugees poured into neighboring Chad, pursued by militiamen who clashed with Chadian government forces along the border. More than 70 militiamen and 10 Chadian soldiers were killed in one gun battle in April. A United Nations observer team reported that non-Arab villages were singled out, while Arab villages were left untouched:
The well-armed Janjaweed quickly gained an advantage over rebel factions. By the spring of 2004, several thousand people – mostly from the non-Arab population – had been killed and as many as a million more had been driven from their homes, causing a major humanitarian crisis. The crisis took on an international dimension when over 100,000 refugees poured into neighboring Chad, pursued by militiamen who clashed with Chadian government forces along the border. More than 70 militiamen and 10 Chadian soldiers were killed in one gun battle in April. A United Nations observer team reported that non-Arab villages were singled out, while Arab villages were left untouched:
 Immediately after the Janjaweed entered the conflict, the rape of women and young girls, often by multiple militiamen and often throughout entire nights, began to be reported at a staggering rate. Children as young as 2 years old were reported victims, while mothers were assaulted in front of their children. Young women were attacked so violently that they were unable to walk following the attack.
Non-Arab people were reportedly raped by Janjaweed militiamen as a result of the Sudanese government's goal of completely eliminating the presence of black Africans and non-Arabs from Darfur. The Washington Post Foreign Service interviewed verified victims of the rapes and recorded that Arabic terms such as "abid" and "zurga" were used, which mean slave and black. One victim, Sawelah Suliman, was told by her assailant, "Black girl, you are too dark. You are like a dog. We want to make a light baby." In an 88-page report, victims from Darfur have also accused the Rapid Support Forces of rape and assault as recently as 2015.
Immediately after the Janjaweed entered the conflict, the rape of women and young girls, often by multiple militiamen and often throughout entire nights, began to be reported at a staggering rate. Children as young as 2 years old were reported victims, while mothers were assaulted in front of their children. Young women were attacked so violently that they were unable to walk following the attack.
Non-Arab people were reportedly raped by Janjaweed militiamen as a result of the Sudanese government's goal of completely eliminating the presence of black Africans and non-Arabs from Darfur. The Washington Post Foreign Service interviewed verified victims of the rapes and recorded that Arabic terms such as "abid" and "zurga" were used, which mean slave and black. One victim, Sawelah Suliman, was told by her assailant, "Black girl, you are too dark. You are like a dog. We want to make a light baby." In an 88-page report, victims from Darfur have also accused the Rapid Support Forces of rape and assault as recently as 2015.
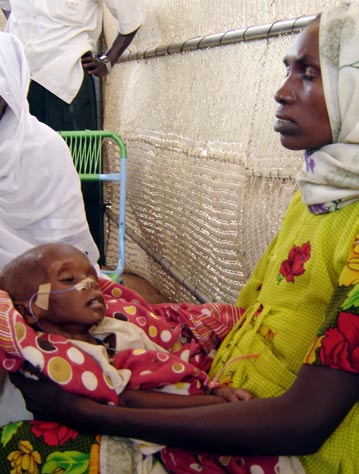 Multiple casualty estimates have been published since the war began, ranging from roughly 10,000 civilians (Sudan government) to hundreds of thousands.
In September 2004, 18 months after the conflict began, the World Health Organization estimated that there had been 50,000 deaths in Darfur, mostly due to starvation. An updated estimate published the following month put the number of deaths for the 6-month period from March to October 2004 due to starvation and disease at 70,000; These figures were criticized because they only considered short periods and did not include deaths from violence. A more recent British Parliamentary Report estimated that over 300,000 people had died and others have published even higher death toll estimates.
In March 2005, the UN's Under-Secretary-General for Humanitarian Affairs and Emergency Relief Coordinator, Emergency Relief Coordinator Jan Egeland estimated that 10,000 people were dying each month, excluding deaths due to ethnic violence. An estimated 2.7 million people had at that time been displaced from their homes, mostly seeking refuge in camps in Darfur's major towns. Two hundred thousand had fled to neighboring Chad. Reports of violent deaths compiled by the UN indicate between 6,000 and 7,000 fatalities from 2004 to 2007.
In May 2005, the Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters (CRED) of the School of Public Health of the Université catholique de Louvain in Brussels, Belgium published an analysis of mortality in Darfur. Their estimate stated that from September 2003 to January 2005, between 98,000 and 181,000 persons died in Darfur, including 63,000 to 146,000 excess deaths.
In August 2010, Dr. Eric Reeves argued that total mortality from all violent causes, direct and indirect, at that point in the conflict, exceeded 500,000. His analysis took account of all previous mortality data and studies, including that by the Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disaster.Quantifying Genocide in Darfur
Multiple casualty estimates have been published since the war began, ranging from roughly 10,000 civilians (Sudan government) to hundreds of thousands.
In September 2004, 18 months after the conflict began, the World Health Organization estimated that there had been 50,000 deaths in Darfur, mostly due to starvation. An updated estimate published the following month put the number of deaths for the 6-month period from March to October 2004 due to starvation and disease at 70,000; These figures were criticized because they only considered short periods and did not include deaths from violence. A more recent British Parliamentary Report estimated that over 300,000 people had died and others have published even higher death toll estimates.
In March 2005, the UN's Under-Secretary-General for Humanitarian Affairs and Emergency Relief Coordinator, Emergency Relief Coordinator Jan Egeland estimated that 10,000 people were dying each month, excluding deaths due to ethnic violence. An estimated 2.7 million people had at that time been displaced from their homes, mostly seeking refuge in camps in Darfur's major towns. Two hundred thousand had fled to neighboring Chad. Reports of violent deaths compiled by the UN indicate between 6,000 and 7,000 fatalities from 2004 to 2007.
In May 2005, the Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters (CRED) of the School of Public Health of the Université catholique de Louvain in Brussels, Belgium published an analysis of mortality in Darfur. Their estimate stated that from September 2003 to January 2005, between 98,000 and 181,000 persons died in Darfur, including 63,000 to 146,000 excess deaths.
In August 2010, Dr. Eric Reeves argued that total mortality from all violent causes, direct and indirect, at that point in the conflict, exceeded 500,000. His analysis took account of all previous mortality data and studies, including that by the Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disaster.Quantifying Genocide in Darfur
Dr. Eric Reeves, 28 April 2006 The UN disclosed on 22 April 2008 that it might have underestimated the Darfur death toll by nearly 50%. In July 2009, ''The Christian Science Monitor'' published an op-ed stating that many of the published mortality rates have been misleading because they include a large number of people who had died of disease and malnutrition, as well as those who died from direct violence.The Genocide in Darfur is not what it seems
Dr. Marc Gustafson, 19 August 2009 In January 2010, the Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters published an article in a special issue of ''The Lancet''. The article, entitled "Patterns of mortality rates in Darfur conflict", estimated with 95% confidence that the excess number of deaths is between 178,258 and 461,520 (with a mean of 298,271), with 80% of these due to disease.
 International attention to the Darfur genocide largely began with reports by Amnesty International in July 2003 and the International Crisis Group in December 2003. However, widespread media coverage did not start until the outgoing United Nations Resident and Humanitarian Coordinator for Sudan, Mukesh Kapila, called Darfur the "world's greatest humanitarian crisis" in March 2004.Prunier, pp. 124–148 Organizations such as STAND: A Student Anti-Genocide Coalition, later under the umbrella of Genocide Intervention Network, and the Save Darfur Coalition emerged and became particularly active in the areas of engaging the United States Congress and President on the issue and pushing for divestment, initially launched by Adam Sterling under the auspices of the Sudan Divestment Task Force.
International attention to the Darfur genocide largely began with reports by Amnesty International in July 2003 and the International Crisis Group in December 2003. However, widespread media coverage did not start until the outgoing United Nations Resident and Humanitarian Coordinator for Sudan, Mukesh Kapila, called Darfur the "world's greatest humanitarian crisis" in March 2004.Prunier, pp. 124–148 Organizations such as STAND: A Student Anti-Genocide Coalition, later under the umbrella of Genocide Intervention Network, and the Save Darfur Coalition emerged and became particularly active in the areas of engaging the United States Congress and President on the issue and pushing for divestment, initially launched by Adam Sterling under the auspices of the Sudan Divestment Task Force.
 In May 2009 the Mandate Darfur was canceled because the "Sudanese government is obstructing the safe passage of Darfurian delegates from Sudan." The Mandate was a conference that would have brought together 300 representatives from different regions of Darfur's civil society. The conference planned was to be held in Addis Ababa sometime in early May.
In May 2009 the Mandate Darfur was canceled because the "Sudanese government is obstructing the safe passage of Darfurian delegates from Sudan." The Mandate was a conference that would have brought together 300 representatives from different regions of Darfur's civil society. The conference planned was to be held in Addis Ababa sometime in early May.
According to China's critics, China threatened to use its veto on the U.N. Security Council to protect Khartoum from sanctions and was able to water down every resolution on Darfur in order to protect its interests. Accusations of the supply of weapons from China, which were then transferred to Darfur by the Sudanese government in violation of the UN arms embargo, continued in 2010. Sarah Wykes, a senior campaigner at Global Witness, an NGO that campaigns for better natural resource governance, says: "Sudan has purchased about $100m in arms from China and has used these weapons against civilians in Darfur." According to the report Following the Thread: Arms and Ammunition Tracing in Sudan and South Sudan, released in May 2014 by the Swiss research group Small Arms Survey, "Over the period 2001–12, Khartoum's reports to UN Comtrade reveal significant fluctuation in annual conventional arms imports. The majority of the Sudanese government's total self-reported imports of small arms and light weapons, their ammunition, and ‘conventional weapons’ over the period originated in China (58 per cent), followed by Iran (13 per cent), St. Vincent and the Grenadines (9 per cent), and Ukraine (8 per cent)." The report found that Chinese weapons were pervasive among most parties to the Sudanese conflicts, including the war in Darfur, but identified few if any weapons of Russian origin. (The section "Chinese weapons and ammunition" receives 20 pages in the report, whereas the only mention of Russian arms is to be found in the sentence "the majority of...mines [in South Sudan] have been of Chinese and Soviet/Russian origin."). China and Russia denied they had broken UN sanctions. China has a close relationship with Sudan and increased its military co-operation with the government in early 2007. Because of Sudan's plentiful supply of oil, China considers good relations with Sudan to be a strategic necessity. China has direct commercial interests in Sudan's oil. China's state-owned company CNPC controls between 60 and 70 percent of Sudan's total oil production. Additionally, it owns the largest single share (40 percent) of Sudan's national oil company, Greater Nile Petroleum Operating Company. China consistently opposed economic and non-military sanctions on Sudan. In March 2007, threats of boycotting the Olympic games came from French presidential candidate François Bayrou, in an effort to stop China's support. Sudan divestment efforts concentrated on PetroChina, the national petroleum company with extensive investments in Sudan.
Photographer's Account – "The Cost of Silence: A Traveling Exhibition"
{{DEFAULTSORT:Darfur War Conflicts in 2022 2000s conflicts 2000s in Sudan 2010s conflicts 2010s in Sudan War in Darfur, Civil wars post-1945 Ethnicity-based civil wars Responsibility to protect Proxy wars Genocides in Africa
Sudan Liberation Movement
The Sudan Liberation Movement/Army ( ar, حركة تحرير السودان ''Ḥarakat Taḥrīr Al-Sūdān''; abbreviated SLM, SLA, or SLM/A) is a Sudanese rebel group active in Darfur, Sudan. It was founded as the Darfur Liberation FrontFlin ...
(SLM) and the Justice and Equality Movement
The Justice and Equality Movement (JEM; ar, حركة العدل والمساواة, ') is an opposition group in Sudan founded by Khalil Ibrahim. Gibril Ibrahim has led the group since January 2012 after the death of Khalil, his brother, in Dec ...
(JEM) rebel groups began fighting against the government of Sudan
Government of Sudan is the federal provisional government created by the constitution of Sudan having the executive, parliament, and the judiciary. Previously, a ''president'' was head of state, head of government, and commander-in-chief of t ...
, which they accused of oppressing Darfur's non-Arab
The Arabs (singular: Arab; singular ar, عَرَبِيٌّ, DIN 31635: , , plural ar, عَرَب, DIN 31635: , Arabic pronunciation: ), also known as the Arab people, are an ethnic group mainly inhabiting the Arab world in Western Asia, ...
population. The government responded to attacks by carrying out a campaign of ethnic cleansing against Darfur's non-Arabs. This resulted in the death of hundreds of thousands of civilians and the indictment of Sudan's president, Omar al-Bashir, for genocide
Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word (, "race, people") with the Lat ...
, war crimes, and crimes against humanity by the International Criminal Court
The International Criminal Court (ICC or ICCt) is an intergovernmental organization and international tribunal seated in The Hague, Netherlands. It is the first and only permanent international court with jurisdiction to prosecute individuals f ...
.
One side of the conflict is mainly composed of the Sudanese military, police and the Janjaweed
The Janjaweed ( ar, جنجويد, Janjawīd, lit=mounted gunman; also transliterated ''Janjawid'') are a Sudanese Arab militia group that operate in Sudan, particularly Darfur, and eastern Chad. Using the United Nations definition, the Janjaweed ...
, a Sudanese militia
A militia () is generally an army or some other fighting organization of non-professional soldiers, citizens of a country, or subjects of a state, who may perform military service during a time of need, as opposed to a professional force of r ...
group whose members are mostly recruited among Arabized
Arabization or Arabisation ( ar, تعريب, ') describes both the process of growing Arab influence on non-Arab populations, causing a language shift by the latter's gradual adoption of the Arabic language and incorporation of Arab culture, aft ...
indigenous Africans and a small number of Bedouin of the northern Rizeigat
The Rizeigat, or Rizigat, or Rezeigat (Standard Arabic Rizayqat) are a Muslim and Arab tribe of the nomadic Bedouin Baggara (Standard Arabic Baqqara) people in Sudan's Darfur region. The Rizeigat belong to the greater Baggara Arabs fraternity of ...
; the majority of other Arab groups in Darfur remained uninvolved.
The other side is made up of rebel groups, notably the SLM/A and the JEM, recruited primarily from the non-Arab Muslim Fur
Fur is a thick growth of hair that covers the skin of mammals. It consists of a combination of oily guard hair on top and thick underfur beneath. The guard hair keeps moisture from reaching the skin; the underfur acts as an insulating blanket t ...
, Zaghawa Zaghawa may refer to:
* Zaghawa people
* Zaghawa language
Zaghawa is a Saharan language spoken by the Zaghawa people of east-central Chad (in the Sahel) and northwestern Sudan (Darfur). The people who speak this language call it Beria, from ''Be ...
, and Masalit The Masalit (Masalit language, Masalit: ''masala/masara''; ar, ماساليت) are an ethnic group inhabiting western Sudan and eastern Chad. They speak the Masalit language
Overview
The Masalit primarily live in Geneina, the capital of west Darfu ...
ethnic groups. The African Union and the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
also have a joint peacekeeping mission in the region, named UNAMID. Although the Sudanese government publicly denies that it supported the Janjaweed, evidence supports claims that it provided financial assistance and weapons and coordinated joint attacks, many against civilians.Uppsala Conflict Data Program
The Uppsala Conflict Data Program (UCDP) is a data collection program on organized violence, based at Uppsala University in Sweden. The UCDP is a leading provider of data on organized violence and armed conflict, and it is the oldest ongoing data ...
br>Conflict Encyclopedia, Sudan, one-sided conflict, Janjaweed – civiliansEstimates of the number of human casualties range up to several hundred thousand dead, from either combat or starvation and disease. Mass displacements and coercive migrations forced millions into refugee camps or across the border, creating a
humanitarian crisis
A humanitarian crisis (or sometimes humanitarian disaster) is defined as a singular event or a series of events that are threatening in terms of health, safety or well-being of a community or large group of people. It may be an internal or extern ...
. Former U.S.
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
Secretary of State Colin Powell described the situation as a genocide or acts of genocide.
The Sudanese government and the JEM signed a ceasefire agreement in February 2010, with a tentative agreement to pursue peace. The JEM has the most to gain from the talks and could see semi-autonomy much like South Sudan
South Sudan (; din, Paguot Thudän), officially the Republic of South Sudan ( din, Paankɔc Cuëny Thudän), is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered by Ethiopia, Sudan, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the ...
. However, talks were disrupted by accusations that the Sudanese army launched raids and air strikes against a village, violating the Tolu agreement. The JEM, the largest rebel group in Darfur, vowed to boycott negotiations.
The August 2019 Draft Constitutional Declaration, signed by military and civilian representatives during the Sudanese Revolution, requires that a peace process
A peace process is the set of sociopolitical negotiations, agreements and actions that aim to solve a specific armed conflict.
Definitions
Prior to an armed conflict occurring, peace processes can include the prevention of an intra-state or in ...
leading to a peace agreement be made in Darfur and other regions of armed conflict in Sudan within the first six months of the 39-month transition period to democratic civilian government.
A comprehensive peace agreement was signed on 31 August 2020 between the Sudanese authorities and several rebel factions to end armed hostilities.
Origins of the conflict
Darfur,Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
for "the home of the Fur
Fur is a thick growth of hair that covers the skin of mammals. It consists of a combination of oily guard hair on top and thick underfur beneath. The guard hair keeps moisture from reaching the skin; the underfur acts as an insulating blanket t ...
", was not a traditional part of the states organized along the upper Nile
The Nile, , Bohairic , lg, Kiira , Nobiin: Áman Dawū is a major north-flowing river in northeastern Africa. It flows into the Mediterranean Sea. The Nile is the longest river in Africa and has historically been considered the longest ...
valley but instead organized as an independent sultanate in the 14th century. Owing to the migration of the Banu Hilal
The Banu Hilal ( ar, بنو هلال, translit=Banū Hilāl) was a confederation of Arabian tribes from the Hejaz and Najd regions of the Arabian Peninsula that emigrated to North Africa in the 11th century. Masters of the vast plateaux of t ...
tribe in the 11th century AD, the peoples of the Nile valley became heavily Arabicized
Arabization or Arabisation ( ar, تعريب, ') describes both the process of growing Arab influence on non-Arab populations, causing a language shift by the latter's gradual adoption of the Arabic language and incorporation of Arab culture, aft ...
while the hinterlands remained closer to native Sudanese cultures. It was first annexed to the Egyptian
Egyptian describes something of, from, or related to Egypt.
Egyptian or Egyptians may refer to:
Nations and ethnic groups
* Egyptians, a national group in North Africa
** Egyptian culture, a complex and stable culture with thousands of years of ...
Sudan in 1875 and then surrendered by its governor Slatin Pasha
Major-General Rudolf Anton Carl Freiherr von Slatin, Geh. Rat, (7 June 1857, in Ober Sankt Veit, Hietzing, Vienna – 4 October 1932, in Vienna) was an Anglo-Austrian soldier and administrator in the Sudan.
Early life
Rudolf Carl Slatin was ...
to the Mahdia
Mahdia ( ar, المهدية ') is a Tunisian coastal city with 62,189 inhabitants, south of Monastir and southeast of Sousse.
Mahdia is a provincial centre north of Sfax. It is important for the associated fish-processing industry, as well as w ...
in 1883. Following the Anglo-Egyptian victory in the Mahdist War, Sultan Ali Dinar
Ali Dinar ( ar, علي دينار; 1856 – November 6, 1916) was a Sultan of the Sultanate of Darfur and ruler from the Keira dynasty.
In 1898, with the decline of the Mahdists, he managed to regain Darfur's independence.
A rebellion ...
was reinstated as a British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
client before being deposed by a 1916 expedition after he made overtures in favor of Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
amid the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
. Subsequently, Darfur remained a province of the Anglo-Egyptian Sudan
Anglo-Egyptian Sudan ( ar, السودان الإنجليزي المصري ') was a condominium of the United Kingdom and Egypt in the Sudans region of northern Africa between 1899 and 1956, corresponding mostly to the territory of present-day ...
and the independent Republic of the Sudan
Sudan ( or ; ar, السودان, as-Sūdān, officially the Republic of the Sudan ( ar, جمهورية السودان, link=no, Jumhūriyyat as-Sūdān), is a country in Northeast Africa. It shares borders with the Central African Republic ...
.
There are several different explanations for the origins of the present conflict. One explanation involves the land disputes between semi-nomad
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the po ...
ic livestock herders and those who practice sedentary agriculture. Water access has also been identified as a major source of the conflict.
The Darfur crisis is also related to a second conflict. In southern Sudan, civil war has raged for decades between the northern, Arab-dominated government and Christian and animist black southerners. Yet another origin is conflict between the Islamist, Khartoum-based national government and two rebel groups
Rebellion, uprising, or insurrection is a refusal of obedience or order. It refers to the open resistance against the orders of an established authority.
A rebellion originates from a sentiment of indignation and disapproval of a situation and ...
based in Darfur: the Sudan Liberation Army and the Justice and Equality Movement.
Allegations of apartheid
In early 1991, non-Arabs of the Zaghawa tribe of Sudan attested that they were victims of an intensifying Arabapartheid
Apartheid (, especially South African English: , ; , "aparthood") was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. Apartheid was ...
campaign, segregating Arabs and non-Arabs. Sudanese Arabs, who controlled the government, were widely referred to as practicing apartheid against Sudan's non-Arab citizens. The government was accused of "deftly manipulat(ing) Arab solidarity" to carry out policies of apartheid and ethnic cleansing.Vukoni Lupa Lasaga, "The slow, violent death of apartheid in Sudan," 19 September 2006, Norwegian Council for Africa.
American University economist George Ayittey
George B. N. Ayittey (13 October 1945 – 28 January 2022) was a Ghanaian economist, author, and president of the Free Africa Foundation in Washington DC. He was a professor at American University, and an associate scholar at the Foreign Polic ...
accused the Arab government of Sudan of practicing racism
Racism is the belief that groups of humans possess different behavioral traits corresponding to inherited attributes and can be divided based on the superiority of one race over another. It may also mean prejudice, discrimination, or antagonis ...
against black citizens. According to Ayittey, "In Sudan... the Arabs monopolized power and excluded blacks – Arab apartheid." Many African commentators joined Ayittey in accusing Sudan of practising Arab apartheid.
Alan Dershowitz
Alan Morton Dershowitz ( ; born September 1, 1938) is an American lawyer and former law professor known for his work in U.S. constitutional law and American criminal law. From 1964 to 2013, he taught at Harvard Law School, where he was appoin ...
claimed Sudan was an example of Apartheid
Apartheid (, especially South African English: , ; , "aparthood") was a system of institutionalised racial segregation that existed in South Africa and South West Africa (now Namibia) from 1948 to the early 1990s. Apartheid was ...
. Former Canadian
Canadians (french: Canadiens) are people identified with the country of Canada. This connection may be residential, legal, historical or cultural. For most Canadians, many (or all) of these connections exist and are collectively the source of ...
Minister of Justice
A justice ministry, ministry of justice, or department of justice is a ministry or other government agency in charge of the administration of justice. The ministry or department is often headed by a minister of justice (minister for justice in a ...
Irwin Cotler
Irwin Cotler, PC, OC, OQ (born May 8, 1940) is a retired Canadian politician who was Member of Parliament for Mount Royal from 1999 to 2015. He served as the Minister of Justice and Attorney General of Canada from 2003 until the Liberal gov ...
echoed the accusation.
Timeline
Beginning
Authors Julie Flint and Alex de Waal marked the onset of the genocide on 26 February 2003, when a group calling itself theDarfur Liberation Front
The Sudan Liberation Movement/Army ( ar, حركة تحرير السودان ''Ḥarakat Taḥrīr Al-Sūdān''; abbreviated SLM, SLA, or SLM/A) is a Sudanese rebel group active in Darfur, Sudan. It was founded as the Darfur Liberation FrontFlint ...
(DLF) publicly claimed credit for an attack on Golo, the headquarters of Jebel Marra
The Marrah Mountains or Marra Mountains ( Fur, Fugo Marra; ar, جبل مرة, Jebel Marra are a range of volcanic peaks in a massif that rises up to . They are the highest mountains in Sudan.
Geography
The mountains are located in the center of ...
District. Prior to this attack, however, conflict had broken out, as rebels attacked police stations, army outposts and military convoys and the government engaged in a massive air and land assault on the rebel stronghold in the Marrah Mountains
The Marrah Mountains or Marra Mountains ( Fur, Fugo Marra; ar, جبل مرة, Jebel Marra are a range of volcanic peaks in a massif that rises up to . They are the highest mountains in Sudan.
Geography
The mountains are located in the center of ...
. The rebels' first military action was a successful attack on an army garrison on 25 February 2002. The government had been aware of a unified rebel movement since an attack on the Golo police station in June, 2002. Flint and de Waal date the beginning of the rebellion to 21 July 2001, when a group of Zaghawa Zaghawa may refer to:
* Zaghawa people
* Zaghawa language
Zaghawa is a Saharan language spoken by the Zaghawa people of east-central Chad (in the Sahel) and northwestern Sudan (Darfur). The people who speak this language call it Beria, from ''Be ...
and Fur
Fur is a thick growth of hair that covers the skin of mammals. It consists of a combination of oily guard hair on top and thick underfur beneath. The guard hair keeps moisture from reaching the skin; the underfur acts as an insulating blanket t ...
met in Abu Gamra and swore oaths on the Qur'an
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , s ...
to work together to defend against government-sponsored attacks on their villages. Nearly all of Darfur's residents are Muslim, including the Janjaweed
The Janjaweed ( ar, جنجويد, Janjawīd, lit=mounted gunman; also transliterated ''Janjawid'') are a Sudanese Arab militia group that operate in Sudan, particularly Darfur, and eastern Chad. Using the United Nations definition, the Janjaweed ...
, as well as government leaders in Khartoum
Khartoum or Khartum ( ; ar, الخرطوم, Al-Khurṭūm, din, Kaartuɔ̈m) is the capital of Sudan. With a population of 5,274,321, its metropolitan area is the largest in Sudan. It is located at the confluence of the White Nile, flowing n ...
.
On 25 March 2003, the rebels seized the garrison town of Tine along the Chadian border, seizing large quantities of supplies and arms. Despite a threat by President Omar al-Bashir to "unleash" the army, the military had little in reserve. The army was already deployed in both the south, where the Second Sudanese Civil War
The Second Sudanese Civil War was a conflict from 1983 to 2005 between the central Sudanese government and the Sudan People's Liberation Army. It was largely a continuation of the First Sudanese Civil War of 1955 to 1972. Although it originated ...
was drawing to an end, and the east, where rebels sponsored by Eritrea were threatening a newly constructed pipeline from the central oilfields to Port Sudan
Port Sudan ( ar, بور سودان, Būr Sūdān) is a port city in eastern Sudan, and the capital of the state of Red Sea. , it has 489,725 residents. Located on the Red Sea, Port Sudan is recognized as Sudan's main seaport and the source of 90% ...
. The rebel guerilla tactic of hit-and-run raids proved almost impossible for the army, untrained in desert operations, to counter. However, its aerial bombardment of rebel positions on the mountain was devastating.
 At 5:30 am on 25 April 2003, the
At 5:30 am on 25 April 2003, the Darfur genocide
The Darfur genocide is the systematic killing of ethnic Darfuri people which has occurred during the ongoing conflict in Western Sudan. It has become known as the first genocide of the 21st century. The genocide, which is being carried out agai ...
arose when the Sudan Liberation Movement and the JEM, which is the largest rebel group in Darfur, entered Al-Fashir
Al Fashir, Al-Fashir or El Fasher ( ar, الفاشر) is the capital city of North Darfur, Sudan. It is a large town in the Darfur region of northwestern Sudan, northeast of Nyala, Sudan.
"Al-Fashir" (description)
''Encyclopædia Brit ...
, the capital city of North Darfur and attacked the sleeping garrison. In the next four hours, four Antonov
Antonov State Enterprise ( uk, Державне підприємство «Антонов»), formerly the Aeronautical Scientific-Technical Complex named after Antonov (Antonov ASTC) ( uk, Авіаційний науково-технічни� ...
bombers and helicopter gunships (according to the government; seven according to the rebels) were destroyed on the ground, 75 soldiers, pilots and technicians were killed and 32 were captured, including the commander of the air base, a Major General
Major general (abbreviated MG, maj. gen. and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. The disappearance of the "sergeant" in the title explains the apparent confusion of ...
. The success of the raid was unprecedented in Sudan; in the twenty years of the war in the south, the rebel Sudan People's Liberation Army (SPLA) had never before carried out such an operation.
The Al-Fashir raid was a turning point, both militarily and psychologically. The armed forces had been humiliated by the raid, placing the government in a difficult strategic situation. The incompetent armed forces needed to be retrained and redeployed amid concerns about the loyalty of the many Darfurian non-commissioned officers and soldiers. Responsibility for prosecuting the war was given to Sudanese military intelligence. Nevertheless, in the middle months of 2003, rebels won 34 of 38 engagements. In May, the SLA destroyed a battalion at Kutum
Kutum is a town in the Sudanese state of North Darfur. It lies northwest of the state capital, Al-Fashir. The town is located along a wadi and therefore also known as Wadi Kutum. It lies north along the Marrah Mountains; the Kutum volcanic fi ...
, killing 500 and taking 300 prisoners; in mid-July, 250 were killed in a second attack on Tine. The SLA began to infiltrate farther east, threatening to extend the war into Kordofan
Kordofan ( ar, كردفان ') is a former province of central Sudan. In 1994 it was divided into three new federal states: North Kordofan, South Kordofan and West Kordofan. In August 2005, West Kordofan State was abolished and its territory ...
.
Given that the army was consistently losing, the war effort switched to emphasize three elements: military intelligence, the air force and the Janjaweed
The Janjaweed ( ar, جنجويد, Janjawīd, lit=mounted gunman; also transliterated ''Janjawid'') are a Sudanese Arab militia group that operate in Sudan, particularly Darfur, and eastern Chad. Using the United Nations definition, the Janjaweed ...
. The latter were armed Baggara
The Baggāra ( ar, البَقَّارَة "heifer herder") or Chadian Arabs are a nomadic confederation of people of mixed Arab and Arabized indigenous African ancestry, inhabiting a portion of the Sahel mainly between Lake Chad and the Nile ri ...
herders whom the government had used to suppress a Masalit The Masalit (Masalit language, Masalit: ''masala/masara''; ar, ماساليت) are an ethnic group inhabiting western Sudan and eastern Chad. They speak the Masalit language
Overview
The Masalit primarily live in Geneina, the capital of west Darfu ...
uprising from 1986 to 1999. The Janjaweed became the center of the new counter-insurgency strategy. Though the government consistently denied supporting them, military resources were poured into Darfur and the Janjaweed were outfitted as a paramilitary force, complete with communication equipment and some artillery. The military planners were aware of the probable consequences of such a strategy: similar methods undertaken in the Nuba Mountains
The Nuba Mountains ( ar, جبال النوبة), also referred to as the Nuba Hills, is an area located in South Kordofan, Sudan. The area is home to a group of indigenous ethnic groups known collectively as the Nuba peoples. In the Middle Ages ...
and around the southern oil fields during the 1990s had resulted in massive human rights violations and forced displacements.
2004–2005
In 2004, Chad brokered negotiations inN'Djamena
N'Djamena ( ) is the capital and largest city of Chad. It is also a special statute region, divided into 10 districts or ''arrondissements''.
The city serves as the centre of economic activity in Chad. Meat, fish and cotton processing are the c ...
, leading to the April 8 Humanitarian Ceasefire Agreement
Following the escalation of the Darfur conflict in the Sudan, Chad brokered negotiations in N'Djamena led to the Humanitarian Ceasefire Agreement between the Sudanese government and the two rebel groups, the Sudanese Justice and Equality Movemen ...
between the Sudanese government, the JEM, and the SLA. One group that did not participate in the April cease-fire talks or agreement, the National Movement for Reform and Development
The National Movement for Reform and Development (NMRD) is a Sudanese rebel group based in the region of Darfur. The group was formed when it broke away from the Justice and Equality Movement in 2004. The NMRD came into existence because its foun ...
, split from the JEM in April. Janjaweed and rebel attacks continued despite the ceasefire, and the African Union (AU) formed a Ceasefire Commission
Following the escalation of the Darfur conflict in the Sudan, Chad brokered negotiations in N'Djamena led to the Humanitarian Ceasefire Agreement between the Sudanese government and the two rebel groups, the Sudanese Justice and Equality Movement ...
(CFC) to monitor its observance.
 In August, the African Union sent 150 Rwandan troops to protect the ceasefire monitors. However, it soon became apparent that 150 troops would not be enough, and they were subsequently joined by 150
In August, the African Union sent 150 Rwandan troops to protect the ceasefire monitors. However, it soon became apparent that 150 troops would not be enough, and they were subsequently joined by 150 Nigeria
Nigeria ( ), , ig, Naìjíríyà, yo, Nàìjíríà, pcm, Naijá , ff, Naajeeriya, kcg, Naijeriya officially the Federal Republic of Nigeria, is a country in West Africa. It is situated between the Sahel to the north and the Gulf o ...
n troops.
On 18 September, the United Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, an ...
issued Resolution 1564 declaring that the Sudan government had not met its commitments and expressing concern at helicopter attacks and assaults by the Janjaweed. It welcomed the intention of the African Union to enhance its monitoring mission and urged all member states to support such efforts.
During April, 2005, after the Sudan government signed a ceasefire agreement with Sudan People's Liberation Army which led to the end of the Second Sudanese Civil War
The Second Sudanese Civil War was a conflict from 1983 to 2005 between the central Sudanese government and the Sudan People's Liberation Army. It was largely a continuation of the First Sudanese Civil War of 1955 to 1972. Although it originated ...
, the African Union Mission in Sudan
The African Union Mission in Sudan (AMIS) was an African Union (AU) peacekeeping force operating primarily in the country's western region of Darfur to perform peacekeeping operations related to the Darfur conflict. It was founded in 2004, with a ...
(AMIS) force was increased by 600 troops and 80 military observers. In July, the force was increased by about 3,300 (with a budget of 220 million dollars). In April, 2005, AMIS was increased to about 7,000.
The scale of the crisis led to warnings of an imminent disaster, with United Nations Secretary-General
The secretary-general of the United Nations (UNSG or SG) is the chief administrative officer of the United Nations and head of the United Nations Secretariat, one of the six principal organs of the United Nations.
The role of the secretary-g ...
Kofi Annan
Kofi Atta Annan (; 8 April 193818 August 2018) was a Ghanaian diplomat who served as the seventh secretary-general of the United Nations from 1997 to 2006. Annan and the UN were the co-recipients of the 2001 Nobel Peace Prize. He was the founde ...
warning about the risk of genocide. The scale of the Janjaweed campaign led to comparisons with the Rwandan genocide
The Rwandan genocide occurred between 7 April and 15 July 1994 during the Rwandan Civil War. During this period of around 100 days, members of the Tutsi minority ethnic group, as well as some moderate Hutu and Twa, were killed by armed H ...
, a parallel denied by the Sudanese government. Independent observers noted that the tactics, which included dismemberment and killing of noncombatants, including young children and infants, were more akin to the ethnic cleansing used in the Yugoslav wars
The Yugoslav Wars were a series of separate but related Naimark (2003), p. xvii. ethnic conflicts, wars of independence, and insurgencies that took place in the SFR Yugoslavia from 1991 to 2001. The conflicts both led up to and resulted from ...
and warned that the region's remoteness meant that hundreds of thousands of people were effectively cut off from aid. The Brussels-based International Crisis Group had reported in May 2004 that over 350,000 people could potentially die as a result of starvation and disease.'Dozens killed' in Sudan attack(BBC) 24 May 2004
 On 10 July 2005, Ex-SPLA leader
On 10 July 2005, Ex-SPLA leader John Garang
John Garang de Mabior (June 23, 1945 – July 30, 2005) was a Sudanese politician and revolutionary leader. From 1983 to 2005, he led the Sudan People's Liberation Army (SPLA) after the Second Sudanese Civil War, the comprehensive peace agreeme ...
was sworn in as Sudan's vice-president.Sudan ex-rebel joins government(BBC) 10 July 2005 However, on 30 July, Garang died in a helicopter crash.Sudan VP Garang killed in crash
(BBC) 1 August 2005 Despite improved security, talks between the various rebels in the Darfur region progressed slowly. An attack on the Chadian town of
Adré
Adré (Arabic: أدري) is the main town of the Assoungha department in the Ouaddaï Region of Chad. It is located very close to Chad's eastern border with Sudan, 400m away. The town is served by Adré Airport.
History
The Chadian-Sudanese ...
near the Sudanese border led to the death of 300 rebels in December. Sudan was blamed for the attack, which was the second in the region in three days.Chad fightback 'kills 300 rebels'(BBC) 20 December 2005 Escalating tensions led the
government of Chad
The Government of Chad has been ruled by Mahamat Déby since 20th April 2021.
The Republic of Chad maintains an embassy in the United States at 2401 Massachusetts Avenue, NW, Washington D.C.
Cabinet
See also
* Minister of Foreign Affairs ( ...
to declare its hostility toward Sudan and to call for Chadians to mobilise against the "common enemy".Chad in 'state of war' with SudanBy Stephanie Hancock, BBC News,
N'Djamena
N'Djamena ( ) is the capital and largest city of Chad. It is also a special statute region, divided into 10 districts or ''arrondissements''.
The city serves as the centre of economic activity in Chad. Meat, fish and cotton processing are the c ...
, 23 December 2005 (See Chad-Sudan conflict)
2006
 On 5 May 2006, the Sudanese government signed the
On 5 May 2006, the Sudanese government signed the Darfur Peace Agreement
The Darfur Peace Agreement may refer to one of three peace agreements that were signed by the Government of Sudan and Darfur-based rebel groups in 2006, 2011 and 2020 with the intention of ending the Darfur Conflict.
Abuja Agreement (2006)
Th2006 ...
along with the faction of the SLA led by Minni Minnawi
Suliman Arcua Minnawi ( ar, سليمان أركو مناوي), known as "Minni Minnawi" (; born December 12, 1968 in Furawiyya, North Darfur), is a Sudanese politician who was the leader of the largest faction of the Sudanese Liberation Army. A ...
. However, the agreement was rejected by the smaller Justice and Equality Movement
The Justice and Equality Movement (JEM; ar, حركة العدل والمساواة, ') is an opposition group in Sudan founded by Khalil Ibrahim. Gibril Ibrahim has led the group since January 2012 after the death of Khalil, his brother, in Dec ...
and a rival faction of the SLA led by Abdul Wahid al Nur
Abdul Wahid Mohamed al Nur (also Abdel Wahid el-Nur or Abdulwahid Mohammed Nour; ar, عبد الواحد محمد نور, ''ʿAbd al-Wāḥid Muḥammad Nūr''; born in 1968) is the leader of the rebel Sudan Liberation Movement (al Nur) faction ...
. The accord was orchestrated by chief negotiator Salim Ahmed Salim
Salim Ahmed Salim ( ar, سليم احمد سليم, sw, Salim Ahmad Salim, born 23 January 1942) is a Tanzanian politician and diplomat who has worked in the international diplomatic arena since the early 1960s.
Early life
Salim was born in wh ...
(working on behalf of the African Union), U.S. Deputy Secretary of State
The deputy secretary of state of the United States is the principal deputy to the secretary of state. The current deputy secretary of state is Wendy Ruth Sherman, serving since April 2021 under secretary of state Antony Blinken. If the secretary ...
Robert B. Zoellick
Robert Bruce Zoellick (; ; born July 25, 1953) is an American public official and lawyer who was the eleventh president of the World Bank, a position he held from July 1, 2007 to June 30, 2012. He was previously a managing director of Goldman Sach ...
, AU representatives and other foreign officials operating in Abuja, Nigeria.
The 115-page agreement included agreements on national and state power-sharing, demilitarization of the Janjaweed and other militias, an integration of SLM/A and JEM troops into the Sudanese Armed Forces
The Sudanese Armed Forces (SAF; ar, القوات المسلحة السودانية, Al-Quwwat al-Musallaha as-Sudaniyah) are the military forces of the Republic of the Sudan. In 2011, IISS estimated the regular forces' numbers at personnel, whi ...
and police, a system of federal
Federal or foederal (archaic) may refer to:
Politics
General
*Federal monarchy, a federation of monarchies
*Federation, or ''Federal state'' (federal system), a type of government characterized by both a central (federal) government and states or ...
wealth-sharing for the promotion of Darfurian economic interests, a referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a direct vote by the electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a representative. This may result in the adoption of a ...
on the future status of Darfur and measures to promote the flow of humanitarian aid.
Representatives of the African Union, Nigeria, Libya
Libya (; ar, ليبيا, Lībiyā), officially the State of Libya ( ar, دولة ليبيا, Dawlat Lībiyā), is a country in the Maghreb region in North Africa. It is bordered by the Mediterranean Sea to the north, Egypt to the east, Suda ...
, the United States, the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the European mainland, continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotlan ...
, the United Nations, the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
, the Arab League, Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
, Canada, Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of Jan Mayen and the ...
and the Netherlands
)
, anthem = ( en, "William of Nassau")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of the Netherlands
, established_title = Before independence
, established_date = Spanish Netherl ...
served as witnesses.
July and August 2006 saw renewed fighting, international aid organizations considering leaving due to attacks against their personnel. Annan called for 18,000 international peacekeepers in Darfur to replace the 7,000-man AMIS force. In one incident at Kalma, seven women, who ventured out of a refugee camp to gather firewood, were gang-raped, beaten and robbed by the Janjaweed. When they had finished, the attackers stripped them naked and jeered at them as they fled.
In a private meeting on 18 August, Hédi Annabi
Hédi Annabi (4 September 1943 – 12 January 2010) was a Tunisian diplomat and Special Representative of the United Nations Secretary-General, Head of the UN Stabilization Mission in Haiti (MINUSTAH). He was previously an Assistant-Secretary-G ...
, Assistant Secretary-General for Peacekeeping Operations
Peacekeeping comprises activities intended to create conditions that favour lasting peace. Research generally finds that peacekeeping reduces civilian and battlefield deaths, as well as reduces the risk of renewed warfare.
Within the United N ...
, warned that Sudan appeared to be preparing for a major military offensive. The warning came a day after UN Commission on Human Rights
The United Nations Commission on Human Rights (UNCHR) was a functional commission within the overall framework of the United Nations from 1946 until it was replaced by the United Nations Human Rights Council in 2006. It was a subsidiary body of ...
special investigator Sima Samar
Sima Samar ( fa, سیما سمر; born 3 February 1957) is an Afghan woman and human rights advocate, activist and social worker within national and international forums, who served as Minister of Women's Affairs of Afghanistan from December 2 ...
stated that Sudan's efforts remained poor despite the May Agreement. On 19 August, Sudan reiterated its opposition to replacing AMIS with a UN force, resulting in the US issuing a "threat" to Sudan over the "potential consequences".
On 25 August, Sudan rejected attending a United Nations Security Council
The United Nations Security Council (UNSC) is one of the six principal organs of the United Nations (UN) and is charged with ensuring international peace and security, recommending the admission of new UN members to the General Assembly, an ...
(UNSC) meeting to explain its plan to send 10,000 Sudanese soldiers to Darfur instead of the proposed 20,000 UN peacekeeping force. The Security Council announced it would hold the meeting despite Sudan's absence. Also on 24 August, the International Rescue Committee reported that hundreds of women were raped and sexually assaulted around the Kalma refugee camp during the previous several weeks and that the Janjaweed were reportedly using rape to cause women to be humiliated and ostracised by their own communities. On 25 August, the head of the U.S. State Department's Bureau of African Affairs
In the United States government, the Bureau of African Affairs (AF) is part of the U.S. Department of State and is charged with advising the Secretary of State on matters of Sub-Saharan Africa. The bureau was established in 1958. It is headed b ...
, Assistant Secretary Jendayi Frazer
Jendayi Elizabeth Frazer (born 1961) is the former U.S. Assistant Secretary of State for African Affairs, heading the Bureau of African Affairs. She was a Distinguished Service Professor at Carnegie Mellon University's Heinz College and Departm ...
, warned that the region faced a security crisis unless the UN peacekeeping force deployed.
On 26 August, two days before the UNSC meeting and Frazer was due to arrive in Khartoum
Khartoum or Khartum ( ; ar, الخرطوم, Al-Khurṭūm, din, Kaartuɔ̈m) is the capital of Sudan. With a population of 5,274,321, its metropolitan area is the largest in Sudan. It is located at the confluence of the White Nile, flowing n ...
, Paul Salopek
Paul Salopek (born February 9, 1962 in Barstow, California) is a journalist and writer from the United States. He is a two-time Pulitzer Prize winner and was raised in central Mexico.
Salopek has reported globally for the Chicago Tribune, Forei ...
, a U.S. ''National Geographic Magazine
''National Geographic'' (formerly the ''National Geographic Magazine'', sometimes branded as NAT GEO) is a popular American monthly magazine published by National Geographic Partners. Known for its photojournalism, it is one of the most widely ...
'' journalist, appeared in court in Darfur facing charges of espionage; he had crossed into the country illegally from Chad, circumventing the Sudanese government's official restrictions on foreign journalists. He was later released after direct negotiation with President al-Bashir. This came a month after Tomo Križnar
Tomo Križnar (born 26 August 1954) is a peace activist, notable for delivering video cameras in Southern Kordofan to the local ethnic Nuba civilians in order to help them collect the evidence of North Sudan military's war crimes against them. ...
, a Slovenia
Slovenia ( ; sl, Slovenija ), officially the Republic of Slovenia (Slovene: , abbr.: ''RS''), is a country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Italy to the west, Austria to the north, Hungary to the northeast, Croatia to the southeast, an ...
n presidential envoy, was sentenced to two years in prison for spying.
Proposed UN peacekeeping force
On 31 August 2006, the UNSC approved a resolution to send a new peacekeeping force of 17,300 to the region. Sudan expressed strong opposition to the resolution. On 1 September, African Union officials reported that Sudan had launched a major offensive in Darfur, killing more than 20 civilians and displacing over 1,000. On 5 September, Sudan asked the existing AU force to leave by the end of the month, adding that "they have no right to transfer this assignment to the United Nations or any other party. This right rests with the government of Sudan." On 4 September, in a move not viewed as surprising, Chad's presidentIdriss Déby
Idriss Déby Itno ' (18 June 1952 – 20 April 2021) was a Chadian politician and military officer who was the president of Chad from 1990 until his death in 2021.
Déby was a member of the Bidayat clan of the Zaghawa ethnic group. A high-ranki ...
voiced support for the UN peacekeeping force. The AU, whose mandate expired on 30 September 2006, confirmed that AMIS would leave. The next day, however, a senior US State Department official told reporters that the AU force might remain past the deadline.
Autumn
On 8 September, António Guterres, head of theUnited Nations High Commissioner for Refugees
The United Nations High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) is a United Nations agency mandated to aid and protect refugees, forcibly displaced communities, and stateless people, and to assist in their voluntary repatriation, local integrati ...
, said Darfur faced a "humanitarian catastrophe". On 12 September, Sudan's European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
envoy Pekka Haavisto
Pekka Olavi Haavisto (born 23 March 1958) is a Finnish politician of the Green League who has been serving as the Minister for Foreign Affairs since 2019.
Haavisto returned to the Finnish Parliament in the Finnish parliamentary election of M ...
claimed that the Sudanese army was "bombing civilians in Darfur". A World Food Programme
The World Food Programme; it, Programma alimentare mondiale; es, Programa Mundial de Alimentos; ar, برنامج الأغذية العالمي, translit=barnamaj al'aghdhiat alealami; russian: Всемирная продовольствен� ...
official reported that food aid had been blocked from reaching at least 355,000 people. Annan said, "the tragedy in Darfur has reached a critical moment. It merits this council's closest attention and urgent action."
On 14 September, the leader of the Sudan Liberation Movement, Minni Minnawi
Suliman Arcua Minnawi ( ar, سليمان أركو مناوي), known as "Minni Minnawi" (; born December 12, 1968 in Furawiyya, North Darfur), is a Sudanese politician who was the leader of the largest faction of the Sudanese Liberation Army. A ...
, stated that he did not object to the UN peacekeeping force, rejecting the Sudanese government's view that such a deployment would be an act of Western invasion. Minnawi claimed that AMIS "can do nothing because the AU mandate is very limited". Khartoum remained opposed to UN involvement, with Al-Bashir depicting it as a colonial plan and stating that "we do not want Sudan to turn into another Iraq."
On 2 October the AU announced that it would extend its presence until 31 December 2006."Genocide survivors urges EU sanctions over Darfur", ''
Reuters
Reuters ( ) is a news agency owned by Thomson Reuters Corporation. It employs around 2,500 journalists and 600 photojournalists in about 200 locations worldwide. Reuters is one of the largest news agencies in the world.
The agency was esta ...
'', 20 October 2006 Two hundred UN troops were sent to reinforce the AU force. On 6 October, the UNSC voted to extend the mandate of the United Nations Mission in Sudan
The United Nations Mission in the Sudan (UNMIS) was established by the UN Security Council under Resolution 1590 of 24 March 2005, in response to the signing of the Comprehensive Peace Agreement between the government of the Sudan and the Sudan ...
until 30 April 2007. On 9 October, the Food and Agriculture Organization
The Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations (FAO)french: link=no, Organisation des Nations unies pour l'alimentation et l'agriculture; it, Organizzazione delle Nazioni Unite per l'Alimentazione e l'Agricoltura is an intern ...
listed Darfur as the most pressing food emergency out of the forty countries listed on its ''Crop Prospects and Food Situation'' report. On 10 October, the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights, Louise Arbour
Louise Bernice Arbour (born February 10, 1947) is a Canadian lawyer, prosecutor and jurist.
Arbour was the UN High Commissioner for Human Rights, a former justice of the Supreme Court of Canada and the Court of Appeal for Ontario and a former ...
, claimed that the Sudanese government had prior knowledge of attacks by Janjaweed militias in Buram, South Darfur
South Darfur State ( ar, ولاية جنوب دارفور Wilāyat Ǧanūb Dārfūr; Janob Darfor) is one of the wilayat or states of Sudan. It is one of the five states that compose the region of Darfur in western Sudan.
Overview
Prior to the ...
the month before, in which hundreds of civilians were killed.
 On 12 October, Nigerian Foreign Minister
On 12 October, Nigerian Foreign Minister Joy Ogwu
Joy Uche Angela Ogwu (born August 22, 1946) is a former foreign minister of Nigeria and a former permanent representative of Nigeria to the United Nations in New York 2008–2017. She is the first woman to hold the post of Permanent Representat ...
arrived in Darfur for a two-day visit. She urged the Sudanese government to accept the UN proposal. Nigerian President Olusegun Obasanjo
Chief Olusegun Matthew Okikiola Ogunboye Aremu Obasanjo, , ( ; yo, Olúṣẹ́gun Ọbásanjọ́ ; born 5 March 1937) is a Nigerian political and military leader who served as Nigeria's head of state from 1976 to 1979 and later as its presid ...
spoke against "stand ngby and see nggenocide taking place in Darfur." On 13 October, US President George W. Bush
George Walker Bush (born July 6, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 43rd president of the United States from 2001 to 2009. A member of the Republican Party, Bush family, and son of the 41st president George H. W. Bush, he ...
imposed further sanctions against those deemed complicit in the atrocities under the ''Darfur Peace and Accountability Act
The Darfur Peace and Accountability Act (H.R. 3127/S. 1462, ) or DPAA restates the United States government's position that the Darfur conflict constitutes genocide, and asks the government to expand the African Union peacekeeping force in Darfur ...
of 2006''. The measures were said to strengthen existing sanctions by prohibiting US citizens from engaging in oil-related transactions with Sudan (although US companies had been prohibited from doing business with Sudan since 1997), freezing the assets of complicit parties and denying them entry to the US.
The lack of funding and equipment for the AU mission meant that the work of aid workers in Darfur was severely limited by fighting. Some warned that the humanitarian situation could deteriorate to levels seen in 2003 and 2004, when UN officials called Darfur the world's worst humanitarian crisis.
On 22 October, the Sudan government told UN envoy Jan Pronk
Johannes Pieter "Jan" Pronk Jr. (; born 16 March 1940) is a retired Dutch politician and diplomat of the Labour Party (PvdA) and activist.
Pronk studied Economics at the Rotterdam School of Economics obtaining a Master of Economics degree and ...
to leave the country within three days. Pronk, the senior UN official in the country, had been heavily criticized by the Sudanese army after he posted a description of several recent military defeats in Darfur to his personal blog. On 1 November, the US announced that it would formulate an international plan which it hoped the Sudanese government would find more palatable. On 9 November, senior Sudanese presidential advisor Nafie Ali Nafie told reporters that his government was prepared to start unconditional talks with the National Redemption Front (NRF) rebel alliance, but noted he saw little use for a new peace agreement. The NRF, which had rejected the May Agreement and sought a new peace agreement, did not comment.
In late 2006, Darfur Arabs started their own rebel group, the Popular Forces Troops, and announced on 6 December that they had repulsed an assault by the Sudanese army at Kas-Zallingi the previous day. They were the latest of numerous Darfur Arab groups to oppose the government since 2003, some of which had signed political accords with rebel movements.
The same period saw an example of a tribe-based split within the Arab forces, when relations between the farming Terjem and nomadic, camel-herding Mahria tribes became tense. Terjem leaders accused the Mahria of kidnapping a Terjem boy, while Mahria leaders said the Terjem had been stealing their animals. Ali Mahamoud Mohammed, the wali, or governor, of South Darfur, said the fighting began in December when the Mahria drove their camels south in a seasonal migration, trampling through Terjem territory near the Bulbul River. Fighting resumed in July 2007.Gettleman, Jeffrey,Chaos in Darfur on rise as Arabs fight with Arabs
", news article, ''The New York Times'', 3 September 2007, pp 1, A7
Proposed compromise UN force and Sudanese offensive
On 17 November reports of a potential deal to place a "compromise peacekeeping force" in Darfur were announced, but would later appear to have been rejected by Sudan. The UN claimed on 18 November that Sudan had agreed to the deployment of UN peacekeepers. Sudan's Ministry of Foreign Affairs (Sudan), Foreign Minister Lam Akol stated that "there should be no talk about a mixed force" and that the UN's role should be restricted to technical support. Also on 18 November, the AU reported that Sudanese military and Sudanese-backed militias had launched a ground and air operation in the region that resulted in about 70 civilian deaths. The AU stated that this "was a flagrant violation of security agreements". On 25 November a spokesperson for UN High Commissioner for Human Rights accused the Sudanese government of having committed "a deliberate and unprovoked attack" against civilians in Sirba on 11 November, which claimed the lives of at least 30 people. The Commissioner's statement maintained that "contrary to the government's claim, it appears that the Sudanese Armed Forces launched a deliberate and unprovoked attack on civilians and their property in Sirba," and that this also involved "extensive and wanton destruction and looting of civilian property".2007
According to the Save Darfur Coalition, New Mexico Bill Richardson, Governor Bill Richardson and al-Bashir agreed to a cease-fire whereby the Sudanese "government and rebel groups will cease hostilities for a period of 60 days while they work towards a lasting peace." In addition, the Save Darfur press release stated that the agreement "included a number of concessions to improve humanitarian aid and media access to Darfur." Despite the formality of a ceasefire there have been further media reports of killings and other violence. On Sunday 15 April 2007, African Union peacekeepers were targeted and killed. ''The New York Times'' reported that "a confidential United Nations report says the government of Sudan is flying arms and heavy military equipment into Darfur in violation of Security Council resolutions and painting Sudanese military planes white to disguise them as United Nations or African Union aircraft." On 28 February Sudan's humanitarian affairs minister, Ahmed Haroun, and a Janjaweed militia leader, Ali Kushayb, were charged by theInternational Criminal Court
The International Criminal Court (ICC or ICCt) is an intergovernmental organization and international tribunal seated in The Hague, Netherlands. It is the first and only permanent international court with jurisdiction to prosecute individuals f ...
with 51 counts of war crimes and crimes against humanity. Ahmed Haroun said he "did not feel guilty," his conscience was clear, and that he was ready to defend himself.
On 31 March Janjaweed militiamen killed up to 400 people in the eastern border region of Chad near Sudan. The border villages of Tiero and Marena were encircled and then fired upon. The women were robbed and the men shot according to the UNHCR. Many of those who survived the initial attack, ended up dying due to exhaustion and dehydration, often while fleeing. On 14 April 2007, more attacks were reported by the UNHCR in Tiero and Marena.
On 18 April George W. Bush, President Bush gave a speech at the US United States Holocaust Memorial Museum, Holocaust Memorial Museum criticizing the Sudanese government and threatened further Economic sanctions, sanctions if the situation did not improve.
Al-Bashir and Deby signed a peace agreement on 3 May 2007 aimed at reducing tension between their countries. The accord was brokered by Saudi Arabia. It asserted that neither country would harbor, train or fund armed movements opposed to the other. Reuters reported that "Deby's fears that Mahamat Nouri, Nouri's UFDD may have been receiving Saudi as well as Sudanese support could have pushed him to sign the Saudi-mediated pact with Bashir". Colin Thomas-Jensen, an expert on Chad and Darfur at the International Crisis Group think-tank expressed doubts as to whether "this new deal will lead to any genuine thaw in relations or improvement in the security situation". Chadian rebel Union of Forces for Democracy and Development (UFDD) which had fought a hit-and-run war against Deby's forces in eastern Chad since 2006, stated that the Saudi-backed peace deal would not stop its military campaign.
Oxfam announced on 17 June that it would permanently pull out of Gereida, the largest refugee camp, holding more than 130,000. The agency cited inaction by local authorities from the Sudan Liberation Movement (SLM), which controls the region, in addressing security concerns and violence against aid workers. An employee of the Non Governmental Organization, NGO Action by Churches Together was murdered in June in West Darfur. Vehicle hijackings also made them consider leaving.
BBC News reported that a huge underground lake had been found. This find could eliminate the competition for water resources.
France and Britain announced they would push for a UN resolution to dispatch African Union and United Nations peacekeepers to Darfur and would push for an immediate cease-fire in Darfur and are prepared to provide "substantial" economic aid "as soon as a cease-fire makes it possible."
A 14 July 2007 article noted that in the past two months up to 75,000 Arabs from Chad and Niger had crossed into Darfur. Most have been relocated by Sudanese government to former villages of displaced non-Arab people.
A hybrid UN/AU force was finally approved on 31 July with the unanimously approved United Nations Security Council Resolution 1769. UNAMID was to take over from AMIS by 31 December at the latest, and had an initial mandate up to 31 July 2008.
On 31 July, Mahria gunmen surrounded mourners at the funeral of an important Terjem sheik and killed 60 with rocket-propelled grenades (RPGs) and belt-fed machine guns.
From 3–5 August a conference was held in Arusha to unite the rebel groups to streamline the subsequent peace negotiations with the government. Most senior rebel leaders attended, with the notable exception of Abdul Wahid al Nur
Abdul Wahid Mohamed al Nur (also Abdel Wahid el-Nur or Abdulwahid Mohammed Nour; ar, عبد الواحد محمد نور, ''ʿAbd al-Wāḥid Muḥammad Nūr''; born in 1968) is the leader of the rebel Sudan Liberation Movement (al Nur) faction ...
, who headed a rather small splinter group of the SLA/M that he had initially founded in 2003, was considered to be the representatives of a large part of the displaced Fur people. His absence was damaging to the peace talks. International officials stated that there is "no John Garang
John Garang de Mabior (June 23, 1945 – July 30, 2005) was a Sudanese politician and revolutionary leader. From 1983 to 2005, he led the Sudan People's Liberation Army (SPLA) after the Second Sudanese Civil War, the comprehensive peace agreeme ...
in Darfur", referring to the leader of the negotiating team of South Sudan
South Sudan (; din, Paguot Thudän), officially the Republic of South Sudan ( din, Paankɔc Cuëny Thudän), is a landlocked country in East Africa. It is bordered by Ethiopia, Sudan, Central African Republic, Democratic Republic of the ...
, who was universally accepted by the various South Sudanese rebel groups.
The participants were Gamali Galaleiddine, Khalil Abdalla Adam, Salah Abu Surra, Khamis Abdallah Abakar, Ahmed Abdulshafi Bassey, Ahmed Abdelshafi, Abdalla Yahya, Khalil Ibrahim (of the Justice and Equality Movement
The Justice and Equality Movement (JEM; ar, حركة العدل والمساواة, ') is an opposition group in Sudan founded by Khalil Ibrahim. Gibril Ibrahim has led the group since January 2012 after the death of Khalil, his brother, in Dec ...
) and Ahmed Ibrahim Ali Diraige. Closed-door meetings between the AU-UN and rebel leaders, as well as among rebel leaders took place. Eight more participants arrived on 4 August (including Jar el-Neby, Salah Adam Isaac and Suleiman Marajan), while the SLM Unity faction boycotted the talks because the Sudanese government had threatened to arrest Suleiman Jamous if he left the hospital. The rebel leaders aimed to unify their positions and demands, which included compensation for the victims and autonomy for Darfur. They eventually reached agreement on joint demands, including power and wealth sharing, security, land and humanitarian issues.
In the months through August, Arab tribes that had worked together in the Janjaweed militia began falling out among themselves, and further splintered. Thousands of Terjem and Mahria gunmen traveled hundreds of miles to fight in the strategic Bulbul river valley. Farther south, Habanniya and Salamat tribes clashed. The fighting did not result in as much killing as in 2003 and 2004. United Nations officials said the groups might be trying to seize land before peacekeepers arrived.
On 18 September, JEM stated that if the peace talks with Khartoum
Khartoum or Khartum ( ; ar, الخرطوم, Al-Khurṭūm, din, Kaartuɔ̈m) is the capital of Sudan. With a population of 5,274,321, its metropolitan area is the largest in Sudan. It is located at the confluence of the White Nile, flowing n ...
should fail, they would step up their demands from self-determination to independence.
On 30 September, the rebels Haskanita raids, overran an AMIS base, killing at least 12 peacekeepers in "the heaviest loss of life and biggest attack on the African Mission" during a raid at the end of Ramadan season.
Peace talks started on 27 October in Sirte, Libya. The following groups attended:
* Justice and Equality Movement splinters:
** Justice and Equality Movement–Collective Leadership, led by Bahr Idriss Abu Garda
** Justice and Equality Movement–Azraq, led by Idriss Ibrahim Azraq
** National Movement for Reform and Development
The National Movement for Reform and Development (NMRD) is a Sudanese rebel group based in the region of Darfur. The group was formed when it broke away from the Justice and Equality Movement in 2004. The NMRD came into existence because its foun ...
, led by Khalil Abdullah
* Revolutionary Democratic Forces Front, led by Salah Abu Surrah
* United Revolutionary Force Front, led by Alhadi Agabeldour
* Sudan Liberation Movement–G19, led by Khamees Abdullah
* Sudan Federal Democratic Alliance, led by Ahmed Ibrahim Diraige
The following groups did not attend:
* Justice and Equality Movement
The Justice and Equality Movement (JEM; ar, حركة العدل والمساواة, ') is an opposition group in Sudan founded by Khalil Ibrahim. Gibril Ibrahim has led the group since January 2012 after the death of Khalil, his brother, in Dec ...
, led by Khalil Ibrahim; they object to the presence of rebel groups they say had no constituency and no place at the table.
* Sudan Liberation Movement (Abdel Wahed), led by Abdel Wahed Mohamed el-Nur; the group has few forces, but its leader is highly respected; refused to attend until a force was deployed to stem the Darfur violence.
* Sudan Liberation Movement–Unity, originally led by Abdallah Yehya, includes many other prominent figures (Sherif Harir, Abu Bakr Kadu, Ahmed Kubur); the group with the largest number of rebel fighters; object for the same reason as JEM.
* Ahmed Abdel Shafi, a notable rebel enjoying strong support from the Fur tribe.
Faced with a boycott from the most important rebel factions, the talks were rebranded as an "advanced consultation phase", with official talks likely to start in November or December.
On 15 November, nine rebel groups – six SLM factions, the Democratic Popular Front, the Sudanese Revolutionary Front and the Justice and Equality Movement–Field Revolutionary Command – signed a Charter of Unification and agreed to operate under the name of SLM/A henceforth. On 30 November it was announced that Darfur's rebel movements had united into two large groups and were now ready to negotiate in an orderly manner with the government.
2008
A fresh government/militia offensive trapped thousands of refugees along the Chadian border, the rebels and humanitarian workers said on 20 February. As of 21 February, the total dead in Darfur stood at 450,000 with an estimated 3,245,000 people displaced. On 10 May 2008 Sudanese government soldiers and Darfur rebels clashed in the city of Omdurman, opposite the capital ofKhartoum
Khartoum or Khartum ( ; ar, الخرطوم, Al-Khurṭūm, din, Kaartuɔ̈m) is the capital of Sudan. With a population of 5,274,321, its metropolitan area is the largest in Sudan. It is located at the confluence of the White Nile, flowing n ...
, over the control of a military headquarters. They also raided a police base from which they stole police vehicles. A Sudanese police spokesperson said that the leader of the assailants, Mohamed Saleh Garbo, and his intelligence chief, Mohamed Nur Al-Deen, were killed in the clash.
Witnesses said that heavy gunfire could be heard in the west of Sudan's capital. Sudanese troops backed by tanks, artillery, and helicopter gunships were immediately deployed to Omdurman, and fighting raged for several hours. After seizing the strategic military airbase at Wadi-Sayedna, the Sudanese soldiers eventually defeated the rebels. A JEM force headed to the Al-Ingaz bridge to cross the White Nile into Khartoum. By late afternoon, Sudanese TV claimed that the rebels had been "completely repulsed", while showing live images of burnt vehicles and corpses on the streets.
The government imposed a curfew in Khartoum from 5 pm to 6 am, while aid agencies told their workers in the capital to stay indoors.
 Some 93 soldiers and 13 policemen were killed along with 30 civilians in the attack on Khartoum and Omdurman. Sudanese forces confirmed that they found the bodies of 90 rebels and had spotted dozens more strewn outside the city limits. While Sudanese authorities claimed that up to 400 rebels could have been killed, the rebels stated that they lost 45 fighters dead or wounded. Sudanese authorities also claimed to have destroyed 40 rebel vehicles and captured 17.
Some 93 soldiers and 13 policemen were killed along with 30 civilians in the attack on Khartoum and Omdurman. Sudanese forces confirmed that they found the bodies of 90 rebels and had spotted dozens more strewn outside the city limits. While Sudanese authorities claimed that up to 400 rebels could have been killed, the rebels stated that they lost 45 fighters dead or wounded. Sudanese authorities also claimed to have destroyed 40 rebel vehicles and captured 17.
2009
 Martin Luther Agwai, General Martin Agwai, head of the joint African Union-United Nations mission in Darfur, said the war was over in the region, although low-level disputes remained. There was still "Banditry, localised issues, people trying to resolve issues over water and land at a local level. But real war as such, I think we are over that," he said.
Martin Luther Agwai, General Martin Agwai, head of the joint African Union-United Nations mission in Darfur, said the war was over in the region, although low-level disputes remained. There was still "Banditry, localised issues, people trying to resolve issues over water and land at a local level. But real war as such, I think we are over that," he said.
2010 to 2012
In December 2010, representatives of the Liberation and Justice Movement, an umbrella organisation of ten rebel groups formed in February 2010, started a fresh round of talks with the Sudanese Government in Doha. A new rebel group, the Sudanese Alliance Resistance Forces in Darfur was formed and JEM planned further talks. Talks ended on 19 December with agreement only on basic principles; these included a regional authority and a referendum on autonomy. The possibility of a Darfuri Vice-President was discussed. In January 2011, the leader of the Liberation and Justice Movement, Dr. Tijani Sese, stated that the movement had accepted the core proposals of the Darfur peace document as proposed by the mediators in Doha. The proposals included a $300,000,000 compensation package for victims of atrocities in Darfur and special courts to conduct trials of persons accused of human rights violations. Proposals for a new Darfur Regional Authority were included. This authority would have an executive council of 18 ministers and would remain in place for five years. The current three Darfur states and state governments would continue to exist during this period. In February, the Sudanese Government rejected the idea of a single region headed by a vice-president from the region. On 29 January, the LJM and JEM leaders issued a joint statement affirming their commitment to the Doha negotiations and intention to attend the Doha forum on 5 February. The Sudanese government postponed decision to attend the forum due to beliefs that an internal peace process without the involvement of rebel groups might be possible. Later in February, the Sudanese Government agreed to return to Doha with a view to complete a new peace agreement by the end of that month. On 25 February, both LJM and JEM announced that they had rejected the peace document proposed by the mediators in Doha. The main sticking points were the issues of a Darfuri vice-president and compensation for victims. The Sudanese government did not comment on the peace document. On 9 March, it was announced that two more states would be established in Darfur: Central Darfur around Zalingei and Eastern Darfur around Ed Daein. The rebel groups protested and stated that this was a bid to further divide Darfur's influence. Advising both the LJM and JEM during the Doha peace negotiations was the Public International Law & Policy Group (PILPG). Led by Dr. Paul Williams (professor), Paul Williams and Matthew T. Simpson, PILPG's team provided legal support. In June, a new Darfur Peace Agreement (2011) was proposed by the Doha mediators. This agreement was to supersede the Darfur Peace Agreement#Abuja Agreement (2006), Abuja Agreement of 2005 and when signed, would halt preparations for a Darfur status referendum. The proposed document included provisions for a Darfuri Vice-President and an administrative structure that included three States of Sudan, states and a strategic regional authority, the Darfur Regional Authority. The agreement was signed by the Government of Sudan and the Liberation and Justice Movement on 14 July 2011. Little progress occurred after September 2012 and the situation slowly worsened and violence was escalating. The population of displaced Sudanese in IDP camps also increased.2013
South Darfur
South Darfur State ( ar, ولاية جنوب دارفور Wilāyat Ǧanūb Dārfūr; Janob Darfor) is one of the wilayat or states of Sudan. It is one of the five states that compose the region of Darfur in western Sudan.
Overview
Prior to the ...
capital of Nyala, Sudan, Nyala were taken by the SLA.
On 27 April, following weeks of fighting, a coalition that included SLA and JEM said that they had taken Um Rawaba in North Kordofan, outside Darfur, and that they were headed for Khartoum to topple the president. The head of an SLA faction, Abdel Wahid Mohammed al-Nur, called it "a significant shift in the war". An estimated 300,000 were displaced by violence from January through May.
In North Darfur, the Rezeigat tribe and the Beni Hussein group signed a peace deal during July after an eruption of violence between the two groups killed hundreds. Later in July, the Misseriya and Salamat Arab tribes announced a ceasefire after battles killed over 200 people. The UN security counsel also announced a review of its UNAMID mission.
During the first week of August, the Maalia claimed the Rezeigat had killed five members of their tribe in the southeastern region of Adila. They responded by seizing 400 Rizeigat cattle on 6 August. Community leaders intervened to prevent escalation. When the Maalia failed to return the cattle, violence broke out on 10 August. The Rezeigat attacked and reportedly destroyed a Maaliya compound. In the battle, 77 Maaliya and 36 Rezeigat were killed, and another 200 people were injured. Both sides said Land Cruiser vehicles were used in the battle. The Maaliya accused the Rezeigat of attacking and burning villages while employing "heavy weaponry". On 11 August, the fighting spread to several other areas in southeastern Darfur. The violence reportedly arose over a land dispute.
2014
On 19 March, peacekeepers said they had received recent reports of villages that were attacked and burned after the UN expressed concern over the increasing number of internally displaced persons. UNAMID said that the attacks were in Hashaba, about 100 kilometers north-west of the cityAl-Fashir
Al Fashir, Al-Fashir or El Fasher ( ar, الفاشر) is the capital city of North Darfur, Sudan. It is a large town in the Darfur region of northwestern Sudan, northeast of Nyala, Sudan.
"Al-Fashir" (description)
''Encyclopædia Brit ...
, the state capital of North Darfur.
In November, local media reported that 200 women and girls had been raped by Sudanese soldiers in Tabit (town), Tabit. Sudan denied it and did not permit the UN (who said their first inquiry was inconclusive "in part due to the heavy presence of military and police") to make another inquiry. An investigation by Human Rights Watch (HRW) released in February said 221 were raped by government soldiers in "a mass rape that could constitute crimes against humanity". Witnesses reported three separate operations were carried out in one and a half days. Property was looted, men arrested, residents beaten and women and girls raped. Most of the town's population are Fur people. It had been controlled by rebel forces previously but HRW found no evidence that the rebel fighters were in or close to the village when it was attacked.
3,300 villages were destroyed in 2014 in attacks on civilians according to the UN Panel of Experts. Government forces or those aligned with them were behind most attacks. There were more than 400,000 attacks during the first ten months of the year. The report said that it was "highly probable that civilian communities were targeted as a result of their actual or perceived affiliations with armed opposition groups" and that "such attacks were carried out with impunity".
2015
2016
In September 2016, the Sudanese government reportedly launched chemical weapon attacks on civilian populations in Darfur, killing at least 250 people; the majority of the victims were children. It is believed that the munitions contained mustard gas or other blister agents.2017
2018
Reports from UNAMID and the ACJPS, African Center for Justice and Peace Studies suggest that low-level violence continued in Darfur through early 2018, with Sudanese government forces attacking communities in the Jebel Marra area. As UNAMID forces began to be drawn down with an eye to exiting Darfur, there were competing views on the levels of unrest in the region: UN officials pointed to a significant reduction in the scale and distribution of violence in Darfur, while other NGOS such as Human Rights Watch, HRW highlighted persistent pockets of unrest. In 2018, Darfur was bombed and peace was signed; see 2019.2019
The August 2019 Draft Constitutional Declaration, signed by military and civilian representatives during the 2018–19 Sudanese protests, 2018–19 Sudanese Revolution, requires that a peace agreement be made in Darfur and other regions of armed conflict in Sudan within the first six months of the 39-month transition period to democratic civilian government. In December 2019, ''The Guardian'' reported that irrigation projects built around community-based weirs are enabling "green shoots of peace" to appear, helping to end this conflict. This project was conducted with funding from theEuropean Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational political and economic union of member states that are located primarily in Europe. The union has a total area of and an estimated total population of about 447million. The EU has often been de ...
and was overseen by the United Nations Environment Programme, United Nations Environmental Program.
2020
Janjaweed militia leader Ali Kushayb was arrested in the Central African Republic on 9 June 2020, thirteen years after he was charged by the International Criminal Court with 51 crimes against humanity and war crimes. 2020 Darfur attacks, Three mass shootings took place in Darfur in July 2020. On 31 August 2020, a peace deal was signed in Juba, South Sudan, between the Sovereignty Council of Sudan and several rebel groups, including the Sudan Revolutionary Front (SRF), Sudan Liberation Movement/Army (SLM),Justice and Equality Movement
The Justice and Equality Movement (JEM; ar, حركة العدل والمساواة, ') is an opposition group in Sudan founded by Khalil Ibrahim. Gibril Ibrahim has led the group since January 2012 after the death of Khalil, his brother, in Dec ...
, Transitional Revolutionary Council, and Sudan People's Liberation Movement-North (SPLM–N).
Under the terms of the agreement, the factions that signed will be entitled to three seats on the Sovereignty Council (Sudan), sovereignty council, a total of five ministers in the Cabinet of Sudan, transitional cabinet and a quarter of seats in the Transitional Legislative Council (Sudan), transitional legislature. At a regional level, signatories will be entitled between 30 and 40% of the seats on transitional legislatures of their home states or regions.
Notably absent were rebel factions led by Abdul Wahid al Nur
Abdul Wahid Mohamed al Nur (also Abdel Wahid el-Nur or Abdulwahid Mohammed Nour; ar, عبد الواحد محمد نور, ''ʿAbd al-Wāḥid Muḥammad Nūr''; born in 1968) is the leader of the rebel Sudan Liberation Movement (al Nur) faction ...
and Abdelaziz al-Hilu who refused to be part of the agreement. On 3 October 2020, the SRF, SPLM–N led by Malik Agar and SLM led by Minni Minnawi signed another peace deal with the Sudanese government, with the absence of both al Nur and al-Hilu. However, the deal included terms to integrate rebels into the security forces, and to grant them political representation and economic and land rights, in addition to a 10-year plan to invest $750 million to develop southern and western regions, and to guarantee the return for displaced people.
In December, Sudan started to deploy troops to South Darfur
South Darfur State ( ar, ولاية جنوب دارفور Wilāyat Ǧanūb Dārfūr; Janob Darfor) is one of the wilayat or states of Sudan. It is one of the five states that compose the region of Darfur in western Sudan.
Overview
Prior to the ...
"in large numbers", following recent tribal violence between the Masalit The Masalit (Masalit language, Masalit: ''masala/masara''; ar, ماساليت) are an ethnic group inhabiting western Sudan and eastern Chad. They speak the Masalit language
Overview
The Masalit primarily live in Geneina, the capital of west Darfu ...
and Fula people, Fula.
The United Nations and African Union peacekeeping mission (UNAMID) ended its mission on 31 December, with a complete withdrawal scheduled for 30 June. There are currently some 4,000 troops, 480 police advisers, 1,631 police, 483 international civilian staff, and 945 national civilian staff in the region.
2021
Fighting between Masalit people and Arab nomads in Al Geneina District, West Darfur, left 84 dead and 160 wounded, including soldiers, on 16 January. This was two weeks after the United Nations withdrew its peacekeepers from the region after 13 years. Based on a statement from the Darfur Bar Association, the fresh violence initiated after a member of an Arab tribe was stabbed by another member of the Masalit tribe. Following the unrest, a high profile delegation authorized by Sudanese Prime Minister Abdalla Hamdok was sent to the region in order to assess the situation. Separately, clashes were also reported to have erupted in the eastern part of Sudan on Thursday and Friday between two ethnic groups, the Beni Amer and Nuba atPort Sudan
Port Sudan ( ar, بور سودان, Būr Sūdān) is a port city in eastern Sudan, and the capital of the state of Red Sea. , it has 489,725 residents. Located on the Red Sea, Port Sudan is recognized as Sudan's main seaport and the source of 90% ...
.
On 17 January, a curfew was put in place by the Sudanese authorities, including a state of emergency in Sudan’s West Darfur region.
As of 18 January, the death toll was reported to have reached at least 129 people, including women and children, since the beginning of the clashes between the Arabs and non-Arabs in West Darfur on Friday, according to the ABC News.
However, the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
has urged the Sudanese government to see to the de-escalation of the violence in West Darfur and safeguard civilian lives.
On 20 January, the residence of the provincial Governor of West Darfur Mohammed Abdalla al-Douma, was under an attempted attack by unidentified gunmen. Security forces managed to repel the attack without any reports of casualties or destruction of properties. Meanwhile, reports from local media suggested that during the assassination attempt, several blasts were heard all over the state.
On 24 January, the UN refugee agency revealed that since the initial outbreak of tribal clashes in Darfur earlier this January, at least 250 people have lost their lives. Three humanitarian workers were also among those who were killed, the agency added. Also, more than 100,000 people are believed to have been displaced, fleeing into neighboring Chad, with about 3,500 of them being mostly women and children.
On 28 March, Al-Hilu, leader of SPLA-North, signed a peace agreement with the Sudanese government in Juba, South Sudan, which would guarantee freedom of religion in a civil, democratic Sudan that would also have a single unified army to protect national security.
On 5 April, fresh tribal clashes erupted in West Darfur’s El Geneina, which led to the death of at least 40 people, the United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoniz ...
revealed.During the three days of clashes, at least 58 people were also said to have been injured, according to the VOA News. Later in the evening, Sudan’s defense council declared a state of emergency and also deployed troops to the troubled region of West Darfur state.
As of 6 April, the West Darfur State Doctors' Committee reported that the death toll had reached 50, with 132 others injured, according to the Middle East Online. According to the UN, reports suggest that there has been the destruction of humanitarian facilities, civilian lives, including women and children, during the violence in the region. Also, the decision to declare a state of emergency in the region was applauded by the UN envoy for Sudan, Volker Peretz and he urged the government to ensure the protection of humanitarian organizations, so as to provide services to the victims of the violence.
On 7 April, 37 more deaths were recorded by the Sudanese doctors’ committee in West Darfur, increasing the total death toll to 87, according to Al Jazeera.
On 8 April, the governor of the West Darfur state, Mohamed Abdallah Douma stated in a news conference that at least 132 people had been killed during the days of unrest in the state. However, the Western Darfur State Doctors Committee has placed the death toll to be at least 125 during the sixth day of tribal clashes consecutively, with 208 others wounded, according to CNN.
The UN has called on the authorities to ensure that citizens are protected and that an immediate investigation of the clashes is launched. They also maintained that all the perpetrators of the violence must be held responsible, in order to attain justice for those affected during the clashes, including immediate deployment of security forces to the region.
On 12 April, following several days of violence in West Darfur that led to the death of at least 144 people, the leader of Sudan reportedly visited the region, according to ABC News. Meanwhile, the head of the ruling sovereign council, Gen. Abdel-Fattah Burhan, including high-ranking security and military officials, also visited the provincial capital of West Darfur, Genena, where they held separate talks with the Arab Rizeigat and the non-Arab Masalit tribes. After the visit made by the Khartoum delegation, the Dar Masalit Displaced People expressed their refusal to accept the result of the mediation headed by El Burhan. They blamed the paramilitary Rapid Support Forces for the unrest in the region.
On 14 April, a statement released by the U.N. refugee agency confirmed that the violence in the capital of West Darfur, El Geneina had stopped, based on reports which suggested that there haven’t been any shootings for the past four days. The days of deadly tribal clashes have compelled at least 1,860 people to flee into the neighboring Chad, the agency added. Most of the refugees are believed to be women, children, and the elderly. Babar Baloch, a spokesman for the UN High Commissioner for Refugees (UNHCR) maintained that the refugees arriving revealed that their homes and properties were being destroyed.
On 28 April, clashes reportedly erupted during a sit-in protest in South Darfur’s Bielel between security forces and protesters. In an attempt by the Sudanese security forces to forcefully disperse the protesters, one woman was said to have been killed while leaving at least eight others wounded. Tear gas was said to have been used to disperse the crowd by a joint force from both the army and the police, including the firing of live rounds.
Meanwhile, at the secretariat of the state government in Nyala, Sudan, Nyala, protesters gathered in front of the building to protest against an attack on their village, Gassat Enjemet, which left three people dead and others wounded.
On 5 May, thousands of displaced people affected by the heavy clashes in El Geneina, have requested that they want to go back to their homes. They made the request due to the awful living conditions in their shelters, the acting governor of West Darfur, Mohamed Zakaria revealed.
On 29 May, a group of armed men reportedly opened fire in a market in West Darfur’s Foro Baranga. As a result of the shooting, one person was said to have been killed, leaving five others seriously wounded. Angry protests erupted following the attack, with protesters setting many shops ablaze and also blocking all main roads leading to the town. According to Al Jazeera, some people threatened the doctors at the hospital to attend to their wounded patients and leave other patients.
On 5 June, clashes between the Arab Taisha and ethnic African Fallata tribes in South Darfur’s Um Dafuq claimed the lives of at least 36 people, with 37 others wounded. An aid worker who spoke on the condition of anonymity revealed that the clash erupted as a result of a land dispute between the two conflicting parties. Subsequently, a certain state of calm was said to have been attained, following the deployment of more troops to the South Darfur’s Um Dafuk.
Janjaweed participation
 The well-armed Janjaweed quickly gained an advantage over rebel factions. By the spring of 2004, several thousand people – mostly from the non-Arab population – had been killed and as many as a million more had been driven from their homes, causing a major humanitarian crisis. The crisis took on an international dimension when over 100,000 refugees poured into neighboring Chad, pursued by militiamen who clashed with Chadian government forces along the border. More than 70 militiamen and 10 Chadian soldiers were killed in one gun battle in April. A United Nations observer team reported that non-Arab villages were singled out, while Arab villages were left untouched:
The well-armed Janjaweed quickly gained an advantage over rebel factions. By the spring of 2004, several thousand people – mostly from the non-Arab population – had been killed and as many as a million more had been driven from their homes, causing a major humanitarian crisis. The crisis took on an international dimension when over 100,000 refugees poured into neighboring Chad, pursued by militiamen who clashed with Chadian government forces along the border. More than 70 militiamen and 10 Chadian soldiers were killed in one gun battle in April. A United Nations observer team reported that non-Arab villages were singled out, while Arab villages were left untouched:
The 23 Fur villages in the Shattaya Administrative Unit have been completely depopulated, looted and burnt to the ground (the team observed several such sites driving through the area for two days). Meanwhile, dotted alongside these charred locations are unharmed, populated and functioning Arab settlements. In some locations, the distance between a destroyed Fur village and an Arab village is less than 500 meters.A 2011 study examined 1,000 interviews with black African participants who fled from 22 village clusters to various refugee camps in 2003 and 2004. The study found: 1) the frequency of hearing racial epithets during an attack was 70% higher when it was led by the Janjaweed alone compared to official police forces; it was 80% higher when the Janjaweed and the Sudanese Government attacked together; 2) the risk of displacement was nearly 110% higher during a joint attack compared to when the police or Janjaweed acted alone, and 85% higher when Janjaweed forces attacked alone compared to when the attack was only perpetrated by government forces; 3) attacks on food and water supplies made it 129% more likely for inhabitants to be displaced compared to attacks that involved house burnings or killings; 4) perpetrators knew and took "special advantage" of the susceptibility of Darfur residents to attacks focused on basic resources. This vulnerability came against the backdrop of increased regional desertification.
Rape of women and young girls
 Immediately after the Janjaweed entered the conflict, the rape of women and young girls, often by multiple militiamen and often throughout entire nights, began to be reported at a staggering rate. Children as young as 2 years old were reported victims, while mothers were assaulted in front of their children. Young women were attacked so violently that they were unable to walk following the attack.
Non-Arab people were reportedly raped by Janjaweed militiamen as a result of the Sudanese government's goal of completely eliminating the presence of black Africans and non-Arabs from Darfur. The Washington Post Foreign Service interviewed verified victims of the rapes and recorded that Arabic terms such as "abid" and "zurga" were used, which mean slave and black. One victim, Sawelah Suliman, was told by her assailant, "Black girl, you are too dark. You are like a dog. We want to make a light baby." In an 88-page report, victims from Darfur have also accused the Rapid Support Forces of rape and assault as recently as 2015.
Immediately after the Janjaweed entered the conflict, the rape of women and young girls, often by multiple militiamen and often throughout entire nights, began to be reported at a staggering rate. Children as young as 2 years old were reported victims, while mothers were assaulted in front of their children. Young women were attacked so violently that they were unable to walk following the attack.
Non-Arab people were reportedly raped by Janjaweed militiamen as a result of the Sudanese government's goal of completely eliminating the presence of black Africans and non-Arabs from Darfur. The Washington Post Foreign Service interviewed verified victims of the rapes and recorded that Arabic terms such as "abid" and "zurga" were used, which mean slave and black. One victim, Sawelah Suliman, was told by her assailant, "Black girl, you are too dark. You are like a dog. We want to make a light baby." In an 88-page report, victims from Darfur have also accused the Rapid Support Forces of rape and assault as recently as 2015.
Mortality figures
 Multiple casualty estimates have been published since the war began, ranging from roughly 10,000 civilians (Sudan government) to hundreds of thousands.
In September 2004, 18 months after the conflict began, the World Health Organization estimated that there had been 50,000 deaths in Darfur, mostly due to starvation. An updated estimate published the following month put the number of deaths for the 6-month period from March to October 2004 due to starvation and disease at 70,000; These figures were criticized because they only considered short periods and did not include deaths from violence. A more recent British Parliamentary Report estimated that over 300,000 people had died and others have published even higher death toll estimates.
In March 2005, the UN's Under-Secretary-General for Humanitarian Affairs and Emergency Relief Coordinator, Emergency Relief Coordinator Jan Egeland estimated that 10,000 people were dying each month, excluding deaths due to ethnic violence. An estimated 2.7 million people had at that time been displaced from their homes, mostly seeking refuge in camps in Darfur's major towns. Two hundred thousand had fled to neighboring Chad. Reports of violent deaths compiled by the UN indicate between 6,000 and 7,000 fatalities from 2004 to 2007.
In May 2005, the Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters (CRED) of the School of Public Health of the Université catholique de Louvain in Brussels, Belgium published an analysis of mortality in Darfur. Their estimate stated that from September 2003 to January 2005, between 98,000 and 181,000 persons died in Darfur, including 63,000 to 146,000 excess deaths.
In August 2010, Dr. Eric Reeves argued that total mortality from all violent causes, direct and indirect, at that point in the conflict, exceeded 500,000. His analysis took account of all previous mortality data and studies, including that by the Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disaster.Quantifying Genocide in Darfur
Multiple casualty estimates have been published since the war began, ranging from roughly 10,000 civilians (Sudan government) to hundreds of thousands.
In September 2004, 18 months after the conflict began, the World Health Organization estimated that there had been 50,000 deaths in Darfur, mostly due to starvation. An updated estimate published the following month put the number of deaths for the 6-month period from March to October 2004 due to starvation and disease at 70,000; These figures were criticized because they only considered short periods and did not include deaths from violence. A more recent British Parliamentary Report estimated that over 300,000 people had died and others have published even higher death toll estimates.
In March 2005, the UN's Under-Secretary-General for Humanitarian Affairs and Emergency Relief Coordinator, Emergency Relief Coordinator Jan Egeland estimated that 10,000 people were dying each month, excluding deaths due to ethnic violence. An estimated 2.7 million people had at that time been displaced from their homes, mostly seeking refuge in camps in Darfur's major towns. Two hundred thousand had fled to neighboring Chad. Reports of violent deaths compiled by the UN indicate between 6,000 and 7,000 fatalities from 2004 to 2007.
In May 2005, the Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters (CRED) of the School of Public Health of the Université catholique de Louvain in Brussels, Belgium published an analysis of mortality in Darfur. Their estimate stated that from September 2003 to January 2005, between 98,000 and 181,000 persons died in Darfur, including 63,000 to 146,000 excess deaths.
In August 2010, Dr. Eric Reeves argued that total mortality from all violent causes, direct and indirect, at that point in the conflict, exceeded 500,000. His analysis took account of all previous mortality data and studies, including that by the Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disaster.Quantifying Genocide in DarfurDr. Eric Reeves, 28 April 2006 The UN disclosed on 22 April 2008 that it might have underestimated the Darfur death toll by nearly 50%. In July 2009, ''The Christian Science Monitor'' published an op-ed stating that many of the published mortality rates have been misleading because they include a large number of people who had died of disease and malnutrition, as well as those who died from direct violence.The Genocide in Darfur is not what it seems
Dr. Marc Gustafson, 19 August 2009 In January 2010, the Centre for Research on the Epidemiology of Disasters published an article in a special issue of ''The Lancet''. The article, entitled "Patterns of mortality rates in Darfur conflict", estimated with 95% confidence that the excess number of deaths is between 178,258 and 461,520 (with a mean of 298,271), with 80% of these due to disease.
International response
 International attention to the Darfur genocide largely began with reports by Amnesty International in July 2003 and the International Crisis Group in December 2003. However, widespread media coverage did not start until the outgoing United Nations Resident and Humanitarian Coordinator for Sudan, Mukesh Kapila, called Darfur the "world's greatest humanitarian crisis" in March 2004.Prunier, pp. 124–148 Organizations such as STAND: A Student Anti-Genocide Coalition, later under the umbrella of Genocide Intervention Network, and the Save Darfur Coalition emerged and became particularly active in the areas of engaging the United States Congress and President on the issue and pushing for divestment, initially launched by Adam Sterling under the auspices of the Sudan Divestment Task Force.
International attention to the Darfur genocide largely began with reports by Amnesty International in July 2003 and the International Crisis Group in December 2003. However, widespread media coverage did not start until the outgoing United Nations Resident and Humanitarian Coordinator for Sudan, Mukesh Kapila, called Darfur the "world's greatest humanitarian crisis" in March 2004.Prunier, pp. 124–148 Organizations such as STAND: A Student Anti-Genocide Coalition, later under the umbrella of Genocide Intervention Network, and the Save Darfur Coalition emerged and became particularly active in the areas of engaging the United States Congress and President on the issue and pushing for divestment, initially launched by Adam Sterling under the auspices of the Sudan Divestment Task Force.
 In May 2009 the Mandate Darfur was canceled because the "Sudanese government is obstructing the safe passage of Darfurian delegates from Sudan." The Mandate was a conference that would have brought together 300 representatives from different regions of Darfur's civil society. The conference planned was to be held in Addis Ababa sometime in early May.
In May 2009 the Mandate Darfur was canceled because the "Sudanese government is obstructing the safe passage of Darfurian delegates from Sudan." The Mandate was a conference that would have brought together 300 representatives from different regions of Darfur's civil society. The conference planned was to be held in Addis Ababa sometime in early May.
International Criminal Court
In March 2005, the UN Security Council formally referred the situation in Darfur to the Prosecutor of the International Criminal Court, taking into account the report of the International Commission of Inquiry on Darfur, authorized by United Nations Security Council Resolution 1564 of 2004, but without mentioning specific crimes. Two permanent members of the Security Council, the United States and China, abstained from the vote on the referral resolution. In April 2007, the Judges of theInternational Criminal Court
The International Criminal Court (ICC or ICCt) is an intergovernmental organization and international tribunal seated in The Hague, Netherlands. It is the first and only permanent international court with jurisdiction to prosecute individuals f ...
issued arrest warrants against the former Minister of State for the Interior, Ahmed Haroun, and a Janjaweed leader, Ali Kushayb, for crimes against humanity and war crimes. The Sudan Government said that the ICC had no jurisdiction to try Sudanese citizens and that it would not surrender the two men.
On 14 July 2008, the Prosecutor filed ten charges of war crimes against Sudan's incumbent President Omar al-Bashir, including three counts of genocide, five of crimes against humanity and two of murder. The Prosecutor claimed that Mr. al-Bashir "masterminded and implemented a plan to destroy in substantial part" three tribal groups in Darfur because of their ethnicity. Leaders from three Darfur tribes sued ICC prosecutor Luis Moreno Ocampo for libel, defamation, and igniting hatred and tribalism.
After an arrest warrant was issued for the Sudanese president in March 2009, the Prosecutor appealed to add genocide charges. However, the Pre-Trial Chamber found that there was no reasonable ground to support the contention that he had a specific intent to commit genocide (''dolus specialis''), which is an intention to destroy, in whole or in part, a protected group. The definition adopted by the Pre-Trial Chamber is the definition of the Genocide Convention, the Rome Statute, and some ICTY cases. On 3 February 2010 the Appeals Chamber of the ICC found that the Pre-Trial Chamber had applied "an erroneous standard of proof when evaluating the evidence submitted by the Prosecutor" and that the Prosecutor's application for a warrant of arrest on the genocide charges should be sent back to the Pre-Trial Chamber to review based on the correct legal standard. In July 2010, al-Bashir was charged with three counts of genocide in Darfur by the International Criminal Court
The International Criminal Court (ICC or ICCt) is an intergovernmental organization and international tribunal seated in The Hague, Netherlands. It is the first and only permanent international court with jurisdiction to prosecute individuals f ...
for orchestrating the Darfur genocide.
Al-Bashir was the first incumbent head of state charged with crimes under the Rome Statute. He rejected the charges and said, "Whoever has visited Darfur, met officials and discovered their ethnicities and tribes ... will know that all of these things are lies."
It is expected that al-Bashir will not face trial in The Hague until he is apprehended in a nation which accepts ICC jurisdiction, as Sudan is not a party to the Rome Statute, which it signed but did not ratify. Payam Akhavan, a professor of international law at McGill University in Montreal and a former war crimes prosecutor, says although he may not go to trial, "He will effectively be in prison within the Sudan itself...Al-Bashir now is not going to be able to leave the Sudan without facing arrest." The Prosecutor warned that authorities could arrest the President if he enters international airspace. The Sudanese government has announced that the Presidential plane would be accompanied by jet fighters. However, the Arab League announced solidarity with al-Bashir. Since the warrant, he has visited Qatar and Egypt. The African Union also condemned the charges.
Some analysts think that the ICC indictment is counterproductive and harms the peace process. Only days after the ICC indictment, al-Bashir expelled 13 international aid organizations from Darfur and disbanded three domestic aid organizations. In the aftermath of the expulsions, conditions in the displaced camps deteriorated. Previous ICC indictments, such as the arrest warrants of the LRA leadership in the ongoing war in northern Uganda, were also accused of harming peace processes by criminalizing one side of a war.
Foreign support for the Sudanese government
Al-Bashir sought the assistance of non-western countries after the West, led by America, imposed sanctions against him. He said, "From the first day, our policy was clear: To look eastward, toward China, Malaysia, India, Pakistan, Indonesia, and even Korea and Japan, even if the Western influence upon some [of these] countries is strong. We believe that the Chinese expansion was natural because it filled the space left by Western governments, the United States, and international funding agencies. The success of the Sudanese experiment in dealing with China without political conditions or pressures encouraged other African countries to look toward China." In 2007, Amnesty International issued a report accusing China and Russia of supplying arms, ammunition and related equipment to Sudan, some of which the government may have transferred to Darfur in violation of a UN arms embargo. The report claims that Sudan imported 10–20 combat aircraft from China in the early-mid-2000s, including three Nanchang Q-5, A-5 Fantan fighters that have been sighted in Darfur. The report provides evidence that the Sudan Air Force conducted indiscriminate aerial bombings of villages in Darfur and eastern Chad using ground attack fighters and repurposed Antonov transport planes. However, it does not specify whether the ground attack fighters in question are those purchased from China in the early-mid-2000s, and the Antonovs' origin remains unclear. The report also lists seven Soviet- or Russian-made Mi-24 Hind gunships that had been deployed to Darfur, though without specifying which country sold them to Sudan, or when. While noting that Russia sold arms worth tens of millions of dollars to Sudan in 2005 alone, the report does not specifically identify any weapons sold to Sudan by Russia after the outbreak of the Darfur conflict or after the imposition of the UNSC ban on arms transfers to Darfur, and it does not provide any evidence that any such weapons were deployed to Darfur. The NGO Human Rights First claimed that over 90% of the light weapons currently being imported by Sudan and used in the conflict are from China. Human rights advocates and opponents of the Sudanese government portray China's role in providing weapons and aircraft as a cynical attempt to obtain oil, just as colonial powers once supplied African chieftains with the military means to maintain control as they extracted natural resources.According to China's critics, China threatened to use its veto on the U.N. Security Council to protect Khartoum from sanctions and was able to water down every resolution on Darfur in order to protect its interests. Accusations of the supply of weapons from China, which were then transferred to Darfur by the Sudanese government in violation of the UN arms embargo, continued in 2010. Sarah Wykes, a senior campaigner at Global Witness, an NGO that campaigns for better natural resource governance, says: "Sudan has purchased about $100m in arms from China and has used these weapons against civilians in Darfur." According to the report Following the Thread: Arms and Ammunition Tracing in Sudan and South Sudan, released in May 2014 by the Swiss research group Small Arms Survey, "Over the period 2001–12, Khartoum's reports to UN Comtrade reveal significant fluctuation in annual conventional arms imports. The majority of the Sudanese government's total self-reported imports of small arms and light weapons, their ammunition, and ‘conventional weapons’ over the period originated in China (58 per cent), followed by Iran (13 per cent), St. Vincent and the Grenadines (9 per cent), and Ukraine (8 per cent)." The report found that Chinese weapons were pervasive among most parties to the Sudanese conflicts, including the war in Darfur, but identified few if any weapons of Russian origin. (The section "Chinese weapons and ammunition" receives 20 pages in the report, whereas the only mention of Russian arms is to be found in the sentence "the majority of...mines [in South Sudan] have been of Chinese and Soviet/Russian origin."). China and Russia denied they had broken UN sanctions. China has a close relationship with Sudan and increased its military co-operation with the government in early 2007. Because of Sudan's plentiful supply of oil, China considers good relations with Sudan to be a strategic necessity. China has direct commercial interests in Sudan's oil. China's state-owned company CNPC controls between 60 and 70 percent of Sudan's total oil production. Additionally, it owns the largest single share (40 percent) of Sudan's national oil company, Greater Nile Petroleum Operating Company. China consistently opposed economic and non-military sanctions on Sudan. In March 2007, threats of boycotting the Olympic games came from French presidential candidate François Bayrou, in an effort to stop China's support. Sudan divestment efforts concentrated on PetroChina, the national petroleum company with extensive investments in Sudan.
Criticism of international response
Gérard Prunier, a scholar specializing in African conflicts, argued that the world's most powerful countries have limited themselves to expressing concern and demand for the United Nations to take action. The UN, lacking initiative and will, initially left the African Union to deploy a token force without a mandate to protect civilians. On 16 October 2006, Minority Rights Group International, Minority Rights Group (MRG) published a critical report, challenging that the UN and the great powers could have prevented the crisis and that few lessons appeared to have been drawn from theRwandan genocide
The Rwandan genocide occurred between 7 April and 15 July 1994 during the Rwandan Civil War. During this period of around 100 days, members of the Tutsi minority ethnic group, as well as some moderate Hutu and Twa, were killed by armed H ...
. MRG's executive director, Mark Lattimer, stated that: "this level of crisis, the killings, rape and displacement could have been foreseen and avoided ... Darfur would just not be in this situation had the UN systems got its act together after Rwanda: their action was too little too late." On 20 October 120 genocide survivors of The Holocaust, and the Khmer Rouge period (1975–1979), Cambodian and Rwandan genocides, backed by six aid agencies, submitted an open letter to the European Union, calling on them to do more, proposing a UN peacekeeping force as "the only viable option."
In the media
''Watchers of the Sky'', a 2014 documentary by Edet Belzberg, interviews former journalist and United States Ambassador to the United Nations Samantha Power about the war in Darfur. Also featured is Luis Moreno Ocampo, former International Criminal Court, ICC jurist and lead prosecutor on the International Criminal Court investigation in Darfur, ICC investigation in Darfur. Brutality of militias, violence used by armed forces, corruption and human right abuse were also shown in ER (TV series), ''ER'' television series (e.g. episodes 12x19, 12x20), and in 2007 documentaries ''They Turned Our Desert Indo Fire'' and ''The Devil Came on Horseback''.See also
*Banu Hilal
The Banu Hilal ( ar, بنو هلال, translit=Banū Hilāl) was a confederation of Arabian tribes from the Hejaz and Najd regions of the Arabian Peninsula that emigrated to North Africa in the 11th century. Masters of the vast plateaux of t ...
* Bibliography of the Darfur conflict
* Boswells School
* Breidjing Camp
* Chadian Civil War (2005–10)
* Command responsibility
* Darfur genocide
The Darfur genocide is the systematic killing of ethnic Darfuri people which has occurred during the ongoing conflict in Western Sudan. It has become known as the first genocide of the 21st century. The genocide, which is being carried out agai ...
* Genocides in history
* List of civil wars
* List of famines
* List of wars 2003–present
* List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll
* Lost Boys of Sudan
* Second Sudanese Civil War
The Second Sudanese Civil War was a conflict from 1983 to 2005 between the central Sudanese government and the Sudan People's Liberation Army. It was largely a continuation of the First Sudanese Civil War of 1955 to 1972. Although it originated ...
* Slavery in Sudan
* Team Darfur
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * *External links
*Photographer's Account – "The Cost of Silence: A Traveling Exhibition"
{{DEFAULTSORT:Darfur War Conflicts in 2022 2000s conflicts 2000s in Sudan 2010s conflicts 2010s in Sudan War in Darfur, Civil wars post-1945 Ethnicity-based civil wars Responsibility to protect Proxy wars Genocides in Africa