DN Geminorum on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
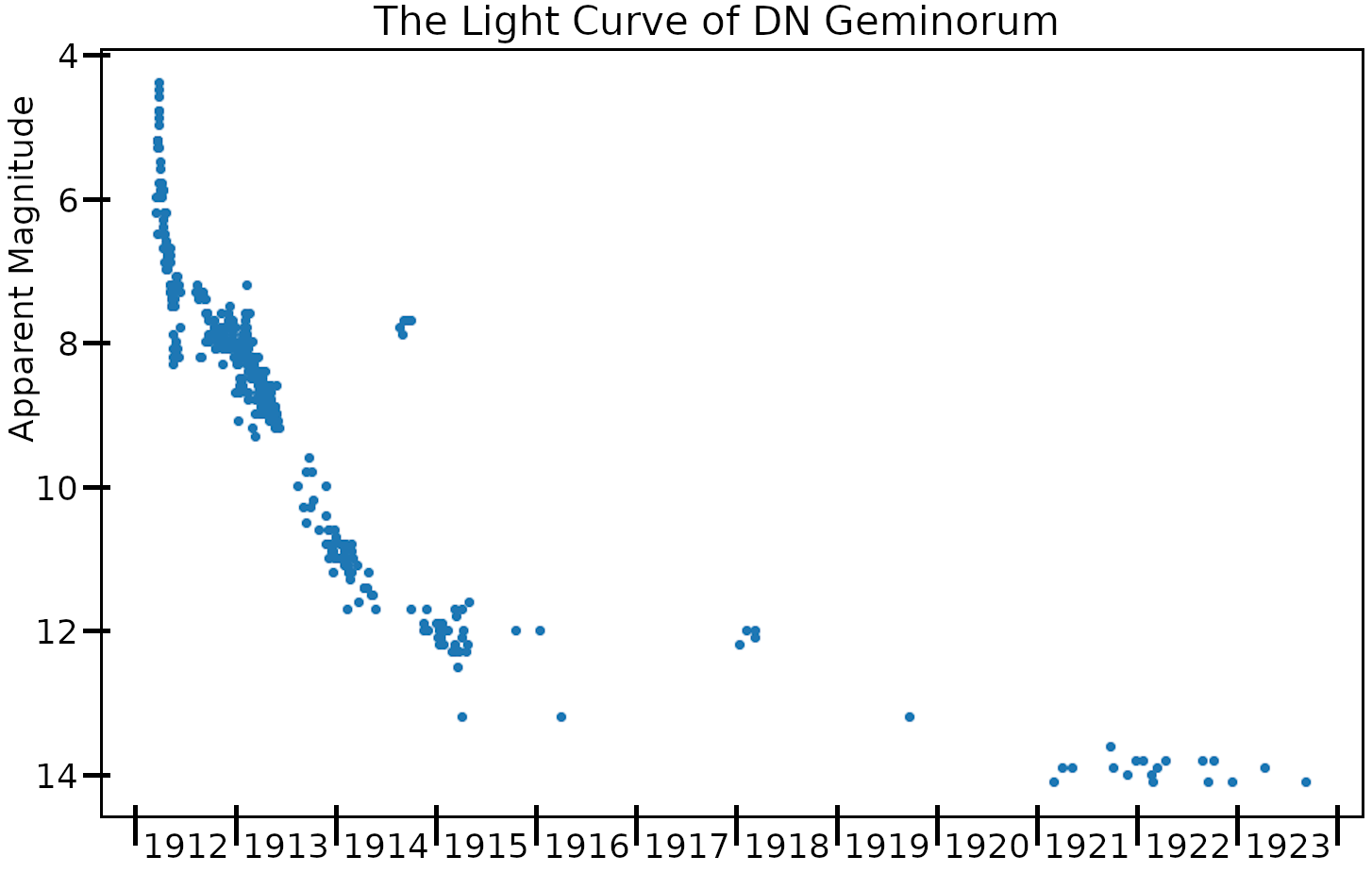 DN Geminorum or Nova Geminorum 1912 was a classical nova which lit up in 1912 in the constellation
DN Geminorum or Nova Geminorum 1912 was a classical nova which lit up in 1912 in the constellation
 DN Geminorum or Nova Geminorum 1912 was a classical nova which lit up in 1912 in the constellation
DN Geminorum or Nova Geminorum 1912 was a classical nova which lit up in 1912 in the constellation Gemini
Gemini may refer to:
Space
* Gemini (constellation), one of the constellations of the zodiac
** Gemini in Chinese astronomy
* Project Gemini, the second U.S. crewed spaceflight program
* Gemini Observatory, consisting of telescopes in the Norther ...
. It was discovered by Norwegian variable star observer Sigurd Einbu on March 12, 1912 before reaching peak brightness, which allowed early-stage spectra to be collected by Yerkes Observatory
Yerkes Observatory ( ) is an astronomical observatory located in Williams Bay, Wisconsin, United States. The observatory was operated by the University of Chicago Department of Astronomy and Astrophysics from its founding in 1897 to 2018. Owner ...
. The nova reached a maximum brightness of around 3.5 mag Mag, MAG or mags may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* ''MAG'' (video game), 2010
* ''Mag'' (Slovenian magazine), 1995–2010
* '' The Mag'', a British music magazine
Businesses and organisations
* MacKenzie Art Gallery, in Regina, Sask ...
before declining, which means it was visible to the naked eye. Its brightness decreased over the following 36 days by 3 magnitudes as it gradually faded from sight. The light curve
In astronomy, a light curve is a graph of light intensity of a celestial object or region as a function of time, typically with the magnitude of light received on the y axis and with time on the x axis. The light is usually in a particular frequ ...
saw two maxima a few months after the outburst, along with strong oscillations. Today its brightness is visual magnitude 15.5.
This is a close binary star system consisting of a white dwarf
A white dwarf is a stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very dense: its mass is comparable to the Sun's, while its volume is comparable to the Earth's. A white dwarf's faint luminosity comes ...
with 93% of the Sun's mass
The solar mass () is a standard unit of mass in astronomy, equal to approximately . It is often used to indicate the masses of other stars, as well as stellar clusters, nebulae, galaxies and black holes. It is approximately equal to the mass of ...
– the source for the nova explosion – and a lower mass red dwarf companion from which the white dwarf is accreting matter. The system is located approximately 4,500 light years from the Sun based on parallax, with its visual magnitude being diminished by an extinction
Extinction is the termination of a kind of organism or of a group of kinds (taxon), usually a species. The moment of extinction is generally considered to be the death of the last individual of the species, although the capacity to breed and ...
of due to interstellar dust
Cosmic dust, also called extraterrestrial dust, star dust or space dust, is dust which exists in outer space, or has fallen on Earth. Most cosmic dust particles measure between a few molecules and 0.1 mm (100 micrometers). Larger particles are c ...
. Observations of this system showed a sinusoidal variation in luminosity with a period of , which is likely the orbital period
The orbital period (also revolution period) is the amount of time a given astronomical object takes to complete one orbit around another object. In astronomy, it usually applies to planets or asteroids orbiting the Sun, moons orbiting planets ...
for the pair. This oscillation may be caused by irradiation of the companion star by the white dwarf.
References
{{Novae Novae Gemini (constellation) 050480 Geminorum, DN 1912 in science