Crwth on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The crwth (, also called a crowd or rote or crotta) is a bowed
 The name ' is Welsh, derived from a
The name ' is Welsh, derived from a
 A variety of string instruments so designated are thought to have been played in Wales since at least Roman times. Continuous, clear records of the use of ''crwth'' to denote an instrument of the
A variety of string instruments so designated are thought to have been played in Wales since at least Roman times. Continuous, clear records of the use of ''crwth'' to denote an instrument of the
Website of Bob Evans (Bragod)
Fflach record label
Website AuraInstruments of Medieval Instruments makers (Slovakia)
Bibliography and scholarly literature by J. Marshall Bevil
Article about last remaining crwths and their sound chamber beneath the fingerboard.
{{Authority control Bowed lyres Early musical instruments English musical instruments Welsh musical instruments Celtic musical instruments String instruments with sympathetic strings Welsh music history
lyre
The lyre () is a string instrument, stringed musical instrument that is classified by Hornbostel–Sachs as a member of the History of lute-family instruments, lute-family of instruments. In organology, a lyre is considered a yoke lute, since it ...
, a type of stringed instrument, associated particularly with Welsh music, now archaic but once widely played in Europe. Four historical examples have survived and are to be found in St Fagans National Museum of History
St Fagans National Museum of History ( ; cy, Sain Ffagan: Amgueddfa Werin Cymru, links=no), commonly referred to as St Fagans after the village where it is located, is an open-air museum in Cardiff chronicling the historical lifestyle, cultur ...
(Cardiff
Cardiff (; cy, Caerdydd ) is the capital city, capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of Wales. It forms a Principal areas of Wales, principal area, officially known as the City and County of Cardiff ( cy, Dinas a ...
); National Library of Wales
The National Library of Wales ( cy, Llyfrgell Genedlaethol Cymru), Aberystwyth, is the national legal deposit library of Wales and is one of the Welsh Government sponsored bodies. It is the biggest library in Wales, holding over 6.5 million ...
(Aberystwyth
Aberystwyth () is a university and seaside town as well as a community in Ceredigion, Wales. Located in the historic county of Cardiganshire, means "the mouth of the Ystwyth". Aberystwyth University has been a major educational location i ...
); Warrington Museum & Art Gallery
Warrington Museum & Art Gallery is on Bold Street in the Cultural Quarter of Warrington in a
Grade II listed building that it shares with the town's Central Library. The Museum and the Library originally opened in 1848 as the first rate-sup ...
; and the Museum of Fine Arts, Boston
The Museum of Fine Arts (often abbreviated as MFA Boston or MFA) is an art museum in Boston, Massachusetts. It is the 20th-largest art museum in the world, measured by public gallery area. It contains 8,161 paintings and more than 450,000 works ...
(US).
Origin of the name
 The name ' is Welsh, derived from a
The name ' is Welsh, derived from a Proto-Celtic
Proto-Celtic, or Common Celtic, is the ancestral proto-language of all known Celtic languages, and a descendant of Proto-Indo-European. It is not attested in writing but has been partly reconstructed through the comparative method. Proto-Celt ...
noun ''*-'' ("round object") which refers to a swelling or bulging out, a pregnant appearance or a protuberance, and it is speculated that it came to be used for the instrument because of its bulging shape. Other Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
*Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Foo ...
words for violin
The violin, sometimes known as a '' fiddle'', is a wooden chordophone ( string instrument) in the violin family. Most violins have a hollow wooden body. It is the smallest and thus highest-pitched instrument ( soprano) in the family in regu ...
also have meanings referring to rounded appearances. In Gaelic, for example, "" can mean "hump" or "hunch" as well as harp
The harp is a stringed musical instrument that has a number of individual strings running at an angle to its soundboard; the strings are plucked with the fingers. Harps can be made and played in various ways, standing or sitting, and in orc ...
or violin
The violin, sometimes known as a '' fiddle'', is a wooden chordophone ( string instrument) in the violin family. Most violins have a hollow wooden body. It is the smallest and thus highest-pitched instrument ( soprano) in the family in regu ...
. Like several other English loanwords from Welsh, the name is one of the few words in the English language in which the letter W is used as a vowel
A vowel is a syllabic speech sound pronounced without any stricture in the vocal tract. Vowels are one of the two principal classes of speech sounds, the other being the consonant. Vowels vary in quality, in loudness and also in quantity (len ...
.
The traditional English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
name is crowd (or rote), and the variants ', ' and ' are little-used today. In Medieval Latin
Medieval Latin was the form of Literary Latin used in Roman Catholic Western Europe during the Middle Ages. In this region it served as the primary written language, though local languages were also written to varying degrees. Latin functioned ...
it is called the ''chorus'' or '. The Welsh word ' means a performer on the crwth. The Irish word is ''cruit'', although it also was used on occasion to designate certain small harp
The harp is a stringed musical instrument that has a number of individual strings running at an angle to its soundboard; the strings are plucked with the fingers. Harps can be made and played in various ways, standing or sitting, and in orc ...
s. The English surname
In some cultures, a surname, family name, or last name is the portion of one's personal name that indicates one's family, tribe or community.
Practices vary by culture. The family name may be placed at either the start of a person's full name ...
s Crewther, Crowder, Crother and Crowther denote a player of the crowd, as do the Scottish names MacWhirter and MacWhorter.
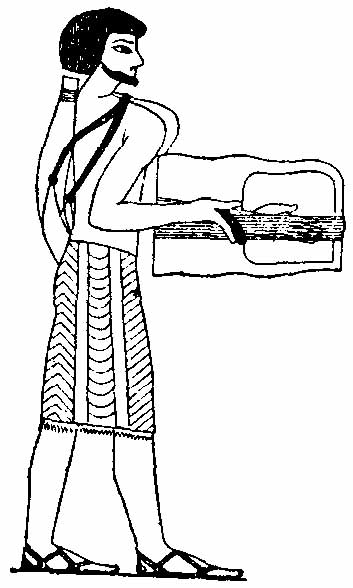
In this article ''crwth'' denotes the modern, or most recent, form of the instrument (see picture).
History

 A variety of string instruments so designated are thought to have been played in Wales since at least Roman times. Continuous, clear records of the use of ''crwth'' to denote an instrument of the
A variety of string instruments so designated are thought to have been played in Wales since at least Roman times. Continuous, clear records of the use of ''crwth'' to denote an instrument of the lyre
The lyre () is a string instrument, stringed musical instrument that is classified by Hornbostel–Sachs as a member of the History of lute-family instruments, lute-family of instruments. In organology, a lyre is considered a yoke lute, since it ...
(or the Byzantine bowed lyre) class date from the 11th century. Medieval instruments somewhat resembling the crwth appear in pictures (first in Continental Europe) as far back as the 11th century, shortly after bowing was first known in the West. In Wales, the crwth long took second place to the harp
The harp is a stringed musical instrument that has a number of individual strings running at an angle to its soundboard; the strings are plucked with the fingers. Harps can be made and played in various ways, standing or sitting, and in orc ...
in the musical hierarchy.
Schlesinger in the ''1911 Encyclopædia Britannica
A notable ongoing event was the race for the South Pole.
Events January
* January 1 – A decade after federation, the Northern Territory and the Australian Capital Territory are added to the Commonwealth of Australia.
* ...
'' mentioned the crwth in an article about transition of instruments from the lyre to plucked and bowed instruments:
Physical description and playing technique
The crwth consists of a fairly simple box construction with a flat,fret
A fret is any of the thin strips of material, usually metal wire, inserted laterally at specific positions along the neck or fretboard of a stringed instrument. Frets usually extend across the full width of the neck. On some historical instru ...
less fingerboard
The fingerboard (also known as a fretboard on fretted instruments) is an important component of most stringed instruments. It is a thin, long strip of material, usually wood, that is laminated to the front of the neck of an instrument. The s ...
and six gut strings, purportedly tuned gg´c´c´´d´d´´. The original report of that tuning (Edward Jones, ''Musical and Poetical Relicks of the Welsh Bards''; London: 1784), from which most subsequent others appear to draw their information, uses arbitrary pitch designations for illustrative purposes. Jones also states that the tuning procedure began by tightening the highest string as much as possible without breaking it, subsequently tuning the others to it intervallically. Such was not an uncommon practice in the days before standardized pitch and was, in fact, mentioned in other manuals on string instrument playing.
While Jones's report was widely read and used as the basis of a number of subsequent accounts, and therefore today is often considered to be evidence of a standard tuning, it is more likely that a variety of tunings were experimented with and in some cases employed, as was and still is the case with many other string instruments, particularly those within folk culture
Folklore is shared by a particular group of people; it encompasses the traditions common to that culture, subculture or group. This includes oral traditions such as tales, legends, proverbs and jokes. They include material culture, ranging fro ...
s. A second tuning, reported by William Bingley (''A Tour Round North Wales''; London: 1800), features the drones tuned in octaves, with the strings over the fingerboard tuned in paired fifths rather than seconds. However this tuning is almost certainly derived from later violin playing and is impractical given that the crwth is equipped with a flat bridge and therefore designed to play all six strings simultaneously.
Traditionally the soundbox, or resonator, and a surmounting yoke in the shape of an inverted U (see picture of player), were carved as a single unit from a block of maple
''Acer'' () is a genus of trees and shrubs commonly known as maples. The genus is placed in the family Sapindaceae.Stevens, P. F. (2001 onwards). Angiosperm Phylogeny Website. Version 9, June 2008 nd more or less continuously updated since h ...
or sycamore. The soundboard, or belly
Belly may refer to:
Anatomy
* The abdomen, the part of the body between the pelvis and the thorax; or the stomach
** A beer belly, an overhang of fat above the waist, presumed to be caused by regular beer drinking
** Belly dance
* The fleshy, cent ...
, a separate piece (the upper surface, nearest the strings), was most often made of deal
A deal, or deals may refer to:
Places United States
* Deal, New Jersey, a borough
* Deal, Pennsylvania, an unincorporated community
* Deal Lake, New Jersey
Elsewhere
* Deal Island (Tasmania), Australia
* Deal, Kent, a town in England
* Deal, a ...
or some other soft wood, and the bridge
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually someth ...
was usually made of cherry
A cherry is the fruit of many plants of the genus ''Prunus'', and is a fleshy drupe (stone fruit).
Commercial cherries are obtained from cultivars of several species, such as the sweet ''Prunus avium'' and the sour '' Prunus cerasus''. The n ...
or some other fruitwood. Two soundholes, or circular openings about an inch to an inch and a quarter in diameter, were cut into the soundboard to allow pulsating air from the soundbox to escape and strengthen the tone. The two G strings (to use Jones's terminology – see above) ran parallel to the fingerboard, but not over it, so those strings were used as fixed-pitch drones which could be plucked by the player's left thumb. The remaining strings, which were tightened and loosened with metal harp
The harp is a stringed musical instrument that has a number of individual strings running at an angle to its soundboard; the strings are plucked with the fingers. Harps can be made and played in various ways, standing or sitting, and in orc ...
wrest-pins and a tuning key or wrench
A wrench or spanner is a tool used to provide grip and mechanical advantage in applying torque to turn objects—usually rotary fasteners, such as nuts and bolts—or keep them from turning.
In the UK, Ireland, Australia, and New Zeal ...
, were usually bowed with a horsehair and wood bow. One characteristic feature of the crwth is that one leg of the bridge
A bridge is a structure built to span a physical obstacle (such as a body of water, valley, road, or rail) without blocking the way underneath. It is constructed for the purpose of providing passage over the obstacle, which is usually someth ...
goes through a soundhole (see picture of player) and rests on the back of the instrument (the bottom of the soundbox). Although it has been conjectured that this is a primitive attempt at a sound post, or ''anima'', something the instrument lacks, it is equally likely that it is designed to take some of the downward pressure of the tightened strings off the soundboard. Since that piece is flat, unbraced, and usually made of soft wood, it is much weaker than the belly of a violin.
All surviving pictures of crwth players show a playing position with the lower end of the crwth braced against the chest, supported with a strap around the player's neck (see picture). The sound of the crwth was described by medieval poet Gruffydd ap Dafydd ap Hywel as 'in the hand a hundred voices' (yn y llaw yn gan llais'), referring to the rich sound of six strings sounded simultaneously in harmony. Along with the harp and timpan, the six-stringed crwth was one of the three main string instruments of the Welsh according to the medieval Triads, and an instrument of the aristocracy with its own native repertoire and a strict examination system though which a master crwth player had to pass. A three-stringed version also existed which required less skill and was played by minstrels.
The tone of the crwth is softer and rougher than the modern violin, and has a comfortable melody range of an octave by the use of third position, although it is possible to reach an octave and a half by the use of higher positions. It's sound that goes well with the timbres of the harp
The harp is a stringed musical instrument that has a number of individual strings running at an angle to its soundboard; the strings are plucked with the fingers. Harps can be made and played in various ways, standing or sitting, and in orc ...
and pibgorn Pibgorn may refer to:
* Pibgorn (instrument)
The pibgorn is a Welsh species of idioglot reed aerophone. The name translates literally as "pipe-horn". It is also historically known as cornicyll and pib-corn. It utilises a single reed (Welsh: "cal ...
( hornpipe). For all its technical limitations, the crwth has great charm, and is much more than a historical curiosity. Research over about the last thirty-five years, and particularly experimentation with tunings, have shown it to have been much more versatile and facile than was once assumed, although it definitely was not a prototype of modern orchestral bowed string instruments, which emerged from an altogether different branch of the complex string family tree. Historically, it represents the logical end of a line of development, not an early stage of another.
Welsh legends
There are a number of legends in Wales related to '' Crythor Du'' or "The Black Crwth Player", the most notable of which is "Y Crythor Du a'r Bleiddiaid" or "The Black Crwth Player and the Wolves", where the main character escapes attack from a pack of hungry wolves by playing in turn forcefully, melodiously and gently. Another legend has a player and his servant dying of cold in Beddgelert, noted by Welsh antiquarian Edward Llwyd. There is also the "Cave of the black crwth player" near Criccieth, which is said to have been the inspiration for the tune ''Ffarwél Ned Puw'' or 'Farewell Dick the Piper'.Today
A number of modern reconstructions of the crwth have been made; makers include Guy Flockhart, Nial Cain, Michael J. King, Hank Taylor and Gerard Kilbride. A handful of folk musicians are reviving the tradition of playing this instrument, among them Cass Meurig, who is the best-known modern player and who in 2004 released the album ''Crwth'', the world's second CD of crwth music, in 2004 on the Fflach:tradd label. (Meurig also plays with the groups Fernhill and Pigyn Clust.) Other musicians include Bob Evans ( Bragod), Dan Morris ( Cilmeri), and Sedayne. The repertoire of surviving crwth tunes is very small, although many other traditional tunes can be adapted for the instrument and new tunes are being written for it. It is also used by several early music groups, including Cancionero.See also
* Tromba marinaReferences
External links
Website of Bob Evans (Bragod)
Fflach record label
Website AuraInstruments of Medieval Instruments makers (Slovakia)
Bibliography and scholarly literature by J. Marshall Bevil
Article about last remaining crwths and their sound chamber beneath the fingerboard.
{{Authority control Bowed lyres Early musical instruments English musical instruments Welsh musical instruments Celtic musical instruments String instruments with sympathetic strings Welsh music history