Crimean khanate on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Crimean Khanate ( crh, , or ), officially the Great Horde and Desht-i Kipchak () and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary ( la, Tartaria Minor), was a Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to 1783, the longest-lived of the Turkic khanates that succeeded the empire of the
 The first known
The first known  The multi-ethnic population of Crimea then consisted mainly of those who lived in the steppe and foothills of the Peninsula
The multi-ethnic population of Crimea then consisted mainly of those who lived in the steppe and foothills of the Peninsula
 The sons of Hacı I Giray contended against each other to succeed him. The
The sons of Hacı I Giray contended against each other to succeed him. The  In 1475, the Ottomans imprisoned Meñli I Giray for three years for resisting the invasion. After returning from captivity in
In 1475, the Ottomans imprisoned Meñli I Giray for three years for resisting the invasion. After returning from captivity in
 The Crimeans had a complex relationship with
The Crimeans had a complex relationship with
 In the middle of the 16th century, the Crimean Khanate asserted a claim to be the successor to the Golden Horde, which entailed asserting the right of rule over the Tatar khanates of the Caspian-Volga region, particularly the
In the middle of the 16th century, the Crimean Khanate asserted a claim to be the successor to the Golden Horde, which entailed asserting the right of rule over the Tatar khanates of the Caspian-Volga region, particularly the
 The decline of the Crimean Khanate was a consequence of the weakening of the Ottoman Empire and a change in Eastern Europe's balance of power favouring its neighbours. Crimean Tatars often returned from Ottoman campaigns without booty, and Ottoman subsidies were less likely for unsuccessful campaigns. Without sufficient guns, the Tatar cavalry suffered a significant loss against European and Russian armies with modern equipment. By the late 17th century,
The decline of the Crimean Khanate was a consequence of the weakening of the Ottoman Empire and a change in Eastern Europe's balance of power favouring its neighbours. Crimean Tatars often returned from Ottoman campaigns without booty, and Ottoman subsidies were less likely for unsuccessful campaigns. Without sufficient guns, the Tatar cavalry suffered a significant loss against European and Russian armies with modern equipment. By the late 17th century,  In the first half of the 17th century,
In the first half of the 17th century,
 Crimean law was based on Tatar law, Islamic law, and, in limited matters, Ottoman law. The leader of the Muslim establishment was the
Crimean law was based on Tatar law, Islamic law, and, in limited matters, Ottoman law. The leader of the Muslim establishment was the
 The
The
 One of the notable constructors of Crimean art and architecture was Qırım Giray, who in 1764 commissioned the fountain master Omer the Persian to construct the Bakhchisaray Fountain. The Bakhchisaray Fountain or ''Fountain of Tears'' is a real case of life imitating art. The fountain is known as the embodiment of love of one of the last Crimean Khans, Khan Qırım Giray for his young wife, and his grief after her early death. The Khan was said to have fallen in love with a Polish girl in his
One of the notable constructors of Crimean art and architecture was Qırım Giray, who in 1764 commissioned the fountain master Omer the Persian to construct the Bakhchisaray Fountain. The Bakhchisaray Fountain or ''Fountain of Tears'' is a real case of life imitating art. The fountain is known as the embodiment of love of one of the last Crimean Khans, Khan Qırım Giray for his young wife, and his grief after her early death. The Khan was said to have fallen in love with a Polish girl in his
File:Fountain of Selim II Giray.jpg, Fountain of
Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragmen ...
. Established by Hacı I Giray
Hacı I Giray (1397–1466, ruled circa 1441–1466) was the founder of the Crimean Khanate and the Giray dynasty of Crimea. As the Golden Horde was breaking up, he established himself in Crimea and spent most of his life fighting off other warlo ...
in 1441, it was regarded as the direct heir to the Golden Horde and to Desht-i-Kipchak.
In 1783, violating the 1774 Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca
The Treaty of Küçük Kaynarca ( tr, Küçük Kaynarca Antlaşması; russian: Кючук-Кайнарджийский мир), formerly often written Kuchuk-Kainarji, was a peace treaty signed on 21 July 1774, in Küçük Kaynarca (today Kayn ...
(which had guaranteed non-interference of both Russia and the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
in the affairs of the Crimean Khanate), the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
annexed
Annexation (Latin ''ad'', to, and ''nexus'', joining), in international law, is the forcible acquisition of one state's territory by another state, usually following military occupation of the territory. It is generally held to be an illegal act ...
the khanate. Among the European powers, only France came out with an open protest against this act, due to the longstanding Franco-Ottoman alliance
The Franco-Ottoman Alliance, also known as the Franco-Turkish Alliance, was an alliance established in 1536 between the King of France Francis I and the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire Suleiman I. The strategic and sometimes tactical alliance was o ...
.
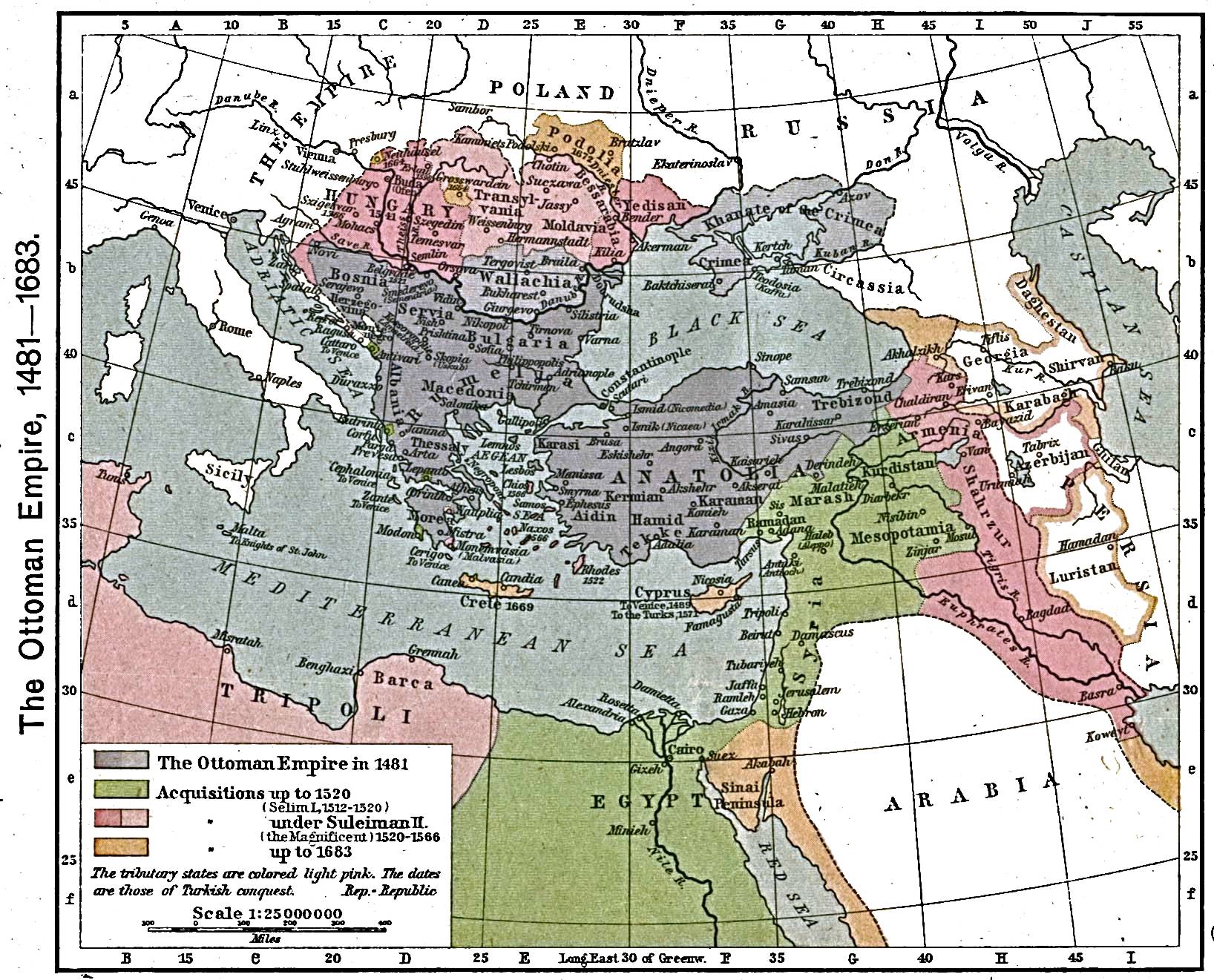
Naming and geography
Crimean khans, considering their state as the heir and legal successor of theGolden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragmen ...
and Desht-i Kipchak
The name Cumania originated as the Latin exonym for the Cuman–Kipchak confederation, which was a tribal confederation in the western part of the Eurasian Steppe, between the 10th and 13th centuries. The confederation was dominated by two ...
, called themselves khans of "the Great Horde, the Great State and the Throne of the Crimea". The full title of the Crimean khans, used in official documents and correspondence with foreign rulers, varying slightly from document to document during the three centuries of the khanate's existence, was as follows: "By the Grace and help of the blessed and highest Lord, the great padishah of the Great Horde, and the Great State, and the Throne of the Crimea, and all the Nogai, and the mountain Circassians, and the tats and tavgachs, and The Kipchak steppe and all the Tatars" ( crh, , ).
According to Oleksa Hayvoronsky, the inhabitants of the Crimean Khanate in Crimean Tatar usually referred to their state as "Qırım yurtu, Crimean Yurt", which can be translated into English as "the country of Crimea" or "Crimean country".
English-speaking writers during the 18th and early 19th centuries often called the territory of the Crimean Khanate and of the Lesser Nogai Horde
The Lesser Nogai Horde, not to be confused with the (Greater) Nogai Horde on the Caspian,
was the Nogai Tatar territory in Kuban (on the eastern shore of the Sea of Azov), allied with the Crimean Khanate, during the 16th and 17th centuries.
T ...
''Little Tartary'' (or subdivided it as ''Crim Tartary'' (also ''Krim Tartary'') and ''Kuban Tartary''). The name "Little Tartary" distinguished the area from (Great) Tartary
Tartary ( la, Tartaria, french: Tartarie, german: Tartarei, russian: Тартария, Tartariya) or Tatary (russian: Татария, Tatariya) was a blanket term used in Western European literature and cartography for a vast part of Asia bound ...
– those areas of central and northern Asia inhabited by Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West, Central, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging to ...
or Tatars
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different Turki ...
.
The London-based cartographer Herman Moll in a map of c. 1729 shows "Little Tartary" as including the Crimean peninsula and the steppe between Dnieper and in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different Turki ...
Mius River
The Mius (, ) is a river in Eastern Europe that flows through Ukraine and Russia. It is long, and has a drainage basin of .Миус
as far north as the Dnieper bend and the upper Tor River
The Tor River (Bahasa Indonesia: ''Sungai Tor'') is a river in Western New Guinea with a total length of . Sungai Torin Geonames.org (cc-by) post updated 2013-05-07; database downloaded 2015-11-27
See also
*List of rivers of Western New Guinea ...
(a tributary of the Donets
The Seversky Donets () or Siverskyi Donets (), usually simply called the Donets, is a river on the south of the East European Plain. It originates in the Central Russian Upland, north of Belgorod, flows south-east through Ukraine (Kharkiv, D ...
).
The Khanate included the Crimean peninsula
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
and the adjacent steppes, mostly corresponding to parts of South Ukraine between the Dnieper
}
The Dnieper () or Dnipro (); , ; . is one of the major transboundary rivers of Europe, rising in the Valdai Hills near Smolensk, Russia, before flowing through Belarus and Ukraine to the Black Sea. It is the longest river of Ukraine an ...
and the Donets
The Seversky Donets () or Siverskyi Donets (), usually simply called the Donets, is a river on the south of the East European Plain. It originates in the Central Russian Upland, north of Belgorod, flows south-east through Ukraine (Kharkiv, D ...
rivers (i.e. including most of present-day Zaporizhzhia Oblast
Zaporizhzhia Oblast ( uk, Запорі́зька о́бласть, translit=Zaporizka oblast), also referred to as Zaporizhzhia ( uk, Запорі́жжя, links=no), is an oblast (province) of southeast Ukraine. Its capital is Zaporizhzhia. The ...
, left-Dnepr parts of Kherson Oblast
Kherson Oblast ( uk, Херсо́нська о́бласть, translit=Khersónsʹka óblastʹ, ), also known as Khersonshchyna ( uk, Херсо́нщина, ), is an oblast (province) in southern Ukraine, currently claimed and partly occupied ...
, besides minor parts of southeastern Dnipropetrovsk Oblast
Dnipropetrovsk Oblast ( uk, Дніпропетро́вська о́бласть, translit=Dnipropetrovska oblast), also referred to as Dnipropetrovshchyna ( uk, Дніпропетро́вщина), is an oblast (province) of central-eastern Ukr ...
and western Donetsk Oblast
The Donetsk Oblast ( ukr, Донецька область, Donetska oblast, ), also referred to as Donechchyna ( ukr, Донеччина, links=no), is an oblast of eastern Ukraine. It is Ukraine's most populous province, with around 4.1 mill ...
). The territory controlled by the Crimean Khanate shifted throughout its existence due to the constant incursions by the Cossacks
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or ...
, who had lived along the Don since the disintegration of the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragmen ...
in the 15th century.
History
Pre-history
 The first known
The first known Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West, Central, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging to ...
appeared in Crimea in the 6th century, during the conquest of the Crimea by The Turkic Kaganate. In the 11th century, Cumans
The Cumans (or Kumans), also known as Polovtsians or Polovtsy (plural only, from the Russian exonym ), were a Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the Cuman–Kipchak confederation. After the Mongol invasion (1237), many so ...
(Kipchaks) appeared in Crimea, who later became the ruling and state-forming people of the Golden Horde and the Crimean Khanate. In the middle of the 13th century, the northern steppe lands of the Crimea, inhabited mainly by Turkic peoples
The Turkic peoples are a collection of diverse ethnic groups of West, Central, East, and North Asia as well as parts of Europe, who speak Turkic languages.. "Turkic peoples, any of various peoples whose members speak languages belonging to ...
— Cumans
The Cumans (or Kumans), also known as Polovtsians or Polovtsy (plural only, from the Russian exonym ), were a Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the Cuman–Kipchak confederation. After the Mongol invasion (1237), many so ...
, became the possession of Ulus Juchi
Jochi Khan (Mongolian script, Mongolian: mn, Зүчи, ; kk, Жошы, Joşy جوشى; ; crh, Cuçi, Джучи, جوچى; also spelled Juchi; Djochi, and Jöchi c. 1182– February 1227) was a Mongol army commander who was the eldest son o ...
, known as the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragmen ...
or Ulu Ulus. In this era, the role of Turkic peoples increased. Since this time, the local Kipchaks took the name of Tatars
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different Turki ...
(''tatarlar'').
In the Horde period, the khans of the Golden Horde were the Supreme rulers of the Crimea, but their governors — in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different Turki ...
Emir
Emir (; ar, أمير ' ), sometimes transliterated amir, amier, or ameer, is a word of Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or cer ...
s — exercised direct control. The first formally recognized ruler in the Crimea is considered Aran-Timur, the nephew of Batu Khan
Batu Khan ( – 1255),, ''Bat haan'', tt-Cyrl, Бату хан; ; russian: хан Баты́й was a Mongol ruler and founder of the Golden Horde, a constituent of the Mongol Empire. Batu was a son of Jochi, thus a grandson of Genghis K ...
of the Golden Horde, who received this area from Mengu-Timur
Munkh Tumur or Möngke Temür ( mn, ᠮᠦᠨᠺᠬᠲᠡᠮᠦᠷ, Мөнхтөмөр; russian: Мангутемир, Mangutemir) (?–1280), son of Toqoqan Khan and Köchu Khatun of Oirat (daughter of Toralchi Küregen and granddaughter of ...
, and the first center of the Crimea was the ancient city Qırım (Solhat). This name then gradually spread to the entire Peninsula. The second center of Crimea was the valley adjacent to Qırq Yer and Bağçasaray.
 The multi-ethnic population of Crimea then consisted mainly of those who lived in the steppe and foothills of the Peninsula
The multi-ethnic population of Crimea then consisted mainly of those who lived in the steppe and foothills of the Peninsula Kipchaks
The Kipchaks or Qipchaks, also known as Kipchak Turks or Polovtsians, were a Turkic nomadic people and confederation that existed in the Middle Ages, inhabiting parts of the Eurasian Steppe. First mentioned in the 8th century as part of the ...
(Cumans), Crimean Greeks, Crimean Goths
The Crimean Goths were Greuthungi-Gothic tribes who remained in the lands around the Black Sea, especially in Crimea. They were the longest-lasting of the Gothic communities. Their existence is well attested through the ages, though the exact p ...
, Alans
The Alans (Latin: ''Alani'') were an ancient and medieval Iranian nomadic pastoral people of the North Caucasus – generally regarded as part of the Sarmatians, and possibly related to the Massagetae. Modern historians have connected the A ...
, and Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, ''hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora ...
, who lived mainly in cities and mountain villages. The Crimean nobility was mostly of both Kipchak and Horden origin.
Horde rule for the peoples who inhabited the Crimean Peninsula was, in general, painful. The rulers of the Golden Horde repeatedly organized punitive campaigns in the Crimea, when the local population refused to pay tribute. An example being a well-known campaign of the Nogai Khan
Nogai, or Noğay (; also spelled Nogay, Nogaj, Nohai, Nokhai, Noqai, Ngoche, Noche, Kara Nokhai, and Isa Nogai; died 1299/1300) was a general and kingmaker of the Golden Horde and a great-great-grandson of Genghis Khan. His grandfather was Bo'al/ ...
in 1299, which resulted in a number of Crimean cities suffering. As in other regions of the Horde, separatist tendencies soon began to manifest themselves in Crimea.
In 1303, in Crimea, the most famous written monument of the Kypchak or Cuman language was created (named in Kypchak
The Kipchaks or Qipchaks, also known as Kipchak Turks or Polovtsians, were a Turkic nomadic people and confederation that existed in the Middle Ages, inhabiting parts of the Eurasian Steppe. First mentioned in the 8th century as part of the Sec ...
"tatar tili") — "Codex Cumanicus
The Codex Cumanicus is a linguistic manual of the Middle Ages, designed to help Catholic missionaries communicate with the Cumans, a nomadic Turkic people. It is currently housed in the Library of St. Mark, in Venice (BNM ms Lat. Z. 549 (=1597 ...
", which is the oldest memorial of the Crimean Tatar language
Crimean Tatar () also called Crimean (), is a Kipchak Turkic language spoken in Crimea and the Crimean Tatar diasporas of Uzbekistan, Turkey, Romania, and Bulgaria, as well as small communities in the United States and Canada. It should ...
and of great importance for the history of Kypchak and Oghuz dialects — as directly related to the Kipchaks of the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
steppes and Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a p ...
.
There are legends that in the 14th century, the Crimea was repeatedly ravaged by the army of the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was Partitions of Poland, partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire, Habsburg Empire of ...
. Grand Duke of Lithuania
The monarchy of Lithuania concerned the monarchical head of state of Lithuania, which was established as an absolute and hereditary monarchy. Throughout Lithuania's history there were three ducal dynasties that managed to stay in power— Ho ...
Olgerd
Algirdas ( be, Альгерд, Alhierd, uk, Ольгерд, Ольґерд, Olherd, Olgerd, pl, Olgierd; – May 1377) was the Grand Duke of Lithuania. He ruled the Lithuanians and Ruthenians from 1345 to 1377. With the help of his bro ...
broke the Tatar army in 1363 near the mouth of the Dnieper, and then invaded the Crimea, devastated Chersonesos
Chersonesus ( grc, Χερσόνησος, Khersónēsos; la, Chersonesus; modern Russian and Ukrainian: Херсоне́с, ''Khersones''; also rendered as ''Chersonese'', ''Chersonesos'', contracted in medieval Greek to Cherson Χερσών; ...
and seized valuable church objects there. There is a similar legend about his successor Vitovt
Vytautas (c. 135027 October 1430), also known as Vytautas the Great ( Lithuanian: ', be, Вітаўт, ''Vitaŭt'', pl, Witold Kiejstutowicz, ''Witold Aleksander'' or ''Witold Wielki'' Ruthenian: ''Vitovt'', Latin: ''Alexander Vitoldus'', O ...
, who in 1397 went on a Crimean campaign to Caffa
uk, Феодосія, Теодосія crh, Kefe
, official_name = ()
, settlement_type=
, image_skyline = THEODOSIA 01.jpg
, imagesize = 250px
, image_caption = Genoese fortress of Caffa
, image_shield = Fe ...
and again destroyed Chersonesos. Vitovt is also known in Crimean history for giving refuge in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania to a significant number of Tatars and Karaites, whose descendants now live in Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
and Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
. In 1399 Vitovt, who came to the aid of the Horde Khan Tokhtamysh
Tokhtamysh ( kz, Тоқтамыс, tt-Cyrl, Тухтамыш, translit=Tuqtamış, fa, توقتمش),The spelling of Tokhtamysh varies, but the most common spelling is Tokhtamysh. Tokhtamısh, Toqtamysh, ''Toqtamış'', ''Toqtamıs'', ''Toktamy ...
, was defeated on the banks of the Vorskla River by Tokhtamysh's rival Timur-Kutluk, on whose behalf the Horde was ruled by the Emir Edigei, and made peace.
During the reign of Canike Hanım, Tokhtamysh's daughter, in Qırq-Or, she supported Hacı I Giray
Hacı I Giray (1397–1466, ruled circa 1441–1466) was the founder of the Crimean Khanate and the Giray dynasty of Crimea. As the Golden Horde was breaking up, he established himself in Crimea and spent most of his life fighting off other warlo ...
in the struggle against the descendants of Tokhtamysh
Tokhtamysh ( kz, Тоқтамыс, tt-Cyrl, Тухтамыш, translit=Tuqtamış, fa, توقتمش),The spelling of Tokhtamysh varies, but the most common spelling is Tokhtamysh. Tokhtamısh, Toqtamysh, ''Toqtamış'', ''Toqtamıs'', ''Toktamy ...
, Kichi-Muhammada and Sayid Ahmad, who as well as Hacı Giray claimed full power in the Crimea and probably saw him as her heir to the Crimean throne. In the sources of the 16th—18th centuries, the opinion according to which the separation of the Crimean Tatar state was raised to Tokhtamysh, and Canike was the most important figure in this process, completely prevailed.
Establishment
The Crimean Khanate originated in the early 15th century when certain clans of theGolden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragmen ...
Empire ceased their nomadic life in the Desht-i Kipchak
The name Cumania originated as the Latin exonym for the Cuman–Kipchak confederation, which was a tribal confederation in the western part of the Eurasian Steppe, between the 10th and 13th centuries. The confederation was dominated by two ...
(Kypchak Steppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate gras ...
s of today's Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inva ...
and southern Russia) and decided to make Crimea their ''yurt'' (homeland). At that time, the Golden Horde of the Mongol empire had governed the Crimean peninsula as an ulus
Ulus may refer to:
Places
* Ulus, Bartın, a district in Bartin Province, Turkey
*Ulus, Ankara, an important quarter in central Ankara, Turkey
** Ulus (Ankara Metro), an underground station of the Ankara Metro
Other uses
* ''Ulus'' (newspaper), a ...
since 1239, with its capital at Qirim ( Staryi Krym). The local separatists invited a Genghisid contender for the Golden Horde throne, Hacı Giray, to become their khan
Khan may refer to:
*Khan (inn), from Persian, a caravanserai or resting-place for a travelling caravan
*Khan (surname), including a list of people with the name
*Khan (title), a royal title for a ruler in Mongol and Turkic languages and used by ...
. Hacı Giray accepted their invitation and traveled from exile in Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
. He warred for independence against the Horde from 1420 to 1441, in the end achieving success. But Hacı Giray then had to fight off internal rivals before he could ascend the throne of the khanate in 1449, after which he moved its capital to ''Qırq Yer'' (today part of Bahçeseray). The khanate included the Crimean Peninsula
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
(except the south and southwest coast and ports, controlled by the Republic of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa ( lij, Repúbrica de Zêna ; it, Repubblica di Genova; la, Res Publica Ianuensis) was a medieval and early modern maritime republic from the 11th century to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italian coast. During the La ...
& Trebizond Empire) as well as the adjacent steppe.
Ottoman protectorate
 The sons of Hacı I Giray contended against each other to succeed him. The
The sons of Hacı I Giray contended against each other to succeed him. The Ottomans
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
intervened and installed one of the sons, Meñli I Giray, on the throne. Menli I Giray, took the imperial title "Sovereign of Two Continents and Khan of Khans of Two Seas."
In 1475 the Ottoman forces, under the command of Gedik Ahmet Pasha
Gedik Ahmed Pasha (; died 18 November 1482) was an Ottoman statesman and admiral who served as Grand Vizier and Kapudan Pasha (Grand Admiral of the Ottoman Navy) during the reigns of sultans Mehmed II and Bayezid II.
Very little was known abou ...
, conquered the Greek Principality of Theodoro
The Principality of Theodoro ( el, Αὐθεντία πόλεως Θεοδωροῦς καὶ παραθαλασσίας), also known as Gothia ( el, Γοτθία) or the Principality of Theodoro-Mangup, was a Greek principality in the southern p ...
and the Genoese colonies at Cembalo, Soldaia
Sudak (Ukrainian & Russian: Судак; crh, Sudaq; gr, Σουγδαία; sometimes spelled Sudac or Sudagh) is a town, multiple former Eastern Orthodox bishopric and double Latin Catholic titular see. It is of regional significance in Crimea, ...
, and Caffa
uk, Феодосія, Теодосія crh, Kefe
, official_name = ()
, settlement_type=
, image_skyline = THEODOSIA 01.jpg
, imagesize = 250px
, image_caption = Genoese fortress of Caffa
, image_shield = Fe ...
(modern Feodosiya). Thenceforth the khanate was a protectorate of the Ottoman Empire. The Ottoman sultan enjoyed veto power over the selection of new Crimean khans. The Empire annexed the Crimean coast but recognized the legitimacy of the khanate rule of the steppes, as the khans were descendants of Genghis Khan
Genghis Khan (born Temüjin; ; xng, Temüjin, script=Latn; ., name=Temujin – August 25, 1227) was the founder and first Great Khan (Emperor) of the Mongol Empire, which became the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in history a ...
.
 In 1475, the Ottomans imprisoned Meñli I Giray for three years for resisting the invasion. After returning from captivity in
In 1475, the Ottomans imprisoned Meñli I Giray for three years for resisting the invasion. After returning from captivity in Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
, he accepted the suzerainty
Suzerainty () is the rights and obligations of a person, state or other polity who controls the foreign policy and relations of a tributary state, while allowing the tributary state to have internal autonomy. While the subordinate party is ca ...
of the Ottoman Empire. Nevertheless, Ottoman sultans treated the khans more as allies than subjects. The khans continued to have a foreign policy independent from the Ottomans in the steppes of Little Tartary
The Crimean Khanate ( crh, , or ), officially the Great Horde and Desht-i Kipchak () and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary ( la, Tartaria Minor), was a Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to 1783, the long ...
. The khans continued to mint coins and use their names in Friday prayers, two important signs of sovereignty. They did not pay tribute to the Ottoman Empire; instead the Ottomans paid them in return for their services of providing skilled outriders and frontline cavalry in their campaigns. Later on, Crimea lost power in this relationship as the result of a crisis in 1523, during the reign of Meñli's successor, Mehmed I Giray. He died that year and beginning with his successor, from 1524 on, Crimean khans were appointed by the Sultan.
The alliance of the Crimean Tatars and the Ottomans was comparable to the Polish–Lithuanian union Polish–Lithuanian can refer to:
* Polish–Lithuanian union (1385–1569)
* Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth (1569–1795)
* Polish-Lithuanian identity as used to describe groups, families, or individuals with histories in the Polish–Lithuanian ...
in its importance and durability. The Crimean cavalry became indispensable for the Ottomans' campaigns against Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
, Hungary
Hungary ( hu, Magyarország ) is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning of the Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Cr ...
, and Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
.
Victory over the Golden Horde
In 1502, Meñli I Giray defeated the last khan of theGreat Horde
The Great Horde (''Uluğ Orda'') was a rump state of the Golden Horde that existed from the mid-15th century to 1502. It was centered at the core of the Golden Horde at Sarai. Both the Khanate of Astrakhan and the Khanate of Crimea broke away ...
, which put an end to the Horde's claims on Crimea. The Khanate initially chose as its capital Salaçıq near the Qırq Yer fortress. Later, the capital was moved a short distance to Bahçeseray, founded in 1532 by Sahib I Giray
Sahib I Giray (1501–1551) was Khan of Kazan for three years and Khan of Crimea for nineteen years. His father was the Crimean Khan Meñli I Giray. Sahib was placed on the throne of Kazan by his ambitious brother Mehmed of Crimea and driven ou ...
. Both Salaçıq and the Qırq Yer fortress today are part of the expanded city of Bahçeseray.
Slave trade
The slave trade was the backbone of the economy of the Crimean Khanate. The Crimeans frequently mounted raids into theDanubian principalities
The Danubian Principalities ( ro, Principatele Dunărene, sr, Дунавске кнежевине, translit=Dunavske kneževine) was a conventional name given to the Principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia, which emerged in the early 14th c ...
, Poland–Lithuania, and Muscovy to enslave people whom they could capture; for each captive, the khan received a fixed share (savğa) of 10% or 20%. These campaigns by Crimean forces were either ("sojourns"), officially declared military operations led by the khans themselves, or ''çapuls'' ("despoiling"), raids undertaken by groups of noblemen, sometimes illegally because they contravened treaties concluded by the khans with neighbouring rulers.
For a long time, until the early 18th century, the khanate maintained a massive slave trade
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
with the Ottoman Empire and the Middle East, exporting about 2 million slaves from Russia and Poland–Lithuania over the period 1500–1700. Caffa
uk, Феодосія, Теодосія crh, Kefe
, official_name = ()
, settlement_type=
, image_skyline = THEODOSIA 01.jpg
, imagesize = 250px
, image_caption = Genoese fortress of Caffa
, image_shield = Fe ...
, an Ottoman city on Crimean peninsula (and thus not part of the Khanate), was one of the best known and significant trading ports and slave markets. In 1769, a last major Tatar raid resulted in the capture of 20,000 Russian and Ruthenian slaves.
Author and historian Brian Glyn Williams
Brian Glyn Williams is a professor of Islamic History at the University of Massachusetts Dartmouth who worked for the CIA. As an undergraduate, he attended Stetson University, graduating with a Bachelor of Arts in 1988. He received his PhD in Mi ...
writes:
Early modern sources are full of descriptions of sufferings of Christian slaves captured by the Crimean Tatars in the course of their raids:
Alliances and conflicts with Poland and Zaporozhian Cossacks
 The Crimeans had a complex relationship with
The Crimeans had a complex relationship with Zaporozhian Cossacks
The Zaporozhian Cossacks, Zaporozhian Cossack Army, Zaporozhian Host, (, or uk, Військо Запорізьке, translit=Viisko Zaporizke, translit-std=ungegn, label=none) or simply Zaporozhians ( uk, Запорожці, translit=Zaporoz ...
who lived to the north of the khanate in modern Ukraine. The Cossacks provided a measure of protection against Tatar raids for Poland–Lithuania and received subsidies for their service. They also raided Crimean and Ottoman possessions in the region. At times Crimean Khanate made alliances with the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
and the Zaporizhian Sich
The Zaporozhian Sich ( ua, Запорозька Січ, ; also uk, Вольностi Вiйська Запорозького Низового, ; Free lands of the Zaporozhian Host the Lower) was a semi-autonomous polity and proto-state of C ...
. The assistance of İslâm III Giray during the Khmelnytsky Uprising
The Khmelnytsky Uprising,; in Ukraine known as Khmelʹnychchyna or uk, повстання Богдана Хмельницького; lt, Chmelnickio sukilimas; Belarusian: Паўстанне Багдана Хмяльніцкага; russian: � ...
in 1648 contributed greatly to the initial momentum of military successes for the Cossacks. The relationship with the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth was also exclusive, as it was the home dynasty of the Girays, who sought sanctuary in Lithuania in the 15th century before establishing themselves on the Crimean peninsula.Struggle with Muscovy
 In the middle of the 16th century, the Crimean Khanate asserted a claim to be the successor to the Golden Horde, which entailed asserting the right of rule over the Tatar khanates of the Caspian-Volga region, particularly the
In the middle of the 16th century, the Crimean Khanate asserted a claim to be the successor to the Golden Horde, which entailed asserting the right of rule over the Tatar khanates of the Caspian-Volga region, particularly the Kazan Khanate
The Khanate of Kazan ( tt, Казан ханлыгы, Kazan xanlıgı; russian: Казанское ханство, Kazanskoye khanstvo) was a medieval Tatar Turkic state that occupied the territory of former Volga Bulgaria between 1438 and 155 ...
and Astrakhan Khanate
The Khanate of Astrakhan, also referred to as the Xacitarxan Khanate, was a Tatar state that arose during the break-up of the Golden Horde. The Khanate existed in the 15th and 16th centuries in the area adjacent to the mouth of the Volga river, a ...
. This claim pitted it against Muscovy for dominance in the region. A successful campaign by Devlet I Giray
Devlet I Giray (1512–1577, r. 1551–1577, ; ', ) was a Crimean Khan. His long and eventful reign saw many highly significant historical events: the fall of Kazan to Russia in 1552, the fall of the Astrakhan Khanate to Russia in 1556, th ...
upon the Russian capital in 1571 culminated in the burning of Moscow, and he thereby gained the sobriquet, Taht Alğan (seizer of the throne). The following year, however, the Crimean Khanate lost access to the Volga once and for all due to its catastrophic defeat in the Battle of Molodi.
Don Cossacks
Don Cossacks (russian: Донские казаки, Donskie kazaki) or Donians (russian: донцы, dontsy) are Cossacks who settled along the middle and lower Don. Historically, they lived within the former Don Cossack Host (russian: До ...
reached lower Don, Donets
The Seversky Donets () or Siverskyi Donets (), usually simply called the Donets, is a river on the south of the East European Plain. It originates in the Central Russian Upland, north of Belgorod, flows south-east through Ukraine (Kharkiv, D ...
and Azov
Azov (russian: Азов), previously known as Azak,
is a town in Rostov Oblast, Russia, situated on the Don River just from the Sea of Azov, which derives its name from the town. Population:
History
Early settlements in the vicinity
The mout ...
by the 1580s and thus became the north-eastern neighbours of the khanate. They attracted peasants, serfs and gentry fleeing internal conflicts, over-population and intensifying exploitation. Just as Zaporozhians protected the southern borders of the Commonwealth, Don Cossacks protected Muscovy and themselves attacked the khanate and Ottoman fortresses.
Relationship with Circassians
Under the influence of theCrimean Tatars
, flag = Flag of the Crimean Tatar people.svg
, flag_caption = Flag of Crimean Tatars
, image = Love, Peace, Traditions.jpg
, caption = Crimean Tatars in traditional clothing in front of the Khan's Palace ...
and of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
, large numbers of Circassians
The Circassians (also referred to as Cherkess or Adyghe; Adyghe and Kabardian: Адыгэхэр, romanized: ''Adıgəxər'') are an indigenous Northwest Caucasian ethnic group and nation native to the historical country-region of Circassia ...
converted to Islam
Islam (; ar, ۘالِإسلَام, , ) is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion centred primarily around the Quran, a religious text considered by Muslims to be the direct word of God (or '' Allah'') as it was revealed to Muhammad, the ...
from Christianity. Circassian mercenaries and recruits played an important role in the khan's armies, khans often married Circassian women and it was a custom for young Crimean princes to spend time in Circassia training in the art of warfare. Several conflicts occurred between Circassians and Crimean Tatars in the 18th century, with the former defeating an army of Khan Kaplan Giray and Ottoman auxiliaries in the battle of Kanzhal
The Kanzhal War () or Crimean-Circassian War of 1708 was military conflict in 1708 fought between 7,000 Circassians led by Kurgoqo Atajuq and 30,000-100,000 Crimean Tatars led by Qaplan I Giray, which resulted in Circassian victory. It played a ...
.
Decline
The Turkish traveler writerEvliya Çelebi
Derviş Mehmed Zillî (25 March 1611 – 1682), known as Evliya Çelebi ( ota, اوليا چلبى), was an Ottoman explorer who travelled through the territory of the Ottoman Empire and neighboring lands over a period of forty years, recording ...
mentions the impact of Cossack
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or ...
raids from Azak
Azov (russian: Азов), previously known as Azak,
is a town in Rostov Oblast, Russia, situated on the Don River just from the Sea of Azov, which derives its name from the town. Population:
History
Early settlements in the vicinity
The mout ...
upon the territories of the Crimean Khanate. These raids ruined trade routes and severely depopulated many important regions. By the time Evliya Çelebi had arrived almost all the towns he visited were affected by the Cossack raids. In fact, the only place Evliya Çelebi considered safe from the Cossacks was the Ottoman fortress at Arabat.
 The decline of the Crimean Khanate was a consequence of the weakening of the Ottoman Empire and a change in Eastern Europe's balance of power favouring its neighbours. Crimean Tatars often returned from Ottoman campaigns without booty, and Ottoman subsidies were less likely for unsuccessful campaigns. Without sufficient guns, the Tatar cavalry suffered a significant loss against European and Russian armies with modern equipment. By the late 17th century,
The decline of the Crimean Khanate was a consequence of the weakening of the Ottoman Empire and a change in Eastern Europe's balance of power favouring its neighbours. Crimean Tatars often returned from Ottoman campaigns without booty, and Ottoman subsidies were less likely for unsuccessful campaigns. Without sufficient guns, the Tatar cavalry suffered a significant loss against European and Russian armies with modern equipment. By the late 17th century, Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
became too strong a power for Crimea to pillage and the Treaty of Karlowitz
The Treaty of Karlowitz was signed in Karlowitz, Military Frontier of Archduchy of Austria (present-day Sremski Karlovci, Serbia), on 26 January 1699, concluding the Great Turkish War of 1683–1697 in which the Ottoman Empire was defeated by ...
(1699) outlawed further raids. The era of great slave raids in Russia and Ukraine was over, although brigands and Nogay raiders continued their attacks and Russian hatred of the Khanate did not decrease. These politico-economic losses led in turn to erosion of the khan's support among noble clans, and internal conflicts for power ensued. The Nogays, who provided a significant portion of the Crimean military forces, also took back their support from the khans towards the end of the empire.
 In the first half of the 17th century,
In the first half of the 17th century, Kalmyks
The Kalmyks ( Kalmyk: Хальмгуд, ''Xaľmgud'', Mongolian: Халимагууд, ''Halimaguud''; russian: Калмыки, translit=Kalmyki, archaically anglicised as ''Calmucks'') are a Mongolic ethnic group living mainly in Russia, w ...
formed the Kalmyk Khanate
The Kalmyk Khanate ( xal-RU, Хальмг хана улс, ''Xal'mg xana uls'') was an Oirat khanate on the Eurasian steppe. It extended over modern Kalmykia and surrounding areas in the North Caucasus, including Stavropol and Astrakhan. Duri ...
in the Lower Volga and under Ayuka Khan conducted many military expeditions against the Crimean Khanate and Nogays
The Nogais ( Nogai: Ногай, , Ногайлар, ) are a Turkic ethnic group who live in the North Caucasus region. Most are found in Northern Dagestan and Stavropol Krai, as well as in Karachay-Cherkessia and Astrakhan Oblast; some als ...
. By becoming an important ally and later part of the Russian Empire and taking an oath to protect its southeastern borders, the Kalmyk Khanate took an active part in all Russian war campaigns in the 17th and 18th centuries, providing up to 40,000 fully equipped horsemen.
The united Russian and Ukrainian forces attacked the Khanate during the Chigirin Campaigns
Chyhyryn ( uk, Чигирин, ) is a city and historic site located in Cherkasy Raion of Cherkasy Oblast of central Ukraine. From 1648 to 1669 the city was a Hetman residence. After a forced relocation of the Ruthenian Orthodox metropolitan see ...
and the Crimean Campaigns. It was during the Russo-Turkish War (1735–1739)
The Russo-Turkish War of 1735–1739 between Russia and the Ottoman Empire was caused by the Ottoman Empire's war with Persia and continuing raids by the Crimean Tatars. The war also represented Russia's continuing struggle for access to the ...
that the Russians, under the command of Field-Marshal Münnich, finally managed to penetrate the Crimean Peninsula itself, burning and destroying everything on their way.
More warfare ensued during the reign of Catherine II
, en, Catherine Alexeievna Romanova, link=yes
, house =
, father = Christian August, Prince of Anhalt-Zerbst
, mother = Joanna Elisabeth of Holstein-Gottorp
, birth_date =
, birth_name = Princess Sophie of Anhal ...
. The Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774)
The Russo-Turkish War of 1768–1774 was a major armed conflict that saw Russian arms largely victorious against the Ottoman Empire. Russia's victory brought parts of Moldavia, the Yedisan between the rivers Bug and Dnieper, and Crimea into th ...
resulted in the Treaty of Kuchuk-Kainarji, which made the Crimean Khanate independent from the Ottoman Empire and aligned it with the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
.
The rule of the last Crimean khan Şahin Giray
Şahin Giray, Shahin Khan Girai ( crh, شاهين كراى, Şahin Geray, 1745—1787) was the last Khan of Crimea on two occasions (1777–1782, 1782–1783).
Life
He was born in 1745 in Edirne. He studied in Greece and Venice. He reputedly ...
was marked with increasing Russian influence and outbursts of violence from the khan administration towards internal opposition. On 8 April 1783, in violation of the treaty (some parts of which had been already violated by Crimeans and Ottomans), Catherine II intervened in the civil war, de facto annexing the whole peninsula as the Taurida Oblast
Taurida Oblast (russian: Таврическая область, ''Tavricheskaya oblast′'') was an oblast (province) of the Russian Empire. It roughly corresponded to most of the Crimean Peninsula and parts of the Southern Ukraine regions. It ...
. In 1787, Şahin Giray took refuge in the Ottoman Empire and was eventually executed, on Rhodes
Rhodes (; el, Ρόδος , translit=Ródos ) is the largest and the historical capital of the Dodecanese islands of Greece. Administratively, the island forms a separate municipality within the Rhodes regional unit, which is part of the S ...
, by the Ottoman authorities for betrayal. The royal Giray family survives to this day.
Through the 1792 Treaty of Jassy
The Treaty of Jassy, signed at Jassy (''Iași'') in Moldavia (presently in Romania), was a pact between the Russian and Ottoman Empires ending the Russo-Turkish War of 1787–92 and confirming Russia's increasing dominance in the Black Sea.
...
(Iaşi), the Russian frontier was extended to the Dniester River
The Dniester, ; rus, Дне́стр, links=1, Dnéstr, ˈdⁿʲestr; ro, Nistru; grc, Τύρᾱς, Tyrās, ; la, Tyrās, la, Danaster, label=none, ) ( ,) is a transboundary river in Eastern Europe. It runs first through Ukraine and t ...
and the takeover of Yedisan was complete. The 1812 Treaty of Bucharest transferred Bessarabia
Bessarabia (; Gagauz: ''Besarabiya''; Romanian: ''Basarabia''; Ukrainian: ''Бессара́бія'') is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds o ...
to Russian control.
Government
All Khans were from the Giray clan, which traced its right to rule to its descent fromGenghis Khan
Genghis Khan (born Temüjin; ; xng, Temüjin, script=Latn; ., name=Temujin – August 25, 1227) was the founder and first Great Khan (Emperor) of the Mongol Empire, which became the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in history a ...
. According to the tradition of the steppes, the ruler was legitimate only if he was of Genghisid royal descent (i.e. "ak süyek"). Although the Giray dynasty was the symbol of government, the khan actually governed with the participation of Qaraçı Beys, the leaders of the noble clans such as Şirin, Barın, Arğın, Qıpçaq, and in the later period, Mansuroğlu and Sicavut. After the collapse of the Astrakhan Khanate
The Khanate of Astrakhan, also referred to as the Xacitarxan Khanate, was a Tatar state that arose during the break-up of the Golden Horde. The Khanate existed in the 15th and 16th centuries in the area adjacent to the mouth of the Volga river, a ...
in 1556, an important element of the Crimean Khanate were the Nogays
The Nogais ( Nogai: Ногай, , Ногайлар, ) are a Turkic ethnic group who live in the North Caucasus region. Most are found in Northern Dagestan and Stavropol Krai, as well as in Karachay-Cherkessia and Astrakhan Oblast; some als ...
, most of whom transferred their allegiance from Astrakhan to Crimea. Circassians
The Circassians (also referred to as Cherkess or Adyghe; Adyghe and Kabardian: Адыгэхэр, romanized: ''Adıgəxər'') are an indigenous Northwest Caucasian ethnic group and nation native to the historical country-region of Circassia ...
(Atteghei) and Cossacks
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or ...
also occasionally played roles in Crimean politics, alternating their allegiance between the khan and the beys.
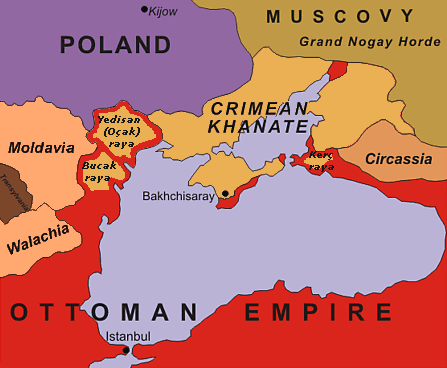
The Nogay pastoral nomads north of the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
were nominally subject to the Crimean Khan. They were divided into the following groups: Budjak
Budjak or Budzhak ( Bulgarian and Ukrainian: Буджак; ro, Bugeac; Gagauz and Turkish: ''Bucak''), historically part of Bessarabia until 1812, is a historical region in Ukraine and Moldova. Lying along the Black Sea between the Danu ...
(from the Danube to the Dniester), Yedisan
Yedisan (also ''Jedisan'' or ''Edisan''; tr, Yedisan; uk, Єдисан; ro, Edisan; russian: Едисан) was a conditional name for Özi așaSancağı (Ochakiv Sanjak) of Silistra Eyalet, a territory located in today's Southern Ukraine b ...
(from the Dniester to the Bug), Jamboyluk (Bug to Crimea), Yedickul (north of Crimea) and Kuban
Kuban ( Russian and Ukrainian: Кубань; ady, Пшызэ) is a historical and geographical region of Southern Russia surrounding the Kuban River, on the Black Sea between the Don Steppe, the Volga Delta and the Caucasus, and separated ...
.
Internal affairs
Internally, the khanate territory was divided among the beys, and beneath the beys were mirzas from noble families. The relationship of peasants or herdsmen to their mirzas was notfeudal
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structur ...
. They were free and the Islamic law
Sharia (; ar, شريعة, sharīʿa ) is a body of religious law that forms a part of the Islamic tradition. It is derived from the religious precepts of Islam and is based on the sacred scriptures of Islam, particularly the Quran and the ...
protected them from losing their rights. Apportioned by village, the land was worked in common and taxes were assigned to the whole village. The tax was one tenth of an agricultural product, one twentieth of a herd animal, and a variable amount of unpaid labor. During the reforms by the last khan Şahin Giray
Şahin Giray, Shahin Khan Girai ( crh, شاهين كراى, Şahin Geray, 1745—1787) was the last Khan of Crimea on two occasions (1777–1782, 1782–1783).
Life
He was born in 1745 in Edirne. He studied in Greece and Venice. He reputedly ...
, the internal structure was changed following the Turkish pattern: the nobles' landholdings were proclaimed the domain of the khan and reorganized into ''qadılıqs'' (provinces governed by representatives of the khan).
Crimean law
 Crimean law was based on Tatar law, Islamic law, and, in limited matters, Ottoman law. The leader of the Muslim establishment was the
Crimean law was based on Tatar law, Islamic law, and, in limited matters, Ottoman law. The leader of the Muslim establishment was the mufti
A Mufti (; ar, مفتي) is an Islamic jurist qualified to issue a nonbinding opinion (''fatwa'') on a point of Islamic law (''sharia''). The act of issuing fatwas is called ''iftāʾ''. Muftis and their ''fatwas'' played an important role ...
, who was selected from among the local Muslim clergy. His major duty was neither judicial nor theological, but financial. The mufti's administration controlled all of the vakif lands and their enormous revenues. Another Muslim official, appointed not by the clergy but the Ottoman sultan, was the kadıasker
A kazasker or kadıasker ( ota, قاضی عسكر, ''ḳāḍī'asker'', "military judge") was a chief judge in the Ottoman Empire, so named originally because his jurisdiction extended to the cases of soldiers, who were later tried only by their ...
, the overseer of the khanate's judicial districts, each under jurisdiction of a kadi. In theory, kadis answered to the kadiaskers, but in practice they answered to the clan leaders and the khan. The kadis determined the day to day legal behavior of Muslims in the khanate.
Non-Muslim minorities
Substantial non-Muslim minorities —Greeks
The Greeks or Hellenes (; el, Έλληνες, ''Éllines'' ) are an ethnic group and nation indigenous to the Eastern Mediterranean and the Black Sea regions, namely Greece, Cyprus, Albania, Italy, Turkey, Egypt, and, to a lesser extent, ot ...
, Armenians
Armenians ( hy, հայեր, ''hayer'' ) are an ethnic group native to the Armenian highlands of Western Asia. Armenians constitute the main population of Armenia and the ''de facto'' independent Artsakh. There is a wide-ranging diaspora ...
, Crimean Goths
The Crimean Goths were Greuthungi-Gothic tribes who remained in the lands around the Black Sea, especially in Crimea. They were the longest-lasting of the Gothic communities. Their existence is well attested through the ages, though the exact p ...
, Adyghe (Circassians), Venetians, Genoese, Crimean Karaites
The Crimean Karaites or Krymkaraylar (Crimean Karaim: Кърымкъарайлар, ''Qrımqaraylar'', singular къарай, ''qaray''; Trakai dialect: ''karajlar'', singular ''karaj''; he, קראי מזרח אירופה; crh, Qaraylar; ), a ...
and Qırımçaq Jews — lived principally in the cities, mostly in separate districts or suburbs. Under the ''millet
Millets () are a highly varied group of small-seeded grasses, widely grown around the world as cereal crops or grains for fodder and human food. Most species generally referred to as millets belong to the tribe Paniceae, but some millets a ...
'' system, they had their own religious and judicial institutions. They were subject to extra taxes in exchange for exemption from military service, living like Crimean Tatars and speaking dialects of Crimean Tatar. Mikhail Kizilov writes: "According to Marcin Broniewski (1578), the Tatars seldom cultivated the soil themselves, with most of their land tilled by the Polish, Ruthenian, Russian, and Walachian (Moldavian) slaves."
The Jewish population was concentrated in Çufut Kale ('Jewish Fortress'), a separate town near Bahçeseray that was the Khan's original capital. As with other minorities, they spoke a Turkic language. Crimean law granted them special financial and political rights as a reward, according to local folklore, for historic services rendered to an ''uluhane'' (first wife of a Khan). The capitation tax on Jews in Crimea was levied by the office of the uluhane in Bahçeseray.Fisher p. 34 Much like the Christian population of Crimea, the Jews were actively involved in the slave trade. Both Christians and Jews also often redeemed Christian and Jewish captives of Tatar raids in Eastern Europe.
Economy
 The
The nomad
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the po ...
ic part of the Crimean Tatars and all the Nogays were cattle breeders. Crimea had important trading ports where the goods arrived via the Silk Road
The Silk Road () was a network of Eurasian trade routes active from the second century BCE until the mid-15th century. Spanning over 6,400 kilometers (4,000 miles), it played a central role in facilitating economic, cultural, political, and rel ...
were exported to the Ottoman Empire and Europe. Crimean Khanate had many large cities such as the capital Bahçeseray, Gözleve (Yevpatoria), Karasu Bazaar (Karasu-market) and Aqmescit
Simferopol () is the second-largest city in the Crimean Peninsula. The city, along with the rest of Crimea, is internationally recognised as part of Ukraine, and is considered the capital of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea. However, it is ...
(White-mosque) having numerous ''hans'' (caravansarai
A caravanserai (or caravansary; ) was a roadside inn where travelers ( caravaners) could rest and recover from the day's journey. Caravanserais supported the flow of commerce, information and people across the network of trade routes covering ...
s and merchant quarters), tanners, and mills. Many monuments constructed under the Crimean Khanate were destroyed or left in ruins after the Russian invasion.A history of Ukraine, Paul Robert Magocsi, 347, 1996 Mosques, in particular were demolished or remade into Orthodox churches. The settled Crimean Tatars were engaged in trade, agriculture, and artisanry. Crimea was a center of wine, tobacco, and fruit cultivation. Bahçeseray kilim
A kilim ( az, Kilim کیلیم; tr, Kilim; tm, Kilim; fa, گلیم ''Gilīm'') is a flat tapestry- woven carpet or rug traditionally produced in countries of the former Persian Empire, including Iran, the Balkans and the Turkic countries. Ki ...
s (oriental rug
An oriental rug is a heavy textile made for a wide variety of utilitarian and symbolic purposes and produced in " Oriental countries" for home use, local sale, and export.
Oriental carpets can be pile woven or flat woven without pile, using v ...
s) were exported to Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
, and knives made by Crimean Tatar artisans were deemed the best by the Caucasian tribes. Crimea was also renowned for manufacture of silk and honey.
The slave trade
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
(15th-17th century) in captured Ukrainians and Russians was one of the major sources of income of Crimean Tartar and Nogay nobility. In this process, known as ''harvesting the steppe'', raiding parties would go out and capture, and then enslave the local Christian peasants living in the countryside. In spite of the dangers, Polish and Russian serfs
Serfdom was the status of many peasants under feudalism, specifically relating to manorialism, and similar systems. It was a condition of debt bondage and indentured servitude with similarities to and differences from slavery, which developed ...
were attracted to the freedom offered by the empty steppes of Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, Україна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inva ...
. The slave raids entered Russian and Cossack folklore and many '' dumy'' were written elegising the victims' fates. This contributed to a hatred for the Khanate that transcended political or military concerns. But in fact, there were always small raids committed by both Tatars and Cossacks
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or ...
, in both directions.The Russian Annexation of the Crimea 1772-1783, page 26
The last recorded major Crimean raid
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a p ...
, before those in the Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774)
The Russo-Turkish War of 1768–1774 was a major armed conflict that saw Russian arms largely victorious against the Ottoman Empire. Russia's victory brought parts of Moldavia, the Yedisan between the rivers Bug and Dnieper, and Crimea into th ...
took place during the reign of Peter I Peter I may refer to:
Religious hierarchs
* Saint Peter (c. 1 AD – c. 64–88 AD), a.k.a. Simon Peter, Simeon, or Simon, apostle of Jesus
* Pope Peter I of Alexandria (died 311), revered as a saint
* Peter I of Armenia (died 1058), Catholicos ...
(1682–1725).
Crimean art and architecture
Selim II Giray fountain
TheSelim II Giray
Selim II Giray (reigned 1743–1748, lived 1708–1748) was a khan of the Crimean Khanate. His father was Qaplan I Giray and his son was future khan Qaplan II Giray (1770). He was obedient to and praised by the Turks and kept peace with Russia by ...
fountain, built in 1747, is considered one of the masterpieces of Crimean Khanate's hydraulic engineering designs and is still marveled in modern times. It consists of small ceramic
A ceramic is any of the various hard, brittle, heat-resistant and corrosion-resistant materials made by shaping and then firing an inorganic, nonmetallic material, such as clay, at a high temperature. Common examples are earthenware, porcelain, ...
pipes, boxed in an underground stone tunnel, stretching back to the spring source more than away. It was one of the finest sources of water in Bakhchisaray
Bakhchysarai ( crh, Bağçasaray, italic=yes; russian: Бахчисара́й; ua, Бахчисара́й; tr, Bahçesaray) is a town in Crimea, a territory recognized by a majority of countries as part of Ukraine and annexed by Russia as the ...
.
Bakhchisaray Fountain
 One of the notable constructors of Crimean art and architecture was Qırım Giray, who in 1764 commissioned the fountain master Omer the Persian to construct the Bakhchisaray Fountain. The Bakhchisaray Fountain or ''Fountain of Tears'' is a real case of life imitating art. The fountain is known as the embodiment of love of one of the last Crimean Khans, Khan Qırım Giray for his young wife, and his grief after her early death. The Khan was said to have fallen in love with a Polish girl in his
One of the notable constructors of Crimean art and architecture was Qırım Giray, who in 1764 commissioned the fountain master Omer the Persian to construct the Bakhchisaray Fountain. The Bakhchisaray Fountain or ''Fountain of Tears'' is a real case of life imitating art. The fountain is known as the embodiment of love of one of the last Crimean Khans, Khan Qırım Giray for his young wife, and his grief after her early death. The Khan was said to have fallen in love with a Polish girl in his harem
Harem ( Persian: حرمسرا ''haramsarā'', ar, حَرِيمٌ ''ḥarīm'', "a sacred inviolable place; harem; female members of the family") refers to domestic spaces that are reserved for the women of the house in a Muslim family. A har ...
. Despite his battle-hardened harshness, he was grievous and wept when she died, astonishing all those who knew him. He commissioned a marble fountain to be made, so that the rock would weep, like him, forever.Johnstone, Sarah. ''Ukraine''. Lonely Planet, 2005.
Selim II Giray
Selim II Giray (reigned 1743–1748, lived 1708–1748) was a khan of the Crimean Khanate. His father was Qaplan I Giray and his son was future khan Qaplan II Giray (1770). He was obedient to and praised by the Turks and kept peace with Russia by ...
File:Bakhchysarai 04-14 img11 Palace Fountain of Tears.jpg, The Bakhchisaray Fountain
Regions and administration
;Main regions outside of ''Qirim yurt'' (the peninsula) * Kaztsiv ulus (located inKuban
Kuban ( Russian and Ukrainian: Кубань; ady, Пшызэ) is a historical and geographical region of Southern Russia surrounding the Kuban River, on the Black Sea between the Don Steppe, the Volga Delta and the Caucasus, and separated ...
)
* Yedychkul Horde
* Djambayluk Horde
* Yedisan Horde
* Budjak Horde
The Budjak Horde or Belgorod Horde formed part of the Nogai Horde in the 17th and 18th centuries. It settled in the northern Black Sea coast area under protectorate of the Crimean Khanate and the Ottoman Empire's Sanjak of Ozu (Yedisan). Its cap ...
* Prohnoinsk Palanka (possibly leased to the Zaporizhian Host) (located on the Kinburn peninsula)
* Silistra Province, Ottoman Empire
The Eyalet of Silistra or Silistria ( ota, ایالت سیلیستره; ''Eyālet-i Silistre''), later known as Özü Eyalet ( ota, ایالت اوزی; ''Eyālet-i Özi'') meaning Province of Ochakiv was an ''eyalet'' of the Ottoman Empire along ...
for sometime governed by Bakhchisaray
Bakhchysarai ( crh, Bağçasaray, italic=yes; russian: Бахчисара́й; ua, Бахчисара́й; tr, Bahçesaray) is a town in Crimea, a territory recognized by a majority of countries as part of Ukraine and annexed by Russia as the ...
The peninsula itself was divided by the khan's family and several ''beys''. An estate controlled by a bey was called a ''beylik''. Beys in the khanate were as important as the Polish ''Magnat
The magnate term, from the late Latin ''magnas'', a great man, itself from Latin ''magnus'', "great", means a man from the higher nobility, a man who belongs to the high office-holders, or a man in a high social position, by birth, wealth or ot ...
s''. Directly to the khan belonged Cufut-Qale
__NOTOC__
Chufut-Kale ( crh, Çufut Qale, italic=yes ; Russian and Ukrainian: Чуфут-Кале - ''Chufut-Kale''; Karaim: Кала - קלעה - ''Kala'') is a medieval city-fortress in the Crimean Mountains that now lies in ruins. It is a nati ...
, Bakhchisaray
Bakhchysarai ( crh, Bağçasaray, italic=yes; russian: Бахчисара́й; ua, Бахчисара́й; tr, Bahçesaray) is a town in Crimea, a territory recognized by a majority of countries as part of Ukraine and annexed by Russia as the ...
, and Staryi Krym (Eski Qirim). The khan also possessed all the salt lakes and the villages around them, as well as the woods around the rivers Alma, Kacha, and Salgir
The Salhyr or Salgir (Cyrillic: Салгир; ) is the longest river of the Crimean Peninsula. Its length is 204 km, and its drainage basin is 3,750 km². The average discharge of the water is 2 m³/s.Kalga'' who was next in the line of succession of the khan's family. He usually administered the eastern portion of the peninsula. The Kalga was also Chief Commander of the Crimean Army in the absence of the Khan. The next administrative position, called ''Nureddin,'' was also assigned to the khan's family. He administrated the western region of the peninsula. There also was a specifically assigned position for the khan's mother or sister — ''Ana-beim'' — which was similar to the Ottomans'
The Bağçasaray Palace of the Crimean Khans
Tatar.Net
* '' Дубровин Н. Ф.'
Присоединение Крыма к России.
В 4-х тт. — СПб.: Тип. Императорской Академии наук, 1885—1889. * * ''Гайворонский О.'
— Симферополь: Доля, 2003. — * '' Базилевич В. М.'
Из истории московско-крымских отношений в первой половине XVII века.
— Киев: Тип. 2-й артели, 1914. — 23 с. * '' Бантыш-Каменский Н. Н.'
Реестр делам крымского двора с 1474 по 1779 год.
— Симферополь: Тип. Таврическ. губернск. правления, 1893. * '' Смирнов В. Д.'
Крымское ханство под верховенством Оттоманской Порты в XVIII в. до присоединения его к России
— Одесса: Тип. А. Шульце, 1889. * ''Смирнов В. Д.'
— М.: Ломоносовъ, 2014. — * ''Смирнов В. Д.'
Сборник некоторых важных известий и официальных документов касательно Турции, России и Крыма
— СПб., 1881. * '' Шваб М. М.'
Русско-крымские отношения середины XVI — первых лет XVII веков в отечественной историографии 1940-х — 2000-х гг.
— Сургут, 2011. * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{Authority control History of Crimea Ottoman period in Ukraine Historical Turkic states History of the Ottoman Empire in Europe Islam in Ukraine Tatar states Tsardom of Russia 1440s establishments in the Ottoman Empire 1780s disestablishments in the Ottoman Empire 1440s establishments in Europe 1783 disestablishments in Europe States and territories established in 1441 States and territories disestablished in 1783 Vassal states of the Ottoman Empire Former monarchies
valide sultan #REDIRECT Valide sultan
{{redirect category shell, {{R from move{{R from miscapitalization{{R unprintworthy ...
. The senior wife of the Khan carried a rank of ''Ulu-beim'' and was next in importance to the Nureddin.
By the end of the khanate regional offices of the ''kaimakans'', who administered smaller regions of the Crimean Khanate, were created.
* Or Qapı (Perekop) had special status. The fortress was controlled either directly by the khan's family or by the family of Shirin.
Ottoman Empire territories
* Kefe Eyalet, a seat of Ottomans in Crimea until 1774 *Silistra Eyalet
The Eyalet of Silistra or Silistria ( ota, ایالت سیلیستره; ''Eyālet-i Silistre''), later known as Özü Eyalet ( ota, ایالت اوزی; ''Eyālet-i Özi'') meaning Province of Ochakiv was an ''eyalet'' of the Ottoman Empire along ...
, the western coast of Black Sea, later Danube Vilayet
See also
*List of Turkic dynasties and countries
The following is a list of dynasties, states or empires which are Turkic-speaking, of Turkic origins, or both. There are currently six recognised Turkic sovereign states. Additionally, there are six federal subjects of Russia in which a Turkic ...
* List of Turkic states and empires
The following is a list of dynasties, states or empires which are Turkic-speaking, of Turkic origins, or both. There are currently six recognised Turkic sovereign states. Additionally, there are six federal subjects of Russia in which a Turkic l ...
* Vassal and tributary states of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire had a number of tributary and vassal states throughout its history. Its tributary states would regularly send tribute to the Ottoman Empire, which was understood by both states as also being a token of submission. In exchang ...
* Little Tartary
The Crimean Khanate ( crh, , or ), officially the Great Horde and Desht-i Kipchak () and in old European historiography and geography known as Little Tartary ( la, Tartaria Minor), was a Crimean Tatar state existing from 1441 to 1783, the long ...
* Novorossiya
Novorossiya, literally "New Russia", is a historical name, used during the era of the Russian Empire for an administrative area that would later become the southern mainland of Ukraine: the region immediately north of the Black Sea and Crimea. ...
* Great Russia
Great Russia, sometimes Great Rus' (russian: Великая Русь, , , , , ), is a name formerly applied to the territories of "Russia proper", the land that formed the core of Muscovy and later Russia. This was the land to which the et ...
* Little Russia
Little Russia (russian: Малороссия/Малая Россия, Malaya Rossiya/Malorossiya; uk, Малоросія/Мала Росія, Malorosiia/Mala Rosiia), also known in English as Malorussia, Little Rus' (russian: Малая Ру� ...
* List of Crimean khans
This is a list of khans of the Crimean Khanate, a state which existed in present-day southern Ukraine from 1441 until 1783. Crimean Tatars, although not a part of the Ukrainian ethnos, are deeply interconnected, having ruled a large part o ...
* List of Crimean Tatars
A partial list of notable Crimean Tatars, in alphabetical order:
Civil rights activists
* Reşat Amet – murdered activist
* Mustafa Dzhemilev – leader of the Mejlis
* Emir-Usein Kuku – human rights defender
* Musa Mamut – committed ...
* List of Ukrainian rulers
This is a list that encompasses and includes all reigning leaders/rulers in the history of Ukraine.
This page includes the titles of the Grand Prince of Kyiv, Grand Prince of Chernigov, Grand Prince of Pereyaslavl, Grand Prince of Galici ...
* Russo-Crimean Wars
The Russo-Crimean Wars were fought between the forces of the Tsardom of Russia and the Crimean Khanate during the 16th century over the region around the Volga River.
In the 16th century, the Wild Steppes in Russia were exposed to the Khana ...
* Cossacks
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or ...
* Kipchaks
The Kipchaks or Qipchaks, also known as Kipchak Turks or Polovtsians, were a Turkic nomadic people and confederation that existed in the Middle Ages, inhabiting parts of the Eurasian Steppe. First mentioned in the 8th century as part of the ...
* Nogai Horde
The Nogai Horde was a confederation founded by the Nogais that occupied the Pontic–Caspian steppe from about 1500 until they were pushed west by the Kalmyks and south by the Russians in the 17th century. The Mongol tribe called the Manghuds co ...
* Lipka Tatars
The Lipka Tatars (Lipka – refers to ''Lithuania'', also known as Lithuanian Tatars; later also – Polish Tatars, Polish-Lithuanian Tatars, ''Lipkowie'', ''Lipcani'', ''Muślimi'', ''Lietuvos totoriai'') are a Turkic ethnic group who origina ...
* Eurasians
* Nomadic people
A nomad is a member of a community without fixed habitation who regularly moves to and from the same areas. Such groups include hunter-gatherers, pastoral nomads (owning livestock), tinkers and trader nomads. In the twentieth century, the po ...
* Tatar invasions
* Russo–Crimean War (1571)
* Ottoman wars in Europe
A series of military conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and various European states took place from the Late Middle Ages up through the early 20th century. The earliest conflicts began during the Byzantine–Ottoman wars, waged in Anatolia in ...
* Ottoman-Habsburg wars
* List of the Muslim Empires
This article includes a list of successive Islamic states and Muslim dynasties beginning with the time of the Islamic prophet Muhammad (570–632 CE) and the early Muslim conquests that spread Islam outside of the Arabian Peninsula, and continu ...
* List of Sunni Muslim dynasties
The following is a list of Sunni Muslim dynasties.
Asia
Middle East Arabian Peninsula
* Banu Wajih (926–965)
* Sharif of Mecca (967–1925)
* Al Uyuniyun (1076–1253)
* Sulaymanids (1063–1174)
* Mahdids (1159–1174)
*Kathiri (Hadhramau ...
* Mongol invasions
The Mongol invasions and conquests took place during the 13th and 14th centuries, creating history's largest contiguous empire: the Mongol Empire (1206-1368), which by 1300 covered large parts of Eurasia. Historians regard the Mongol devastation ...
* Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire of the 13th and 14th centuries was the largest contiguous land empire in history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, ...
* Mount & Blade: With Fire & Sword
Notes
References
Works cited
* * * *External links
The Bağçasaray Palace of the Crimean Khans
Tatar.Net
Further reading
** '' Дубровин Н. Ф.'
Присоединение Крыма к России.
В 4-х тт. — СПб.: Тип. Императорской Академии наук, 1885—1889. * * ''Гайворонский О.'
— Симферополь: Доля, 2003. — * '' Базилевич В. М.'
Из истории московско-крымских отношений в первой половине XVII века.
— Киев: Тип. 2-й артели, 1914. — 23 с. * '' Бантыш-Каменский Н. Н.'
Реестр делам крымского двора с 1474 по 1779 год.
— Симферополь: Тип. Таврическ. губернск. правления, 1893. * '' Смирнов В. Д.'
Крымское ханство под верховенством Оттоманской Порты в XVIII в. до присоединения его к России
— Одесса: Тип. А. Шульце, 1889. * ''Смирнов В. Д.'
— М.: Ломоносовъ, 2014. — * ''Смирнов В. Д.'
Сборник некоторых важных известий и официальных документов касательно Турции, России и Крыма
— СПб., 1881. * '' Шваб М. М.'
Русско-крымские отношения середины XVI — первых лет XVII веков в отечественной историографии 1940-х — 2000-х гг.
— Сургут, 2011. * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{Authority control History of Crimea Ottoman period in Ukraine Historical Turkic states History of the Ottoman Empire in Europe Islam in Ukraine Tatar states Tsardom of Russia 1440s establishments in the Ottoman Empire 1780s disestablishments in the Ottoman Empire 1440s establishments in Europe 1783 disestablishments in Europe States and territories established in 1441 States and territories disestablished in 1783 Vassal states of the Ottoman Empire Former monarchies