Cree Indians on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Cree ( cr, néhinaw, script=Latn, , etc.; french: link=no, Cri) are a North American Indigenous people. They live primarily in
 The Cree are generally divided into eight groups based on dialect and region. These divisions do not necessarily represent ethnic sub-divisions within the larger ethnic group:
*''
The Cree are generally divided into eight groups based on dialect and region. These divisions do not necessarily represent ethnic sub-divisions within the larger ethnic group:
*''
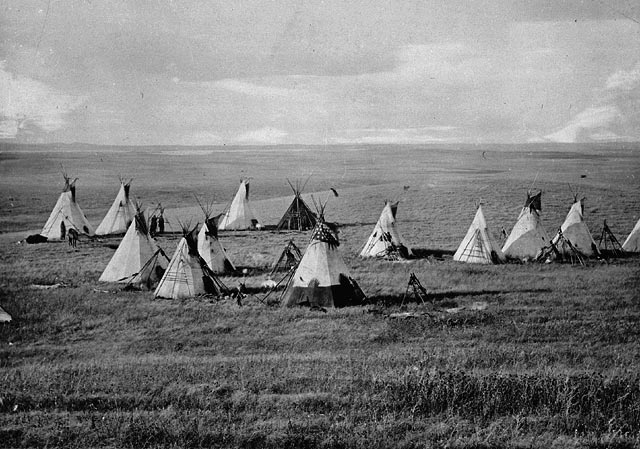 As hunter-gatherers, the basic unit of organization for Cree peoples was the ''lodge'', a group of perhaps eight or a dozen people, usually the families of two separate but related married couples, who lived together in the same
As hunter-gatherers, the basic unit of organization for Cree peoples was the ''lodge'', a group of perhaps eight or a dozen people, usually the families of two separate but related married couples, who lived together in the same 
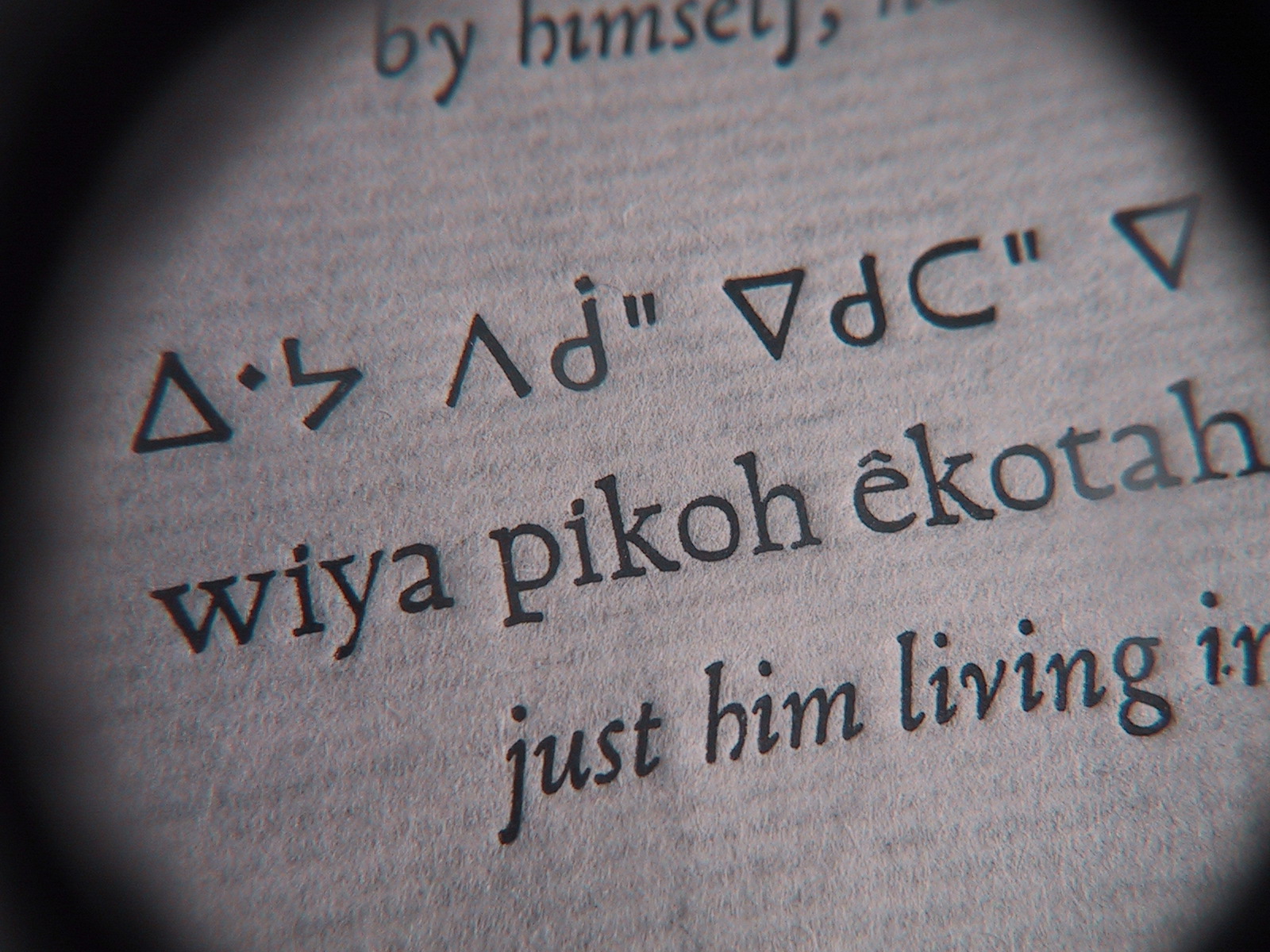 The Cree language (also known in the most broad classification as Cree-Montagnais, Cree-Montagnais-Naskapi, to show the groups included within it) is the name for a group of closely related
The Cree language (also known in the most broad classification as Cree-Montagnais, Cree-Montagnais-Naskapi, to show the groups included within it) is the name for a group of closely related
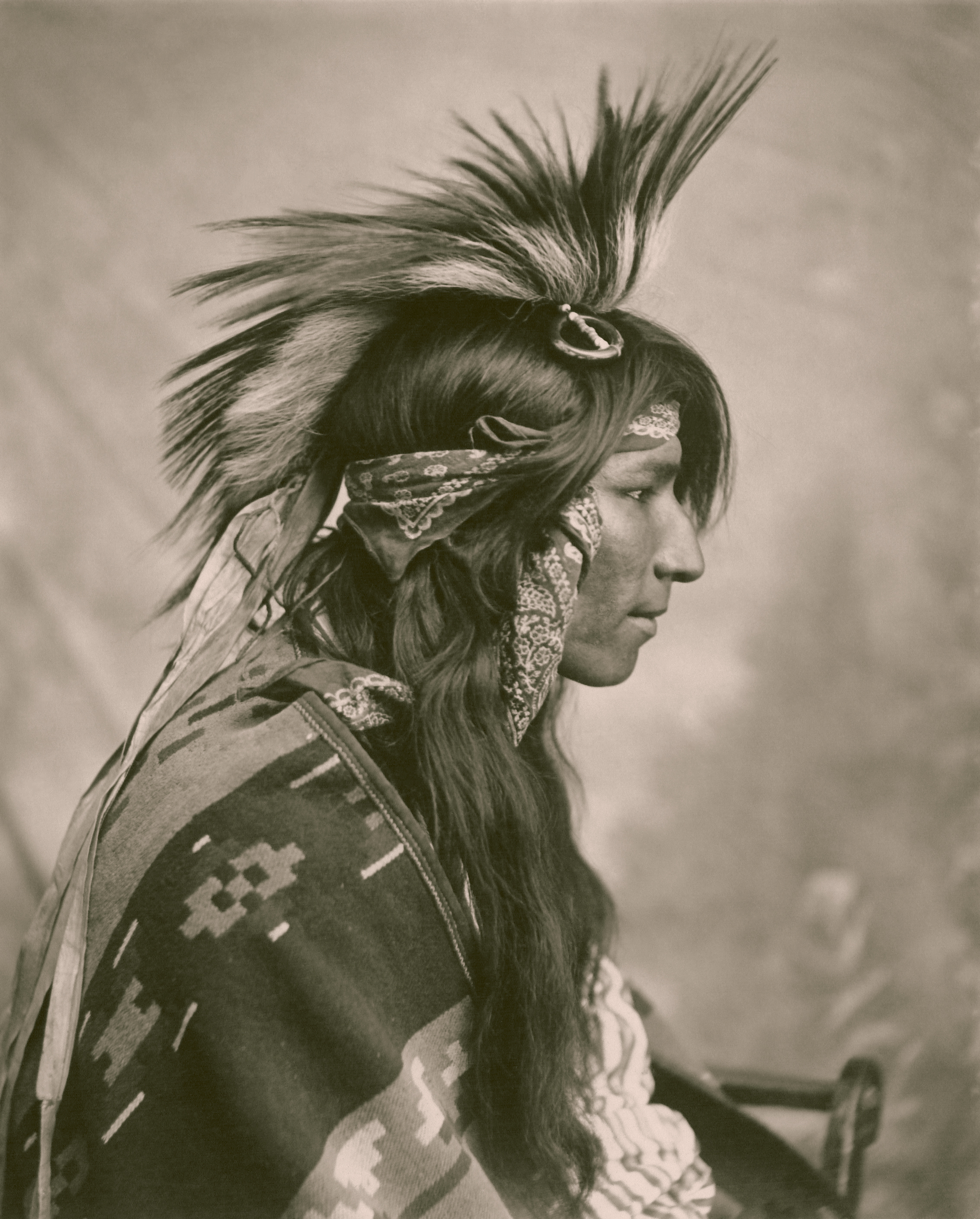 The Cree are the largest group of
The Cree are the largest group of
File:Group of Crees (HS85-10-27756).jpg, Group of Cree people
File:Merasty women and girls - Cree - The Pas Manitoba 1942.jpg, Merasty women and girls, Cree, The Pas,
 Conseil de la Nation Atikamekw, officially named Atikamekw Sipi – Conseil de la Nation Atikamekw, is a tribal council in Quebec, Canada. It is composed of three Atikamekw First Nations. The council is based in La Tuque, Quebec. The Atikamekw are inhabitants of the area they refer to as
Conseil de la Nation Atikamekw, officially named Atikamekw Sipi – Conseil de la Nation Atikamekw, is a tribal council in Quebec, Canada. It is composed of three Atikamekw First Nations. The council is based in La Tuque, Quebec. The Atikamekw are inhabitants of the area they refer to as



 * Janice Acoose, author, of Sakimay (
* Janice Acoose, author, of Sakimay (
Cree cultural site
The East Cree language web
The Cree-Innu linguistic atlas
Grand Council of the Crees (GCC) and Cree Nation Government
– Official website
Canada Government – Summary of the Agreement on the Cree Nation Governance
The Plains Cree – Ethnographic, Historical and Comparative Study by David Mandelbaum
Lac La Ronge Band website
Little Red River Cree Nation website
Brief history of Cree
from
CBC Digital Archives – James Bay Project and the Cree
Fisher River Cree Nation Official Website
The Gift of Language and Culture website
CBC Digital Archives – Eeyou Istchee: Land of the Cree
{{authority control Algonquian peoples First Nations in Alberta First Nations in British Columbia First Nations in Manitoba First Nations in Ontario First Nations in Quebec First Nations in Saskatchewan First Nations in the Northwest Territories Great Lakes tribes Plains tribes Native American tribes in Montana
Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic Ocean to the Pacific Ocean and northward into the Arctic Ocean, covering over , making it the world's second-largest country by tot ...
, where they form one of the country's largest First Nations
First Nations or first peoples may refer to:
* Indigenous peoples, for ethnic groups who are the earliest known inhabitants of an area.
Indigenous groups
*First Nations is commonly used to describe some Indigenous groups including:
**First Natio ...
.
In Canada, over 350,000 people are Cree or have Cree ancestry. The major proportion of Cree in Canada live north and west of Lake Superior
Lake Superior in central North America is the largest freshwater lake in the world by surface areaThe Caspian Sea is the largest lake, but is saline, not freshwater. and the third-largest by volume, holding 10% of the world's surface fresh wa ...
, in Ontario
Ontario ( ; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada.Ontario is located in the geographic eastern half of Canada, but it has historically and politically been considered to be part of Central Canada. Located in Central C ...
, Manitoba
, image_map = Manitoba in Canada 2.svg
, map_alt = Map showing Manitoba's location in the centre of Southern Canada
, Label_map = yes
, coordinates =
, capital = Winn ...
, Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a province in western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on the south by the U.S. states of Montana and North Dak ...
, Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is bordered by British Columbia to the west, Saskatchewan to the east, the Northwest Ter ...
and the Northwest Territories. About 27,000 live in Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
.
In the United States, Cree people historically lived from Lake Superior westward. Today, they live mostly in Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columb ...
, where they share the Rocky Boy Indian Reservation
Rocky Boy's Indian Reservation (also known as Rocky Boy Reservation) is one of seven Native American reservations in the U.S. state of Montana. Established by an act of Congress on September 7, 1916, it was named after ''Ahsiniiwin'' ( Stone Ch ...
with Ojibwe
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains.
According to the U.S. census, in the United States Ojibwe people are one of ...
(Chippewa) people.
The documented westward migration over time has been strongly associated with their roles as traders and hunters in the North American fur trade.
Sub-groups / Geography
Naskapi
The Naskapi (Nascapi, Naskapee, Nascapee) are an Indigenous people of the Subarctic native to the historical country St'aschinuw (ᒋᑦ ᐊᔅᒋᓄᐤ, meaning 'our nclusiveland'), which is located in northern Quebec and Labrador, neighb ...
'' and '' Montagnais'' (together known as the '' Innu'') are inhabitants of an area they refer to as ''Nitassinan
Nitassinan ( moe, script=Cans, i=no, ᓂᑕᔅᓯᓇᓐ) is the ancestral homeland of the Innu, an indigenous people of Eastern Quebec and Labrador, Canada. Nitassinan means "our land" in the Innu language. The territory covers the eastern por ...
''. Their territories comprise most of the present-day political jurisdictions of eastern Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
and Labrador
, nickname = "The Big Land"
, etymology =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Canada
, subdivision_type1 = Province
, subdivision_name1 ...
. Their cultures are differentiated, as some of the Naskapi are still caribou hunters and more nomadic than many of the Montagnais. The Montagnais have more settlements. The total population of the two groups in 2003 was about 18,000 people, of which 15,000 lived in Quebec. Their dialects and languages are the most distinct from the Cree spoken by the groups west of Lake Superior.
*'' Atikamekw'' are inhabitants of the area they refer to as ''Nitaskinan
Nitaskinan is the ancestral homeland of the Atikamekw people. It is located in the valley of the Saint-Maurice River in Quebec, Canada. It covers an area of 80,000 km2 (30,000 sq. mi.) On 8 September 2014, the Conseil de la Nation Atikamek ...
'' (Our Land), in the upper St. Maurice River valley of Quebec (about north of Montreal
Montreal ( ; officially Montréal, ) is the second-most populous city in Canada and most populous city in the Canadian province of Quebec. Founded in 1642 as '' Ville-Marie'', or "City of Mary", it is named after Mount Royal, the triple ...
). Their population is around 8,000.
*East Cree
East Cree, also known as (Eastern) James Bay Cree, and East Main Cree, is a group of Cree dialects spoken in Quebec, Canada on the east coast of lower Hudson Bay and James Bay, and inland southeastward from James Bay. Cree is one of the most spok ...
– Grand Council of the Crees; approximately 18,000 Cree ( in Coastal Dialect / in Inland Dialect) of Eeyou Istchee and Nunavik regions of Northern Quebec Northern Quebec (french: le nord du Québec) is a geographic term denoting the northerly, more remote and less populated parts of the Canadian province of Quebec.Alexandre Robaey"Charity group works with Indigenous communities to feed Northern Queb ...
.
* Moose Cree – Moose Factory
Moose Factory is a community in the Cochrane District, Ontario, Canada. It is located on Moose Factory Island, near the mouth of the Moose River, which is at the southern end of James Bay. It was the first English-speaking settlement in lands n ...
in the Northeastern Ontario
Northeastern Ontario is a secondary region of Northern Ontario in the Canadian province of Ontario, which lies north of Lake Huron and east of Lake Superior.
Northeastern Ontario consists of the districts of Algoma, Sudbury, Cochrane, Timiskami ...
; this group lives on Moose Factory Island
Moose Factory Island is an island in the Moose River, Ontario, Canada, about from its mouth at James Bay. It is adjacent to the community of Moosonee across the Moose River, from which it is accessible by water taxi. The island is home to the co ...
, near the mouth of the Moose River, at the southern end of James Bay. ("Factory" used to refer to a trading post.)
*Swampy Cree
The Swampy Cree people, also known by their autonyms ''Néhinaw'', ''Maskiki Wi Iniwak'', ''Mushkekowuk,'' ''Maškékowak'' or ''Maskekon'' (and therefore also ''Muskegon'' and ''Muskegoes'') or by exonyms including ''West Main Cree,'' ''Lowlan ...
– this group lives in northern Manitoba along the Hudson Bay coast and adjacent inland areas to the south and west, and in Ontario along the coast of Hudson Bay and James Bay. Some also live in eastern Saskatchewan around Cumberland House
Cumberland House was a mansion on the south side of Pall Mall in London, England. It was built in the 1760s by Matthew Brettingham for Prince Edward, Duke of York and Albany and was originally called York House. The Duke of York died in 1767 ...
. Their dialect has 4,500 speakers.
*Woodland Cree
The ''Saāwithiniwak'' or Woodland Cree, are a Cree people, calling themselves Nîhithaw in their own dialect of the language. They are the largest indigenous group in northern Alberta and are an Algonquian people. Prior to the 18th century, t ...
and Rocky Cree – a group in northern Alberta, Manitoba, and Saskatchewan.
* Plains Cree – a total of 34,000 people in Manitoba, Saskatchewan, Alberta, and Montana.
Due to the many dialects of the Cree language, the people have no modern collective autonym
Autonym may refer to:
* Autonym, the name used by a person to refer to themselves or their language; see Exonym and endonym
* Autonym (botany), an automatically created infrageneric or infraspecific name
See also
* Nominotypical subspecies, in zo ...
. The Plains Cree and Attikamekw refer to themselves using modern forms of the historical , namely and , respectively. Moose Cree, East Cree, Naskapi, and Montagnais all refer to themselves using modern dialectal forms of the historical , meaning 'man.' Moose Cree use the form , coastal East Cree and Naskapi use (variously spelled , , and ), inland East Cree use (variously spelled and ), and Montagnais use and , depending on dialect. The Cree use "Cree," "cri," "Naskapi, or "montagnais" to refer to their people only when speaking French or English.
Political aboriginal organization
Historical
 As hunter-gatherers, the basic unit of organization for Cree peoples was the ''lodge'', a group of perhaps eight or a dozen people, usually the families of two separate but related married couples, who lived together in the same
As hunter-gatherers, the basic unit of organization for Cree peoples was the ''lodge'', a group of perhaps eight or a dozen people, usually the families of two separate but related married couples, who lived together in the same wigwam
A wigwam, wickiup, wetu (Wampanoag), or wiigiwaam (Ojibwe, in syllabics: ) is a semi-permanent domed dwelling formerly used by certain Native American tribes and First Nations people and still used for ceremonial events. The term ''wickiup' ...
(domed tent) or tipi
A tipi , often called a lodge in English, is a conical tent, historically made of animal hides or pelts, and in more recent generations of canvas, stretched on a framework of wooden poles. The word is Siouan, and in use in Dakhótiyapi, Lakȟó ...
(conical tent), and the ''band
Band or BAND may refer to:
Places
*Bánd, a village in Hungary
*Band, Iran, a village in Urmia County, West Azerbaijan Province, Iran
* Band, Mureș, a commune in Romania
*Band-e Majid Khan, a village in Bukan County, West Azerbaijan Province, I ...
'', a group of lodges who moved and hunted together. In the case of disagreement, lodges could leave bands and bands could be formed and dissolved with relative ease. However, as there is safety in numbers, all families would want to be part of some band, and banishment was considered a very serious punishment. Bands would usually have strong ties to their neighbours through intermarriage and would assemble together at different parts of the year to hunt and socialize together. Besides these regional gatherings, there was no higher-level formal structure, and decisions of war and peace were made by consensus with allied bands meeting together in council. People could be identified by their '' clan'', which is a group of people claiming descent from the same common ancestor; each clan would have a representative and a vote in all important councils held by the band (compare: Anishinaabe clan system
The Anishinaabe, like most Algonquian-speaking groups in North America, base their system of kinship on patrilineal clans or totems. The Ojibwe word for clan () was borrowed into English as totem. The clans, based mainly on animals, were in ...
).
Each band remained independent of each other. However, Cree-speaking bands tended to work together and with their neighbours against outside enemies. Those Cree who moved onto the Great Plains and adopted bison hunting
Bison hunting (hunting of the American bison, also commonly known as the American buffalo) was an activity fundamental to the economy and society of the Plains Indians peoples who inhabited the vast grasslands on the Interior Plains of North ...
, called the Plains Cree, were allied with the Assiniboine
The Assiniboine or Assiniboin people ( when singular, Assiniboines / Assiniboins when plural; Ojibwe: ''Asiniibwaan'', "stone Sioux"; also in plural Assiniboine or Assiniboin), also known as the Hohe and known by the endonym Nakota (or Nakod ...
, the Metis Nation, and the Saulteaux
The Saulteaux (pronounced , or in imitation of the French pronunciation , also written Salteaux, Saulteau and other variants), otherwise known as the Plains Ojibwe, are a First Nations band government in Ontario, Manitoba, Saskatchewan, A ...
in what was known as the "Iron Confederacy
The Iron Confederacy or Iron Confederation (also known as Cree-Assiniboine in English or cr, script=Latn, Nehiyaw-Pwat, label=none in Cree) was a political and military alliance of Plains Indians of what is now Western Canada and the northern Un ...
", which was a major force in the North American fur trade from the 1730s to the 1870s. The Cree and the Assiniboine were important intermediaries in the Indian trading networks on the northern plains.
When a band went to war, they would nominate a temporary military commander, called a . loosely translated as "war chief". This office was different from that of the "peace chief", a leader who had a role more like that of diplomat. In the run-up to the 1885 North-West Rebellion, Big Bear was the leader of his band, but once the fighting started Wandering Spirit became war leader.

Contemporary
There have been several attempts to create a national political organization that would represent all Cree peoples, at least as far back as a 1994 gathering at the Opaskwayak Cree First Nation reserve.Name
The name "Cree" is derived from the Algonkian-languageexonym
An endonym (from Greek: , 'inner' + , 'name'; also known as autonym) is a common, ''native'' name for a geographical place, group of people, individual person, language or dialect, meaning that it is used inside that particular place, group, ...
, which the Ojibwa used for tribes around Hudson Bay. The French colonists and explorers, who spelled the term , , , , and , used the term for numerous tribes which they encountered north of Lake Superior, in Manitoba, and west of there. The French used these terms to refer to various groups of peoples in Canada, some of which are now better distinguished as Severn Anishinaabe
The Anishinaabeg (adjectival: Anishinaabe) are a group of culturally related Indigenous peoples present in the Great Lakes region of Canada and the United States. They include the Ojibwe (including Saulteaux and Oji-Cree), Odawa, Potawat ...
(Ojibwa), who speak dialects different from the Algonquin.
Depending on the community, the Cree may call themselves by the following names: the , and ; or , or . These names are derived from the historical autonym
Autonym may refer to:
* Autonym, the name used by a person to refer to themselves or their language; see Exonym and endonym
* Autonym (botany), an automatically created infrageneric or infraspecific name
See also
* Nominotypical subspecies, in zo ...
(of uncertain meaning) or from the historical autonym (meaning "person"). Cree using the latter autonym tend to be those living in the territories of Quebec and Labrador.
Language
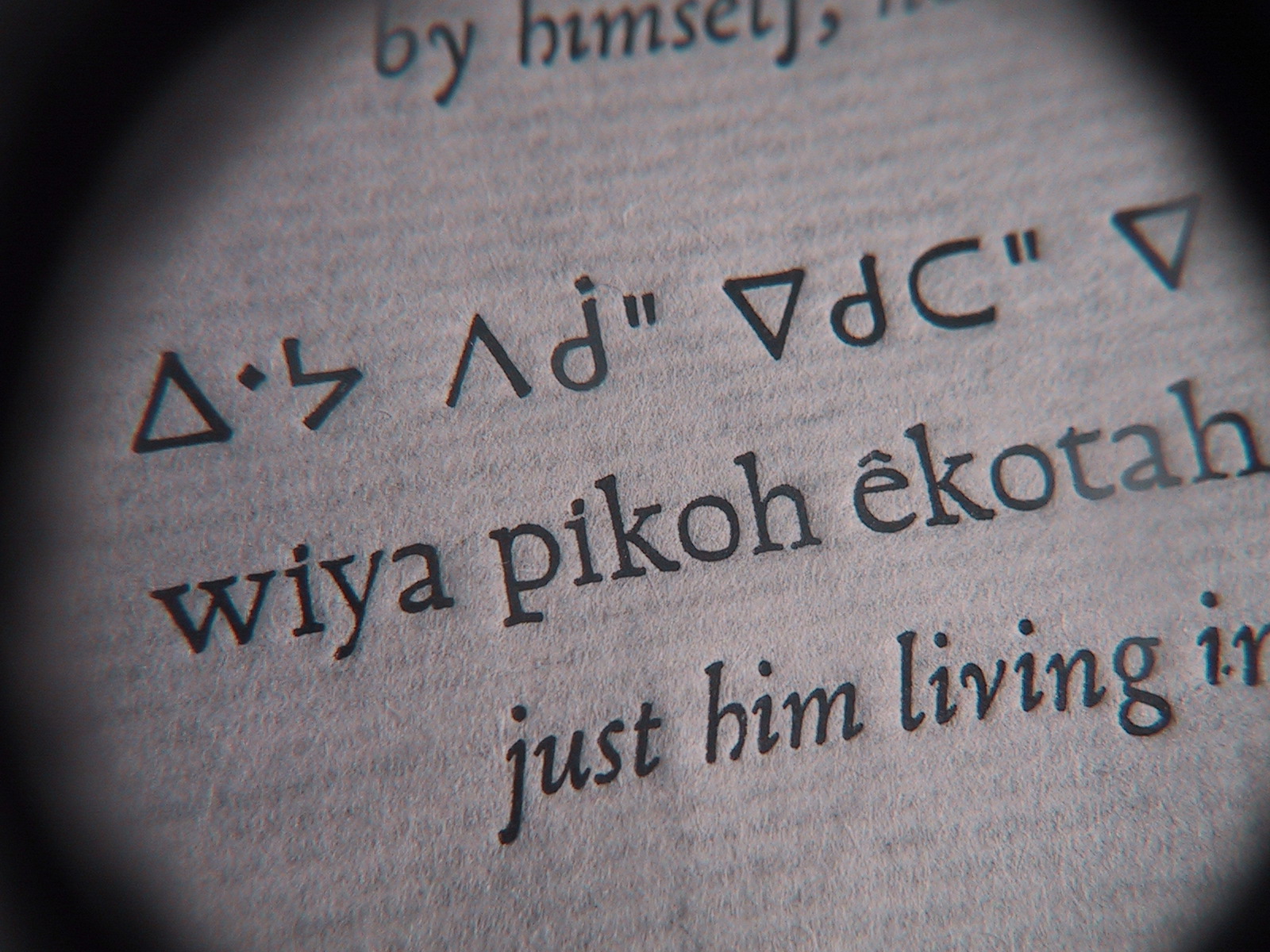 The Cree language (also known in the most broad classification as Cree-Montagnais, Cree-Montagnais-Naskapi, to show the groups included within it) is the name for a group of closely related
The Cree language (also known in the most broad classification as Cree-Montagnais, Cree-Montagnais-Naskapi, to show the groups included within it) is the name for a group of closely related Algonquian languages
The Algonquian languages ( or ; also Algonkian) are a subfamily of indigenous American languages that include most languages in the Algic language family. The name of the Algonquian language family is distinguished from the orthographically simi ...
, the mother tongue (i.e. language first learned and still understood) of approximately 96,000 people, and the language most often spoken at home of about 65,000 people across Canada, from the Northwest Territories to Labrador
, nickname = "The Big Land"
, etymology =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Canada
, subdivision_type1 = Province
, subdivision_name1 ...
. It is the most widely spoken aboriginal language in Canada. The only region where Cree has official status is in the Northwest Territories, together with eight other aboriginal languages.
The two major groups: Nehiyaw and Innu, speak a mutually intelligible Cree dialect continuum
A dialect continuum or dialect chain is a series of language varieties spoken across some geographical area such that neighboring varieties are mutually intelligible, but the differences accumulate over distance so that widely separated varie ...
, which can be divided by many criteria. In a dialect continuum, "It is not so much a language, as a chain of dialects, where speakers from one community can very easily understand their neighbours, but a Plains Cree speaker from Alberta would find a Quebec Cree speaker difficult to speak to without practice."
One major division between the groups is that the Eastern group palatalizes the sound to either (c) or to (č) when it precedes front vowels. There is also a major difference in grammatical vocabulary (particles) between the groups. Within both groups, another set of variations has arisen around the pronunciation of the Proto-Algonquian
Proto-Algonquian (commonly abbreviated PA) is the proto-language from which the various Algonquian languages are descended. It is generally estimated to have been spoken around 2,500 to 3,000 years ago, but there is less agreement on where it was ...
phoneme
In phonology and linguistics, a phoneme () is a unit of sound that can distinguish one word from another in a particular language.
For example, in most dialects of English, with the notable exception of the West Midlands and the north-wes ...
''*l'', which can be realized as or (th) by different groups. Yet in other dialects, the distinction between (ē) and (ī) has been lost, merging to the latter. In more western dialects, the distinction between and (š) has been lost, both merging to the former. "Cree is a not a typologically harmonic language. Cree has both prefixes and suffixes, both prepositions and postpositions, and both prenominal and postnominal modifiers (e.g. demonstratives can appear in both positions)."
Golla counts Cree dialects as eight of 55 North American languages that have more than 1,000 speakers and which are being actively acquired by children.
Identity and ethnicity
In Canada
 The Cree are the largest group of
The Cree are the largest group of First Nations
First Nations or first peoples may refer to:
* Indigenous peoples, for ethnic groups who are the earliest known inhabitants of an area.
Indigenous groups
*First Nations is commonly used to describe some Indigenous groups including:
**First Natio ...
in Canada, with 220,000 members and 135 registered bands. Together, their reserve lands are the largest of any First Nations group in the country. The largest Cree band and the second largest First Nations Band in Canada after the Six Nations Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to ...
is the Lac La Ronge Band in northern Saskatchewan.
Given the traditional Cree acceptance of mixed marriages, it is acknowledged by academics that all bands are ultimately of mixed heritage and multilingualism and multiculturalism was the norm. In the West, mixed bands of Cree, Saulteaux and Assiniboine, all partners in the Iron Confederacy
The Iron Confederacy or Iron Confederation (also known as Cree-Assiniboine in English or cr, script=Latn, Nehiyaw-Pwat, label=none in Cree) was a political and military alliance of Plains Indians of what is now Western Canada and the northern Un ...
, are the norm. However, in recent years, as indigenous languages have declined across western Canada where there were once three languages spoken on a given reserve, there may now only be one. This has led to a simplification of identity, and it has become "fashionable" for bands in many parts of Saskatchewan to identify as "Plains Cree" at the expense of a mixed Cree-Salteaux history. There is also a tendency for bands to recategorize themselves as "Plains Cree" instead of Woods Cree or Swampy Cree. Neal McLeod argues this is partly due to the dominant culture's fascination with Plains Indian
Plains Indians or Indigenous peoples of the Great Plains and Canadian Prairies are the Native American tribes and First Nation band governments who have historically lived on the Interior Plains (the Great Plains and Canadian Prairies) of ...
culture as well as the greater degree of written standardization and prestige
Prestige refers to a good reputation or high esteem; in earlier usage, ''prestige'' meant "showiness". (19th c.)
Prestige may also refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media Films
* ''Prestige'' (film), a 1932 American film directed by Tay Garnet ...
Plains Cree enjoys over other Cree dialects.
The Métis (from the French, – of mixed ancestry) are people of mixed ancestry, such as Cree (or Anishinaabe) and French, English, or Scottish heritage. According to Aboriginal Affairs and Northern Development Canada
Aborigine, aborigine or aboriginal may refer to:
*Aborigines (mythology), in Roman mythology
* Indigenous peoples, general term for ethnic groups who are the earliest known inhabitants of an area
*One of several groups of indigenous peoples, see ...
, the Métis were historically the children of French fur traders and Cree women or, from unions of English or Scottish traders and northern Dene
The Dene people () are an indigenous group of First Nations who inhabit the northern boreal and Arctic regions of Canada. The Dene speak Northern Athabaskan languages. ''Dene'' is the common Athabaskan word for "people". The term "Dene" ha ...
women (Anglo-Métis
A 19th century community of the Métis people of Canada, the Anglo-Métis, more commonly known as Countryborn, were children of fur traders; they typically had Scots (Orcadian, mainland Scottish), or English fathers and Aboriginal mothers.B ...
). The Métis National Council defines a Métis as "a person who self-identifies as Métis, is distinct from other Aboriginal peoples, is of historic Métis Nation Ancestry and who is accepted by the Métis Nation".
Manitoba
, image_map = Manitoba in Canada 2.svg
, map_alt = Map showing Manitoba's location in the centre of Southern Canada
, Label_map = yes
, coordinates =
, capital = Winn ...
, 1942
File:Chief King of the Wind (HS85-10-27755).jpg, Chief King of the Wind
File:Chief Thundercloud (HS85-10-27757).jpg, Chief Thundercloud
File:Chief Duckhunter (HS85-10-27759).jpg, Chief Duckhunter
File:Edward S. Curtis Collection People 095.jpg, Cree girl (1928)
File:Woman of the Snake tribe and woman of the Cree tribe 0066v.jpg, alt=, Illustration of a Snake woman (left) and a Cree woman (right), c. 1840–1843, Karl Bodmer
Johann Carl Bodmer (11 February 1809 – 30 October 1893) was a Swiss-French printmaker, etcher, lithographer, zinc engraver, draughtsman, painter, illustrator and hunter. Known as Karl Bodmer in literature and paintings, as a Swiss and French c ...
In the United States
At one time the Cree lived in northern Minnesota, North Dakota and Montana. Today, American Cree are enrolled in thefederally recognized
This is a list of federally recognized tribes in the contiguous United States of America. There are also federally recognized Alaska Native tribes. , 574 Indian tribes were legally recognized by the Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA) of the United ...
Chippewa Cree
The Chippewa Cree Tribe (Officially in cr, italics=no, ᐅᒋᐻᐤ ᓀᐃᔭᐤ, translit=''ocipwêw nêiyaw'')Montana Department of Justice, Official Tribally issued license plate of Chippewa Cree TriLink/ref> is a federally recognized tribe ...
tribe, located on the Rocky Boy Indian Reservation
Rocky Boy's Indian Reservation (also known as Rocky Boy Reservation) is one of seven Native American reservations in the U.S. state of Montana. Established by an act of Congress on September 7, 1916, it was named after ''Ahsiniiwin'' ( Stone Ch ...
, and in minority as "Landless Cree" on the Fort Peck Indian Reservation
The Fort Peck Indian Reservation ( asb, húdam wįcášta, dak, Waxchį́ca oyáte) is located near Fort Peck, Montana, in the northeast part of the state. It is the home of several federally recognized bands of Assiniboine, Nakota, Lakota, ...
and as "Landless Cree" and "Rocky Boy Cree" on the Fort Belknap Indian Reservation
The Fort Belknap Indian Reservation ( ats, ’ak3ɔ́ɔyɔ́ɔ, lit=the fence or ats, ’ɔ’ɔ́ɔ́ɔ́nííítaan’ɔ, lit=Gros Ventre tribe, label=none) is shared by two Native American tribes, the A'aninin (Gros Ventre) and the Nakoda ...
, all in Montana
Montana () is a state in the Mountain West division of the Western United States. It is bordered by Idaho to the west, North Dakota and South Dakota to the east, Wyoming to the south, and the Canadian provinces of Alberta, British Columb ...
. The Chippewa Cree share the reservation with the Pembina Band of Chippewa Indians Pembina Band of Chippewa Indians (Ojibwe: ''Aniibiminani-ziibiwininiwag'')
are a historical band of Chippewa (Ojibwe), originally living along the Red River of the North and its tributaries.
Through the treaty process with the United States, the Pe ...
, who form the "Chippewa" ( Ojibwa) half of the Chippewa Cree tribe. On the other Reservations, the Cree minority share the Reservation with the Assiniboine
The Assiniboine or Assiniboin people ( when singular, Assiniboines / Assiniboins when plural; Ojibwe: ''Asiniibwaan'', "stone Sioux"; also in plural Assiniboine or Assiniboin), also known as the Hohe and known by the endonym Nakota (or Nakod ...
, Gros Ventre
The Gros Ventre ( , ; meaning "big belly"), also known as the Aaniiih, A'aninin, Haaninin, Atsina, and White Clay, are a historically Algonquian-speaking Native American tribe located in north central Montana. Today the Gros Ventre people are ...
and Sioux tribes. Traditionally, the southern limits of the Cree territory in Montana were the Missouri River and the Milk River.
First contact
In Manitoba, the Cree were first contacted by Europeans in 1682, at the mouth of the Nelson and Hayes rivers by aHudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business di ...
(HBC) party traveling about inland. In the south, contact was later. In 1732 in what is now northwestern Ontario, Pierre Gaultier de Varennes, sieur de La Vérendrye
Pierre Gaultier de Varennes, sieur de La Vérendrye (17 November 1685 – 5 December 1749) was a French Canadian military officer, fur trader, and explorer. In the 1730s, he and his four sons explored the area west of Lake Superior and ...
, met with an assembled group of 200 Cree warriors near present-day Fort Frances, as well as with the Monsoni, (a branch of the Ojibwe
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains.
According to the U.S. census, in the United States Ojibwe people are one of ...
). Both groups had donned war paint in preparation to an attack on the Dakota
Dakota may refer to:
* Dakota people, a sub-tribe of the Sioux
** Dakota language, their language
Dakota may also refer to:
Places United States
* Dakota, Georgia, an unincorporated community
* Dakota, Illinois, a town
* Dakota, Minnesota, ...
and another group of Ojibwe.
After acquiring firearms from the HBC, the Cree moved as traders into the plains, acting as middlemen with the HBC.
First Nation communities
Naskapi
The Naskapi are the Innu First Nations inhabiting a region of northeasternQuebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
and Labrador
, nickname = "The Big Land"
, etymology =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Canada
, subdivision_type1 = Province
, subdivision_name1 ...
, Canada. The Naskapi are traditionally nomadic peoples, in contrast with the territorial Montagnais, the other segment of Innu. The Naskapi language and culture is quite different from the Montagnais, in which the dialect changes from y to n as in "Iiyuu" versus "Innu". is the Innu dialect spoken by the Naskapi. Today, the Naskapi are settled into two communities: Kawawachikamach Quebec and Natuashish, Newfoundland and Labrador.
The Naskapi Nation of Kawawachikamach
Naskapi Nation of Kawawachikamach ( nsk, script=Cans, ᓇᔅᑲᐱ ᐃᔪᒡ ᐅᑕ ᑲᐛᐛᒋᑲᒪᒡ, translit=Naskapi Iyuch Uta Kawâwâchikamach, french: links=no, Nation Naskapi de Kawawachikamach) is a First Nation band government in Que ...
is located in the Naskapi village
The following is a list of the types of local and supralocal territorial units in Quebec, including those used solely for statistical purposes, as defined by the Ministry of Municipal Affairs, Regions and Land Occupancy and compiled by the Inst ...
of Kawawachikamach, northeast of Schefferville
Schefferville is a town in the Canadian province of Quebec. Schefferville is in the heart of the Naskapi and Innu territory in northern Quebec, less than 2 km (1¼ miles) from the border with Labrador on the north shore of Knob Lake. It i ...
, Quebec. The village is in the reserve of the same name.
The Mushuau Innu First Nation, located in the community of Natuashish, Newfoundland and Labrador, is located in the Natuashish 2 reserve on the coast of Labrador
, nickname = "The Big Land"
, etymology =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Canada
, subdivision_type1 = Province
, subdivision_name1 ...
.
Montagnais
Eastern Montagnais
Innus of Ekuanitshit
Innus of Ekuanitshit (French: ''Les Innus d'Ekuanitshit'') are a First Nation band in Quebec, Canada. They live primarily in the Indian reserve of Mingan on the north coast of the St Lawrence River. , the band had a registered population of 677 ...
live on their reserve of Mingan, Quebec
Mingan, also known as Ekuanitshit in Innu-aimun, is an Innu First Nations reserve in the Canadian province of Quebec, at the mouth of the Mingan River on Mingan Bay of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence. It belongs to the Innu band of Ekuanitshit. Geo ...
, at the mouth of the Mingan River
Mingan River (french: Rivière Mingan) is a salmon river of the Côte-Nord region of Quebec. It flows from north to south and empties into the Gulf of Saint Lawrence.
Location
The Mingan River's source is in the Canadian Shield.
It descends to ...
of the Saint Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from Lake Ontario in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connectin ...
in the (north shore) region.
Innu Takuaikan Uashat Mak Mani-Utenam
Innu Takuaikan Uashat Mak Mani-Utenam is an Innu First Nations band government in Quebec, Canada. It is based in Sept-Îles in the Côte-Nord region on the North shore of the Saint Lawrence River. It owns two reserves: Maliotenam 27A and Uasha ...
based in Sept-Îles, Quebec, in the region on the Saint Lawrence River. They own two reserves: Maliotenam 27A, east of Sept-Îles, and Uashat 27, within Sept-Îles.
Innu Nation of Matimekush-Lac John
Innu Nation of Matimekush-Lac John (or La Nation Innu Matimekush-Lac John in French) is a First Nation band government based out of Schefferville, Quebec, Canada. The members of the band are Innu people and speak the Innu language, an Algonquia ...
is based out of Schefferville, Quebec. One reserve, Matimekosh, is an enclave of Schefferville. The other, Lac-John
Lac-John is a First Nations reserve on John Lake in the Côte-Nord region of Quebec, Canada, about north-east from the centre of Schefferville. Together with the Matimekosh Reserve, it belongs to the Innu Nation of Matimekush-Lac John. It is g ...
, is outside the town.
Première Nation des Innus de Nutashkuan is based on their reserve of Natashquan 1 or Nutashkuan. The reserve is located on the north shore of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence
, image = Baie de la Tour.jpg
, alt =
, caption = Gulf of St. Lawrence from Anticosti National Park, Quebec
, image_bathymetry = Golfe Saint-Laurent Depths fr.svg
, alt_bathymetry = Bathymetry ...
at the mouth of the Natashquan River.
located in the community of Pakuashipi
Pakuashipi (Pakua Shipi, or Pakua Shipu in Innu-aimun and St-Augustin Indian Settlement) is an Innu community in the Canadian province of Quebec, located on the north shore of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence in the Côte-Nord region. It is on the we ...
, Quebec, on the western shore of the mouth of the Saint-Augustin River
The Saint-Augustin River (french: Rivière Saint-Augustin, Innu: ''Pakut-shipu'') is a salmon river in the Côte-Nord region of Quebec, Canada. It empties into the Gulf of Saint Lawrence.
Location
The Saint-Augustin River has its source in the ...
on the north shore of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence in the region. The community is adjacent to the settlement of Saint-Augustin.
are located at La Romaine, Quebec
La Romaine, also known as Unamenshipit in Innu-aimun, is an Innu First Nations reserve in the Côte-Nord region of Quebec, Canada, at the mouth of the Olomane River on the Gulf of Saint Lawrence. It belongs to the Innu band of Unamen Shipu. Bei ...
at the mouth of the Olomane River on the Gulf of Saint Lawrence. They have one reserve; Romaine 2.
Sheshatshiu Innu First Nation
The Sheshatshiu Innu First Nation is located in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada. This First Nations band government is centred on the community of Sheshatshiu.
The current chief of the Sheshatshiu Innu First Nation is Eugene ...
located in the community of Sheshatshiu
Sheshatshiu () is an Innu federal reserve and designated place in the Canadian province of Newfoundland and Labrador. The reserve is approximately north of Happy Valley-Goose Bay. Some references may spell the community's name as Sheshatshit, ...
in Labrador and is located approximately north of Happy Valley-Goose Bay
Happy Valley-Goose Bay (Inuit: ''Vâli'') is a town in the province of Newfoundland and Labrador, Canada.
Located in the central part of Labrador on the coast of Lake Melville and the Churchill River, Happy Valley-Goose Bay is the largest popul ...
. Sheshatshiu is located adjacent to the Inuit
Inuit (; iu, ᐃᓄᐃᑦ 'the people', singular: Inuk, , dual: Inuuk, ) are a group of culturally similar indigenous peoples inhabiting the Arctic and subarctic regions of Greenland, Labrador, Quebec, Nunavut, the Northwest Territories ...
community of North West River
North West River is a small town located in central Labrador. Established in 1743 as a trading post by French Fur Trader Louis Fornel, the community later went on to become a hub for the Hudson's Bay Company and home to a hospital and school s ...
. The Sheshatshiu Nation has one reserve, Sheshatshiu 3.
Western Montagnais
Pekuakamiulnuatsh First Nation is located on the reserve of Mashteuiatsh in the Saguenay–Lac-Saint-Jean region, north ofRoberval, Quebec
Roberval is a city on the south-western shore of Lac Saint-Jean in the Le Domaine-du-Roy Regional County Municipality of Quebec, Canada. With a population of 9,840 in the Canada 2021 Census, it is the fourth largest city on this lake after Alma, ...
, on the western shore of Lac Saint-Jean
Lac Saint-Jean (Canadian French: ) is a large, relatively shallow lake in south-central Quebec, Canada, in the Laurentian Highlands. It is situated north of the Saint Lawrence River, into which it drains via the Saguenay River. It covers an area ...
.
Bande des Innus de Pessamit based in Pessamit
Pessamit (formerly Betsiamites, or Bersimis), is a First Nations reserve and Innu community in the Canadian province of Quebec, located about southwest from Baie-Comeau along the north shore of the Saint Lawrence River at the mouth of the Betsia ...
, Quebec, is located about southwest of Baie-Comeau
Baie-Comeau (; 2021 city population 20,687; CA population 26,643) is a city located approximately north-east of Quebec City in the Côte-Nord region of the province of Quebec, Canada. It is located on the shores of the Saint Lawrence River nea ...
along the north shore of the Saint Lawrence River at the mouth of the Betsiamites River
The Betsiamites (also called Bersimis) is a river of Côte-Nord, Quebec, Canada, which joins the Saint Lawrence River.
The Pipmuacan Reservoir, impounded by the Bersimis-1 Dam, is roughly halfway down its course.Natural Resources Canada, Atlas ...
. It is across the river directly north of Rimouski, Quebec
Rimouski ( ) is a city in Quebec, Canada. Rimouski is located in the Bas-Saint-Laurent region, at the mouth of the Rimouski River. It has a population of 48,935 (as of 2021). Rimouski is the site of Université du Québec à Rimouski (UQAR), the ...
. Pessamit is northeast of Quebec City.
Innue Essipit
Innue Essipit is an Innu First Nation in Quebec, Canada. It owns one reserve named Essipit where one-third of its population live, located in the Côte-Nord region on the North shore of the Saint Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (french: ...
are based in their reserve of Essipit
Essipit (known as Les Escoumins until 1996) is an Innu Indian reserve in the Canadian province of Quebec, located on the north shore of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence in the Côte-Nord region. It belongs to the Innue Essipit First Nation.
The reserve ...
, adjacent to the village of Les Escoumins, Quebec
Les Escoumins is a municipality in La Haute-Côte-Nord Regional County Municipality in the Côte-Nord region of Quebec. It is located on the north shore of the Saint Lawrence River.
Its economy is mostly based on the service sectors, especially ...
. The community is on the north shore of the Saint Lawrence River at the mouth of the Escoumins River in the region, northeast of Tadoussac
Tadoussac () is a village in Quebec, Canada, at the confluence of the Saguenay and Saint Lawrence rivers. The indigenous Innu call the place ''Totouskak'' (plural for ''totouswk'' or ''totochak'') meaning "bosom", probably in reference to the tw ...
and northeast of Québec.
Atikamekw ()
 Conseil de la Nation Atikamekw, officially named Atikamekw Sipi – Conseil de la Nation Atikamekw, is a tribal council in Quebec, Canada. It is composed of three Atikamekw First Nations. The council is based in La Tuque, Quebec. The Atikamekw are inhabitants of the area they refer to as
Conseil de la Nation Atikamekw, officially named Atikamekw Sipi – Conseil de la Nation Atikamekw, is a tribal council in Quebec, Canada. It is composed of three Atikamekw First Nations. The council is based in La Tuque, Quebec. The Atikamekw are inhabitants of the area they refer to as Nitaskinan
Nitaskinan is the ancestral homeland of the Atikamekw people. It is located in the valley of the Saint-Maurice River in Quebec, Canada. It covers an area of 80,000 km2 (30,000 sq. mi.) On 8 September 2014, the Conseil de la Nation Atikamek ...
("Our Land"), in the upper Saint-Maurice River valley. The First Nations:
* Atikamekw d'Opitciwan
Atikamekw of Opitciwan (French language, French: ''Atikamekw d'Opitciwan'') are an Atikamekw First Nations in Canada, First Nation in Quebec, Canada. In 2016, it has a registered population of 2,937 members. They live primarily on an Indian reserve ...
live in Obedjiwan, Quebec on the north shore of Gouin Reservoir in the Mauricie region. Their reserve, Obedjiwan 28, contains the community. It is located approximately by road west of Saguenay and east of Val-d'Or
Val-d'Or (, , ; "Golden Valley" or "Valley of Gold") is a city in Quebec, Canada with a population of 32,752 inhabitants according to the Canada 2021 Census. The city is located in the Abitibi-Témiscamingue region near La Vérendrye Wildlife ...
.
* Atikamekw of Manawan are based in Manawan, Quebec, on the south-western shores of Lake Métabeskéga in the Lanaudière
Lanaudière (, ) is one of the seventeen administrative regions of Quebec, Canada, situated immediately to the northeast of Montreal. It has a total population ( 2016 Census) of 494,796 inhabitants, an increase of 4.9% over the 2011 census.
Geog ...
region. The reserve is located by road northeast of Mont-Laurier
Mont-Laurier () is a town and incorporated municipality in northwest Quebec, Canada, located on the banks of the Lièvre River (''Rivière du Lièvre''), a tributary of the Ottawa River. Known as the "Capital of the Haute-Laurentides", the motto ...
or north of Montreal.
* Conseil des Atikamekw de Wemotaci
Wemotaci Atikamekw Council ( French: ''Conseil des Atikamekw de Wemotaci'') is the band council of the Atikamekw of Wemotaci, Quebec. In 2016, the band has a registered population of 1,918 members. It has two Indian reserves: Coucoucache 24A and t ...
in Wemotaci, Quebec
Wemotaci (designated as Weymontachie 23 until 1997) is a First Nations reserve on the north shore of the Saint-Maurice River at the mouth of the Manouane River in the Mauricie region of Quebec, Canada. Together with the Obedjiwan and the Couco ...
on the north shore of the Saint-Maurice River at the mouth of the Manouane River in the Mauricie region approximately north of Trois-Rivières
Trois-Rivières (, – 'Three Rivers') is a city in the Mauricie administrative region of Quebec, Canada, at the confluence of the Saint-Maurice and Saint Lawrence rivers, on the north shore of the Saint Lawrence River across from the city of ...
. The Nation owns two reserves; the first is around Wemotaci while the second is Coucoucache 24 on the north shore of Reservoir Blanc on the Saint-Maurice River. Coucoucache 24 is not inhabited and is only accessible by boat.
James Bay Cree
Eeyou Istchee is aterritory equivalent to a regional county municipality An equivalent territory (french: territoire équivalent), formally known as territory equivalent to a regional county municipality (french: territoires équivalents à une MRC), is a territorial unit used by Statistics Canada and the Institut de la ...
(TE) of Nord-du-Québec
Nord-du-Québec (; en, Northern Quebec) is the largest, but the least populous, of the seventeen administrative regions of Quebec, Canada. With nearly of land area, and very extensive lakes and rivers, it covers much of the Labrador Peninsu ...
represented by the Grand Council of the Crees. On 24 July 2012, the Quebec government signed an accord with the Cree Nation that resulted in the abolition of the neighbouring municipality of Baie-James
The Municipality of Baie-James (french: Municipalité de Baie-James) was a municipality in northern Quebec, Canada, which existed from 1971 to 2012. Located to the east of James Bay, Baie-James covered of land, making it the largest incorporat ...
and the creation of the new Eeyou Istchee James Bay Regional Government
Eeyou Istchee James Bay Regional Government (french: Gouvernement régional d’Eeyou Istchee Baie-James, cr, ᐄᔨᔨᐤ ᐊᔅᒌ ᒉᐃᒥᔅ ᐯᐃ ᐊᔅᒌᐤ ᑎᐹᔨᐦᒋᒑᐎᓐ, italic=no ) is a local municipality in the (TE) in ...
, providing for the residents of surrounding Jamésie
Jamésie is a territory equivalent to a regional county municipality (TE) of Nord-du-Québec, Canada.
Its geographical code is 991 and together with Kativik TE and Eeyou Istchee TE it forms the administrative région and census division (CD ...
TE and Eeyou Istchee to jointly govern the territory formerly governed by the municipality of Baie-James. Eeyou Istchee is a territory of eight enclaves within Jamésie plus one enclave (Whapmagoostui) within Kativik TE. Each enclave is a combination of a Cree reserved land (TC) and a Cree village municipality
The following is a list of the types of local and supralocal territorial units in Quebec, including those used solely for statistical purposes, as defined by the Ministry of Municipal Affairs, Regions and Land Occupancy and compiled by the Ins ...
(VC), both with the same name.
* Cree Nation of Chisasibi
The Cree Nation of Chisasibi is a Cree First Nation in Quebec, Canada. It is headquartered at the Cree village of Chisasibi in the Eeyou Istchee territory in Northern Quebec. The nation also has a ''terre réservée crie'' or Cree reserved la ...
is at the Cree village of Chisasibi on the south shore of La Grande River
La Grande River (french: La Grande Rivière; cr, Chisasibi, script=latn; both meaning "great river") is a river in northwestern Quebec, Canada, which rises in the highlands of north central Quebec and flows roughly west to drain into James Bay. ...
on the eastern shore of James Bay
James Bay (french: Baie James; cr, ᐐᓂᐯᒄ, Wînipekw, dirty water) is a large body of water located on the southern end of Hudson Bay in Canada. Both bodies of water extend from the Arctic Ocean, of which James Bay is the southernmost pa ...
. The Nation's reserve is Chisasibi TC. Chisasibi is accessible via road and its airport. It is northwest of Chibougamau via the and the James Bay Road
The James Bay Road (french: Route de la Baie James), officially the Route Billy-Diamond Highway, is a remote wilderness highway winding its way through the Canadian Shield in northwestern Quebec and reaches into the James Bay region. It starts in ...
. (Chibougamau is by road north of Montreal).
* Eastmain (Cree Nation) is located at Eastmain
Eastmain ( ; cr, ᐄᔅᒣᐃᓐ/Îsmein) is a Cree community located on east coast of James Bay at the mouth of the Eastmain River, Quebec, Canada. It is a small coastal Cree village with a population of 924 people in the 2021 Canadian Censu ...
VC and Eastmain
Eastmain ( ; cr, ᐄᔅᒣᐃᓐ/Îsmein) is a Cree community located on east coast of James Bay at the mouth of the Eastmain River, Quebec, Canada. It is a small coastal Cree village with a population of 924 people in the 2021 Canadian Censu ...
TC is the reserve. The Nation is located on the east coast of James Bay at the mouth of the Eastmain River
The Eastmain River, formerly written East Main, is a river in west central Quebec. It rises in central Quebec and flows west to James Bay, draining an area of . The First Nations Cree village of Eastmain is located beside the mouth.
Name
East ...
. Eastmain is northwest of Chibougamau via the and the James Bay Road.
* Cree Nation of Mistissini is based in the Cree village of Mistissini, located in the south-east corner of the largest natural lake in Quebec, Lake Mistassini
Lake Mistassini () is the largest natural lake by surface area in the province of Quebec, Canada, with a total surface area of approximately and a net area (water surface area only) of . It is located in the Jamésie region of the province, appro ...
. The associated reserve is Mistissini TC. Mistissini is northeast of Chibougamau on Route 167.
* Cree Nation of Nemaska is headquartered at Nemaska VC and its reserve is Nemaska TC located on the western shores of Lake Champion. The village is the seat of the Grand Council of the Crees. Nemaska is northwest of Chibougamau, at km 300 of the .
* Oujé-Bougoumou Cree Nation is located in the Cree village of Oujé-Bougoumou
Oujé-Bougoumou (; cr, ᐆᒉᐳᑯᒨ / Ûcêpukumû, the linguistic basis for the name of the nearby town Chibougamau, which in the Cree language refers to the narrows of a body of water, and was where Cree people gathered seasonally) is th ...
on the shores of Opémisca Lake. Oujé-Bougoumou is unique from the other Nations of Eeyou Istchee in that it doesn't have an associated reserve. The village is due west of Chibougamau.
* The Crees of the Waskaganish First Nation
The Crees of the Waskaganish First Nation or Cree Nation of Waskaganish is a Cree First Nation of Canada. Waskaganish ( cr, ᐙᔅᑳᐦᐄᑲᓂᔥ/Wâskâhîkaniš) means ''Little House''. It is headquartered in the Cree village of Waskagan ...
is located at Waskaganish
Waskaganish ( cr, ᐙᔅᑳᐦᐄᑲᓂᔥ/Wâskâhîkaniš, Little House; ) is a Cree community of over 2,500 people at the mouth of the Rupert River on the south-east shore of James Bay in Northern Quebec, Canada. Waskaganish is part of the ...
VC at the mouth of the Rupert River
The Rupert River is one of the largest rivers in Quebec, Canada. From its headwaters in Lake Mistassini, the largest natural lake in Quebec, it flows west into Rupert Bay on James Bay. The Rupert drains an area of .
There is some extremely la ...
on the south-east shore of James Bay. The associated reserve is Waskaganish
Waskaganish ( cr, ᐙᔅᑳᐦᐄᑲᓂᔥ/Wâskâhîkaniš, Little House; ) is a Cree community of over 2,500 people at the mouth of the Rupert River on the south-east shore of James Bay in Northern Quebec, Canada. Waskaganish is part of the ...
TC. Founded in 1668 as Charles Fort, two years before the creation of the HBC, the community is on the site of the first fur trading post of the Hudson's Bay Company
The Hudson's Bay Company (HBC; french: Compagnie de la Baie d'Hudson) is a Canadian retail business group. A fur trading business for much of its existence, HBC now owns and operates retail stores in Canada. The company's namesake business di ...
. After the HBC was formed, the community was known as Fort Rupert, Rupert Fort, or Rupert House after Prince Rupert of the Rhine, the first governor of the HBC.
* Cree First Nation of Waswanipi is located in the Cree village of Waswanipi
Waswanipi may refer to:
*Waswanipi, Quebec, a Cree village in Eeyou Istchee, Quebec, Canada
*Waswanipi (Cree village municipality), a Cree Reserved Land located in Eeyou Istchee, Quebec, Canada
*Waswanipi River, a tributary of Matagami Lake in Que ...
and the reserve is Waswanipi
Waswanipi may refer to:
*Waswanipi, Quebec, a Cree village in Eeyou Istchee, Quebec, Canada
*Waswanipi (Cree village municipality), a Cree Reserved Land located in Eeyou Istchee, Quebec, Canada
*Waswanipi River, a tributary of Matagami Lake in Que ...
TC. The Nation is located near the confluence of the Chibougamau and Waswanipi River
The Waswanipi River is a tributary of Matagami Lake. The Waswanipi River flows in the Municipality of Eeyou Istchee Baie-James in the administrative region of Nord-du-Québec, in Quebec, Canada.
Geography
The main hydrographic slopes adjacent t ...
s.
* Cree Nation of Wemindji is headquartered at Wemindji
Wemindji ( cr, ᐐᒥᓂᒌ/Wîminicî) is a small Cree community on the east coast of James Bay at the mouth of the Maquatua River in Quebec, Canada. Its legal name is the Cree Nation of Wemindji. The community is a part of the Abitibi-Baie-Ja ...
VC and its reserve is Wemindji
Wemindji ( cr, ᐐᒥᓂᒌ/Wîminicî) is a small Cree community on the east coast of James Bay at the mouth of the Maquatua River in Quebec, Canada. Its legal name is the Cree Nation of Wemindji. The community is a part of the Abitibi-Baie-Ja ...
TC. The village is on the east coast of James Bay at the mouth of the and is north of Chibougamau via the .
* located at Whapmagoostui
Whapmagoostui ( cr, ᐙᐱᒫᑯᔥᑐᐃ/Wâpimâkuštui, "place of the beluga") is the northernmost Cree village in Quebec, Canada, located at the mouth of the Great Whale River (french: Grande Rivière de la Baleine) on the coast of Hudson B ...
VC, is the northernmost Cree village, located at the mouth of the Great Whale River
The Great Whale River () is a river in Nunavik, Quebec, Canada. It flows from Lac Saint-Luson through Lac Bienville west to Hudson Bay. While lower section of the river (after Lac Bienville) has very powerful current, with many waterfalls (up to ...
on the coast of Hudson Bay in Kativik TE. The village is just south of the river while the Inuit village of Kuujjuarapik
Kuujjuarapik (also spelled Kuujjuaraapik; iu, ᑰᔾᔪᐊᕌᐱᒃ ''little great river'') is the southernmost northern village (Inuit community) at the mouth of the Great Whale River (french: Grande Rivière de la Baleine) on the coast of H ...
is on the north shore.
* Cree Nation of Washaw Sibi was recognized as the tenth Cree Nation Community at the 2003 Annual General Assembly of the Cree Nation. The Nation does not yet have a community or reserve recognized by either the Canadian or Quebec governments but the Nation has chosen an area about 40 minutes' drive south of Matagami.
Moose Cree
Moose Cree ( cr, script=Latn, Mōsonī or ), also known as Moosonee are located inNortheastern Ontario
Northeastern Ontario is a secondary region of Northern Ontario in the Canadian province of Ontario, which lies north of Lake Huron and east of Lake Superior.
Northeastern Ontario consists of the districts of Algoma, Sudbury, Cochrane, Timiskami ...
.
Constance Lake First Nation
Constance Lake First Nation ( ojs, ᑾᐣᐢᑕᐣᐢ ᓴᑲᐦᐃᑲᐣ) is an Oji-Cree First Nations band government located on the shores of Constance Lake near Hearst, Cochrane District in northeastern Ontario, Canada. It is directly nort ...
is the only Cree member of Matawa First Nations
Matawa First Nations (Ojibwe: ᒫᑕᐙ (''maadawaa'', "to fork, to confluence"); unpointed: ᒪᑕᐧᐊ), officially as the Matawa First Nations Management, Inc., is a non-profit Regional Chiefs' Council representing Ojibway and Cree First Nat ...
. They are located on their reserves, Constance Lake 92
Constance Lake 92 is a First Nations reserve in Cochrane District, Ontario. It is one of the reserves of the Constance Lake First Nation
Constance Lake First Nation ( ojs, ᑾᐣᐢᑕᐣᐢ ᓴᑲᐦᐃᑲᐣ) is an Oji-Cree First Nations ban ...
and English River 66, in the Cochrane District
Cochrane District is a district and census division in Northeastern Ontario in the Canadian province of Ontario. It was created in 1921 from parts of Timiskaming and Thunder Bay districts.
In 2016, the population was 79,682. The land area of th ...
, Ontario.
Mushkegowuk Council
Mushkegowuk Council (pointed: ᐅᒪᐡᑫᑯ ᐅᑭᒫᐎᐎᐣ (''omashkeko okimāwiwin''); unpointed: ᐅᒪᐡᑫᑯ ᐅᑭᒪᐎᐎᐣ), or officially as the Mushkegowuk Tribal Council, is a non-profit regional chiefs' council representing Cre ...
, based in Moose Factory, Ontario
Moose Factory is a community in the Cochrane District, Ontario, Canada. It is located on Moose Factory Island, near the mouth of the Moose River, which is at the southern end of James Bay. It was the first English-speaking settlement in lands no ...
, represents chiefs from seven First Nations across Ontario. Moose Cree members are: Chapleau Cree First Nation
Chapleau Cree First Nation ( cr, ᔕᑊᓗ ᐃᓂᓂᐗᐠ, ''šaplo ininiwak'') is a Mushkegowuk Cree First Nation located by Chapleau Township, Sudbury District, Ontario, Canada. The First Nation have reserved for themselves the Chapleau 75 I ...
, Kashechewan First Nation
The Kashechewan First Nation (, cr, ᑫᔒᒋᐗᓐ ᐃᓕᓕᐗᒃ, kêšîciwan ililiwak) is a Cree First Nation band government located near James Bay in Northern Ontario, Canada. The community is located on the northern shore of the Alban ...
, Missanabie Cree First Nation
Missanabie Cree First Nation ( cr, masinâpôy ininiwak, ᒪᓯᓈᐴᔾ ᐃᓂᓂᐗᐠ) is a "Treaty 9" Nation. The nation is named after Missinaibi River and Lake, around which the traditional territory of the nation is located. The name "Missa ...
, Moose Cree First Nation
The Moose Cree First Nation (formerly known as Moose Factory Band of Indians) ( cr, ᒨᓱᓂᔨ ᐃᓕᓕᐗᒃ, môsoniyi ililiwak) is a Cree First Nation band government in northern Ontario, Canada. Their traditional territory is on the west s ...
, and Taykwa Tagamou Nation Taykwa Tagamou Nation ( cr, ᑕᐟᑾ ᑕᑲᒪᐤ ᐃᓂᓂᐗᐠ tatkwa takamaw ininiwak, formerly known as New Post First Nation, is a Cree First Nations band government whose reserve community is located in the Cochrane District in Ontario, Ca ...
. The Chapleau Cree First Nation and their two reserves, Chapleau Cree Fox Lake and Chapleau 75, are located outside of Chapleau, Ontario
Chapleau is a township in Sudbury District, Ontario, Canada. It is home to one of the world's largest wildlife preserves. Chapleau has a population of 1,942 according to the 2016 Canadian census.
The major industries within the town are the log ...
in the Sudbury District
The Sudbury District is a district in Northeastern Ontario in the Canadian province of Ontario. It was created in 1894 from townships of eastern Algoma District and west Nipissing District.
The overwhelming majority of the district (about 92%) ...
. The Kashechewan First Nation community is located on the northern shore of the Albany River
Albany, derived from the Gaelic for Scotland, most commonly refers to:
*Albany, New York, the capital of the State of New York and largest city of this name
* Albany, Western Australia, port city in the Great Southern
Albany may also refer to: ...
on James Bay. The Hudson's Bay Company established a post, Fort Albany, at this location between 1675 and 1679. Kashechewan First Nation is one of two communities that were established from Old Fort Albany, the other being Fort Albany First Nation
Fort Albany First Nation ( cr, ᐲᐦᑖᐯᒄ ᐃᓕᓕᐗᒃ pîhtâpek ililiwak, "lagoon Cree") is a Cree First Nation in Cochrane District in Northeastern Ontario, Canada, within the territory covered by Treaty 9. Situated on the southern ...
. The two Nations share the Fort Albany 67 reserve. The Missanabie Cree First Nation signed Treaty 9
''Treaty No. 9'' (also known as ''The James Bay Treaty'') is a numbered treaty first signed in 1905-1906 between Anishinaabe (Algonquin and Ojibway) and Omushkegowuk Cree communities and the Canadian Crown, which includes both the governm ...
in 1906 but did not receive any reserved lands until 2018. The Missanabie reserve is in the Missanabie, Ontario area. The Moose Cree First Nation is based in Moose Factory
Moose Factory is a community in the Cochrane District, Ontario, Canada. It is located on Moose Factory Island, near the mouth of the Moose River, which is at the southern end of James Bay. It was the first English-speaking settlement in lands n ...
in the Cochrane District. Moose Factory was founded in 1672–1673 by Charles Bayly
Charles Bayly, ( fl. 1630–1680), the first overseas governor of the Hudson's Bay Company, likely spent his early years in the court of Queen Henrietta Maria, the wife of Charles I. He was an English born French Roman Catholic in this Protes ...
, the first overseas governor of the Hudson's Bay Company, and was the company's second post. It was the first English settlement in what is now Ontario. The Nation has two reserves: Factory Island 1 on Moose Factory Island
Moose Factory Island is an island in the Moose River, Ontario, Canada, about from its mouth at James Bay. It is adjacent to the community of Moosonee across the Moose River, from which it is accessible by water taxi. The island is home to the co ...
, an island in the Moose River, about from its mouth at James Bay; and Moose Factory 68
Moose Factory 68 is a First Nations reserve on the Moose River in Cochrane District, Ontario. It is one of two reserves of the Moose Cree First Nation
The Moose Cree First Nation (formerly known as Moose Factory Band of Indians) ( cr, ᒨᓱ� ...
, a tract of land about upstream on the Moose River. The Taykwa Tagamou Nation has two reserves, New Post 69, and their main reserve, New Post 69A outside Cochrane, Ontario along the Abitibi River
The Abitibi River is a river in northeastern Ontario, Canada, which flows northwest from Lake Abitibi to join the Moose River which empties into James Bay. This river is long, and descends . It is the fifth longest river entirely in Ontario
A ...
.
Wabun Tribal Council Wabun Tribal Council is a non-profit Regional Chiefs' Council representing Ojibway and Cree First Nations in northern Ontario, Canada. The Council provides advisory services and program delivery to its seven Status and non-Status member-Nations.
B ...
is a regional chief's council based in Timmins, Ontario
Timmins ( ) is a city in northeastern Ontario, Canada, located on the Mattagami River. The city is the fourth-largest city in the Northeastern Ontario region with a population of 41,145 (2021). The city's economy is based on natural resource ex ...
representing Ojibway and Cree First Nations in northern Ontario. Moose Cree members are: Brunswick House First Nation
Brunswick House First Nation is an Ojibway-Cree First Nations in the Canadian province of Ontario, located in the Sudbury District, northeast of Sault Ste Marie, Ontario. The First Nation have reserved for themselves the Mountbatten 76A Indian Re ...
and Matachewan First Nation
Matachewan First Nation is an Ojibway and Cree First Nation reserve located in the Timiskaming District of Ontario, Canada. As of March, 2012, they had a total registered population of 642 people, of which 40 people lived on their own reserves.
...
. Brunswick House's reserves are Mountbatten 76A
Mountbatten 76A is a First Nations reserve near Kinogama in Sudbury District, Ontario. It is one of two reserves of the Brunswick House First Nation
Brunswick House First Nation is an Ojibway-Cree First Nations in the Canadian province of Ontar ...
and Duck Lake 76B located in the Sudbury District near Chapleau, Ontario. The Matachewan First Nation is on the Matachewan 72 reserve near Matachewan
Matachewan is a township in Timiskaming, Northeastern Ontario, Canada, located at the end of Ontario Highway 66 along the Montreal River. The name is derived from the Cree word for "meeting of the currents".
The town's main economy is based o ...
township in the Timiskaming District
Timiskaming is a district and census division in Northeastern Ontario in the Canadian province of Ontario. The district was created in 1912 from parts of Algoma, Nipissing, and Sudbury districts. In 1921, Cochrane District was created from pa ...
.
Swampy Cree
Located in Ontario
Fort Severn First Nation
Fort Severn First Nation ( [] in Swampy Cree language, Cree) is a Western Swampy Cree First Nations in Canada, First Nation band government located on Hudson Bay and is the most Extreme communities of Canada, northern community in Ontario, Canad ...
and their reserve, Fort Severn 89, located on the mouth of the Severn River on Hudson Bay, is the most northern community in Ontario. It is a member of Keewaytinook Okimakanak Council Keewaytinook Okimakanak Council (Oji-Cree:ᑮᐌᑎᓅᐠ ᐅᑭᒫᐦᑳᓇᐠ (''Giiwedinoog Ogimaakaanag''), unpointed ᑭᐌᑎᓄᐠ ᐅᑭᒪᑲᓇᐠ, which means "Northern Chiefs") is a non-political Chiefs Council in northwestern Ontario, C ...
.
Mushkegowuk Council
Mushkegowuk Council (pointed: ᐅᒪᐡᑫᑯ ᐅᑭᒫᐎᐎᐣ (''omashkeko okimāwiwin''); unpointed: ᐅᒪᐡᑫᑯ ᐅᑭᒪᐎᐎᐣ), or officially as the Mushkegowuk Tribal Council, is a non-profit regional chiefs' council representing Cre ...
, based in Moose Factory, Ontario
Moose Factory is a community in the Cochrane District, Ontario, Canada. It is located on Moose Factory Island, near the mouth of the Moose River, which is at the southern end of James Bay. It was the first English-speaking settlement in lands no ...
, represents chiefs from seven First Nations across Ontario. Swampy Cree members are: Fort Albany First Nation
Fort Albany First Nation ( cr, ᐲᐦᑖᐯᒄ ᐃᓕᓕᐗᒃ pîhtâpek ililiwak, "lagoon Cree") is a Cree First Nation in Cochrane District in Northeastern Ontario, Canada, within the territory covered by Treaty 9. Situated on the southern ...
and Attawapiskat First Nation. Fort Albany First Nation is located at Fort Albany, Ontario, on the southern shore of the Albany River at James Bay. The reserve, Fort Albany 67, is shared with the Kashechewan First Nation. The Attawapiskat First Nation is located at mouth of the Attawapiskat River on James Bay. The community is on the Attawapiskat 91A reserve. The Attawapiskat 91 reserve is on both shores of the Ekwan River, upstream from the mouth on James Bay.
Independent from a Tribal Council is the Weenusk First Nation
Weenusk First Nation ( cr, ᐐᓈᐢᑯ ᐃᓂᓂᐗᐠ, italic=no (); unpointed: ᐧᐃᓇᐢᑯ ᐃᓂᓂᐧᐊᐠ) is a Cree First Nation band government in the Canadian province of Ontario. In September, 2007, its total registered population w ...
located in Peawanuck
Peawanuck is an isolated Cree community in the Kenora District, Ontario, Canada. It is located near the confluence of the Winisk and Shamattawa rivers, about 35 km from the Winisk River's end in Hudson Bay. Its population is 237.
Its popu ...
in the Kenora District. The community was located on their reserve of Winisk 90 on the mouth of the Winisk River on James Bay but the community was destroyed in the 1986 Winisk flood and the community had to be relocated to Peawanuck.
Located in Manitoba
Keewatin Tribal Council
Keewatin Tribal Council is a tribal council representing 11 First Nation band governments in the province of Manitoba. Its head offices are located in Thompson, Manitoba, with a secondary office in Winnipeg.
Members
The Keewatin Tribal Counci ...
is a Tribal Council based in Thompson, Manitoba
Thompson (population 13,678) is the largest city in the Northern Region of Manitoba and is situated along the Burntwood River, north of Winnipeg. Originally founded in 1956 as a mining town, it now primarily serves as the "Hub of the North", ...
that represents eleven First Nations, of which five are Swampy Cree, across northern Manitoba. Fox Lake Cree Nation is based in Gillam, northeast of Thompson via Provincial Road 280 (PR 280), and has several reserves along the Nelson River
The Nelson River is a river of north-central North America, in the Canadian province of Manitoba. The river drains Lake Winnipeg and runs before it ends in Hudson Bay. Its full length (including the Saskatchewan River and Bow River) is , i ...
. Shamattawa First Nation
The Shamattawa First Nation ( cr, ᑭᓭᒫᑖᐘ, kisêmâtâwa) () is a remote First Nations community in northern Manitoba, Canada, located in the reserve of Shamattawa 1.
Shamattawa 1 is located on the banks of the Gods River where the E ...
is located on their reserve, Shamattawa 1, on the banks of the Gods River
The Gods River is a remote wilderness river in the Hudson Bay drainage basin in Northern Region, Manitoba, Northern Manitoba, Canada. Its flows from its source at Gods Lake to its mouth at the Hayes River. The Hayes River flows to Hudson Bay.
The ...
where the Echoing River joins. The community is very remote; only connected via air or via winter ice roads to other First Nation communities. The Tataskweyak Cree Nation
The Tataskweyak Cree Nation ( cr, ᑕᑕᐢᑿᔭᕽ, tataskwayak) (Formerly known as ''Split Lake Cree First Nation'' in English) is a First Nations band government whose primary community is located at Split Lake, Manitoba, on the Nelson River ...
is located in the community of Split Lake, Manitoba within the Split Lake 171 reserve, northeast of Thompson on PR 280, on the lake of the same name on the Nelson River system. War Lake First Nation possess several reserves but are located on the Mooseocoot reserve in the community of Ilford, Manitoba
Ilford is an Indian settlement in northern Manitoba, Canada. The Mooseocoot Indian reserve is located within the community boundary and is populated by the War Lake First Nation.
Ilford is above sea level.
Demographics
In the 2011 Census, Il ...
, east of York Landing. York Factory First Nation
York Factory First Nation (Cree: )—sometimes referred to as York Landing First Nation or York Factory Cree Nation—is a First Nations community in northern Manitoba, Canada.
Its main reserve is York Landing (; ), which is located along the ea ...
is based on the reserve of York Landing, south of Split Lake via ferry. York Factory
York Factory was a settlement and Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) factory (trading post) located on the southwestern shore of Hudson Bay in northeastern Manitoba, Canada, at the mouth of the Hayes River, approximately south-southeast of Churchill. ...
was a settlement and Hudson's Bay Company (HBC) trading post, established in 1684, on the shore of Hudson Bay, at the mouth of the Hayes River
The Hayes River is a river in Northern Manitoba, Canada, that flows from Molson Lake to Hudson Bay at York Factory. It was historically an important river in the development of Canada and is now a Canadian Heritage River and the longest natura ...
. In 1956, the trading post was closed and the community was moved inland to the current site.
Swampy Cree Tribal Council is, as the name suggests, a Tribal Council of seven Swampy Cree First Nations across northern Manitoba and is based in The Pas
The Pas ( ; french: Le Pas) is a town in Manitoba, Canada, located at the confluence of the Pasquia River and the Saskatchewan River and surrounded by the unorganized Northern Region of the province. It is approximately northwest of the provinc ...
. The Chemawawin Cree Nation (also Rocky Cree) are based on their reserve Chemawawin 2, adjacent to Easterville, Manitoba
Easterville is an unincorporated community, designated as a northern community, in the Canadian province of Manitoba.
It is situated 200 kilometres southeast of The Pas and 100 kilometres (40 km by air) west of Grand Rapids, on the south ...
, southeast of The Pas. Mathias Colomb First Nation
The Mathias Colomb Cree Nation (MCCN) ( cr, ᐸᑲᑕᐚᑲᐣ, pukatawâkan) —also known as Mathias Colomb First Nation, Mathias Colomb (Cree) First Nation, and Pukatawagan/Mathias Colomb Cree Nation—is a remote First Nations community in ...
(also Rocky Cree) is located in the community of Pukatawagan
Pukatawagan is a First Nations community about north of The Pas in Manitoba. It is part of the Mathias Colomb First Nation. It can be reached by train from The Pas by a branch of the Keewatin Railway Company, a passenger service provided by Vi ...
on the Pukatawagan 198 reserve. Misipawistik Cree Nation
Misipawistik Cree Nation (MCN; formerly Grand Rapids First Nation, Cree: ᒥᓯ ᐹᐏᐢᑎᐠ misi-pâwistik, ''meaning: at the big rapids'') is a Cree community in northern Manitoba. ''Misipawistik'' in the local Cree language means 'Rushing R ...
(also Rocky Cree) is located near Grand Rapids, Manitoba
Grand Rapids is a town in Manitoba, Canada, on the northwestern shore of Lake Winnipeg where the Saskatchewan River enters the lake. As the name implies, the river had a significant drop at this point (more than in less than ). In modern days, ...
, north of Winnipeg at the mouth of the Saskatchewan River
The Saskatchewan River (Cree: ''kisiskāciwani-sīpiy'', "swift flowing river") is a major river in Canada. It stretches about from where it is formed by the joining together of the North Saskatchewan and South Saskatchewan Rivers to Lake Winn ...
as it runs into Lake Winnipeg. Mosakahiken Cree Nation
The Mosakahiken Cree Nation (Cree: ᒨᓵᑲᐦᐃᑲᐣ môsâkahikan)Ogg, Arden (August 19 2015)
Cree Names of Cree-speaking Communities across CanadLink/ref> is a First Nations located around the community of Moose Lake in northern Manitoba.
...
(also Rocky Cree) is located around the community of Moose Lake about southeast of The Pas on their main reserve, Moose Lake 31A. Opaskwayak Cree Nation
The Opaskwayak Cree Nation (; OCN, Cree: ᐅᐸᐢᑿᔭᐠ , ''opâskwêyâhk'', meaning: at the wooded narrows) is a First Nations band government in Manitoba, Canada. Most of the on-reserve population lives near The Pas on the OCN 21E reser ...
(also Rocky Cree) has several reserves but most of the population lives on the Opaskwayak 21E reserve, immediately north of and across the Saskatchewan River from The Pas. The Sapotaweyak Cree Nation
The Sapotaweyak Cree Nation (SCN, cr, ᓵᐳᐦᑕᐍᔮᕽ, sâpohtawêyâhk, ''meaning: "golden eagle"'') is a First Nations band government whose reserves are located in northern Manitoba, north-east of Swan River, approximately 400 kilometr ...
is located in the Shoal River 65A reserve adjacent to the community of Pelican Rapids, about south of The Pas. Wuskwi Sipihk First Nation has several reserves but the main reserve is Swan Lake 65C which contains the settlement of Indian Birch, about south of The Pas.
Not affiliated with any Tribal Council: Fisher River Cree Nation
Fisher River ( cr, ᐅᒉᑯ ᓰᐱᐩ, ocêko-sîpiy) is a Cree First Nations reserve located approximately 193 km north of Manitoba's capital city, Winnipeg. The Fisher River Cree Nation is composed of two reserves; Fisher River 44 and F ...
, Marcel Colomb First Nation
Marcel Colomb First Nation (MCFN) ( cr, ᓇᒦᐏ ᓵᑲᐦᐃᑲᐣ, namîwi-sâkahikan), Band #328, is a First Nations Band of approximately 449 Registered Swampy Cree (Maškēkowak / nēhinawak) and Rocky Cree (Asinīskāwiyiniwak) located in ...
, and Norway House Cree Nation
The Norway House Cree Nation ( cr, Kinosao Sipi, ᑭᓄᓭᐏ ᓰᐱᐩ. SRO: kinosêwi-sîpiy) is based at Norway House, Manitoba, which is located on the Playgreen Lake section of the Nelson River system. The people are Swampy Cree from the Ro ...
. Fisher River Cree Nation
Fisher River ( cr, ᐅᒉᑯ ᓰᐱᐩ, ocêko-sîpiy) is a Cree First Nations reserve located approximately 193 km north of Manitoba's capital city, Winnipeg. The Fisher River Cree Nation is composed of two reserves; Fisher River 44 and F ...
, located approximately north of Winnipeg
Winnipeg () is the capital and largest city of the province of Manitoba in Canada. It is centred on the confluence of the Red and Assiniboine rivers, near the longitudinal centre of North America. , Winnipeg had a city population of 749, ...
in Koostatak on Lake Winnipeg
Lake Winnipeg (french: Lac Winnipeg, oj, ᐑᓂᐸᑲᒥᐠᓴᑯ˙ᑯᐣ, italics=no, Weenipagamiksaguygun) is a very large, relatively shallow lake in North America, in the province of Manitoba, Canada. Its southern end is about north of t ...
, control the Fisher River 44 and 44A reserves. Marcel Colomb First Nation
Marcel Colomb First Nation (MCFN) ( cr, ᓇᒦᐏ ᓵᑲᐦᐃᑲᐣ, namîwi-sâkahikan), Band #328, is a First Nations Band of approximately 449 Registered Swampy Cree (Maškēkowak / nēhinawak) and Rocky Cree (Asinīskāwiyiniwak) located in ...
is located outside of Lynn Lake on the Black Sturgeon reserve on Hughes Lake, northwest of Thompson via Provincial Road 391. Norway House Cree Nation
The Norway House Cree Nation ( cr, Kinosao Sipi, ᑭᓄᓭᐏ ᓰᐱᐩ. SRO: kinosêwi-sîpiy) is based at Norway House, Manitoba, which is located on the Playgreen Lake section of the Nelson River system. The people are Swampy Cree from the Ro ...
is located in Norway House
Norway House is a population centre of over 5,000 people, some north of Lake Winnipeg, on the bank of the eastern channel of Nelson River, in the province of Manitoba, Canada. The population centre shares the name ''Norway House'' with the north ...
which is located on the Playgreen Lake
Playgreen Lake, or Play Green Lake, is a lake in the province of Manitoba in Canada. The lake covers an area of and it is a part of the Nelson River watershed. The lake is the ninth largest lake in the province. It is located along the Nelson Rive ...
section of the Nelson River
The Nelson River is a river of north-central North America, in the Canadian province of Manitoba. The river drains Lake Winnipeg and runs before it ends in Hudson Bay. Its full length (including the Saskatchewan River and Bow River) is , i ...
system on the north side of Lake Winnipeg. In 1821, Norway House became the principal inland fur trading depot for the Hudson's Bay Company. Norway House was also where Treaty 5
''Treaty Five'' is a treaty that was first established in September, 1875, between Queen Victoria and Saulteaux and Swampy Cree non-treaty band governments and peoples around Lake Winnipeg in the District of Keewatin.
A written text is includ ...
was signed. They control more than 80 reserves from less than to their largest, Norway House 17, at over . The Nation is one of the most populous in Canada with 8,599 people .
Located in Saskatchewan
Prince Albert Grand Council The Prince Albert Grand Council (PAGC) is a Tribal Council representing the band governments of twelve First Nations in the province of Saskatchewan. Its head offices are located in the city of Prince Albert. The Tribal Council was created in 197 ...
is based in Prince Albert, Saskatchewan
Prince Albert is the third-largest city in Saskatchewan, Canada, after Saskatoon and Regina. It is situated near the centre of the province on the banks of the North Saskatchewan River. The city is known as the "Gateway to the North" because ...
and is owned by twelve First Nations of which three are Swampy Cree. Cumberland House Cree Nation
Cumberland House Cree Nation ( cr, ᑳ ᒥᓂᐢᑎᑯ ᒥᓇᐦᐃᑯᐢᑳᕽ ''kâ-ministiko-minahikoskâhk'', meaning ''Island that's in a pine forest'')Wolvengrey, Arok, editor. Cree: Words. Regina, University of Regina Press, 2001https: ...
is based in Cumberland House, Saskatchewan
Cumberland House is a community in Census Division No. 18 in northeast Saskatchewan, Canada on the Saskatchewan River. It is the oldest settler community in Saskatchewan and has a population of about 2,000 people. Cumberland House Provincial Pa ...
on the Cumberland House Cree Nation 20 reserve, southwest of Flin Flon
Flin Flon (pop. 5,185 in 2016 census; 4,982 in Manitoba and 203 in Saskatchewan) is a mining city, located on a correction line on the border of the Canadian provinces of Manitoba and Saskatchewan, with the majority of the city located within M ...
, Manitoba. Cumberland House
Cumberland House was a mansion on the south side of Pall Mall in London, England. It was built in the 1760s by Matthew Brettingham for Prince Edward, Duke of York and Albany and was originally called York House. The Duke of York died in 1767 ...
, founded in 1774 by Samuel Hearne
Samuel Hearne (February 1745 – November 1792) was an English explorer, fur-trader, author, and naturalist. He was the first European to make an overland excursion across northern Canada to the Arctic Ocean, actually Coronation Gulf, via the C ...
, was the site of the HBC's first inland fur-trading post. The Red Earth First Nation
Red Earth Cree Nation ( cr, ᑳ ᒥᐦᑿᐢᑮᐘᑳᕽ ''kâ-mihkwaskîwakâhk'') is a Cree community in Saskatchewan, Canada
Canada is a country in North America. Its ten provinces and three territories extend from the Atlantic O ...
is located in the community of Red Earth, on the banks of the Carrot River, on the Carrot River 29A reserve. Close by is the Red Earth 29 reserve, about east of Nipawin. Shoal Lake Cree Nation
The Shoal Lake Cree Nation ( cr, ᐹᐦᒁᐤ ᓵᑲᐦᐃᑲᓂᕽ ''pâhkwâw-sâkahikanihk'') is a Swampy Cree First Nations band government in Saskatchewan, Canada located east of Nipawin. The Cree
The Cree ( cr, néhinaw, script=L ...
is located in Pakwaw Lake, on the Shoal Lake 28A reserve, east of Nipawin.
Woodland Cree
Rocky Cree ()
The Keewatin Tribal Council, described under Swampy Cree, also represents Rocky Cree First Nations in Manitoba. The Barren Lands First Nation is located on the north shore ofReindeer Lake
Reindeer Lake is a lake in western Canada located on the border between north-eastern Saskatchewan and north-western Manitoba, with the majority in Saskatchewan. The name of the lake appears to be a translation of the Algonquian name. It is ...
close to the Saskatchewan border. It has one reserve, Brochet 197, northwest of Thompson, adjoining the village of Brochet
''Constructions Aéronautiques Maurice Brochet'' was a French manufacturer of light aircraft established by Maurice Brochet (18 June 1899 – 16 June 1969) in Neauphle-le-Château in 1947.
Aircraft design and construction
Initially, the firm s ...
. The Bunibonibee Cree Nation
Bunibonibee Cree Nation ( cr, ᐸᓂᑇᓂᐱᐩ, panipwânipiy), formerly known as Oxford House First Nation and as Oxford House Band of Indians, is a First Nation located along the eastern shoreline of Oxford Lake at the headwaters of the Hayes ...
is located along the eastern shoreline of Oxford Lake
Oxford Lake is a lake on the Hayes River in Manitoba, Canada. The lake is in size and sits at a surface elevation of .
Description
Oxford Lake is a vaguely man-shaped lake, with a 'head' on the east, a 'neck', a northwest-southeast shoulder line ...
at the headwaters of the Hayes River
The Hayes River is a river in Northern Manitoba, Canada, that flows from Molson Lake to Hudson Bay at York Factory. It was historically an important river in the development of Canada and is now a Canadian Heritage River and the longest natura ...
. The Nation controls several reserves with the main reserve being Oxford House 24 adjacent to the community of Oxford House, Manitoba
Oxford House ( cr, ᐸᓂᑇᓂᐱᐩ, Bunibonibee/panipwânipiy) is a First Nations Cree community in northern Manitoba, located on the Oxford House 24 Indian reserve. The community is located along the eastern shore of Oxford Lake at the mouth ...
, southeast of Thompson. God's Lake First Nation
God's Lake First Nation ( cr, manto sakahigan, ᒪᓂᑐ ᓵᑲᐦᐃᑲᐣ) is a First Nations band government whose reserve is primarily located at an area known as God's Lake Narrows, about 250 kilometers southeast of Thompson, Manitoba. Ther ...
is located in the God's Lake Narrows area on the shore of God's Lake
Gods Lake is a lake in northeastern Manitoba in Canada. The lake covers an area of with a net (water surface) area of , making it the 7th largest lake in the province. It lies north of Island Lake at an elevation of , approximately east of Th ...
. The main reserve is God's Lake 23, southeast of Thompson. The Manto Sipi Cree Nation also live on God's Lake in the community of God's River on the God's River 86A reserve, about northeast of God's Lake Narrows. All of the Rocky Cree communities of Keewatin Tribal Council are remote; only connected via air and ice road during winter months.
Five of the Swampy Cree Tribal Council First Nations contain Rocky Cree populations: Chemawawin Cree Nation, Mathias Colomb First Nation
The Mathias Colomb Cree Nation (MCCN) ( cr, ᐸᑲᑕᐚᑲᐣ, pukatawâkan) —also known as Mathias Colomb First Nation, Mathias Colomb (Cree) First Nation, and Pukatawagan/Mathias Colomb Cree Nation—is a remote First Nations community in ...
, Misipawistik Cree Nation
Misipawistik Cree Nation (MCN; formerly Grand Rapids First Nation, Cree: ᒥᓯ ᐹᐏᐢᑎᐠ misi-pâwistik, ''meaning: at the big rapids'') is a Cree community in northern Manitoba. ''Misipawistik'' in the local Cree language means 'Rushing R ...
, Mosakahiken Cree Nation
The Mosakahiken Cree Nation (Cree: ᒨᓵᑲᐦᐃᑲᐣ môsâkahikan)Ogg, Arden (August 19 2015)
Cree Names of Cree-speaking Communities across CanadLink/ref> is a First Nations located around the community of Moose Lake in northern Manitoba.
...
, Opaskwayak Cree Nation
The Opaskwayak Cree Nation (; OCN, Cree: ᐅᐸᐢᑿᔭᐠ , ''opâskwêyâhk'', meaning: at the wooded narrows) is a First Nations band government in Manitoba, Canada. Most of the on-reserve population lives near The Pas on the OCN 21E reser ...
.
In Saskatchewan, the Prince Albert Grand Council, described under Swampy Cree, also has Rocky Cree members. The Lac La Ronge First Nation
The Lac La Ronge Indian Band ( cr, ᒥᐢᑕᐦᐃ ᓵᑲᐦᐃᑲᓂᕽ, mistahi-sâkahikanihk) is a Woodland Cree First Nation in northern Saskatchewan, it is the largest Cree band government in Canada and the largest First Nation in Saskat ...
is one of the most populous First Nations in Canada with a registered population of 11,604 . The Nation is based in La Ronge
La Ronge is a northern town in the boreal forest of central Saskatchewan, Canada. Its location is approximately north of Prince Albert where Highway 2 becomes Highway 102. La Ronge lies on the western shore of Lac la Ronge, is adjacent ...
on the Lac la Ronge 156 reserve but has other communities on other reserves. La Ronge is north of Prince Albert at the north end of Saskatchewan Highway 2
Highway 2 is a provincial highway in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. It is the longest highway in Saskatchewan at 809 km (503 mi). The highway is partially divided and undivided. However, only about near Moose Jaw, near Cham ...
. The Montreal Lake First Nation, on their reserves of Montreal Lake 106, is on the southern shore of Montreal Lake, north of Prince Albert. Peter Ballantyne Cree Nation
The Peter Ballantyne Cree Nation (Rocky cr, ᐊᓯᓃᐢᑳᐏᑎᓂᐘᐠ, Asinîskâwitiniwak) is a Woodland Cree First Nation in northern Saskatchewan consisting of eight communities: Denare Beach (Amisk Lake), Deschambault Lake, Kinoosao, ...
is also a populous First Nation with 11,563 people . The Nation has eight communities and controls a large number of reserves; the administrative center is Pelican Narrows, Saskatchewan
Pelican Narrows is a northern village in the boreal forest of central Saskatchewan, Canada. Its location is northwest of Creighton by Hanson Lake Road and Highway 135. Its name in Cree is ''Opawikoscikan'' which means "The Narrows ...
, northeast of Flin Flon, Manitoba. The Sturgeon Lake First Nation
The Sturgeon Lake First Nation ( cr, ᓇᒦᐏ ᓵᑲᐦᐃᑲᓂᕽ, namîwi-sâkahikanihk) is a Cree First Nation band government in Saskatchewan, Canada. Its location is on the eastern shore of Sturgeon Lake about 30 km northwest of Prince ...
is located on the Sturgeon Lake 101
Sturgeon Lake 101 is an Indian reserve of the Sturgeon Lake First Nation in Saskatchewan. It is 29 kilometres northwest of Prince Albert. In the 2016 Canadian Census
The 2016 Canadian census was an enumeration of Canadian residents, which coun ...
reserve on the eastern shore of Sturgeon Lake about northwest of Prince Albert.
Not affiliated with any Tribal Council are Cross Lake First Nation
Cross Lake First Nation ( cr, ᐱᒥᒋᑲᒫᐠ ᓃᐦᐃᖬᐑ, pimicikamâk nîhithawî, lit=Cree of the Lake that lies Athwart or ' 'Otter People') is a band of Cree First Nations people in Canada governed under the Indian Act. Its membersR.S ...
, Nisichawayasihk Cree Nation
The Nisichawayasihk Cree Nation (NCN; cr, ᓂᓯᒐᐚᔭᓯᕽ, nisicawâyasihk; formerly the Nelson House First Nation) is a Cree First Nations community centered in Nelson House, Manitoba, Canada. Its main reserve is Nelson House 170.
Nelson ...
, and O-Pipon-Na-Piwin Cree Nation The O-Pipon-Na-Piwin Cree Nation ( cr, ᐅᐱᐴᓇᐱᐏᐣ, opiponipîwin) is a First Nations band government with over 1,500 Cree registered members centred in the settlement of South Indian Lake in Manitoba, Canada. South Indian Lake is loca ...
. The Cross Lake First Nation
Cross Lake First Nation ( cr, ᐱᒥᒋᑲᒫᐠ ᓃᐦᐃᖬᐑ, pimicikamâk nîhithawî, lit=Cree of the Lake that lies Athwart or ' 'Otter People') is a band of Cree First Nations people in Canada governed under the Indian Act. Its membersR.S ...
is a populous Nation with a registered population of 9,138 people . The Nation is in Cross Lake, Manitoba
Cross Lake is the name of two closely related, adjoining but independent communities in the Canadian province of Manitoba. One of the Cross Lakes is the Cross Lake Indian Reserve ( Pimicikamak Cree) of the Cross Lake First Nation where the main ...
on the Cross Lake 19 reserve, north of Lake Winnipeg. The Nisichawayasihk Cree Nation
The Nisichawayasihk Cree Nation (NCN; cr, ᓂᓯᒐᐚᔭᓯᕽ, nisicawâyasihk; formerly the Nelson House First Nation) is a Cree First Nations community centered in Nelson House, Manitoba, Canada. Its main reserve is Nelson House 170.
Nelson ...
is based in Nelson House, Manitoba Nelson House ( cr, ᓂᓯᒐᐚᔭᓯᕽ, nisicawâyasihk) is a designated place in northern Manitoba, Canada adjacent to the Nelson House 170 Indian Reserve, which is part of the Nisichawayasihk Cree Nation. It is located approximately northwest o ...
on the Nelson House 170 reserve located south of Thompson. The O-Pipon-Na-Piwin Cree Nation The O-Pipon-Na-Piwin Cree Nation ( cr, ᐅᐱᐴᓇᐱᐏᐣ, opiponipîwin) is a First Nations band government with over 1,500 Cree registered members centred in the settlement of South Indian Lake in Manitoba, Canada. South Indian Lake is loca ...
is located in the settlement of South Indian Lake, northwest of Thompson. Marcel Colomb First Nation
Marcel Colomb First Nation (MCFN) ( cr, ᓇᒦᐏ ᓵᑲᐦᐃᑲᐣ, namîwi-sâkahikan), Band #328, is a First Nations Band of approximately 449 Registered Swampy Cree (Maškēkowak / nēhinawak) and Rocky Cree (Asinīskāwiyiniwak) located in ...
, listed under Swampy Cree, also has a Rocky Cree population.
Woods Cree ()
The Canoe Lake Cree First Nation is based in Canoe Narrows, Saskatchewan on the Canoe Lake 165 reserve. The Nation is a member of the Meadow Lake Tribal Council. TheBigstone Cree Nation
The Bigstone Cree Nation ( cr, ᐅᐸᓯᑯᓂᐍᐤ, opasikoniwew) is a First Nations band government in Alberta, Canada. As Woodland Cree, they are a western branch of the larger Cree nation, and are a party to Treaty 8 with Canada. The Bigst ...
is based in Wabasca, Alberta
Wabasca, also known as Wabasca-Desmarais, is a hamlet in northern Alberta, Canada within the Municipal District (MD) of Opportunity No. 17. It is located between and along the South and North Wabasca Lakes, at the intersection of Highway 813 ...
, about northeast of Slave Lake, on the Wabasca 166A
Wabasca 166A is an Indian reserve of the Bigstone Cree Nation in Alberta, located within the Municipal District of Opportunity No. 17. In the 2016 Canadian Census
The 2016 Canadian census was an enumeration of Canadian residents, which counted ...
reserve. The Nation is not associated with a Tribal Council. The Bigstone Cree Nation was divided into two bands in 2010, with one group continuing under the former name, and the other becoming the Peerless Trout First Nation
The Peerless Trout First Nation is a First Nations band government in northern Alberta, Canada, that is based out of Peerless Lake. It is part of the Treaty 8 Confederacy and was formed as Alberta's forty-fifth First Nation in 2010.
The Pee ...
.
The Fort McMurray First Nation
Fort McMurray First Nation ( cr, ᓂᐢᑕᐚᔮᐤ, nistawâyâw) is a Cree and Chipewyan band government located near Fort McMurray, Alberta.
It is a member of the Athabasca Tribal Council and a Treaty 8 nation. The Athabasca Tribal Counci ...
is located on the reserves Gregoire Lake 176 and 176A located about southeast of Fort McMurray
Fort McMurray ( ) is an urban service area in the Regional Municipality of Wood Buffalo in Alberta, Canada. It is located in northeast Alberta, in the middle of the Athabasca oil sands, surrounded by boreal forest. It has played a significan ...
near Anzac, Alberta on Gregoire Lake. They are the only Cree member of the Athabasca Tribal Council.
Kee Tas Kee Now Tribal Council
Kee Tas Kee Now Tribal Council is a Tribal Council representing First Nation communities in north-central Alberta, Canada. The council is based in Atikameg, Alberta.
Member First Nations
Current First Nation members are:
* Loon River First Nation ...
is based in Atikameg, Alberta
Atikameg is a settlement in Alberta, Canada. It is located along Highway 750, north-east from High Prairie. It lies on the north-western shore of Utikuma Lake at an elevation of .
Atikameg means ''little whitefish'' in Cree. The settlement is ...
with five members: The Loon River First Nation
The Loon River First Nation ( cr, ᒫᑿ ᓰᐲᐩ, mâkwa-sîpîy)is a First Nations band government in northern Alberta. A signatory to Treaty 8, it controls three Indian reserves
In Canada, an Indian reserve (french: réserve indienne) is ...
is headquartered in Red Earth Creek with reserves to the immediate west near Loon Lake. The
Lubicon Lake Band is based in the settlement of Little Buffalo, approximately east of Peace River
The Peace River (french: links=no, rivière de la Paix) is a river in Canada that originates in the Rocky Mountains of northern British Columbia and flows to the northeast through northern Alberta. The Peace River joins the Athabasca River in th ...
. The Peerless Trout First Nation
The Peerless Trout First Nation is a First Nations band government in northern Alberta, Canada, that is based out of Peerless Lake. It is part of the Treaty 8 Confederacy and was formed as Alberta's forty-fifth First Nation in 2010.
The Pee ...
is located in Peerless Lake on the Peerless Trout 238 reserve, about west of Red Earth Creek. Whitefish Lake First Nation
The Whitefish Lake First Nation ( cr, ᐊᑎᐦᑲᒣᐠ, atihkamek) is a First Nations band government in northern Alberta. Headquartered in Atikameg, it controls three Indian reserves, Utikoomak Lake 155, Utikoomak Lake 155A, and Utikoomak ...
is based in Atikameg, on the western shore of Utikuma Lake
Utikuma Lake is a large lake in north-central Alberta, Canada. It is located north of the Lesser Slave Lake, between the Bicentennial Highway and Highway 750.
It has a total surface of with island area. The shallow lake (maximum depth is ...
on the Utikoomak Lake 155
Utikoomak Lake 155 is an Indian reserve of the Whitefish Lake First Nation in Alberta, located within Northern Sunrise County and Big Lakes County. It is 61 kilometers north of High Prairie, Alberta, High Prairie. In the 2016 Canadian Census, it r ...
reserve, north of High Prairie
High Prairie is a town in northern Alberta, Canada within Big Lakes County. It is located at the junction of Highway 2 and Highway 749, approximately northeast of Valleyview and west of Slave Lake.
History
Describes the nature of the ...
. The Woodland Cree First Nation is located in the hamlet of Cadotte Lake on the Woodland Cree 226 reserve, northeast of Peace River.
Lesser Slave Lake Indian Regional Council Lesser Slave Lake Indian Regional Council is a Tribal Council representing First Nation communities around Lesser Slave Lake in Alberta, Canada. The council is based in Slave Lake, Alberta.
Member First Nations
Current First Nation members are:
* ...
, based out of the town of Slave Lake
Slave Lake is a town in northern Alberta, Canada that is surrounded by the Municipal District of Lesser Slave River No. 124. It is approximately northwest of Edmonton. It is located on the southeast shore of Lesser Slave Lake at the junction o ...
, Alberta is, as the name suggests, a Tribal Council of First Nations surrounding Lesser Slave Lake
Lesser Slave Lake (french: Petit lac des Esclaves)—known traditionally as "Beaver Lake" (ᐊᒥᐢᐠ ᓵᑲᐦᐃᑲᐣ amisk sâkâhikan in the Plains Cree language, and T’saat’ine migeh in Dene Zhatıé) or "Beaver people were over the ...
. Member Nations include: The Driftpile First Nation
The Driftpile First Nation (or the Driftpile Cree Nation) ( cr, ᒪᐦᑕᐦᑕᑲᐤ ᓯᐱᕀᐩ, mihtatakaw sîpîy) is a Treaty 8 First Nation with a reserve, Drift Pile River 150, located on the southern shore of the Lesser Slave Lake on Al ...
, based in Driftpile, on the Drift Pile River 150
Drift Pile River 150 is an Indian reserve of the Driftpile Cree Nation in Alberta, located within Big Lakes County. It is 6 kilometers southeast of Lesser Slave Lake. In the 2016 Canadian Census
The 2016 Canadian census was an enumeration of Ca ...
reserve, west of Slave Lake.
The Kapawe'no First Nation
The Kapawe'no First Nation ( cr, ᑲᐹᐏᐣ, kapâwin) is a band government in Alberta, Canada. It is headquartered at Grouard, Alberta, which is near High Prairie.
Indian Reserves
Six Indian reserves are governed by the band:
* Kapawe'no Fi ...
is headquartered at Grouard
Grouard, also known as Grouard Mission, is a hamlet in northern Alberta within Big Lakes County. It was previously an incorporated municipality between 1909 and 1944.
Grouard is located north of Highway 2, approximately northeast of Grande ...
, which is near High Prairie
High Prairie is a town in northern Alberta, Canada within Big Lakes County. It is located at the junction of Highway 2 and Highway 749, approximately northeast of Valleyview and west of Slave Lake.
History
Describes the nature of the ...
. They have six reserves, predominately located west of Lesser Slave Lake. The Sawridge First Nation
The Sawridge First Nation is a First Nations band government in northern Alberta. Headquartered in the town of Slave Lake, it controls two Indian reserves, Sawridge 150G
Sawridge 150G is an Indian reserve of the Sawridge First Nation in Albert ...
is based in Slave Lake and the two reserves, Sawridge 150G
Sawridge 150G is an Indian reserve of the Sawridge First Nation in Alberta, located within the Municipal District of Lesser Slave River No. 124. It is adjacent to the eastern boundary of the town of Slave Lake
Slave Lake is a town in norther ...
and 150H, are adjacent to the town. The Sucker Creek First Nation is based in Enilda
Enilda is a hamlet in northern Alberta within Big Lakes County, located west of Highway 49, approximately northeast of Grande Prairie.
The community's name is that of Adline Tompkins, an early postmaster's wife, spelled backwards.
Demograp ...
, east of High Prairie, on the Sucker Creek 150A reserve. Finally, the Swan River First Nation
The Swan River First Nation ( cr, ᐚᐱᓯᐤ ᓰᐱᐩ, wâpisiw-sîpiy) is a First Nations band government in northern Alberta. Located near Kinuso, it controls two Indian reserves, Swan River 150E
Swan River 150E is a Cree First Nation ...
, near Kinuso
Kinuso ( cr, script=Cans, ᑭᓄᓭᐤ, ) is a hamlet in northern Alberta, Canada within Big Lakes County, and surrounded by the Swan River First Nation reserve. It is located approximately west of Slave Lake and 71 km east of High Prairie ...
, west of Slave Lake, controls the Swan River 150E and Assineau River 150F
Assineau River 150F is an Indian reserve of the Swan River First Nation in Alberta
Alberta ( ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is part of Western Canada and is one of the three prairie provinces. Alberta is ...
reserves.
The Little Red River Cree Nation
The Little Red River Cree Nation ( cr, ᒥᐦᒁᑲᒦᐏ ᓰᐲᓯᐢ, mihkwâkamîwi-sîpîsis) is a First Nations band government in northern Alberta, headquartered at John D'Or Prairie.
Indian Reserves
There are three Indian Reserves under th ...
is based out of the settlement of John D'Or Prairie
John D'Or Prairie is a First Nations settlement within the John D'Or Prairie 215 Indian reserve in northern Alberta, Canada. It is located on the Lawrence River, upstream from the Peace River, and south of the Caribou Mountains. It has an eleva ...
, Alberta, east of Fort Vermilion
Fort Vermilion is a hamlet on the Peace River in northern Alberta, Canada, within Mackenzie County.
Established in 1788, Fort Vermilion shares the title of oldest European settlement in Alberta with Fort Chipewyan. Fort Vermilion contains many ...
, on the John D'Or Prairie 215
John D'Or Prairie 215 ''(Jean D’Or in French)'' is an Indian reserve of the Little Red River Cree Nation in northern Alberta, Canada. It is located east of the Town of High Level on Highway 58 and is surrounded by Mackenzie County
Mackenzi ...
reserve. They are a member of the North Peace Tribal Council The North Peace Tribal Council represents five First Nations in northwestern Alberta, Canada. The North Peace Tribal Council was incorporated in 1987, by the Beaver First Nation, Dene Tha' First Nation, Little Red River Cree First Nation, and Tallcr ...
based out of High Level, Alberta
High Level is a town in northern Alberta, Canada. It is located at the intersection of the Mackenzie Highway (Highway 35) and Highway 58, approximately north of Edmonton and south of Yellowknife, Northwest Territories. High Level is located wi ...
.
The Mikisew Cree First Nation
Mikisew Cree First Nation ( cr, ᒥᑭᓯᐤ, mikisiw, ''meaning: "golden eagle"'') is an Indigenous First Nations government of Woodland Cree people in northeastern Alberta and in Northwest Territories, Canada.
Most Mikisew Cree First Nation ...
is based in the community of Fort Chipewyan
Fort Chipewyan , commonly referred to as Fort Chip, is a hamlet in northern Alberta, Canada, within the Regional Municipality (RM) of Wood Buffalo. It is located on the western tip of Lake Athabasca, adjacent to Wood Buffalo National Park, app ...
on the western tip of Lake Athabasca
Lake Athabasca (; French: ''lac Athabasca''; from Woods Cree: , "herethere are plants one after another") is located in the north-west corner of Saskatchewan and the north-east corner of Alberta between 58° and 60° N in Canada. The lake ...
, approximately north of Fort McMurray. They are not a member of a Tribal Council. Fort Chipewyan, one of the oldest European settlements in Alberta, was established in 1788 by the North West Company as a fur trading post.
Western Cree Tribal Council is based out of Valleyview, Alberta
Valleyview is a town in northwest Alberta, Canada. It is surrounded by the Municipal District of Greenview No. 16 and in Census Division No. 18.
It is at the junction of Highway 43 and Highway 49, between the Little Smoky River and Sturgeo ...
. Cree member Nations are: Duncan's First Nation is based in Brownvale, adjacent to the reserve Duncan's 151A, southwest of Peace River. The Sturgeon Lake Cree Nation is on the Sturgeon Lake 154 reserve, west of Valleyview.
Plains Cree ()
Downstream people ()
Battlefords Agency Tribal Chiefs is a Tribal Council located inNorth Battleford, Saskatchewan
North Battleford is a city in west-central Saskatchewan, Canada. It is the seventh largest city in the province and is directly across the North Saskatchewan River from the Town of Battleford. Together, the two communities are known as "The Bat ...
. Members are: Ahtahkakoop First Nation
Ahtahkakoop First Nation ( cr, ᐊᑖᐦᑲᑯᐦᑊ ''atâhkakohp'', meaning ''Starblanket'', name of the first chief of the Band) is a Cree First Nation band government in Shell Lake, Saskatchewan, Canada. The Ahtahkakoop First Nation governme ...
, Moosomin First Nation The Moosomin First Nation ( cr, ᒨᓱᒥᓂᕽ ''môsominihk'')Wolvengrey, Arok, editor. Cree: Words. Regina, University of Regina Press, 2001https://itwewina.altlab.app/word/m%C3%B4sominihk//ref> is a Cree First Nation band government in Cochin, ...
, Mosquito-Grizzly Bear's Head-Lean Man, Red Pheasant First Nation
The Red Pheasant Cree Nation ( cr, ᒥᑭᓯᐘᒌᕽ, mikisiwacîhk) is a Plains Cree First Nations band government in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. The band's sole reserve, Red Pheasant 108, is south of North Battleford.
History ...
, Saulteaux First Nation, and Sweetgrass First Nation.
File Hills Qu'Appelle Tribal Council
Fort Qu'Appelle is a town in Canadian province of Saskatchewan located in the Qu'Appelle River valley north-east of Regina, between Echo and Mission Lakes of the Fishing Lakes. It is not to be confused with the once-significant nearby to ...
is a Tribal Council based in Fort Qu'Appelle, Saskatchewan
Fort Qu'Appelle is a town in Canadian province of Saskatchewan located in the Qu'Appelle River valley north-east of Regina, between Echo and Mission Lakes of the Fishing Lakes. It is not to be confused with the once-significant nearby t ...
. Cree member Nations are: Little Black Bear First Nation, Muscowpetung Saulteaux Nation, Nekaneet Cree Nation, Okanese First Nation
The Okanese First Nation ( cr, ᐅᑭᓃᐢ, ''okinîs'', literal meaning: ''Little Rose-hip'')Wolvengrey, Arok, editor. Cree: Words. Regina, University of Regina Press, 2001https://itwewina.altlab.app/word/okin%C3%AEs@3//ref> is a Cree-Saulteaux ...
, Pasqua First Nation
Pasqua First Nation ( cr, ᐸᐢᒁᐤ paskwâw) is a Saulteaux- Cree First Nation in southern Saskatchewan, Canada. Their reserves include:
* Last Mountain Lake 80A, shared with 6 other bands
* Pasqua 79
* Treaty Four Reserve Grounds 77, shared ...
, Peepeekisis Cree Nation, Piapot Cree Nation
Piapot First Nation ( cr, ᓀᐦᐃᔭᐏᑇᑎᓈᕽ ''nêhiyaw-pwâtinâhk'') is a Cree First Nation in southern Saskatchewan, Canada.
Reserves
* Haylands 75A
* Last Mountain Lake 80A
* Piapot 75
* Piapot 75E
* Piapot Cree First Nation 75F
* ...
, and Star Blanket Cree Nation
Star Blanket Cree Nation ( cr, ᐊᒑᐦᑯᓴ ᑳ ᐅᑕᑯᐦᐱᐟ ''acâhkosa kâ-otakohpit'', meaning ''One who has stars as a blanket'') is a First Nations band government in Saskatchewan, Canada. Its reserves are in the Fort Qu'Appelle ...
Meadow Lake Tribal Council is a Tribal Council based in Meadow Lake, Saskatchewan
Meadow Lake is a city in the boreal forest of northwestern Saskatchewan, Canada. Its location is about northeast of Lloydminster and north of North Battleford. Founded as a trading post in 1799, it became a village in 1931 and a town in 1 ...
with nine member First Nations. The members with Plains Cree populations are Flying Dust First Nation
The Flying Dust First Nation ( cr, ᑳ ᐅᐦᐹᐘᐦᑳᐢᑕᕽ ''kâ-ohpâwahkâstahk'') is a Cree First Nation band government located adjacent to the city of Meadow Lake in Saskatchewan, Canada. Highway 55
The following highways are ...
, Makwa Sahgaiehcan First Nation, Ministikwan Lake Cree Nation
Ministikwan Lake Cree Nation ( cr, ᒥᓂᐢᑎᑿᐣ, ministikwan)is a Cree First Nation in Saskatchewan, Canada. Their reserve
Reserve or reserves may refer to:
Places
* Reserve, Kansas, a US city
* Reserve, Louisiana, a census-designated ...
, and Waterhen Lake First Nation
Saskatoon Tribal Council is, as the name suggests, a Tribal Council-based out of Saskatoon, Saskatchewan
Saskatoon () is the largest city in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan. It straddles a bend in the South Saskatchewan River in the central region of the province. It is located along the Trans-Canada Yellowhead Highway, and has served as th ...
. Cree member Nations are: Mistawasis Nêhiyawak, Muskeg Lake Cree Nation
The Muskeg Lake Cree Nation ( cr, script=Cans, ᒪᐢᑫᑯ ᓵᑲᐦᐃᑲᐣ, ) is a Cree First Nation band government in Marcelin, Saskatchewan, Canada.
The Muskeg Lake Cree Nation is affiliated with the Saskatoon Tribal Council, along with ...
, Muskoday First Nation, and One Arrow First Nation
One Arrow First Nation ( cr, ᑳ ᐯᔭᒁᐢᑯᓇᒼ ''kâ-pêyakwâskonam'') is a Cree First Nations band government in Bellevue, Saskatchewan, Canada. Its main reserve is located just south of Batoche near the South Saskatchewan River abou ...
.
Touchwood Agency Tribal Council
Touchwood is decayed wood used for tinder. The phrase "touch wood" is another way of describing knocking on wood. The terms may also refer to
Geography in Canada
* Touchwood Hills, a range of hills in Saskatchewan
* Rural Municipality of Touchwoo ...
, based in Punnichy, Saskatchewan, is a Tribal Council of four First Nations, collectively known as the Touchwood Hills Cree (). The Cree Nations are: Day Star First Nation
Day Star First Nation ( cr, ᑮᓯᑳᐘᒑᕽ ''kîsikâwacâhk'')Wolvengrey, Arok, editor. Cree: Words. Regina, University of Regina Press, 2001https://itwewina.altlab.app/word/k%C3%AEsik%C3%A2wac%C3%A2hk@2//ref> is a First Nations band governm ...
, George Gordon First Nation
The George Gordon First Nation ( cr, ᐳᓵᑲᓇᒌᕽ ''posâkanacîhk'') is a First Nations band government located near the village of Punnichy, Saskatchewan, in Canada. The nation has an enrolled population of 3,752 people, 1,191 of whom liv ...
, Kawacatoose First Nation
The Kawacatoose First Nation ( cr, ᑲᐚᐦᑲᑐᐢ ''kawâhkatos'')Wolvengrey, Arok, editor. Cree: Words. Regina, University of Regina Press, 2001https://itwewina.altlab.app/word/kaw%C3%A2hkatos@2//ref> is a Plains Cree First Nations band gov ...
, and Muskowekwan First Nation
Muskowekwan First Nation ( oj, Mashkawigwaning) is a Saulteaux (Ojibway) First Nation who inhabit approximately 100 km northwest of Melville, Saskatchewan, Canada. As of May, 2008, the First Nation has 1,517 registered people, of which their ...
.
Yorkton Tribal Council is a Tribal Council based in Yorkton, Saskatchewan
Yorkton is a city located in south-eastern Saskatchewan, Canada. It is about 450 kilometres north-west of Winnipeg and 300 kilometres south-east of Saskatoon and is the sixth largest city in the province.
As of 2017 the census population of th ...
. Cree members are: Kahkewistahaw First Nation
Kahkewistahaw First Nation ( cr, ᑳᐦ ᑮᐑᐢᑕᐦᐋᐤ kâh-kîwîstahâw) is a Saulteaux- and Cree-speaking First Nation in southern Saskatchewan, Canada. The name Kahkewistahaw means "Eagle flying in the air". Their reserves include:
...
and Ocean Man First Nation
The Ocean Man First Nation ( cr, ᑭᐦᒋᑲᒦᐏᔨᐣ ''kihcikamîwiyin'') is an Assiniboine, Cree, and Saulteaux band government in southeastern Saskatchewan, Canada. Chief ''Kitchi-Kah-Me-Win'' (Great Seaman or Ocean Man, also spelt Kiche ...
.
Without affiliation with any Tribal Council: Beardy's and Okemasis' Cree Nation
Beardy's and Okemasis' Cree Nation is a Cree First Nations band government in Saskatchewan, Canada. Their reserves include:
* Beardy's & Okemasis' 96 & 97
* Beardy's & Okemasis' 96 & 97A
* Beardy's & Okemasis' 96 & 97B
* Beardy's & Okemasis' ...
, Cowessess First Nation, Ochapowace Nation
The Ochapowace Nation ( cr, ᐅᒑᐳᐍᐢ ''ocâpowês'') is a Cree First Nation in southern Saskatchewan, Canada.
Reserves
Reserves include:
* Ochapowace 71
* Ochapowace 71-1
* Ochapowace 71-2
* Ochapowace 71-3
* Ochapowace 71-4
* Ochapowa ...
, Onion Lake Cree Nation, Pheasant Rump Nakota First Nation The Pheasant Rump Nakota First Nation ( asb, Šiyónidè oyáde)Collette, Vincent. “Nakoda Vocabulary and Phrases.” Academia.edu, November 14, 2017Link is a First Nation in the Canadian province of Saskatchewan, who reside on the Pheasant Rump ...
, White Bear First Nations.
Upstream people ()
Agency Chiefs Tribal Council is a Tribal Council located inSpiritwood, Saskatchewan
Spiritwood is a town in the boreal forest of central Saskatchewan, Canada with a population of approximately 1,000.
Its location is 125 km west of Prince Albert and about 110 km northeast of North Battleford at the junction of Highway ...
representing three First Nations: Pelican Lake First Nation
Pelican Lake First Nation ( cr, ᒐᐦᒐᐦᑭᐤ ᓵᑲᐦᐃᑲᓂᕽ ''cahcahkiw-sâkahikanihk'', meaning: ''at the Pelican Lake'') is a member of the Federation of Saskatchewan First Nations, the body that represents 74 First Nations in Sask ...
, Big River First Nation, and Witchekan Lake First Nation.
Battlefords Tribal Council is based in North Battleford, Saskatchewan
North Battleford is a city in west-central Saskatchewan, Canada. It is the seventh largest city in the province and is directly across the North Saskatchewan River from the Town of Battleford. Together, the two communities are known as "The Bat ...
, The three member Nations are Lucky Man Cree Nation
The Lucky Man Cree Nation ( cr, ᐸᐯᐍ papêwê) is a Cree First Nation in Saskatchewan, Canada. After spending more than a hundred years amalgamated into the Little Pine First Nation, the band was awarded the Lucky Man Reserve, on the easte ...
, Little Pine First Nation, and Poundmaker First Nation.
Interlake Reserves Tribal Council is a Tribal Council based in Fairford, Manitoba. The council has six Nations as members but the only Cree member is Peguis First Nation
Peguis First Nation (formerly St. Peter's Band, oj, Oshki-ishkonigan meaning ''new reserve'') is the largest First Nations community in Manitoba, Canada, with a population of approximately 10,300 people (3,521 on reserve and 6,504 off reserve). ...
.
Without affiliation with any Tribal Council: Big Island Lake Cree Nation, Thunderchild First Nation Thunderchild First Nation is an independent Cree First Nations band government in Turtleford, Saskatchewan, Canada with no affiliation with any Tribal Council. It is located approximately 113 kilometers northwest of North Battleford. European sett ...
.
Tribal Chiefs Ventures is a Tribal council based in Edmonton with the following Cree members: Beaver Lake Cree Nation
The Beaver Lake Cree Nation is a First Nations band government located northeast of Edmonton, Alberta, representing people of the Cree ethno-linguistic group in the area around Lac La Biche, Alberta, where the band office is currently located. ...
, Heart Lake First Nation, Frog Lake First Nation, and Kehewin Cree Nation
The Kehewin Cree Nation ( cr, ᑭᐦᐁᐤ ᓀᐦᐃᔭᐤ ᐊᐢᑭᐩ, kihêw nehiyaw askiy) is a First Nations band government in northern Alberta. A signatory to Treaty 6, it controls one Indian reserve, Kehewin 123
Kehewin 123 is an Indian ...
.
Beaver Hills Cree ()
Maskwacis Cree Tribal Council is based in the unincorporated community ofMaskwacis
Maskwacis (; cr, ᒪᐢᑿᒌᐢ, ), renamed in 2014 from Hobbema (), is an unincorporated community in central Alberta, Canada at intersection of Highway 2A and Highway 611, approximately south of the City of Edmonton. The community consists ...
, (formerly Hobbema) Alberta, located south of Edmonton
Edmonton ( ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Alberta. Edmonton is situated on the North Saskatchewan River and is the centre of the Edmonton Metropolitan Region, which is surrounded by Alberta's central region. The city ancho ...
. The members are Ermineskin Cree Nation
Ermineskin Cree Nation also known as the Ermineskin Tribe ( cr, ᓀᔮᐢᑵᔮᕽ, ), is a Cree First Nations band government in Alberta, Canada. A signatory to Treaty 6, Ermineskin is one of the Four Nations of Maskwacis, Alberta's largest ...
, Louis Bull Tribe
The Louis Bull Tribe ( cr, ᑭᓭ ᐸᑎᓇᕽ, kisipatnahk) is a First Nations band government in Alberta, Canada. One of the "four nations" of Maskwacis, it controls one Indian reserve, Louis Bull 138B, and shares ownership of another, Pigeon ...
, Montana First Nation
The Montana First Nation ( cr, ᐊᑳᒥᕽ, ) is a First Nations band government in Alberta, Canada. It is a Treaty 6 government. Formerly the Montana Band of Indians, it is one of four First Nations in the area of Maskwacis.
Indian Reserves
...
, and Samson Cree Nation
The Samson Cree Nation, ( cr, ᓃᐱᓰᐦᑯᐹᕽ, nîpisîhkopâhk, translation=at willow grove) also known as the Samson First Nation, is one of four band governments in the area of Maskwacis, Alberta, Canada.
Indian Reserves
Three Indian R ...
. All four members have individual reserves that surround the community of Maskwacis: Ermineskin 138
Ermineskin 138 is an Indian reserve of the Ermineskin Cree Nation in Alberta, located between Ponoka County and the County of Wetaskiwin No. 10. Part of the Maskwacis community, it is 13 kilometres south of Wetaskiwin
Wetaskiwin ( ) is a ...
, Louis Bull 138B
Louis Bull 138B is an Indian reserve of the Louis Bull First Nation in Alberta, located within County of Wetaskiwin No. 10. One of four reserves making up the Maskwacis community, it is 16 kilometers southwest of Wetaskiwin. In the 2016 Canadian ...
, Montana 139
Montana 139 is an Indian reserve of the Montana First Nation in Alberta, located within Ponoka County. Part of the Maskwacis community, it is 24 kilometers south of Wetaskiwin. In the 2016 Canadian Census, it recorded a population of 630 living ...
, Samson 137, and Samson 137A
Samson 137A is an Indian reserve of the Samson Cree Nation in Alberta, located within Ponoka County. In the 2016 Canadian Census
The 2016 Canadian census was an enumeration of Canadian residents, which counted a population of 35,151,728, a cha ...
. And all four share the reserve of Pigeon Lake 138A
Pigeon Lake 138A is an Indian reserve in Alberta. It is located west of Wetaskiwin along Pigeon Lake. It is at an elevation of . It is shared between the Samson Cree Nation, the Montana Cree Nation, the Louis Bull Tribe, and the Ermineskin ...
, about to the northwest.
Yellowhead Tribal Council is based in Morinville, Alberta. Member nations are: Alexander First Nation
Alexander First Nation ( cr, Kipohtakaw / ᑭᐳᐦᑕᑲᐤ) is a First Nations band government, headquartered west of Morinville, Alberta. This First Nation is part of the Cree ethno-linguistic group, is a member of the Yellowhead Tribal Co ...
, Alexis Nakota Sioux First Nation
The Alexis Nakota Sioux Nation ( sto, Cade Wicashdabi) no. 437 is a Nakoda First Nation which reserves near Edmonton, Hinton, and Whitecourt, in the Canadian province of Alberta, and headquartered at 54° N and 114°, about west of Edmonton. ...
, O'Chiese First Nation
The O'Chiese First Nation () is a Saulteaux First Nation in Alberta, Canada. The First Nation's homeland is the O'Chiese 203 Indian reserve, located approximately 52 km northwest of Rocky Mountain House. Also reserved is the O'Chiese Cemeter ...
, and Sunchild First Nation. The Alexander First Nation
Alexander First Nation ( cr, Kipohtakaw / ᑭᐳᐦᑕᑲᐤ) is a First Nations band government, headquartered west of Morinville, Alberta. This First Nation is part of the Cree ethno-linguistic group, is a member of the Yellowhead Tribal Co ...
is located on the reserve of Alexander 134
Alexander 134 is an Indian reserve of the Alexander First Nation in Alberta, located within Sturgeon County. It is located about northwest of Edmonton. In the 2016 Canadian Census
The 2016 Canadian census was an enumeration of Canadian residen ...
, west of Morinville
Morinville is a town in the Edmonton Metropolitan Region of Alberta, Canada. It is approximately north of Edmonton along Highway 2.
History
Morinville was settled by Jean-Baptiste Morin, a priest and missionary of the Missionary Oblates ...
and northwest of Edmonton. Alexis Nakota Sioux First Nation
The Alexis Nakota Sioux Nation ( sto, Cade Wicashdabi) no. 437 is a Nakoda First Nation which reserves near Edmonton, Hinton, and Whitecourt, in the Canadian province of Alberta, and headquartered at 54° N and 114°, about west of Edmonton. ...
is based on the Alexis 133
Alexis 133 is an Indian reserve of the Alexis Nakota Sioux Nation in Alberta, located within Lac Ste. Anne County. It is 70 kilometres northwest of Edmonton
Edmonton ( ) is the capital city of the Canadian province of Alberta. Edmonton is ...
reserve, outside Glenevis, northwest of Edmonton. The O'Chiese First Nation
The O'Chiese First Nation () is a Saulteaux First Nation in Alberta, Canada. The First Nation's homeland is the O'Chiese 203 Indian reserve, located approximately 52 km northwest of Rocky Mountain House. Also reserved is the O'Chiese Cemeter ...
and Sunchild First Nation control the reserves O'Chiese 203
O'Chiese 203 is an Indian reserve in Alberta, Canada and is one of two reserves under the administration of the O'Chiese First Nation, a Saulteaux government. It is located northwest of Red Deer. It is at an elevation of . The reserve is bordere ...
and Sunchild 202 which are adjacent to each other northwest of Rocky Mountain House
Rocky Mountain House is a town in west-central Alberta, Canada. It is approximately west of Red Deer at the confluence of the Clearwater and North Saskatchewan Rivers, and at the crossroads of Highway 22 (Cowboy Trail) and Highway 11 (David T ...
.
Not affiliated with any Tribal Council: Enoch Cree Nation
The Enoch Cree Nation #440 ( cr, script=Cans, ᒪᐢᑫᑯᓯᐦᐠ, ) is a First Nations band government in Alberta, Canada. Members of the Nation are of Cree ancestry and speak the Plains Cree dialect of the Cree language group. The band i ...
, Paul First Nation
The Paul First Nation, more commonly known as the Paul Band, is a First Nations band government based in Wabamun, Alberta of mixed Cree and Nakoda (Stoney) origin. They are party to Treaty Six and had the Buck Lake Indian Reserve 133C and Wab ...
, and Saddle Lake Cree Nation
Saddle Lake Cree Nation ( cr, ᐅᓂᐦᒋᑭᐢᑿᐱᐏᓂᕽ, onihcikiskwapiwinihk) is a Plains Cree, First Nations community, located in the ''Amiskwacīwiyiniwak'' (" Beaver Hills") region of central Alberta, Canada. The Nation is a signator ...
Enoch Cree Nation
The Enoch Cree Nation #440 ( cr, script=Cans, ᒪᐢᑫᑯᓯᐦᐠ, ) is a First Nations band government in Alberta, Canada. Members of the Nation are of Cree ancestry and speak the Plains Cree dialect of the Cree language group. The band i ...
is located on their main reserve, Enoch Cree Nation 135
Enoch Cree Nation 135, ( cr, ᒪᐢᑫᑯᓯᐦᐠ, translit=maskêkosihk ) previously known as Stony Plain No. 135, is an Indian reserve of the Enoch Cree Nation #440 in Alberta. It is adjacent to the City of Edmonton to the east and Parkland ...
, adjacent to the western boundary of the city of Edmonton. The Paul First Nation
The Paul First Nation, more commonly known as the Paul Band, is a First Nations band government based in Wabamun, Alberta of mixed Cree and Nakoda (Stoney) origin. They are party to Treaty Six and had the Buck Lake Indian Reserve 133C and Wab ...
is based on the Wabamun 133A reserve, west of Edmonton. Saddle Lake Cree Nation
Saddle Lake Cree Nation ( cr, ᐅᓂᐦᒋᑭᐢᑿᐱᐏᓂᕽ, onihcikiskwapiwinihk) is a Plains Cree, First Nations community, located in the ''Amiskwacīwiyiniwak'' (" Beaver Hills") region of central Alberta, Canada. The Nation is a signator ...
is one of the most populous Nations in Canada with 11,235 people . The Nation is located in Saddle Lake, Alberta
Saddle Lake is a First Nations community in central Alberta. It is located on Saddle Lake Cree Nation 125 and is governed by the Saddle Lake Cree Nation.
The community is located on Highway 652, approximately northeast of the City of Edmonton, ...
on the Saddle Lake 125
Saddle Lake 125 is an Indian reserve of the Saddle Lake Cree Nation in Alberta, located between Smoky Lake County and the County of St. Paul No. 19. It is 24 kilometres west of St. Paul.
Uniquely in Alberta, the Saddle Lake Cree Nation did not gi ...
reserve, west of St. Paul, Alberta.
United States
Fort Peck Indian Reservation
The Fort Peck Indian Reservation ( asb, húdam wįcášta, dak, Waxchį́ca oyáte) is located near Fort Peck, Montana, in the northeast part of the state. It is the home of several federally recognized bands of Assiniboine, Nakota, Lakota, ...
located near Fort Peck, Montana
Chippewa Cree
The Chippewa Cree Tribe (Officially in cr, italics=no, ᐅᒋᐻᐤ ᓀᐃᔭᐤ, translit=''ocipwêw nêiyaw'')Montana Department of Justice, Official Tribally issued license plate of Chippewa Cree TriLink/ref> is a federally recognized tribe ...
on the Rocky Boy's Indian Reservation in northern Montana
Fort Belknap Indian Reservation
The Fort Belknap Indian Reservation ( ats, ’ak3ɔ́ɔyɔ́ɔ, lit=the fence or ats, ’ɔ’ɔ́ɔ́ɔ́nííítaan’ɔ, lit=Gros Ventre tribe, label=none) is shared by two Native American tribes, the A'aninin (Gros Ventre) and the Nakoda ...
located at Fort Belknap Agency, Montana
Other First Nations
Papaschase First Nation, removed from land that now makes up southeast Edmonton, were a party to Treaty 6 but are not recognized by the Canadian government.Ethnobotany
The Cree use the pitch ofAbies balsamea
''Abies balsamea'' or balsam fir is a North American fir, native to most of eastern and central Canada ( Newfoundland west to central Alberta) and the northeastern United States (Minnesota east to Maine, and south in the Appalachian Mountains to ...
for menstrual irregularity, and take an infusion of the bark and sometimes the wood for coughs. They use the pitch and grease used as an ointment for scabies and boils. They apply a poultice
A poultice, also called a cataplasm, is a soft moist mass, often heated and medicated, that is spread on cloth and placed over the skin to treat an aching, inflamed, or painful part of the body. It can be used on wounds, such as cuts.
'Poultice ...
of pitch applied to cuts. They also use a decoction of pitch and sturgeon oil used for tuberculosis
Tuberculosis (TB) is an infectious disease usually caused by '' Mycobacterium tuberculosis'' (MTB) bacteria. Tuberculosis generally affects the lungs, but it can also affect other parts of the body. Most infections show no symptoms, i ...
, and take an infusion of bark for tuberculosis. They also use the boughs to make brush shelters and use the wood to make paddles.
Hudson Bay Cree subgroup
The Hudson Bay Cree use a decoction of the leaves of ''Kalmia angustifolia
''Kalmia angustifolia'' is a flowering shrub in the family Ericaceae, commonly known as sheep laurel. It is distributed in eastern North America from Ontario and Quebec south to Virginia. It grows commonly in dry habitats in the boreal forest, a ...
'' for diarrhea, but they consider the plant to be poisonous.
Woods Cree subgroup
TheWoods Cree
Woods Cree is an indigenous language spoken in Northern Manitoba, Northern Saskatchewan and Northern Alberta, Canada. It is part of the Cree-Montagnais-Naskapi dialect continuum. The dialect continuum has around 116,000 speakers; the exact popu ...
make use of Ribes glandulosum using a decoction
Decoction is a method of extraction by boiling herbal or plant material (which may include stems, roots, bark and rhizomes) to dissolve the chemicals of the material. It is the most common preparation method in various herbal-medicine systems. Dec ...
of the stem, either by itself or mixed with wild red raspberry, to prevent clotting after birth, eat the berries as food, and use the stem to make a bitter tea. They make use of Vaccinium myrtilloides
''Vaccinium myrtilloides'' is a shrub with common names including common blueberry, velvetleaf huckleberry, velvetleaf blueberry, Canadian blueberry, and sourtop blueberry. It is common in much of North America, reported from all 10 Canadian provi ...
, using a decoction
Decoction is a method of extraction by boiling herbal or plant material (which may include stems, roots, bark and rhizomes) to dissolve the chemicals of the material. It is the most common preparation method in various herbal-medicine systems. Dec ...
of leafy stems used to bring menstruation and prevent pregnancy, to make a person sweat, to slow excessive menstrual bleeding, to bring blood after childbirth, and to prevent miscarriage. They also use the berries to dye porcupine quills, eat the berries raw, make them into jam and eat it with fish and bannock, and boil or pound the sun-dried berries into pemmican
Pemmican (also pemican in older sources) is a mixture of tallow, dried meat, and sometimes dried berries. A calorie-rich food, it can be used as a key component in prepared meals or eaten raw. Historically, it was an important part of indigenou ...
. They use the berries of the ''minus'' subspecies of Vaccinium myrtilloides
''Vaccinium myrtilloides'' is a shrub with common names including common blueberry, velvetleaf huckleberry, velvetleaf blueberry, Canadian blueberry, and sourtop blueberry. It is common in much of North America, reported from all 10 Canadian provi ...
to colour porcupine quills, and put the firm, ripe berries on a string to wear as a necklace.Leighton, Anna L., 1985, Wild Plant Use by the Woods Cree () of East-Central Saskatchewan, Ottawa. National Museums of Canada. Mercury Series, page 64 They also incorporate the berries of the ''minus'' subspecies of ''Vaccinium myrtilloides
''Vaccinium myrtilloides'' is a shrub with common names including common blueberry, velvetleaf huckleberry, velvetleaf blueberry, Canadian blueberry, and sourtop blueberry. It is common in much of North America, reported from all 10 Canadian provi ...
'' into their cuisine. They store the berries by freezing them outside during the winter, mix the berries with boiled fish eggs, livers, air bladders and fat and eat them, eat the berries raw as a snack food, and stew them with fish or meat.
Cree people

 * Janice Acoose, author, of Sakimay (
* Janice Acoose, author, of Sakimay (Saulteaux
The Saulteaux (pronounced , or in imitation of the French pronunciation , also written Salteaux, Saulteau and other variants), otherwise known as the Plains Ojibwe, are a First Nations band government in Ontario, Manitoba, Saskatchewan, A ...
) and Ninankawe Marival Métis ancestry
* Nathaniel Arcand
Nathaniel Arcand (born November 13, 1971) is a Canadian actor. He is known for his first major role in the Canadian drama series ''North of 60'', in which for three seasons he played William MacNeil, smart-mouthed and cocky, a troubled, misunders ...
(Alexander First Nation
Alexander First Nation ( cr, Kipohtakaw / ᑭᐳᐦᑕᑲᐤ) is a First Nations band government, headquartered west of Morinville, Alberta. This First Nation is part of the Cree ethno-linguistic group, is a member of the Yellowhead Tribal Co ...
), actor
* Ethan Bear
Ethan Bear (born June 26, 1997) is an Indigenous Canadian professional ice hockey defenceman for the Vancouver Canucks of the National Hockey League (NHL). He was drafted in the fifth round, 124th overall, by the Edmonton Oilers in the 2015 NHL ...
, (b. 1997), NHL
The National Hockey League (NHL; french: Ligue nationale de hockey—LNH, ) is a professional ice hockey league in North America comprising 32 teams—25 in the United States and 7 in Canada. It is considered to be the top ranked professional ...
hockey player for the Carolina Hurricanes
The Carolina Hurricanes (colloquially known as the Canes) are a professional ice hockey team based in Raleigh, North Carolina. They compete in the National Hockey League (NHL) as a member of the Metropolitan Division in the Eastern Conference ...
* Irene Bedard
Irene Bedard (born July 22, 1967) is an American actress, who has played mostly lead Native American roles in a variety of films. She is perhaps best known for the role of Suzy Song in the 1998 film '' Smoke Signals'', an adaptation of a Sherma ...
, actress
* Robyn Bourgeois, author and academic
* Joe Buffalo, actor and skateboarder
* Ashley Callingbull-Burnham (Enoch Cree Nation
The Enoch Cree Nation #440 ( cr, script=Cans, ᒪᐢᑫᑯᓯᐦᐠ, ) is a First Nations band government in Alberta, Canada. Members of the Nation are of Cree ancestry and speak the Plains Cree dialect of the Cree language group. The band i ...
), 2015 Mrs. Universe winner, actress and first nations activist
* Harold Cardinal
Harold Cardinal (January 27, 1945 – June 3, 2005) was a Cree writer, political leader, teacher, negotiator, and lawyer. Throughout his career he advocated, on behalf of all First Nation peoples, for the right to be "the red tile in the Can ...
, writer, political leader, teacher, and lawyer
* Lorne Cardinal
Lorne Cardinal (born 6 January 1964) is a Canadian stage, television and film actor, best known for portraying Davis Quinton on ''Corner Gas''. He is a former rugby union player.
Early life
Cardinal was born on a reserve of the Sucker Creek ...
, actor
* Tantoo Cardinal
Tantoo Cardinal CM (born Rose Marie Cardinal; July 20, 1950) is a Canadian actress of Cree and Métis heritage. In 2009, she was made a member of the Order of Canada "for her contributions to the growth and development of Aboriginal performing ...
, actor
* Jonathan Cheechoo, NHL
The National Hockey League (NHL; french: Ligue nationale de hockey—LNH, ) is a professional ice hockey league in North America comprising 32 teams—25 in the United States and 7 in Canada. It is considered to be the top ranked professional ...
and KHL
The Kontinental Hockey League (KHL; russian: Континентальная хоккейная лига (КХЛ), Kontinental'naya khokkeynaya liga) is an international professional ice hockey league founded in 2008. It comprises member clubs b ...
hockey player
* Belinda Daniels
Belinda kakiyosēw Daniels is a nēhiyaw Canadian educator and language activist known for efforts to teach and revitalize nēhiyawēwin.
Early life and education
Daniels is a member of Sturgeon Lake First Nation, SK and was raised by her gra ...
, language teacher
*Billy Diamond
Billy Diamond (May 19, 1949 – September 30, 2010) was the Chief of the Waskaganish, Quebec Cree from 1970 to 1976, the Grand Chief of the Grand Council of the Crees from 1974 to 1984, and a successful businessman who founded Air Creebec.
Diamond ...
, political leader, first Grand Chief of the Grand Council of the Crees (Eeyou Istchee)
* Neil Diamond, filmmaker
* Connie Fife, poet
* Theoren Fleury
Theoren Wallace "Theo" Fleury (born June 29, 1968) is a Canadian former professional ice hockey player, author, and motivational speaker. Fleury played for the Calgary Flames, Colorado Avalanche, New York Rangers, and Chicago Blackhawks of the ...
, retired NHL hockey player, humanitarian, spokesperson, and author
* Ralph Garvin Steinhauer, tenth Lieutenant Governor of Alberta
The lieutenant governor of Alberta () is the viceregal representative in Alberta of the . The lieutenant governor is appointed in the same manner as the other provincial viceroys in Canada and is similarly tasked with carrying out most of the m ...
and first Aboriginal to hold that post.
* Edward Gamblin, musician
* Mary Greyeyes (1920–2011), the first First Nations
First Nations or first peoples may refer to:
* Indigenous peoples, for ethnic groups who are the earliest known inhabitants of an area.
Indigenous groups
*First Nations is commonly used to describe some Indigenous groups including:
**First Natio ...
woman to join the Canadian Armed Forces
* Michael Greyeyes
Michael Greyeyes (born June 4, 1967) (Muskeg Lake Cree Nation) is an Indigenous Canadian actor, dancer, choreographer, director, and educator.
In 1996, Greyeyes portrayed Crazy Horse in the television film ''Crazy Horse''. In 2018, Greyeyes port ...
, actor
* Tomson Highway
Tomson Highway (born 6 December 1951) is an Indigenous Canadian playwright, novelist, and children's author. He is best known for his plays ''The Rez Sisters'' and ''Dry Lips Oughta Move to Kapuskasing'', both of which won the Dora Mavor Moore ...
, playwright, librettist of the first Cree-language opera
* Tyson Houseman
Tyson Connor Houseman (born February 9, 1990) is a Canadian actor who appeared in '' The Twilight Saga: New Moon'' as Quil Ateara. Tyson currently performs with two professional theater companies, touring all over the world.
Background
House ...
, actor
* Helen Knott
Helen Knott is an Indigenous poet-writer, grassroots activist, leader and social worker from the Prophet River First Nation. She is of Dane-Zaa, Nehiyaw, Métis, and European descent. Residing in Fort St. John, British Columbia, Canada, Knott ...
, activist and author
* Melina Laboucan-Massimo, climate justice advocate
* Cody Lightning
Cody Lightning (born August 8, 1986) is a Cree actor from Edmonton, Alberta, Canada.Kerry Benjoe, "Indigenous film world filled with people passionate about their art". ''Regina Leader-Post'', December 12, 2015. He is the son of Georgina Lightning ...
, actor
* Ovide Mercredi
Ovide William Mercredi (born January 30, 1946) is a Canadian politician. He is Cree and a former National Chief of the Assembly of First Nations. He is also the former president of the Manitoba New Democratic Party.
Early life and career
A ...
, National chief of the Assembly of First Nations
The Assembly of First Nations (AFN) is an assembly of Canadian First Nations (Indian bands) represented by their chiefs. Established in 1982 and modelled on the United Nations General Assembly, it emerged from the National Indian Brotherhood, ...
* Delia Opekokew
Delia Opekokew is a Cree lawyer and writer from the Canoe Lake First Nation in Saskatchewan, Canada. She was the first First Nations woman lawyer to ever be admitted to the bar association in Ontario and in Saskatchewan,
, lawyer and activist
* Bronson Pelletier, actor
* Romeo Saganash, Member of Parliament for Abitibi—Baie-James—Nunavik—Eeyou, Quebec
* Buffy Sainte-Marie
Buffy Sainte-Marie, (born Beverly Sainte-Marie, February 20, 1941) is an Indigenous Canadian-American ( Piapot Cree Nation) singer-songwriter, musician, composer, visual artist, educator, pacifist, and social activist. While working in these ...
, singer
* Paul Seesequasis, writer and journalist
* Roseanne Supernault, actress
* Clayton Thomas-Müller
Clayton Thomas-Müller is a Cree activist and writer from Canada, most noted for his memoir ''Life in the City of Dirty Water''.Shawn Conner"In new memoir, activist Thomas-Muller traces impact of extraction industries on First Nations, and his own ...
, activist and memoirist
* Richard Throssel
Richard Throssel (1882–1933) was a Cree photographer, who documented life on the Crow Reservation at the beginning of the 20th century.
Background
Richard Throssel was born in Marengo, Washington Territory in 1882. Throssel is best known for h ...
(1882–1933), photographer
* Michelle Thrush
Michelle Thrush (born February 6, 1967) is a Canadian actress and First Nations activist for Aboriginal Canadians and the other Indigenous peoples of the Americas. She is best known for her leading role as Gail Stoney in '' Blackstone'', for which ...
, actor
* Loretta Todd
Loretta Sarah Todd is a Canadian Indigenous film director. Her first dramatic feature, ''Monkey Beach,'' is based on the iconic novel by Eden Robinson, recently launched to a strong audience and critical response, screening at TIFF Industry Select ...
, film director
* Gordon Tootoosis
Gordon Tootoosis, (October 25, 1941 – July 5, 2011) was a First Nations actor of Cree and Stoney descent. Tootoosis was a descendant of Yellow Mud Blanket, brother of the famous Cree leader Pîhtokahanapiwiyin. He was acclaimed for his comm ...
, actor
* Shane Yellowbird
Shane Yellowbird (July 7, 1979April 25, 2022) was a Canadian country music singer-songwriter from Hobbema, Alberta. A Cree, in 2007, he was named the Aboriginal Entertainer of the Year at the Aboriginal People's Choice Music Awards, Chevy Truck ...
, country singer
* Alfred Young Man ( Chippewa Cree Indians of the Rocky Boy's Reservation, b. 1948), educator, writer, curator, artist
See also
*Cree syllabics
Cree syllabics are the versions of Canadian Aboriginal syllabics used to write Cree dialects, including the original syllabics system created for Cree and Ojibwe. There are two main varieties of syllabics for Cree: Western Cree syllabics and ...
* (Cree law)
* James Bay Cree hydroelectric conflict
The James Bay Cree hydroelectric conflict refers to the resistance by James Bay Cree to the James Bay Hydroelectric Project and the Quebec Government, beginning in 1971.
The First Phase
The Quebec government announced plans in April 1971 for ...
* Michif
Michif (also Mitchif, Mechif, Michif-Cree, Métif, Métchif, French Cree) is one of the languages of the Métis people of Canada and the United States, who are the descendants of First Nations (mainly Cree, Nakota, and Ojibwe) and fur trade work ...
* Okichitaw
Okichitaw ( ) is a martial art that incorporates the fighting techniques of the Plains Cree First Nations. It was defined and taught by a Canadian martial artist, George J. Lépine.
History
Origins
In his youth, founder George J. Lépine ...
* Shaking Tent Ceremony
Notes
References
* *External links
Cree cultural site
The East Cree language web
The Cree-Innu linguistic atlas
Grand Council of the Crees (GCC) and Cree Nation Government
– Official website
Canada Government – Summary of the Agreement on the Cree Nation Governance
The Plains Cree – Ethnographic, Historical and Comparative Study by David Mandelbaum
Lac La Ronge Band website
Little Red River Cree Nation website
Brief history of Cree
from
Canadian Geographic
''Canadian Geographic'' is a magazine published by the Royal Canadian Geographical Society, (RCGS) based in Ottawa, Ontario.
History and profile
After the Society was founded in 1929, the magazine was established the next year in May 1930 unde ...
CBC Digital Archives – James Bay Project and the Cree
Fisher River Cree Nation Official Website
The Gift of Language and Culture website
CBC Digital Archives – Eeyou Istchee: Land of the Cree
{{authority control Algonquian peoples First Nations in Alberta First Nations in British Columbia First Nations in Manitoba First Nations in Ontario First Nations in Quebec First Nations in Saskatchewan First Nations in the Northwest Territories Great Lakes tribes Plains tribes Native American tribes in Montana