County of Baden on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The County of Baden (
 The land that became the County of Baden was originally ruled by the
The land that became the County of Baden was originally ruled by the 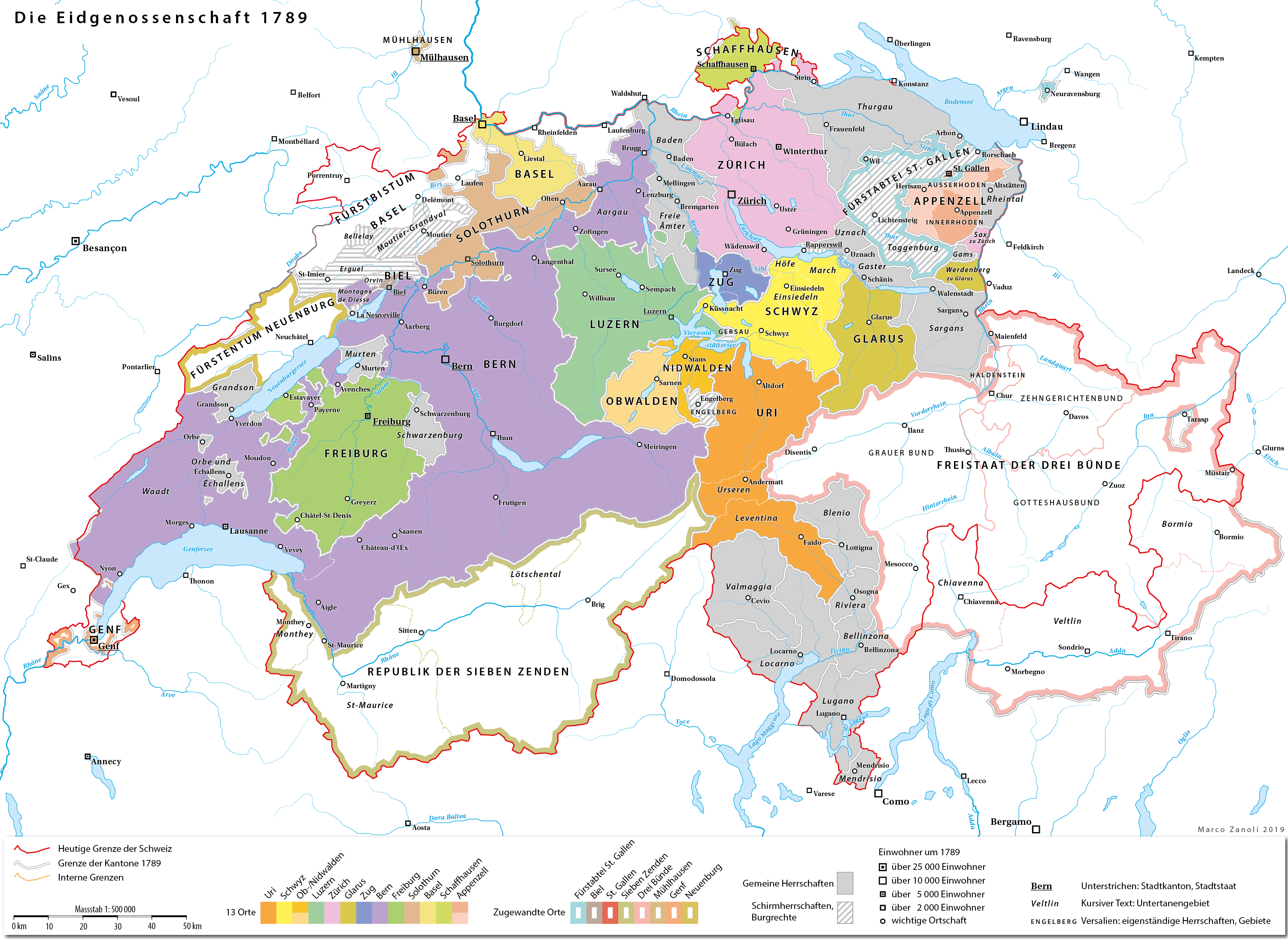 The Confederates retained much of the Habsburg legal structure, which caused a number of problems. The local nobility had the right to hold the low court in only about one fifth of the territory. There were over 30 different nobles who had the right to hold courts scattered around the surrounding lands. All these overlapping jurisdictions caused numerous conflicts, but gradually the Confederation was able to acquire these rights in the County. The cities of Baden, Bremgarten and
The Confederates retained much of the Habsburg legal structure, which caused a number of problems. The local nobility had the right to hold the low court in only about one fifth of the territory. There were over 30 different nobles who had the right to hold courts scattered around the surrounding lands. All these overlapping jurisdictions caused numerous conflicts, but gradually the Confederation was able to acquire these rights in the County. The cities of Baden, Bremgarten and  The governor's income came from a death tax (converted in 1666 into an annual tax), a tax on people leaving the county, a
The governor's income came from a death tax (converted in 1666 into an annual tax), a tax on people leaving the county, a
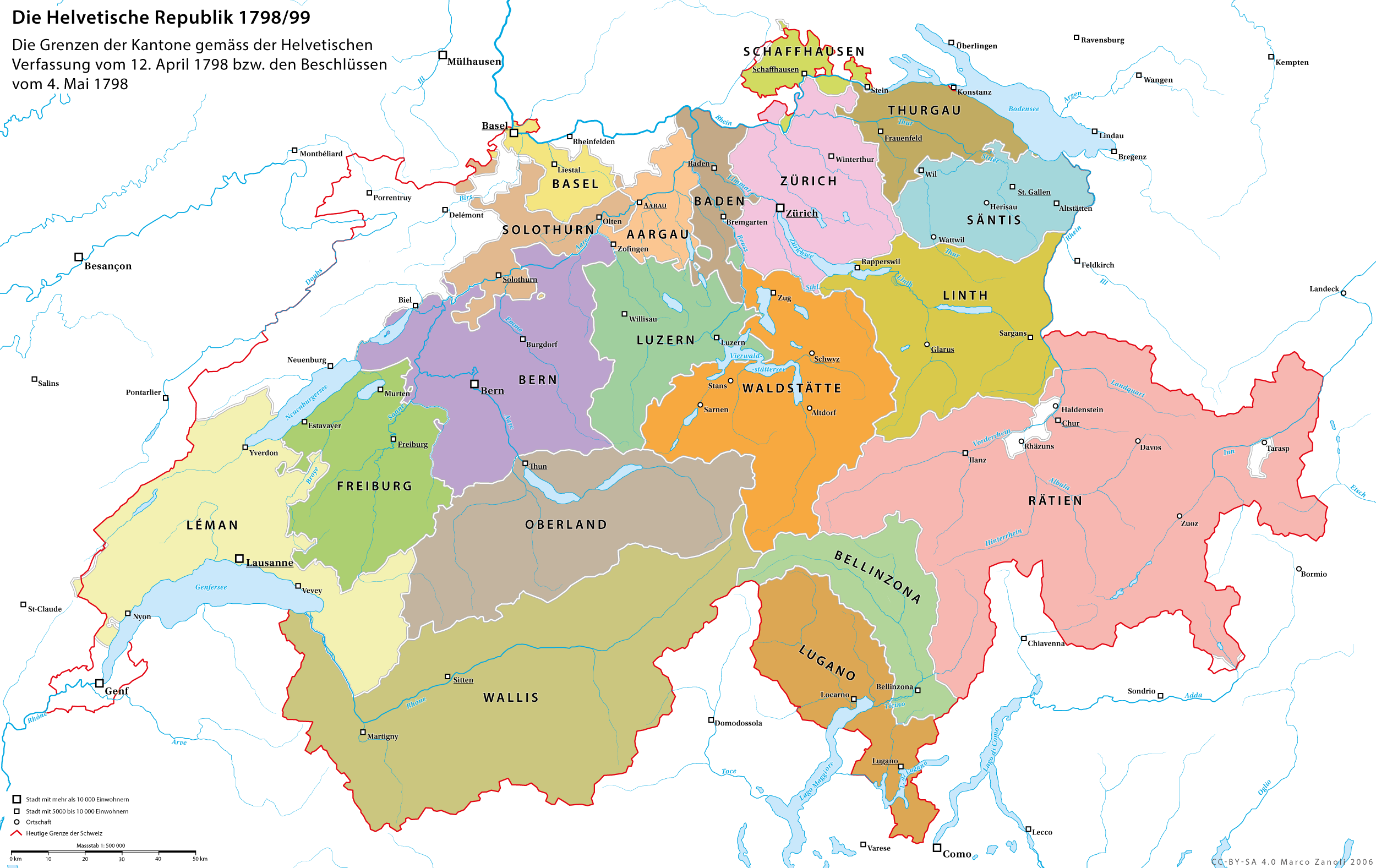 The County of Baden was dissolved after the 1798 French invasion. On 19 March 1798, the governments of Zurich and Bern agreed to the creation of the short lived Canton of Baden in the Helvetic Republic. With the
The County of Baden was dissolved after the 1798 French invasion. On 19 March 1798, the governments of Zurich and Bern agreed to the creation of the short lived Canton of Baden in the Helvetic Republic. With the
German
German(s) may refer to:
* Germany (of or related to)
** Germania (historical use)
* Germans, citizens of Germany, people of German ancestry, or native speakers of the German language
** For citizens of Germany, see also German nationality law
**Ge ...
: ''Grafschaft Baden'') was a condominium of the Old Swiss Confederacy and is now part of the Swiss Canton of Aargau. The county was established in 1415 after the Swiss conquest of the Aargau and was ruled as a shared condominium until 1798 when it became part of the short lived Canton of Baden.
History
 The land that became the County of Baden was originally ruled by the
The land that became the County of Baden was originally ruled by the Counts of Lenzburg
The Counts of Lenzburg (also Counts of Baden by the early 12th century) were a comital family in the Duchy of Swabia in the 11th and 12th centuries, controlling substantial portions of the '' pagi'' of Aargau and Zürichgau.
After the extinction ...
. Once that family's main line died out, it came under the Kyburgs and then in 1264 the Habsburgs. The exact territories in the county changed often, but originally included the western part of the Zürich
, neighboring_municipalities = Adliswil, Dübendorf, Fällanden, Kilchberg, Maur, Oberengstringen, Opfikon, Regensdorf, Rümlang, Schlieren, Stallikon, Uitikon, Urdorf, Wallisellen, Zollikon
, twintowns = Kunming, San Francisco
Zürich ...
gau and parts of the territory between the Rhine
), Surselva, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source1_coordinates=
, source1_elevation =
, source2 = Rein Posteriur/Hinterrhein
, source2_location = Paradies Glacier, Graubünden, Switzerland
, source2_coordinates=
, so ...
, Aare
The Aare () or Aar () is a tributary of the High Rhine and the longest river that both rises and ends entirely within Switzerland.
Its total length from its source to its junction with the Rhine comprises about , during which distance it descen ...
and Reuss rivers. In the 14th Century the territory of Baden became a triangle between the Limmat and Reuss rivers, though it was later divided further. As part of the Habsburg bailiwick of Aargau, it was managed by a bailiff, who had his seat in the town of Baden
Baden (; ) is a historical territory in South Germany, in earlier times on both sides of the Upper Rhine but since the Napoleonic Wars only East of the Rhine.
History
The margraves of Baden originated from the House of Zähringen. Baden i ...
.
On 16 November 1414, Emperor Sigismund
Sigismund of Luxembourg (15 February 1368 – 9 December 1437) was a monarch as King of Hungary and Croatia ('' jure uxoris'') from 1387, King of Germany from 1410, King of Bohemia from 1419, and Holy Roman Emperor from 1433 until his death in ...
called the Council of Constance to settle the Western Schism
The Western Schism, also known as the Papal Schism, the Vatican Standoff, the Great Occidental Schism, or the Schism of 1378 (), was a split within the Catholic Church lasting from 1378 to 1417 in which bishops residing in Rome and Avignon b ...
between the three pope
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
s ( Benedict XIII, Gregory XII
Pope Gregory XII ( la, Gregorius XII; it, Gregorio XII; – 18 October 1417), born Angelo Corraro, Corario," or Correr, was head of the Catholic Church from 30 November 1406 to 4 July 1415. Reigning during the Western Schism, he was oppose ...
, and John XXIII
Pope John XXIII ( la, Ioannes XXIII; it, Giovanni XXIII; born Angelo Giuseppe Roncalli, ; 25 November 18813 June 1963) was head of the Catholic Church and sovereign of the Vatican City State from 28 October 1958 until his death in June 19 ...
), all of whom claimed legitimacy. Frederick IV of Habsburg sided with John XXIII. When John XXIII was declared an antipope, he fled the city with Frederick's help. The emperor then declared the Habsburg lands forfeited and ordered the neighboring countries to conquer those lands for the emperor. The city-state of Bern had already pledged their support of the emperor against the Habsburgs in 1414, and so they were ready to invade. The rest of the Confederation quickly followed.
The territory was quickly conquered in 1415 by the Confederation. Under Habsburg rule Aargau was divided into multiple sections (german: Ämter), which were maintained under the Confederation. Bern, Lucerne and Zurich were each given a portion of the conquered region to administer. The Freie Ämter
The Freiamt or ''Freie Ämter'' ( en, Free Office or ''Free Administrative Unit'', though it is not usually translated into English) is a region in Switzerland and is located in the southeast of Canton of Aargau. It comprises the area between th ...
and the ''Amt'' of Baden were collectively administered as subject territories by the rest of the Confederation. Under the Confederation, the ''Amt'' of Baden became the County of Baden. The county included the former Ämter of Baden and Siggenthal, the Bishop of Constance
The Prince-Bishopric of Constance, (german: Hochstift Konstanz, Fürstbistum Konstanz, Bistum Konstanz) was a small ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire from the mid-12th century until its secularisation in 1802–1803. In his dua ...
's vogt
During the Middle Ages, an (sometimes given as modern English: advocate; German: ; French: ) was an office-holder who was legally delegated to perform some of the secular responsibilities of a major feudal lord, or for an institution such as ...
ei of Klingnau
Klingnau is a municipality in the district of Zurzach in the canton of Aargau in Switzerland.
History
Klingnau is first mentioned in 1239 as ''Chlingenowe''. Ulrich of Klingen acquired land from the monastery of St. Blaise in 1239 to found ...
, Zurzach
Zurzach is a municipality in the district of Zurzach in the canton of Aargau in Switzerland. On 1 January 2022 the former municipalities of Bad Zurzach, Baldingen, Böbikon, Kaiserstuhl, Rekingen, Rietheim, Rümikon and Wislikofen
Wislik ...
and Kaiserstuhl as well as the parish
A parish is a territorial entity in many Christian denominations, constituting a division within a diocese. A parish is under the pastoral care and clerical jurisdiction of a priest, often termed a parish priest, who might be assisted by one o ...
of Leuggern
Leuggern is a municipality in the district of Zurzach in the canton of Aargau in Switzerland.
History
The remains of a Roman era Rhine fortifications watchtower have been discovered in Felsenau. The modern municipality of Leuggern is first menti ...
on the left side of the Aare.
Initially ownership of the county was shared between the seven cantons which had participated in the invasion. Starting in 1443 this was expanded into all Eight Cantons or ''Acht Orte''. It was divided into eight inner (Rohrdorf, Birmenstorf, Gebenstorf, Dietikon, Wettingen, Siggenthal, Ehrendingen, Leuggern) and three outer districts (Klingnau, Zurzach, Kaiserstuhl), which included the parishes of Kadelburg, Lienheim and Hohentengen on the right bank of the Rhine.
 The Confederates retained much of the Habsburg legal structure, which caused a number of problems. The local nobility had the right to hold the low court in only about one fifth of the territory. There were over 30 different nobles who had the right to hold courts scattered around the surrounding lands. All these overlapping jurisdictions caused numerous conflicts, but gradually the Confederation was able to acquire these rights in the County. The cities of Baden, Bremgarten and
The Confederates retained much of the Habsburg legal structure, which caused a number of problems. The local nobility had the right to hold the low court in only about one fifth of the territory. There were over 30 different nobles who had the right to hold courts scattered around the surrounding lands. All these overlapping jurisdictions caused numerous conflicts, but gradually the Confederation was able to acquire these rights in the County. The cities of Baden, Bremgarten and Mellingen
Mellingen is a historic town and a municipality in the district of Baden in the canton of Aargau in Switzerland. The town is located on the Reuss.
History
Mellingen is first mentioned in 1045 as ''Mellingen'' though this comes from a 16th-cen ...
became the administrative centers and held the high courts. Together with the courts, the three administrative centers had considerable local autonomy, but were ruled by a governor who was appointed by the ''Acht Orte'' every two years. After the Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
victory at the Second Battle of Villmergen, the administration of the County changed slightly. Instead of the ''Acht Orte'' appointing a bailiff together, Zurich and Bern each appointed the governor for 7 out of 16 years while Glarus
, neighboring_municipalities= Glarus Nord, Glarus Süd, Muotathal (SZ), Innerthal (SZ)
, twintowns= Wiesbaden-Biebrich (Germany)
}
Glarus (; gsw, Glaris; french: Glaris; it, Glarona; rm, Glaruna) is the capital of the canton of Glarus ...
appointed him for the remaining 2 years.
The governor lived in the ''Landvogteischloss'' (Governor's Castle) in Baden, which was expanded in 1486–90. The governor had his own lower court and he was the appellate court
A court of appeals, also called a court of appeal, appellate court, appeal court, court of second instance or second instance court, is any court of law that is empowered to hear an appeal of a trial court or other lower tribunal. In much of ...
for the local lords' courts. He appointed some of the local administrators and the high court judges at Baden. The governor cast the deciding vote in the event of the tie in the high court. Due to the limited jurisdiction and the short, two year appointment, the governor's power was limited. The local courts and village mayors had quite a bit of autonomy.
 The governor's income came from a death tax (converted in 1666 into an annual tax), a tax on people leaving the county, a
The governor's income came from a death tax (converted in 1666 into an annual tax), a tax on people leaving the county, a tolerance tax
Tolerance tax or toleration tax (; german: Toleranzgebührer; ) was a tax that was levied against Jews of the Kingdom of Hungary, then part of the Austrian Empire, between 1747 and 1797.JewishGen. Hungary: Assorted Census Records, 1781-1850 atab ...
on the Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
and customs fees. However, customs fees brought in so little that in the 17th century, the right to collect duties
A duty (from "due" meaning "that which is owing"; fro, deu, did, past participle of ''devoir''; la, debere, debitum, whence "debt") is a commitment or expectation to perform some action in general or if certain circumstances arise. A duty may ...
was auctioned off to the highest bidder. The county was the only federal condominium in the 17th century where Jews were tolerated. In 1774, they were restricted to just two towns: Endingen and Lengnau. While the rural upper class tried several times to finally expel the Jews, the financial interests of the authorities prevented this. The Jews were directly subordinate to the governor starting in 1696 when they were forced to buy a protecting and shielding letter every 16 years from the governor. The region was rarely profitable and being appointed a governor usually only resulted in modest wealth.
Until the 18th Century, the vast majority of residents in the County lived from agriculture. They mostly grew grain, but in the Limmat, Aare and Surb Surbtal is a river valley region in the Canton of Aargau, Switzerland.
Geography
The ''Surbtal'' (literally ''Surb valley'') is situated parallel to the Limmat Valley (''Limmattal'') in the Baden and Zurzach districts of the Canton of Aargau ...
valleys there was some viticulture
Viticulture (from the Latin word for '' vine'') or winegrowing (wine growing) is the cultivation and harvesting of grapes. It is a branch of the science of horticulture. While the native territory of '' Vitis vinifera'', the common grape vine, ...
. Most of the County's market towns
A market town is a settlement most common in Europe that obtained by custom or royal charter, in the Middle Ages, a market right, which allowed it to host a regular market; this distinguished it from a village or city. In Britain, small rural ...
held only local markets, which, however, provided a solid income source for the increasing degree indebted County. The chaotic legal structure and fragmented land ownership combined with a tradition of dividing the land among all the heirs in an inheritance prevented any large scale reforms. The governor tried in the 18th century to reform and standardize laws and ownership across the County, but with limited success. With an ever-changing administration, the County lacked a coherent long-term economic policy or support for reforms. By the end of the 18th century there were no factories or mills and only a few small cottage industries
The putting-out system is a means of subcontracting work. Historically, it was also known as the workshop system and the domestic system. In putting-out, work is contracted by a central agent to subcontractors who complete the project via remote ...
along the border with Zurich. Road construction first became a priority after 1750, when Zurich and Bern began appointing a governor for seven years.
During the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and ...
, some of the municipalities converted to the new faith. However, starting in 1531, some of the old parishes were converted back to the old faith. The governors were appointed from both Catholic and Protestant cantons and since they changed every two years, neither faith gained a majority in the County. The towns of Tegerfelden and Zurzach had a large Reformed majority, while many other towns had a strong minority. The Reformed parishes were under the authority of the ecclesiastical court in Zurich, except for Birmenstorf and Gebenstorf which were under the Bernese court. The Jews of the Surbtal formed a Beth din
A beit din ( he, בית דין, Bet Din, house of judgment, , Ashkenazic: ''beis din'', plural: batei din) is a Rabbinic Judaism, rabbinical court of Judaism. In ancient times, it was the building block of the legal system in the Biblical Land of ...
or rabbinical court with Tiengen. In the 18th century, they built two large synagogues.
History since 1798
Canton
 The County of Baden was dissolved after the 1798 French invasion. On 19 March 1798, the governments of Zurich and Bern agreed to the creation of the short lived Canton of Baden in the Helvetic Republic. With the
The County of Baden was dissolved after the 1798 French invasion. On 19 March 1798, the governments of Zurich and Bern agreed to the creation of the short lived Canton of Baden in the Helvetic Republic. With the Act of Mediation
The Act of Mediation () was issued by Napoleon Bonaparte, First Consul of the French Republic on 19 February 1803 establishing the Swiss Confederation. The act also abolished the previous Helvetic Republic, which had existed since the invasi ...
in 1803, the Canton of Baden was dissolved, becoming part of Aargau.
District
Portions of the lands of the former County of Baden became the District of Baden, firstly in the Canton of Baden and then in the Canton of Aargau (from 1803). Upon the merging of the canton of Baden into Aargau in 1803, the district gained the municipalities ofWürenlingen
Würenlingen is a municipality in the district of Baden in the canton of Aargau in Switzerland.
Geography
Würenlingen has an area, , of . Of this area, 29.2% is used for agricultural purposes, while 49.4% is forested. Of the rest of the land ...
, Bellikon, Künten, Remetschwil, Stetten, Mellingen
Mellingen is a historic town and a municipality in the district of Baden in the canton of Aargau in Switzerland. The town is located on the Reuss.
History
Mellingen is first mentioned in 1045 as ''Mellingen'' though this comes from a 16th-cen ...
, Wohlenschwil
Wohlenschwil is a municipality in the district of Baden in the canton of Aargau in Switzerland.
History
On June 3, 1653 Wohlenschwil was the site of the Battle of Wohlenschwil, which ended the Swiss peasant war of 1653. Despite a peace treat ...
and Mägenwil
Mägenwil is a municipality in the district of Baden in the canton of Aargau in Switzerland.
History
Mägenwil is first mentioned in 924 as ''Maganwilare''. In 1273 it was mentioned as ''Echwile''.
Geography
Mägenwil has an area, , of . Of ...
(from neighbouring districts of the canton of Baden) but had to give up Hüttikon
Hüttikon is a municipality in the district of Dielsdorf in the canton of Zürich in Switzerland.
History
Hüttikon is first mentioned in 883 as ''Huttinchova''.
Geography
Hüttikon has an area of . Of this area, 52.2% is used for agricultur ...
, Oetwil an der Limmat
Oetwil an der Limmat is a municipality in the district of Dietikon in the canton of Zürich in Switzerland, located in the Limmat Valley (German: ''Limmattal'').
History
Oetwil an der Limmat is first mentioned around 850 as ''Otenwilare''.
Geog ...
, Dietikon
Dietikon is the fifth biggest city of the canton of Zürich in Switzerland, after Zürich, Winterthur, Uster and Dübendorf. It is the capital of the same-named district of Dietikon and part of the Zürich metropolitan area.
Geography
The i ...
and Schlieren
Schlieren ( ; , ) are optical inhomogeneities in transparent media that are not necessarily visible to the human eye. Schlieren physics developed out of the need to produce high-quality lenses devoid of such inhomogeneities. These inhomogeneiti ...
to the Canton of Zurich.
After World War II, this formerly agrarian region saw striking growth and became the district with the largest and densest population in the Canton (110,000 in 1990, 715 persons per km2).
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Baden, CountyBaden
Baden (; ) is a historical territory in South Germany, in earlier times on both sides of the Upper Rhine but since the Napoleonic Wars only East of the Rhine.
History
The margraves of Baden originated from the House of Zähringen. Baden i ...
Former condominiums of Switzerland
States and territories established in 1415
Aargau
Former vassal states
15th-century establishments in the Old Swiss Confederacy
1410s establishments in the Holy Roman Empire
1415 establishments in Europe
18th-century disestablishments in the Old Swiss Confederacy
1798 disestablishments in the Holy Roman Empire