Cosimo de Medici on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Cosimo di Giovanni de' Medici (27 September 1389 ŌĆō 1 August 1464) was an Italian banker and politician who established the
 Cosimo inherited both his wealth and his expertise in banking from his father Giovanni, who had gone from being a moneylender to join the bank of his relative Vieri di Cambio de' Medici. Giovanni had been running Vieri's branch in Rome independently since the dissolution of the latter's bank into three separate and independent entities until 1397, when he left
Cosimo inherited both his wealth and his expertise in banking from his father Giovanni, who had gone from being a moneylender to join the bank of his relative Vieri di Cambio de' Medici. Giovanni had been running Vieri's branch in Rome independently since the dissolution of the latter's bank into three separate and independent entities until 1397, when he left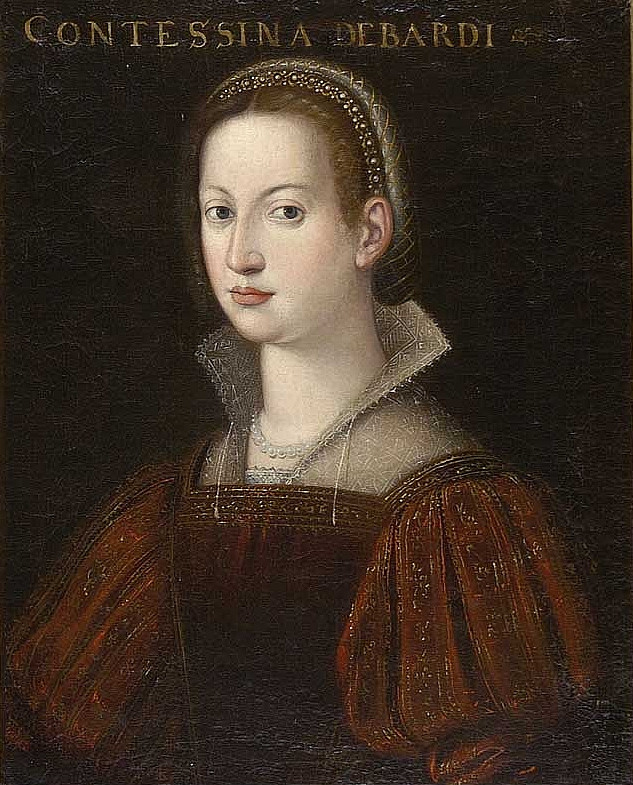  About 1415, Cosimo married Contessina de' Bardi (the daughter of Alessandro di Sozzo Bardi, count of Vernio, and Camilla Pannocchieschi). The wedding was arranged by his father as an effort to reaffirm relations with the long-standing noble Bardi family, who had operated one of the richest banks in Europe until its spectacular collapse in 1345; they nevertheless remained highly influential in the financial sphere. Only part of the Bardi family were involved in this marriage alliance, for some of the branches considered themselves the opponents of the Medici clan. The couple had two sons: Piero the Gouty (b. 1416) and Giovanni de' Medici (b. 1421). Cosimo also had an illegitimate son, Carlo, by a Circassian slave, who would go on to become a
About 1415, Cosimo married Contessina de' Bardi (the daughter of Alessandro di Sozzo Bardi, count of Vernio, and Camilla Pannocchieschi). The wedding was arranged by his father as an effort to reaffirm relations with the long-standing noble Bardi family, who had operated one of the richest banks in Europe until its spectacular collapse in 1345; they nevertheless remained highly influential in the financial sphere. Only part of the Bardi family were involved in this marriage alliance, for some of the branches considered themselves the opponents of the Medici clan. The couple had two sons: Piero the Gouty (b. 1416) and Giovanni de' Medici (b. 1421). Cosimo also had an illegitimate son, Carlo, by a Circassian slave, who would go on to become a
 Cosimo's power over Florence stemmed from his wealth, which he used to control the votes of office holders in the municipal councils, most importantly the Signoria of Florence. As Florence was proud of its "
Cosimo's power over Florence stemmed from his wealth, which he used to control the votes of office holders in the municipal councils, most importantly the Signoria of Florence. As Florence was proud of its " In 1433, Cosimo's power over Florence began to look like a menace to the anti-Medici party led by figures such as Palla Strozzi and the
In 1433, Cosimo's power over Florence began to look like a menace to the anti-Medici party led by figures such as Palla Strozzi and the
 On his death in 1464 at
On his death in 1464 at
 Cosimo was also noted for his patronage of culture and the arts during the Renaissance and spent the family fortune liberally to enrich the civic life of Florence. According to Salviati's ''Zibaldone'', Cosimo stated: "All those things have given me the greatest satisfaction and contentment because they are not only for the honor of God but are likewise for my own remembrance. For fifty years, I have done nothing else but earn money and spend money; and it became clear that spending money gives me greater pleasure than earning it."
Additionally, his patronage of the arts both recognized and proclaimed the humanistic responsibility of the civic duty that came with wealth.
Cosimo hired the young Michelozzo Michelozzi to create what is today perhaps the prototypical Florentine
Cosimo was also noted for his patronage of culture and the arts during the Renaissance and spent the family fortune liberally to enrich the civic life of Florence. According to Salviati's ''Zibaldone'', Cosimo stated: "All those things have given me the greatest satisfaction and contentment because they are not only for the honor of God but are likewise for my own remembrance. For fifty years, I have done nothing else but earn money and spend money; and it became clear that spending money gives me greater pleasure than earning it."
Additionally, his patronage of the arts both recognized and proclaimed the humanistic responsibility of the civic duty that came with wealth.
Cosimo hired the young Michelozzo Michelozzi to create what is today perhaps the prototypical Florentine 
The Medici Family.com: Cosimo I
Internet Archive.org: Cosimo de' Medici (1899)
ŌĆō ''biography by K. Dorothea Ewart Vernon''. * ŌĆ
BIVIO: Biblioteca Virtuale On-Line: Biography in "Le vite" from Vespasiano da Bisticci
{{DEFAULTSORT:Medici, Cosimo 01 Rulers of Florence Italian bankers Medieval bankers 1389 births 1464 deaths 15th-century people of the Republic of Florence Cosimo 01 Italian nobility Ambassadors of the Republic of Florence Burials at San Lorenzo, Florence 15th-century rulers in Europe Book and manuscript collectors Italian art patrons 15th-century Italian businesspeople
Medici family
The House of Medici ( , ) was an Italian banking family and political dynasty that first began to gather prominence under Cosimo de' Medici, in the Republic of Florence during the first half of the 15th century. The family originated in the Mug ...
as effective rulers of Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico ...
during much of the Italian Renaissance
The Italian Renaissance ( it, Rinascimento ) was a period in Italian history covering the 15th and 16th centuries. The period is known for the initial development of the broader Renaissance culture that spread across Europe and marked the trans ...
. His power derived from his wealth as a banker, and inter-marriage with other powerful and rich families. He was a patron of arts, learning and architecture. He spent over 600,000 gold florins
The Florentine florin was a gold coin struck from 1252 to 1533 with no significant change in its design or metal content standard during that time. It had 54 grains (3.499 grams, 0.113 troy ounce) of nominally pure or 'fine' gold with a purcha ...
(approx. $500 million inflation adjusted) on art and culture, including Donatello's David
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''D─üw┼½d''; grc-koi, ╬ö╬▒Žģ╬É╬┤, Dau├Łd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ßŗ│ßŗŖßēĄ, ''Dawit''; xcl, į┤šĪųéš½š®, ''Dawit╩┐''; cu, ąöą░ą▓├Łą┤čŖ, ''David┼Ł''; possibly meaning "beloved one". w ...
, the first freestanding nude
Nudity is the state of being in which a human is without clothing.
The loss of body hair was one of the physical characteristics that marked the biological evolution of modern humans from their hominin ancestors. Adaptations related to h ...
male sculpture since antiquity. Despite his influence, his power was not absolute; Florence's legislative councils at times resisted his proposals throughout his life, and he was viewed as first among equals, rather than an autocrat.Martines, Lauro (2011). ''The Social World of the Florentine Humanists, 1390ŌĆō1460''. University of Toronto Press. p. 8.
Biography
Early life and family business
Cosimo de' Medici was born inFlorence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico ...
to Giovanni di Bicci de' Medici
Giovanni di Bicci de' Medici (c. 1360 – February 1429) was an Italian banker and founder of the Medici Bank. While other members of the Medici family, such as Chiarissimo di Giambuono de' Medici, who served in the Signoria of Florence i ...
and his wife Piccarda Bueri
Piccarda Bueri (1368ŌĆō1433) was an Italian noblewoman of the Renaissance.
Life
She was the daughter of Edoardo Bueri, a member of a family of ancient lineage from Florence with economic interests in other cities; the family was in fact in Veron ...
on 27 September 1389. At the time, it was customary to indicate the name of one's father in one's name for the purpose of distinguishing the identities of two like-named individuals; thus, Giovanni was the son of Bicci, and Cosimo's name was properly rendered Cosimo di Giovanni de' Medici. He was born along with a twin brother Damiano, who survived only a short time. The twins were named after Saints Cosmas and Damian
Cosmas and Damian ( ar, ┘é┘Åž▓┘ģž¦ ┘łž»┘ģ┘Ŗž¦┘å, translit=Qozma wa Demyaan; grc-gre, ╬Ü╬┐Žā╬╝ߊȎé ╬║╬▒ßĮČ ╬ö╬▒╬╝╬╣╬▒╬ĮŽīŽé, translit=Kosm├Īs kai Damian├│s; la, Cosmas et Damianus; AD) were two Arabs, Arab physicians in the town Cyrrhus, and ...
, whose feast day was then celebrated on 27 September; Cosimo would later celebrate his own birthday on that day, his "name day
In Christianity, a name day is a tradition in many countries of Europe and the Americas, among other parts of Christendom. It consists of celebrating a day of the year that is associated with one's baptismal name, which is normatively that of a ...
", rather than on the actual date of his birth. Cosimo also had a brother Lorenzo, known as " Lorenzo the Elder", who was some six years his junior and participated in the family's banking enterprise.
 Cosimo inherited both his wealth and his expertise in banking from his father Giovanni, who had gone from being a moneylender to join the bank of his relative Vieri di Cambio de' Medici. Giovanni had been running Vieri's branch in Rome independently since the dissolution of the latter's bank into three separate and independent entities until 1397, when he left
Cosimo inherited both his wealth and his expertise in banking from his father Giovanni, who had gone from being a moneylender to join the bank of his relative Vieri di Cambio de' Medici. Giovanni had been running Vieri's branch in Rome independently since the dissolution of the latter's bank into three separate and independent entities until 1397, when he left Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
to return to Florence to found his own bank, the Medici Bank
The Medici Bank (Italian: ''Banco dei Medici'' ) was a financial institution created by the Medici family in Italy during the 15th century (1397ŌĆō1494). It was the largest and most respected bank in Europe during its prime. There are some estima ...
. Over the next two decades, the Medici Bank opened branches in Rome, Geneva
Geneva ( ; french: Gen├©ve ) frp, Gen├©va ; german: link=no, Genf ; it, Ginevra ; rm, Genevra is the second-most populous city in Switzerland (after Z├╝rich) and the most populous city of Romandy, the French-speaking part of Switzerland. Situa ...
, Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
, and temporarily in Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, ╬Ø╬Ą╬¼ŽĆ╬┐╬╗╬╣Žé, Ne├Īpolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adm ...
; the majority of profits was derived from Rome. The branch manager in Rome was a papal ''depositario generale'' who managed Church finances in return for a commission.George Holmes: ''How the Medici became the PopeŌĆÖs Bankers.'' In: Nicolai Rubinstein (Ed.): ''Florentine Studies. Politics and Society in Renaissance Florence'', London 1968, pp. 357ŌĆō380; Raymond de Roover: ''The Rise and Decline of the Medici Bank 1397ŌĆō1494'', Cambridge (Massachusetts)/London 1963, p. 46 f., 198, 203; Volker Reinhardt: ''Die Medici'', 4., revised edition, Munich 2007, S. 21; John R. Hale: ''Die Medici und Florenz'', Stuttgart 1979, p. 13; Alison Williams Lewin: ''Negotiating Survival'', Madison 2003, p. 210 f. Cosimo would later expand the bank throughout western Europe and opened offices in London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
, Pisa
Pisa ( , or ) is a city and ''comune'' in Tuscany, central Italy, straddling the Arno just before it empties into the Ligurian Sea. It is the capital city of the Province of Pisa. Although Pisa is known worldwide for its leaning tower, the ci ...
, Avignon
Avignon (, ; ; oc, Avinhon, label= Proven├¦al or , ; la, Avenio) is the prefecture of the Vaucluse department in the Provence-Alpes-C├┤te d'Azur region of Southeastern France. Located on the left bank of the river Rh├┤ne, the commune had ...
, Bruges
Bruges ( , nl, Brugge ) is the capital and largest City status in Belgium, city of the Provinces of Belgium, province of West Flanders in the Flemish Region of Belgium, in the northwest of the country, and the sixth-largest city of the countr ...
, Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city ...
, and L├╝beck
L├╝beck (; Low German also ), officially the Hanseatic City of L├╝beck (german: Hansestadt L├╝beck), is a city in Northern Germany. With around 217,000 inhabitants, L├╝beck is the second-largest city on the German Baltic coast and in the state ...
. The far-flung branches of the Medici rendered it the best bank for the business of the papacy, since it enabled bishoprics in many parts of Europe to pay their fees into the nearest branch, whose manager would then issue a papal license, and the popes could more easily order a variety of wares ŌĆō such as spices, textiles, and relics ŌĆō through the bankers' wholesale trade. In fifteen years, Giovanni would make a profit of 290,791 florins.
In 1415, Cosimo allegedly accompanied the Antipope John XXIII
Baldassarre Cossa (c. 1370 ŌĆō 22 December 1419) was Pisan antipope John XXIII (1410ŌĆō1415) during the Western Schism. The Catholic Church regards him as an antipope, as he opposed Pope Gregory XII whom the Catholic Church now recognizes as t ...
at the Council of Constance
The Council of Constance was a 15th-century ecumenical council recognized by the Catholic Church, held from 1414 to 1418 in the Bishopric of Constance in present-day Germany. The council ended the Western Schism by deposing or accepting the r ...
. In 1410, Giovanni lent John XXIII, then simply known as Baldassare Cossa, the money to buy himself the office of cardinal
Cardinal or The Cardinal may refer to:
Animals
* Cardinal (bird) or Cardinalidae, a family of North and South American birds
**'' Cardinalis'', genus of cardinal in the family Cardinalidae
**'' Cardinalis cardinalis'', or northern cardinal, t ...
, which he repaid by making the Medici Bank head of all papal finances once he claimed the papacy. This gave the Medici family tremendous power, allowing them, for instance, to threaten defaulting debtors with excommunication. But misfortune hit the Medici Bank in 1415, when the Council of Constance unseated John XXIII, thus taking away the near monopoly they had held on the finances of the Roman Curia; thereafter, the Medici Bank had to compete with other banks. However, after the Spini Bank of Florence went insolvent in 1420, they again secured priority. John XXIII, facing the enmity of a church council at which he was accused of a large variety of offenses against the Church, was confined by Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor
Sigismund of Luxembourg (15 February 1368 ŌĆō 9 December 1437) was a monarch as King of Hungary and Croatia ('' jure uxoris'') from 1387, King of Germany from 1410, King of Bohemia from 1419, and Holy Roman Emperor from 1433 until his death i ...
to Heidelberg Castle
Heidelberg Castle (german: Heidelberger Schloss) is a ruin in Germany and landmark of Heidelberg. The castle ruins are among the most important Renaissance structures north of the Alps.
The castle has only been partially rebuilt since its demoli ...
until the Medici paid his ransom and granted him asylum.
In the same year as John's dethronement (1415), Cosimo was named " Priore of the Republic f Florence. Later he acted frequently as an ambassador
An ambassador is an official envoy, especially a high-ranking diplomat who represents a state and is usually accredited to another sovereign state or to an international organization as the resident representative of their own government or s ...
for Florence and demonstrated a prudence for which he became renowned.
 About 1415, Cosimo married Contessina de' Bardi (the daughter of Alessandro di Sozzo Bardi, count of Vernio, and Camilla Pannocchieschi). The wedding was arranged by his father as an effort to reaffirm relations with the long-standing noble Bardi family, who had operated one of the richest banks in Europe until its spectacular collapse in 1345; they nevertheless remained highly influential in the financial sphere. Only part of the Bardi family were involved in this marriage alliance, for some of the branches considered themselves the opponents of the Medici clan. The couple had two sons: Piero the Gouty (b. 1416) and Giovanni de' Medici (b. 1421). Cosimo also had an illegitimate son, Carlo, by a Circassian slave, who would go on to become a
About 1415, Cosimo married Contessina de' Bardi (the daughter of Alessandro di Sozzo Bardi, count of Vernio, and Camilla Pannocchieschi). The wedding was arranged by his father as an effort to reaffirm relations with the long-standing noble Bardi family, who had operated one of the richest banks in Europe until its spectacular collapse in 1345; they nevertheless remained highly influential in the financial sphere. Only part of the Bardi family were involved in this marriage alliance, for some of the branches considered themselves the opponents of the Medici clan. The couple had two sons: Piero the Gouty (b. 1416) and Giovanni de' Medici (b. 1421). Cosimo also had an illegitimate son, Carlo, by a Circassian slave, who would go on to become a prelate
A prelate () is a high-ranking member of the Christian clergy who is an ordinary or who ranks in precedence with ordinaries. The word derives from the Latin , the past participle of , which means 'carry before', 'be set above or over' or 'pre ...
.
Giovanni withdrew from the Medici Bank in 1420, leaving its leadership to both of his surviving sons. He left them 179,221 florins upon his death in 1429. Two-thirds of this came from the business in Rome, while only a tenth came from Florence; even Venice offered better returns than Florence. The brothers would earn two-thirds of the profits from the bank, with the other third going to a partner. Besides the bank, the family owned much land in the area surrounding Florence, including Mugello
The Mugello is a historic region and valley in northern Tuscany, in Italy, corresponding to the course of the River Sieve. It is located to the north of the city of Florence and includes the northernmost portion of the Metropolitan City of ...
, the place from which the family originally came.
Florentine politics
 Cosimo's power over Florence stemmed from his wealth, which he used to control the votes of office holders in the municipal councils, most importantly the Signoria of Florence. As Florence was proud of its "
Cosimo's power over Florence stemmed from his wealth, which he used to control the votes of office holders in the municipal councils, most importantly the Signoria of Florence. As Florence was proud of its "democracy
Democracy (From grc, ╬┤╬Ę╬╝╬┐╬║Žü╬▒Žä╬»╬▒, d─ōmokrat├Ła, ''d─ōmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which the people have the authority to deliberate and decide legislation (" direct democracy"), or to choose g ...
", he pretended to have little political ambition and did not often hold public office. Enea Silvio Piccolomini, Bishop of Siena
Siena ( , ; lat, Sena Iulia) is a city in Tuscany, Italy. It is the capital of the province of Siena.
The city is historically linked to commercial and banking activities, having been a major banking center until the 13th and 14th centur ...
and later Pope Pius II
Pope Pius II ( la, Pius PP. II, it, Pio II), born Enea Silvio Bartolomeo Piccolomini ( la, Aeneas Silvius Bartholomeus, links=no; 18 October 1405 ŌĆō 14 August 1464), was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 19 Augu ...
, said of him:
 In 1433, Cosimo's power over Florence began to look like a menace to the anti-Medici party led by figures such as Palla Strozzi and the
In 1433, Cosimo's power over Florence began to look like a menace to the anti-Medici party led by figures such as Palla Strozzi and the Albizzi
The Albizzi family () was a Florentine family originally based in Arezzo, who were rivals of the Medici and Alberti families. They were at the centre of Florentine oligarchy from 1382, in the reaction that followed the Ciompi revolt, to the ris ...
family, headed by Rinaldo degli Albizzi. In September of that year, Cosimo was imprisoned in the Palazzo Vecchio
The Palazzo Vecchio ( "Old Palace") is the town hall of Florence, Italy. It overlooks the Piazza della Signoria, which holds a copy of Michelangelo's ''David'' statue, and the gallery of statues in the adjacent Loggia dei Lanzi.
Originally ...
for his part in a failure to conquer the Republic of Lucca, but he managed to turn the jail term into one of exile. Some prominent Florentines, such as Francesco Filelfo
Francesco Filelfo ( la, Franciscus Philelphus; 25 July 1398 ŌĆō 31 July 1481) was an Italian Renaissance humanist.
Biography
Filelfo was born at Tolentino, in the March of Ancona. He is believed to be a third cousin of Leonardo da Vinci. At t ...
, demanded his execution, a fate that may have been almost certain without the intervention of the monk Ambrogio Traversari
Ambrogio Traversari, also referred to as Ambrose of Camaldoli (138620 October 1439), was an Italian monk and theologian who was a prime supporter of the papal cause in the 15th century. He is honored as a saint by the Camaldolese Order.
Biography ...
on his behalf. Cosimo traveled to Padua
Padua ( ; it, Padova ; vec, P├Ādova) is a city and ''comune'' in Veneto, northern Italy. Padua is on the river Bacchiglione, west of Venice. It is the capital of the province of Padua. It is also the economic and communications hub of the ...
and then to Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
, taking his bank along with him and finding friends and sympathizers wherever he went for his willingness to accept exile rather than resume the bloody conflicts that had chronically afflicted the streets of Florence. Venice sent an envoy to Florence on his behalf and requested that they rescind the order of banishment. When they refused, Cosimo settled down in Venice, his brother Lorenzo accompanying him. However, prompted by his influence and his money, others followed him, such as the architect Michelozzo
Michelozzo di Bartolomeo Michelozzi (1396 ŌĆō 7 October 1472) was an Italian architect and sculptor. Considered one of the great pioneers of architecture during the Renaissance, Michelozzo was a favored Medici architect who was extensively em ...
, whom Cosimo commissioned to design a library as a gift to the Venetian people. Within a year, the flight of capital from Florence was so great that the decree of exile had to be lifted. Cosimo returned a year later, in 1434, to influence the government of Florence (especially through the Pitti
Pitti, also known as Pakshipitti (''pakshi'' meaning "bird" in Malayalam, Telugu and Tamil), is an uninhabited coral islet in the Union Territory of Lakshadweep, India.
Geography
It is located at about 24 km to the north of Kavaratti ...
and Soderini families) for the last 30 years of his life of 75 years.
Cosimo's time in exile instilled in him the need to quash the factionalism that resulted in his exile in the first place. In order to do this, he instigated a series of constitutional changes with the help of favorable priors in the Signoria to secure his power through influence.
Following the death of Filippo Maria Visconti
Filippo Maria Visconti (3 September 1392 ŌĆō 13 August 1447)
, who had ruled the Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan ( it, Ducato di Milano; lmo, Ducaa de Milan) was a state in northern Italy, created in 1395 by Gian Galeazzo Visconti, then the lord of Milan, and a member of the important Visconti family, which had been ruling the city sin ...
from 1412 until his death in 1447, Cosimo sent Francesco I Sforza
Francesco I Sforza (; 23 July 1401 ŌĆō 8 March 1466) was an Italian condottiero who founded the Sforza dynasty in the duchy of Milan, ruling as its (fourth) duke from 1450 until his death. In the 1420s, he participated in the War of L' ...
to establish himself in Milan to prevent an impending military advance from the Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Rep├╣blega de Ven├©sia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Rep├╣blega V├©neta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Seren├¼sima Rep├╣blega de Ven├©sia ...
. Francesco Sforza was a ''condottiere
''Condottieri'' (; singular ''condottiero'' or ''condottiere'') were Italian captains in command of mercenary companies during the Middle Ages and of multinational armies during the early modern period. They notably served popes and other Euro ...
'', a mercenary soldier
A mercenary, sometimes also known as a soldier of fortune or hired gun, is a private individual, particularly a soldier, that joins a military conflict for personal profit, is otherwise an outsider to the conflict, and is not a member of any o ...
who had stolen land from the papacy and proclaimed himself its lord. He had yearned to establish himself at Milan as well, an ambition that was aided by the fact that the current Visconti head lacked legitimate children save for a daughter, Bianca, whom Sforza ultimately married in November 1441 after a failed attempt at winning her hand from her father. The resultant balance of power with Milan and Florence on the one side and Venice and the Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples ( la, Regnum Neapolitanum; it, Regno di Napoli; nap, Regno 'e Napule), also known as the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was ...
on the other created nearly half a century of peace that enabled the development of the Renaissance
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ide ...
in Italy. However, despite the benefits to Florence from keeping Venice at bay, the intervention in Milan was unpopular among Cosimo's fellow citizens, primarily because they were called upon to finance the Sforza succession. The Milanese made a brief attempt at democracy before Sforza was finally acclaimed duke by the city in February 1450.
In terms of foreign policy, Cosimo worked to create peace in northern Italy through the creation of a balance of power between Florence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico ...
, Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, ╬Ø╬Ą╬¼ŽĆ╬┐╬╗╬╣Žé, Ne├Īpolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adm ...
, Venice and Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city ...
during the wars in Lombardy
The Wars in Lombardy were a series of conflicts between the Republic of Venice and the Duchy of Milan and their respective allies, fought in four campaigns in a struggle for hegemony in Northern Italy that ravaged the economy of Lombardy and ...
between 1423 and 1454 and the discouragement of outside powers (notably the French and the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
) from interfering in Italian affairs. In 1439, he was instrumental in convincing Pope Eugene IV
Pope Eugene IV ( la, Eugenius IV; it, Eugenio IV; 1383 ŌĆō 23 February 1447), born Gabriele Condulmer, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 3 March 1431 to his death in February 1447. Condulmer was a Venetian, and ...
to move the Ecumenical
Ecumenism (), also spelled oecumenism, is the concept and principle that Christians who belong to different Christian denominations should work together to develop closer relationships among their churches and promote Christian unity. The adjec ...
Council of Ferrara to Florence. The arrival of many notable Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
figures from the Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantino ...
, including Emperor John VIII Palaiologos, for this event further inspired the growing interest in ancient Greek arts and literature.
Death
Careggi
The Villa Medici at Careggi is a patrician villa in the hills near Florence, Tuscany, central Italy.
History
The villa was among the first of a number of Medici villas, notable as the site of the Platonic Academy founded by Cosimo de' Medici, ...
, Cosimo was succeeded by his son Piero, father of Lorenzo the Magnificent. After Cosimo's death, the Signoria awarded him the title ''Pater Patriae
''Pater Patriae'' (plural ''Patres Patriae''), also seen as ''Parens Patriae'', is a Latin honorific meaning "Father of the Country", or more literally, "Father of the Fatherland". It is also used of U.S. President George Washington, the Swed ...
'', "Father of the Fatherland", an honour once awarded to Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC ŌĆō 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, and academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the esta ...
, and had it carved upon his tomb in the Church of San Lorenzo.
Patronage
Cosimo de' Medici used his personal fortune to control the Florentine political system and to sponsor orators, poets and philosophers, as well as a series of artistic accomplishments.Arts
 Cosimo was also noted for his patronage of culture and the arts during the Renaissance and spent the family fortune liberally to enrich the civic life of Florence. According to Salviati's ''Zibaldone'', Cosimo stated: "All those things have given me the greatest satisfaction and contentment because they are not only for the honor of God but are likewise for my own remembrance. For fifty years, I have done nothing else but earn money and spend money; and it became clear that spending money gives me greater pleasure than earning it."
Additionally, his patronage of the arts both recognized and proclaimed the humanistic responsibility of the civic duty that came with wealth.
Cosimo hired the young Michelozzo Michelozzi to create what is today perhaps the prototypical Florentine
Cosimo was also noted for his patronage of culture and the arts during the Renaissance and spent the family fortune liberally to enrich the civic life of Florence. According to Salviati's ''Zibaldone'', Cosimo stated: "All those things have given me the greatest satisfaction and contentment because they are not only for the honor of God but are likewise for my own remembrance. For fifty years, I have done nothing else but earn money and spend money; and it became clear that spending money gives me greater pleasure than earning it."
Additionally, his patronage of the arts both recognized and proclaimed the humanistic responsibility of the civic duty that came with wealth.
Cosimo hired the young Michelozzo Michelozzi to create what is today perhaps the prototypical Florentine palazzo
A palace is a grand residence, especially a royal residence, or the home of a head of state or some other high-ranking dignitary, such as a bishop or archbishop. The word is derived from the Latin name pal─ütium, for Palatine Hill in Rome which ...
, the austere and magnificent Palazzo Medici. The building still includes, as its only 15th-century interior that is largely intact, the Magi Chapel frescoed by Benozzo Gozzoli
Benozzo Gozzoli (4 October 1497) was an Italian Renaissance painter from Florence. A pupil of Fra Angelico, Gozzoli is best known for a series of murals in the Magi Chapel of the Palazzo Medici-Riccardi, depicting festive, vibrant processions ...
, completed in 1461 with portraits of members of the Medici family parading through Tuscany in the guise of the Three Wise Men. He was a patron and confidante of Fra Angelico
Fra Angelico (born Guido di Pietro; February 18, 1455) was an Italian painter of the Early Renaissance, described by Vasari in his '' Lives of the Artists'' as having "a rare and perfect talent".Giorgio Vasari, ''Lives of the Artists''. Pengu ...
, Fra Filippo Lippi, and Donatello
Donato di Niccol├▓ di Betto Bardi ( ŌĆō 13 December 1466), better known as Donatello ( ), was a Florentine sculptor of the Renaissance period. Born in Florence, he studied classical sculpture and used this to develop a complete Renaissance st ...
, whose famed David
David (; , "beloved one") (traditional spelling), , ''D─üw┼½d''; grc-koi, ╬ö╬▒Žģ╬É╬┤, Dau├Łd; la, Davidus, David; gez , ßŗ│ßŗŖßēĄ, ''Dawit''; xcl, į┤šĪųéš½š®, ''Dawit╩┐''; cu, ąöą░ą▓├Łą┤čŖ, ''David┼Ł''; possibly meaning "beloved one". w ...
and Judith Slaying Holofernes
''Judith Slaying Holofernes'' is a painting by the Italian early Baroque artist Artemisia Gentileschi, completed in 1612-13 and now at the Museo Capodimonte, Naples, Italy.
The picture is considered one of her iconic works. The canvas shows Jud ...
were Medici commissions. His patronage enabled the eccentric and bankrupt architect Brunelleschi
Filippo Brunelleschi ( , , also known as Pippo; 1377 ŌĆō 15 April 1446), considered to be a founding father of Renaissance architecture, was an Italian architect, designer, and sculptor, and is now recognized to be the first modern engineer, ...
to complete the dome of Santa Maria del Fiore (the "Duomo
''Duomo'' (, ) is an Italian term for a church with the features of, or having been built to serve as, a cathedral, whether or not it currently plays this role. Monza Cathedral, for example, has never been a diocesan seat and is by definition n ...
") in 1436.

Libraries
In 1444, Cosimo de' Medici founded the first public library in Florence, at San Marco, which was of central importance to thehumanist
Humanism is a philosophical stance that emphasizes the individual and social potential and agency of human beings. It considers human beings the starting point for serious moral and philosophical inquiry.
The meaning of the term "human ...
movement in Florence during the Renaissance. It was designed by Michelozzo
Michelozzo di Bartolomeo Michelozzi (1396 ŌĆō 7 October 1472) was an Italian architect and sculptor. Considered one of the great pioneers of architecture during the Renaissance, Michelozzo was a favored Medici architect who was extensively em ...
, a student of Lorenzo Ghiberti
Lorenzo Ghiberti (, , ; 1378 ŌĆō 1 December 1455), born Lorenzo di Bartolo, was an Italian Renaissance sculptor from Florence, a key figure in the Early Renaissance, best known as the creator of two sets of bronze doors of the Florence Baptistery ...
who later collaborated with Donatello
Donato di Niccol├▓ di Betto Bardi ( ŌĆō 13 December 1466), better known as Donatello ( ), was a Florentine sculptor of the Renaissance period. Born in Florence, he studied classical sculpture and used this to develop a complete Renaissance st ...
and was also a good friend and patron to Cosimo. Cosimo contributed the funds necessary to repair the library and provide it with a book collection, which people were allowed to use at no charge. "That Cosimo de'Medici was able to finance the construction of such a site placed him in a privileged position of leadership in the city. He hand-selected those individuals who were given access to this laboratory of learning, and, through this social dynamic, he actively shaped the politics of the Republic." He also commissioned Michelozzo to design a library for his grandson, Lorenzo de' Medici. His first library, however, was designed by Michelozzo while the two were in Venice, where Cosimo had been temporarily exiled. In 1433, in gratitude for the hospitality of that city, he left it as a gift, his only such work outside Florence. His libraries were noted for their Renaissance style of architecture and distinguished artwork.
Cosimo had grown up with only three books, but by the time he was thirty, his collection had grown to 70 volumes. After being introduced to humanism by a group of literati who had asked for his help in preserving books, he grew to love the movement and gladly sponsored the effort to renew Greek and Roman civilization through literature, for which book collecting was a central activity. "Heartened by the romantic wanderlust of a true bibliophile, the austere banker even embarked on several journeys in the hunt for books, while guaranteeing just about any undertaking that involved books. He financed trips to nearly every European town as well as to Syria, Egypt, and Greece organized by Poggio Bracciolini
Gian Francesco Poggio Bracciolini (11 February 1380 ŌĆō 30 October 1459), usually referred to simply as Poggio Bracciolini, was an Italian scholar and an early Renaissance humanist. He was responsible for rediscovering and recovering many clas ...
, his chief book scout." He engaged 45 copyists under the bookseller Vespasiano da Bisticci to transcribe manuscripts and paid off the debts of Niccol├▓ de' Niccoli
Niccol├▓ de' Niccoli (1364 ŌĆō 22 January 1437) was an Italian Renaissance humanist.
He was born and died in Florence, and was one of the chief figures in the company of learned men which gathered around the patronage of Cosimo de' Medici. Nic ...
after his death in exchange for control over his collection of some 800 manuscripts valued at around 6,000 florins. These manuscripts that Cosimo acquired from Niccoli would later be the cornerstone of the Laurentian Library
The Laurentian Library (Biblioteca Medicea Laurenziana or BML) is a historic library in Florence, Italy, containing more than 11,000 manuscripts and 4,500 early printed books. Built in a cloister of the Medicean Basilica di San Lorenzo di Firenze ...
, a library in Florence founded by Cosimo's grandson, Lorenzo de' Medici
Lorenzo di Piero de' Medici (; 1 January 1449 ŌĆō 8 April 1492) was an Italian statesman, banker, ''de facto'' ruler of the Florentine Republic and the most powerful and enthusiastic patron of Renaissance culture in Italy. Also known as Lorenzo ...
.
Philosophy
In the realm of philosophy, Cosimo, influenced by the lectures ofGemistus Pletho
Georgios Gemistos Plethon ( el, ╬ō╬ĄŽÄŽü╬│╬╣╬┐Žé ╬ō╬Ą╬╝╬╣ŽāŽäŽīŽé ╬Ā╬╗╬«╬ĖŽē╬Į; la, Georgius Gemistus Pletho /1360 ŌĆō 1452/1454), commonly known as Gemistos Plethon, was a Greek scholar and one of the most renowned philosophers of the late By ...
n, supported Marsilio Ficino
Marsilio Ficino (; Latin name: ; 19 October 1433 ŌĆō 1 October 1499) was an Italian scholar and Catholic priest who was one of the most influential humanist philosophers of the early Italian Renaissance. He was an astrologer, a revive ...
and his attempts at reviving Neo-Platonism
Neoplatonism is a strand of Platonic philosophy that emerged in the 3rd century AD against the background of Hellenistic philosophy and religion. The term does not encapsulate a set of ideas as much as a chain of thinkers. But there are some id ...
. Cosimo commissioned Ficino's Latin translation of the complete works of Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, ╬Ā╬╗╬¼ŽäŽē╬Į ; 428/427 or 424/423 ŌĆō 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
(the first ever complete translation) and collected a vast library that he shared with intellectuals such as Niccol├▓ de' Niccoli
Niccol├▓ de' Niccoli (1364 ŌĆō 22 January 1437) was an Italian Renaissance humanist.
He was born and died in Florence, and was one of the chief figures in the company of learned men which gathered around the patronage of Cosimo de' Medici. Nic ...
and Leonardo Bruni
Leonardo Bruni (or Leonardo Aretino; c. 1370 ŌĆō March 9, 1444) was an Italian humanist, historian and statesman, often recognized as the most important humanist historian of the early Renaissance. He has been called the first modern historian. ...
. He also established a Platonic Academy
The Academy ( Ancient Greek: ß╝ł╬║╬▒╬┤╬Ę╬╝╬»╬▒) was founded by Plato in c. 387 BC in Athens. Aristotle studied there for twenty years (367ŌĆō347 BC) before founding his own school, the Lyceum. The Academy persisted throughout the Hellenisti ...
in Florence in 1445. He provided his grandson Lorenzo de' Medici with an education in the studia humanitatis
The Latin school was the grammar school of 14th- to 19th-century Europe, though the latter term was much more common in England. Emphasis was placed, as the name indicates, on learning to use Latin. The education given at Latin schools gave gre ...
. Cosimo certainly had an influence on Renaissance intellectual life, but it was Lorenzo who would later be deemed to have been the greatest patron.
Fictional depictions
Roberto Rossellini
Roberto Gastone Zeffiro Rossellini (8 May 1906 ŌĆō 3 June 1977) was an Italian film director, producer, and screenwriter. He was one of the most prominent directors of the Italian neorealist cinema, contributing to the movement with films such ...
's three-part television miniseries ''The Age of the Medici
''The Age of the Medici'', originally released in Italy as ''L'et├Ā di Cosimo de Medici'' (''The Age of Cosimo de Medici''), is a 1973 3-part TV series about the Renaissance in Florence, directed by Roberto Rossellini. The series was shot in Engl ...
'' (1973) has Cosimo as its central character (the original Italian title is ''L'et├Ā di Cosimo de' Medici'', meaning "The Age of Cosimo de' Medici"). The first part, ''The Exile of Cosimo'', and the second part, ''The Power of Cosimo'', focus on Cosimo's political struggles and on his patronage of the arts and sciences in Florence. Cosimo is portrayed by Italian actor Marcello Di Falco.
Frank Spotnitz's eight-part television series '' Medici: Masters of Florence'' (2016) depicts the rise of the powerful banking family after the death of Giovanni (played by Dustin Hoffman
Dustin Lee Hoffman (born August 8, 1937) is an American actor and filmmaker. As one of the key actors in the formation of New Hollywood, Hoffman is known for his versatile portrayals of antiheroes and emotionally vulnerable characters. He is th ...
), as his son Cosimo ( Richard Madden) takes over as head of the family. The sixteen-part sequel, ''Medici
The House of Medici ( , ) was an Italian banking family and political dynasty that first began to gather prominence under Cosimo de' Medici, in the Republic of Florence during the first half of the 15th century. The family originated in the Mu ...
'' (2019ŌĆō2020), follows the career of Cosimo's grandson, Lorenzo the Magnificent (Daniel Sharman
Daniel Andrew Sharman (born 25 April 1986) is an English actor. He is known for his roles as Isaac Lahey on the television series '' Teen Wolf'' (2012ŌĆō2014), Kaleb Westphall / Kol Mikaelson on '' The Originals'' (2014ŌĆō2015), Troy Otto on ' ...
).
See also
*History of Florence
Florence ( it, Firenze) weathered the decline of the Western Roman Empire to emerge as a financial hub of Europe, home to several banks including that of the politically powerful Medici family. The city's wealth supported the development of a ...
* Villa Medici at Cafaggiolo
References
Further reading
*Burckhardt, Jacob
Carl Jacob Christoph Burckhardt (25 May 1818 – 8 August 1897) was a Swiss historian of art and culture and an influential figure in the historiography of both fields. He is known as one of the major progenitors of cultural history. Sigfri ...
, ''The Civilization of the Renaissance in Italy'' (1860) 1878.
* Connell, William. ''Society and Individual in Renaissance Florence'', 2002.
* Cook, Jon (2003). "Why Renaissance? Why Florence?" ''History Review'', 47, 44ŌĆō46.
* De Roover, R. ''The Rise and Decline of the Medici Bank, 1397ŌĆō1494.'' Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 1963.
* Durant, Will (1953). ''The Renaissance.'' The Story of Civilization. New York: Simon and Schuster. 1953.
* for the Palazzo Medici.
* Kent, Dale. ''Cosimo De' Medici and the Florentine Renaissance: The patron's oeuvre''. New Haven: Yale University Press, 2000.
* Martin Roberts, ''Italian Renaissance''. Longman, 1992.
* Meehan, William F. III (2007). "The Importance of Cosimo de Medici in Library History." Indiana libraries, 26(3), 15ŌĆō17. Retrieved from: http://hdl.handle.net/1805/1579
* Parks, Tim. ''Medici Money: Banking, Metaphysics, and Art in Fifteenth-Century Florence''. New York: W. W. Norton, 2005.
*
*
External links
The Medici Family.com: Cosimo I
Internet Archive.org: Cosimo de' Medici (1899)
ŌĆō ''biography by K. Dorothea Ewart Vernon''. * ŌĆ
BIVIO: Biblioteca Virtuale On-Line: Biography in "Le vite" from Vespasiano da Bisticci
{{DEFAULTSORT:Medici, Cosimo 01 Rulers of Florence Italian bankers Medieval bankers 1389 births 1464 deaths 15th-century people of the Republic of Florence Cosimo 01 Italian nobility Ambassadors of the Republic of Florence Burials at San Lorenzo, Florence 15th-century rulers in Europe Book and manuscript collectors Italian art patrons 15th-century Italian businesspeople