Coronal hole on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
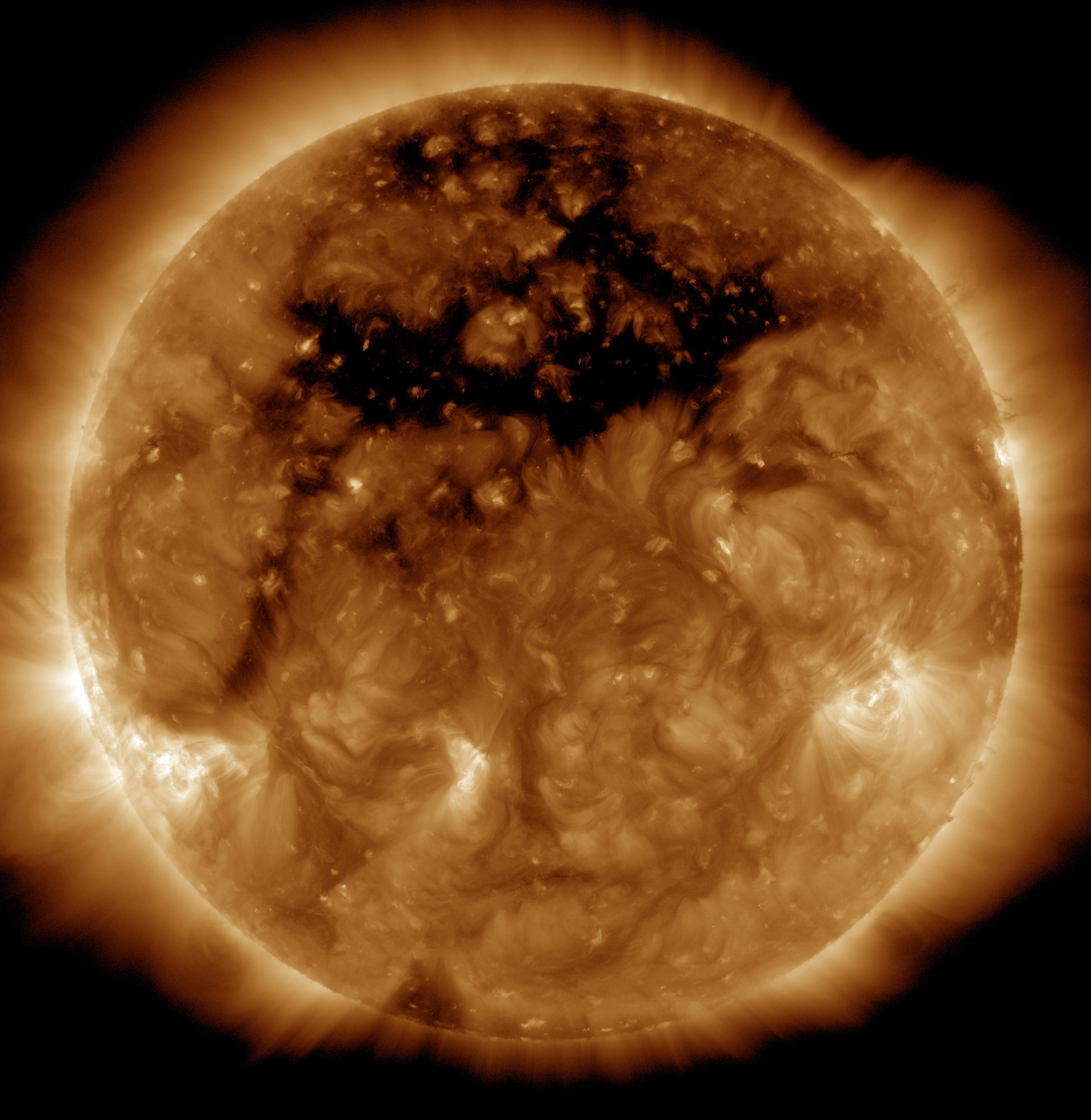 A coronal hole is a temporary region of relatively cool, less dense plasma in the
A coronal hole is a temporary region of relatively cool, less dense plasma in the
 Coronal hole size and population correspond with the
Coronal hole size and population correspond with the
 A coronal hole is a temporary region of relatively cool, less dense plasma in the
A coronal hole is a temporary region of relatively cool, less dense plasma in the solar corona
A corona ( coronas or coronae) is the outermost layer of a star's atmosphere. It consists of plasma.
The Sun's corona lies above the chromosphere and extends millions of kilometres into outer space. It is most easily seen during a total solar ...
where the Sun's magnetic field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to ...
extends into interplanetary space
Interplanetary may refer to:
* Interplanetary space, the space between the planets of the Solar System
* Interplanetary spaceflight, travel between planets
*The interplanetary medium, the material that exists in interplanetary space
*The InterPl ...
as an open field.Freedman, Roger A., and William J. Kaufmann III. "Our Star, the Sun." Universe. 8th ed. New York: W.H. Freeman, 2008. 419–420. Print. Compared to the corona's usual closed magnetic field that arches between regions of opposite magnetic polarity, the open magnetic field of a coronal hole allows solar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the sol ...
to escape into space at a much quicker rate. This results in decreased temperature and density of the plasma at the site of a coronal hole, as well as an increased speed in the average solar wind measured in interplanetary space. If streams of high-speed solar wind from coronal holes encounter the Earth, they can cause major displays of aurorae. Near solar minimum, when activity such as coronal mass ejections is less frequent, such streams are the main cause of geomagnetic storms and associated aurorae.
History
In the 1960s, coronal holes showed up on X-ray images taken by sounding rockets and in observations at radio wavelengths by the Sydney Chris Cross radio telescope, but at the time, what they were was unclear. Their true nature was recognized in the 1970s, whenX-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
telescopes
A telescope is a device used to observe distant objects by their emission, absorption, or reflection of electromagnetic radiation. Originally meaning only an optical instrument using lenses, curved mirrors, or a combination of both to observ ...
in the Skylab
Skylab was the first United States space station, launched by NASA, occupied for about 24 weeks between May 1973 and February 1974. It was operated by three separate three-astronaut crews: Skylab 2, Skylab 3, and Skylab 4. Major operations ...
mission were flown above the Earth's atmosphere to reveal the structure of the corona.
Solar cycle
 Coronal hole size and population correspond with the
Coronal hole size and population correspond with the solar cycle
The solar cycle, also known as the solar magnetic activity cycle, sunspot cycle, or Schwabe cycle, is a nearly periodic 11-year change in the Sun's activity measured in terms of variations in the number of observed sunspots on the Sun's surf ...
. As the Sun heads toward solar maximum, the coronal holes move closer and closer to the Sun's poles. During solar maxima, the number of coronal holes decreases until the magnetic fields on the Sun reverse. Afterwards, new coronal holes appear near the new poles. The coronal holes then increase in size and number, extending farther from the poles as the Sun moves toward a solar minimum again.
Solar wind
Coronal holes generally dischargesolar wind
The solar wind is a stream of charged particles released from the upper atmosphere of the Sun, called the corona. This plasma mostly consists of electrons, protons and alpha particles with kinetic energy between . The composition of the sol ...
at a speed about twice the average. The escaping solar wind is known to travel along open magnetic field lines that pass through the coronal hole area. Since coronal holes are regions in the Sun's corona that have much lower densities and temperatures than most of the corona, these regions are very thin, which contributes to the solar wind, since particles within the chromosphere can more easily break through.
Influence on space weather
During solar minima, coronal holes are the primary sources ofspace weather
Space weather is a branch of space physics and aeronomy, or heliophysics, concerned with the time varying conditions within the Solar System, including the solar wind, emphasizing the space surrounding the Earth, including conditions in the ...
disturbances, including aurorae. Typically, geomagnetic
Earth's magnetic field, also known as the geomagnetic field, is the magnetic field that extends from Earth's interior out into space, where it interacts with the solar wind, a stream of charged particles emanating from the Sun. The magnetic f ...
(and proton
A proton is a stable subatomic particle, symbol , H+, or 1H+ with a positive electric charge of +1 ''e'' elementary charge. Its mass is slightly less than that of a neutron and 1,836 times the mass of an electron (the proton–electron mass ...
) storms originating from coronal holes have a gradual commencement (over hours) and are not as severe as storms caused by coronal mass ejection
A coronal mass ejection (CME) is a significant release of plasma and accompanying magnetic field from the Sun's corona into the heliosphere. CMEs are often associated with solar flares and other forms of solar activity, but a broadly accept ...
s (CMEs), which usually have a sudden onset. Because coronal holes can last for several solar rotations (i.e. several months), predicting the recurrence of this type of disturbance is often possible significantly farther in advance than for CME-related disturbances.
See also
*Heliophysics
Heliophysics (from the prefix " helio", from Attic Greek ''hḗlios'', meaning Sun, and the noun "physics": the science of matter and energy and their interactions) is the physics of the Sun and its connection with the Solar System. NASA define ...
* List of solar storms
References
Further reading
# # Jiang, Y., Chen, H., Shen, Y., Yang, L., & Li, K. (2007, January). Hα dimming associated with the eruption of a coronal sigmoid in the quiet Sun. ''Solar Physics'', 240(1), 77–87. {{DEFAULTSORT:Coronal Hole Solar phenomena