Cornishman on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Cornish people or Cornish ( kw, Kernowyon, ang, Cornƿīelisċ) are an
and a recognised national minority in the
 A campaign for the inclusion of a Cornish tick-box in the nationality section of the 2011 census failed to win the support of Parliament in 2009. As a consequence, posters were created by the census organisation and
A campaign for the inclusion of a Cornish tick-box in the nationality section of the 2011 census failed to win the support of Parliament in 2009. As a consequence, posters were created by the census organisation and
 Traditionally, the Cornish are thought to have been descended from the Iron Age
Traditionally, the Cornish are thought to have been descended from the Iron Age  Throughout
Throughout
 The
The  Cornish was the most widely spoken language west of the River Tamar until around the mid-1300s, when
Cornish was the most widely spoken language west of the River Tamar until around the mid-1300s, when
 The
The
 The Cornish people are concentrated in Cornwall, but after the
The Cornish people are concentrated in Cornwall, but after the
 From the beginning of Australia's colonial period until after the Second World War, people from the United Kingdom made up a large majority of people coming to Australia, meaning that many Australian-born people can trace their origins to Britain. The Cornish people in particular were actively encouraged to emigrate to Australia following the demise of Cornish mining in the 19th century. A "vigorous recruiting campaign" was launched to encourage the Cornish to aid with
From the beginning of Australia's colonial period until after the Second World War, people from the United Kingdom made up a large majority of people coming to Australia, meaning that many Australian-born people can trace their origins to Britain. The Cornish people in particular were actively encouraged to emigrate to Australia following the demise of Cornish mining in the 19th century. A "vigorous recruiting campaign" was launched to encourage the Cornish to aid with
 In 1825 a band of 60 Cornishmen left Falmouth for Mineral del Monte in central
In 1825 a band of 60 Cornishmen left Falmouth for Mineral del Monte in central
 The survival of a distinct
The survival of a distinct
 The
The

 Cornish cuisine is a regional variety of
Cornish cuisine is a regional variety of
 With its comparatively small, rural population, major contribution by the Cornish to national sport in the United Kingdom has been limited.. There are no teams affiliated to the Cornwall County Football Association that play in the Football League of
With its comparatively small, rural population, major contribution by the Cornish to national sport in the United Kingdom has been limited.. There are no teams affiliated to the Cornwall County Football Association that play in the Football League of

 The politics of Cornwall take place within a wider national political framework of a constitutional monarchy, in which the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, United Kingdom's monarch is head of state and the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom is the head of government, and the supranational framework of the
The politics of Cornwall take place within a wider national political framework of a constitutional monarchy, in which the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, United Kingdom's monarch is head of state and the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom is the head of government, and the supranational framework of the
www.cornwall.gov.uk
the website of
www.cornishculture.co.uk
an online guide to Cornish Celtic culture {{Good article Cornish people, Brythonic Celts Celtic ethnic groups Ethnic groups in the United Kingdom
ethnic group
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
native to, or associated with Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a Historic counties of England, historic county and Ceremonial counties of England, ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people ...
:and a recognised national minority in the
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, commonly known as the United Kingdom (UK) or Britain, is a country in Europe, off the north-western coast of the continental mainland. It comprises England, Scotland, Wales and ...
, which can trace its roots to the ancient Britons
The Britons ( *''Pritanī'', la, Britanni), also known as Celtic Britons or Ancient Britons, were people of Celtic language and culture who inhabited Great Britain from at least the British Iron Age and into the Middle Ages, at which point the ...
who inhabited southern and central Great Britain
Great Britain is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean off the northwest coast of continental Europe. With an area of , it is the largest of the British Isles, the largest European island and the ninth-largest island in the world. It ...
before the Roman conquest. Many in Cornwall today continue to assert a distinct identity separate from or in addition to English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
or British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
identities. Cornish identity has been adopted by migrants into Cornwall, as well as by emigrant and descendant communities from Cornwall, the latter sometimes referred to as the Cornish diaspora
The Cornish diaspora ( kw, keskar kernewek) consists of Cornish people and their descendants who emigrated from Cornwall, United Kingdom. The diaspora is found within the United Kingdom, and in countries such as the United States, Canada, Austral ...
. Although not included as an tick-box option in the UK census, the numbers of those writing in a Cornish ethnic and national identity are officially recognised and recorded.
Throughout classical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
, the ancient Britons formed a series of tribes
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in part due to confli ...
, cultures and identities in Great Britain; the Dumnonii
The Dumnonii or Dumnones were a British tribe who inhabited Dumnonia, the area now known as Devon and Cornwall (and some areas of present-day Dorset and Somerset) in the further parts of the South West peninsula of Britain, from at least the Ir ...
and Cornovii
The Cornovii is the name by which two, or three, tribes were known in Roman Britain. One tribe was in the area centred on present-day Shropshire, one was in Caithness in northernmost Scotland, and there was probably one in Cornwall. The name h ...
were the Celtic tribes
This is a list of Celtic tribes, organized in order of the likely ethnolinguistic kinship of the peoples and tribes.
In Classical antiquity, Celts were a large number and a significant part of the population in many regions of Western Europe ...
who inhabited what was to become Cornwall during the Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age ( Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age ( Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly ...
, Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lett ...
and post-Roman periods. The name Cornwall and its demonym
A demonym (; ) or gentilic () is a word that identifies a group of people (inhabitants, residents, natives) in relation to a particular place. Demonyms are usually derived from the name of the place (hamlet, village, town, city, region, province, ...
Cornish are derived from the Celtic Cornovii tribe. The Anglo-Saxon invasion and settlement of Britain in the 5th and 6th centuries restricted the Romano-British culture and language gradually into the north and west of Great Britain whilst the inhabitants of southern and eastern Britain became English. The Cornish people, who shared the Brythonic language with the Welsh and Bretons across the sea, were referred to in the Old English
Old English (, ), or Anglo-Saxon, is the earliest recorded form of the English language, spoken in England and southern and eastern Scotland in the early Middle Ages. It was brought to Great Britain by Anglo-Saxon settlers in the mid-5th ...
language as the "Westwalas" meaning West Welsh. The Battle of Deorham
The Battle of Deorham (or Dyrham) is claimed as a decisive military encounter between the West Saxons and the Britons of the West Country in 577. The battle, which was a major victory for Wessex's forces led by Ceawlin and his son, Cuthwine, ...
between the Britons and Anglo-Saxons
The Anglo-Saxons were a cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo-Saxons happened ...
is thought to have resulted in a loss of landlinks with the people of Wales.
The Cornish people and their Brythonic Cornish language
Cornish (Standard Written Form: or ) , is a Southwestern Brittonic language of the Celtic language family. It is a revived language, having become extinct as a living community language in Cornwall at the end of the 18th century. However, ...
experienced a process of anglicisation
Anglicisation is the process by which a place or person becomes influenced by English culture or British culture, or a process of cultural and/or linguistic change in which something non-English becomes English. It can also refer to the influe ...
and attrition during the medieval
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire a ...
and early modern periods. By the 18th century, and following the creation of the Kingdom of Great Britain
The Kingdom of Great Britain (officially Great Britain) was a sovereign country in Western Europe from 1 May 1707 to the end of 31 December 1800. The state was created by the 1706 Treaty of Union and ratified by the Acts of Union 1707, wh ...
, the Cornish language and identity had faded, largely replaced by the English language
English is a West Germanic language of the Indo-European language family, with its earliest forms spoken by the inhabitants of early medieval England. It is named after the Angles, one of the ancient Germanic peoples that migrated to the ...
(albeit Cornish-influenced West Country dialects
West Country English is a group of English language varieties and accents used by much of the native population of South West England, the area sometimes popularly known as the West Country.
The West Country is often defined as encompass ...
and Anglo-Cornish
The Cornish dialect (also known as Cornish English, Cornu-English, kw, Sowsnek Kernowek) is a dialect of English spoken in Cornwall by Cornish people. Dialectal English spoken in Cornwall is to some extent influenced by Cornish grammar, an ...
) or British identity. A Celtic revival
The Celtic Revival (also referred to as the Celtic Twilight) is a variety of movements and trends in the 19th, 20th and 21st centuries that see a renewed interest in aspects of Celtic culture. Artists and writers drew on the traditions of Gae ...
during the early-20th century enabled a cultural self-consciousness in Cornwall that revitalised the Cornish language and roused the Cornish to express a distinctly Celtic heritage. The Cornish language was granted official recognition under the European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages
The European Charter for Regional or Minority Languages (ECRML) is a European treaty (CETS 148) adopted in 1992 under the auspices of the Council of Europe to protect and promote historical regional and minority languages in Europe. However, th ...
in 2002, and in 2014 the Cornish people were recognised and afforded protection by the UK Government under the Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities
The Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities (FCNM) is a multilateral treaty of the Council of Europe aimed at protecting the rights of minorities. It came into effect in 1998 and by 2009 it had been ratified by 39 member ...
.
In the 2021 census, the population of Cornwall, including the Isles of Scilly
The Isles of Scilly (; kw, Syllan, ', or ) is an archipelago off the southwestern tip of Cornwall, England. One of the islands, St Agnes, is the most southerly point in Britain, being over further south than the most southerly point of th ...
, was recorded as 570,300. The Cornish self-government movement has called for greater recognition of Cornish culture, politics, and language, and urged that Cornish people be accorded greater status, exemplified by the call for them to be one of the listed ethnic groups in the United Kingdom Census 2011
A census of the population of the United Kingdom is taken every ten years. The 2011 census was held in all countries of the UK on 27 March 2011. It was the first UK census which could be completed online via the Internet. The Office for Nationa ...
form.
Classification
Both geographic and historical factors distinguish the Cornish as an ethnic group further supported by identifiable genetic variance between the populations of Cornwall, neighbouring Devon and England as published in a 2012 Oxford University study. Throughout medieval andEarly Modern Britain
Early modern Britain is the history of the island of Great Britain roughly corresponding to the 16th, 17th and 18th centuries. Major historical events in early modern British history include numerous wars, especially with France, along with the E ...
, the Cornish were at some points accorded the same status as the English and Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peopl ...
and considered a separate race or nation, distinct from their neighbours, with their own language, society and customs. A process of Anglicisation
Anglicisation is the process by which a place or person becomes influenced by English culture or British culture, or a process of cultural and/or linguistic change in which something non-English becomes English. It can also refer to the influe ...
between 1485 and 1700 led to the Cornish adopting English language, culture and civic identity, a view reinforced by Cornish historian A. L. Rowse
Alfred Leslie Rowse (4 December 1903 – 3 October 1997) was a British historian and writer, best known for his work on Elizabethan England and books relating to Cornwall.
Born in Cornwall and raised in modest circumstances, he was encour ...
who said they were gradually "absorbed into the mainstream of English life". Although "decidedly modern" and "largely retrospective" in its identity politics
Identity politics is a political approach wherein people of a particular race, nationality, religion, gender, sexual orientation, social background, social class, or other identifying factors develop political agendas that are based upon these i ...
, Cornish and Celtic associations have advanced the notion of a distinct Cornish national and ethnic identity since the late 20th century. In the United Kingdom Census 2001
A nationwide census, known as Census 2001, was conducted in the United Kingdom on Sunday, 29 April 2001. This was the 20th UK census and recorded a resident population of 58,789,194.
The 2001 UK census was organised by the Office for Nationa ...
, despite no explicit "Cornish" option being available, approximately 34,000 people in Cornwall and 3,500 people elsewhere in the UK—a combined total equal to nearly 7 per cent of the population of Cornwall—identified themselves as ethnic Cornish by writing this in under the "other" ethnicity option. The census figures show a change in identity from West to East, in Penwith
Penwith (; kw, Pennwydh) is an area of Cornwall, England, United Kingdom, located on the peninsula of the same name. It is also the name of a former local government district, whose council was based in Penzance. The area is named after ...
9.2 per cent identified as ethnically Cornish, in Kerrier
Kerrier ( kw, Keryer) was a local government district in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It was the most southerly district in the United Kingdom, other than the Isles of Scilly. Its council was based in Camborne (). Other towns in the distr ...
it was 7.5 per cent, in Carrick 6.6 per cent, Restormel
Restormel ( kw, Rostorrmel) was a borough of Cornwall, England, United Kingdom, one of the six administrative divisions that made up the county. Its council was based in St Austell; its other towns included Newquay.
The borough was named after ...
6.3 per cent, North Cornwall 6 per cent, and Caradon
Caradon was a local government district in Cornwall, United Kingdom. It contained five towns: Callington, Liskeard, Looe, Saltash and Torpoint, and over 80 villages and hamlets within 41 civil parishes. Its District Council was based in Lisk ...
5.6 per cent. Weighting of the 2001 Census data gives a figure of 154,791 people with Cornish ethnicity living in Cornwall.
The Cornish have been described as "a special case" in England, with an "ethnic rather than regional identity". Structural changes to the politics of the United Kingdom
The United Kingdom is a unitary state with devolution that is governed within the framework of a parliamentary democracy under a constitutional monarchy in which the monarch, currently Charles III, King of the United Kingdom, is the head ...
, particularly the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are located primarily in Europe, Europe. The union has a total area of ...
and devolution
Devolution is the statutory delegation of powers from the central government of a sovereign state to govern at a subnational level, such as a regional or local level. It is a form of administrative decentralization. Devolved territories ...
, have been cited as the main stimulus to "a growing interest in Cornish identity and distinctiveness" in late-20th century Britain. The British are the citizens of the United Kingdom, a people who by convention consist of four national groups: the English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
, Northern Irish
Northern Irish people is a demonym for all people born in Northern Ireland or people who are entitled to reside in Northern Ireland without any restriction on their period of residence. Most Northern Irish people either identify as Northern ...
, Scots and Welsh
Welsh may refer to:
Related to Wales
* Welsh, referring or related to Wales
* Welsh language, a Brittonic Celtic language spoken in Wales
* Welsh people
People
* Welsh (surname)
* Sometimes used as a synonym for the ancient Britons (Celtic peopl ...
. In the 1990s it was said that the notion that the Cornish are to be classified as a nation comparable to the English, Irish, Scots and Welsh, "has practically vanished from the popular consciousness" outside Cornwall, and that, despite a "real and substantive" identity, the Cornish "struggle for recognition as a national group distinct from the English". However, in 2014, after a 15-year campaign, the UK government officially recognised the Cornish as a national minority under the Council of Europe
The Council of Europe (CoE; french: Conseil de l'Europe, ) is an international organisation founded in the wake of World War II to uphold human rights, democracy and the rule of law in Europe. Founded in 1949, it has 46 member states, with a p ...
's Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities
The Framework Convention for the Protection of National Minorities (FCNM) is a multilateral treaty of the Council of Europe aimed at protecting the rights of minorities. It came into effect in 1998 and by 2009 it had been ratified by 39 member ...
, giving the Cornish the same status as the Welsh, Scots and Irish within the UK.
Inhabitants of Cornwall may have multiple political
Politics (from , ) is the set of activities that are associated with making decisions in groups, or other forms of power relations among individuals, such as the distribution of resources or status. The branch of social science that studi ...
allegiances, adopting mixed, dual or hyphenated identities such as "Cornish first and British second", "Cornish and British and European", or, like Phil Vickery (a rugby union
Rugby union, commonly known simply as rugby, is a close-contact team sport that originated at Rugby School in the first half of the 19th century. One of the two codes of rugby football, it is based on running with the ball in hand. In it ...
prop for the England national rugby union team
The England national rugby union team represents England in men's international rugby union. They compete in the annual Six Nations Championship with France, Ireland, Italy, Scotland and Wales. England have won the championship on 29 occasion ...
and British and Irish Lions
The British & Irish Lions is a rugby union team selected from players eligible for the national teams of England, Ireland, Scotland, and Wales. The Lions are a test side and most often select players who have already played for their national ...
), describe themselves as "Cornish" and "English". Meanwhile, another international rugby union player, Josh Matavesi
Joshua Lewis Matavesi (born 5 October 1990) is a rugby union player, who currently plays for Japanese side Toyota Industries Shuttles Aichi, and formerly played for the Fiji national team at international level. Matavesi was born in Cornwall, E ...
, describes himself as Cornish- Fijian and Cornish not English.
A survey by Plymouth University
The University of Plymouth is a public research university based predominantly in Plymouth, England, where the main campus is located, but the university has campuses and affiliated colleges across South West England. With students, it is th ...
in 2000 found that 30% of children in Cornwall felt "Cornish, not English". A 2004 survey on national identity by the finance firm Morgan Stanley
Morgan Stanley is an American multinational investment management and financial services company headquartered at 1585 Broadway in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. With offices in more than 41 countries and more than 75,000 employees, the fir ...
found that 44% of respondents in Cornwall saw themselves as Cornish rather than British or English. A 2008 University of Exeter
, mottoeng = "We Follow the Light"
, established = 1838 - St Luke's College1855 - Exeter School of Art1863 - Exeter School of Science 1955 - University of Exeter (received royal charter)
, type = Public
, ...
study conducted in 16 towns across Cornwall found that 59% felt themselves to be Cornish and 41% felt "More Cornish than English", while for over a third of respondents the Cornish identity formed their primary ''national'' identity. Genealogy and family history were considered to be the chief criteria for 'being' Cornish, particularly among those who possessed such ties, while being born in Cornwall was also held to be important.
A 2008 study by the University of Edinburgh
The University of Edinburgh ( sco, University o Edinburgh, gd, Oilthigh Dhùn Èideann; abbreviated as ''Edin.'' in post-nominals) is a public research university based in Edinburgh, Scotland. Granted a royal charter by King James VI in 1 ...
of 15- and 16-year-old schoolchildren in Cornwall found that 58% of respondents felt themselves to be either 'Fairly' or 'Very much' Cornish. The other 42% may be the result of in-migration to the area during the second half of the twentieth century.
A 2010 study by the University of Exeter
, mottoeng = "We Follow the Light"
, established = 1838 - St Luke's College1855 - Exeter School of Art1863 - Exeter School of Science 1955 - University of Exeter (received royal charter)
, type = Public
, ...
into the meaning of contemporary Cornish identity across Cornwall found that there was a "west-east distance decay in the strength of the Cornish identity." The study was conducted amongst the farming community as they were deemed to be the socio-professional group most objectively representative of Cornishness. All participants categorised themselves as Cornish and identified Cornish as their primary ethnic group orientation. Those in the west primarily thought of themselves as Cornish and British/Celtic, while those in the east tended to think of themselves as Cornish and English. All participants in West Cornwall who identified as Cornish and not English described people in East Cornwall, without hesitation, as equally Cornish as themselves. Those who identified as Cornish and English stressed the primacy of their Cornishness and a capacity to distance themselves from their Englishness. Ancestry was seen as the most important criterion for being categorised as Cornish, above place of birth or growing up in Cornwall. This study supports a 1988 study by Mary McArthur that had found that the meanings of Cornishness varied substantially, from local to national identity. Both studies also observed that the Cornish were less materialistic than the English. The Cornish generally saw the English, or city people, as being "less friendly and more aggressively self-promoting and insensitive." The Cornish saw themselves as friendly, welcoming and caring.
In November 2010 British Prime Minister, David Cameron
David William Donald Cameron (born 9 October 1966) is a British former politician who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom from 2010 to 2016 and Leader of the Conservative Party from 2005 to 2016. He previously served as Leader o ...
, said "I think Cornish national identity is very powerful" and that his government would "devolve a lot of power to Cornwall – that will go to the Cornish unitary authority."
2011 and 2021 UK Census
 A campaign for the inclusion of a Cornish tick-box in the nationality section of the 2011 census failed to win the support of Parliament in 2009. As a consequence, posters were created by the census organisation and
A campaign for the inclusion of a Cornish tick-box in the nationality section of the 2011 census failed to win the support of Parliament in 2009. As a consequence, posters were created by the census organisation and Cornwall Council
Cornwall Council ( kw, Konsel Kernow) is the unitary authority for Cornwall in the United Kingdom, not including the Isles of Scilly, which has its own unitary council. The council, and its predecessor Cornwall County Council, has a tradition ...
which advised residents how they could identify themselves as Cornish by writing it in the national identity and ethnicity sections and record Cornish in the main language section. Additionally, people could record Cornwall as their country of birth.
Like other identities, Cornish has an allocated census code, (06), the same as for 2001, which applied and was counted throughout Britain. People were first able to record their ethnicity as Cornish in the 2001 UK Census, and some 37,000 people did so by writing it in.
A total of 83,499 people in England and Wales were described as having a Cornish national identity. 59,456 of these were described as Cornish only, 6,261 as Cornish and British, and 17,782 as Cornish and at least one other identity, with or without British. Within Cornwall the total was 73,220 (14% of the population) with 52,793 (9.9%) as Cornish only, 5,185 (1%) as Cornish and British, and 15,242 (2.9%) as Cornish and at least one other identity, with or without British.
In Scotland 467 people described themselves as having Cornish national identity. 254 with Cornish identity only, 39 as Scottish and Cornish, and 174 having Cornish identity and at least one other UK identity (excluding Scottish).
In the 2021 census, 89,084 people in England and Wales described their national identity as Cornish only and 10,670 as Cornish and British. Within Cornwall, 79,938 people (14.0% of the population) specified a Cornish only identity and 9,146 (1.6%) Cornish in combination with British.
Schools census (PLASC)
Since 2006 school children in Cornwall have been able to record themselves as ethnically Cornish on the annual Schools Census (PLASC). Since then the number identifying as Cornish has risen from 24% to 46%. The Department for Education recommends that parents and guardians determine the ethnicity of children at primary schools whilst pupils at secondary schools can decide their own ethnicity. *2006: 23.7 percent – 17,218 pupils out of 72,571 *2007: 27.3 percent – 19,988 pupils out of 72,842 *2008: 30.3 percent – 21,610 pupils out of 71,302 *2009: 33.9 percent – 23,808 pupils out of 70,275 *2010: 37.2 percent – 26,140 pupils out of 69,950 *2011: 40.9 percent – 28,584 pupils out of 69,811 *2012: 43.0 percent – 30,181 pupils out of 69,909 *2013: 46.0 percent – 32,254 pupils out of 70,097History
Ancestral roots
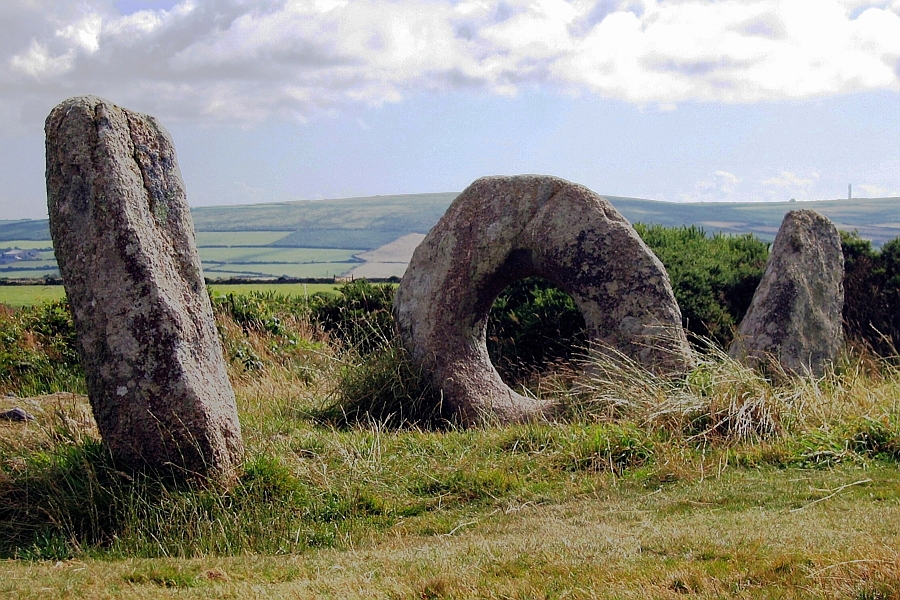
 Traditionally, the Cornish are thought to have been descended from the Iron Age
Traditionally, the Cornish are thought to have been descended from the Iron Age Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancient ...
, making them distinct from the English, many (but not all) of whom are descended from the Anglo-Saxons
The Anglo-Saxons were a cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo-Saxons happened ...
who colonised Great Britain from their homelands in northern Europe and drove the Celts to Britain's western and northern fringes. Recent genetic studies based on ancient DNA have complicated this picture, however. During the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in some areas, and other early features of urban civilization. The Bronze Age is the second pri ...
, most of the people that had inhabited Britain since the Neolithic era were replaced by Beaker People
The Bell Beaker culture, also known as the Bell Beaker complex or Bell Beaker phenomenon, is an archaeological culture named after the inverted-bell beaker drinking vessel used at the very beginning of the European Bronze Age. Arising from ar ...
, while scholars have argued that the introduction of the Celtic languages and material culture into Britain and Ireland was by means of cultural diffusion, rather than any substantial migration. Genetic evidence has also suggested that while ancestry inherited from the Anglo-Saxons makes up a significant part of the modern English gene pool (one study suggested an average 38% contribution in eastern England), they did not displace all of the previous inhabitants. A 2015 study found that modern Cornish populations had less Anglo-Saxon ancestry than people from central and southern England, and that they were genetically distinct from their neighbors in Devon
Devon ( , historically known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South West England. The most populous settlement in Devon is the city of Plymouth, followed by Devon's county town, the city of Exeter. Devo ...
. The study also suggested that populations traditionally labelled as "Celtic" showed significant diversity, rather than a unified genetic identity.
 Throughout
Throughout classical antiquity
Classical antiquity (also the classical era, classical period or classical age) is the period of cultural history between the 8th century BC and the 5th century AD centred on the Mediterranean Sea, comprising the interlocking civilizations of ...
the Celts spoke Celtic languages
The Celtic languages (usually , but sometimes ) are a group of related languages descended from Proto-Celtic. They form a branch of the Indo-European language family. The term "Celtic" was first used to describe this language group by Edward ...
, and formed a series of tribes, cultures and identities, notably the Picts
The Picts were a group of peoples who lived in what is now northern and eastern Scotland (north of the Firth of Forth) during Late Antiquity and the Early Middle Ages. Where they lived and what their culture was like can be inferred from ea ...
and Gaels
The Gaels ( ; ga, Na Gaeil ; gd, Na Gàidheil ; gv, Ny Gaeil ) are an ethnolinguistic group native to Ireland, Scotland and the Isle of Man in the British Isles. They are associated with the Gaelic languages: a branch of the Celtic langua ...
in the north and the Britons
British people or Britons, also known colloquially as Brits, are the citizens of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland, the British Overseas Territories, and the Crown dependencies.: British nationality law governs mod ...
in the south. The Britons were themselves a divided people; although they shared the Brythonic languages
The Brittonic languages (also Brythonic or British Celtic; cy, ieithoedd Brythonaidd/Prydeinig; kw, yethow brythonek/predennek; br, yezhoù predenek) form one of the two branches of the Insular Celtic language family; the other is Goidelic. ...
, they were tribal, and divided into regional societies, and within them sub-groups. Examples of these tribal societies were the Brigantes
The Brigantes were Ancient Britons who in pre-Roman times controlled the largest section of what would become Northern England. Their territory, often referred to as Brigantia, was centred in what was later known as Yorkshire. The Greek geog ...
in the north, and the Ordovices
The Ordovīcēs (Common Brittonic: *''Ordowīcī'') were one of the Celtic tribes living in Great Britain before the Roman invasion. Their tribal lands were located in present-day North Wales and England, between the Silures to the south and the ...
, the Demetae
The Demetae were a Celtic people of Iron Age and Roman period, who inhabited modern Pembrokeshire and Carmarthenshire in south-west Wales, and gave their name to the county of Dyfed.
Classical references
They are mentioned in Ptolemy's ''Geograp ...
, the Silures
The Silures ( , ) were a powerful and warlike tribe or tribal confederation of ancient Britain, occupying what is now south east Wales and perhaps some adjoining areas. They were bordered to the north by the Ordovices; to the east by the Dobun ...
and the Deceangli
The Deceangli or Deceangi (Welsh: Tegeingl) were one of the Celtic tribes living in Britain, prior to the Roman invasion of the island. The tribe lived in the region near the modern city of Chester but it is uncertain whether their territory co ...
in the west. In the extreme southwest, what was to become Cornwall, were the Dumnonii
The Dumnonii or Dumnones were a British tribe who inhabited Dumnonia, the area now known as Devon and Cornwall (and some areas of present-day Dorset and Somerset) in the further parts of the South West peninsula of Britain, from at least the Ir ...
and Cornovii
The Cornovii is the name by which two, or three, tribes were known in Roman Britain. One tribe was in the area centred on present-day Shropshire, one was in Caithness in northernmost Scotland, and there was probably one in Cornwall. The name h ...
, who lived in the Kingdom of Dumnonia
Dumnonia is the Latinised name for a Brythonic kingdom that existed in Sub-Roman Britain between the late 4th and late 8th centuries CE in the more westerly parts of present-day South West England. It was centred in the area of modern Devon, ...
. The Roman conquest of Britain
The Roman conquest of Britain refers to the conquest of the island of Britain by occupying Roman forces. It began in earnest in AD 43 under Emperor Claudius, and was largely completed in the southern half of Britain by 87 when the Stan ...
in the 1st century introduced Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
to Britain, who upon their arrival initially recorded the Dumnonii, but later reported on the Cornovii, who were possibly a sub-group of the Dumnonii. Although the Romans colonised much of central and southern Britain, Dumnonia was "virtually unaffected" by the conquest; Roman rule had little or no impact on the region, meaning it could flourish as a semi- or fully independent kingdom which evidence shows was sometimes under the dominion of the kings of the Britons, and sometimes to have been governed by its own Dumnonian monarchy, either by the title of duke or king. This petty kingdom
A petty kingdom is a kingdom described as minor or "petty" (from the French 'petit' meaning small) by contrast to an empire or unified kingdom that either preceded or succeeded it (e.g. the numerous kingdoms of Anglo-Saxon England unified into ...
shared strong linguistic, political and cultural links with Brittany
Brittany (; french: link=no, Bretagne ; br, Breizh, or ; Gallo: ''Bertaèyn'' ) is a peninsula, historical country and cultural area in the west of modern France, covering the western part of what was known as Armorica during the period ...
, a peninsula on continental Europe
Continental Europe or mainland Europe is the contiguous continent of Europe, excluding its surrounding islands. It can also be referred to ambiguously as the European continent, – which can conversely mean the whole of Europe – and, by ...
south of Cornwall inhabited by Britons; the Cornish and Breton language
Breton (, ; or in Morbihan) is a Southwestern Brittonic language of the Celtic language family spoken in Brittany, part of modern-day France. It is the only Celtic language still widely in use on the European mainland, albeit as a member of ...
s were nearly indistinguishable in this period, and both Cornwall and Brittany remain dotted with dedications to the same Celtic saint
In religious belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of holiness, likeness, or closeness to God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and denomination. In Catholic, Eastern Or ...
s.
The Sack of Rome in the year 410 prompted a complete Roman departure from Britain
The end of Roman rule in Britain was the transition from Roman Britain to post-Roman Britain. Roman rule ended in different parts of Britain at different times, and under different circumstances.
In 383, the usurper Magnus Maximus withdrew tr ...
, and Cornwall then experienced an influx of Celtic Christian
Celtic Christianity ( kw, Kristoneth; cy, Cristnogaeth; gd, Crìosdaidheachd; gv, Credjue Creestee/Creestiaght; ga, Críostaíocht/Críostúlacht; br, Kristeniezh; gl, Cristianismo celta) is a form of Christianity that was common, or held ...
missionaries from Ireland who had a profound effect upon the early Cornish people, their culture, faith and architecture. The ensuing decline of the Roman Empire
The fall of the Western Roman Empire (also called the fall of the Roman Empire or the fall of Rome) was the loss of central political control in the Western Roman Empire, a process in which the Empire failed to enforce its rule, and its vas ...
encouraged the Anglo-Saxon invasion of Britain
The Anglo-Saxon settlement of Britain is the process which changed the language and culture of most of what became England from Romano-British to Germanic. The Germanic-speakers in Britain, themselves of diverse origins, eventually develo ...
. The Angles
The Angles ( ang, Ængle, ; la, Angli) were one of the main Germanic peoples who settled in Great Britain in the post-Roman period. They founded several kingdoms of the Heptarchy in Anglo-Saxon England. Their name is the root of the name ...
, Jutes
The Jutes (), Iuti, or Iutæ ( da, Jyder, non, Jótar, ang, Ēotas) were one of the Germanic tribes who settled in Great Britain after the departure of the Romans. According to Bede, they were one of the three most powerful Germanic nation ...
, Frisii
The Frisii were an ancient Germanic tribe living in the low-lying region between the Rhine–Meuse–Scheldt delta and the River Ems, and the presumed or possible ancestors of the modern-day ethnic Dutch.
The Frisii lived in the coastal are ...
and Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
, Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and ear ...
from northern Europe, established petty kingdoms and settled in different regions of what was to become England, and parts of southern Scotland
Scotland (, ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. Covering the northern third of the island of Great Britain, mainland Scotland has a border with England to the southeast and is otherwise surrounded by the Atlantic Ocean to ...
, progressively defeating the Britons in battle. The Saxons of the Kingdom of Wessex
la, Regnum Occidentalium Saxonum
, conventional_long_name = Kingdom of the West Saxons
, common_name = Wessex
, image_map = Southern British Isles 9th century.svg
, map_caption = S ...
in particular were expanding their territory westwards towards Cornwall. The Cornish were frequently embattled with the West Saxons, who used their Germanic word ''walha
''Walhaz'' is a reconstructed Proto-Germanic word meaning 'foreigner', or more specifically 'Roman', 'Romance-speaker' or '(romanized) Celt', and survives in English as ' Welsh'. The term was used by the ancient Germanic peoples to describe in ...
'' (modern English: Welsh) meaning "stranger" or "foreigner", to describe their opponents, later specifying them as the ''Westwalas'' (West Welsh) or ''Cornwalas'' (the Cornish). Conflict continued until King Athelstan of England determined that the River Tamar
The Tamar (; kw, Dowr Tamar) is a river in south west England, that forms most of the border between Devon (to the east) and Cornwall (to the west). A part of the Tamar Valley is a World Heritage Site due to its historic mining activities.
T ...
be the formal boundary between the West Saxons and the Cornish in the year 936, making Cornwall one of the last retreats of the Britons encouraging the development of a distinct Cornish identity; Brittonic culture in Britain became confined to Cornwall, parts of Devon
Devon ( , historically known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South West England. The most populous settlement in Devon is the city of Plymouth, followed by Devon's county town, the city of Exeter. Devo ...
, North West England
North West England is one of nine official regions of England and consists of the ceremonial counties of England, administrative counties of Cheshire, Cumbria, Greater Manchester, Lancashire and Merseyside. The North West had a population of ...
, South West Scotland
South West Scotland is an ambiguous term that can include Ayrshire, Galloway, Dumfriesshire, the Stewartry of Kirkcudbright, as well as Lanarkshire, Renfrewshire. However the inclusion or exclusion of these areas is to an extent arbitrary: the only ...
and Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
. Although a treaty was agreed, Anglo-Saxon political influence stretched westwards until some time in the late 10th century when "Cornwall was definitively incorporated into the Kingdom of England
The Kingdom of England (, ) was a sovereign state on the island of Great Britain from 12 July 927, when it emerged from various Anglo-Saxon kingdoms, until 1 May 1707, when it united with Scotland to form the Kingdom of Great Britain.
On ...
".
Anglicisation and rebellion
Norman conquest of England
The Norman Conquest (or the Conquest) was the 11th-century invasion and occupation of England by an army made up of thousands of Norman, Breton, Flemish, and French troops, all led by the Duke of Normandy, later styled William the Conqu ...
, which began with an invasion by the troops of William, Duke of Normandy (later, King William I of England
William I; ang, WillelmI (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England, reigning from 1066 until his death in 10 ...
) in 1066, resulted in the removal of the Anglo-Saxon derived monarchy, aristocracy, and clerical hierarchy and its replacement by Normans
The Normans ( Norman: ''Normaunds''; french: Normands; la, Nortmanni/Normanni) were a population arising in the medieval Duchy of Normandy from the intermingling between Norse Viking settlers and indigenous West Franks and Gallo-Romans. ...
, Scandinavian Vikings from northern France. and their Breton allies, who, in many cases, maintained rule in the Brittonic-speaking parts of the conquered lands. The shire
Shire is a traditional term for an administrative division of land in Great Britain and some other English-speaking countries such as Australia and New Zealand. It is generally synonymous with county. It was first used in Wessex from the begin ...
s of England were progressively divided amongst the companions of William I of England, who served as England's new nobility. The English would come to absorb the Normans, but the Cornish "vigorously resisted" their influence. At the time of the conquest, legend has it that Cornwall was under the governance of Condor
Condor is the common name for two species of New World vultures, each in a monotypic genus. The name derives from the Quechua ''kuntur''. They are the largest flying land birds in the Western Hemisphere.
They are:
* The Andean condor (''Vu ...
, reported by later antiquarian
An antiquarian or antiquary () is an fan (person), aficionado or student of antiquities or things of the past. More specifically, the term is used for those who study history with particular attention to ancient artifact (archaeology), artifac ...
s to be the last Earl of Cornwall to be directly descended from the ancient monarchy of Cornwall. The Earldom of Cornwall had held devolved
Devolution is the statutory delegation of powers from the central government of a sovereign state to govern at a subnational level, such as a regional or local level. It is a form of administrative decentralization. Devolved territories ...
semi-sovereignty
Sovereignty is the defining authority within individual consciousness, social construct, or territory. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the perso ...
from England, but in 1067 was granted to Robert, Count of Mortain
Robert, Count of Mortain, 2nd Earl of Cornwall (–) was a Norman nobleman and the half-brother (on their mother's side) of King William the Conqueror. He was one of the very few proven companions of William the Conqueror at the Battle of Hast ...
, King William I's half-brother, and ruled thereafter by an Anglo-Norman Anglo-Norman may refer to:
*Anglo-Normans, the medieval ruling class in England following the Norman conquest of 1066
*Anglo-Norman language
**Anglo-Norman literature
*Anglo-Norman England, or Norman England, the period in English history from 1066 ...
aristocracy; in the ''Domesday Book
Domesday Book () – the Middle English spelling of "Doomsday Book" – is a manuscript record of the "Great Survey" of much of England and parts of Wales completed in 1086 by order of King William I, known as William the Conqueror. The manusc ...
'', the record of the great survey of England completed in 1086, "virtually all" landowners in Cornwall "had English names, making it impossible to be sure who was Cornish and who was English by race".. However, there was a persistent and "continuing differentiation" between the English and Cornish peoples during the Middle Ages, as evidenced by documents such as the 1173 charter
A charter is the grant of authority or rights, stating that the granter formally recognizes the prerogative of the recipient to exercise the rights specified. It is implicit that the granter retains superiority (or sovereignty), and that the re ...
of Truro
Truro (; kw, Truru) is a cathedral city and civil parish in Cornwall, England. It is Cornwall's county town, sole city and centre for administration, leisure and retail trading. Its population was 18,766 in the 2011 census. People of Truro ...
which made explicit mention of both peoples as distinct.
The Earldom of Cornwall passed to various English nobles
Nobility is a social class found in many societies that have an aristocracy. It is normally ranked immediately below royalty. Nobility has often been an estate of the realm with many exclusive functions and characteristics. The character ...
throughout the High Middle Ages
The High Middle Ages, or High Medieval Period, was the periodization, period of European history that lasted from AD 1000 to 1300. The High Middle Ages were preceded by the Early Middle Ages and were followed by the Late Middle Ages, which ended ...
, but in 1337 the earldom was given the status of a duchy
A duchy, also called a dukedom, is a medieval country, territory, fief, or domain ruled by a duke or duchess, a ruler hierarchically second to the king or queen in Western European tradition.
There once existed an important difference between ...
, and Edward, the Black Prince
Edward of Woodstock, known to history as the Black Prince (15 June 1330 – 8 June 1376), was the eldest son of King Edward III of England, and the heir apparent to the English throne. He died before his father and so his son, Richard II, suc ...
, the first son and heir of King Edward III of England
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring ...
, became the first Duke of Cornwall
Duke of Cornwall is a title in the Peerage of England, traditionally held by the eldest son of the reigning British monarch, previously the English monarch. The duchy of Cornwall was the first duchy created in England and was established by a r ...
as a means for the prince to raise his own capital. Large parts of Cornwall were owned by Edward, 1st Duke of Cornwall, and successive English Dukes of Cornwall became the largest landowners in Cornwall; The monarchy of England established two special administrative institutions in Cornwall, the first being the Duchy of Cornwall
The Duchy of Cornwall ( kw, Duketh Kernow) is one of two royal duchies in England, the other being the Duchy of Lancaster. The eldest son of the reigning British monarch obtains possession of the duchy and the title of 'Duke of Cornwall' at ...
(one of only two in the Kingdom of England) and the second being the Cornish Stannary Courts and Parliaments
Stannary law (derived from the la, stannum for tin) is the body of English law that governs tin mining in Devon and Cornwall; although no longer of much practical relevance, the stannary law remains part of the law of the United Kingdom and i ...
(which governed Cornwall's tin industry). These two institutions allowed "ordinary Cornish people to believe that they had been granted a unique constitutional status to reflect their unique cultural identity". However, the Duchy of Cornwall gradually lost its political autonomy from England, a state which became increasingly centralised in London, and by the early-Tudor period
The Tudor period occurred between 1485 and 1603 in England and Wales and includes the Elizabethan period during the reign of Elizabeth I until 1603. The Tudor period coincides with the dynasty of the House of Tudor in England that began wit ...
the Cornish had begun to see themselves as "a conquered people whose culture, liberties, and prosperity had been downgraded by the English". This view was exacerbated in the 1490s by heavy taxation imposed by King Henry VII of England
Henry VII (28 January 1457 – 21 April 1509) was King of England and Lord of Ireland from his seizure of the crown on 22 August 1485 until his death in 1509. He was the first monarch of the House of Tudor.
Henry's mother, Margaret Beauf ...
upon the impoverished Cornish to raise funds for his military campaigns against King James IV of Scotland
James IV (17 March 1473 – 9 September 1513) was King of Scotland from 11 June 1488 until his death at the Battle of Flodden in 1513. He inherited the throne at the age of fifteen on the death of his father, James III, at the Battle of Sau ...
and Perkin Warbeck
Perkin Warbeck ( 1474 – 23 November 1499) was a pretender to the English throne claiming to be Richard of Shrewsbury, Duke of York, who was the second son of Edward IV and one of the so-called " Princes in the Tower". Richard, were he alive ...
,. as well as Henry VII's suspension of the privileges of the Cornish Stannaries. Having provided "more than their fair share of soldiers and sailors" for the conflict in northern England
Northern England, also known as the North of England, the North Country, or simply the North, is the northern area of England. It broadly corresponds to the former borders of Angles, Angle Northumbria, the Anglo-Scandinavian Scandinavian York, K ...
, and feeling aggrieved at "Cornwall's status as England's poorest county", a popular uprising
Rebellion, uprising, or insurrection is a refusal of obedience or order. It refers to the open resistance against the orders of an established authority.
A rebellion originates from a sentiment of indignation and disapproval of a situation and ...
out of Cornwall ensued—the Cornish rebellion of 1497. The rebellion was initially a political march from St Keverne to London led by Thomas Flamank and Michael An Gof
Michael Joseph (died 27 June 1497), better known as Michael An Gof, was one of the leaders of the Cornish rebellion of 1497, along with Thomas Flamank.
Background
The rebels marched on London to protest against King Henry VII's levy of a ...
, motivated by a "mixture of reasons"; to raise money for charity; to celebrate their community; to present their grievances to the Parliament of England
The Parliament of England was the legislature of the Kingdom of England from the 13th century until 1707 when it was replaced by the Parliament of Great Britain. Parliament evolved from the great council of bishops and peers that advise ...
, but gathered pace across the West Country
The West Country (occasionally Westcountry) is a loosely defined area of South West England, usually taken to include all, some, or parts of the counties of Cornwall, Devon, Dorset, Somerset, Bristol, and, less commonly, Wiltshire, Glouc ...
as a revolt against the king.
Middle English
Middle English (abbreviated to ME) is a form of the English language that was spoken after the Norman conquest of 1066, until the late 15th century. The English language underwent distinct variations and developments following the Old Englis ...
began to be adopted as a common language of the Cornish people. As late as 1542 Andrew Boorde
Andrew Boorde (or Borde) (''c.'' 1490April 1549) was an English traveller, physician and writer.
Life
Born at Boords Hill, Holms Dale, Sussex, he was educated at the University of Oxford, and was admitted a member of the Carthusian order whil ...
, an English traveller, physician and writer, wrote that in Cornwall there were two languages, "Cornysshe" and "Englysshe", but that "there may be many men and women" in Cornwall who could not understand English. While the Norman language
Norman or Norman French (, french: Normand, Guernésiais: , Jèrriais: ) is a Romance language which can be classified as one of the Oïl languages along with French, Picard and Walloon. The name "Norman French" is sometimes used to descri ...
was in use by much of the English aristocracy, Cornish was used as a ''lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups ...
'', particularly in the remote far west of Cornwall. Many Cornish landed gentry
The landed gentry, or the ''gentry'', is a largely historical British social class of landowners who could live entirely from rental income, or at least had a country estate. While distinct from, and socially below, the British peerage, t ...
chose mottos in the Cornish language for their coat of arms
A coat of arms is a heraldic visual design on an escutcheon (i.e., shield), surcoat, or tabard (the latter two being outer garments). The coat of arms on an escutcheon forms the central element of the full heraldic achievement, which in its ...
, highlighting its socially high status.. However, in 1549 and following the English Reformation
The English Reformation took place in 16th-century England when the Church of England broke away from the authority of the pope and the Catholic Church. These events were part of the wider European Protestant Reformation, a religious and poli ...
, King Edward VI of England
Edward VI (12 October 1537 – 6 July 1553) was King of England and Ireland from 28 January 1547 until his death in 1553. He was crowned on 20 February 1547 at the age of nine. Edward was the son of Henry VIII and Jane Seymour and the first ...
commanded that the Book of Common Prayer
The ''Book of Common Prayer'' (BCP) is the name given to a number of related prayer books used in the Anglican Communion and by other Christian churches historically related to Anglicanism. The original book, published in 1549 in the reign ...
, an Anglican
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of t ...
liturgical text in the English language, should be introduced to all churches in his kingdom, meaning that Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
and Celtic customs and services should be discontinued. The Prayer Book Rebellion
The Prayer Book Rebellion or Western Rising was a popular revolt in Cornwall and Devon in 1549. In that year, the ''Book of Common Prayer (1549), Book of Common Prayer'', presenting the theology of the English Reformation, was introduced. The ...
was a militant revolt in Cornwall and parts of neighbouring Devon
Devon ( , historically known as Devonshire , ) is a ceremonial and non-metropolitan county in South West England. The most populous settlement in Devon is the city of Plymouth, followed by Devon's county town, the city of Exeter. Devo ...
against the Act of Uniformity 1549
The Act of Uniformity 1549, was an Act of the Parliament of England, passed on 21 January 1549.
It was the logical successor of the Edwardian Injunctions of 1547 and the Sacrament Act of the same year which had taken piecemeal steps towards ...
, which outlawed all languages from church services apart from English,. and is specified as a testament to the affection and loyalty the Cornish people held for the Cornish language. In the rebellion, separate risings occurred simultaneously in Bodmin
Bodmin () is a town and civil parish in Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is situated south-west of Bodmin Moor.
The extent of the civil parish corresponds fairly closely to that of the town so is mostly urban in character. It is borde ...
in Cornwall, and Sampford Courtenay
Sampford Courtenay is a village and civil parish in West Devon in England, most famous for being the place where the Western Rebellion, otherwise known as the Prayerbook rebellion, first started, and where the rebels made their final stand. I ...
in Devon—which would both converge at Exeter
Exeter () is a city in Devon, South West England. It is situated on the River Exe, approximately northeast of Plymouth and southwest of Bristol.
In Roman Britain, Exeter was established as the base of Legio II Augusta under the personal comm ...
, laying siege to the region's largest Protestant city. However, the rebellion was suppressed, thanks largely to the aid of foreign mercenaries in a series of battles in which "hundreds were killed", effectively ending Cornish as the common language of the Cornish people. The Anglicanism of the Reformation served as a vehicle for Anglicisation in Cornwall; Protestantism had a lasting cultural effect upon the Cornish by way of linking Cornwall more closely with England, while lessening political and linguistic ties with the Bretons
The Bretons (; br, Bretoned or ''Vretoned,'' ) are a Celtic ethnic group native to Brittany. They trace much of their heritage to groups of Brittonic speakers who emigrated from southwestern Great Britain, particularly Cornwall and Devon, ...
of Brittany..
The English Civil War
The English Civil War (1642–1651) was a series of civil wars and political machinations between Parliamentarians (" Roundheads") and Royalists led by Charles I (" Cavaliers"), mainly over the manner of England's governance and issues of r ...
, a series of armed conflicts and political machinations between Parliamentarians and Royalists
A royalist supports a particular monarch as head of state for a particular kingdom, or of a particular dynastic claim. In the abstract, this position is royalism. It is distinct from monarchism, which advocates a monarchical system of governm ...
, polarised the populations of England and Wales. However, Cornwall in the English Civil War
Cornwall played a significant role in the English Civil War, being a Royalist enclave in the generally Parliamentarian south-west.
Civil War military actions in Cornwall and the South West
The English Civil War lasted nearly nine years, having ...
was a staunchly Royalist enclave, an "important focus of support for the Royalist cause".. Cornish soldiers were used as scouts and spies during the war, for their language was not understood by English Parliamentarians. The peace that followed the close of the war led to a further shift to the English language by the Cornish people, which encouraged an influx of English people to Cornwall. By the mid-17th century the use of the Cornish language had retreated far enough west to prompt concern and investigation by antiquarian
An antiquarian or antiquary () is an fan (person), aficionado or student of antiquities or things of the past. More specifically, the term is used for those who study history with particular attention to ancient artifact (archaeology), artifac ...
s, such as William Scawen
William Scawen (1600–1689) was one of the pioneers in the revival of the Cornish language. He was a politician who sat in the House of Commons in 1640 and fought for the Royalist cause in the English Civil War.
Life
Scawen was the son of Robe ...
. As the Cornish language diminished the people of Cornwall underwent a process of English enculturation
Enculturation is the process by which people learn the dynamics of their surrounding culture and acquire values and norms appropriate or necessary to that culture and its worldviews.Grusec, Joan E.; Hastings, Paul D. ''Handbook of Socialization: ...
and assimilation
Assimilation may refer to:
Culture
* Cultural assimilation, the process whereby a minority group gradually adapts to the customs and attitudes of the prevailing culture and customs
** Language shift, also known as language assimilation, the prog ...
, becoming "absorbed into the mainstream of English life".
Industry, revival and the modern period
 The
The Industrial Revolution
The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in Great Britain, continental Europe, and the United States, that occurred during the period from around 1760 to about 1820–1840. This transition included going f ...
had a major impact upon the Cornish people. Cornwall's economy was fully integrated into England's,. and mining in Cornwall
Mining in Cornwall and Devon, in the southwest of England, began in the early Bronze Age, around 2150 BC. Tin, and later copper, were the most commonly extracted metals. Some tin mining continued long after the mining of other metals had be ...
, always an important source of employment and stability of the Cornish, experienced a process of industrialisation resulting in 30 per cent of Cornwall's adult population being employed by its mines. During this period, efforts were made by Cornish engineers to design steam engine
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be ...
s with which to power water pumps for Cornish mines thus aiding the extraction of mineral ore. Industrial scale tin and copper mining operations in Cornwall melded Cornish identity with engines and heavy industry,. and Cornwall's leading mining engineer
Mining in the engineering discipline is the extraction of minerals from underneath, open pit, above or on the ground. Mining engineering is associated with many other disciplines, such as mineral processing, exploration, excavation, geology, a ...
, Richard Trevithick
Richard Trevithick (13 April 1771 – 22 April 1833) was a British inventor and mining engineer. The son of a mining captain, and born in the mining heartland of Cornwall, Trevithick was immersed in mining and engineering from an early age. He w ...
, became "as much a part of Cornwall's heritage as any legendary giant from its Celtic past". Trevithick's most significant success was a high-pressure steam engine used to pump water and refuse from mines, but he was also the builder of the first full-scale working railway steam locomotive
A steam locomotive is a locomotive that provides the force to move itself and other vehicles by means of the expansion of steam. It is fuelled by burning combustible material (usually coal, oil or, rarely, wood) to heat water in the loco ...
. On 21 February 1804, the world's first locomotive-hauled railway journey took place as Trevithick's unnamed steam locomotive hauled a train along the tramway of the Penydarren
: ''For Trevithick's Pen-y-darren locomotive, see Richard Trevithick.''
Penydarren is a community and electoral ward in Merthyr Tydfil County Borough in Wales.
Description
The area is most notable for being the site of a 1st-century Roman fort, ...
ironworks, near Merthyr Tydfil
Merthyr Tydfil (; cy, Merthyr Tudful ) is the main town in Merthyr Tydfil County Borough, Wales, administered by Merthyr Tydfil County Borough Council. It is about north of Cardiff. Often called just Merthyr, it is said to be named after T ...
in Wales.
The construction of the Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament on 31 August 1835 and ran ...
during the Victorian era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the period of Queen Victoria's reign, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. The era followed the Georgian period and preceded the Edwa ...
allowed for an influx of tourists to Cornwall from across Great Britain. Well into the Edwardian era
The Edwardian era or Edwardian period of British history spanned the reign of King Edward VII, 1901 to 1910 and is sometimes extended to the start of the First World War. The death of Queen Victoria in January 1901 marked the end of the Vic ...
and interwar period
In the history of the 20th century, the interwar period lasted from 11 November 1918 to 1 September 1939 (20 years, 9 months, 21 days), the end of the First World War to the beginning of the Second World War. The interwar period was relative ...
, Cornwall was branded as a rural retreat, a "primitive land of magic and romance", and as an "earlier incarnation of Englishness, a place more English than an England ravaged by modernity".. Cornwall, the United Kingdom's only region with a subtropical-like climate, became a centre for English tourism, its coastline dominated by resort town
A resort town, often called a resort city or resort destination, is an urban area where tourism or vacationing is the primary component of the local culture and economy. A typical resort town has one or more actual resorts in the surrounding ...
s increasingly composed of bungalow
A bungalow is a small house or cottage that is either single-story or has a second story built into a sloping roof (usually with dormer windows), and may be surrounded by wide verandas.
The first house in England that was classified as a b ...
s and villa
A villa is a type of house that was originally an ancient Roman upper class country house. Since its origins in the Roman villa, the idea and function of a villa have evolved considerably. After the fall of the Roman Republic, villas became ...
s. John Nichols Thom, or Mad Tom, (1799 – 31 May 1838) was a Cornishman self-declared messiah who, in the 19th century led the last battle to be fought on English soil, known as the Battle of Bossenden Wood. While not akin to the Cornish rebellions of the past, he did attract some Cornish support as well as mostly Kentish labourers, although his support was primarily of religious followers.
In the latter half of the 19th century Cornwall experienced rapid deindustrialisation, with the closure of mines in particular considered by the Cornish to be both an economic and cultural disaster. This, coupled with the rise of Romantic nationalism
Romantic nationalism (also national romanticism, organic nationalism, identity nationalism) is the form of nationalism in which the state claims its political legitimacy as an organic consequence of the unity of those it governs. This includes ...
in Europe inspired and influenced a Celtic Revival
The Celtic Revival (also referred to as the Celtic Twilight) is a variety of movements and trends in the 19th, 20th and 21st centuries that see a renewed interest in aspects of Celtic culture. Artists and writers drew on the traditions of Gae ...
in Cornwall, a social, linguistic and artistic movement interested in Cornish medieval ethnology
Ethnology (from the grc-gre, ἔθνος, meaning 'nation') is an academic field that compares and analyzes the characteristics of different peoples and the relationships between them (compare cultural, social, or sociocultural anthropology). ...
. This Revivalist upsurge investigated Cornwall's pre-industrial culture, using the Cornish language as the "principal badge of ornishnationality and ethnic kinship". The first effective revival of Cornish began in 1904 when Henry Jenner
Henry Jenner (8 August 1848 – 8 May 1934) was a British scholar of the Celtic languages, a Cornish cultural activist, and the chief originator of the Cornish language revival.
Jenner was born at St Columb Major on 8 August 1848. He was th ...
, a Celtic language enthusiast, published his book ''Handbook of the Cornish Language''. His orthography
An orthography is a set of conventions for writing a language, including norms of spelling, hyphenation, capitalization, word breaks, emphasis, and punctuation.
Most transnational languages in the modern period have a writing system, and ...
, Unified Cornish
Unified Cornish (UC) (''Kernewek Uny '', ''KU'') is a variety of the Cornish language of the Cornish revival. Developed gradually by Robert Morton Nance during and before the 1930s, it derived its name from its standardisation of the variant spe ...
, was based on Cornish as it was spoken in the 18th century, although his pupil Robert Morton Nance
Robert Morton Nance (1873–1959) was a British writer and leading authority on the Cornish language, a nautical archaeologist, and joint founder of the Old Cornwall Society.
Nance wrote many books and pamphlets on the Cornish language, inclu ...
later steered the revival more towards the Middle Cornish
Cornish (Standard Written Form: or ) , is a Southwestern Brittonic language of the Celtic language family. It is a revived language, having become extinct as a living community language in Cornwall at the end of the 18th century. However, ...
that had been used in the 16th century, before the language became influenced by English.
The visit of King George IV to Scotland
The visit of George IV to Scotland in 1822 was the first visit of a reigning monarch to Scotland in nearly two centuries, the last being by King Charles II for his Scottish coronation in 1651. Government ministers had pressed the King to bring ...
in 1822 reinvigorated Scottish national identity
Scottish national identity is a term referring to the sense of national identity, as embodied in the shared and characteristic culture, languages and traditions, of the Scottish people.
Although the various dialects of Gaelic, the Scots lan ...
, melding it with romanticist notions of tartan
Tartan ( gd, breacan ) is a patterned cloth consisting of criss-crossed, horizontal and vertical bands in multiple colours. Tartans originated in woven wool, but now they are made in other materials. Tartan is particularly associated with Sc ...
, kilt
A kilt ( gd, fèileadh ; Irish: ''féileadh'') is a garment resembling a wrap-around knee-length skirt, made of twill woven worsted wool with heavy pleats at the sides and back and traditionally a tartan pattern. Originating in the Scottish ...
s and the Scottish Highlands
The Highlands ( sco, the Hielands; gd, a’ Ghàidhealtachd , 'the place of the Gaels') is a historical region of Scotland. Culturally, the Highlands and the Lowlands diverged from the Late Middle Ages into the modern period, when Lowland S ...
.. As Pan-Celticism
Pan-Celticism ( ga, Pan-Cheilteachas, Scottish Gaelic: ''Pan-Cheilteachas'', Breton: ''Pan-Keltaidd'', Welsh: ''Pan-Geltaidd,'' Cornish: ''Pan-Keltaidd,'' Manx: ''Pan-Cheltaghys''), also known as Celticism or Celtic nationalism is a politic ...
gathered pace in the early 20th century, Cornishman L. C. R. Duncombe-Jewell and the Cowethas Kelto-Kernuak (a Cornish language interest group) asserted the use of Cornish kilts and tartans
Cornish kilts and tartans are thought to be a modern tradition started in the early to mid 20th century. The first modern kilt was plain black, and other patterns followed. It is documented that a garment known as a ''bracca'' (a reddish checker ...
as a "national dress ... common to all Celtic countries". In 1924 the Federation of Old Cornwall Societies was formed to facilitate, preserve and maintain Celticity in Cornwall, followed by the similar Gorseth Kernow
Gorsedh Kernow (Cornish Gorsedd) is a non-political Cornish organisation, based in Cornwall, United Kingdom, which exists to maintain the national Celtic spirit of Cornwall. It is based on the Welsh-based Gorsedd, which was founded by Iolo Morg ...
in 1928, and the formation of the Cornish nationalist political party Mebyon Kernow in 1951. Increased interest and communication across the Celtic nations
The Celtic nations are a cultural area and collection of geographical regions in Northwestern Europe where the Celtic languages and cultural traits have survived. The term ''nation'' is used in its original sense to mean a people who shar ...
in Celtic languages and culture during the 1960s and 1970s spurred on the popularisation of the Cornish self-government movement. Since devolution
Devolution is the statutory delegation of powers from the central government of a sovereign state to govern at a subnational level, such as a regional or local level. It is a form of administrative decentralization. Devolved territories ...
in Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland, enthusiasts for Cornish culture have pressed for the Cornish language to be taught formally in Cornish schools, while Cornish nationalists have demanded greater political autonomy for Cornwall, for example that it be constituted as the United Kingdom's fifth consistuent country with its own Cornish Assembly
A Cornish Assembly ( kw, Senedh Kernow) is a proposed devolved law-making assembly for Cornwall along the lines of the Scottish Parliament, the Senedd (Welsh Parliament) and the Northern Ireland Assembly in the United Kingdom.
The campaign fo ...
.
Geographic distribution
 The Cornish people are concentrated in Cornwall, but after the
The Cornish people are concentrated in Cornwall, but after the Age of Discovery
The Age of Discovery (or the Age of Exploration), also known as the early modern period, was a period largely overlapping with the Age of Sail, approximately from the 15th century to the 17th century in European history, during which seafa ...
in the early modern period were involved in the British colonisation of the Americas
The British colonization of the Americas was the history of establishment of control, settlement, and colonization of the continents of the Americas by England, Scotland and, after 1707, Great Britain. Colonization efforts began in the late ...
and other transcontinental and transatlantic migrations Transatlantic migration refers to the movement of people across the Atlantic Ocean in order to settle on the continents of North and South America. It usually refers to migrations after Christopher Columbus' voyage to the Americas in 1492. For earli ...
. Initially, the number of migrants was comparatively small, with those who left Cornwall typically settling in North America or else amongst the ports and plantation
A plantation is an agricultural estate, generally centered on a plantation house, meant for farming that specializes in cash crops, usually mainly planted with a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. Th ...
s of the Caribbean
The Caribbean (, ) ( es, El Caribe; french: la Caraïbe; ht, Karayib; nl, De Caraïben) is a region of the Americas that consists of the Caribbean Sea, its islands (some surrounded by the Caribbean Sea and some bordering both the Caribbean ...
.
In the first half of the 19th century, the Cornish people were leaders in tin and copper smelting, while mining in Cornwall
Mining in Cornwall and Devon, in the southwest of England, began in the early Bronze Age, around 2150 BC. Tin, and later copper, were the most commonly extracted metals. Some tin mining continued long after the mining of other metals had be ...
was the people's major occupation. Increased competition from Australia, British Malaya
The term "British Malaya" (; ms, Tanah Melayu British) loosely describes a set of states on the Malay Peninsula and the island of Singapore that were brought under British hegemony or control between the late 18th and the mid-20th century. ...
and Bolivia
, image_flag = Bandera de Bolivia (Estado).svg
, flag_alt = Horizontal tricolor (red, yellow, and green from top to bottom) with the coat of arms of Bolivia in the center
, flag_alt2 = 7 × 7 square p ...
, coupled with the depletion of mineral deposits brought about an economic decline for Cornish mining lasting half a century, and prompting mass human migration
Human migration is the movement of people from one place to another with intentions of settling, permanently or temporarily, at a new location (geographic region). The movement often occurs over long distances and from one country to another (ex ...
from Cornwall. In each decade from 1861 to 1901, "around 20% of the Cornish male population migrated abroad"—three times that of the average of England and Wales
England and Wales () is one of the three legal jurisdictions of the United Kingdom. It covers the constituent countries England and Wales and was formed by the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542. The substantive law of the jurisdiction is En ...
—and totalling over a quarter of a million people lost to emigration between 1841 and 1901. There was a displacement of skilled Cornish engineers, farmers, merchants, miners and tradesmen, but their commercial and occupational expertise, particularly in hard rock mining
Underground hard-rock mining refers to various underground mining techniques used to excavate "hard" minerals, usually those containing metals, such as ore containing gold, silver, iron, copper, zinc, nickel, tin, and lead. It also involves the ...
, was highly valued by the communities they met. Within Great Britain, Cornish families were attracted from Cornwall to North East England
North East England is one of nine official regions of England at the first level of ITL for statistical purposes. The region has three current administrative levels below the region level in the region; combined authority, unitary author ...
—particularly on Teesside
Teesside () is a built-up area around the River Tees in the north of England, split between County Durham and North Yorkshire. The name was initially used as a county borough in the North Riding of Yorkshire.
Historically a hub for heavy manu ...
—to partake in coal mining as a means to earn wealth by using their mining skill. This has resulted in a concentration of Cornish names on and around Teesside that persists into the 21st century.
Large numbers of the 19th century Cornish emigrants eventually returned to Cornwall, whilst the rate of emigration from Cornwall declined after World War I.. However, the global connections of the remaining Cornish diaspora
The Cornish diaspora ( kw, keskar kernewek) consists of Cornish people and their descendants who emigrated from Cornwall, United Kingdom. The diaspora is found within the United Kingdom, and in countries such as the United States, Canada, Austral ...
, which is concentrated in English-speaking countries
The following is a list of English-speaking population by country, including information on both native speakers and second-language speakers.
List
* The European Union is a supranational union composed of 27 member states. The total E ...
such as Australia, Canada, South Africa and the United States, are "very strong". Their outreach has contributed to the international spread of Methodism
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related denominations of Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's b ...
, a movement within Protestant
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
Christianity that was popular with the Cornish people at the time of their mass migration.. "Cousin Jacks" is a nickname for the overseas Cornish, thought to derive from the practice of Cornishmen asking if job vacancies could be filled by their cousin named Jack in Cornwall.
Australia
 From the beginning of Australia's colonial period until after the Second World War, people from the United Kingdom made up a large majority of people coming to Australia, meaning that many Australian-born people can trace their origins to Britain. The Cornish people in particular were actively encouraged to emigrate to Australia following the demise of Cornish mining in the 19th century. A "vigorous recruiting campaign" was launched to encourage the Cornish to aid with
From the beginning of Australia's colonial period until after the Second World War, people from the United Kingdom made up a large majority of people coming to Australia, meaning that many Australian-born people can trace their origins to Britain. The Cornish people in particular were actively encouraged to emigrate to Australia following the demise of Cornish mining in the 19th century. A "vigorous recruiting campaign" was launched to encourage the Cornish to aid with mining in Australia
Mining in Australia has long been a significant primary sector industry and contributor to the Australian economy by providing export income, royalty payments and employment. Historically, mining booms have also encouraged population growth ...
because of their experience and expertise.. Free passage to South Australia in particular was granted to hundreds of Cornish miners and their families, so much so, that a large Cornish community gathered in Australia's Copper Coast
Copper Coast is a region of South Australia situated in Northern Yorke Peninsula and comprising the towns of Wallaroo, Kadina, Moonta, Paskeville and Port Hughes. The area approximately bounded by Wallaroo, Kadina and Moonta is also known a ...
, and South Australia's Yorke Peninsula
The Yorke Peninsula is a peninsula located northwest and west of Adelaide in South Australia, between Spencer Gulf on the west and Gulf St Vincent on the east. The peninsula is separated from Kangaroo Island to the south by Investigator Str ...
became known as "Little Cornwall". It has been estimated between 1837 and 1840, 15 per cent of all assisted migrants to South Australia were Cornish.
Cornish settlement impacted upon social, cultural and religious life throughout the history of South Australia. Cornish identity was embraced strongly in the Yorke Peninsula, but also in the more outlying mining towns of Kapunda and Burra, where Cornish miners constituted a sizeable community.. Methodism
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related denominations of Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's b ...
, was the main form of religious practice for the Cornish. Methodist sensibilities were held with strong conviction by the migrant Cornish in a direct rivalry with Catholic Irish people
The Irish ( ga, Muintir na hÉireann or ''Na hÉireannaigh'') are an ethnic group and nation native to the island of Ireland, who share a common history and culture. There have been humans in Ireland for about 33,000 years, and it has bee ...
in Australia. The Kernewek Lowender
The Kernewek Lowender (officially the Kernewek Lowender Copper Coast Cornish Festival) is a Cornish-themed biennial festival held in the Copper Coast towns of Kadina, Moonta and Wallaroo on Yorke Peninsula, South Australia. 'Kernewek Lowender' ...
is the largest Cornish festival in the world, held in the Kadina, Moonta and Wallaroo
Wallaroo is a common name for several species of moderately large macropods, intermediate in size between the kangaroos and the wallabies. The word "wallaroo" is from the Dharug ''walaru'', and not a portmanteau of the words "kangaroo" and "wal ...
towns on the Yorke Peninsula, which attracts tens of thousands of visitors bi-annually..
Canada
European fishing ventures in and aroundNewfoundland
Newfoundland and Labrador (; french: Terre-Neuve-et-Labrador; frequently abbreviated as NL) is the easternmost province of Canada, in the country's Atlantic region. The province comprises the island of Newfoundland and the continental region ...
during the 16th century were the earliest Cornish activity in what was to become Canada. However, permanent settlement by the Cornish across the Atlantic Ocean was rare until at least the 19th century. The British colonisation of the Americas
The British colonization of the Americas was the history of establishment of control, settlement, and colonization of the continents of the Americas by England, Scotland and, after 1707, Great Britain. Colonization efforts began in the late ...
encouraged additional migration of the Cornish to the Canadas
The Canadas is the collective name for the provinces of Lower Canada and Upper Canada, two historical British colonies in present-day Canada. The two colonies were formed in 1791, when the British Parliament passed the '' Constitutional Act'', ...
, particularly by those who served in Great Britain's Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Fr ...
. The creation of the colony of British North America
British North America comprised the colonial territories of the British Empire in North America from 1783 onwards. English colonisation of North America began in the 16th century in Newfoundland, then further south at Roanoke and Jamestow ...
spurred more people from Cornwall to settle in North America; they were registered as English migrants. Many Cornish (and other West Country) immigrants who had been agricultural labourers settled in an area of what is now South Central Ontario in what were the counties of Northumberland, Durham and Ontario, ranging from the towns of Port Hope and Cobourg in the east, to Whitby in the west and to the north ends of those counties.
Mexico
Mexico
Mexico (Spanish language, Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a List of sovereign states, country in the southern portion of North America. It is borders of Mexico, bordered to the north by the United States; to the so ...
with of mining machinery with which to apply their mining skill and technologies to resuscitate Mexico's ailing silver mining
Silver mining is the extraction of silver from minerals, starting with mining. Because silver is often found in intimate combination with other metals, its extraction requires elaborate technologies. In 2008, ca.25,900 metric tons were consumed ...
industry after the neglect caused by the Mexican War of Independence
The Mexican War of Independence ( es, Guerra de Independencia de México, links=no, 16 September 1810 – 27 September 1821) was an armed conflict and political process resulting in Mexico's independence from Spain. It was not a single, co ...
. Following their sea voyage they attempted to dock at Veracruz
Veracruz (), formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave), is one of the 31 states which, along with Me ...
but were forced away by the Spanish to a beach at Mocambo from where they hauled their machinery through jungle and swamp to Santa Fe. During this haul through the jungle, the Cornishmen and their Mexican helpers fell victim to yellow fever
Yellow fever is a viral disease of typically short duration. In most cases, symptoms include fever, chills, loss of appetite, nausea, muscle pains – particularly in the back – and headaches. Symptoms typically improve within five days. ...
, resulting in 30 Cornish and 100 Mexican fatalities. The fever forced the survivors to abandon their equipment and head inland up into the mountains to Xalapa to try to escape the mosquitos for three months, until the end of the rainy season. Once the rainy season closed the Cornish and Mexican miners continued their "Great Trek" to Mineral del Monte, transporting their machinery to an altitude of above sea level and arriving at their destination on 1 May 1826. Following their arrival, the Cornish community flourished and stayed in central Mexico until the Mexican Revolution
The Mexican Revolution ( es, Revolución Mexicana) was an extended sequence of armed regional conflicts in Mexico from approximately 1910 to 1920. It has been called "the defining event of modern Mexican history". It resulted in the destruction ...
in 1910. Although the Cornish community in Mexico broadly returned to Cornwall, they left a cultural legacy; Cornish pasties, Cornish mining museums and a Cornish Mexican Cultural Society
The Cornish-Mexican Cultural Society ( es, Sociedad Cultural Cornish Mexicana) is a society that tries to advance awareness of the historical and modern links between Cornwall and Mexico’s “Little Cornwall”, the area of Pachuca and Real del ...
are all part of the local heritage and tradition in and around Mineral del Monte.
South Africa
TheWitwatersrand Gold Rush
The Witwatersrand Gold Rush was a gold rush in 1886 that led to the establishment of Johannesburg, South Africa. It was a part of the Mineral Revolution.
Origins
In the modern day province of Mpumalanga, gold miners in the alluvial mines of ...
of 1886 encouraged large numbers of Cornish miners to migrate to the South African Republic
The South African Republic ( nl, Zuid-Afrikaansche Republiek, abbreviated ZAR; af, Suid-Afrikaanse Republiek), also known as the Transvaal Republic, was an independent Boer Republic in Southern Africa which existed from 1852 to 1902, when i ...
.. Although an international gold rush, the Cornish overwhelmingly formed the skilled labour force in the Witwatersrand
The Witwatersrand () (locally the Rand or, less commonly, the Reef) is a , north-facing scarp in South Africa. It consists of a hard, erosion-resistant quartzite metamorphic rock, over which several north-flowing rivers form waterfalls, which ...
, until the outbreak of the Second Boer War
The Second Boer War ( af, Tweede Vryheidsoorlog, , 11 October 189931 May 1902), also known as the Boer War, the Anglo–Boer War, or the South African War, was a conflict fought between the British Empire and the two Boer Republics (the So ...
prompted a retreat.
United States
The discovery oflead ore
Lead is a chemical element with the symbol Pb (from the Latin ) and atomic number 82. It is a heavy metal that is denser than most common materials. Lead is soft and malleable, and also has a relatively low melting point. When freshly cut, l ...
and copper in North America prompted an influx of Cornish miners to the continent, particularly around the Upper Mississippi River
The Upper Mississippi River is the portion of the Mississippi River upstream of St. Louis, Missouri, United States, at the confluence of its main tributary, the Missouri River.
History
In terms of geologic and hydrographic history, the Upper ...
. By the early 19th century Cornish people were present in the Upper Peninsula of Michigan
The Upper Peninsula of Michigan – also known as Upper Michigan or colloquially the U.P. – is the northern and more elevated of the two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; it is separated from the Lower Peninsula by ...
—particularly the mining town of Ishpeming
Ishpeming ( ) is a city in Marquette County in the Upper Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. The population was 6,470 at the 2010 census, less than it was in the 1950s and 1960s when the iron ore mines employed more workers. A statue of a ...
. Additional waves of Cornish migrants followed the California Gold Rush
The California Gold Rush (1848–1855) was a gold rush that began on January 24, 1848, when gold was found by James W. Marshall at Sutter's Mill in Coloma, California. The news of gold brought approximately 300,000 people to California f ...
of the mid-19th century; in the 1890s it was estimated that in California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
's Grass Valley, over 60 per cent of the population was Cornish. It has a tradition of carols
A carol is a festive song, generally religious but not necessarily connected with Christian church worship, and sometimes accompanied by a dance. A caroller (or caroler) is someone who sings carols, and is said to be carolling (or caroling).
T ...
stemming from the Cornish who settled the area as gold miners in the 19th century. The carols have become "the identity of the town", some of the members of the Grass Valley Cornish Carol Choir are descendants of the original Cornish settlers.
Most migratory Cornish to the United States were classified as English or British, meaning that the precise number of Cornish American
Cornish Americans ( kw, Amerikanyon gernewek) are Americans who describe themselves as having Cornish ancestry, an ethnic group of Brittonic Celts native to Cornwall and the Scilly Isles, part of England in the United Kingdom. Although Cornis ...
s is difficult to estimate. The aggregate number of immigrants from Cornwall to the United States before World War I is suggested to be around 100,000.
Culture
Cornish culture
The culture of Cornwall ( kw, Gonisogeth Kernow) forms part of the culture of the United Kingdom, but has distinct customs, traditions and peculiarities. Cornwall has many strong local traditions. After many years of decline, Cornish culture h ...
has been attributed to Cornwall's geographic isolation. Contemporaneously, the underlying notion of Cornish culture is that it is distinct from the culture of England
The culture of England is defined by the cultural norms of England and the English people. Owing to England's influential position within the United Kingdom it can sometimes be difficult to differentiate English culture from the culture of the U ...
, despite its anglicisation
Anglicisation is the process by which a place or person becomes influenced by English culture or British culture, or a process of cultural and/or linguistic change in which something non-English becomes English. It can also refer to the influe ...
, and that it is instead part of a Celtic tradition. According to American academic Paul Robert Magocsi
Paul Robert Magocsi (born January 26, 1945 in Englewood, New Jersey) is an American professor of history, political science, and Chair of Ukrainian Studies at the University of Toronto. He has been with the university since 1980, and became ...
, modern-day Cornish activists have claimed several Victorian era
In the history of the United Kingdom and the British Empire, the Victorian era was the period of Queen Victoria's reign, from 20 June 1837 until her death on 22 January 1901. The era followed the Georgian period and preceded the Edwa ...
inventions including the Cornish engine
A Cornish engine is a type of steam engine developed in Cornwall, England, mainly for pumping water from a mine. It is a form of beam engine that uses steam at a higher pressure than the earlier engines designed by James Watt. The engines we ...
, Christmas carol
A Christmas carol is a carol (a song or hymn) on the theme of Christmas, traditionally sung at Christmas itself or during the surrounding Christmas holiday season. The term noel has sometimes been used, especially for carols of French or ...
s, rugby football
Rugby football is the collective name for the team sports of rugby union and rugby league.
Canadian football and, to a lesser extent, American football were once considered forms of rugby football, but are seldom now referred to as such. The ...
and brass bands as part of this Cornish tradition. Cornish cultural tradition is most strongly associated with the people's most historical occupation, mining, an aspect of Cornish history and culture that has influenced its cuisine, symbols and identity. The Cornish writer C. C. Vyvyan wrote in her 1948 book ''Our Cornwall'': "A man might live and die among us and never gain throughout his allotted span of life one glimpse of the essential Cornwall or the essential Cornishman."
Cornwall has its own tradition of Christian saints, derived from Celtic extraction, that have given rise to localised dedications. Saint Piran
Saint Piran or Pyran ( kw, Peran; la, Piranus), died c. 480,Patrons - The Orthodox Church of Archangel Michael and Holy Piran'' Oecumenical Patriarchate, Archdiocese of Thyateira and Great Britain. Laity Moor, Nr Ponsanooth, Cornwall. TR3 7H ...
is the 5th century Christian abbot, supposedly of Irish origin, who is patron saint of both tin miners and Cornwall. According to popular mythology, Piran, an Irish scholar who studied Christianity in Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome refers to Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of the city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom ...
was to be drowned in the Irish Sea
The Irish Sea or , gv, Y Keayn Yernagh, sco, Erse Sie, gd, Muir Èireann , Ulster-Scots: ''Airish Sea'', cy, Môr Iwerddon . is an extensive body of water that separates the islands of Ireland and Great Britain. It is linked to the C ...
by the High Kings of Ireland, but instead floated across to Perranporth
Perranporth ( kw, Porthperan) is a seaside resort town on the north coast of Cornwall, England, United Kingdom. It is 1 mile east of the St Agnes Heritage Coastline, and around 8 miles south-west of Newquay. Perranporth and its long beach ...
in Cornwall by the will of God to preach the Gospel
Gospel originally meant the Christian message (" the gospel"), but in the 2nd century it came to be used also for the books in which the message was set out. In this sense a gospel can be defined as a loose-knit, episodic narrative of the words a ...
. Saint Piran's Flag
Saint Piran's Flag ( kw, Baner Peran) is the flag of Cornwall. The earliest known description of the flag as the Standard of Cornwall was written in 1838. It is used by some Cornish people as a symbol of their identity.
The flag is attribut ...
, a centred white cross on a black field, was described as the "Standard of Cornwall" in 1838 and was re-introduced by Celtic Revival
The Celtic Revival (also referred to as the Celtic Twilight) is a variety of movements and trends in the 19th, 20th and 21st centuries that see a renewed interest in aspects of Celtic culture. Artists and writers drew on the traditions of Gae ...
ists thereafter as a county flag of Cornwall. It has been seized upon by the Cornish people as a symbol of their identity, displayed on cars and flying from buildings including those of Cornwall Council
Cornwall Council ( kw, Konsel Kernow) is the unitary authority for Cornwall in the United Kingdom, not including the Isles of Scilly, which has its own unitary council. The council, and its predecessor Cornwall County Council, has a tradition ...
. St Piran's Day
Saint Piran's Day ( kw, Gool Peran), or the Feast of Saint Piran, is the national day of Cornwall, held on 5 March every year. The day is named after one of the patron saints of Cornwall, Saint Piran, who is also the patron saint of tin miners ...
is an annual patronal fête
In Britain and some of its former colonies, fêtes are traditional public festivals, held outdoors and organised to raise funds for a charity. They typically include entertainment and the sale of goods and refreshments.
Village fêtes
Village f ...
, and the pre-eminent Cornish festival celebrating Cornish culture and history on 5 March.
Language
 The
The Cornish language
Cornish (Standard Written Form: or ) , is a Southwestern Brittonic language of the Celtic language family. It is a revived language, having become extinct as a living community language in Cornwall at the end of the 18th century. However, ...
is derived from the Brythonic
Brittonic or Brythonic may refer to:
*Common Brittonic, or Brythonic, the Celtic language anciently spoken in Great Britain
*Brittonic languages, a branch of the Celtic languages descended from Common Brittonic
*Britons (Celtic people)
The Br ...
branch of the Insular Celtic languages
Insular Celtic languages are the group of Celtic languages of Brittany, Great Britain, Ireland, and the Isle of Man. All surviving Celtic languages are in the Insular group, including Breton, which is spoken on continental Europe in Brittany ...
. It is closely related to the Breton language
Breton (, ; or in Morbihan) is a Southwestern Brittonic language of the Celtic language family spoken in Brittany, part of modern-day France. It is the only Celtic language still widely in use on the European mainland, albeit as a member of ...
, and to a lesser extent shares commonalities with the Welsh language
Welsh ( or ) is a Celtic language of the Brittonic subgroup that is native to the Welsh people. Welsh is spoken natively in Wales, by some in England, and in Y Wladfa (the Welsh colony in Chubut Province, Argentina). Historically, it h ...
, although they are not mutually intelligible
In linguistics, mutual intelligibility is a relationship between languages or dialects in which speakers of different but related varieties can readily understand each other without prior familiarity or special effort. It is sometimes used as a ...
. The language functioned as a community language in Cornwall until a language shift
Language shift, also known as language transfer or language replacement or language assimilation, is the process whereby a speech community shifts to a different language, usually over an extended period of time. Often, languages that are percei ...
to the English language was completed during the late 18th century. The demise of the Cornish language is attributed to English cultural influence, particularly the political and religious dominance of the English Reformation
The English Reformation took place in 16th-century England when the Church of England broke away from the authority of the pope and the Catholic Church. These events were part of the wider European Protestant Reformation, a religious and poli ...
and the Act of Uniformity 1549
The Act of Uniformity 1549, was an Act of the Parliament of England, passed on 21 January 1549.
It was the logical successor of the Edwardian Injunctions of 1547 and the Sacrament Act of the same year which had taken piecemeal steps towards ...
which outlawed all church services within the Kingdom of England that were not in English. The exact date of the death of using the Cornish language is unclear and disputed, but popularly it is claimed that the last monolingual
Monoglottism (Greek μόνος ''monos'', "alone, solitary", + γλῶττα , "tongue, language") or, more commonly, monolingualism or unilingualism, is the condition of being able to speak only a single language, as opposed to multilingualism. ...
Cornish speaker was Dolly Pentreath
Dorothy Pentreath (16 May 1692 aptised– 26 December 1777) was a fishwife from Mousehole, Cornwall, England. She is the best-known of the last fluent speakers of the Cornish language. She is also often credited as the last known native spea ...
, a Mousehole
Mousehole (; kw, Porthenys) is a village and fishing port in Cornwall, England, UK. It is approximately south of Penzance on the shore of Mount's Bay. The village is in the civil parish of Penzance. An islet called St Clement's Isle lies ...
resident who died in 1777.
The revival of Cornish began in 1904 when Henry Jenner
Henry Jenner (8 August 1848 – 8 May 1934) was a British scholar of the Celtic languages, a Cornish cultural activist, and the chief originator of the Cornish language revival.
Jenner was born at St Columb Major on 8 August 1848. He was th ...
, a Celtic language enthusiast, published his book ''Handbook of the Cornish Language''.. He based his work on Cornish as it was spoken in the 18th century, although his pupil Robert Morton Nance
Robert Morton Nance (1873–1959) was a British writer and leading authority on the Cornish language, a nautical archaeologist, and joint founder of the Old Cornwall Society.
Nance wrote many books and pamphlets on the Cornish language, inclu ...
, with his orthography, Unified Cornish
Unified Cornish (UC) (''Kernewek Uny '', ''KU'') is a variety of the Cornish language of the Cornish revival. Developed gradually by Robert Morton Nance during and before the 1930s, it derived its name from its standardisation of the variant spe ...
, later steered the revival more towards the Middle Cornish
Cornish (Standard Written Form: or ) , is a Southwestern Brittonic language of the Celtic language family. It is a revived language, having become extinct as a living community language in Cornwall at the end of the 18th century. However, ...
that had been used in the 16th century, before the language became more heavily influenced by English.. This set the tone for the next few decades; as the revival gained pace, learners of the language disagreed on which style of Cornish to use, and a number of competing orthographies—Unified Cornish, Unified Cornish Revised, Modern Cornish, Kernewek Kemmyn
Kernewek Kemmyn (Common Cornish or "KK") is a variety of the revived Cornish language.
Kernewek Kemmyn was developed, mainly by Ken George in 1986, based upon George's earlier doctoral thesis on the phonological history of Cornish. It takes muc ...
—were in use by the end of the 20th century. A standard written form
The Standard Written Form or SWF ( kw, Furv Skrifys Savonek) of the Cornish language is an orthography standard that is designed to "provide public bodies and the educational system with a universally acceptable, inclusive, and neutral orthograph ...
was agreed in 2008.
Cornish is a restored and living modern language
A modern language is any human language that is currently in use. The term is used in language education to distinguish between languages which are used for day-to-day communication (such as French and German) and dead classical languages such a ...
, but most of its speakers are enthusiasts, persons who have learned the language through private study. Cornish speakers are geographically dispersed, meaning there is no part of Cornwall where it is spoken as a community language. As of 2009, it is taught in fifty primary schools, although regular broadcast in Cornish is limited to a weekly bilingual programme on BBC Radio Cornwall.. Daily life in Cornwall therefore is conducted in the English language, albeit with some regional peculiarities.
''Legends of the Fall'', a novella by American author Jim Harrison
James Harrison (December 11, 1937 – March 26, 2016) was an American poet, novelist, and essayist. He was a prolific and versatile writer publishing over three dozen books in several genres including poetry, fiction, nonfiction, children’s ...
, detailing the lives of a Cornish American
Cornish Americans ( kw, Amerikanyon gernewek) are Americans who describe themselves as having Cornish ancestry, an ethnic group of Brittonic Celts native to Cornwall and the Scilly Isles, part of England in the United Kingdom. Although Cornis ...
family in the early 20th century, contains several Cornish language terms. These were also included in the Academy Award
The Academy Awards, better known as the Oscars, are awards for artistic and technical merit for the American and international film industry. The awards are regarded by many as the most prestigious, significant awards in the entertainment ind ...
winning film of the same name starring Anthony Hopkins
Sir Philip Anthony Hopkins (born 31 December 1937) is a Welsh actor, director, and producer. One of Britain's most recognisable and prolific actors, he is known for his performances on the screen and stage. Hopkins has received many accolad ...
as Col. William Ludlow and Brad Pitt
William Bradley Pitt (born December 18, 1963) is an American actor and film producer. He is the recipient of various accolades, including two Academy Awards, a British Academy Film Award, two Golden Globe Awards, and a Primetime Emmy Awar ...
as Tristan Ludlow.
Literature and folklore
Early medieval
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
Cornwall was associated with the Matter of Britain
The Matter of Britain is the body of medieval literature and legendary material associated with Great Britain and Brittany and the legendary kings and heroes associated with it, particularly King Arthur. It was one of the three great Weste ...
, a national myth
A national myth is an inspiring narrative or anecdote about a nation's past. Such myths often serve as important national symbols and affirm a set of national values. A national myth may sometimes take the form of a national epic or be incorpor ...
recounting a legendary Celtic history of Brittonic warriors, including King Arthur
King Arthur ( cy, Brenin Arthur, kw, Arthur Gernow, br, Roue Arzhur) is a legendary king of Britain, and a central figure in the medieval literary tradition known as the Matter of Britain.
In the earliest traditions, Arthur appears as ...
.. The Matter of Britain was supported by texts such as the ''Historia Regum Britanniae
''Historia regum Britanniae'' (''The History of the Kings of Britain''), originally called ''De gestis Britonum'' (''On the Deeds of the Britons''), is a pseudohistorical account of British history, written around 1136 by Geoffrey of Monmouth. ...
'', a pseudohistorical
Pseudohistory is a form of pseudoscholarship that attempts to distort or misrepresent the historical record, often by employing methods resembling those used in scholarly historical research. The related term cryptohistory is applied to pseudohi ...
account of the history of the ancient Britons, written in the mid-12th century by Geoffrey of Monmouth
Geoffrey of Monmouth ( la, Galfridus Monemutensis, Galfridus Arturus, cy, Gruffudd ap Arthur, Sieffre o Fynwy; 1095 – 1155) was a British cleric from Monmouth, Wales and one of the major figures in the development of British historiography ...
.. The ''Historia Regum Britanniae'' chronicled the lives of legendary kings of the Britons in a narrative spanning a time of two thousand years, beginning with the Trojans
Trojan or Trojans may refer to:
* Of or from the ancient city of Troy
* Trojan language, the language of the historical Trojans
Arts and entertainment Music
* ''Les Troyens'' ('The Trojans'), an opera by Berlioz, premiered part 1863, part 189 ...
founding the ancient British nation and continuing until the Anglo-Saxon invasion of Britain in the 5th century forced the Celtic Britons to the west coast, namely Wales
Wales ( cy, Cymru ) is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It is bordered by England to the east, the Irish Sea to the north and west, the Celtic Sea to the south west and the Bristol Channel to the south. It had a population in ...
and Cornwall. Although broadly thought of as a work of fiction, Geoffrey of Monmouth's work had a lasting effect upon the identity of the Cornish.. His "historical construct" characterised the ancient Britons as heroes, which later helped Celtic revivalists to redefine Cornishness as an identity closely related to ancient heroic Celtic folklore.
Another strand of Cornish folklore is derived from tales of seafaring pirates
Piracy is an act of robbery or criminal violence by ship or boat-borne attackers upon another ship or a coastal area, typically with the goal of stealing cargo and other valuable goods. Those who conduct acts of piracy are called pirates, v ...
and smugglers
Smuggling is the illegal transportation of objects, substances, information or people, such as out of a house or buildings, into a prison, or across an international border, in violation of applicable laws or other regulations.
There are various ...
who thrived in and around Cornwall from the early modern period through to the 19th century. Cornish pirates exploited both their knowledge of the Cornish coastline as well as its sheltered creeks and hidden anchorages. For many fishing village
A fishing village is a village, usually located near a fishing ground, with an economy based on catching fish and harvesting seafood. The continents and islands around the world have coastlines totalling around 356,000 kilometres (221,000 ...
s, loot and contraband provided by pirates supported a strong and secretive underground economy
A black market, underground economy, or shadow economy is a clandestine market or series of transactions that has some aspect of illegality or is characterized by noncompliance with an institutional set of rules. If the rule defines the ...
in Cornwall.
Legendary creature
A legendary creature (also mythical or mythological creature) is a type of fictional entity, typically a hybrid, that has not been proven and that is described in folklore (including myths and legends), but may be featured in historical accoun ...
s that appear in Cornish folklore include buccas, knockers and piskies.. Tales of these creatures are thought to have developed as supernatural
Supernatural refers to phenomena or entities that are beyond the laws of nature. The term is derived from Medieval Latin , from Latin (above, beyond, or outside of) + (nature) Though the corollary term "nature", has had multiple meanings si ...
explanations for the frequent and deadly cave-in
A cave-in is a collapse of a geologic formation, mine or structure which may occur during mining, tunneling, or steep-walled excavation such as trenching. Geologic structures prone to spontaneous cave-ins include alvar, tsingy and other limes ...
s that occurred during 18th-century Cornish tin mining, or else a creation of the oxygen-starved minds of exhausted miners who returned from the underground.
Performing and visual arts

Celtic cross
The Celtic cross is a form of Christian cross featuring a nimbus or ring that emerged in Ireland, France and Great Britain in the Early Middle Ages. A type of ringed cross, it became widespread through its use in the stone high crosses e ...
es, many dating from between the 7th and 15th centuries, are found in Cornwall and have been used as inspiration in modern and contemporary Cornish visual arts. In the 1780s, John Opie
John Opie (16 May 1761 – 9 April 1807) was an English historical and portrait painter. He painted many great men and women of his day, including members of the British Royal Family, and others who were notable in the artistic and literary ...
was the first Cornish-born painter to gain widespread attention; his work was exhibited at the Royal Academy
The Royal Academy of Arts (RA) is an art institution based in Burlington House on Piccadilly in London. Founded in 1768, it has a unique position as an independent, privately funded institution led by eminent artists and architects. Its pur ...
and he was described by Joshua Reynolds
Sir Joshua Reynolds (16 July 1723 – 23 February 1792) was an English painter, specialising in portraits. John Russell said he was one of the major European painters of the 18th century. He promoted the "Grand Style" in painting which depend ...
as "like Caravaggio
Michelangelo Merisi (Michele Angelo Merigi or Amerighi) da Caravaggio, known as simply Caravaggio (, , ; 29 September 1571 – 18 July 1610), was an Italian painter active in Rome for most of his artistic life. During the final four years of h ...
and Velázquez in one". Artists who appreciated the quality of Cornwall's natural light
Natural Light, sometimes Natty Light, is an American reduced-calorie light lager brewed by Anheuser-Busch since its introduction on July 31, 1977. Its ingredients are listed as water, barley malt, cereal grains, yeast, and hops. One serving con ...
, such as J. M. W. Turner
Joseph Mallord William Turner (23 April 177519 December 1851), known in his time as William Turner, was an English Romantic painter, printmaker and watercolourist. He is known for his expressive colouring, imaginative landscapes and turbul ...
, began to visit, with more following after the opening of the Great Western Railway
The Great Western Railway (GWR) was a British railway company that linked London with the southwest, west and West Midlands of England and most of Wales. It was founded in 1833, received its enabling Act of Parliament on 31 August 1835 and ran ...
, including Whistler and Sickert. Stanhope Forbes
Stanhope Alexander Forbes (18 November 1857 – 2 March 1947) was a British artist and a founding member of the influential Newlyn school of painters. He was often called 'the father of the Newlyn School'.Frank Bramley
Frank Bramley RA (6 May 1857 – 9 August 1915) was an English post-impressionist genre painter of the Newlyn School.
Personal life
Bramley was born in Sibsey, near Boston, in Lincolnshire to Charles Bramley from Fiskerton also in Lincoln ...
settled in Cornwall in the 1880s, establishing the Newlyn School
The Newlyn School was an art colony of artists based in or near Newlyn, a fishing village adjacent to Penzance, on the south coast of Cornwall, from the 1880s until the early twentieth century. The establishment of the Newlyn School was reminis ...
of painting ''en plein air
''En plein air'' (; French for 'outdoors'), or ''plein air'' painting, is the act of painting outdoors.
This method contrasts with studio painting or academic rules that might create a predetermined look. The theory of 'En plein air' painting ...
''. By the 1920s, the ceramicist
Ceramic art is art made from ceramic materials, including clay. It may take forms including artistic pottery, including tableware, tiles, figurines and other sculpture. As one of the plastic arts, ceramic art is one of the visual arts. Wh ...
Bernard Leach
Bernard Howell Leach (5 January 1887 – 6 May 1979), was a British studio potter and art teacher. He is regarded as the "Father of British studio pottery".
Biography
Early years (Japan)
Leach was born in Hong Kong. His mother Eleanor (née ...
was established at St Ives, and the St Ives School
The St Ives School refers to a group of artists living and working in the Cornish town of St Ives.naive
Naivety (also spelled naïvety), naiveness, or naïveté is the state of being naive. It refers to an apparent or actual lack of experience and sophistication, often describing a neglect of pragmatism in favor of moral idealism. A ''naïve'' may ...
painters such as Alfred Wallis
Alfred Wallis (18 August 1855 – 29 August 1942) was a British fisherman and artist known for his port landscapes and shipping scenes painted in a naïve style. Having no artistic training, he began painting at the age of 70, using househol ...
, and involving the work of Ben Nicholson
Benjamin Lauder Nicholson, OM (10 April 1894 – 6 February 1982) was an English painter of abstract compositions (sometimes in low relief), landscape and still-life.
Background and training
Nicholson was born on 10 April 1894 in De ...
, his wife Barbara Hepworth
Dame Jocelyn Barbara Hepworth (10 January 1903 – 20 May 1975) was an English artist and sculptor. Her work exemplifies Modernism and in particular modern sculpture. Along with artists such as Ben Nicholson and Naum Gabo, Hepworth was a lea ...
, Naum Gabo
Naum Gabo, born Naum Neemia Pevsner (23 August 1977) (Hebrew: נחום נחמיה פבזנר), was an influential sculptor, theorist, and key figure in Russia's post-Revolution avant-garde and the subsequent development of twentieth-century scul ...
and Patrick Heron.
Religion
Anciently, the religion of the Cornish Britons wasCeltic polytheism
Ancient Celtic religion, commonly known as Celtic paganism, was the religion of the ancient Celtic peoples of Europe. Because the ancient Celts did not have writing, evidence about their religion is gleaned from archaeology, Greco-Roman accounts ...
, a pagan
Paganism (from classical Latin ''pāgānus'' "rural", "rustic", later "civilian") is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions other than Judaism. I ...
, animistic
Animism (from Latin: ' meaning 'breath, spirit, life') is the belief that objects, places, and creatures all possess a distinct spiritual essence. Potentially, animism perceives all things—animals, plants, rocks, rivers, weather systems, h ...
faith, assumed to be led by Druid
A druid was a member of the high-ranking class in ancient Celtic cultures. Druids were religious leaders as well as legal authorities, adjudicators, lorekeepers, medical professionals and political advisors. Druids left no written accounts. Whi ...
s in full or in part. Early Christianity
Early Christianity (up to the First Council of Nicaea in 325) spread from the Levant, across the Roman Empire, and beyond. Originally, this progression was closely connected to already established Jewish centers in the Holy Land and the Jewis ...
is thought to have existed in Cornwall during the 1st century, but limited to individual travellers and visitors, possibly including Priscillian
Priscillian (in Latin: ''Priscillianus''; Gallaecia, - Augusta Treverorum, Gallia Belgica, ) was a wealthy nobleman of Roman Hispania who promoted a strict form of Christian asceticism. He became bishop of Ávila in 380. Certain practices of his f ...
, a Galician theologian who may have been exiled to the Isles of Scilly
The Isles of Scilly (; kw, Syllan, ', or ) is an archipelago off the southwestern tip of Cornwall, England. One of the islands, St Agnes, is the most southerly point in Britain, being over further south than the most southerly point of th ...
. Celtic Christianity
Celtic Christianity ( kw, Kristoneth; cy, Cristnogaeth; gd, Crìosdaidheachd; gv, Credjue Creestee/Creestiaght; ga, Críostaíocht/Críostúlacht; br, Kristeniezh; gl, Cristianismo celta) is a form of Christianity that was common, or held ...
was introduced to Cornwall in the year 520 by Saint Petroc
Saint Petroc or Petrock ( lat-med, Petrocus; cy, Pedrog; french: link=no, Perreux; ) was a British prince and Christian saint.
Probably born in South Wales, he primarily ministered to the Britons of Devon (Dewnans) and Cornwall (Kernow) then ...
, a Brython from the kingdom of Glywysing
Glywysing was, from the sub-Roman period to the Early Middle Ages, a petty kingdom in south-east Wales. Its people were descended from the Iron Age tribe of the Silures, and frequently in union with Gwent, merging to form Morgannwg.
Name and ...
, and other missionaries from Wales, as well as by Gaelic
Gaelic is an adjective that means "pertaining to the Gaels". As a noun it refers to the group of languages spoken by the Gaels, or to any one of the languages individually. Gaelic languages are spoken in Ireland, Scotland, the Isle of Man, an ...
monks and holy women from Ireland; this "formative period" has left a legacy of granite high cross
A high cross or standing cross ( ga, cros ard / ardchros, gd, crois àrd / àrd-chrois, cy, croes uchel / croes eglwysig) is a free-standing Christian cross made of stone and often richly decorated. There was a unique Early Medieval tradit ...
monuments throughout Cornwall. Dedications to many different Cornish saints can also be traced to this period. In the Middle Ages, Roman Catholicism was dominant in Cornwall, and even in the 17th century the Cornish were "fervently Roman Catholic", slow to accept the Protestant Reformation
The Reformation (alternatively named the Protestant Reformation or the European Reformation) was a major movement within Western Christianity in 16th-century Europe that posed a religious and political challenge to the Catholic Church and i ...
, according to some scholars.. The adoption of Anglicanism
Anglicanism is a Western Christian tradition that has developed from the practices, liturgy, and identity of the Church of England following the English Reformation, in the context of the Protestant Reformation in Europe. It is one of t ...
was, eventually, near-universal in Cornwall and facilitated the anglicisation
Anglicisation is the process by which a place or person becomes influenced by English culture or British culture, or a process of cultural and/or linguistic change in which something non-English becomes English. It can also refer to the influe ...
of the Cornish people. A variety of dissenting congregations such as the Quakers and Baptists were to be found in certain districts. Through a combination of tours of Cornwall by John Wesley
John Wesley (; 2 March 1791) was an English cleric, theologian, and evangelist who was a leader of a revival movement within the Church of England known as Methodism. The societies he founded became the dominant form of the independent Meth ...
, rural isolation and compatibility with Cornish tastes and sensibilities, Methodism
Methodism, also called the Methodist movement, is a group of historically related denominations of Protestant Christianity whose origins, doctrine and practice derive from the life and teachings of John Wesley. George Whitefield and John's b ...
, an evangelical revival movement within the Church of England
The Church of England (C of E) is the established Christian church in England and the mother church of the international Anglican Communion. It traces its history to the Christian church recorded as existing in the Roman province of Brit ...
, became the form of Christianity practised by the majority of the population all over Cornwall during the 19th century. During this time other kinds of Methodist churches appeared such as the Bible Christians and there were also Evangelical and Anglo-Catholic
Anglo-Catholicism comprises beliefs and practices that emphasise the Catholic heritage and identity of the various Anglican churches.
The term was coined in the early 19th century, although movements emphasising the Catholic nature of Anglica ...
revivals within the Church of England.
Cuisine
 Cornish cuisine is a regional variety of
Cornish cuisine is a regional variety of British cuisine
British cuisine is the specific set of cooking traditions and practices associated with the United Kingdom. Historically, British cuisine meant "unfussy dishes made with quality local ingredients, matched with simple sauces to accentuate flavou ...
, strongly rooted in a tradition of using local produce,. which is used to create relatively simple dishes.. Most prominent in Cornish cuisine is the pasty
A pasty () is a British baked pastry, a traditional variety of which is particularly associated with Cornwall, South West England, but has spread all over the British Isles. It is made by placing an uncooked filling, typically meat and vegetab ...
(sometimes known as the Cornish pasty) made from diced beef, potato, onion and swede (commonly called 'turnip' by the Cornish), enclosed within a pastry crust and then baked.. One idea of its origins suggests that it evolved as a portable lunch for Cornish miners, the crust serving as a disposable handle that could be held by a miner's hand without soiling the filling. Fish was an important element of the Cornish diet, but international commercial fishing
Commercial fishing is the activity of catching fish and other seafood for commercial profit, mostly from wild fisheries. It provides a large quantity of food to many countries around the world, but those who practice it as an industry must oft ...
was also well established by the 16th century, and tons of pilchards
"Sardine" and "pilchard" are common names for various species of small, oily forage fish in the herring family Clupeidae. The term "sardine" was first used in English during the early 15th century, a folk etymology says it comes from the Ital ...
were exported from Cornwall to France, Italy and Spain every year. Stargazy pie
Stargazy pie (sometimes called starrey gazey pie, stargazey pie and other variants) is a Cornish dish made of baked pilchards (sardines), along with eggs and potatoes, covered with a pastry crust. Although there are a few variations using othe ...
is an occasional festive Cornish dish with the heads of fish standing on their tails, originally pilchards
"Sardine" and "pilchard" are common names for various species of small, oily forage fish in the herring family Clupeidae. The term "sardine" was first used in English during the early 15th century, a folk etymology says it comes from the Ital ...
, piercing a pastry crust. The saffron bun
__NOTOC__
A saffron bun, Cornish tea treat bun or revel bun, is a rich, spiced yeast-leavened sweet bun that is flavoured with saffron and contains dried fruit including currants and raisins similar to a teacake. The main ingredients are plai ...
, also known as the tea treat bun, is a sweet bread with its origins in Cornwall.
Sport
 With its comparatively small, rural population, major contribution by the Cornish to national sport in the United Kingdom has been limited.. There are no teams affiliated to the Cornwall County Football Association that play in the Football League of
With its comparatively small, rural population, major contribution by the Cornish to national sport in the United Kingdom has been limited.. There are no teams affiliated to the Cornwall County Football Association that play in the Football League of England and Wales
England and Wales () is one of the three legal jurisdictions of the United Kingdom. It covers the constituent countries England and Wales and was formed by the Laws in Wales Acts 1535 and 1542. The substantive law of the jurisdiction is En ...
, and the Cornwall County Cricket Club plays as one of the minor counties of English cricket. Viewed as an "important identifier of ethnic affiliation", rugby union
Rugby union, commonly known simply as rugby, is a close-contact team sport that originated at Rugby School in the first half of the 19th century. One of the two codes of rugby football, it is based on running with the ball in hand. In it ...
has become a sport strongly tied with notions of Cornishness,. and since the 20th century, rugby union in Cornwall has emerged as one of the most popular spectator and team sports in Cornwall, with professional Cornish rugby footballers being described as a "formidable force", "naturally independent, both in thought and deed, yet paradoxically staunch English patriots whose top players have represented England with pride and passion". In 1985, sports journalist Alan Gibson made a direct connection between love of rugby in Cornwall and the ancient parish games of hurling and wrestling that existed for centuries before rugby officially began.
Cornish wrestling (also known as Wrasslin') is a regional, folk style of grappling or martial arts. The Cornwall County Wrestling Association was formed in 1923, to standardise the rules of the sport and to promote Cornish wrestling throughout Cornwall and the world. Together with Cornish hurling (a localised form of medieval football), Wrasslin' has been promoted as a distinctly Celtic game, tied closely with Cornish identity.
Surfing was popularised in Cornwall during the late 20th century, and has since become readily associated with Cornishness. The waves around the Cornish coastline are created by low pressure systems from the Atlantic Ocean which unleash powerful swells eastwards creating multiple, excellent surfing conditions in some parts of the coast of Cornwall. Newquay, one of Britain's "premier surfing towns", regularly hosts world championship surfing events.
Institutions and politics

 The politics of Cornwall take place within a wider national political framework of a constitutional monarchy, in which the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, United Kingdom's monarch is head of state and the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom is the head of government, and the supranational framework of the
The politics of Cornwall take place within a wider national political framework of a constitutional monarchy, in which the Monarchy of the United Kingdom, United Kingdom's monarch is head of state and the Prime Minister of the United Kingdom is the head of government, and the supranational framework of the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are located primarily in Europe, Europe. The union has a total area of ...
. Cornish politics are marked by a long tradition of Liberalism.
Important historical institutions were the Duchy of Cornwall
The Duchy of Cornwall ( kw, Duketh Kernow) is one of two royal duchies in England, the other being the Duchy of Lancaster. The eldest son of the reigning British monarch obtains possession of the duchy and the title of 'Duke of Cornwall' at ...
and the Cornish Stannary Courts and Parliaments
Stannary law (derived from the la, stannum for tin) is the body of English law that governs tin mining in Devon and Cornwall; although no longer of much practical relevance, the stannary law remains part of the law of the United Kingdom and i ...
. The Stannary court administered Equity (law), equity, through special laws and legal exemptions, for all matters relating to the tin mines and tin trade in Cornwall. Cornish miners were effectively exempt from the jurisdiction of the law courts at Palace of Westminster, Westminster, except "in such cases as should affect land, life or limb". The ancient privileges of the Stannary Courts and Parliaments were confirmed by successive Royal Charters in the Middle Ages, including those administered by Kings John of England, John, Edward I of England, Edward I and Edward III of England
Edward III (13 November 1312 – 21 June 1377), also known as Edward of Windsor before his accession, was King of England and Lord of Ireland from January 1327 until his death in 1377. He is noted for his military success and for restoring ...
. As the tin mines of Cornwall lost their economic importance during the 18th and 19th centuries, so the Stannary institutions lost political power. The last Stannary parliament was held at Truro
Truro (; kw, Truru) is a cathedral city and civil parish in Cornwall, England. It is Cornwall's county town, sole city and centre for administration, leisure and retail trading. Its population was 18,766 in the 2011 census. People of Truro ...
in 1752, and continued, by adjournments, until 11 September 1753.
As in the rest of Great Britain, the Liberal Party (UK), Liberal Party dominated Cornish politics during the 19th century, although Socialism gained limited support in western Cornwall, and the Labour Party (UK), Labour Party won preference after World War I. Nationalism (or Regionalism (politics), regionalism). in Cornwall traces its roots to the Irish Home Rule bills of the late 19th century, and is represented by the Cornish self-government movement, a political action group that is predominantly organised to promote Cornwall as the national homeland of the Cornish, campaign for devolution
Devolution is the statutory delegation of powers from the central government of a sovereign state to govern at a subnational level, such as a regional or local level. It is a form of administrative decentralization. Devolved territories ...
, and win it the status as a fifth countries of the United Kingdom, country within the UK rather than outright separatism. More "militant" variants of Cornish nationalism however claim that because of historical constitutional peculiarities regarding the constitutional status of Cornwall, status of Cornwall, the law of the European Union does or should not have jurisdiction over Cornwall until Cornish sovereignty is recognised. Popularisation of Cornish nationalism is attributed to a Celtic cultural revival in Cornwall which itself began with a renewed interest in the Cornish language in the 1920s.. The revival of the Cornish language encouraged a parallel revival of Celtic traditions, which by the 1970s had spurred on Cornish nationalism. The United Kingdom's entry into the European Economic Community in 1973 prompted claims that the Cornish should be granted their own devolved
Devolution is the statutory delegation of powers from the central government of a sovereign state to govern at a subnational level, such as a regional or local level. It is a form of administrative decentralization. Devolved territories ...
national assembly—the Cornish Assembly
A Cornish Assembly ( kw, Senedh Kernow) is a proposed devolved law-making assembly for Cornwall along the lines of the Scottish Parliament, the Senedd (Welsh Parliament) and the Northern Ireland Assembly in the United Kingdom.
The campaign fo ...
—comparable to that of the National Assembly for Wales. Mebyon Kernow is a Left-wing politics, left-wing political party based in Cornwall, founded in 1951. Its main objective is attaining greater autonomy for Cornwall through the establishment of a legislative Cornish Assembly. As at 2009 Mebyon Kernow has no Members of Parliament elected to the House of Commons of the United Kingdom, and in the 2009 United Kingdom local elections received 4 per cent of votes to elect councillors to Cornwall Council
Cornwall Council ( kw, Konsel Kernow) is the unitary authority for Cornwall in the United Kingdom, not including the Isles of Scilly, which has its own unitary council. The council, and its predecessor Cornwall County Council, has a tradition ...
, behind the Conservative Party (UK), Conservative Party (34 per cent), Liberal Democrats (UK), Liberal Democrats (28 per cent), and Independent (politician), Independents (23 per cent) Since the 2009 structural changes to local government in England, Cornwall Council has been a Unitary authorities of England, unitary authority, serving as the sole executive, Deliberation, deliberative, and legislative body responsible for local policy, setting council tax, and allocating budgets.
Following the Cornwall Council election in May 2013, the council remained as "no overall control", with the Independent politicians becoming the largest grouping on the council through a modest gain of councillors from the previous election. The Liberal Democrats remained the second largest party after losing 2 councillors and the Conservatives slipped to third after losing over a third of their councillors. The Labour Party (+8), UKIP (+6), and the Green Party (+1) all gained seats, with UKIP and the Greens entering Cornwall Council for the first time. Mebyon Kernow had 6 councilors prior to the election, having added 2 since the 2009 election, their total following the election was reduced to 4.
In the 2015 United Kingdom general election, 2015 general election all Cornish seats were won by the Conservatives. This was repeated in the 2017 United Kingdom general election, 2017 general election.
In the UK's 2021 census plans, a "tickbox" for claiming "Cornish" as a national minority status has not been implemented and is under debate. Since Cornwall was officially given "official national minority status" in 2014, the Cornwall Council's Party Leaders have submitted a letter to the cabinet office of Chloe Smith for the Minister of State. In the coming weeks, Parliament is set to debate The Census Order. If enough Members of Parliament side with the Cornish people and stand in solidarity with their cause, a box to select a "Cornish" identity could be added—reaffirming the official identity they established 6 years prior.
See also
* List of people from Cornwall * List of topics related to CornwallReferences
Citations
Sources
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * (reissue of the work first published in 1878, ''Tourists' guide to Cornwall and the Scilly Isles: containing succinct information concerning all the principal places and objects of interest in the county''; 7 editions, Seventh ed. Revised by H. Michell Whitley, 1895) * * * *Further reading
*Miles, Sibella ''Original Cornish Ballads: chiefly founded on stories humorously told by Mr. Tregellas in his popular lectures on "Peculiarities" : to which are appended some drafts of kindred character from the portfolio of the editress: the whole prefixed by an introductory essay on the peculiar characteristics of the Cornish peasantry''. London: Simpkin, Marshall, 1846.External links
www.cornwall.gov.uk
the website of
Cornwall Council
Cornwall Council ( kw, Konsel Kernow) is the unitary authority for Cornwall in the United Kingdom, not including the Isles of Scilly, which has its own unitary council. The council, and its predecessor Cornwall County Council, has a tradition ...
www.cornishculture.co.uk
an online guide to Cornish Celtic culture {{Good article Cornish people, Brythonic Celts Celtic ethnic groups Ethnic groups in the United Kingdom