Copperplate engraving on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Intaglio ( ; ) is the family of
Intaglio ( ; ) is the family of
 Intaglio ( ; ) is the family of
Intaglio ( ; ) is the family of printing
Printing is a process for mass reproducing text and images using a master form or template. The earliest non-paper products involving printing include cylinder seals and objects such as the Cyrus Cylinder and the Cylinders of Nabonidus. The ...
and printmaking techniques in which the image is incised into a surface and the incised line or sunken area holds the ink. It is the direct opposite of a relief print
Relief printing is a family of printing methods where a printing block, plate or matrix, which has had ink applied to its non-recessed surface, is brought into contact with paper. The non-recessed surface will leave ink on the paper, whereas t ...
where the parts of the matrix that make the image stand ''above'' the main surface.
Normally, copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
or in recent times zinc
Zinc is a chemical element with the symbol Zn and atomic number 30. Zinc is a slightly brittle metal at room temperature and has a shiny-greyish appearance when oxidation is removed. It is the first element in group 12 (IIB) of the periodi ...
sheets, called plates, are used as a surface or matrix, and the incisions are created by etching
Etching is traditionally the process of using strong acid or mordant to cut into the unprotected parts of a metal surface to create a design in intaglio (incised) in the metal. In modern manufacturing, other chemicals may be used on other types ...
, engraving
Engraving is the practice of incising a design onto a hard, usually flat surface by cutting grooves into it with a burin. The result may be a decorated object in itself, as when silver, gold, steel, or glass are engraved, or may provide an in ...
, drypoint
Drypoint is a printmaking technique of the intaglio family, in which an image is incised into a plate (or "matrix") with a hard-pointed "needle" of sharp metal or diamond point. In principle, the method is practically identical to engraving. The ...
, aquatint
Aquatint is an intaglio (printmaking), intaglio printmaking technique, a variant of etching that produces areas of tone rather than lines. For this reason it has mostly been used in conjunction with etching, to give both lines and shaded tone. ...
or mezzotint
Mezzotint is a monochrome printmaking process of the '' intaglio'' family. It was the first printing process that yielded half-tones without using line- or dot-based techniques like hatching, cross-hatching or stipple. Mezzotint achieves tonal ...
, often in combination. Collagraphs may also be printed as intaglio plates.
After the decline of the main relief technique of woodcut
Woodcut is a relief printing technique in printmaking. An artist carves an image into the surface of a block of wood—typically with gouges—leaving the printing parts level with the surface while removing the non-printing parts. Areas tha ...
around 1550, the intaglio techniques dominated both artistic printmaking as well as most types of illustration and popular print
Popular prints is a term for printed images of generally low artistic quality which were sold cheaply in Europe and later the New World from the 15th to 18th centuries, often with text as well as images. They were some of the earliest examples of ...
s until the mid 19th century.
Process
In intaglio printing, the lines to be printed are cut into a metal (e.g. copper) plate by means either of a cutting tool called a burin, held in the hand – in which case the process is called ''engraving''; or through the corrosive action of acid – in which case the process is known as ''etching''. In etching, for example, the plate is pre-covered in a thin, acid-resistant resin or wax ''ground''. Using etching needles or burins, the artist or writer (etcher) engraves their image (therefore to be only where the plate beneath is exposed). The plate's ground side is then dipped into acid, or the acid poured onto it. The acid bites into the surface of the plate where it was exposed. Biting is a printmaking term to describe the acid's etching, or incising, of the image; its duration depends on the acid strength, metal's reactivity, temperature, air pressure and the depth desired. After the plate is sufficiently bitten it is removed from the acid bath, the ground is removed gently and the plate is usually dried or cleaned. To print an intaglio plate, ink or inks are painted, wiped and/or dabbed into the recessed lines (such as with brushes/rubber gloves/rollers). The plate is then rubbed with tarlatan cloth to remove most of its waste (surface ink) and a final smooth wipe is often done with newspaper or old public phone book pages, leaving it in the incisions. Dampened paper will usually be fed against the plate, covered by a blanket, so when pressed by rolling press it is squeezed into the plate's ink-filled grooves with uniform very high pressure. The blanket is then lifted, revealing the paper and printed image. The final stages repeat for each copy needed.History
Intaglio printmaking emerged in Europe well after thewoodcut
Woodcut is a relief printing technique in printmaking. An artist carves an image into the surface of a block of wood—typically with gouges—leaving the printing parts level with the surface while removing the non-printing parts. Areas tha ...
print, with the earliest known surviving examples being undated designs for playing cards made in Germany, using drypoint
Drypoint is a printmaking technique of the intaglio family, in which an image is incised into a plate (or "matrix") with a hard-pointed "needle" of sharp metal or diamond point. In principle, the method is practically identical to engraving. The ...
technique, probably in the late 1430s.Harrison, Charles (2006). "The printed picture in the Renaissance." In Kim Woods (Ed.), ''Making Renaissance Art''. New Haven: Yale University Press. p. 219. Engraving had been used by goldsmith
A goldsmith is a metalworker who specializes in working with gold and other precious metals. Nowadays they mainly specialize in jewelry-making but historically, goldsmiths have also made silverware, platters, goblets, decorative and servicea ...
s to decorate metalwork, including armor, musical instruments and religious objects since ancient times, and the niello
Niello is a black mixture, usually of sulphur, copper, silver, and lead, used as an inlay on engraved or etched metal, especially silver. It is added as a powder or paste, then fired until it melts or at least softens, and flows or is pushed ...
technique, which involved rubbing an alloy into the lines to give a contrasting color, also goes back to late antiquity. Scholars and practitioners of printmaking have suggested that the idea of making prints from engraved plates may well have originated with goldsmiths' practices of taking an impression on paper of a design engraved on an object, in order to keep a record of their work, or to check the quality.
Martin Schongauer
Martin Schongauer (c. 1450–53, Colmar – 2 February 1491, Breisach), also known as Martin Schön ("Martin beautiful") or Hübsch Martin ("pretty Martin") by his contemporaries, was an Alsatian engraver and painter. He was the most important ...
was one of the most significant early artists in the engraving technique, and Albrecht Dürer is one of the most famous intaglio artists. Italian and Dutch engraving began slightly after the Germans, but were well developed by 1500. Drypoint
Drypoint is a printmaking technique of the intaglio family, in which an image is incised into a plate (or "matrix") with a hard-pointed "needle" of sharp metal or diamond point. In principle, the method is practically identical to engraving. The ...
and etching were also German inventions of the fifteenth century, probably by the Housebook Master
Master of the Housebook and Master of the Amsterdam Cabinet are two names used for an engraver and painter working in South Germany in the last quarter of the 15th century. He is apparently the first artist to use drypoint, a form of engraving, ...
and Daniel Hopfer Daniel Hopfer (circa 1470 in Kaufbeuren – 1536 in Augsburg) was a German artist who is widely believed to have been the first to use etching in printmaking, at the end of the fifteenth century. He also worked in woodcut. Although his etchings wer ...
respectively. In the 15th century, woodcut and engraving served to produce both religious and secular imagery. One of the most popular secular uses of engraver's art was in the production of playing cards, a diversion enjoyed by the aristocracy and the common people.
In the nineteenth century, Viennese printer Karel Klíč
Karel Václav Klíč (sometimes written Karl Klietsch, 30 May 1841, Hostinné – 16 November 1926, Vienna) was a Czech painter, photographer, early comics artist, caricaturist, lithographer and illustrator. He was one of the inventors of photogr ...
introduced a combined intaglio and photographic process. Photogravure
Photogravure (in French ''héliogravure'') is a process for printing photographs, also sometimes used for reproductive intaglio printmaking. It is a photo-mechanical process whereby a copper plate is grained (adding a pattern to the plate) and ...
retained the smooth continuous tones of photography but was printed using a chemically etched copper plate. This permitted a photographic image to be printed on regular paper, for inclusion in books or albums.
In the 1940s and 1950s the Italian security printer Gualtiero Giori brought intaglio printing into the era of high-technology by developing the first ever six-colour intaglio printing press, designed to print banknotes which combined more artistic possibilities with greater security.K. M. M. de Leeuw, Jan Bergstra, ''The History of Information Security: a Comprehensive Handbook'' (2007), p. 214
Current usage
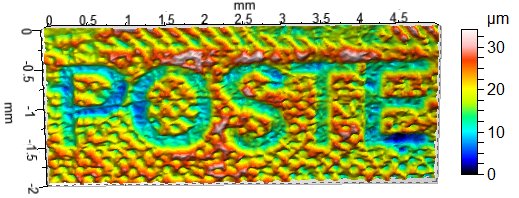
Today, intaglio engraving is used largely for banknotes, passports and some postage stamps. If the letters are cut into the surface of the engraving plate, then, on the print, they stand slightly proud (see image above). The appearance of engraving is sometimes mimicked for items such as wedding invitations, by skeuomorphic embossment of lettering printed by another process (such aslithography
Lithography () is a planographic method of printing originally based on the immiscibility of oil and water. The printing is from a stone (lithographic limestone) or a metal plate with a smooth surface. It was invented in 1796 by the German a ...
or offset).
Intaglio artists
*William Blake
William Blake (28 November 1757 – 12 August 1827) was an English poet, painter, and printmaker. Largely unrecognised during his life, Blake is now considered a seminal figure in the history of the poetry and visual art of the Romantic Age. ...
* Albrecht Dürer
* M. C. Escher
* Helen Frank
* Francisco Goya
Francisco José de Goya y Lucientes (; ; 30 March 174616 April 1828) was a Spanish romantic painter and printmaker. He is considered the most important Spanish artist of the late 18th and early 19th centuries. His paintings, drawings, and e ...
* Michael Hafftka
* Stanley William Hayter
* Edward Hopper
Edward Hopper (July 22, 1882 – May 15, 1967) was an American realist painter and printmaker. While he is widely known for his oil paintings, he was equally proficient as a watercolorist and printmaker in etching.
Hopper created subdued drama ...
* Jasper Johns
Jasper Johns (born May 15, 1930) is an American painter, sculptor, and printmaker whose work is associated with abstract expressionism, Neo-Dada, and pop art. He is well known for his depictions of the American flag and other US-related top ...
* William Kentridge
William Kentridge (born 28 April 1955) is a South African artist best known for his prints, drawings, and animated films, especially noted for a sequence of hand-drawn animated films he produced during the 1990s. The latter are constructed by ...
* Max Klinger
* Käthe Kollwitz
* Mauricio Lasansky
* Martin Lewis
* Lucas van Leyden
* Cheryl Anne Lorance
* Malcolm Myers
* Bruce Onobrakpeya
* Lothar Osterburg
* Gabor Peterdi
Gabor Peterdi (1915 in Pestújhely, Hungary – 2001 in Stamford, Connecticut) was a Hungarian-American painter and printmaker who immigrated to the United States in 1939.
* Gene Kloss
* Pablo Picasso
Pablo Ruiz Picasso (25 October 1881 – 8 April 1973) was a Spanish painter, sculptor, printmaker, ceramicist and Scenic design, theatre designer who spent most of his adult life in France. One of the most influential artists of the 20th ce ...
* Anton Pieck
Anton Franciscus Pieck (19 April 1895 – 24 November 1987) was a Dutch painter, artist and graphic artist. Hiworksare noted for their nostalgic or fairy tale-like character and are widely popular, appearing regularly on cards and calendars. He i ...
* Krishna Reddy
* Rembrandt
* Félicien Rops
Félicien Victor Joseph Rops (7 July 1833 – 23 August 1898) was a Belgian artist associated with Symbolism and the Parisian Fin-de Siecle. He was a painter, illustrator, caricaturist and a prolific and innovative print maker, particularly in ...
* Ludwig von Siegen
Ludwig von Siegen (c. mars 1609 Cologne – c. 1680 Wolfenbüttel, Germany) was a German soldier and amateur engraver, who invented the printmaking technique of mezzotint, a printing-process reliant on mechanical pressure used to print more co ...
* Guillermo Silva Santamaria
* Richard Spare
* Diane Victor
* James Abbott McNeill Whistler
James Abbott McNeill Whistler (; July 10, 1834July 17, 1903) was an American painter active during the American Gilded Age and based primarily in the United Kingdom. He eschewed sentimentality and moral allusion in painting and was a leading pr ...
See also
* History of printing *Rotogravure
Rotogravure (or gravure for short) is a type of intaglio printing process, which involves engraving the image onto an image carrier. In gravure printing, the image is engraved onto a cylinder because, like offset printing and flexography, it ...
– a type of intaglio printing
* Viscosity printing
References
External links
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Intaglio (Printmaking) Printmaking Printing