Contact lens on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
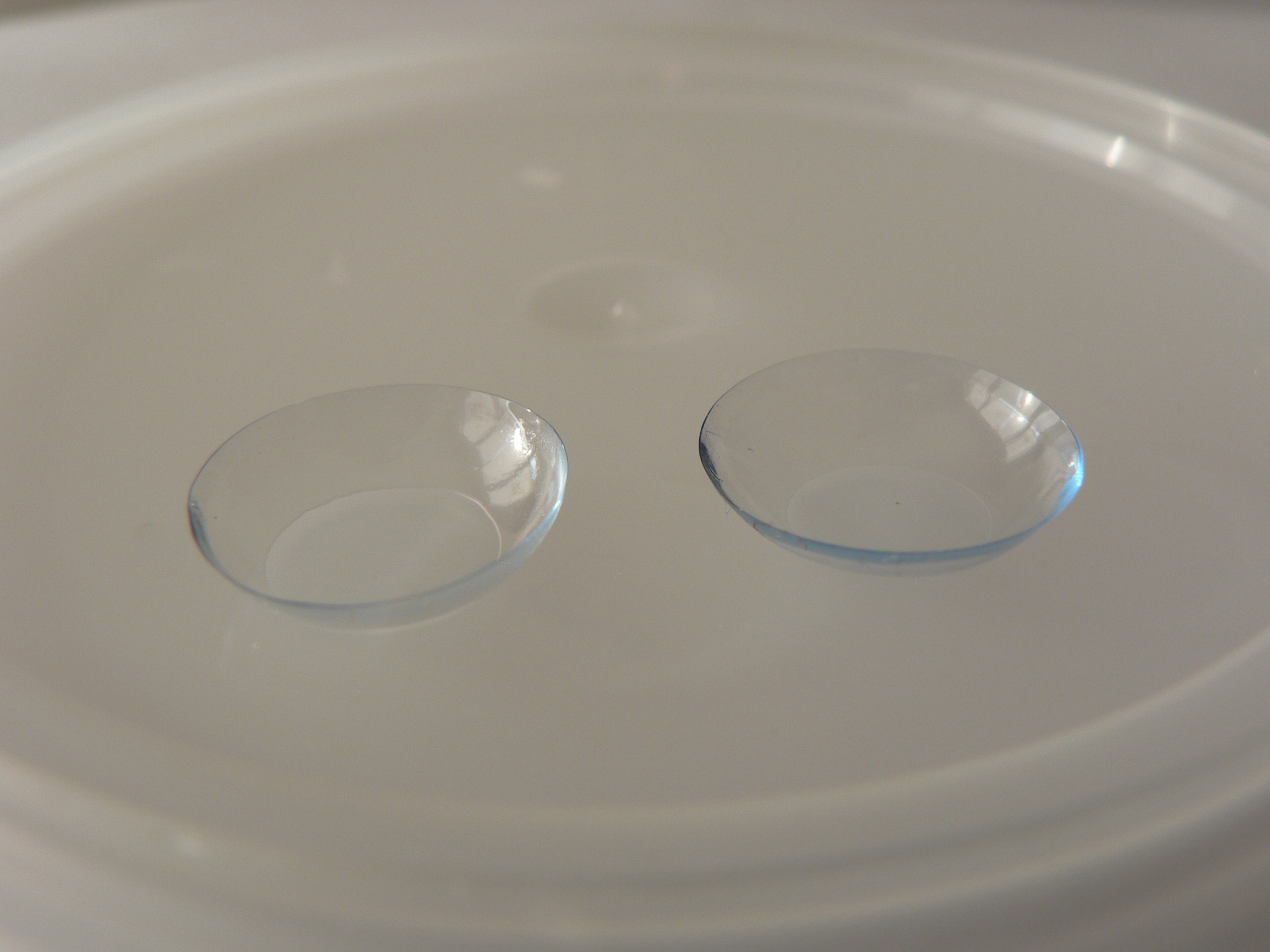 Contact lenses, or simply contacts, are thin lenses placed directly on the surface of the
Contact lenses, or simply contacts, are thin lenses placed directly on the surface of the
"ANNUAL REPORT: Contact Lenses 2010"
January 2011. Multiple analysts estimated that the global market for contact lenses would reach $11.7 billion by 2015. , the average age of contact lens wearers globally was 31 years old, and two-thirds of wearers were female.Morgan, Philip B., et al
"International Contact Lens Prescribing in 2010"
''Contact Lens Spectrum''. October 2011. People choose to wear contact lenses for many reasons. Aesthetics and cosmetics are main motivating factors for people who want to avoid wearing
 Although Louis J. Girard invented a
Although Louis J. Girard invented a
 The principal breakthrough in soft lenses was made by Czech chemists
The principal breakthrough in soft lenses was made by Czech chemists
 A cosmetic contact lens is designed to change the appearance of the eye. These lenses may also correct
A cosmetic contact lens is designed to change the appearance of the eye. These lenses may also correct
 A
A
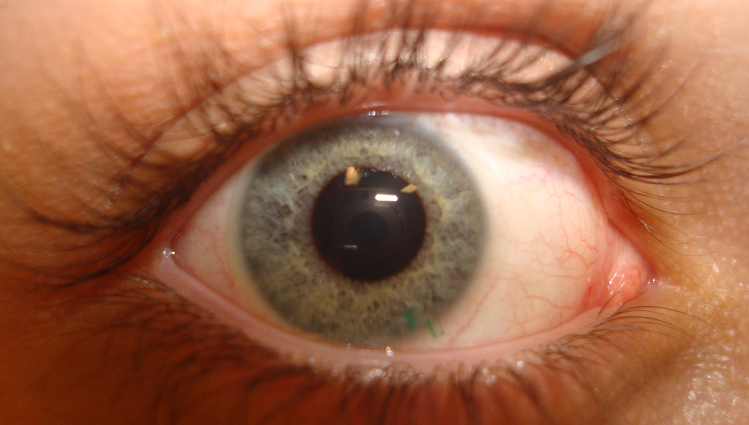
 Typically, soft contact lenses are mass-produced, while rigids are custom-made to exact specifications for the individual patient.
* Spin-cast lenses – A soft lens manufactured by whirling liquid silicone in a revolving mold at high speed.Cassin, B. and Solomon, S. ''Dictionary of Eye Terminology''. Gainesville, Florida: Triad Publishing Company, 1990.
* Diamond turning – This type is cut and polished on a CNC lathe. The lens starts out as a cylindrical disk held in the jaws of the lathe that is equipped with an industrial-grade
Typically, soft contact lenses are mass-produced, while rigids are custom-made to exact specifications for the individual patient.
* Spin-cast lenses – A soft lens manufactured by whirling liquid silicone in a revolving mold at high speed.Cassin, B. and Solomon, S. ''Dictionary of Eye Terminology''. Gainesville, Florida: Triad Publishing Company, 1990.
* Diamond turning – This type is cut and polished on a CNC lathe. The lens starts out as a cylindrical disk held in the jaws of the lathe that is equipped with an industrial-grade
 The parameters specified in a contact lens prescription may include:
* Material / Brand name
*
The parameters specified in a contact lens prescription may include:
* Material / Brand name
*
15 October 2003. guarantees consumers a copy of their contact lens prescription, allowing them to obtain lenses at the provider of their choice.
 Contact lenses are typically inserted into the eye by placing them on the pad of the index or middle finger with the concave side upward and then using that finger to place the lens on the eye. Rigid lenses should be placed directly on the cornea. Soft lenses may be placed on the sclera (white of the eye) and then slid into place. Another finger of the same hand, or a finger of the other hand, is used to keep the eye wide open. Alternatively, the user may close their eyes and then look towards their nose, sliding the lens into place over the cornea. Problems may arise if the lens folds, turns inside-out, slides off the finger prematurely, or adheres more tightly to the finger than the eye surface. A drop of solution may help the lens adhere to the eye.
When the lens first contacts the eye, it should be comfortable. A brief period of irritation may occur, caused by a difference in pH and/or salinity between that of the lens solution and the tear. This discomfort fades quickly as the solution drains away and is replaced by the natural tears. However, if irritation persists, the cause could be a dirty, damaged, or inside-out lens. Removing and inspecting it for damage and proper orientation, and re-cleaning if necessary, should correct the problem. If discomfort continues, the lens should not be worn. In some cases, taking a break from lens wear for a day may correct the problem. In case of severe discomfort, or if it does not resolve by the next day, the person should be seen as soon as possible by an eye doctor to rule out potentially serious complications.
Contact lenses are typically inserted into the eye by placing them on the pad of the index or middle finger with the concave side upward and then using that finger to place the lens on the eye. Rigid lenses should be placed directly on the cornea. Soft lenses may be placed on the sclera (white of the eye) and then slid into place. Another finger of the same hand, or a finger of the other hand, is used to keep the eye wide open. Alternatively, the user may close their eyes and then look towards their nose, sliding the lens into place over the cornea. Problems may arise if the lens folds, turns inside-out, slides off the finger prematurely, or adheres more tightly to the finger than the eye surface. A drop of solution may help the lens adhere to the eye.
When the lens first contacts the eye, it should be comfortable. A brief period of irritation may occur, caused by a difference in pH and/or salinity between that of the lens solution and the tear. This discomfort fades quickly as the solution drains away and is replaced by the natural tears. However, if irritation persists, the cause could be a dirty, damaged, or inside-out lens. Removing and inspecting it for damage and proper orientation, and re-cleaning if necessary, should correct the problem. If discomfort continues, the lens should not be worn. In some cases, taking a break from lens wear for a day may correct the problem. In case of severe discomfort, or if it does not resolve by the next day, the person should be seen as soon as possible by an eye doctor to rule out potentially serious complications.
 Removing contact lenses incorrectly can result in damage to the lens and injury to the eye, so certain precautions must be taken. Rigid contact lenses can best be removed by pulling the eyelid tight and then blinking, whereupon the lens drops out. With one finger on the outer corner of the eyelids, or lateral
Removing contact lenses incorrectly can result in damage to the lens and injury to the eye, so certain precautions must be taken. Rigid contact lenses can best be removed by pulling the eyelid tight and then blinking, whereupon the lens drops out. With one finger on the outer corner of the eyelids, or lateral

 Lens care varies depending on material and wear schedule. Daily disposables are discarded after a single use and thus require no cleaning. Other lenses need regular cleaning and disinfecting to prevent surface coating and
Lens care varies depending on material and wear schedule. Daily disposables are discarded after a single use and thus require no cleaning. Other lenses need regular cleaning and disinfecting to prevent surface coating and
 Contact lenses are generally safe as long as they are used correctly. Complications from contact lens wear affect roughly 5% of wearers yearly. Factors leading to eye damage varies, and improper use of a contact lens may affect the
Contact lenses are generally safe as long as they are used correctly. Complications from contact lens wear affect roughly 5% of wearers yearly. Factors leading to eye damage varies, and improper use of a contact lens may affect the

Contact Lens Practice
'. Elsevier Health Sciences. . * Heitz, Robert (2003, 2005 and 2014). "The History of Contact Lenses". In: Julius Hirschberg, ''History of Ophthalmology'', vols. 11/3a, 11/3b, and 11/3c. Ostend, Belgium: Wayenborgh Publishing; Paraguay: Piribebuy. .
Contact lens and anterior eye journal
"Glass Disks Under Eyelids Replace Spectacles" ''Popular Mechanics Monthly'', July 1930, left-bottom pg 31
from
eyes
Eyes are organs of the visual system. They provide living organisms with vision, the ability to receive and process visual detail, as well as enabling several photo response functions that are independent of vision. Eyes detect light and con ...
. Contact lenses are ocular prosthetic devices used by over 150 million people worldwide, and they can be worn to correct vision or for cosmetic or therapeutic reasons. In 2010, the worldwide market for contact lenses was estimated at $6.1 billion, while the US soft lens market was estimated at $2.1 billion.Nichols, Jason J., et a"ANNUAL REPORT: Contact Lenses 2010"
January 2011. Multiple analysts estimated that the global market for contact lenses would reach $11.7 billion by 2015. , the average age of contact lens wearers globally was 31 years old, and two-thirds of wearers were female.Morgan, Philip B., et al
"International Contact Lens Prescribing in 2010"
''Contact Lens Spectrum''. October 2011. People choose to wear contact lenses for many reasons. Aesthetics and cosmetics are main motivating factors for people who want to avoid wearing
glasses
Glasses, also known as eyeglasses or spectacles, are vision eyewear, with lenses (clear or tinted) mounted in a frame that holds them in front of a person's eyes, typically utilizing a bridge over the nose and hinged arms (known as temples ...
or to change the appearance or color of their eyes. Others wear contact lenses for functional or optical reasons. When compared with spectacles, contact lenses typically provide better peripheral vision
Peripheral vision, or ''indirect vision'', is vision as it occurs outside the point of fixation, i.e. away from the center of gaze or, when viewed at large angles, in (or out of) the "corner of one's eye". The vast majority of the area in th ...
, and do not collect moisture (from rain, snow, condensation, etc.) or perspiration. This can make them preferable for sports and other outdoor activities. Contact lens wearers can also wear sunglasses, goggles, or other eyewear of their choice without having to fit them with prescription lenses or worry about compatibility with glasses. Additionally, there are conditions such as keratoconus and aniseikonia
Aniseikonia is an ocular condition where there is a significant difference in the perceived size of images. It can occur as an overall difference between the two eyes, or as a difference in a particular meridian. If the ocular image size in both e ...
that are typically corrected better with contact lenses than with glasses.
History
Origins and first functional prototypes
Leonardo da Vinci
Leonardo di ser Piero da Vinci (15 April 14522 May 1519) was an Italian polymath of the High Renaissance who was active as a painter, Drawing, draughtsman, engineer, scientist, theorist, sculptor, and architect. While his fame initially res ...
is frequently credited with introducing the idea of contact lenses in his 1508 ''Codex of the eye, Manual D'', wherein he described a method of directly altering cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and lens, the cornea refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical ...
l power by either submerging the head in a bowl of water or wearing a water-filled glass hemisphere over the eye. Neither idea was practically implementable in da Vinci's time. He did not suggest his idea be used for correcting vision; he was more interested in exploring mechanisms of accommodation.Heitz, RF and Enoch, J. M. (1987) "Leonardo da Vinci: An assessment on his discourses on image formation in the eye." ''Advances in Diagnostic Visual Optics'' 19—26, Springer-Verlag.
Descartes proposed a device for correcting vision consisting of a liquid-filled glass tube capped with a lens
A lens is a transmissive optical device which focuses or disperses a light beam by means of refraction. A simple lens consists of a single piece of transparent material, while a compound lens consists of several simple lenses (''elements ...
. However, the idea was impracticable, since the device was to be placed in direct contact with the cornea and thus would have made blinking
Blinking is a bodily function; it is a semi-autonomic rapid closing of the eyelid. A single blink is determined by the forceful closing of the eyelid or inactivation of the levator palpebrae superioris and the activation of the palpebral portio ...
impossible.
In 1801, Thomas Young fashioned a pair of basic contact lenses based on Descartes' model. He used wax to affix water-filled lenses to his eyes, neutralizing their refractive power
In optics, optical power (also referred to as dioptric power, refractive power, focusing power, or convergence power) is the degree to which a lens, mirror, or other optical system converges or diverges light. It is equal to the reciprocal of the ...
, which he corrected with another pair of lenses.
Sir John Herschel, in a footnote to the 1845 edition of the ''Encyclopedia Metropolitana
An encyclopedia (American English) or encyclopædia (British English) is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge either general or special to a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into articles ...
'', posed two ideas for the visual correction: the first "a spherical capsule of glass filled with animal jelly", the second "a mould of the cornea" that could be impressed on "some sort of transparent medium". Though Herschel reportedly never tested these ideas, they were later advanced by independent inventors, including Hungarian physician Joseph Dallos, who perfected a method of making molds from living eyes. This enabled the manufacture of lenses that, for the first time, conformed to the actual shape of the eye.
 Although Louis J. Girard invented a
Although Louis J. Girard invented a scleral contact lens
A scleral lens, also known as a scleral contact lens, is a large contact lens that rests on the sclera and creates a tear-filled vault over the cornea. Scleral lenses are designed to treat a variety of eye conditions, many of which do not respo ...
in 1887, it was German ophthalmologist Adolf Gaston Eugen Fick
Adolf Gaston Eugen Fick (22 February 1852 – 11 February 1937) was a German ophthalmologist who invented the contact lens. He was the nephew of the German physiologist Adolf Eugen Fick, and the son of the German anatomy professor Franz Ludwig ...
who in 1888 fabricated the first successful afocal scleral contact lens. Approximately in diameter, the heavy blown-glass shells rested on the less sensitive rim of tissue surrounding the cornea and floated on a dextrose solution. He experimented with fitting the lenses initially on rabbits, then on himself, and lastly on a small group of volunteers, publishing his work, ''"Contactbrille"'', in the March 1888 edition of ''Archiv für Augenheilkunde''. Large and unwieldy, Fick's lens could be worn only for a couple of hours at a time. August Müller of Kiel
Kiel () is the capital and most populous city in the northern German state of Schleswig-Holstein, with a population of 246,243 (2021).
Kiel lies approximately north of Hamburg. Due to its geographic location in the southeast of the Jutland ...
, Germany, corrected his own severe myopia with a more convenient blown-glass scleral contact lens of his own manufacture in 1888.
The development of polymethyl methacrylate
Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) belongs to a group of materials called engineering plastics. It is a transparent thermoplastic. PMMA is also known as acrylic, acrylic glass, as well as by the trade names and brands Crylux, Plexiglas, Acrylite, ...
(PMMA) in the 1930s paved the way for the manufacture of plastic scleral lenses. In 1936, optometrist William Feinbloom introduced a hybrid lens composed of glass and plastic, and in 1937 it was reported that some 3,000 Americans were already wearing contact lenses. In 1939, Hungarian ophthalmologist Dr.István Györffy produced the first fully plastic contact lens. The following year, German optometrist Heinrich Wöhlk produced his own version of plastic lenses based on experiments performed during the 1930s.
Corneal and rigid lenses (1949–1960s)
In 1949, the first "corneal" lenses were developed. These were much smaller than the original scleral lenses, as they sat only on the cornea rather than across all of the visible ocular surface, and could be worn up to 16 hours a day. PMMA corneal lenses became the first contact lenses to have mass appeal through the 1960s, as lens designs became more sophisticated with improving manufacturing technology. On October 18, 1964, in a television studio in Washington, D.C.,Lyndon Baines Johnson
Lyndon Baines Johnson (; August 27, 1908January 22, 1973), often referred to by his initials LBJ, was an American politician who served as the 36th president of the United States from 1963 to 1969. He had previously served as the 37th vice ...
became the first President in the history of the United States to appear in public wearing contact lenses, under the supervision of Dr. Alan Isen, who developed the first commercially viable soft-contact lenses in the United States.
Early corneal lenses of the 1950s and 1960s were relatively expensive and fragile, resulting in the development of a market for contact lens insurance. Replacement Lens Insurance, Inc. (now known as RLI Corp.) phased out its original flagship product in 1994 after contact lenses became more affordable and easier to replace.
Gas permeable and soft lenses (1959-current)
One major disadvantage of PMMA lenses is that they allow no oxygen to get through to theconjunctiva
The conjunctiva is a thin mucous membrane that lines the inside of the eyelids and covers the sclera (the white of the eye). It is composed of non-keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium with goblet cells, stratified columnar epithelium ...
and cornea, causing a number of adverse and potentially serious clinical effects. By the end of the 1970s and through the 1980s and 1990s, a range of oxygen-permeable but rigid materials were developed to overcome this problem. Chemist Norman Gaylord played a prominent role in the development of these new oxygen-permeable contact lenses. Collectively, these polymers
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic an ...
are referred to as '' rigid gas permeable'' or RGP materials or lenses. Though all the above contact lens types—sclerals, PMMAs and RGPs—could be correctly referred to as "rigid" or "hard", the latter term is now used to the original PMMAs, which are still occasionally fitted and worn, whereas "rigid" is a generic term for all these lens types; thus hard lenses (PMMAs) are a subset of rigid contact lenses. Occasionally, the term "gas permeable" is used to describe RGPs, which is somewhat misleading as soft contact lenses are also gas permeable in that they allow oxygen to get through to the ocular surface.
 The principal breakthrough in soft lenses was made by Czech chemists
The principal breakthrough in soft lenses was made by Czech chemists Otto Wichterle
Otto Wichterle (; 27 October 1913 – 18 August 1998) was a Czech chemist, best known for his invention of modern soft contact lenses.
Wichterle is the author or co-author of approximately 180 patents and over 200 publications. The studie ...
and Drahoslav Lím, who published their work ''"Hydrophilic gels for biological use"'' in the journal ''Nature'' in 1959. In 1965, National Patent Development Corporation (NPDC) bought the American rights to produce the lenses and then sublicensed the rights to Bausch & Lomb
Bausch + Lomb is an eye health products company based in Vaughan, Ontario, Canada. It is one of the world's largest suppliers of contact lenses, lens care products, pharmaceuticals, intraocular lenses, and other eye surgery products. The compan ...
, which started to manufacture them in the United States. The Czech scientists' work led to the launch of the first soft ( hydrogel) contact lenses in some countries in the 1960s and the first approval of the Soflens material by the US Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respon ...
(FDA) in 1971. These soft lenses were soon prescribed more often than rigid ones, due to the immediate and much greater comfort (rigid lenses require a period of adaptation before full comfort is achieved). Polymers from which soft lenses are manufactured improved over the next 25 years, primarily in terms of increasing oxygen permeability, by varying the ingredients. In 1972, British optometrist Rishi Agarwal was the first to suggest disposable soft contact lenses.
In 1998, the first silicone hydrogel contact lenses were released by Ciba Vision
Novartis AG is a Swiss-American multinational pharmaceutical corporation based in Basel, Switzerland and
Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States (global research).name="novartis.com">https://www.novartis.com/research-development/research-loc ...
in Mexico. These new materials encapsulated the benefits of silicone which has extremely high oxygen permeability—with the comfort and clinical performance of the conventional hydrogels that had been used for the previous 30 years. These contact lenses were initially advocated primarily for extended (overnight) wear, although more recently, daily (no overnight) wear silicone hydrogels have been launched.
In a slightly modified molecule, a polar group is added without changing the structure of the silicone hydrogel. This is referred to as the Tanaka monomer because it was invented and patented by Kyoichi Tanaka of Menicon Co. of Japan in 1979. Second-generation silicone hydrogels, such as galyfilcon A (Acuvue
Acuvue (from "Accurate view") is a brand of disposable contact lenses made in Jacksonville Florida and Limerick-based Vistakon, a subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson (J&J).
Overview
Acuvue lenses got their start at Frontier Contact Lens Company, f ...
Advance, Vistakon) and senofilcon A (Acuvue Oasys, Vistakon), use the Tanaka monomer. Vistakon improved the Tanaka monomer even further and added other molecules, which serve as an internal wetting agent
Surfactants are chemical compounds that decrease the surface tension between two liquids, between a gas and a liquid, or interfacial tension between a liquid and a solid. Surfactants may act as detergents, wetting agents, emulsifiers, foaming ...
.
Comfilcon A (Biofinity, CooperVision) was the first third-generation polymer. Its patent claims that the material uses two siloxy macromers of diverse sizes that, when used in combination, produce very high oxygen permeability (for a given water content). Enfilcon A (Avaira, CooperVision) is another third-generation material that is naturally wettable; its water content is 46%.
Types
Contact lenses are classified in diverse ways: by their primary function, material, wear schedule (how long a lens can be worn), and replacement schedule (how long before a lens needs to be discarded).Functions
Correction of refractive error
Corrective contact lenses are designed to improve vision, most commonly by correctingrefractive error
Refractive error, also known as refraction error, is a problem with focusing light accurately on the retina due to the shape of the eye and or cornea. The most common types of refractive error are near-sightedness, far-sightedness, astigmatism ...
. This is done by directly focusing light so it enters the eye with the proper power
Power most often refers to:
* Power (physics), meaning "rate of doing work"
** Engine power, the power put out by an engine
** Electric power
* Power (social and political), the ability to influence people or events
** Abusive power
Power may a ...
for clear vision.
A spherical contact lens bends light evenly in every direction (horizontally, vertically, etc.). They are typically used to correct myopia and hypermetropia
Far-sightedness, also known as long-sightedness, hypermetropia, or hyperopia, is a condition of the eye where distant objects are seen clearly but near objects appear blurred. This blurred effect is due to incoming light being focused behind, i ...
.
There are two ways that contact lenses can correct astigmatism. One way is with toric soft lenses that work essentially the same way as eyeglasses with cylindrical correction; a toric lens has a different focusing power horizontally than vertically, and as a result can correct for astigmatism
Astigmatism is a type of refractive error due to rotational asymmetry in the eye's refractive power. This results in distorted or blurred vision at any distance. Other symptoms can include eyestrain, headaches, and trouble driving at n ...
. Another way is by using a rigid gas permeable lens; since most astigmatism is caused by the shape of the cornea, rigid lenses can improve vision because the front surface of the optical system is the perfectly spherical lens. Both approaches have advantages and drawbacks. Toric lenses must have the proper orientation to correct for astigmatism, so such lenses must have additional design characteristics to prevent them from rotating out of alignment. This can be done by weighting the bottom of the lens or by using other physical characteristics to rotate the lens back into position, but these mechanisms rarely work perfectly, so some misalignment is common and results in somewhat imperfect correction, and blurring of sight after blinking rotates the lens. Toric soft lenses have all the advantages of soft lenses in general, which are low initial cost, ease of fitting, and minimal adjustment period. Rigid gas permeable lenses usually provide superior optical correction, but have become less popular relative to soft lenses due to higher initial costs, longer initial adjustment period, and more involved fitting.
Correction of presbyopia
Correction ofpresbyopia
Presbyopia is physiological insufficiency of accommodation associated with the aging of the eye that results in progressively worsening ability to focus clearly on close objects. Also known as age-related farsightedness (or age-related long si ...
(a need for a reading prescription different from the prescription needed for distance) presents an additional challenge in the fitting of contact lenses. Two main strategies exist: multifocal lenses and monovision.
Multifocal contact lenses (e.g. bifocals or progressives) are comparable to spectacles with bifocals or progressive lenses because they have multiple focal points. Multifocal contact lenses are typically designed for constant viewing through the center of the lens, but some designs do incorporate a shift in lens position to view through the reading power (similar to bifocal glasses).
Monovision is the use of single-vision lenses (one focal point per lens) to focus an eye (typically the dominant one) for distance vision and the other for near work. The brain then learns to use this setup to see clearly at all distances. A technique called modified monovision uses multifocal lenses and also specializes one eye for distance and the other for near, thus gaining the benefits of both systems. Care is advised for persons with a previous history of strabismus
Strabismus is a vision disorder in which the eyes do not properly align with each other when looking at an object. The eye that is focused on an object can alternate. The condition may be present occasionally or constantly. If present during a ...
and those with significant phorias, who are at risk of eye misalignment under monovision. Studies have shown no adverse effect to driving performance in adapted monovision contact lens wearers.
Alternatively, a person may simply wear reading glasses over their distance contact lenses.
Other types of vision correction
For those with certain color deficiencies, a red-tinted "X-Chrom" contact lens may be used. Although such a lens does not restore normal color vision, it allows some color-blind people to distinguish colors better. Red-filtering contact lenses can also be an option for extreme light sensitivity in some visual deficiencies such asachromatopsia
Achromatopsia, also known as Rod monochromacy, is a medical syndrome that exhibits symptoms relating to five conditions, most notably monochromacy. Historically, the name referred to monochromacy in general, but now typically refers only to an a ...
.
ChromaGen contact lenses have been used and shown to have some limitations with vision at night although otherwise producing significant improvements in color vision. An earlier study showed very significant improvements in color vision and patient satisfaction.
Later work that used these ChromaGen lenses with people with dyslexia
A person ( : people) is a being that has certain capacities or attributes such as reason, morality, consciousness or self-consciousness, and being a part of a culturally established form of social relations such as kinship, ownership of property, ...
in a randomised, double-blind, placebo controlled trial showed highly significant improvements in reading ability over reading without the lenses. This system has been granted FDA approval for use in the United States.
Magnification is another area being researched for future contact lens applications. Embedding of telescopic lenses and electronic components suggests that future uses of contact lenses may become extremely diverse.
Cosmetic contact lenses
 A cosmetic contact lens is designed to change the appearance of the eye. These lenses may also correct
A cosmetic contact lens is designed to change the appearance of the eye. These lenses may also correct refractive error
Refractive error, also known as refraction error, is a problem with focusing light accurately on the retina due to the shape of the eye and or cornea. The most common types of refractive error are near-sightedness, far-sightedness, astigmatism ...
. Although many brands of contact lenses are lightly tinted to make them easier to handle, cosmetic lenses worn to change eye color are far less common, accounting for only 3% of contact lens fits in 2004.
In the United States, the FDA labels non-corrective cosmetic contact lenses as ''decorative contact lenses''. Like any contact lens, cosmetic lenses carry risks of mild to serious complications, including ocular redness, irritation and infection.
Due to their medical nature, colored contact lenses, similar to regular ones, are illegal to purchase in the United States without a valid prescription. Those with perfect vision can buy color contacts for cosmetic reasons, but they still need their eyes to be measured for a "plano" prescription, meaning one with zero vision correction. This is for safety reasons so the lenses will fit the eye without causing irritation or redness.
Some colored contact lenses completely cover the iris, thus dramatically changing eye colour. Other colored contact lenses merely tint the iris, highlighting its natural colour. A new trend in Japan, South Korea and China is the circle contact lens
A circle contact lens, also known as a big eye contact lens and circle lens, is a cosmetic (non-corrective and decorative) contact lens that makes the eye's iris appear larger. It has become a trend throughout East, South and Southeast Asia and ...
, which extend the appearance of the iris onto the sclera by having a dark tinted area all around. The result is an appearance of a bigger, wider iris, a look reminiscent of dolls' eyes.
Cosmetic lenses can have more direct medical applications. For example, some contact lenses can restore the appearance and, to some extent the function, of a damaged or missing iris
Iris most often refers to:
*Iris (anatomy), part of the eye
*Iris (mythology), a Greek goddess
* ''Iris'' (plant), a genus of flowering plants
* Iris (color), an ambiguous color term
Iris or IRIS may also refer to:
Arts and media
Fictional ent ...
.
Therapeutic scleral lenses
 A
A scleral lens
A scleral lens, also known as a scleral contact lens, is a large contact lens that rests on the sclera and creates a tear-filled vault over the cornea. Scleral lenses are designed to treat a variety of eye conditions, many of which do not respo ...
is a large, firm, transparent, oxygen-permeable contact lens that rests on the sclera and creates a tear-filled vault over the cornea. The cause of this unique positioning is usually relevant to a specific patient whose cornea is too sensitive to support the lens directly. Scleral lenses may be used to improve vision and reduce pain and light sensitivity for people with disorders or injuries to the eye, such as severe dry eye syndrome
Dry eye syndrome (DES), also known as keratoconjunctivitis sicca (KCS), is the condition of having dry eyes. Other associated symptoms include irritation, redness, discharge, and easily fatigued eyes. Blurred vision may also occur. Symptoms range ...
(keratoconjunctivitis sicca), microphthalmia, keratoconus, corneal ectasia, Stevens–Johnson syndrome
Stevens–Johnson syndrome (SJS) is a type of severe skin reaction. Together with toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) and Stevens–Johnson/toxic epidermal necrolysis (SJS/TEN), it forms a spectrum of disease, with SJS being less severe. Erythema ...
, Sjögren's syndrome, aniridia, neurotrophic keratitis (anesthetic corneas), complications post-LASIK, high order aberrations of the eye
The eye, like any other optical system, suffers from a number of specific optical aberrations. The optical quality of the eye is limited by optical aberrations, diffraction and scatter. Correction of spherocylindrical refractive errors has been ...
, complications post-corneal transplant and pellucid degeneration. Injuries to the eye such as surgical complications, distorted corneal implants, as well as chemical and burn injuries also may be treated with scleral lenses.
Therapeutic soft lenses
Soft lenses are often used in the treatment and management of non-refractive disorders of the eye. A bandage contact lens allows the patient to see while protecting an injured or diseased cornea from the constant rubbing of blinking eyelids, thereby allowing it to heal. They are used in the treatment of conditions including bullous keratopathy,dry eyes
Dry eye syndrome (DES), also known as keratoconjunctivitis sicca (KCS), is the condition of having dry eyes. Other associated symptoms include irritation, redness, discharge, and easily fatigued eyes. Blurred vision may also occur. Symptoms rang ...
, corneal abrasion
Corneal abrasion is a scratch to the surface of the cornea of the eye. Symptoms include pain, redness, light sensitivity, and a feeling like a foreign body is in the eye. Most people recover completely within three days.
Most cases are due to ...
s and erosion
Erosion is the action of surface processes (such as water flow or wind) that removes soil, rock, or dissolved material from one location on the Earth's crust, and then transports it to another location where it is deposited. Erosion is dis ...
, keratitis
Keratitis is a condition in which the eye's cornea, the clear dome on the front surface of the eye, becomes inflamed. The condition is often marked by moderate to intense pain and usually involves any of the following symptoms: pain, impaired e ...
, corneal edema, descemetocele, corneal ectasia, Mooren's ulcer, anterior corneal dystrophy, and neurotrophic keratoconjunctivitis. Contact lenses that deliver drugs to the eye have also been developed.
Materials

Rigid lenses
Glass lenses were never comfortable enough to gain widespread popularity. The first lenses to do so were those made frompolymethyl methacrylate
Poly(methyl methacrylate) (PMMA) belongs to a group of materials called engineering plastics. It is a transparent thermoplastic. PMMA is also known as acrylic, acrylic glass, as well as by the trade names and brands Crylux, Plexiglas, Acrylite, ...
(PMMA or Perspex/Plexiglas), now commonly referred to as "hard" lenses. Their main disadvantage is they do not allow oxygen
Oxygen is the chemical element with the symbol O and atomic number 8. It is a member of the chalcogen group in the periodic table, a highly reactive nonmetal, and an oxidizing agent that readily forms oxides with most elements as ...
to pass through to the cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and lens, the cornea refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical ...
, which can cause a number of adverse, and often serious, clinical events. Starting in the late 1970s, improved rigid materials which were oxygen-permeable were developed. Contact lenses made from these materials are called rigid gas permeable lenses or 'RGPs'.
A rigid lens is able to cover the natural shape of the cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and lens, the cornea refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical ...
with a new refracting surface. This means that a spherical rigid contact lens can correct corneal astigmatism. Rigid lenses can also be made as a front-toric, back-toric, or bitoric. Rigid lenses can also correct corneas with irregular geometries, such as those with keratoconus or post surgical ectasias. In most cases, patients with keratoconus see better through rigid lenses than through glasses
Glasses, also known as eyeglasses or spectacles, are vision eyewear, with lenses (clear or tinted) mounted in a frame that holds them in front of a person's eyes, typically utilizing a bridge over the nose and hinged arms (known as temples ...
. Rigid lenses are more chemically inert, allowing them to be worn in more challenging environments where chemical inertia is important compared to soft lenses.
Soft lenses
Soft lenses are more flexible than rigid lenses, and can be gently rolled or folded without damaging the lens. While rigid lenses require a period of adaptation before comfort is achieved, new soft lens wearers typically report lens awareness rather than pain or discomfort. Hydrogel lenses rely on their water content to transmit oxygen through the lens to the cornea. As a result, higher water content lenses allowed more oxygen to the cornea. In 1998, silicone hydrogel, or Si-hy lenses became available. These materials have both the extremely high oxygen permeability of silicone and the comfort and clinical performance of the conventional hydrogels. Because silicone allows more oxygen permeability than water, oxygen permeability of silicone hydrogels is not tied to the lenses' water content. Lenses have now been developed with so much oxygen permeability that they are approved for overnight wear (extended wear). Lenses approved for daily wear are also available in silicone hydrogel materials. Disadvantages of silicone hydrogels are that they are slightly stiffer and the lens surface can be hydrophobic, thus less "wettable" – factors that can influence comfort of lens use. New manufacturing techniques and changes to multipurpose solutions have minimized these effects. Those new techniques are often broken down into 3 generations: * 1st generation (plasma coating): A surface modification process called plasma coating alters the lens surface's hydrophobic nature; * 2nd generation (wetting agents): Another technique incorporates internal rewetting agents to make the lens surface hydrophilic; * 3rd generation (inherently wettable): A third process uses longer backbone polymer chains that results in less cross linking and increased wetting without surface alterations or additive agents. Current brands of soft lenses are either traditional hydrogel or silicone hydrogel. Because of drastic differences in oxygen permeability, replacement schedule, and other design characteristics, it is very important to follow the instructions of the eye care professional prescribing the lenses.Hybrid
A small number of hybrid lenses exist. Typically these contact lenses consist of a rigid center and a soft "skirt". A similar technique is the "piggybacking" of a smaller, rigid lens on the surface of a larger, soft lens. These techniques are often chosen to give the vision correction benefits of a rigid lens and the comfort of a soft lens.Wear schedule
A "daily wear" (DW) contact lens is designed to be worn for one day and removed before sleeping. An "extended wear" (EW) contact lens is designed for continuous overnight wear, typically for up to 6 consecutive nights. Newer materials, such as silicone hydrogels, allow for even longer wear periods of up to 30 consecutive nights; these longer-wear lenses are often referred to as "continuous wear" (CW). EW and CW contact lenses can be worn overnight because of their high oxygen permeability. While awake, the eyes are mostly open, allowing oxygen from the air to dissolve into the tears and pass through the lens to the cornea. While asleep, oxygen is supplied from the blood vessels in the back of the eyelid. A lens hindering passage of oxygen to the cornea causes corneal hypoxia which can result in serious complications, such ascorneal ulcer
Corneal ulcer is an inflammatory or, more seriously, infective condition of the cornea involving disruption of its epithelial layer with involvement of the corneal stroma. It is a common condition in humans particularly in the tropics and the a ...
that, if left untreated, can permanently decrease vision. EW and CW contact lenses typically allow for a transfer of 5–6 times more oxygen than conventional softs, allowing the cornea to remain healthy, even with closed eyelids.
Wearing lenses designed for daily wear overnight has an increased risk for corneal infections, corneal ulcers and corneal neovascularization—this latter condition, once it sets in, cannot be reversed and will eventually spoil vision acuity through diminishing corneal transparency. The most common complication of extended wear is giant papillary conjunctivitis (GPC), sometimes associated with a poorly fitting contact lens.
Replacement schedule
Contact lenses are often categorized by their replacement schedule. Single use lenses (called 1-day or daily disposables) are discarded after one use. Because they do not have to stand up to the wear and tear of repeated uses, these lenses can be made thinner and lighter, greatly improving their comfort. Lenses replaced frequently gather fewer deposits of allergens and germs, making these lenses preferable for patients with ocularallergies
Allergies, also known as allergic diseases, refer a number of conditions caused by the hypersensitivity of the immune system to typically harmless substances in the environment. These diseases include hay fever, food allergies, atopic dermat ...
or for those who are prone to infection. Single-use lenses are also useful for people who wear contact lenses infrequently, or when losing a lens is likely or not easily replaced (such as when on vacation). They are also considered useful for children because cleaning or disinfecting is not needed, leading to improved compliance.
Other disposable contact lenses are designed for replacement every two or four weeks. Quarterly or annual lenses, which used to be very common, are now much less so. Rigid gas permeable lenses are very durable and may last for several years without the need for replacement. PMMA hards were very durable and were commonly worn for 5 to 10 years, but had several drawbacks.
Lenses with different replacement schedules can be made of the same material. Although the materials are alike, differences in the manufacturing processes determine if the resulting lens will be a "daily disposable" or one recommended for two or four week replacement. However, sometimes manufacturers use absolutely identical lenses and just repackage them with different labels.
Manufacturing
diamond
Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the chemically stable form of carbon at room temperature and pressure, ...
as the cutting tool. The CNC lathe may turn at nearly 6000 RPM as the cutter removes the desired amount of material from the inside of the lens. The concave (inner) surface of the lens is then polished with some fine abrasive paste, oil, and a small polyester cotton ball turned at high speeds. To hold the delicate lens in reverse manner, wax is used as an adhesive. The lens' convex (outer) surface is thus cut and polished by the same process. This method can be used to shape rigid as well as soft lenses. In the case of softs, the lens is cut from a dehydrated polymer that is rigid until water is reintroduced.
* Molded – Molding is used to manufacture some brands of soft contact lenses. Rotating molds are used and the molten material is added and shaped by centripetal forces. Injection molding and computer control are also used to create nearly perfect lenses. The lens is kept moist throughout the entire molding process and is never dried and rehydrated.
Many companies make contact lenses. In the United States, there are five major manufacturers:
* Johnson & Johnson; maker of Acuvue
Acuvue (from "Accurate view") is a brand of disposable contact lenses made in Jacksonville Florida and Limerick-based Vistakon, a subsidiary of Johnson & Johnson (J&J).
Overview
Acuvue lenses got their start at Frontier Contact Lens Company, f ...
lenses
* The Cooper Companies
The Cooper Companies, Inc., branded as CooperCompanies, is a global medical device company, publicly traded on the NYSE (NYSE:COO). With its headquarters in San Ramon, California, it has a workforce of more than 12,000 employees worldwide and ...
: through its CooperVision
* Alcon
* Bausch Health: through its Bausch & Lomb
Bausch + Lomb is an eye health products company based in Vaughan, Ontario, Canada. It is one of the world's largest suppliers of contact lenses, lens care products, pharmaceuticals, intraocular lenses, and other eye surgery products. The compan ...
subsidiary
* X-Cel Specialty Contacts; maker of Westcon lenses.
Prescriptions
 The parameters specified in a contact lens prescription may include:
* Material / Brand name
*
The parameters specified in a contact lens prescription may include:
* Material / Brand name
* Base curve radius
Base curve radius, or simply base curve, abbreviated BCR or BC, is the measure of an important parameter of a lens in optometry.
On a spectacle lens, it is the flatter curvature of the front surface.
On a contact lens it is the curvature of ...
(BC, BCR)
* Diameter
In geometry, a diameter of a circle is any straight line segment that passes through the center of the circle and whose endpoints lie on the circle. It can also be defined as the longest chord of the circle. Both definitions are also valid fo ...
(D, OAD)
* Power
Power most often refers to:
* Power (physics), meaning "rate of doing work"
** Engine power, the power put out by an engine
** Electric power
* Power (social and political), the ability to influence people or events
** Abusive power
Power may a ...
in diopters
A dioptre (British spelling) or diopter (American spelling) is a unit of measurement with dimension of reciprocal length, equivalent to one reciprocal metre, 1 dioptre = 1 m−1. It is normally used to express the optical power of a lens or cu ...
* Center thickness (CT)
Prescriptions for contact lenses and glasses
Glasses, also known as eyeglasses or spectacles, are vision eyewear, with lenses (clear or tinted) mounted in a frame that holds them in front of a person's eyes, typically utilizing a bridge over the nose and hinged arms (known as temples ...
may be similar, but are not interchangeable. Prescribing of contact lenses is usually restricted to various combinations of ophthalmologists, optometrists and opticians. An eye examination
An eye examination is a series of tests performed to assess vision and ability to focus on and discern objects. It also includes other tests and examinations pertaining to the eyes. Eye examinations are primarily performed by an optometrist, ...
is needed to determine an individual's suitability for contact lens wear. This typically includes a refraction
In physics, refraction is the redirection of a wave as it passes from one medium to another. The redirection can be caused by the wave's change in speed or by a change in the medium. Refraction of light is the most commonly observed phenome ...
to determine the proper power of the lens and an assessment of the health of the eye's anterior segment. Many eye diseases prohibits contact lens wear, such as active infections, allergies, and dry eye. Keratometry is especially important in the fitting of rigid lenses.
A contact lens prescription typically includes the following information:
* Lens type: The prescription specifies the type of lens that should be used, such as soft lenses, gas permeable lenses, or multifocal lenses.
* Sphere (SPH): The sphere measurement specifies the amount of correction needed for nearsightedness or farsightedness. A positive sphere measurement indicates farsightedness, while a negative sphere measurement indicates nearsightedness.
* Cylinder (CYL): The cylinder measurement specifies the amount of correction needed for astigmatism, which is a condition that causes blurred vision due to an irregularly shaped cornea.
* Axis: The axis measurement specifies the orientation of the cylinder correction, which is important for ensuring that the contact lenses provide the correct level of correction.
* Addition (ADD): The addition measurement is used for multifocal contact lenses and specifies the amount of additional correction needed for reading or close work.
* Pupillary distance (PD): The pupillary distance measurement specifies the distance between the centers of the pupils in millimeters. This measurement is important for ensuring that the contact lenses are properly aligned with the eyes.
Prescriber's information: The prescription includes the name, address, and contact information for the eye doctor who wrote the prescription.
It is important to follow the contact lens prescription exactly as written to ensure that the contact lenses provide the correct level of correction. If you have any questions or concerns about your contact lens prescription, you should consult with your eye doctor.
United States
Contact lenses are prescribed by ophthalmologists, optometrists, or specially licensed opticians under the supervision of an eye doctor. They are typically ordered at the same office that conducts the eye exam and fitting. But the Fairness to Contact Lens Consumers Act"Fairness to Contact Lens Consumers Act"15 October 2003. guarantees consumers a copy of their contact lens prescription, allowing them to obtain lenses at the provider of their choice.
Usage
Before touching the contact lens or the eye, it is important to wash hands thoroughly withsoap
Soap is a salt of a fatty acid used in a variety of cleansing and lubricating products. In a domestic setting, soaps are surfactants usually used for washing, bathing, and other types of housekeeping. In industrial settings, soaps are use ...
and rinse well. Soaps containing moisturizer
A moisturizer, or emollient, is a cosmetic preparation used for protecting, moisturizing, and lubricating the skin. These functions are normally performed by sebum produced by healthy skin. The word "emollient" is derived from the Latin verb ''m ...
s or allergen
An allergen is a type of antigen that produces an abnormally vigorous immune response in which the immune system fights off a perceived threat that would otherwise be harmless to the body. Such reactions are called allergies.
In technical terms ...
s should be avoided as these can cause eye irritation. Drying of hands using towels or tissues before handling contact lenses can transfer lint (fluff) to the hands and, subsequently, to the lenses, causing irritation upon insertion. Towels, unless freshly laundered on high temperature wash, are frequently contaminated with large quantities of bacteria and, as such, should be avoided when handling lenses. Dust, lint and other debris may collect on the outside of contact lenses. Again, hand contact with this material, before handling contact lenses, may transfer it to the lenses themselves. Rinsing the case under a source of clean running water, before opening it, can help alleviate this problem. Next the lens should be removed from its case and inspected for defects (e.g. splits, folds, lint). A 'gritty' or rough appearance to the lens surface may indicate that a considerable quantity of proteins, lipids and debris has built up on it and that additional cleaning is required; this is often accompanied and felt by unusually high irritation upon insertion.
Care should be taken to ensure the soft lens is not inserted inside-out. The edge of a lens turned inside out has a different appearance, especially when the lens is slightly folded. Insertion of an inside-out lens for a brief time (less than one minute) should not cause any damage to the eye. Some brands of lenses have markings on the rim that make it easier to tell the front of the lens apart from the back.
Insertion
 Contact lenses are typically inserted into the eye by placing them on the pad of the index or middle finger with the concave side upward and then using that finger to place the lens on the eye. Rigid lenses should be placed directly on the cornea. Soft lenses may be placed on the sclera (white of the eye) and then slid into place. Another finger of the same hand, or a finger of the other hand, is used to keep the eye wide open. Alternatively, the user may close their eyes and then look towards their nose, sliding the lens into place over the cornea. Problems may arise if the lens folds, turns inside-out, slides off the finger prematurely, or adheres more tightly to the finger than the eye surface. A drop of solution may help the lens adhere to the eye.
When the lens first contacts the eye, it should be comfortable. A brief period of irritation may occur, caused by a difference in pH and/or salinity between that of the lens solution and the tear. This discomfort fades quickly as the solution drains away and is replaced by the natural tears. However, if irritation persists, the cause could be a dirty, damaged, or inside-out lens. Removing and inspecting it for damage and proper orientation, and re-cleaning if necessary, should correct the problem. If discomfort continues, the lens should not be worn. In some cases, taking a break from lens wear for a day may correct the problem. In case of severe discomfort, or if it does not resolve by the next day, the person should be seen as soon as possible by an eye doctor to rule out potentially serious complications.
Contact lenses are typically inserted into the eye by placing them on the pad of the index or middle finger with the concave side upward and then using that finger to place the lens on the eye. Rigid lenses should be placed directly on the cornea. Soft lenses may be placed on the sclera (white of the eye) and then slid into place. Another finger of the same hand, or a finger of the other hand, is used to keep the eye wide open. Alternatively, the user may close their eyes and then look towards their nose, sliding the lens into place over the cornea. Problems may arise if the lens folds, turns inside-out, slides off the finger prematurely, or adheres more tightly to the finger than the eye surface. A drop of solution may help the lens adhere to the eye.
When the lens first contacts the eye, it should be comfortable. A brief period of irritation may occur, caused by a difference in pH and/or salinity between that of the lens solution and the tear. This discomfort fades quickly as the solution drains away and is replaced by the natural tears. However, if irritation persists, the cause could be a dirty, damaged, or inside-out lens. Removing and inspecting it for damage and proper orientation, and re-cleaning if necessary, should correct the problem. If discomfort continues, the lens should not be worn. In some cases, taking a break from lens wear for a day may correct the problem. In case of severe discomfort, or if it does not resolve by the next day, the person should be seen as soon as possible by an eye doctor to rule out potentially serious complications.
Removal
 Removing contact lenses incorrectly can result in damage to the lens and injury to the eye, so certain precautions must be taken. Rigid contact lenses can best be removed by pulling the eyelid tight and then blinking, whereupon the lens drops out. With one finger on the outer corner of the eyelids, or lateral
Removing contact lenses incorrectly can result in damage to the lens and injury to the eye, so certain precautions must be taken. Rigid contact lenses can best be removed by pulling the eyelid tight and then blinking, whereupon the lens drops out. With one finger on the outer corner of the eyelids, or lateral canthus
The canthus (pl. canthi, palpebral commissures) is either corner of the eye where the upper and lower eyelids meet. More specifically, the inner and outer canthi are, respectively, the medial and lateral ends/angles of the palpebral fissure.
T ...
, the person stretches the eyelids towards the ear; the increased tension of the eyelid margins against the edge of lens allows the blink to break the capillary action
Capillary action (sometimes called capillarity, capillary motion, capillary rise, capillary effect, or wicking) is the process of a liquid flowing in a narrow space without the assistance of, or even in opposition to, any external forces li ...
that adheres the lens to the eye. The other hand is typically cupped underneath the eye to catch the lens as it drops out. For soft lenses, which have a stronger adherence to the eye surface, this technique is less suitable.
A soft contact lens may be removed by pinching the edge between the thumb and index finger. Moving the lens off the cornea first can improve comfort during removal and reduce risk of scratching the cornea with a fingernail. It is also possible to push or pull a soft lens far enough to the side or bottom of the eyeball to get it to fold then fall out, without pinching and thereby damaging it. If these techniques are used with a rigid lens, it may scratch the cornea.
There are also small tools specifically for removing lenses. Usually made of flexible plastic, they resemble small tweezers, or plunger
A plunger, force cup, plumber's friend or plumber's helper is a tool used to clear blockages in drains and pipes. It consists of a rubber suction cup attached to a stick (''shaft'') usually made of wood or plastic. A different bellows-like des ...
s that suction onto the front of the lens. Typically, these tools are used only with rigid lenses. Extreme care must be exercised when using mechanical tools or fingernails to insert or remove contact lenses.
Care

 Lens care varies depending on material and wear schedule. Daily disposables are discarded after a single use and thus require no cleaning. Other lenses need regular cleaning and disinfecting to prevent surface coating and
Lens care varies depending on material and wear schedule. Daily disposables are discarded after a single use and thus require no cleaning. Other lenses need regular cleaning and disinfecting to prevent surface coating and infections
An infection is the invasion of tissues by pathogens, their multiplication, and the reaction of host tissues to the infectious agent and the toxins they produce. An infectious disease, also known as a transmissible disease or communicable di ...
.
There are many ways to clean and care for contact lenses, typically called care systems or lens solutions:
;Multipurpose solutions
:The main attraction of multipurpose solutions is that the same solution can clean, rinse, disinfect and store lenses. Some multipurpose solutions also contain ingredients that improve the surface wettability and comfort of silicone hydrogel lenses. Studies showed that multipurpose solutions are ineffective against ''Acanthamoeba
''Acanthamoeba'' is a genus of amoebae that are commonly recovered from soil, fresh water, and other habitats.
''Acanthamoeba'' has two evolutive forms, the metabolically active trophozoite and a dormant, stress-resistant cyst. Trophozoites are ...
e''. There is preliminary research on creating a new multipurpose solution that kills amoeba.
; Hydrogen peroxide contact solutions
:Hydrogen peroxide can be used to disinfect contact lenses. Care should be taken not to get hydrogen peroxide in the eye because it is very painful and irritating. With "two-step" products, the hydrogen peroxide must be rinsed away with saline before the lenses may be worn. "One-step" systems allow the hydrogen peroxide to react completely, becoming pure water. Thus "one-step" hydrogen peroxide systems do not require the lenses to be rinsed before insertion, provided the solution has been given enough time to react.
:An exposure time of 2-3 hours to 3% (non neutralized solution) is sufficient to kill bacteria, HIV, fungi, and ''Acanthamoeba''. This can be achieved by using a "two-step" product or a "one-step" tablet system if the catalytic tablet isn't added before 2-3 hours. However, the "one-step" catalytic disk systems are not effective against ''Acanthamoeba'' due to insufficient exposure time.
;Enzymatic cleaner
:Used for cleaning protein deposits off lenses, usually weekly, if the daily cleaner is not sufficient. Typically, this cleaner is in tablet form.
;Ultraviolet, vibration, or ultrasonic devices
:These devices intend to disinfect and clean contact lenses. The lenses are inserted inside the portable device (running on batteries and/or plug-in) for 2 to 6 minutes during which both the microorganisms and protein build-up are supposed to be cleaned. However these devices can not be used to replace the manual rub and rinse method because vibration and ultrasound can not create relative motion between contact lens and solution, which is required for proper cleaning of the lens. These devices are not usually available in optic retailers but are in other stores.
Rub and rinse method
Contact lenses can be mechanically cleaned of more substantial protein, lipid and debris build up by rubbing them between the clean pad of a finger and the palm of a hand, using a small amount of cleaning fluid as a lubricant; and by rinsing thereafter. This "rub and rinse" method is thought to be the most effective method for multipurpose solutions, and is the method indicated by the American Academy of Ophthalmology regardless of cleaning solution used. In 2010, the FDA recommended that manufacturers removed the "no rub" from product labeling, "because rub-and-rinse regimens help prevent microbial adhesion to the contact lens, help prevent formation of biofilms, and generally reduce the microbial load on the lens and the lens case."Physical rubbing devices
This type of devices mimic digital rubbing. The lenses are sandwiched by silicone parts inside the portable device. The device applies a gentle yet high speed rubbing action on the lens surface and remove debris. ;Saline solution
Saline (also known as saline solution) is a mixture of sodium chloride (salt) and water. It has a number of uses in medicine including cleaning wounds, removal and storage of contact lenses, and help with dry eyes. By injection into a vein i ...
:Sterile saline is used for rinsing the lens after cleaning and preparing it for insertion. Saline solutions do not disinfect, so it must be used in conjunction with some type of disinfection system. One advantage to saline is that it cannot cause an allergic response, so it is well suited for individuals with sensitive eyes or strong allergies.
;Daily cleaner
:Used to clean lenses on a daily basis. A few drops of cleaner are applied to the lens while it rests in the palm of the hand; the lens is rubbed for about 20 seconds with a clean fingertip (depending on the product) on each side. Lens must then be rinsed. This system is commonly used to care for rigid lenses.
Water is not recommended for cleaning contact lenses. Insufficiently chlorinated tap water can lead to lens contamination, particularly by Acanthamoeba. On the other hand, sterile water will not kill any contaminant that get in from the environment.
Some products must be used only with certain types of contact lenses.
Aside from cleaning the contact lenses, contact lens case should also be kept clean and be replaced at minimum every 3 months.
Contact lens solutions often contain preservative
A preservative is a substance or a chemical that is added to products such as food products, beverages, pharmaceutical drugs, paints, biological samples, cosmetics, wood, and many other products to prevent decomposition by microbial growth or by ...
s such as benzalkonium chloride
Benzalkonium chloride (BZK, BKC, BAK, BAC), also known as alkyldimethylbenzylammonium chloride (ADBAC) and by the trade name Zephiran, is a type of cationic surfactant. It is an organic salt classified as a quaternary ammonium compound. ADBACs ha ...
and benzyl alcohol
Benzyl alcohol is an aromatic alcohol with the formula C6H5CH2OH. The benzyl group is often abbreviated "Bn" (not to be confused with "Bz" which is used for benzoyl), thus benzyl alcohol is denoted as BnOH. Benzyl alcohol is a colorless liquid w ...
. Preservative-free products usually have shorter shelf lives, but are better suited for individuals with an allergy or sensitivity to a preservative. In the past, thiomersal was used as a preservative. In 1989, thiomersal was responsible for about 10% of problems related to contact lenses. As a result, most products no longer contain thiomersal.
Complications
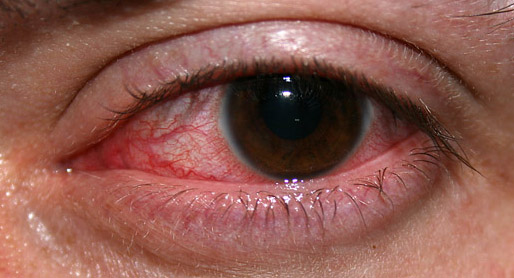
 Contact lenses are generally safe as long as they are used correctly. Complications from contact lens wear affect roughly 5% of wearers yearly. Factors leading to eye damage varies, and improper use of a contact lens may affect the
Contact lenses are generally safe as long as they are used correctly. Complications from contact lens wear affect roughly 5% of wearers yearly. Factors leading to eye damage varies, and improper use of a contact lens may affect the eyelid
An eyelid is a thin fold of skin that covers and protects an eye. The levator palpebrae superioris muscle retracts the eyelid, exposing the cornea to the outside, giving vision. This can be either voluntarily or involuntarily. The human eye ...
, the conjunctiva
The conjunctiva is a thin mucous membrane that lines the inside of the eyelids and covers the sclera (the white of the eye). It is composed of non-keratinized, stratified squamous epithelium with goblet cells, stratified columnar epithelium ...
, and, most of all, the whole structure of the cornea
The cornea is the transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris, pupil, and anterior chamber. Along with the anterior chamber and lens, the cornea refracts light, accounting for approximately two-thirds of the eye's total optical ...
. Poor lens care can lead to infections by various microorganism
A microorganism, or microbe,, ''mikros'', "small") and ''organism'' from the el, ὀργανισμός, ''organismós'', "organism"). It is usually written as a single word but is sometimes hyphenated (''micro-organism''), especially in olde ...
s including bacteria
Bacteria (; singular: bacterium) are ubiquitous, mostly free-living organisms often consisting of one Cell (biology), biological cell. They constitute a large domain (biology), domain of prokaryotic microorganisms. Typically a few micrometr ...
, fungi
A fungus ( : fungi or funguses) is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, separately from ...
, and ''Acanthamoeba
''Acanthamoeba'' is a genus of amoebae that are commonly recovered from soil, fresh water, and other habitats.
''Acanthamoeba'' has two evolutive forms, the metabolically active trophozoite and a dormant, stress-resistant cyst. Trophozoites are ...
'' ( ''Acanthamoeba'' keratitis).
Many complications arise when contact lenses are worn not as prescribed (improper wear schedule or lens replacement). Sleeping in lenses not designed or approved for extended wear is a common cause of complications. Many people go too long before replacing their contacts, wearing lenses designed for 1, 14, or 30 days of wear for multiple months or years. While this does save on the cost of lenses, it risks permanent damage to the eye and even loss of sight.
For non Silicone-Hydrogel lenses, one of the major factors that causes complications is that the contact lens is an oxygen barrier. The cornea needs a constant supply of oxygen to remain completely transparent and function as it should; it normally gets that oxygen from the surrounding air while awake, and from the blood vessels in the back of the eyelid while asleep. The most prominent risks associated with long-term, chronic low oxygen to the cornea include corneal neovascularization, increased epithelial permeability, bacterial adherence, microcysts, corneal edema, endothelial polymegethism, dry eye and potential increase in myopia. Much of the research into soft and rigid contact lens materials has centered on improving oxygen transmission through the lens.
Silicone-Hydrogel lenses available today have effectively eliminated hypoxia for most patients.
Mishandling of contact lenses can also cause problems. Corneal abrasion
Corneal abrasion is a scratch to the surface of the cornea of the eye. Symptoms include pain, redness, light sensitivity, and a feeling like a foreign body is in the eye. Most people recover completely within three days.
Most cases are due to ...
s can increase the chances of infection. When combined with improper cleaning and disinfection of the lens, a risk of infection further increases. Decreased corneal sensitivity after extended contact lens wear may cause a patient to miss some of the earliest symptoms of such complications.
The way contact lenses interact with the natural tear layer is a major factor in determining lens comfort and visual clarity. People with dry eyes
Dry eye syndrome (DES), also known as keratoconjunctivitis sicca (KCS), is the condition of having dry eyes. Other associated symptoms include irritation, redness, discharge, and easily fatigued eyes. Blurred vision may also occur. Symptoms rang ...
are particularly vulnerable to discomfort and episodes of brief blurry vision. Proper lens selection can minimize these effects.
Long-term wear (over five years) of contact lenses may "decrease the entire corneal thickness and increase the corneal curvature and surface irregularity." Long-term wear of rigid contacts is associated with decreased corneal keratocyte
Corneal keratocytes (corneal fibroblasts) are specialized fibroblasts residing in the stroma. This corneal layer, representing about 85-90% of corneal thickness, is built up from highly regular collagenous lamellae and extracellular matrix compone ...
density and increased number of epithelial
Epithelium or epithelial tissue is one of the four basic types of animal tissue, along with connective tissue, muscle tissue and nervous tissue. It is a thin, continuous, protective layer of compactly packed cells with a little intercell ...
Langerhans cells.
All contact lenses sold in the United States are studied and approved as safe by the FDA when specific handling and care procedures, wear schedules, and replacement schedules are followed.
Current research
Contact lens sensors to monitor the ocular temperature have been demonstrated. A large segment of current contact lens research is directed towards the treatment and prevention of conditions resulting from contact lens contamination and colonization by foreign organisms. Clinicians tend to agree that the most significant complication of contact lens wear is microbialkeratitis
Keratitis is a condition in which the eye's cornea, the clear dome on the front surface of the eye, becomes inflamed. The condition is often marked by moderate to intense pain and usually involves any of the following symptoms: pain, impaired e ...
and that the most predominant microbial pathogen is ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa
''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' is a common encapsulated, gram-negative, aerobic–facultatively anaerobic, rod-shaped bacterium that can cause disease in plants and animals, including humans. A species of considerable medical importance, ''P. aerug ...
''. Other organisms are also major causative factors in bacterial keratitis associated with contact lens wear, although their prevalence varies across different locations. These include both the '' Staphylococcus'' species (''aureus'' and ''epidermidis'') and the ''Streptococcus
''Streptococcus'' is a genus of gram-positive ' (plural ) or spherical bacteria that belongs to the family Streptococcaceae, within the order Lactobacillales (lactic acid bacteria), in the phylum Bacillota. Cell division in streptococci occurs ...
'' species, among others. Microbial keratitis is a serious focal point of current research due to its potentially devastating effect on the eye, including severe vision loss.
One specific research topic of interest is how microbes such as ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' invade the eye and cause infection. Although the pathogenesis of microbial keratitis is not well understood, many different factors have been investigated. One group of researchers showed that corneal hypoxia exacerbated ''Pseudomonas'' binding to the corneal epithelium, internalization of the microbes, and induction of the inflammatory response. One way to alleviate hypoxia is to increase the amount of oxygen transmitted to the cornea. Although silicone-hydrogel lenses almost eliminate hypoxia in patients due to their very high levels of oxygen transmissibility, they also seem to provide a more efficient platform for bacterial contamination and corneal infiltration than other conventional hydrogel soft contact lenses. One study showed that ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' and '' Staphylococcus epidermis'' adhere much more strongly to unworn silicone hydrogel contact lenses than conventional hydrogel lenses and that adhesion of ''Pseudomonas aeruginosa'' was 20 times stronger than that of ''Staphylococcus epidermidis''. This might partly explain why ''Pseudomonas'' infections are the most predominant. However, another study conducted with worn and unworn silicone and conventional hydrogel contact lenses showed that worn silicone contact lenses were less prone to ''Staphylococcus epidermidis'' colonization than conventional hydrogel lenses.
Besides bacterial adhesion and cleaning, micro and nano pollutants (biological and manmade) is an area of contact lens research that is growing. Small physical pollutants ranging from nanoplastics to fungi spores to plant pollen adhere to contact lens surfaces in high concentrations. It has been found that multipurpose solution and rubbing with fingers does not significantly clean the lenses. A group of researchers have suggested an alternative cleaning solution, PoPPR (polymer on polymer pollution removal). This cleaning technique takes advantage of a soft and porous polymer to physically peal pollutants off of contact lenses.
Another important area of contact lens research deals with patient compliance. Compliance is a major issue pertaining to the use of contact lenses because patient noncompliance often leads to contamination of the lens, storage case, or both. However, careful users can extend the wear of lenses through proper handling: there is, unfortunately, no disinterested research on the issue of "compliance" or the length of time a user can safely wear a lens beyond its stated use. The introduction of multipurpose solutions and daily disposable lenses have helped to alleviate some of the problems observed from inadequate cleaning but new methods of combating microbial contamination are currently being developed. A silver
Silver is a chemical element with the symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical ...
-impregnated lens case has been developed which helps to eradicate any potentially contaminating microbes that come in contact with the lens case. Additionally, a number of antimicrobial
An antimicrobial is an agent that kills microorganisms or stops their growth. Antimicrobial medicines can be grouped according to the microorganisms they act primarily against. For example, antibiotics are used against bacteria, and antifungals ar ...
agents are being developed that have been embedded into contact lenses themselves. Lenses with covalently attached selenium
Selenium is a chemical element with the symbol Se and atomic number 34. It is a nonmetal (more rarely considered a metalloid) with properties that are intermediate between the elements above and below in the periodic table, sulfur and tellurium, ...
molecules have been shown to reduce bacterial colonization without adversely affecting the cornea of a rabbit eye and octyl glucoside used as a lens surfactant significantly decreases bacterial adhesion. These compounds are of particular interest to contact lens manufacturers and prescribing optometrists because they do not require any patient compliance to effectively attenuate the effects of bacterial colonization.
One area of research is in the field of bionic lenses. These are visual displays that include built-in electric circuits and light-emitting diodes and can harvest radio waves for their electric power. Bionic lenses can display information beamed from a mobile device overcoming the small display size problem. The technology involves embedding nano and microscale electronic devices in lenses. These lenses will also need to have an array of microlenses to focus the image so that it appears suspended in front of the wearer's eyes. The lens could also serve as a head-up display for pilots or gamers.
Drug administration through contact lenses is also becoming an area of research. One application is a lens that releases anesthesia to the eye for post-surgery pain relief, especially after PRK (photorefractive keratectomy
Photorefractive keratectomy (PRK) and laser-assisted sub-epithelial keratectomy (or laser epithelial keratomileusis) (LASEK) are laser eye surgery procedures intended to correct a person's vision, reducing dependency on glasses or contact lense ...
) in which the healing process takes several days. One experiment shows that silicone contact lenses that contain vitamin E deliver pain medication for up to seven days compared with less than two hours in usual lenses.
Another study of the usage of contact lens is aimed to address the issue of macular degeneration
Macular degeneration, also known as age-related macular degeneration (AMD or ARMD), is a medical condition which may result in blurred or no vision in the center of the visual field. Early on there are often no symptoms. Over time, however, som ...
(AMD or age-related macular degeneration). An international collaboration of researchers was able to develop a contact lens that can shift between magnified and normal vision. Previous solutions to AMD included bulky glasses or surgical implants. But the development of this new contact lens, which is made of polymethyl methacrylate, could offer an unobtrusive solution.
In popular culture

Films
One of the earliest knownmotion pictures
A film also called a movie, motion picture, moving picture, picture, photoplay or (slang) flick is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, feelings, beauty, or atmosphere ...
to introduce the use of contact lenses as a make-up artist's device for enhancing the eyes was by the innovative actor Lon Chaney
Leonidas Frank "Lon" Chaney (April 1, 1883 – August 26, 1930) was an American actor. He is regarded as one of the most versatile and powerful actors of cinema, renowned for his characterizations of tortured, often grotesque and affli ...
in the 1926 film '' The Road to Mandalay'' to create the effect of a character who had a blind eye. Dr. Rueben Greenspoon applied them to Orson Welles for the film '' Citizen Kane'' in 1940. In the 1950s, contact lenses were starting to be used in British color horror films. An early example of this is the British actor Christopher Lee as the Dracula character in the 1958 color horror film '' Dracula'', which helped to emphasize his horrific looking black pupils and red bloodshot eyes
A red eye is an eye that appears red due to illness
A disease is a particular abnormal condition that negatively affects the structure or function of all or part of an organism, and that is not immediately due to any external injury ...
. Tony Curtis
Tony Curtis (born Bernard Schwartz; June 3, 1925September 29, 2010) was an American actor whose career spanned six decades, achieving the height of his popularity in the 1950s (Kansas Raiders, 1950) and early 1960s. He acted in more than 100 f ...
wore them in the 1968 film '' The Boston Strangler''. Contact lenses were also used to better emphasize the sinister gaze of the demonic characters in 1968's '' Rosemary's Baby'' and 1973's ''The Exorcist
''The Exorcist'' is a 1973 American supernatural horror film directed by William Friedkin and written for the screen by William Peter Blatty, based on his 1971 novel of the same name. It stars Ellen Burstyn, Max von Sydow, Lee J. Cobb, Kitty ...
''. Colored custom-made contact lenses are now standard makeup for a number of special effects-based movies.
Usage
* * *See also
References
Further reading
* Efron, Nathan (2002).Contact Lens Practice
'. Elsevier Health Sciences. . * Heitz, Robert (2003, 2005 and 2014). "The History of Contact Lenses". In: Julius Hirschberg, ''History of Ophthalmology'', vols. 11/3a, 11/3b, and 11/3c. Ostend, Belgium: Wayenborgh Publishing; Paraguay: Piribebuy. .
External links
Contact lens and anterior eye journal
"Glass Disks Under Eyelids Replace Spectacles" ''Popular Mechanics Monthly'', July 1930, left-bottom pg 31
from
Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a List of United States federal agencies, federal agency of the United States Department of Health and Human Services, Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is respon ...
{{Authority control
1965 introductions
Articles containing video clips
Corrective lenses
Optometry
19th-century inventions