Conspiracy theorist on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A conspiracy theory is an explanation for an event or situation that invokes a
A conspiracy theory is an explanation for an event or situation that invokes a
 The term "conspiracy theory" is itself the subject of a conspiracy theory, which claims the term was popularized by the
The term "conspiracy theory" is itself the subject of a conspiracy theory, which claims the term was popularized by the
 Conspiracy theorists often take advantage of
Conspiracy theorists often take advantage of
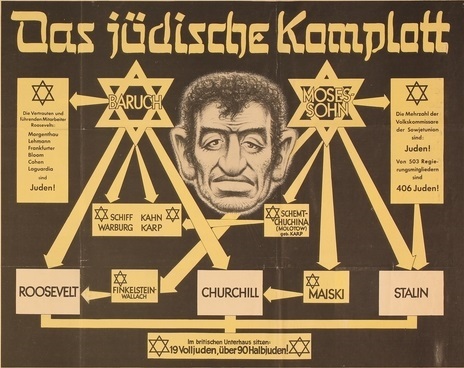 Historically, conspiracy theories have been closely linked to
Historically, conspiracy theories have been closely linked to
"Wall Streeters like conspiracy theories. Always have"
, ''Time'', 1 October 2009. According to Berlet and Lyons, "Conspiracism is a particular narrative form of scapegoating that frames demonized enemies as part of a vast insidious plot against the common good, while it valorizes the scapegoater as a hero for sounding the alarm".
 The philosopher Karl Popper described the central problem of conspiracy theories as a form of fundamental attribution error, where every event is generally perceived as being intentional and planned, greatly underestimating the effects of randomness and unintended consequences. In his book ''The Open Society and Its Enemies'', he used the term "the conspiracy theory of society" to denote the idea that social phenomena such as "war, unemployment, poverty, shortages ... [are] the result of direct design by some powerful individuals and groups." Popper argued that totalitarianism was founded on conspiracy theories which drew on imaginary plots which were driven by paranoid scenarios predicated on tribalism, chauvinism, or racism. He also noted that conspirators very rarely achieved their goal.
Historically, real conspiracies have usually had little effect on history and have had unforeseen consequences for the conspirators, in contrast to conspiracy theories which often posit grand, sinister organizations, or world-changing events, the evidence for which has been erased or obscured. As described by Bruce Cumings, history is instead "moved by the broad forces and large structures of human collectivities".
The philosopher Karl Popper described the central problem of conspiracy theories as a form of fundamental attribution error, where every event is generally perceived as being intentional and planned, greatly underestimating the effects of randomness and unintended consequences. In his book ''The Open Society and Its Enemies'', he used the term "the conspiracy theory of society" to denote the idea that social phenomena such as "war, unemployment, poverty, shortages ... [are] the result of direct design by some powerful individuals and groups." Popper argued that totalitarianism was founded on conspiracy theories which drew on imaginary plots which were driven by paranoid scenarios predicated on tribalism, chauvinism, or racism. He also noted that conspirators very rarely achieved their goal.
Historically, real conspiracies have usually had little effect on history and have had unforeseen consequences for the conspirators, in contrast to conspiracy theories which often posit grand, sinister organizations, or world-changing events, the evidence for which has been erased or obscured. As described by Bruce Cumings, history is instead "moved by the broad forces and large structures of human collectivities".
online
* * * * * De Graaf, Beatrice and Zwierlein, Cornel (eds.
''Security and Conspiracy in History, 16th to 21st Century''
Historical Social Research 38, Special Issue, 2013 * Fleming, Chris and Emma A. Jane. ''Modern Conspiracy: The Importance of Being Paranoid''. New York and London: Bloomsbury, 2014. . * Goertzel, Ted. "Belief in conspiracy theories." ''Political Psychology'' (1994): 731–742
online
* Harris, Lee
''"The Trouble with Conspiracy Theories"''
The American, 12 January 2013. * Hofstadter, Richard. ''The paranoid style in American politics'' (1954)
online
* * * * * * * Oliver, J. Eric, and Thomas J. Wood. "Conspiracy theories and the paranoid style (s) of mass opinion." ''American Journal of Political Science'' 58.4 (2014): 952–96
online
* * * * * * Slosson, W
''"The 'Conspiracy' Superstition"''
The Unpopular Review, Vol. VII, N°. 14, 1917. * Sunstein, Cass R., and Adrian Vermeule. "Conspiracy theories: Causes and cures." ''Journal of Political Philosophy'' 17.2 (2009): 202–227
online
* Uscinski, Joseph E. and Joseph M. Parent, ''American Conspiracy Theories'' (2014
excerpt
* Uscinski, Joseph E. "The 5 Most Dangerous Conspiracy Theories of 2016
''POLITICO Magazine'' (Aug 22, 2016)
* * Wood, Gordon S. "Conspiracy and the paranoid style: causality and deceit in the eighteenth century." ''William and Mary Quarterly'' (1982): 402–441
in jstor
Conspiracy Theories
''Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Conspiracy Theory Conspiracy theories, Barriers to critical thinking Fringe theory Pejorative terms
 A conspiracy theory is an explanation for an event or situation that invokes a
A conspiracy theory is an explanation for an event or situation that invokes a conspiracy
A conspiracy, also known as a plot, is a secret plan or agreement between persons (called conspirers or conspirators) for an unlawful or harmful purpose, such as murder or treason, especially with political motivation, while keeping their agr ...
by sinister and powerful groups, often political in motivation, when other explanations are more probable.Additional sources:
*
*
*
* The term has a negative connotation, implying that the appeal to a conspiracy is based on prejudice or insufficient evidence. A conspiracy theory is not the same as a conspiracy
A conspiracy, also known as a plot, is a secret plan or agreement between persons (called conspirers or conspirators) for an unlawful or harmful purpose, such as murder or treason, especially with political motivation, while keeping their agr ...
; instead, it refers to a hypothesized conspiracy with specific characteristics, such as an opposition to the mainstream consensus among those people (such as scientist
A scientist is a person who conducts scientific research to advance knowledge in an area of the natural sciences.
In classical antiquity, there was no real ancient analog of a modern scientist. Instead, philosophers engaged in the philosop ...
s or historians
A historian is a person who studies and writes about the past and is regarded as an authority on it. Historians are concerned with the continuous, methodical narrative and research of past events as relating to the human race; as well as the st ...
) who are qualified to evaluate its accuracy.
Conspiracy theories resist falsification and are reinforced by circular reasoning
Circular may refer to:
* The shape of a circle
* ''Circular'' (album), a 2006 album by Spanish singer Vega
* Circular letter (disambiguation)
** Flyer (pamphlet), a form of advertisement
* Circular reasoning, a type of logical fallacy
* Circula ...
: both evidence against the conspiracy and an absence of evidence for it are re-interpreted as evidence of its truth, whereby the conspiracy becomes a matter of faith rather than something that can be proven or disproven. Studies have linked belief in conspiracy theories to distrust of authority and political cynicism. Some researchers suggest that conspiracist ideation—belief in conspiracy theories—may be psychologically harmful or pathological, and that it is correlated with lower analytical thinking Analytical reasoning, also known as analytical thinking, refers to the ability to look at information, be it qualitative or quantitative in nature, and discern patterns within the information. Analytical reasoning involves deductive reasoning with ...
, low intelligence
Intelligence has been defined in many ways: the capacity for abstraction, logic, understanding, self-awareness, learning, emotional knowledge, reasoning, planning, creativity, critical thinking, and problem-solving. More generally, it can ...
, psychological projection
Psychological projection is the process of misinterpreting what is "inside" as coming from "outside". It forms the basis of empathy by the projection of personal experiences to understand someone else's subjective world. In its malignant forms, i ...
, paranoia
Paranoia is an instinct or thought process that is believed to be heavily influenced by anxiety or fear, often to the point of delusion and irrationality. Paranoid thinking typically includes persecutory beliefs, or beliefs of conspiracy c ...
, and Machiavellianism
Machiavellianism or Machiavellian may refer to:
Politics
*Machiavellianism (politics), the supposed political philosophy of Niccolò Machiavelli
*Political realism
Psychology
*Machiavellianism (psychology), a personality trait centered on cold an ...
. Psychologists usually attribute belief in conspiracy theories and finding a conspiracy where there is none to a number of psychopathological conditions such as paranoia
Paranoia is an instinct or thought process that is believed to be heavily influenced by anxiety or fear, often to the point of delusion and irrationality. Paranoid thinking typically includes persecutory beliefs, or beliefs of conspiracy c ...
, schizotypy
In psychology, schizotypy is a theoretical concept that posits a continuum of personality characteristics and experiences, ranging from normal dissociative, imaginative states to extreme states of mind related to psychosis, especially schizophr ...
, narcissism
Narcissism is a self-centered personality style characterized as having an excessive interest in one's physical appearance or image and an excessive preoccupation with one's own needs, often at the expense of others.
Narcissism exists on a co ...
, and insecure attachment
Attachment theory is a psychological, evolutionary and ethological theory concerning relationships between humans. The most important tenet is that young children need to develop a relationship with at least one primary caregiver for norm ...
, or to a form of cognitive bias
A cognitive bias is a systematic pattern of deviation from norm (philosophy), norm or rationality in judgment. Individuals create their own "subjective reality" from their perception of the input. An individual's construction of reality, not the ...
called "illusory pattern perception
Apophenia () is the tendency to perceive meaningful connections between unrelated things. The term (German: ' from the Greek verb ''ἀποφαίνειν'' (apophaínein)) was coined by psychiatrist Klaus Conrad in his 1958 publication on the ...
". However, a 2020 review article found that most cognitive scientists
Cognition refers to "the mental action or process of acquiring knowledge and understanding through thought, experience, and the senses". It encompasses all aspects of intellectual functions and processes such as: perception, attention, thought, ...
view conspiracy theorizing as typically nonpathological, given that unfounded belief in conspiracy is common across cultures both historical and contemporary, and may arise from innate human tendencies towards gossip and group cohesion.
Historically, conspiracy theories have been closely linked to prejudice
Prejudice can be an affective feeling towards a person based on their perceived group membership. The word is often used to refer to a preconceived (usually unfavourable) evaluation or classification of another person based on that person's per ...
, propaganda
Propaganda is communication that is primarily used to influence or persuade an audience to further an agenda, which may not be objective and may be selectively presenting facts to encourage a particular synthesis or perception, or using loaded ...
, witch hunt
A witch-hunt, or a witch purge, is a search for people who have been labeled witches or a search for evidence of witchcraft. The classical period of witch-hunts in Early Modern Europe and Colonial America took place in the Early Modern perio ...
s, war
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular o ...
s, and genocide
Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word (, "race, people") with the ...
s. They are often strongly believed by the perpetrators of terrorist
Terrorism, in its broadest sense, is the use of criminal violence to provoke a state of terror or fear, mostly with the intention to achieve political or religious aims. The term is used in this regard primarily to refer to intentional violen ...
attacks, and were used as justification by Timothy McVeigh
Timothy James McVeigh (April 23, 1968 – June 11, 2001) was an American domestic terrorist responsible for the 1995 Oklahoma City bombing that killed 168 people, 19 of whom were children, injured more than 680 others, and destroyed one-third ...
and Anders Breivik
Anders is a male name in Scandinavian languages and Fering North Frisian, an equivalent of the Greek Andreas ("manly") and the English Andrew. It originated from Andres via metathesis.
In Sweden, Anders has been one of the most common names fo ...
, as well as by governments such as Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
, the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
, and Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula ...
. AIDS denialism
HIV/AIDS denialism is the belief, despite conclusive evidence to the contrary, that the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) does not cause acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Some of its proponents reject the existence of HIV, while oth ...
by the government of South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring coun ...
, motivated by conspiracy theories, caused an estimated 330,000 deaths from AIDS, QAnon
QAnon ( , ) is an American political conspiracy theory and political movement. It originated in the American far-right political sphere in 2017. QAnon centers on fabricated claims made by an anonymous individual or individuals known as "Q". ...
and denialism about the 2020 United States presidential election
The 2020 United States presidential election was the 59th quadrennial presidential election, held on Tuesday, November 3, 2020. The Democratic ticket of former vice president Joe Biden and the junior U.S. senator from California Kamala H ...
results led to the January 6 United States Capitol attack
On January 6, 2021, following the defeat of then- U.S. President Donald Trump in the 2020 presidential election, a mob of his supporters attacked the United States Capitol Building in Washington, D.C. The mob was seeking to keep Trump in p ...
, while belief in conspiracy theories about genetically modified foods led the government of Zambia
Zambia (), officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of Central, Southern and East Africa, although it is typically referred to as being in Southern Africa at its most central point. Its neighbours are t ...
to reject food aid during a famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenomenon is usually accompan ...
, at a time when three million people in the country were suffering from hunger
In politics, humanitarian aid, and the social sciences, hunger is defined as a condition in which a person does not have the physical or financial capability to eat sufficient food to meet basic Human nutrition, nutritional needs for a sustaine ...
. Conspiracy theories are a significant obstacle to improvements in public health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals". Analyzing the det ...
, encouraging opposition to vaccination
Vaccination is the administration of a vaccine to help the immune system develop immunity from a disease. Vaccines contain a microorganism or virus in a weakened, live or killed state, or proteins or toxins from the organism. In stimulat ...
and water fluoridation
Water fluoridation is the controlled adjustment of fluoride to a public water supply solely to reduce tooth decay. Fluoridated water contains fluoride at a level that is effective for preventing cavities; this can occur naturally or by adding ...
among others, and have been linked to outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases. Other effects of conspiracy theories include reduced trust in scientific evidence
Scientific evidence is evidence that serves to either support or counter a scientific theory or hypothesis, although scientists also use evidence in other ways, such as when applying theories to practical problems. "Discussions about empirical ev ...
, radicalization and ideological reinforcement of extremist
Extremism is "the quality or state of being extreme" or "the advocacy of extreme measures or views". The term is primarily used in a political or religious sense to refer to an ideology that is considered (by the speaker or by some implied share ...
groups, and negative consequences for the economy
An economy is an area of the production, distribution and trade, as well as consumption of goods and services. In general, it is defined as a social domain that emphasize the practices, discourses, and material expressions associated with th ...
.
Conspiracy theories once limited to fringe audiences have become commonplace in mass media
Mass media refers to a diverse array of media technologies that reach a large audience via mass communication. The technologies through which this communication takes place include a variety of outlets.
Broadcast media transmit informati ...
, the internet
The Internet (or internet) is the global system of interconnected computer networks that uses the Internet protocol suite (TCP/IP) to communicate between networks and devices. It is a '' network of networks'' that consists of private, p ...
, and social media
Social media are interactive media technologies that facilitate the creation and sharing of information, ideas, interests, and other forms of expression through virtual communities and networks. While challenges to the definition of ''social me ...
, emerging as a cultural phenomenon
The bandwagon effect is the tendency for people to adopt certain behaviors, styles, or attitudes simply because others are doing so. More specifically, it is a cognitive bias by which public opinion or behaviours can alter due to particular act ...
of the late 20th and early 21st centuries. They are widespread around the world and are often commonly believed, some even being held by the majority of the population. Interventions to reduce the occurrence of conspiracy beliefs include maintaining an open society
Open society (french: société ouverte) is a term coined by French philosopher Henri Bergson in 1932, and describes a dynamic system inclined to moral universalism.Thomas Mautner (2005), 2nd ed. ''The Penguin Dictionary of Philosophy'' Open s ...
and improving the analytical thinking Analytical reasoning, also known as analytical thinking, refers to the ability to look at information, be it qualitative or quantitative in nature, and discern patterns within the information. Analytical reasoning involves deductive reasoning with ...
skills of the general public.
Etymology and usage
The ''Oxford English Dictionary
The ''Oxford English Dictionary'' (''OED'') is the first and foundational historical dictionary of the English language, published by Oxford University Press (OUP). It traces the historical development of the English language, providing a c ...
'' defines ''conspiracy theory'' as "the theory that an event or phenomenon occurs as a result of a conspiracy between interested parties; ''spec.'' a belief that some covert but influential agency (typically political in motivation and oppressive in intent) is responsible for an unexplained event." It cites a 1909 article in ''The American Historical Review
''The American Historical Review'' is a quarterly academic history journal and the official publication of the American Historical Association. It targets readers interested in all periods and facets of history and has often been described as the ...
'' as the earliest usage example, although it also appeared in print for several decades before.
The earliest known usage was by the American author Charles Astor Bristed
Charles Astor Bristed (October 6, 1820 – January 14, 1874) was an American scholar and author, sometimes writing under the pen name Carl Benson. He was the first American to write a full-length defense of Americanisms and is the earliest known ...
, in a letter to the editor published in ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'' on January 11, 1863. He used it to refer to claims that British aristocrats were intentionally weakening the United States during the American Civil War in order to advance their financial interests.
The word "conspiracy" derives from the Latin ''con-'' ("with, together") and ''spirare'' ("to breathe").
Robert Blaskiewicz comments that examples of the term were used as early as the nineteenth century and states that its usage has always been derogatory. According to a study by Andrew McKenzie-McHarg, in contrast, in the nineteenth century the term ''conspiracy theory'' simply "suggests a plausible postulate of a conspiracy" and "did not, at this stage, carry any connotations, either negative or positive", though sometimes a postulate so-labeled was criticized.
 The term "conspiracy theory" is itself the subject of a conspiracy theory, which claims the term was popularized by the
The term "conspiracy theory" is itself the subject of a conspiracy theory, which claims the term was popularized by the CIA
The Central Intelligence Agency (CIA ), known informally as the Agency and historically as the Company, is a civilian foreign intelligence service of the federal government of the United States, officially tasked with gathering, processing, ...
in order to discredit conspiratorial believers, particularly critics of the Warren Commission
The President's Commission on the Assassination of President Kennedy, known unofficially as the Warren Commission, was established by President Lyndon B. Johnson through on November 29, 1963, to investigate the assassination of United States P ...
, by making them a target of ridicule. In his 2013 book ''Conspiracy Theory in America'', political scientist Lance deHaven-Smith suggested that the term entered everyday language in the United States after 1964, the year in which the Warren Commission published its findings on the Kennedy assassination
John F. Kennedy, the 35th president of the United States, was assassinated on Friday, November 22, 1963, at 12:30 p.m. CST in Dallas, Texas, while riding in a presidential motorcade through Dealey Plaza. Kennedy was in the vehicle with ...
, with ''The New York Times'' running five stories that year using the term. However, deHaven-Smith's suggestion has been criticized by Michael Butter, a Professor of American Literary and Cultural History at the University of Tübingen
The University of Tübingen, officially the Eberhard Karl University of Tübingen (german: Eberhard Karls Universität Tübingen; la, Universitas Eberhardina Carolina), is a public research university located in the city of Tübingen, Baden-W� ...
, on the grounds that a CIA document which deHaven-Smith referenced, ''Concerning Criticism of the Warren Report'', which was publicly released in 1976 after a Freedom of Information Act Freedom of Information Act may refer to the following legislations in different jurisdictions which mandate the national government to disclose certain data to the general public upon request:
* Freedom of Information Act 1982, the Australian act
* ...
request, does not contain the phrase "conspiracy theory" in the singular, and only mentions "conspiracy theories" once, in the sentence "Conspiracy theories have frequently thrown suspicion on our organisation , for example, by falsely alleging that Lee Harvey Oswald worked for us."
Difference from conspiracy
A conspiracy theory is not simply about aconspiracy
A conspiracy, also known as a plot, is a secret plan or agreement between persons (called conspirers or conspirators) for an unlawful or harmful purpose, such as murder or treason, especially with political motivation, while keeping their agr ...
, which refers to any covert plan involving two or more people. In contrast, the term "conspiracy theory" refers to ''hypothesized'' conspiracies that have specific characteristics. For example, conspiracist beliefs invariably oppose the mainstream consensus among those people who are qualified to evaluate their accuracy, such as scientist
A scientist is a person who conducts scientific research to advance knowledge in an area of the natural sciences.
In classical antiquity, there was no real ancient analog of a modern scientist. Instead, philosophers engaged in the philosop ...
s or historians
A historian is a person who studies and writes about the past and is regarded as an authority on it. Historians are concerned with the continuous, methodical narrative and research of past events as relating to the human race; as well as the st ...
. Conspiracy theorists see themselves as having privileged access to socially persecuted knowledge or a stigmatized mode of thought that separates them from the masses who believe the official account. Michael Barkun
__NOTOC__
Michael Barkun (born April 8, 1938) is an American academic who serves as Professor Emeritus of political science at the Maxwell School of Citizenship and Public Affairs, Syracuse University, specializing in political and religious ext ...
describes a conspiracy theory as a "template imposed upon the world to give the appearance of order to events".
Real conspiracies, even very simple ones, are difficult to conceal and routinely experience unexpected problems. In contrast, conspiracy theories suggest that conspiracies are unrealistically successful and that groups of conspirators, such as bureaucracies, can act with near-perfect competence and secrecy. The causes of events or situations are simplified to exclude complex or interacting factors, as well as the role of chance and unintended consequences. Nearly all observations are explained as having been deliberately planned by the alleged conspirators.
In conspiracy theories, the conspirators are usually claimed to be acting with extreme malice. As described by Robert Brotherton:
Examples
A conspiracy theory may take any matter as its subject, but certain subjects attract greater interest than others. Favored subjects include famous deaths and assassinations, morally dubious government activities, suppressed technologies, and "false flag
A false flag operation is an act committed with the intent of disguising the actual source of responsibility and pinning blame on another party. The term "false flag" originated in the 16th century as an expression meaning an intentional misr ...
" terrorism. Among the longest-standing and most widely recognized conspiracy theories are notions concerning the assassination of John F. Kennedy
John F. Kennedy, the 35th president of the United States, was assassinated on Friday, November 22, 1963, at 12:30 p.m. CST in Dallas, Texas, while riding in a presidential motorcade through Dealey Plaza. Kennedy was in the vehicle with ...
, the 1969 Apollo moon landings, and the 9/11 terrorist attacks
The September 11 attacks, commonly known as 9/11, were four coordinated suicide terrorist attacks carried out by al-Qaeda against the United States on Tuesday, September 11, 2001. That morning, nineteen terrorists hijacked four commerci ...
, as well as numerous theories pertaining to alleged plots for world domination by various groups, both real and imaginary.
Popularity
Conspiracy beliefs are widespread around the world. In rural Africa, common targets of conspiracy theorizing include societal elites, enemy tribes, and the Western world, with conspirators often alleged to enact their plans via sorcery or witchcraft; one common belief identifies modern technology as itself being a form of sorcery, created with the goal of harming or controlling the people. InChina
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
, one widely published conspiracy theory claims that a number of events including the rise of Hitler
Adolf Hitler's rise to power began in the newly established Weimar Republic in September 1919 when Hitler joined the '' Deutsche Arbeiterpartei'' (DAP; German Workers' Party). He rose to a place of prominence in the early years of the party. Be ...
, the 1997 Asian financial crisis
The Asian financial crisis was a period of financial crisis that gripped much of East Asia and Southeast Asia beginning in July 1997 and raised fears of a worldwide economic meltdown due to financial contagion. However, the recovery in 1998– ...
, and climate change
In common usage, climate change describes global warming—the ongoing increase in global average temperature—and its effects on Earth's climate system. Climate change in a broader sense also includes previous long-term changes to ...
were planned by the Rothschild family
The Rothschild family ( , ) is a wealthy Ashkenazi Jewish family originally from Frankfurt that rose to prominence with Mayer Amschel Rothschild (1744–1812), a court factor to the German Landgraves of Hesse-Kassel in the Free City of Fr ...
, which may have led to effects on discussions about China's currency policy.
Conspiracy theories once limited to fringe audiences have become commonplace in mass media
Mass media refers to a diverse array of media technologies that reach a large audience via mass communication. The technologies through which this communication takes place include a variety of outlets.
Broadcast media transmit informati ...
, contributing to conspiracism emerging as a cultural phenomenon
The bandwagon effect is the tendency for people to adopt certain behaviors, styles, or attitudes simply because others are doing so. More specifically, it is a cognitive bias by which public opinion or behaviours can alter due to particular act ...
in the United States of the late 20th and early 21st centuries. The general predisposition to believe conspiracy theories cuts across partisan and ideological lines. Conspiratorial thinking is correlated with antigovernmental orientations and a low sense of political efficacy, with conspiracy believers perceiving a governmental threat to individual rights and displaying a deep skepticism that who one votes for really matters.
Conspiracy theories are often commonly believed, some even being held by the majority of the population. A broad cross-section of Americans today gives credence to at least some conspiracy theories. For instance, a study conducted in 2016 found that 10% of Americans think the chemtrail conspiracy theory
The chemtrail conspiracy theory is the erroneous belief that long-lasting condensation trails are "chemtrails" consisting of chemical or biological agents left in the sky by high-flying aircraft, sprayed for nefarious purposes undisclosed to ...
is "completely true" and 20–30% think it is "somewhat true". This puts "the equivalent of 120 million Americans in the 'chemtrails are real' camp." Belief in conspiracy theories has therefore become a topic of interest for sociologists, psychologists and experts in folklore
Folklore is shared by a particular group of people; it encompasses the traditions common to that culture, subculture or group. This includes oral traditions such as tales, legends, proverbs and jokes. They include material culture, rangin ...
.
Conspiracy theories are widely present on the Web
Web most often refers to:
* Spider web, a silken structure created by the animal
* World Wide Web or the Web, an Internet-based hypertext system
Web, WEB, or the Web may also refer to:
Computing
* WEB, a literate programming system created by ...
in the form of blog
A blog (a Clipping (morphology), truncation of "weblog") is a discussion or informational website published on the World Wide Web consisting of discrete, often informal diary-style text entries (posts). Posts are typically displayed in Reverse ...
s and YouTube
YouTube is a global online video sharing and social media platform headquartered in San Bruno, California. It was launched on February 14, 2005, by Steve Chen, Chad Hurley, and Jawed Karim. It is owned by Google, and is the second mo ...
videos, as well as on social media
Social media are interactive media technologies that facilitate the creation and sharing of information, ideas, interests, and other forms of expression through virtual communities and networks. While challenges to the definition of ''social me ...
. Whether the Web has increased the prevalence of conspiracy theories or not is an open research question. The presence and representation of conspiracy theories in search engine
A search engine is a software system designed to carry out web searches. They search the World Wide Web in a systematic way for particular information specified in a textual web search query. The search results are generally presented in a ...
results has been monitored and studied, showing significant variation across different topics, and a general absence of reputable, high-quality links in the results.
One conspiracy theory that propagated through former US President Barack Obama's time in office claimed that he was born in Kenya, instead of Hawaii where he was actually born. Former governor of Arkansas and political opponent of Obama Mike Huckabee
Michael Dale Huckabee (born August 24, 1955) is an American politician, Baptist minister, and political commentator who served as the 44th governor of Arkansas from 1996 to 2007. He was a candidate for the Republican Party presidential nominati ...
made headlines in 2011 when he, among other members of Republican
Republican can refer to:
Political ideology
* An advocate of a republic, a type of government that is not a monarchy or dictatorship, and is usually associated with the rule of law.
** Republicanism, the ideology in support of republics or agains ...
leadership, continued to question Obama's citizenship status.
Types
A conspiracy theory can be local or international, focused on single events or covering multiple incidents and entire countries, regions and periods of history. According to Ruseell Muirhead and Nancy Rosenblum, historically, traditional conspiracism has entailed a "theory", but over time, "conspiracy" and "theory" have become decoupled, as modern conspiracism is often without any kind of theory behind it.Walker's five kinds
Jesse Walker (2013) has identified five kinds of conspiracy theories: * The "Enemy Outside" refers to theories based on figures alleged to be scheming against a community from without. * The "Enemy Within" finds the conspirators lurking inside the nation, indistinguishable from ordinary citizens. * The "Enemy Above" involves powerful people manipulating events for their own gain. * The "Enemy Below" features the lower classes working to overturn the social order. * The "Benevolent Conspiracies" are angelic forces that work behind the scenes to improve the world and help people.Barkun's three types
Michael Barkun
__NOTOC__
Michael Barkun (born April 8, 1938) is an American academic who serves as Professor Emeritus of political science at the Maxwell School of Citizenship and Public Affairs, Syracuse University, specializing in political and religious ext ...
has identified three classifications of conspiracy theory:
* ''Event conspiracy theories''. This refers to limited and well-defined events. Examples may include such conspiracies theories as those concerning the Kennedy assassination
John F. Kennedy, the 35th president of the United States, was assassinated on Friday, November 22, 1963, at 12:30 p.m. CST in Dallas, Texas, while riding in a presidential motorcade through Dealey Plaza. Kennedy was in the vehicle with ...
, 9/11
The September 11 attacks, commonly known as 9/11, were four coordinated suicide terrorist attacks carried out by al-Qaeda against the United States on Tuesday, September 11, 2001. That morning, nineteen terrorists hijacked four commerci ...
, and the spread of AIDS.
* ''Systemic conspiracy theories''. The conspiracy is believed to have broad goals, usually conceived as securing control of a country, a region, or even the entire world. The goals are sweeping, whilst the conspiratorial machinery is generally simple: a single, evil organization implements a plan to infiltrate and subvert existing institutions. This is a common scenario in conspiracy theories that focus on the alleged machinations of Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, Freemasons
Freemasonry or Masonry refers to fraternal organisations that trace their origins to the local guilds of stonemasons that, from the end of the 13th century, regulated the qualifications of stonemasons and their interaction with authorities ...
, Communism
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, ...
, or the Catholic Church
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the List of Christian denominations by number of members, largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics Catholic Church by country, worldwide . It is am ...
.
* ''Superconspiracy theories''. For Barkun, such theories link multiple alleged conspiracies together hierarchically. At the summit is a distant but all-powerful evil force. His cited examples are the ideas of David Icke
David Vaughan Icke (; born 29 April 1952) is an English conspiracy theorist and a former footballer and sports broadcaster. He has written over 20 books, self-published since the mid-1990s, and spoken in more than 25 countries.
In 1990, Ick ...
and Milton William Cooper
Milton William "Bill" Cooper (May 6, 1943 – November 5, 2001) was an American conspiracy theorist, radio broadcaster, and author known for his 1991 book ''Behold a Pale Horse'', in which he warned of multiple global conspiracies, some i ...
.
Rothbard: shallow vs. deep
Murray Rothbard
Murray Newton Rothbard (; March 2, 1926 – January 7, 1995) was an American economist of the Austrian School, economic historian, political theorist, and activist. Rothbard was a central figure in the 20th-century American libertarian ...
argues in favor of a model that contrasts "deep" conspiracy theories to "shallow" ones. According to Rothbard, a "shallow" theorist observes an event and asks '' Cui bono''? ("Who benefits?"), jumping to the conclusion that a posited beneficiary is responsible for covertly influencing events. On the other hand, the "deep" conspiracy theorist begins with a hunch and then seeks out evidence. Rothbard describes this latter activity as a matter of confirming with certain facts one's initial paranoia.
Lack of evidence
Belief in conspiracy theories is generally based not on evidence, but in the faith of the believer.Noam Chomsky
Avram Noam Chomsky (born December 7, 1928) is an American public intellectual: a linguist, philosopher, cognitive scientist, historian, social critic, and political activist. Sometimes called "the father of modern linguistics", Chomsky i ...
contrasts conspiracy theory to institutional analysis
Institutional analysis is that part of the social sciences which studies how institutions—i.e., structures and mechanisms of social order and cooperation governing the behavior of two or more individuals—behave and function according to both e ...
which focuses mostly on the public, long-term behavior of publicly known institutions, as recorded in, for example, scholarly documents or mainstream media
In journalism, mainstream media (MSM) is a term and abbreviation used to refer collectively to the various large mass news media that influence many people and both reflect and shape prevailing currents of thought. Chomsky, Noam, ''"What makes ma ...
reports. Conspiracy theory conversely posits the existence of secretive coalitions of individuals and speculates on their alleged activities. Belief in conspiracy theories is associated with biases in reasoning, such as the conjunction fallacy
The conjunction fallacy (also known as the Linda problem) is an inference from an array of particulars, in violation of the laws of probability, that a conjoint set of two or more conclusions is likelier than any single member of that same set. It ...
.
Clare Birchall at King's College London
King's College London (informally King's or KCL) is a public research university located in London, England. King's was established by royal charter in 1829 under the patronage of King George IV and the Duke of Wellington. In 1836, King's ...
describes conspiracy theory as a "form of popular knowledge or interpretation". The use of the word 'knowledge' here suggests ways in which conspiracy theory may be considered in relation to legitimate modes of knowing. The relationship between legitimate and illegitimate knowledge, Birchall claims, is closer than common dismissals of conspiracy theory contend.
Theories involving multiple conspirators that are proven to be correct, such as the Watergate scandal
The Watergate scandal was a major political scandal in the United States involving the administration of President Richard Nixon from 1972 to 1974 that led to Nixon's resignation. The scandal stemmed from the Nixon administration's contin ...
, are usually referred to as investigative journalism
Investigative journalism is a form of journalism in which reporters deeply investigate a single topic of interest, such as serious crimes, political corruption, or corporate wrongdoing. An investigative journalist may spend months or years res ...
or historical analysis
Historiography is the study of the methods of historians in developing history as an academic discipline, and by extension is any body of historical work on a particular subject. The historiography of a specific topic covers how historians hav ...
rather than conspiracy theory. By contrast, the term "Watergate conspiracy theory" is used to refer to a variety of hypotheses in which those convicted in the conspiracy were in fact the victims of a deeper conspiracy. There are also attempts to analyze the theory of conspiracy theories (conspiracy theory theory) to ensure that the term "conspiracy theory" is used to refer to narratives that have been debunked by experts, rather than as a generalized dismissal.
Rhetoric
Conspiracy theory rhetoric exploits several importantcognitive bias
A cognitive bias is a systematic pattern of deviation from norm (philosophy), norm or rationality in judgment. Individuals create their own "subjective reality" from their perception of the input. An individual's construction of reality, not the ...
es, including proportionality bias, attribution bias, and confirmation bias
Confirmation bias is the tendency to search for, interpret, favor, and recall information in a way that confirms or supports one's prior beliefs or values. People display this bias when they select information that supports their views, ignoring ...
. Their arguments often take the form of asking reasonable questions, but without providing an answer based on strong evidence. Conspiracy theories are most successful when proponents can gather followers from the general public, such as in politics, religion and journalism. These proponents may not necessarily believe the conspiracy theory; instead, they may just use it in an attempt to gain public approval. Conspiratorial claims can act as a successful rhetorical strategy to convince a portion of the public via appeal to emotion
Appeal to emotion or ''argumentum ad passiones'' (meaning the same in Latin) is an informal fallacy characterized by the manipulation of the recipient's emotions in order to win an argument, especially in the absence of factual evidence. This kind ...
.
Conspiracy theories typically justify themselves by focusing on gaps or ambiguities in knowledge, and then arguing that the true explanation for this must be a conspiracy. In contrast, any evidence that directly supports their claims is generally of low quality. For example, conspiracy theories are often dependent on eyewitness testimony
Eyewitness testimony is the account a bystander or victim gives in the courtroom, describing what that person observed that occurred during the specific incident under investigation. Ideally this recollection of events is detailed; however, this is ...
, despite its unreliability, while disregarding objective analyses of the evidence.
Conspiracy theories are not able to be falsified and are reinforced by fallacious arguments. In particular, the logical fallacy circular reasoning
Circular may refer to:
* The shape of a circle
* ''Circular'' (album), a 2006 album by Spanish singer Vega
* Circular letter (disambiguation)
** Flyer (pamphlet), a form of advertisement
* Circular reasoning, a type of logical fallacy
* Circula ...
is used by conspiracy theorists: both evidence against the conspiracy and an absence of evidence for it are re-interpreted as evidence of its truth, whereby the conspiracy becomes a matter of faith rather than something that can be proved or disproved. The epistemic strategy of conspiracy theories has been called "cascade logic": each time new evidence becomes available, a conspiracy theory is able to dismiss it by claiming that even more people must be part of the cover-up. Any information that contradicts the conspiracy theory is suggested to be disinformation by the alleged conspiracy. Similarly, the continued lack of evidence directly supporting conspiracist claims is portrayed as confirming the existence of a conspiracy of silence; the fact that other people have not found or exposed any conspiracy is taken as evidence that those people are part of the plot, rather than considering that it may be because no conspiracy exists. This strategy lets conspiracy theories insulate themselves from neutral analyses of the evidence, and makes them resistant to questioning or correction, which is called "epistemic self-insulation".
 Conspiracy theorists often take advantage of
Conspiracy theorists often take advantage of false balance
False balance, also bothsidesism, is a media bias in which journalists present an issue as being more balanced between opposing viewpoints than the evidence supports. Journalists may present evidence and arguments out of proportion to the act ...
in the media. They may claim to be presenting a legitimate alternative viewpoint that deserves equal time to argue its case; for example, this strategy has been used by the Teach the Controversy
The "teach the controversy" campaign of the Discovery Institute seeks to promote the pseudoscientific principle of intelligent design (a variant of traditional creationism) as part of its attempts to discredit the teaching of evolution in Uni ...
campaign to promote intelligent design, which often claims that there is a conspiracy of scientists suppressing their views. If they successfully find a platform to present their views in a debate format, they focus on using rhetorical ''ad hominems'' and attacking perceived flaws in the mainstream account, while avoiding any discussion of the shortcomings in their own position.
The typical approach of conspiracy theories is to challenge any action or statement from authorities, using even the most tenuous justifications. Responses are then assessed using a double standard, where failing to provide an immediate response to the satisfaction of the conspiracy theorist will be claimed to prove a conspiracy. Any minor errors in the response are heavily emphasized, while deficiencies in the arguments of other proponents are generally excused.
In science, conspiracists may suggest that a scientific theory can be disproven by a single perceived deficiency, even though such events are extremely rare. In addition, both disregarding the claims and attempting to address them will be interpreted as proof of a conspiracy. Other conspiracist arguments may not be scientific; for example, in response to the IPCC Second Assessment Report in 1996, much of the opposition centered on promoting a procedural objection to the report's creation. Specifically, it was claimed that part of the procedure reflected a conspiracy to silence dissenters, which served as motivation for opponents of the report and successfully redirected a significant amount of the public discussion away from the science.
Consequences
 Historically, conspiracy theories have been closely linked to
Historically, conspiracy theories have been closely linked to prejudice
Prejudice can be an affective feeling towards a person based on their perceived group membership. The word is often used to refer to a preconceived (usually unfavourable) evaluation or classification of another person based on that person's per ...
, witch hunt
A witch-hunt, or a witch purge, is a search for people who have been labeled witches or a search for evidence of witchcraft. The classical period of witch-hunts in Early Modern Europe and Colonial America took place in the Early Modern perio ...
s, war
War is an intense armed conflict between states, governments, societies, or paramilitary groups such as mercenaries, insurgents, and militias. It is generally characterized by extreme violence, destruction, and mortality, using regular o ...
s, and genocide
Genocide is the intentional destruction of a people—usually defined as an ethnic, national, racial, or religious group—in whole or in part. Raphael Lemkin coined the term in 1944, combining the Greek word (, "race, people") with the ...
s. They are often strongly believed by the perpetrators of terrorist
Terrorism, in its broadest sense, is the use of criminal violence to provoke a state of terror or fear, mostly with the intention to achieve political or religious aims. The term is used in this regard primarily to refer to intentional violen ...
attacks, and were used as justification by Timothy McVeigh
Timothy James McVeigh (April 23, 1968 – June 11, 2001) was an American domestic terrorist responsible for the 1995 Oklahoma City bombing that killed 168 people, 19 of whom were children, injured more than 680 others, and destroyed one-third ...
, Anders Breivik
Anders is a male name in Scandinavian languages and Fering North Frisian, an equivalent of the Greek Andreas ("manly") and the English Andrew. It originated from Andres via metathesis.
In Sweden, Anders has been one of the most common names fo ...
and Brenton Tarrant, as well as by governments such as Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
and the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nationa ...
. AIDS denialism
HIV/AIDS denialism is the belief, despite conclusive evidence to the contrary, that the human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) does not cause acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). Some of its proponents reject the existence of HIV, while oth ...
by the government of South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring coun ...
, motivated by conspiracy theories, caused an estimated 330,000 deaths from AIDS, while belief in conspiracy theories about genetically modified foods led the government of Zambia
Zambia (), officially the Republic of Zambia, is a landlocked country at the crossroads of Central, Southern and East Africa, although it is typically referred to as being in Southern Africa at its most central point. Its neighbours are t ...
to reject food aid during a famine
A famine is a widespread scarcity of food, caused by several factors including war, natural disasters, crop failure, population imbalance, widespread poverty, an economic catastrophe or government policies. This phenomenon is usually accompan ...
, at a time when 3 million people in the country were suffering from hunger
In politics, humanitarian aid, and the social sciences, hunger is defined as a condition in which a person does not have the physical or financial capability to eat sufficient food to meet basic Human nutrition, nutritional needs for a sustaine ...
.
Conspiracy theories are a significant obstacle to improvements in public health
Public health is "the science and art of preventing disease, prolonging life and promoting health through the organized efforts and informed choices of society, organizations, public and private, communities and individuals". Analyzing the det ...
. People who believe in health-related conspiracy theories are less likely to follow medical advice, and more likely to use alternative medicine instead. Conspiratorial anti-vaccination beliefs, such as Big Pharma conspiracy theory, conspiracy theories about pharmaceutical companies, can result in reduced vaccination rates and have been linked to outbreaks of vaccine-preventable diseases. Health-related conspiracy theories often inspire resistance to water fluoridation
Water fluoridation is the controlled adjustment of fluoride to a public water supply solely to reduce tooth decay. Fluoridated water contains fluoride at a level that is effective for preventing cavities; this can occur naturally or by adding ...
, and contributed to the impact of the Lancet MMR autism fraud.
Conspiracy theories are a fundamental component of a wide range of radicalized and extremist groups, where they may play an important role in reinforcing the ideology and psychology of their members as well as further radicalizing their beliefs. These conspiracy theories often share common themes, even among groups that would otherwise be fundamentally opposed, such as the Antisemitism, antisemitic conspiracy theories found among political extremists on both the far right and far left. More generally, belief in conspiracy theories is associated with holding extreme and uncompromising viewpoints, and may help people in maintaining those viewpoints. While conspiracy theories are not always present in extremist groups, and do not always lead to violence when they are, they can make the group more extreme, provide an enemy to direct hatred towards, and isolate members from the rest of society. Conspiracy theories are most likely to inspire violence when they call for urgent action, appeal to prejudices, or demonize and scapegoat enemies.
Conspiracy theorizing in the workplace can also have economic consequences. For example, it leads to lower job satisfaction and lower commitment, resulting in workers being more likely to leave their jobs. Comparisons have also been made with the effects of workplace rumors, which share some characteristics with conspiracy theories and result in both decreased productivity and increased stress. Subsequent effects on managers include reduced profits, reduced trust from employees, and damage to the company's image.
Conspiracy theories can divert attention from important social, political, and scientific issues. In addition, they have been used to discredit scientific evidence to the general public or in a legal context. Conspiratorial strategies also share characteristics with those used by lawyers who are attempting to discredit expert testimony, such as claiming that the experts have ulterior motives in testifying, or attempting to find someone who will provide statements to imply that expert opinion is more divided than it actually is.
It is possible that conspiracy theories may also produce some compensatory benefits to society in certain situations. For example, they may help people identify governmental deceptions, particularly in repressive societies, and encourage government transparency. However, real conspiracies are normally revealed by people working within the system, such as whistleblowers and journalists, and most of the effort spent by conspiracy theorists is inherently misdirected. The most dangerous conspiracy theories are likely to be those that incite violence, scapegoat disadvantaged groups, or spread misinformation about important societal issues.
Interventions
The primary defense against conspiracy theories is to maintain anopen society
Open society (french: société ouverte) is a term coined by French philosopher Henri Bergson in 1932, and describes a dynamic system inclined to moral universalism.Thomas Mautner (2005), 2nd ed. ''The Penguin Dictionary of Philosophy'' Open s ...
, in which many sources of reliable information are available, and government sources are known to be credible rather than propaganda. Additionally, independent nongovernmental organizations are able to correct misinformation without requiring people to trust the government. Other approaches to reduce the appeal of conspiracy theories in general among the public may be based in the emotional and social nature of conspiratorial beliefs. For example, interventions that promote analytical thinking Analytical reasoning, also known as analytical thinking, refers to the ability to look at information, be it qualitative or quantitative in nature, and discern patterns within the information. Analytical reasoning involves deductive reasoning with ...
in the general public are likely to be effective. Another approach is to intervene in ways that decrease negative emotions, and specifically to improve feelings of personal hope and empowerment.
Joseph Pierre has also noted that mistrust in authoritative institutions is the core component underlying many conspiracy theories and that this mistrust creates an epistemic vacuum and makes individuals searching for answers vulnerable to misinformation. Therefore, one possible solution is offering consumers a seat at the table to mend their mistrust in institutions. Regarding the challenges of this approach, Dr. Pierre has said, "The challenge with acknowledging areas of uncertainty within a public sphere is that doing so can be weaponized to reinforce a post-truth view of the world in which everything is debatable, and any counter-position is just as valid. Although I like to think of myself as a middle of the road kind of individual, it is important to keep in mind that the truth does not always lie in the middle of a debate, whether we are talking about climate change, vaccines, or antipsychotic medications."
It has been suggested that directly countering misinformation can be counterproductive. For example, since conspiracy theories can reinterpret disconfirming information as part of their narrative, refuting a claim can result in accidentally reinforcing it. In addition, publishing criticism of conspiracy theories can result in legitimizing them. In this context, possible interventions include carefully selecting which conspiracy theories to refute, requesting additional analyses from independent observers, and introducing cognitive diversity into conspiratorial communities by undermining their poor epistemology. Any legitimization effect might also be reduced by responding to more conspiracy theories rather than fewer.
However, presenting people with factual corrections, or highlighting the logical contradictions in conspiracy theories, has been demonstrated to have a positive effect in many circumstances. For example, this has been studied in the case of informing believers in 9/11 conspiracy theories about statements by actual experts and witnesses. One possibility is that criticism is most likely to backfire if it challenges someone's worldview or identity. This suggests that an effective approach may be to provide criticism while avoiding such challenges.
Psychology
The widespread belief in conspiracy theories has become a topic of interest for sociologists, psychologists, and experts in folklore since at least the 1960s, when John F. Kennedy assassination conspiracy theories, a number of conspiracy theories arose regarding John F. Kennedy assassination, the assassination of U.S. President John F. Kennedy. Sociologist Türkay Salim Nefes underlines the political nature of conspiracy theories. He suggests that one of the most important characteristics of these accounts is their attempt to unveil the "real but hidden" power relations in social groups. The term "conspiracism" was popularized by academic Frank P. Mintz in the 1980s. According to Mintz, conspiracism denotes "belief in the primacy of conspiracies in the unfolding of history": Research suggests, on a psychological level, conspiracist ideation—belief in conspiracy theories—can be harmful or pathological, and is highly correlated withpsychological projection
Psychological projection is the process of misinterpreting what is "inside" as coming from "outside". It forms the basis of empathy by the projection of personal experiences to understand someone else's subjective world. In its malignant forms, i ...
, as well as with paranoia
Paranoia is an instinct or thought process that is believed to be heavily influenced by anxiety or fear, often to the point of delusion and irrationality. Paranoid thinking typically includes persecutory beliefs, or beliefs of conspiracy c ...
, which is predicted by the degree of a person's Machiavellianism
Machiavellianism or Machiavellian may refer to:
Politics
*Machiavellianism (politics), the supposed political philosophy of Niccolò Machiavelli
*Political realism
Psychology
*Machiavellianism (psychology), a personality trait centered on cold an ...
. The propensity to believe in conspiracy theories is strongly associated with the mental health disorder of schizotypy
In psychology, schizotypy is a theoretical concept that posits a continuum of personality characteristics and experiences, ranging from normal dissociative, imaginative states to extreme states of mind related to psychosis, especially schizophr ...
. Conspiracy theories once limited to fringe audiences have become commonplace in mass media
Mass media refers to a diverse array of media technologies that reach a large audience via mass communication. The technologies through which this communication takes place include a variety of outlets.
Broadcast media transmit informati ...
, emerging as a cultural phenomenon
The bandwagon effect is the tendency for people to adopt certain behaviors, styles, or attitudes simply because others are doing so. More specifically, it is a cognitive bias by which public opinion or behaviours can alter due to particular act ...
of the late 20th and early 21st centuries. Exposure to conspiracy theories in news media and popular entertainment increases receptiveness to conspiratorial ideas, and has also increased the social acceptability of fringe beliefs.
Conspiracy theories often make use of complicated and detailed arguments, including ones which appear to be analytical or scientific. However, belief in conspiracy theories is primarily driven by emotion. One of the most widely confirmed facts about conspiracy theories is that belief in a single conspiracy theory tends to promote belief in other unrelated conspiracy theories as well. This even applies when the conspiracy theories directly contradict each other, e.g. believing that Osama bin Laden was already dead before his compound in Pakistan was attacked makes the same person more likely to believe that he is still alive. One conclusion from this finding is that the content of a conspiracist belief is less important than the idea of a coverup by the authorities. Analytical thinking aids in reducing belief in conspiracy theories, in part because it emphasizes rational and critical cognition.
Some psychological scientists assert that explanations related to conspiracy theories can be, and often are "internally consistent" with strong beliefs that had previously been held prior to the event that sparked the conspiracy. People who believe in conspiracy theories tend to believe in other unsubstantiated claims – including pseudoscience and paranormal phenomena.
Attractions
Psychological motives for believing in conspiracy theories can be categorized as epistemic, existential, or social. These motives are particularly acute in vulnerable and disadvantaged populations. However, it does not appear that the beliefs help to address these motives; in fact, they may be self-defeating, acting to make the situation worse instead. For example, while conspiratorial beliefs can result from a perceived sense of empowerment, powerlessness, exposure to conspiracy theories immediately suppresses personal feelings of autonomy and control. Furthermore, they also make people less likely to take actions that could improve their circumstances. This is additionally supported by the fact that conspiracy theories have a number of disadvantageous attributes. For example, they promote a negative and distrustful view of other people and groups, who are allegedly acting based on antisocial and cynical motivations. This is expected to lead to increased Social alienation, alienation and anomie, and reduced social capital. Similarly, they depict the public as ignorant and powerless against the alleged conspirators, with important aspects of society determined by malevolent forces, a viewpoint which is likely to be disempowering. Each person may endorse conspiracy theories for one of many different reasons. The most consistently demonstrated characteristics of people who find conspiracy theories appealing are a feeling of Social alienation, alienation, unhappiness or dissatisfaction with their situation, an unconventional worldview, and a feeling of disempowerment. While various aspects of personality affect susceptibility to conspiracy theories, none of the Big Five personality traits are associated with conspiracy beliefs. The political scientistMichael Barkun
__NOTOC__
Michael Barkun (born April 8, 1938) is an American academic who serves as Professor Emeritus of political science at the Maxwell School of Citizenship and Public Affairs, Syracuse University, specializing in political and religious ext ...
, discussing the usage of "conspiracy theory" in contemporary American culture, holds that this term is used for a belief that explains an event as the result of a secret plot by exceptionally powerful and cunning conspirators to achieve a malevolent end. According to Barkun, the appeal of conspiracism is threefold:
* First, conspiracy theories claim to explain what institutional analysis
Institutional analysis is that part of the social sciences which studies how institutions—i.e., structures and mechanisms of social order and cooperation governing the behavior of two or more individuals—behave and function according to both e ...
cannot. They appear to make sense out of a world that is otherwise confusing.
* Second, they do so in an appealingly simple way, by dividing the world sharply between Manichaeism, the forces of light, and the forces of darkness. They trace all evil back to a single source, the conspirators and their agents.
* Third, conspiracy theories are often presented as special, esotericism, secret knowledge unknown or unappreciated by others. For conspiracy theorists, the masses are a sheeple, brainwashed herd, while the conspiracy theorists in the know can congratulate themselves on penetrating the plotters' deceptions."
This third point is supported by research of Roland Imhoff, professor in Social Psychology at the Johannes Gutenberg University Mainz. The research suggests that the smaller the minority believing in a specific theory, the more attractive it is to conspiracy theorists.
Humanistic psychology, Humanistic psychologists argue that even if a posited cabal behind an alleged conspiracy is almost always perceived as hostile, there often remains an element of reassurance for theorists. This is because it is a consolation to imagine that difficulties in human affairs are created by humans, and remain within human control. If a cabal can be implicated, there may be a hope of breaking its power or of joining it. Belief in the power of a cabal is an implicit assertion of human dignity—an unconscious affirmation that man is responsible for his own destiny.
People formulate conspiracy theories to explain, for example, power relations in social groups and the perceived existence of evil forces. Proposed psychological origins of conspiracy theorising include projection; the personal need to explain "a significant event [with] a significant cause;" and the product of various kinds and stages of thought disorder, such as paranoid disposition, ranging in severity to diagnosable mental illnesses. Some people prefer socio-political explanations over the insecurity of encountering randomness, random, unpredictable, or otherwise inexplicable events.Justin Fox"Wall Streeters like conspiracy theories. Always have"
, ''Time'', 1 October 2009. According to Berlet and Lyons, "Conspiracism is a particular narrative form of scapegoating that frames demonized enemies as part of a vast insidious plot against the common good, while it valorizes the scapegoater as a hero for sounding the alarm".
Origins
Some psychologists believe that a search for meaning is common in conspiracism. Once cognized,confirmation bias
Confirmation bias is the tendency to search for, interpret, favor, and recall information in a way that confirms or supports one's prior beliefs or values. People display this bias when they select information that supports their views, ignoring ...
and avoidance of cognitive dissonance may reinforce the belief. In a context where a conspiracy theory has become embedded within a social group, communal reinforcement may also play a part.
Inquiry into possible motives behind the accepting of irrational conspiracy theories has linked these beliefs to distress resulting from an event that occurred, such as the September 11 attacks, events of 9/11. Additionally, research done by Manchester Metropolitan University suggests that "delusional ideation" is the most likely condition that would indicate an elevated belief in conspiracy theories. Studies also show that an increased attachment to these irrational beliefs lead to a decrease in desire for civic engagement. Belief in conspiracy theories is correlated with low intelligence, lower analytical thinking, anxiety disorders, paranoia
Paranoia is an instinct or thought process that is believed to be heavily influenced by anxiety or fear, often to the point of delusion and irrationality. Paranoid thinking typically includes persecutory beliefs, or beliefs of conspiracy c ...
, and authoritarian beliefs.
Professor Quassim Cassam argues that conspiracy theorists hold their beliefs due to flaws in their thinking and more precisely, their intellectual character. He cites philosopher Linda Trinkaus Zagzebski and her book ''Virtues of the Mind'' in outlining intellectual virtues (such as humility, caution and carefulness) and intellectual vices (such as gullibility, carelessness and closed-mindedness). Whereas intellectual virtues help in reaching sound examination, intellectual vices "impede effective and responsible inquiry", meaning that those who are prone to believing in conspiracy theories possess certain vices while lacking necessary virtues.
Some researchers have suggested that conspiracy theories could be partially caused by psychological mechanisms the human brain possesses for detecting dangerous coalitions. Such a mechanism could have been useful in the small-scale environment humanity evolved in but are mismatched in a modern, complex society and thus "misfire", perceiving conspiracies where none exist.
Projection
Some historians have argued thatpsychological projection
Psychological projection is the process of misinterpreting what is "inside" as coming from "outside". It forms the basis of empathy by the projection of personal experiences to understand someone else's subjective world. In its malignant forms, i ...
is prevalent amongst conspiracy theorists. This projection, according to the argument, is manifested in the form of attribution of undesirable characteristics of the self to the conspirators. Historian Richard Hofstadter stated that:
Hofstadter also noted that "sexual freedom" is a vice frequently attributed to the conspiracist's target group, noting that "very often the fantasies of true believers reveal strong sadomasochistic outlets, vividly expressed, for example, in the delight of anti-Masons with the cruelty of Masonic punishments."
Sociology
In addition to psychological factors such as conspiracist ideation, sociological factors also help account for who believes in which conspiracy theories. Such theories tend to get more traction among election losers in society, for example, and the emphasis of conspiracy theories by elites and leaders tends to increase belief among followers who have higher levels of conspiracy thinking. Christopher Hitchens described conspiracy theories as the "exhaust fumes of democracy": the unavoidable result of a large amount of information circulating among a large number of people. Conspiracy theories may be emotionally satisfying, by assigning blame to a group to which the theorist does not belong and so absolving the theorist of moral or political responsibility in society. Likewise, Roger Cohen writing for ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'' has said that, "captive minds; ... resort to conspiracy theory because it is the ultimate refuge of the powerless. If you cannot change your own life, it must be that some greater force controls the world."
Sociological historian Holger Herwig found in studying German explanations for the origins of World War I, "Those events that are most important are hardest to understand because they attract the greatest attention from myth makers and charlatans."
Justin Fox of ''Time (magazine), Time'' magazine argues that Wall Street traders are among the most conspiracy-minded group of people, and ascribes this to the reality of some financial market conspiracies, and to the ability of conspiracy theories to provide necessary orientation in the market's day-to-day movements.
Influence of critical theory
French sociologist Bruno Latour suggests that the widespread popularity of conspiracy theories in mass culture may be due, in part, to the pervasive presence of Marxist-inspired critical theory and similar ideas in academia since the 1970s. Latour notes that about 90% of contemporary social criticism in academia displays one of two approaches, which he terms "the ''fact position'' and the ''fairy position''". * The "fairy position" is fetish (disambiguation), anti-fetishist, arguing that "objects of belief" (e.g., religion, arts) are merely concepts onto which power is projected; Latour contends that those who use this approach show biases towards confirming their own dogmatic suspicions as most "scientifically supported". While the complete facts of the situation and correct methodology are ostensibly important to them, Latour proposes that the scientific process is instead laid on as a patina to one's pet theories to lend a sort of reputation high ground. * The "fact position" argues that external forces (e.g., economics, gender) dominate individuals, often covertly and without their awareness. Latour concludes that each of these two approaches in academia has led to a polarized, inefficient atmosphere highlighted (in both approaches) by its causticness. "Do you see now why it feels so good to be a critical mind?" asks Latour: no matter which position you take, "You're always right!" Latour notes that such social criticism has been appropriated by those he describes as conspiracy theorists, including climate change denial, climate-change denialists and the 9/11 Truth movement: "Maybe I am taking conspiracy theories too seriously, but I am worried to detect, in those mad mixtures of knee-jerk disbelief, punctilious demands for proofs, and free use of powerful explanation from the social neverland, many of the weapons of social critique."Fusion paranoia
Michael Kelly (editor), Michael Kelly, a ''The Washington Post'' journalist and critic of anti-war movements on both the left and right, coined the term "fusion paranoia" to refer to a political convergence of left-wing and right-wing activists around anti-war issues and civil liberties, which he said were motivated by a shared belief in conspiracism or shared Anti-statism, anti-government views. Barkun has adopted this term to refer to how the synthesis of paranoid conspiracy theories, which were once limited to American fringe audiences, has given them mass appeal and enabled them to become commonplace inmass media
Mass media refers to a diverse array of media technologies that reach a large audience via mass communication. The technologies through which this communication takes place include a variety of outlets.
Broadcast media transmit informati ...
, thereby inaugurating an unrivaled period of people actively preparing for apocalypticism, apocalyptic or millenarianism, millenarian scenarios in the United States of the late 20th and early 21st centuries. Barkun notes the occurrence of lone-wolf conflicts with law enforcement acting as proxy for threatening the established political powers.
Viability
As evidence against the reality of an alleged conspiracy grows, the number of alleged conspirators also grow in the minds of conspiracy theorists. This is because alleged conspirators often have competing interests. For example, if Republican President George W. Bush is allegedly responsible for the 9/11 terrorist attacks, and the Democratic party did not pursue exposing this alleged plot, that must mean that both the Democratic and Republican parties are conspirators in the alleged plot. It also assumes that alleged conspirators are so competent that they can fool the entire world, but so incompetent that the conspiracy theorists can find alleged mistakes they make that prove the fraud. At some point, the number of alleged conspirators, combined with the contradictions within the alleged conspirators' interests and competence, becomes so great that maintaining the theory becomes an obvious exercise in absurdity. The physicist David Robert Grimes estimated the time it would take for a conspiracy to be exposed based on the number of people involved. His calculations used data from the PRISM (surveillance program), PRISM surveillance program, the Tuskegee syphilis experiment, and the FBI Laboratory#Controversy, FBI forensic scandal. Grimes estimated that: * A Moon landing conspiracy theories, Moon landing hoax would require the involvement of 411,000 people and would be exposed within 3.68 years; * Global warming conspiracy theory, Climate-change fraud would require a minimum of 29,083 people (published climate scientists only) and would be exposed within 26.77 years, or up to 405,000 people, in which case it would be exposed within 3.70 years; * A vaccination conspiracy would require a minimum of 22,000 people (without drug companies) and would be exposed within at least 3.15 years and at most 34.78 years depending on the number involved; * A conspiracy to Big Pharma conspiracy theory, suppress a cure for cancer would require 714,000 people and would be exposed within 3.17 years. Grimes's study did not consider exposure by sources outside of the alleged conspiracy. It only considered exposure from within the alleged conspiracy through whistleblowers or through incompetence.Politics
 The philosopher Karl Popper described the central problem of conspiracy theories as a form of fundamental attribution error, where every event is generally perceived as being intentional and planned, greatly underestimating the effects of randomness and unintended consequences. In his book ''The Open Society and Its Enemies'', he used the term "the conspiracy theory of society" to denote the idea that social phenomena such as "war, unemployment, poverty, shortages ... [are] the result of direct design by some powerful individuals and groups." Popper argued that totalitarianism was founded on conspiracy theories which drew on imaginary plots which were driven by paranoid scenarios predicated on tribalism, chauvinism, or racism. He also noted that conspirators very rarely achieved their goal.
Historically, real conspiracies have usually had little effect on history and have had unforeseen consequences for the conspirators, in contrast to conspiracy theories which often posit grand, sinister organizations, or world-changing events, the evidence for which has been erased or obscured. As described by Bruce Cumings, history is instead "moved by the broad forces and large structures of human collectivities".
The philosopher Karl Popper described the central problem of conspiracy theories as a form of fundamental attribution error, where every event is generally perceived as being intentional and planned, greatly underestimating the effects of randomness and unintended consequences. In his book ''The Open Society and Its Enemies'', he used the term "the conspiracy theory of society" to denote the idea that social phenomena such as "war, unemployment, poverty, shortages ... [are] the result of direct design by some powerful individuals and groups." Popper argued that totalitarianism was founded on conspiracy theories which drew on imaginary plots which were driven by paranoid scenarios predicated on tribalism, chauvinism, or racism. He also noted that conspirators very rarely achieved their goal.
Historically, real conspiracies have usually had little effect on history and have had unforeseen consequences for the conspirators, in contrast to conspiracy theories which often posit grand, sinister organizations, or world-changing events, the evidence for which has been erased or obscured. As described by Bruce Cumings, history is instead "moved by the broad forces and large structures of human collectivities".
Middle East
Conspiracy theories are a prevalent feature of Arab culture and politics. Variants include conspiracies involving colonialism, Zionism, superpowers, oil, and the war on terrorism, which may be referred to as a war against Islam. For example, '' The Protocols of the Elders of Zion'', an infamous hoax document purporting to be a Jewish plan for world domination, is commonly read and promoted in the Muslim world. Roger Cohen has suggested that the popularity of conspiracy theories in the Arab world is "the ultimate refuge of the powerless". Al-Mumin Said has noted the danger of such theories, for they "keep us not only from the truth but also from confronting our faults and problems". Osama bin Laden and Ayman al-Zawahiri have used conspiracy theories about the United States to gain support for al-Qaeda in the Arab world, and as rhetoric to distinguish themselves from similar groups, although they may not have believed the conspiratorial claims themselves.United States
The historian Richard Hofstadter addressed the role ofparanoia
Paranoia is an instinct or thought process that is believed to be heavily influenced by anxiety or fear, often to the point of delusion and irrationality. Paranoid thinking typically includes persecutory beliefs, or beliefs of conspiracy c ...
and conspiracism throughout History of the United States, U.S. history in his 1964 essay "The Paranoid Style in American Politics". Bernard Bailyn, Bernard Bailyn's classic ''The Ideological Origins of the American Revolution'' (1967) notes that a similar phenomenon could be found in North America during the time preceding the American Revolution. Conspiracism labels people's attitudes as well as the type of conspiracy theories that are more global and historical in proportion.
Harry G. West and others have noted that while conspiracy theorists may often be dismissed as a fringe minority, certain evidence suggests that a wide range of the U.S. maintains a belief in conspiracy theories. West also compares those theories to hypernationalism and religious fundamentalism.
Theologian Robert Jewett and philosopher John Shelton Lawrence attribute the enduring popularity of conspiracy theories in the U.S. to the Cold War, McCarthyism, and Counterculture of the 1960s, counterculture rejection of authority. They state that among both the left-wing and right-wing, there remains a willingness to use real events, such as Soviet plots, inconsistencies in the Warren Commission, Warren Report, and the September 11 attacks, 9/11 attacks, to support the existence of unverified and ongoing large-scale conspiracies.
In his studies of “American political demonology,” historian Michael Paul Rogin too analyzed this paranoid style of politics that has occurred throughout American history. Conspiracy theories frequently identify an imaginary subversive group that is supposedly attacking the nation and requires the government and allied forces to engage in harsh extra-legal repression of those threatening subversives. Rogin cites examples from the Red Scares of 1919, to McCarthy’s anti-communist campaign in the 1950s and more recently fears of immigrant hordes invading the US. Unlike Hofstadter, Rogin saw these "countersubversive" fears as frequently coming from those in power and dominant groups, instead of from the dispossessed. Unlike Robert Jewett, Rogin blamed not the counterculture, but America’s dominant culture of liberal individualism and the fears it stimulated to explain the periodic eruption of irrational conspiracy theories.
The Watergate scandal
The Watergate scandal was a major political scandal in the United States involving the administration of President Richard Nixon from 1972 to 1974 that led to Nixon's resignation. The scandal stemmed from the Nixon administration's contin ...
has also been used to bestow legitimacy to other conspiracy theories, with Richard Nixon himself commenting that it served as a "Rorschach test, Rorschach ink blot" which invited others to fill in the underlying pattern.
Historian Kathryn S. Olmsted cites three reasons why Americans are prone to believing in government conspiracies theories:
#Genuine government overreach and secrecy during the Cold War, such as Watergate, the Tuskegee syphilis experiment, Project MKUltra, and the CIA's assassination attempts on Fidel Castro in collaboration with mobsters.
#Precedent set by official government-sanctioned conspiracy theories for propaganda, such as claims of German infiltration of the U.S. during World War II or the debunked claim that Saddam Hussein and al-Qaeda link allegations, Saddam Hussein played a role in the 9/11 attacks.
#Distrust fostered by the government's spying on and harassment of dissenters, such as the Sedition Act of 1918, COINTELPRO, and as part of various Red Scares.
Alex Jones referenced numerous conspiracy theories for convincing his supporters to endorse Ron Paul over Mitt Romney in the 2012 Republican Party presidential primaries and Donald Trump over Hillary Clinton in the 2016 United States presidential election. Into the 2020s, the QAnon conspiracy theory alleges that Trump is fighting against a Deep state in the United States, deep-state cabal of child sex-abusing and Satan-worshipping Democratic Party (United States), Democrats.
See also
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *References
Informational notes Citations Further reading * * * Burnett, Thom. ''Conspiracy Encyclopedia: The Encyclopedia of Conspiracy Theories'' * Butter, Michael, and Peter Knight. "Bridging the great divide: conspiracy theory research for the 21st century." ''Diogenes'' (2016): 0392192116669289online
* * * * * De Graaf, Beatrice and Zwierlein, Cornel (eds.
''Security and Conspiracy in History, 16th to 21st Century''
Historical Social Research 38, Special Issue, 2013 * Fleming, Chris and Emma A. Jane. ''Modern Conspiracy: The Importance of Being Paranoid''. New York and London: Bloomsbury, 2014. . * Goertzel, Ted. "Belief in conspiracy theories." ''Political Psychology'' (1994): 731–742
online
* Harris, Lee
''"The Trouble with Conspiracy Theories"''
The American, 12 January 2013. * Hofstadter, Richard. ''The paranoid style in American politics'' (1954)
online
* * * * * * * Oliver, J. Eric, and Thomas J. Wood. "Conspiracy theories and the paranoid style (s) of mass opinion." ''American Journal of Political Science'' 58.4 (2014): 952–96
online
* * * * * * Slosson, W
''"The 'Conspiracy' Superstition"''
The Unpopular Review, Vol. VII, N°. 14, 1917. * Sunstein, Cass R., and Adrian Vermeule. "Conspiracy theories: Causes and cures." ''Journal of Political Philosophy'' 17.2 (2009): 202–227
online
* Uscinski, Joseph E. and Joseph M. Parent, ''American Conspiracy Theories'' (2014
excerpt
* Uscinski, Joseph E. "The 5 Most Dangerous Conspiracy Theories of 2016
''POLITICO Magazine'' (Aug 22, 2016)
* * Wood, Gordon S. "Conspiracy and the paranoid style: causality and deceit in the eighteenth century." ''William and Mary Quarterly'' (1982): 402–441
in jstor
External links
Conspiracy Theories
''Internet Encyclopedia of Philosophy'' {{DEFAULTSORT:Conspiracy Theory Conspiracy theories, Barriers to critical thinking Fringe theory Pejorative terms