Confronted animals on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Confronted animals, or confronted-animal as an
from the area of contemporary
 The
The
File:Kerykeia Hamburg MKG.JPG, Ancient Greek herald's staffs (kerykeia), Greece, southern Italy, 5th century BC.
 Confronted leopards appear in a tomb found in Tarchuna (
Confronted leopards appear in a tomb found in Tarchuna (
File:Basel minster capital outside main nave.jpeg, Romanesque capital, northern outside of the main apse of
File:VAM - Luristan Greife.jpg,
 "Powhatan's Mantle" is a cloak of
"Powhatan's Mantle" is a cloak of "Powhatan's Mantle"
at the
Photo--Cylinder Seal-High Res
– Two animals, each held by a
Photo--variation of Tree of life confronted-animals
– One figure is facing toward the observer.
Nomadic Art of the Eastern Eurasian Steppes
an exhibition catalog from The Metropolitan Museum of Art (fully available online as PDF), which contains material on confronted animals Confronted snakes
Photo--confronted snakes
Iconography Animals in art Symmetry Visual motifs
adjective
In linguistics, an adjective (list of glossing abbreviations, abbreviated ) is a word that generally grammatical modifier, modifies a noun or noun phrase or describes its referent. Its semantic role is to change information given by the noun.
Tra ...
, where two animals face each other in a symmetrical
Symmetry (from grc, συμμετρία "agreement in dimensions, due proportion, arrangement") in everyday language refers to a sense of harmonious and beautiful proportion and balance. In mathematics, "symmetry" has a more precise definiti ...
pose, is an ancient bilateral motif in art
Art is a diverse range of human activity, and resulting product, that involves creative or imaginative talent expressive of technical proficiency, beauty, emotional power, or conceptual ideas.
There is no generally agreed definition of wha ...
and artifacts studied in archaeology
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscap ...
and art history
Art history is the study of aesthetic objects and visual expression in historical and stylistic context. Traditionally, the discipline of art history emphasized painting, drawing, sculpture, architecture, ceramics and decorative arts; yet today ...
. The "anti-confronted animals" is the opposing motif, with the animals back to back.
Bilateral symmetry is a dominant aspect of our world and strong representation of it with matching figures often creates a balance that is appealing in artwork.
In ancient art, confronted-animal motifs often involve the Master of Animals, a central human figure between two confronted animals, often grasping them, and are probably part of a unified socio-cultural
Culture () is an umbrella term which encompasses the social behavior, institutions, and Social norm, norms found in human Society, societies, as well as the knowledge, beliefs, arts, laws, Social norm, customs, capabilities, and habits of the ...
motif. A related motif in ancient art is known as the Mistress of Animals.
It is thought that the iconography
Iconography, as a branch of art history, studies the identification, description and interpretation of the content of images: the subjects depicted, the particular compositions and details used to do so, and other elements that are distinct fro ...
sometimes has ritual
A ritual is a sequence of activities involving gestures, words, actions, or objects, performed according to a set sequence. Rituals may be prescribed by the traditions of a community, including a religious community. Rituals are characterized, b ...
and religious associations; for example, the Lion Gate of Mycenae
Mycenae ( ; grc, Μυκῆναι or , ''Mykē̂nai'' or ''Mykḗnē'') is an archaeological site near Mykines in Argolis, north-eastern Peloponnese, Greece. It is located about south-west of Athens; north of Argos; and south of Corinth. Th ...
has a column between the protective, surmounted and confronted lionesses standing with two feet on the ground and two on the same base on which the column rests. The column is thought to represent a goddess, abstracted to avoid taboo
A taboo or tabu is a social group's ban, prohibition, or avoidance of something (usually an utterance or behavior) based on the group's sense that it is excessively repulsive, sacred, or allowed only for certain persons.''Encyclopædia Britannica ...
ed direct representation. Alternatively, the column has also been interpreted as symbolizing the entrance to the palace. The lions are thus guarding the entrance to the palace and the walled fortification simultaneously. The motif called the Tree of Life
The tree of life is a fundamental archetype in many of the world's mythological, religious, and philosophical traditions. It is closely related to the concept of the sacred tree.Giovino, Mariana (2007). ''The Assyrian Sacred Tree: A History ...
, where two confronted animals graze on a shrub or tree, is also very ancient.
Gebel el-Arak Knife
The reverse side of theGebel el-Arak Knife
The Gebel el-Arak Knife, also Jebel el-Arak Knife, is an ivory and flint knife dating from the Naqada II period of Egyptian prehistory (3500—3200 BC), showing Mesopotamian influence. The knife was purchased in 1914 in Cairo by Georges Aaron B ...
handle, displayed at the top of the article, shows two powerful confronted lions, separated by a figure who is grasping them. Of note, the knob on the reverse shows the top end of the hole for a cord or rope, on the suspension lug; this knife may have been worn around the neck ceremonially.
Examples from archaeology
Cylinder seals
Examples of confronted animals exist onCylinder seal
A cylinder seal is a small round cylinder, typically about one inch (2 to 3 cm) in length, engraved with written characters or figurative scenes or both, used in ancient times to roll an impression onto a two-dimensional surface, generally ...
s from Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the F ...
. Deities
A deity or god is a supernatural being who is considered divine or sacred. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines deity as a god or goddess, or anything revered as divine. C. Scott Littleton defines a deity as "a being with powers greate ...
, or hero
A hero (feminine: heroine) is a real person or a main fictional character who, in the face of danger, combats adversity through feats of ingenuity, courage, or Physical strength, strength. Like other formerly gender-specific terms (like ...
es grasping lionesses, cattle, griffin
The griffin, griffon, or gryphon (Ancient Greek: , ''gryps''; Classical Latin: ''grȳps'' or ''grȳpus''; Late Latin, Late and Medieval Latin: ''gryphes'', ''grypho'' etc.; Old French: ''griffon'') is a legendary creature with the body, tail ...
s, or other, imaginary creatures are sometimes found.
Many cylinder seals involving confronted goat
The goat or domestic goat (''Capra hircus'') is a domesticated species of goat-antelope typically kept as livestock. It was domesticated from the wild goat (''C. aegagrus'') of Southwest Asia and Eastern Europe. The goat is a member of the a ...
s surrounding a central Tree of life
The tree of life is a fundamental archetype in many of the world's mythological, religious, and philosophical traditions. It is closely related to the concept of the sacred tree.Giovino, Mariana (2007). ''The Assyrian Sacred Tree: A History ...
on a 'cone' or 'mountain' platform share one common theme. Others may be thought of as deities holding the animals under their control.
Because cylinder seals are numerous and also come from pre-historical periods, back to the fourth or 5th millennium BC
The 5th millennium BC spanned the years 5000 BC to 4001 BC (c. 7 ka to c. 6 ka). It is impossible to precisely date events that happened around the time of this millennium and all dates mentioned here are estimates mostly based on geological an ...
, themes are varied. Another Tree of life type of confronted animals cylinder seal has a "hero grasping water buffalo" and a "bull-man grasping lions", each between the animals; again, the central figure is the "Tree-of-Life" that often is interpreted as representing a goddess.
Confronted snakes
Confrontedsnake
Snakes are elongated, Limbless vertebrate, limbless, carnivore, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other Squamata, squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping Scale (zoology), scales. Ma ...
s are frequent images in many cultures from ancient times to historical periods. Often associated with religious ceremonies and deities, perhaps the most familiar figure known popularly from ancient times is the deity or priestess of Crete depicted holding up two confronted snakes on either side of her.
A chlorite
The chlorite ion, or chlorine dioxide anion, is the halite with the chemical formula of . A chlorite (compound) is a compound that contains this group, with chlorine in the oxidation state of +3. Chlorites are also known as salts of chlorous ac ...
vessefrom the area of contemporary
Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon ...
, Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
is displayed at this link. It depicts three pairs of confronted animals. Two confronted snakes
Snakes are elongated, limbless, carnivorous reptiles of the suborder Serpentes . Like all other squamates, snakes are ectothermic, amniote vertebrates covered in overlapping scales. Many species of snakes have skulls with several more joi ...
are being held in the hands of the central figure; below the snake-pair are a pair of ''anti-confronted-lionesses'' (although they turn their heads to face each other their hind quarters are closely confronted), recumbent. The third similar pair of animals on this item are two anti-confronted bovines with a human or deity between also. Two tumbling lions and other animals are depicted to the right.
Narmer Palette
 The
The Narmer Palette
The Narmer Palette, also known as the Great Hierakonpolis Palette or the Palette of Narmer, is a significant Egyptian archeological find, dating from about the 31st century BC, belonging, at least nominally, to the category of cosmetic palettes. ...
, used to mix cosmetics in the receptacle on one side, has two confronted felines, sometimes called serpopard
The serpopard is a mythical animal known from ancient Egyptian and Mesopotamian art. The word "serpopard" is a modern coinage. It is a portmanteau of "serpent" and "leopard", derived from the interpretation that the creature represents an anim ...
s (because of their exaggerated long necks which look snakelike to some researchers) forming the receptacle. Close examination of the animals with the exaggerated, long necks supports identification as lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large Felidae, cat of the genus ''Panthera'' native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; short, rounded head; round ears; and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphi ...
esses. The entire theme of the Narmer Palette, is about the pharaoh
Pharaoh (, ; Egyptian: ''pr ꜥꜣ''; cop, , Pǝrro; Biblical Hebrew: ''Parʿō'') is the vernacular term often used by modern authors for the kings of ancient Egypt who ruled as monarchs from the First Dynasty (c. 3150 BC) until the an ...
of the newly unified Ancient Egypt represented in two scenes, (palette ''obverse'', palette ''reverse''). On one side the pharaoh wears the crown of Upper Egypt
Upper Egypt ( ar, صعيد مصر ', shortened to , , locally: ; ) is the southern portion of Egypt and is composed of the lands on both sides of the Nile that extend upriver from Lower Egypt in the north to Nubia in the south.
In ancient ...
and on the other, the pharaoh wears the crown of Lower Egypt
Lower Egypt ( ar, مصر السفلى '; ) is the northernmost region of Egypt, which consists of the fertile Nile Delta between Upper Egypt and the Mediterranean Sea, from El Aiyat, south of modern-day Cairo, and Dahshur. Historically, ...
. Thus, it is thought that the lionesses with their intertwining necks are representing two kingdoms, once separate, but now unified under one pharaoh. The lioness Bast had been the protective deity of one kingdom and the lioness Sekhmet
In Egyptian mythology, Sekhmet ( or Sachmis (), also spelled Sakhmet, Sekhet, Sakhet among other spellings, cop, Ⲥⲁⲭⲙⲓ, Sakhmi), is a warrior goddess as well as goddess of healing. She is depicted as a lioness.
Sekhmet is a solar de ...
of the other kingdom, equally important deities in each of the early Egyptian pantheon
Ancient Egyptian deities are the gods and goddesses worshipped in ancient Egypt. The beliefs and rituals surrounding these gods formed the core of ancient Egyptian religion, which emerged sometime in prehistory. Deities represented natural f ...
s. Respectively, they were the special protectors of the pharaoh in each kingdom, who persisted as deities throughout the long history of unified Ancient Egypt. Eventually their roles diverged, however, with one becoming less of the protector and warrior deity and assigned other roles. Typically, many similar deities in the two kingdoms soon were merged, so the retention of both is thought to be the result of the long and strong tradition of each.
Examples of other confronted animals exist on many cosmetic palette
Cosmetic palettes are archaeological Artifact (archaeology), artifacts, originally used in predynastic Egypt, predynastic ancient Egypt, Egypt to grind and apply ingredients for facial or body cosmetics. The decorative palettes of the late 4th mill ...
s of Ancient Egypt that have been discovered. One palette has confronted-hippopotamus
The hippopotamus ( ; : hippopotamuses or hippopotami; ''Hippopotamus amphibius''), also called the hippo, common hippopotamus, or river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic mammal native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of only two extan ...
es; others include giraffes, geese, and other animals familiar to the Egyptians. Bilaterally depicted palm tree
The Arecaceae is a family of perennial flowering plants in the monocot order Arecales. Their growth form can be climbers, shrubs, tree-like and stemless plants, all commonly known as palms. Those having a tree-like form are called palm trees ...
s also are known as well on palettes.
Mycenae Lion Gate
The gate to the citadel ofMycenae
Mycenae ( ; grc, Μυκῆναι or , ''Mykē̂nai'' or ''Mykḗnē'') is an archaeological site near Mykines in Argolis, north-eastern Peloponnese, Greece. It is located about south-west of Athens; north of Argos; and south of Corinth. Th ...
is shown to the right. It crowned the major entrance gateway to the ancient citadel that was the centre of the culture, Mycenaean Greece
Mycenaean Greece (or the Mycenaean civilization) was the last phase of the Bronze Age
The Bronze Age is a historic period, lasting approximately from 3300 BC to 1200 BC, characterized by the use of bronze, the presence of writing in ...
, that predated that of Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders with ...
, and is a well-known example of two confronted lionesses. Debate exists in research of this image, questioning whether these are leopards or lionesses confronted with a column between them that represents the deity, but the characteristic tufts at the end of the tails confirm the species. Many images of lioness related deities are depicted with heavier manes than typical for lionesses, but that may have been the result of attempts to interpretation of the species or, unfamiliarity with the atypical dimorphic differences within this feline species. Alternatively, George Mylonas believed lions were depicted, not lionesses.
Ancient Greek herald's staffs (kerykeia)
In ancient Greece, heralds functioning as private messengers or public criers were referred to as ''kerykes''. The ''keryx'' has functions in political, military, judicional and religious matters. He was identified by his attribute, the herald's staff or ''kerykeion'', in Latin ''caduceus''. The attribute also offered him protection. Hermes, the messenger of the gods, also carries a ''kerykeion''. Kerykeia were often donated to temples by private persons and on state occasions. They are also found in herald's graves, and identify the profession of the buried person.Museum für Kunst und Gewerbe
A museum ( ; plural museums or, rarely, musea) is a building or institution that cares for and displays a collection of artifacts and other objects of artistic, cultural, historical, or scientific importance. Many public museums make thes ...
File:Ancient Greek kerykeion MKG Hamburg.JPG, Ancient Greek herald's staff (''kerykeion''), Bronze, Sicily, 510-490 BC. Museum für Kunst und Gewerbe
A museum ( ; plural museums or, rarely, musea) is a building or institution that cares for and displays a collection of artifacts and other objects of artistic, cultural, historical, or scientific importance. Many public museums make thes ...
Etruscan tomb mural
 Confronted leopards appear in a tomb found in Tarchuna (
Confronted leopards appear in a tomb found in Tarchuna (Tarquinia
Tarquinia (), formerly Corneto, is an old city in the province of Viterbo, Lazio, Central Italy, known chiefly for its ancient Etruscan tombs in the widespread necropoleis, or cemeteries, for which it was awarded UNESCO World Heritage status. ...
), or Tarchna Tarchnal, the chief of the twelve cities of Etruria
Etruria () was a region of Central Italy, located in an area that covered part of what are now most of Tuscany, northern Lazio, and northern and western Umbria.
Etruscan Etruria
The ancient people of Etruria
are identified as Etruscan civiliza ...
, a district in what is described as the Etruscan civilization
The Etruscan civilization () was developed by a people of Etruria in ancient Italy with a common language and culture who formed a federation of city-states. After conquering adjacent lands, its territory covered, at its greatest extent, roughl ...
that existed in Italy from 1200 BC through the 100 BC. It appears in the earliest history of Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus (legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
, which was dominated by it until early in the 330s BC. This mural features confronted leopard
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant species in the genus '' Panthera'', a member of the cat family, Felidae. It occurs in a wide range in sub-Saharan Africa, in some parts of Western and Central Asia, Southern Russia, a ...
s providing protection for a banquet in the afterlife. Frequently felines, lionesses and leopards such as these are confronted with a tree, shrub, or column between them in murals from this culture. The Etruscans are thought to have migrated from the area of Troy, through Greece where they absorbed many cultural elements, to Italy where they founded their culture in prehistoric times.
European art
In Europe, confronted animals are an important motif inanimal style
Animal style art is an approach to decoration found from China to Northern Europe in the early Iron Age, and the barbarian art of the Migration Period, characterized by its emphasis on animal motifs. The zoomorphic style of decoration was used ...
, or zoomorphic
The word ''zoomorphism'' derives from the Greek ζωον (''zōon''), meaning "animal", and μορφη (''morphē''), meaning "shape" or "form". In the context of art, zoomorphism could describe art that imagines humans as non-human animals. It c ...
decoration, Insular art, and the Romanesque. In these contexts there may be little or nothing between the two animals, and the emphasis is on the pair themselves. Human figures are often treated in the same way, often mixed in with animals in decorative schemes - archer
Archery is the sport, practice, or skill of using a bow to shoot arrows.Paterson ''Encyclopaedia of Archery'' p. 17 The word comes from the Latin ''arcus'', meaning bow. Historically, archery has been used for hunting and combat. In mo ...
s were especially popular in the Romanesque period.
The early Anglo-Saxon
The Anglo-Saxons were a Cultural identity, cultural group who inhabited England in the Early Middle Ages. They traced their origins to settlers who came to Britain from mainland Europe in the 5th century. However, the ethnogenesis of the Anglo- ...
ship burial
A ship burial or boat grave is a burial in which a ship or boat is used either as the tomb for the dead and the grave goods, or as a part of the grave goods itself. If the ship is very small, it is called a boat grave. This style of burial was p ...
found in contemporary Great Britain at Sutton Hoo
Sutton Hoo is the site of two early medieval cemeteries dating from the 6th to 7th centuries near the English town of Woodbridge. Archaeologists have been excavating the area since 1938, when a previously undisturbed ship burial containing a ...
, from the seventh century AD, contains famous examples of Migration Period art
Migration Period art denotes the artwork of the Germanic peoples during the Migration period (c. 300 – 900). It includes the Migration art of the Germanic tribes on the continent, as well the start of the Insular art or Hiberno-Saxon art of th ...
. The Sutton Hoo purse-lid has three stylized confronted-animal pairs; the two side pairs, left and right, are identical, and have the animals in the person's clutched grasp. The central confronted animals are even more complex in theme.
Opposed animals are used in Insular art, the style of which is derived from a mixture of Celtic
Celtic, Celtics or Keltic may refer to:
Language and ethnicity
*pertaining to Celts, a collection of Indo-European peoples in Europe and Anatolia
**Celts (modern)
*Celtic languages
**Proto-Celtic language
* Celtic music
*Celtic nations
Sports Fo ...
and northern European design traditions. Confronted animals, or animals intertwined in very intricate patterns, often depicted grabbing at each other to form the "gripping beast" pattern, are a main feature of some periods of Viking art
Viking art, also known commonly as Norse art, is a term widely accepted for the art of Scandinavian Norsemen and Viking settlements further afield—particularly in the British Isles and Iceland—during the Viking Age of the 8th-11th centuries ...
. So intertwined are the animals, they are dissolved into pure ornament, and the individuals are barely discernable from each other. Confronted animals are also frequently seen in European Romanesque art
Romanesque art is the art of Europe from approximately 1000 AD to the rise of the Gothic Art, Gothic style in the 12th century, or later depending on region. The preceding period is known as the Pre-Romanesque period. The term was invented by 1 ...
, for example as decorative patterns in Romanesque architecture
Romanesque architecture is an architectural style of medieval Europe characterized by semi-circular arches. There is no consensus for the beginning date of the Romanesque style, with proposals ranging from the 6th to the 11th century, this lat ...
.
Supporters
In heraldry, supporters, sometimes referred to as ''attendants'', are figures or objects usually placed on either side of the Escutcheon (heraldry), shield and depicted holding it up.
Early forms of supporters are found in medieval seals. H ...
in heraldry
Heraldry is a discipline relating to the design, display and study of armorial bearings (known as armory), as well as related disciplines, such as vexillology, together with the study of ceremony, rank and pedigree. Armory, the best-known branch ...
, not always a matched pair, continue the theme.
Basel Minster
Basel Minster (German: ''Basler Münster'') is a religious building in the Swiss city of Basel, originally a Catholic cathedral and today a Reformed Protestant church.
The original cathedral was built between 1019 and 1500 in Romanesque and ...
File: Abbaye de la Sauve Majeure - Interlaced Asps.JPG, Capital decorated with intertwined beasts derived from Insular art. Grande-Sauve Abbey, France
File:Royal Coat of Arms of the United Kingdom.svg, The Royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom
The royal coat of arms of the United Kingdom, or the royal arms for short, is the arms of dominion of the British monarch, currently King Charles III. These arms are used by the King in his official capacity as monarch of the United Kingdom. Varian ...
has a lion (England) and a unicorn (Scotland) as confronted supporters.
File:Serre-livres, art-déco, par le sculpteur René van Dievoet (1908-1978), août 1944.jpg, Bookends by René van Dievoet (1944).
Asian art
Luristan bronzes, Anatolian "animal" carpets
Confronted-animal motifs are found extensively in Asian art and in textiles, includingrug
Rug or RUG may refer to:
* Rug, or carpet, a textile floor covering
* Rug, slang for a toupée
* Ghent University (''Rijksunversiteit Gent'', or RUG)
* Really Useful Group, or RUG, a company set up by Andrew Lloyd Webber
* Rugby railway station, N ...
s, across Eurasia
Eurasia (, ) is the largest continental area on Earth, comprising all of Europe and Asia. Primarily in the Northern and Eastern Hemispheres, it spans from the British Isles and the Iberian Peninsula in the west to the Japanese archipelago a ...
.
Few examples still exist of a special type of Oriental carpet
A carpet is a textile floor covering typically consisting of an upper layer of pile attached to a backing. The pile was traditionally made from wool, but since the 20th century synthetic fibers such as polypropylene, nylon, or polyester hav ...
, termed "animal carpets" because their main feature are confronted animals. Dated to the 13th–16th century, they represent carpets woven during the transition period between the late Seljuq Seljuk or Saljuq (سلجوق) may refer to:
* Seljuk Empire (1051–1153), a medieval empire in the Middle East and central Asia
* Seljuk dynasty (c. 950–1307), the ruling dynasty of the Seljuk Empire and subsequent polities
* Seljuk (warlord) (d ...
and the early Ottoman empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
. Parallels were shown between the "opposed animal" and "latch-hook" motifs from woven pile rugs and the Lorestān bronzes. These are Early Iron Age
The Iron Age is the final epoch of the three-age division of the prehistory and protohistory of humanity. It was preceded by the Stone Age (Paleolithic, Mesolithic, Neolithic) and the Bronze Age (Chalcolithic). The concept has been mostly appl ...
bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids such ...
artifacts of various individual forms which have been recovered from Lorestān and Kermanshah
Kermanshah ( fa, کرمانشاه, Kermânšâh ), also known as Kermashan (; romanized: Kirmaşan), is the capital of Kermanshah Province, located from Tehran in the western part of Iran. According to the 2016 census, its population is 946,68 ...
areas in west-central Iran
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
.
Carpet fragments discovered in Konya
Konya () is a major city in central Turkey, on the southwestern edge of the Central Anatolian Plateau, and is the capital of Konya Province. During antiquity and into Seljuk times it was known as Iconium (), although the Seljuks also called it D ...
and Beyşehir
Beyşehir () is a large town and district of Konya Province in the Akdeniz region of Turkey. The town is located on the southeastern shore of Lake Beyşehir and is marked to the west and the southwest by the steep lines and forests of the Taurus ...
in Turkey, and Fostat
Fusṭāṭ ( ar, الفُسطاط ''al-Fusṭāṭ''), also Al-Fusṭāṭ and Fosṭāṭ, was the first capital of Egypt under Muslim rule, and the historical centre of modern Cairo. It was built adjacent to what is now known as Old Cairo b ...
in Egypt were dated to the 13th century, which corresponds to the Anatolian Seljuq Period (1243–1302). Rows of horned quadrupeds placed opposite to each other, or birds beside a tree can be recognized on some of these fragments.
A traditional Chinese motif, the fight between phoenix and dragon, is seen in an Anatolian carpet now displayed at the Pergamon Museum
The Pergamon Museum (; ) is a listed building on the Museum Island in the historic centre of Berlin. It was built from 1910 to 1930 by order of German Emperor Wilhelm II according to plans by Alfred Messel and Ludwig Hoffmann in Stripped Class ...
, Berlin, and radiocarbon dated to the mid 15th century. The Chinese motif was probably introduced into Islamic art by the Mongols during the thirteenth century. Another animal carpet showing two medallions with two birds besides a tree was found in the Swedish church of Marby.
Since 1988, seven more carpets of the animal type have been found. They survived in Tibetan monasteries and were removed by monks fleeing to Nepal during the Chinese cultural revolution
The Cultural Revolution, formally known as the Great Proletarian Cultural Revolution, was a sociopolitical movement in the People's Republic of China (PRC) launched by Mao Zedong in 1966, and lasting until his death in 1976. Its stated goal ...
. One of these carpets was acquired by the Metropolitan Museum of Art which parallels a painting by the Sienese artist Gregorio di Cecco: "The Marriage of the Virgin", 1423. It shows large confronted animals, each with a smaller animal inside. An almost complete animal carpet is now at the Museum of Islamic Art, Doha
The Museum of Islamic Art (MIA) is a museum on one end of the Corniche in Doha, Qatar. As per the architect I. M. Pei's specifications, the museum is built on an island off an artificial projecting peninsula near the traditional ''dhow'' harbor ...
.
"Animal carpets" were also depicted in Italian paintings of the 14th and 15th century, and thus represent the earliest Oriental carpets shown in Renaissance paintings
The Renaissance ( , ) , from , with the same meanings. is a period in European history marking the transition from the Middle Ages to modernity and covering the 15th and 16th centuries, characterized by an effort to revive and surpass ideas ...
.
Luristan bronze
Luristan bronzes (rarely "Lorestān", "Lorestāni" etc. in sources in English) are small cast objects decorated with bronze sculpture from the Early Iron Age which have been found in large numbers in Lorestān Province and Kermanshah in wester ...
griffins, 9-7th century BC, Museum of Ancient Near East
The Vorderasiatisches Museum (, '' Near East Museum'') is an archaeological museum in Berlin. It is in the basement of the south wing of the Pergamon Museum and has one of the world's largest collections of Southwest Asian art. 14 halls distri ...
, Berlin.
File:VAM - Luristan Steinböcke.jpg, Luristan bronze ibexes, 9-7th century BC, Museum of Ancient Near East
The Vorderasiatisches Museum (, '' Near East Museum'') is an archaeological museum in Berlin. It is in the basement of the south wing of the Pergamon Museum and has one of the world's largest collections of Southwest Asian art. 14 halls distri ...
, Berlin.
File:Unknown, Turkey, 11th-13th Century - Carpet with Animal Design - Google Art Project.jpg, Animal carpet, Turkey, dated to the 11th–13th century, Museum of Islamic Art, Doha
The Museum of Islamic Art (MIA) is a museum on one end of the Corniche in Doha, Qatar. As per the architect I. M. Pei's specifications, the museum is built on an island off an artificial projecting peninsula near the traditional ''dhow'' harbor ...
File:Marby carpet.jpg, Animal carpet, around 1500, found in Marby Church, Jämtland
Jämtland (; no, Jemtland or , ; Jamtish: ''Jamtlann''; la, Iemptia) is a historical province () in the centre of Sweden in northern Europe. It borders Härjedalen and Medelpad to the south, Ångermanland to the east, Lapland to the north a ...
, Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic country located on ...
. Wool, 160 cm x 112 cm, Swedish History Museum
The Swedish History Museum ( sv, Historiska museet or Statens historiska museum) is a museum located in Stockholm, Sweden, that covers Swedish archaeology and cultural history from the Mesolithic period to present day. Founded in 1866, it operat ...
, Stockholm
File:Phoenix and dragon carpet Anatolia first half or middle 15th century.jpg, Phoenix and Dragon carpet, 164 x 91 cm, Anatolia, circa 1500, Pergamon Museum
The Pergamon Museum (; ) is a listed building on the Museum Island in the historic centre of Berlin. It was built from 1910 to 1930 by order of German Emperor Wilhelm II according to plans by Alfred Messel and Ludwig Hoffmann in Stripped Class ...
, Berlin
File:Jade Openwork Disc with Dragon and Phoenix.JPG, Jade Openwork Disc with Dragon and Phoenix, China, 2nd century BC, Museum of the Mausoleum of the Nanyue King
The Museum of the Western Han Dynasty Mausoleum of the Nanyue King ( Cantonese: Sai Hon Nam Yuet Wong Mou Bok Mat Gun) houses the 2,000-year-old tomb of the Nanyue King Zhao Mo in Guangzhou. Zhao Mo ruled from 137 BC to 122 BC, and his tomb ...
Native North American Art
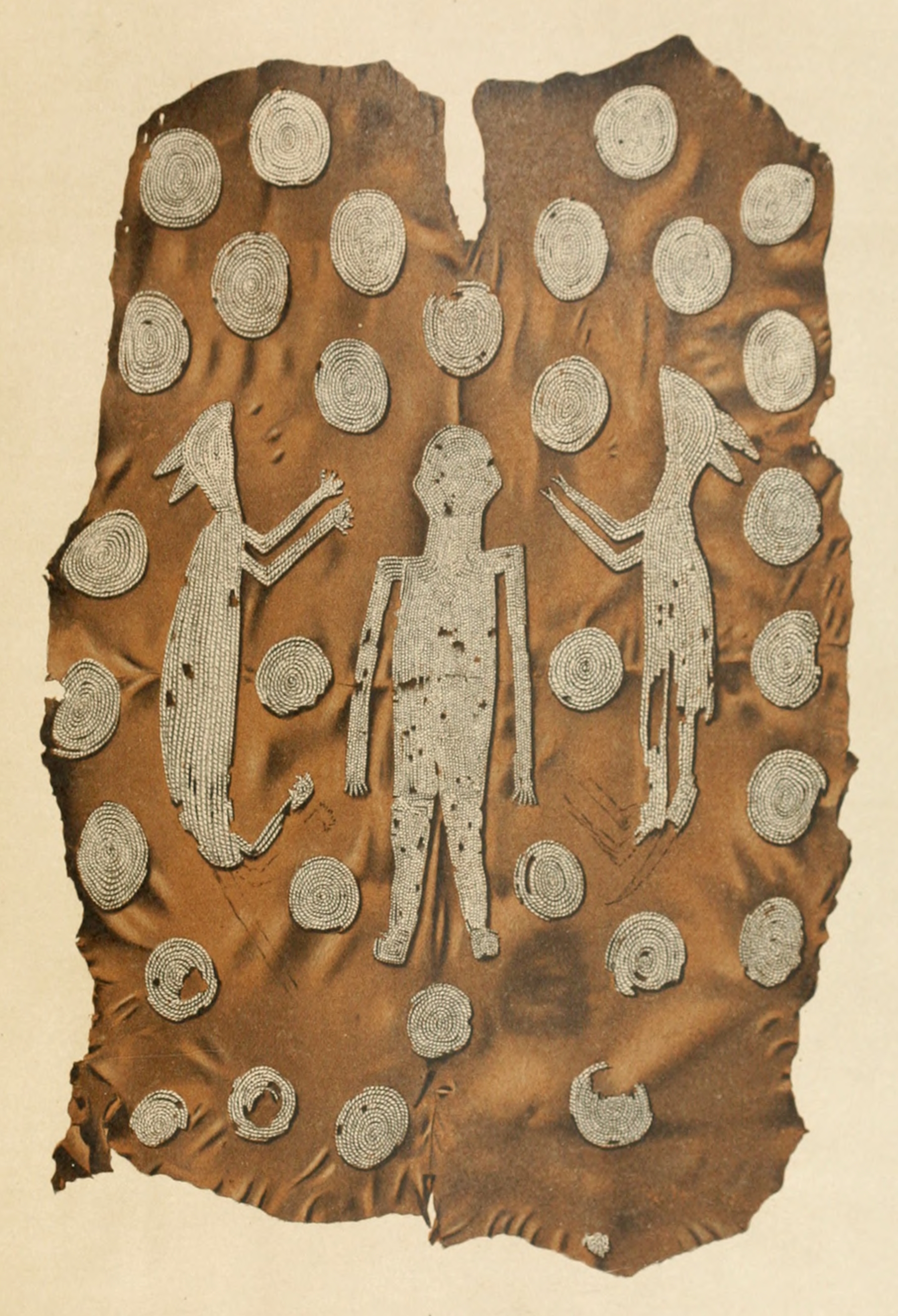
 "Powhatan's Mantle" is a cloak of
"Powhatan's Mantle" is a cloak of deerskin
Leather is a strong, flexible and durable material obtained from the tanning, or chemical treatment, of animal skins and hides to prevent decay. The most common leathers come from cattle, sheep, goats, equine animals, buffalo, pigs and hogs ...
, which originally belonged to a Native American of high social status. Its decoration consists of shell beadwork, depicting a central standing human figure flanked by two upright, opposed quadrupeds and surrounded by 34 discs. The two animals resemble one another in terms of their overall outline, but their tails and paws differ. The left-hand animal has a long tail and round paws with five articulated digits. The right-hand animal has a shorter tail, and its legs end in cloven hoofs. Historically, this artwork was believed to have belonged to Powhatan
The Powhatan people (; also spelled Powatan) may refer to any of the indigenous Algonquian people that are traditionally from eastern Virginia. All of the Powhatan groups descend from the Powhatan Confederacy. In some instances, The Powhatan ...
, who was the paramount chief
A paramount chief is the English-language designation for the highest-level political leader in a regional or local polity or country administered politically with a chief-based system. This term is used occasionally in anthropological and arch ...
of Tsenacommacah
Tsenacommacah (pronounced in English; "densely inhabited land"; also written Tscenocomoco, Tsenacomoco, Tenakomakah, Attanoughkomouck, and Attan-Akamik) is the name given by the Powhatan people to their native homeland, the area encompassing all ...
, an alliance
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
of Algonquian-speaking Virginia Indians
The Native American tribes in Virginia are the indigenous tribes who currently live or have historically lived in what is now the Commonwealth of Virginia in the United States of America.
All of the Commonwealth of Virginia used to be Virgini ...
in the Tidewater region of Virginia
Tidewater refers to the north Atlantic coastal plain region of the United States of America.
Definition
Culturally, the Tidewater region usually includes the low-lying plains of southeast Virginia, northeastern North Carolina, southern Maryl ...
at the time English settlers landed at Jamestown in 1607. "Powhatan's Mantle" is one of the earliest North American artifacts to be collected by Europeans that still survives today.at the
Ashmolean Museum
The Ashmolean Museum of Art and Archaeology () on Beaumont Street, Oxford, England, is Britain's first public museum. Its first building was erected in 1678–1683 to house the cabinet of curiosities that Elias Ashmole gave to the University of ...
, Oxford
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to the ...
See also
*Book of Kells
The Book of Kells ( la, Codex Cenannensis; ga, Leabhar Cheanannais; Dublin, Trinity College Library, MS A. I. 8 sometimes known as the Book of Columba) is an illuminated manuscript Gospel book in Latin, containing the four Gospels of the New ...
* Tierwirbel
*Attitude (heraldry)
In heraldry, the term attitude describes the ''position'' in which a figure (animal or human) is emblazoned as a charge, a supporter, or as a crest. The attitude of an heraldic figure always precedes any reference to the tincture of the figure ...
* Master of Animals
*Supporter
In heraldry, supporters, sometimes referred to as ''attendants'', are figures or objects usually placed on either side of the shield and depicted holding it up.
Early forms of supporters are found in medieval seals. However, unlike the coro ...
References
{{reflistExternal links
Cylinder seal: confronted-animalsPhoto--Cylinder Seal-High Res
– Two animals, each held by a
deity
A deity or god is a supernatural being who is considered divine or sacred. The ''Oxford Dictionary of English'' defines deity as a god or goddess, or anything revered as divine. C. Scott Littleton defines a deity as "a being with powers greate ...
or priest
A priest is a religious leader authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and one or more deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in particu ...
; Center Motif: Tree of life
The tree of life is a fundamental archetype in many of the world's mythological, religious, and philosophical traditions. It is closely related to the concept of the sacred tree.Giovino, Mariana (2007). ''The Assyrian Sacred Tree: A History ...
Photo--variation of Tree of life confronted-animals
– One figure is facing toward the observer.
Nomadic Art of the Eastern Eurasian Steppes
an exhibition catalog from The Metropolitan Museum of Art (fully available online as PDF), which contains material on confronted animals Confronted snakes
Photo--confronted snakes
Iconography Animals in art Symmetry Visual motifs