Column of Justinian on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Column of Justinian was a Roman triumphal column erected in
The Column of Justinian was a Roman triumphal column erected in
De Aedificiis
', I.2.1–11 There is some evidence from the inscriptions on the statue that it may actually have been a reused earlier statue of By the 15th century, the statue, by virtue of its prominent position, was actually believed to be that of the city's founder,
By the 15th century, the statue, by virtue of its prominent position, was actually believed to be that of the city's founder,
3D reconstruction at the ''Byzantium 1200'' project
{{DEFAULTSORT:Column Of Justinian 540s establishments in the Byzantine Empire Buildings and structures completed in the 6th century Buildings of Justinian I
 The Column of Justinian was a Roman triumphal column erected in
The Column of Justinian was a Roman triumphal column erected in Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
by the Byzantine emperor
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, to its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as le ...
Justinian I
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovat ...
in honour of his victories in 543. It stood in the western side of the great square of the Augustaeum
The ''Augustaion'' ( el, ) or, in Latin, ''Augustaeum'', was an important ceremonial square in ancient and medieval Constantinople (modern Istanbul, Turkey), roughly corresponding to the modern ''Aya Sofya Meydanı'' ( Turkish, "Hagia Sophia Squar ...
, between the Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia ( 'Holy Wisdom'; ; ; ), officially the Hagia Sophia Grand Mosque ( tr, Ayasofya-i Kebir Cami-i Şerifi), is a mosque and major cultural and historical site in Istanbul, Turkey. The cathedral was originally built as a Greek Ortho ...
and the Great Palace, and survived until 1515, when it was demolished by the Ottomans
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
.
Description and history
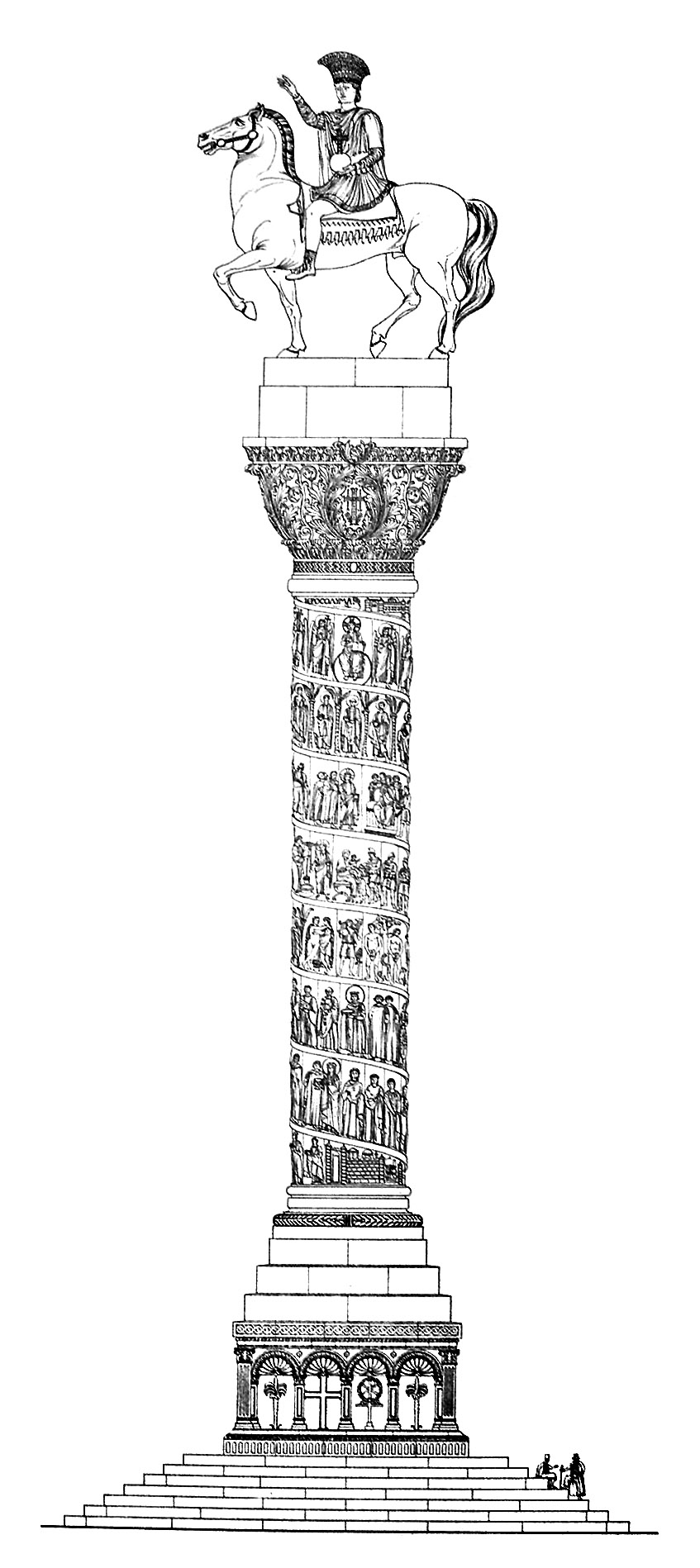
The column was made of brick, and covered with brass plaques.Kazhdan (1991), p. 232 The column stood on a marble pedestal of seven steps, and was topped by a colossal bronzeequestrian statue
An equestrian statue is a statue of a rider mounted on a horse, from the Latin ''eques'', meaning 'knight', deriving from ''equus'', meaning 'horse'. A statue of a riderless horse is strictly an equine statue. A full-sized equestrian statue is a d ...
of the emperor in triumphal attire (the "dress of Achilles
In Greek mythology, Achilles ( ) or Achilleus ( grc-gre, Ἀχιλλεύς) was a hero of the Trojan War, the greatest of all the Greek warriors, and the central character of Homer's ''Iliad''. He was the son of the Nereid Thetis and Peleus, k ...
" as Procopius
Procopius of Caesarea ( grc-gre, Προκόπιος ὁ Καισαρεύς ''Prokópios ho Kaisareús''; la, Procopius Caesariensis; – after 565) was a prominent late antique Greek scholar from Caesarea Maritima. Accompanying the Roman gener ...
calls it), wearing an antique-style muscle cuirass
In classical antiquity, the muscle cuirass ( la, lorica musculata), anatomical cuirass, or heroic cuirass is a type of cuirass made to fit the wearer's torso and designed to mimic an idealized male human physique. It first appears in late Archaic ...
, a plumed helmet of peacock
Peafowl is a common name for three bird species in the genera ''Pavo (genus), Pavo'' and ''Afropavo'' within the tribe Pavonini of the family Phasianidae, the pheasants and their allies. Male peafowl are referred to as peacocks, and female pea ...
feathers (the ''toupha
The toupha or toufa (, ''toûpha'' or τουφίον, ''touphíon'') is a kind of ornamental crest or head-dress with a plumage of the feathers, hair or bristles of exotic animals, worn in classical antiquity as a triumphal decoration. In survivi ...
''), holding a ''globus cruciger
The ''globus cruciger'' ( for, , Latin, cross-bearing orb), also known as "the orb and cross", is an orb surmounted by a cross. It has been a Christian symbol of authority since the Middle Ages, used on coins, in iconography, and with a sceptre ...
'' on his left hand and stretching his right hand to the East.Procopius, De Aedificiis
', I.2.1–11 There is some evidence from the inscriptions on the statue that it may actually have been a reused earlier statue of
Theodosius I
Theodosius I ( grc-gre, Θεοδόσιος ; 11 January 347 – 17 January 395), also called Theodosius the Great, was Roman emperor from 379 to 395. During his reign, he succeeded in a crucial war against the Goths, as well as in two ...
or Theodosius II
Theodosius II ( grc-gre, Θεοδόσιος, Theodosios; 10 April 401 – 28 July 450) was Roman emperor for most of his life, proclaimed ''Augustus (title), augustus'' as an infant in 402 and ruling as the eastern Empire's sole emperor after ...
.Majeska (1984), p. 239
The column survived intact until late Byzantine times, when it was described by Nicephorus Gregoras
Nicephorus Gregoras (; Greek: , ''Nikephoros Gregoras''; c. 1295 – 1360) was a Greek astronomer, historian, and theologian.
Life
Gregoras was born at Heraclea Pontica, where he was raised and educated by his uncle, John, who was the Bisho ...
, as well as by several Russian pilgrims to the city. The latter also mentioned the existence, before the column, of a group of three bronze statues of "pagan (or Saracen
upright 1.5, Late 15th-century German woodcut depicting Saracens
Saracen ( ) was a term used in the early centuries, both in Greek and Latin writings, to refer to the people who lived in and near what was designated by the Romans as Arabia Pe ...
) emperors", placed on shorter columns or pedestals, who kneeled in submission before it. These apparently survived until the late 1420s, but were removed sometime before 1433. The column itself is described as being of great height, 70 meters according to Cristoforo Buondelmonti
Cristoforo Buondelmonti (c. 1385 – c. 1430) was an Italian Franciscan priest and traveler, and a pioneer in promoting first-hand knowledge of Greece and its antiquities throughout the Western world.
Biography
Cristoforo Buondelmonti was born ar ...
. It was visible from the sea, and once, according to Gregoras, when the ''toupha'' fell off, its restoration required the services of an acrobat, who used a rope slung from the roof of the Hagia Sophia
Hagia Sophia ( 'Holy Wisdom'; ; ; ), officially the Hagia Sophia Grand Mosque ( tr, Ayasofya-i Kebir Cami-i Şerifi), is a mosque and major cultural and historical site in Istanbul, Turkey. The cathedral was originally built as a Greek Ortho ...
.
 By the 15th century, the statue, by virtue of its prominent position, was actually believed to be that of the city's founder,
By the 15th century, the statue, by virtue of its prominent position, was actually believed to be that of the city's founder, Constantine the Great
Constantine I ( , ; la, Flavius Valerius Constantinus, ; ; 27 February 22 May 337), also known as Constantine the Great, was Roman emperor from AD 306 to 337, the first one to Constantine the Great and Christianity, convert to Christiani ...
. Other associations were also current: the Italian
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional Ita ...
antiquarian Cyriacus of Ancona
Cyriacus of Ancona or Ciriaco de' Pizzicolli (31 July 1391 – 1453/55) was a restlessly itinerant Italian humanist and antiquarian who came from a prominent family of merchants in Ancona, a maritime republic on the Adriatic. He has been called ...
was told that it represented Heraclius
Heraclius ( grc-gre, Ἡράκλειος, Hērákleios; c. 575 – 11 February 641), was List of Byzantine emperors, Eastern Roman emperor from 610 to 641. His rise to power began in 608, when he and his father, Heraclius the Elder, the Exa ...
. It was therefore widely held that the column, and in particular the large ''globus cruciger'', or "apple", as it was popularly known, represented the city's ''genius loci
In classical Roman religion, a ''genius loci'' (plural ''genii locorum'') was the protective spirit of a place. It was often depicted in religious iconography as a figure holding attributes such as a cornucopia, patera (libation bowl) or snake. ...
''.Finkel (2006), p. 53 Consequently, its fall from the statue's hand, sometime between 1422 and 1427, was seen as a sign of the city's impending doom.Majeska (1984), p. 240 Shortly after their conquest of the city in 1453, the Ottomans
The Ottoman Turks ( tr, Osmanlı Türkleri), were the Turkic founding and sociopolitically the most dominant ethnic group of the Ottoman Empire ( 1299/1302–1922).
Reliable information about the early history of Ottoman Turks remains scarce, ...
removed and dismantled the statue completely as a symbol of their dominion, while the column itself was destroyed around 1515.Finkel (2006), p. 53 Pierre Gilles
Petrus Gyllius or Gillius (or Pierre Gilles) (1490–1555) was a French natural scientist, topographer and translator.
Gilles was born in Albi, southern France. A great traveller, he studied the Mediterranean and Orient, producing such works as ...
, a French scholar living in the city in the 1540s, gave an account of the statue's remaining fragments, which lay in the Topkapi Palace, before being melted to make cannons:
The appearance of the statue itself with its inscriptions is preserved, however, in a 1430s drawing (see left) made at the behest of Cyriacus of Ancona.
References
Sources
* * * * *External links
3D reconstruction at the ''Byzantium 1200'' project
{{DEFAULTSORT:Column Of Justinian 540s establishments in the Byzantine Empire Buildings and structures completed in the 6th century Buildings of Justinian I
Justinian
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovat ...
Justinian
Justinian I (; la, Iustinianus, ; grc-gre, Ἰουστινιανός ; 48214 November 565), also known as Justinian the Great, was the Byzantine emperor from 527 to 565.
His reign is marked by the ambitious but only partly realized ''renovat ...
Equestrian statues in Turkey
Buildings and structures demolished in the 16th century
1515 disestablishments in the Ottoman Empire
543
1515 disestablishments in Europe
Cultural depictions of Justinian I
Statues of monarchs
6th-century sculptures