Color vision study on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A color vision test is used for measuring color vision against a standard. These tests are most often used to diagnose color vision deficiencies (''color blindness''), though several of the standards are designed to categorize normal color vision into sub-levels. With the large prevalence of color vision deficiencies (8% of males) and the wide range of professions that restrict hiring the colorblind for safety or aesthetic reasons, clinical color vision standards must be designed to be fast and simple to implement. Color vision standards for academic use trade speed and simplicity for accuracy and precision.
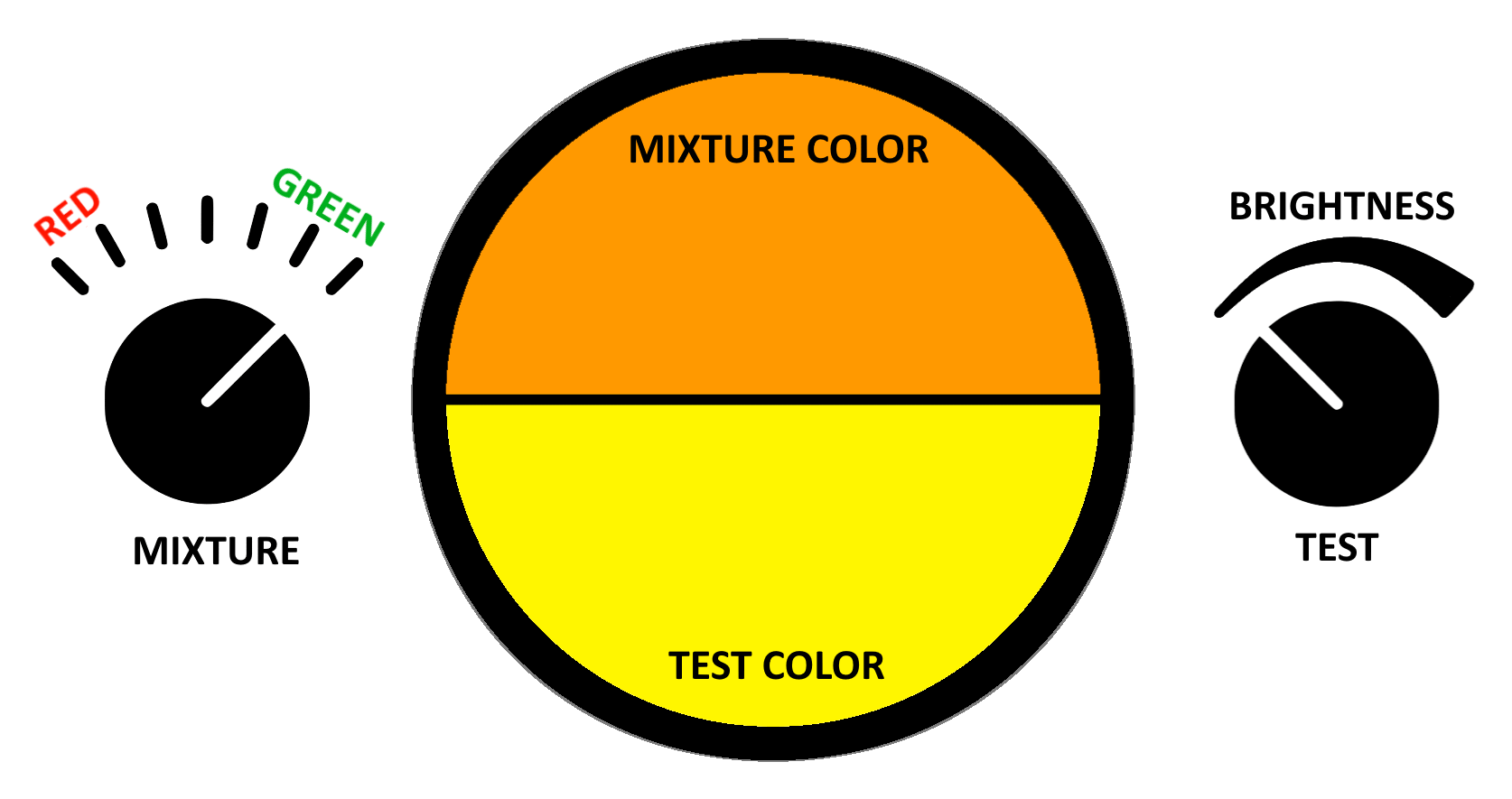 Anomaloscopes are very expensive and require expertise to administer, so are generally only used in academic settings. However, they are very precise, being able to diagnose the type and severity of color blindness with high confidence. An anomaloscope designed to detect red–green color blindness is based on the Rayleigh equation, which compares a mixture of red and green light in variable proportions to a fixed spectral yellow of variable luminosity. The subject must change the two variables until the colors appear to match. The values of the variables at match (and the deviation from the variables of a color normal subject) are used to diagnose the type and severity of colorblindness. For example, deutans will put too much green in the mixture and protans will put too much red in the mixture.
Anomaloscopes are very expensive and require expertise to administer, so are generally only used in academic settings. However, they are very precise, being able to diagnose the type and severity of color blindness with high confidence. An anomaloscope designed to detect red–green color blindness is based on the Rayleigh equation, which compares a mixture of red and green light in variable proportions to a fixed spectral yellow of variable luminosity. The subject must change the two variables until the colors appear to match. The values of the variables at match (and the deviation from the variables of a color normal subject) are used to diagnose the type and severity of colorblindness. For example, deutans will put too much green in the mixture and protans will put too much red in the mixture.
Applications
Color vision standards are used to evaluate the color vision of a subject. They are most commonly applied to job applicants during pre-job screening. The evaluation may be to select against the color vision deficient for roles where basic color vision is required, or to select for individuals with superior color vision for roles where recognition of subtle color difference is required. Alterations to color vision are common symptoms of toxicity and eye health, so color vision standards can also be used to detect conditions of the eye or brain or to track the recovery from these conditions.Pseudoisochromatic plates
A pseudoisochromatic plate (fromGreek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
''pseudo'', meaning "false", ''iso'', meaning "same" and ''chromo'', meaning "color"), often abbreviated as PIP, is a style of standard exemplified by the Ishihara test, generally used for screening of color vision defects
Color blindness or color vision deficiency (CVD) is the decreased ability to see color or differences in color. It can impair tasks such as selecting ripe fruit, choosing clothing, and reading traffic lights. Color blindness may make some aca ...
.
A figure (usually one or more numerals
A numeral is a figure, symbol, or group of figures or symbols denoting a number. It may refer to:
* Numeral system used in mathematics
* Numeral (linguistics), a part of speech denoting numbers (e.g. ''one'' and ''first'' in English)
* Numerical d ...
) is embedded in the plate as a number of spots surrounded by spots of a slightly different color. The figure can be seen with normal color vision, but not with a particular color defect. The figure and background colors must be carefully chosen to appear isochromatic to a color deficient individual, but not an individual with normal color vision.
Pseudoisochromatic Plates are used as ''screening tools'' because they are cheap, fast and simple, but they do not provide precise diagnosis of CVD, and are often followed with another test if a user fails the PIP standard.
Ishihara plates
Ishihara plates hide arabic numerals within PIPs. They are the test most often used to screen for red–green color deficiencies and most often recognized by the public. However, this can be attributed more to its ease of application, and less to do with its precision. The basic Ishihara test may not be useful in diagnosing young, preliterate children, who can't read the numerals, but larger editions contain plates that showcase a simple path to be traced with a finger, rather than numerals.HRR plates
The second most common PIP color vision standard is the HRR color test (developed by Hardy,Rand
The RAND Corporation (from the phrase "research and development") is an American nonprofit global policy think tank created in 1948 by Douglas Aircraft Company to offer research and analysis to the United States Armed Forces. It is finan ...
, and Rittler), which solves many of the criticisms of the Ishihara test. For example, it detects blue-yellow color blindness, is less susceptible to memorization and uses shapes, so it is accessible to the illiterate
Literacy in its broadest sense describes "particular ways of thinking about and doing reading and writing" with the purpose of understanding or expressing thoughts or ideas in written form in some specific context of use. In other words, hum ...
and young children.
Arrangement tests
Arrangement-style color vision standards comprise a spectrum of colors that must be arranged in an array to minimize the difference between adjacent colors. An error score is calculated from incorrectly positioned colors. Lower error scores denote better color vision. Typically, the subject is asked to arrange a set of colored caps or chips between two anchor caps. The Farnsworth–Munsell 100 hue test comprises 4 separate color arrays, each representing 20 arrangeable caps and 2 anchor caps. This gives a total of 88 colors, contrary to the standard's name name. The standard is sensitive enough that it not only can detect color blindness, but also categorize normal color vision into "low", "average" and "superior" levels based on their error score. It is usually not used for the detection of CVD. The Farnsworth D-15 is simpler, comprising a single array, which itself comprises 1 end cap and 15 arrangeable caps. It is primarily used for occupational screening of CVD and is the standard of choice in most US/Canadian Police Forces (after screening with Ishihara). About 50% of people who fail the Ishihara are able to pass the D15.Lanterns
Lanterns project small colored lights to a subject, who is required to identify the color of the lights. The colors are usually restricted to those of typical signal lights, i.e. red, green and yellow, though some lanterns may project other colors. The main signal light colors also happen to be colors of confusion for red-green CVD. Lanterns are usually used for occupational screening as they are more closely related to the actual safety-related color tasks required in those occupations. For example, theFarnsworth Lantern Test
The Farnsworth Lantern Test, or FALANT, is a color vision test originally developed specifically to screen sailors for tasks requiring color vision, such as identifying signal lights at night. It screens for red-green deficiencies, but not the much ...
is used extensively by the United States Armed Forces
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States. The armed forces consists of six service branches: the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, Space Force, and Coast Guard. The president of the United States is ...
and FAA
The Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) is the largest transportation agency of the U.S. government and regulates all aspects of civil aviation in the country as well as over surrounding international waters. Its powers include air traffic m ...
. This test allows about 30% of individuals who fail the ishihara plates (generally those with mild CVD) to pass.
Anomaloscopes
 Anomaloscopes are very expensive and require expertise to administer, so are generally only used in academic settings. However, they are very precise, being able to diagnose the type and severity of color blindness with high confidence. An anomaloscope designed to detect red–green color blindness is based on the Rayleigh equation, which compares a mixture of red and green light in variable proportions to a fixed spectral yellow of variable luminosity. The subject must change the two variables until the colors appear to match. The values of the variables at match (and the deviation from the variables of a color normal subject) are used to diagnose the type and severity of colorblindness. For example, deutans will put too much green in the mixture and protans will put too much red in the mixture.
Anomaloscopes are very expensive and require expertise to administer, so are generally only used in academic settings. However, they are very precise, being able to diagnose the type and severity of color blindness with high confidence. An anomaloscope designed to detect red–green color blindness is based on the Rayleigh equation, which compares a mixture of red and green light in variable proportions to a fixed spectral yellow of variable luminosity. The subject must change the two variables until the colors appear to match. The values of the variables at match (and the deviation from the variables of a color normal subject) are used to diagnose the type and severity of colorblindness. For example, deutans will put too much green in the mixture and protans will put too much red in the mixture.
Digital tests
The graduation of color vision tests to the digital space offers several advantages, but is not trivial. Even if the digital tests mimic a traditional test, the digital version must be requalified or validated and every screen it is viewed on must be well-calibrated. Freely available web-based tests suffer from a lack of validation and typical viewing on uncalibrated screens. However, when well controlled, digital tests offer several significant advantages over their analog counterparts: * They randomize solutions, which eliminates memorization * The test can adapt in real time to the subject's performance (e.g. give more protan questions if the subject appears to be a protan) * They don't suffer from color fading like the pigments/dyes in analog tests. * The variance in test administration is minimized * The tests are immune to mistakes in interpreting the results * Test parameters can be dynamic and vary with time Validated digital tests used for occupational screening include: * Cambridge Color Test (CCT) (Cambridge University
The University of Cambridge is a Public university, public collegiate university, collegiate research university in Cambridge, England. Founded in 1209 and granted a royal charter by Henry III of England, Henry III in 1231, Cambridge is the world' ...
, 1997)
* Colour Assessment and Diagnosis (CAD) Test (City University London
City, University of London, is a public research university in London, United Kingdom, and a member institution of the federal University of London. It was founded in 1894 as the Northampton Institute, and became a university when The City Univ ...
, 2002)
* Colour Vision Assessment (University of Minho
The University of Minho (''Universidade do Minho'') is a public university in Portugal, divided into the following campuses:
* Largo do Paço (rectorate), in Braga
* Campus of Gualtar, in Braga
* Convento dos Congregados, in Braga
* Campus of Az ...
, 2016)
References
{{Color topics, state=collapsed Color vision Diagnostic ophthalmology