Colivă on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Koliva, also spelled, depending on the language, kollyva, kollyba or colivă, is a dish based on boiled wheat that is used liturgically in the Eastern Orthodox Church for commemorations of the dead.
In the Eastern Orthodox Church, koliva is blessed during funerals, as well as during the memorial service (''mnemosyno'') that is performed at various intervals after a person's death and on special occasions, such as the Saturday of Souls (ψυχοσάββατο). It may also be used on the first Friday of
 While recipes may vary widely, the primary ingredient is wheat kernels which have been boiled until they are soft, they are drained very well and spread on a cloth to be just moist, and then sweetened with honey or sugar. Koliva also contains some or all of the following: wheat,
While recipes may vary widely, the primary ingredient is wheat kernels which have been boiled until they are soft, they are drained very well and spread on a cloth to be just moist, and then sweetened with honey or sugar. Koliva also contains some or all of the following: wheat,
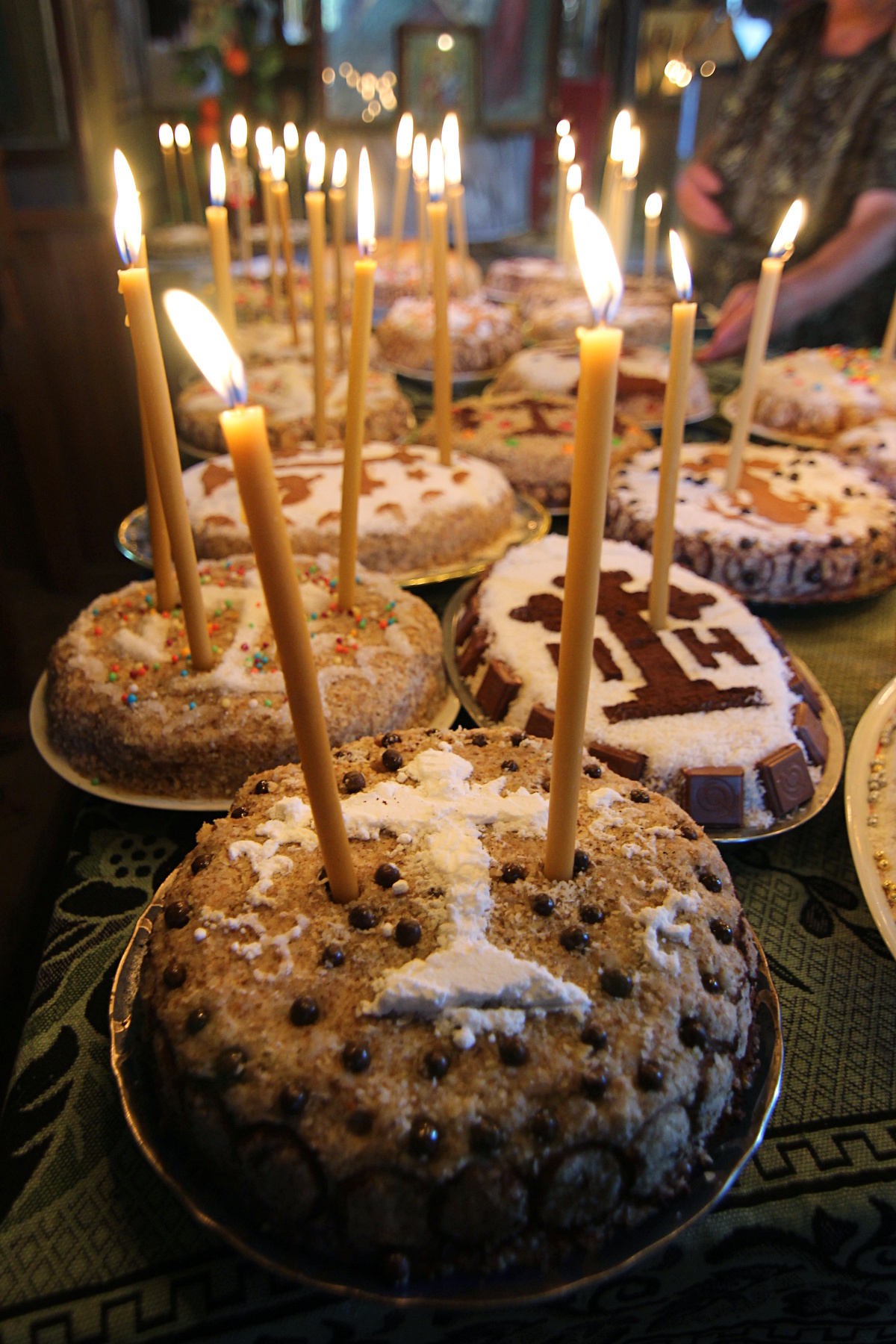 Koliva is used on a number of different occasions:
Koliva is used on a number of different occasions:
THE FEAST OF THE BOILED WHEAT MIRACLE AT THE PATRIARCHATE
'' JERUSALEM PATRIARCHATE Official News Gate. 04/03/2017. Retrieved: 6 March 2017. As a result, this first Saturday of Great Lent has come to be known as
Koliva Recipe
St. Nicholas Center
Theodore Saturday
Icon and
Photo: Blessing koliva at the end of a PanikhidaRomanian Coliva Recipe
Eastern Orthodox liturgy Death customs Religious food and drink Ceremonial food and drink Funeral food and drink Balkan cuisine Bulgarian cuisine Eastern Orthodox Christian cuisine Greek cuisine Ukrainian cuisine Romanian cuisine Russian cuisine Serbian cuisine Slavic cuisine Wheat dishes Porridges Desserts
Great Lent
Great Lent, or the Great Fast, (Greek: Μεγάλη Τεσσαρακοστή or Μεγάλη Νηστεία, meaning "Great 40 Days," and "Great Fast," respectively) is the most important fasting season of the church year within many denominat ...
, at Slava
Slava may refer to:
Ships
* ''Slava'' class cruiser, a modern Russian warship
** Soviet cruiser Slava (1979), now Russian cruiser ''Moskva'', a ''Slava'' class guided missile cruiser sunk during the 2022 Russian invasion of Ukraine
* Russian ba ...
s, or at ''mnemosyna'' in the Christmas meal. In some countries, though not in Greece, it is consumed on nonreligious occasions as well.
A similar food item is widely popular in Lebanon where it is known as ''snuniye'' and, more commonly, as ''berbara'' as it is prepared for Saint Barbara's feast day, December 4, which is celebrated with Halloween
Halloween or Hallowe'en (less commonly known as Allhalloween, All Hallows' Eve, or All Saints' Eve) is a celebration observed in many countries on 31 October, the eve of the Western Christian feast of All Saints' Day. It begins the observanc ...
-like festivities.
Etymology
''Kollyba'', a word which in Greek is the plural form of ''kollybo'' (: nneu
Neu! (; German for "New!"; styled in block capitals) were a West German krautrock band formed in Düsseldorf in 1971 by Klaus Dinger and Michael Rother following their departure from Kraftwerk. The group's albums were produced by Conny Plank, w ...
; itself rarely used), is derived from the Classical Greek word , ''kollybos'' (n masc), i.e. a small coin or a small gold weight. In the Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
period, the neuter plural form of the latter word, i.e. , ''kollyba'', took the meaning of small pies made of boiled wheat. The sense of the ritual food is of a latter period. In Serbian
Serbian may refer to:
* someone or something related to Serbia, a country in Southeastern Europe
* someone or something related to the Serbs, a South Slavic people
* Serbian language
* Serbian names
See also
*
*
* Old Serbian (disambiguat ...
it is called ''Koljivo (Кољиво)'', ''Кутя'' in Bulgarian
Bulgarian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to the country of Bulgaria
* Bulgarians, a South Slavic ethnic group
* Bulgarian language, a Slavic language
* Bulgarian alphabet
* A citizen of Bulgaria, see Demographics of Bulgaria
* Bul ...
, ''Colivă'' in Romanian
Romanian may refer to:
*anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Romania
**Romanians, an ethnic group
**Romanian language, a Romance language
***Romanian dialects, variants of the Romanian language
**Romanian cuisine, traditional ...
, and ''Кутья'' in Russian.
Recipe
 While recipes may vary widely, the primary ingredient is wheat kernels which have been boiled until they are soft, they are drained very well and spread on a cloth to be just moist, and then sweetened with honey or sugar. Koliva also contains some or all of the following: wheat,
While recipes may vary widely, the primary ingredient is wheat kernels which have been boiled until they are soft, they are drained very well and spread on a cloth to be just moist, and then sweetened with honey or sugar. Koliva also contains some or all of the following: wheat, sesame
Sesame ( or ; ''Sesamum indicum'') is a flowering plant in the genus ''Sesamum'', also called benne. Numerous wild relatives occur in Africa and a smaller number in India. It is widely naturalized in tropical regions around the world and is cu ...
seeds, almond
The almond (''Prunus amygdalus'', syn. ''Prunus dulcis'') is a species of tree native to Iran and surrounding countries, including the Levant. The almond is also the name of the edible and widely cultivated seed of this tree. Within the genus ...
s, ground walnuts, cinnamon
Cinnamon is a spice obtained from the inner bark of several tree species from the genus ''Cinnamomum''. Cinnamon is used mainly as an aromatic condiment and flavouring additive in a wide variety of cuisines, sweet and savoury dishes, breakfa ...
, sugar
Sugar is the generic name for sweet-tasting, soluble carbohydrates, many of which are used in food. Simple sugars, also called monosaccharides, include glucose, fructose, and galactose. Compound sugars, also called disaccharides or double ...
, pomegranate seeds, raisins, anise
Anise (; '), also called aniseed or rarely anix is a flowering plant in the family Apiaceae native to Eurasia.
The flavor and aroma of its seeds have similarities with some other spices and herbs, such as star anise, fennel, licorice, and ta ...
and parsley
Parsley, or garden parsley (''Petroselinum crispum'') is a species of flowering plant in the family Apiaceae that is native to the central and eastern Mediterranean region (Sardinia, Lebanon, Israel, Cyprus, Turkey, southern Italy, Greece, Por ...
. Romanians decorate the koliva with crosses of cocoa, chocolate or candy.
The practice of offering koliva is traditional in Greece, Cyprus, Serbia, Bulgaria, Montenegro, Romania, Moldova, Russia and parts of Bosnia-Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and Pars pro toto#Geography, often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of Southern Europe, south and southeast Euro ...
, and among Christians in the Middle East. When served, the koliva mixture, which looks like earth, is shaped into a mound to resemble a grave. The whole is then covered with powdered sugar and the initials of the deceased are outlined on the top. A candle, usually placed in the center of the koliva, is lit at the beginning of the memorial service and extinguished at its end. After the liturgy
Liturgy is the customary public ritual of worship performed by a religious group. ''Liturgy'' can also be used to refer specifically to public worship by Christians. As a religious phenomenon, liturgy represents a communal response to and partic ...
, those attending share in eating the koliva as they speak of the deceased and say, "May God forgive him/her."
Some Orthodox parishes have a designated individual charged with making the koliva. This is in part due to the health risk of fermented wheat if the koliva is not prepared correctly.
Sometimes koliva is made with rice or barley instead of wheat. This custom began as a practical response to a famine that occurred in Soviet Russia, when the faithful did not have wheat available for koliva, so they used rice instead. Some communities continue to use rice for their koliva to this day. In the Japanese Orthodox Church where rice is mainly eaten, koliva is commonly made from rice sweetened with sugar and decorated with raisins, without reference to famine.
History
The origins of koliva predate Christianity. The word koliva itself stems from the Ancient Greek word (''kollybos''), which originally meant "a small coin" and later in the neuter plural form "small pies made of boiled wheat". In the Ancient Greek ''panspermia'', a mixture of cooked seeds and nuts were offered during the pagan festival of theAnthesteria
The Anthesteria (; grc, Ἀνθεστήρια ) was one of the four Athenian festivals in honor of Dionysus. It was held each year from the 11th to the 13th of the month of Anthesterion, around the time of the January or February full moon. The ...
.
In the 5th century AD
koliva in the sense of boiled wheat, constituted along with raw vegetables the diet of monks who refused to eat bread. Available (limitedly) online at the Oxford Reference.
The 12th century canonist Theodore Balsamon maintained that koliva as a ritual food practice was originated by Athanasius of Alexandria
Athanasius I of Alexandria, ; cop, ⲡⲓⲁⲅⲓⲟⲥ ⲁⲑⲁⲛⲁⲥⲓⲟⲩ ⲡⲓⲁⲡⲟⲥⲧⲟⲗⲓⲕⲟⲥ or Ⲡⲁⲡⲁ ⲁⲑⲁⲛⲁⲥⲓⲟⲩ ⲁ̅; (c. 296–298 – 2 May 373), also called Athanasius the Great, ...
during the reign of the Emperor Julian the Apostate
Julian ( la, Flavius Claudius Julianus; grc-gre, Ἰουλιανός ; 331 – 26 June 363) was Roman emperor from 361 to 363, as well as a notable philosopher and author in Greek. His rejection of Christianity, and his promotion of Neoplato ...
.
The association between death and life, between that which is planted in the ground and that which emerges, is deeply embedded in the making and eating of koliva. The ritual food passed from paganism
Paganism (from classical Latin ''pāgānus'' "rural", "rustic", later "civilian") is a term first used in the fourth century by early Christianity, early Christians for people in the Roman Empire who practiced polytheism, or ethnic religions ot ...
to early Christianity in Byzantium
Byzantium () or Byzantion ( grc, Βυζάντιον) was an ancient Greek city in classical antiquity that became known as Constantinople in late antiquity and Istanbul today. The Greek name ''Byzantion'' and its Latinization ''Byzantium'' cont ...
and later spread to the entire Orthodox
Orthodox, Orthodoxy, or Orthodoxism may refer to:
Religion
* Orthodoxy, adherence to accepted norms, more specifically adherence to creeds, especially within Christianity and Judaism, but also less commonly in non-Abrahamic religions like Neo-pag ...
world.
Occasions of use
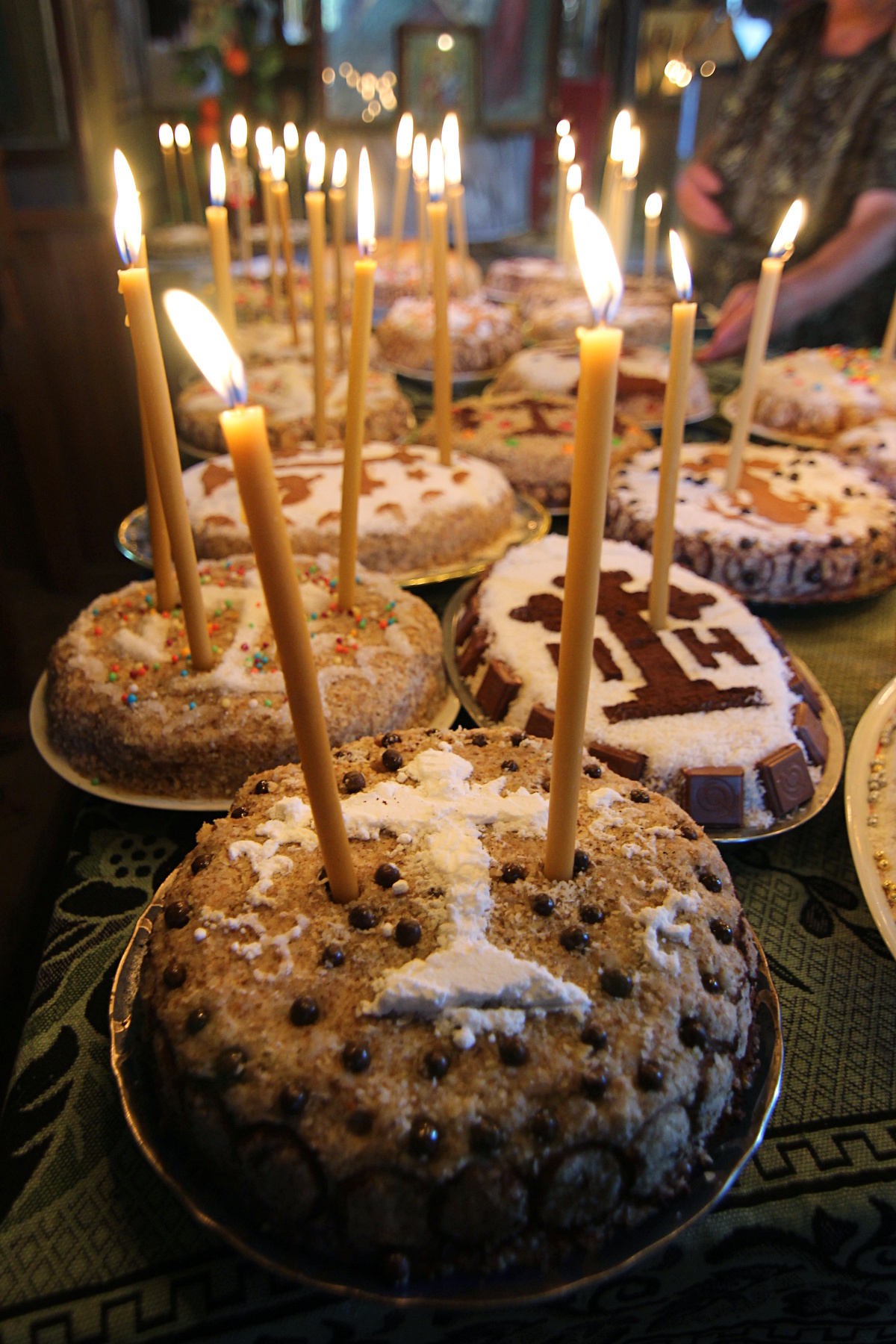 Koliva is used on a number of different occasions:
Koliva is used on a number of different occasions:
St Theodore Saturday
The tradition of blessing and eating koliva at the end of the first week ofGreat Lent
Great Lent, or the Great Fast, (Greek: Μεγάλη Τεσσαρακοστή or Μεγάλη Νηστεία, meaning "Great 40 Days," and "Great Fast," respectively) is the most important fasting season of the church year within many denominat ...
is connected with an event in the reign of Julian the Apostate
Julian ( la, Flavius Claudius Julianus; grc-gre, Ἰουλιανός ; 331 – 26 June 363) was Roman emperor from 361 to 363, as well as a notable philosopher and author in Greek. His rejection of Christianity, and his promotion of Neoplato ...
. The tradition states that the Emperor knew that the Christians would be hungry after the first week of strict fasting, and would go to the marketplaces of Constantinople on Saturday to buy food. So he ordered that blood from pagan sacrifices be sprinkled over all the food that was sold there. This made the food unsuitable as Lenten fare (since the Christians could not eat meat products during Lent), and in general as food for Christians, who are forbidden to eat food from such sacrifices. However, St. Theodore Tyro appeared in the dream to Archbishop Eudoxius and advised him that the people should not eat food bought at the marketplace that day, but only boiled wheat mixed with honey.THE FEAST OF THE BOILED WHEAT MIRACLE AT THE PATRIARCHATE
'' JERUSALEM PATRIARCHATE Official News Gate. 04/03/2017. Retrieved: 6 March 2017. As a result, this first Saturday of Great Lent has come to be known as
Theodore Saturday
: ''For another Saint Theodore, see: Theodore Stratelates or Saint Theodore (disambiguation)''.
Saint Theodore (name), Theodore Tiron ( grc-gre, Ἅγιος Θεόδωρος Τήρων) is one of the two recognized saints called Theodore who ar ...
.
Memorial services
During requiem services ( el,mnemósynon
A memorial service ( Greek: μνημόσυνον, mnemósynon, "memorial"; Slavonic: панихида, panikhída, from Greek παννυχίς, ''pannychis'', "vigil"; Romanian: parastas and Serbian парастос, parastos, from Greek παρ� ...
, script=Latn, Slavonic: ''Panikhida
A memorial service (Greek: μνημόσυνον, mnemósynon, "memorial"; Slavonic: панихида, panikhída, from Greek παννυχίς, ''pannychis'', "vigil"; Romanian: parastas and Serbian парастос, parastos, from Greek παρ ...
'', Romanian
Romanian may refer to:
*anything of, from, or related to the country and nation of Romania
**Romanians, an ethnic group
**Romanian language, a Romance language
***Romanian dialects, variants of the Romanian language
**Romanian cuisine, traditional ...
: ''parastas''), the family or friends of the departed will often prepare koliva which are placed in front of the memorial table before which the service is chanted.
Memorial services are held on the third, ninth, and fortieth days after the repose of an Orthodox Christian, as well as on the one-year anniversary. In addition, there are several Soul Saturdays during the church year (mostly during Great Lent), as well as Radonitsa (on the second Tuesday after Pascha), on each of which general commemorations are made for all the departed.
Funerals
During the Greek, Romanian, Bulgarian, Serbian and Russian Orthodox funeral services it is offered to all who attend the funeral.Commemoration of saints
It is also customary in the Slavic practice on the feast of the Patron Saint of a church or of a family, or on the feast of saints of special significance to offer koliva. Instead of serving a memorial service, the koliva is set in front of an icon of the saint and a Moleben is served to that saint. In Lebanon, it is traditionally prepared by the Antiochian Orthodox community for the feast of Saint Barbara.See also
*Kollyvades Movement The Kollyvades ( el, Κολλυβάδες) were the members of a movement within the Eastern Orthodox Church that began in the second half of the eighteenth century among the monastic community of Mount Athos, which was concerned with the restoratio ...
* Memorial service (Orthodox)
* Prayer for the dead
* Kutia - a sweet grain pudding, traditionally served in Russian, Belarus, Ukrainian, Polish and Lithuanian culture
Culture of Lithuania combines an indigenous heritage, represented by the unique Lithuanian language, with Nordic cultural aspects and Christian traditions resulting from historical ties with Poland. Although linguistic resemblances represent st ...
s.
* Panikhida
A memorial service (Greek: μνημόσυνον, mnemósynon, "memorial"; Slavonic: панихида, panikhída, from Greek παννυχίς, ''pannychis'', "vigil"; Romanian: parastas and Serbian парастос, parastos, from Greek παρ ...
* Prosphora
* Radonitsa
* Saturday of Souls
Saturday of Souls (or Soul Saturday) is a day set aside for the commemoration of the dead within the liturgical year of the Eastern Orthodox and Eastern Catholic Churches. Saturday is a traditional day of prayer for the dead, because Christ lay d ...
Notes
{{notelistReferences
External links
Koliva Recipe
St. Nicholas Center
Theodore Saturday
Icon and
Synaxarion
Synaxarion or Synexarion (plurals Synaxaria, Synexaria; el, Συναξάριον, from συνάγειν, ''synagein'', "to bring together"; cf. etymology of ''synaxis'' and ''synagogue''; Latin: ''Synaxarium'', ''Synexarium''; cop, ⲥⲩⲛⲁ ...
Photo: Blessing koliva at the end of a Panikhida
Eastern Orthodox liturgy Death customs Religious food and drink Ceremonial food and drink Funeral food and drink Balkan cuisine Bulgarian cuisine Eastern Orthodox Christian cuisine Greek cuisine Ukrainian cuisine Romanian cuisine Russian cuisine Serbian cuisine Slavic cuisine Wheat dishes Porridges Desserts