Coal mining in Australia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Coal is mined in every state of Australia. The largest black coal resources occur in
Coal is mined in every state of Australia. The largest black coal resources occur in 
 Coal mining in Australia has been criticized, due to carbon dioxide emissions during combustion. This criticism is primarily directed at thermal coal, for its connection to coal-fired power stations as a major source of carbon dioxide emissions, and the link to climate change in Australia and worldwide. Coal was responsible for 30% (164 million tonnes) of Australia's greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, not counting methane and export coal, in 2019. Coal as a fuel was responsible for 41% (160 million tonnes) of carbon dioxide emissions in Australia in 2020.
The
Coal mining in Australia has been criticized, due to carbon dioxide emissions during combustion. This criticism is primarily directed at thermal coal, for its connection to coal-fired power stations as a major source of carbon dioxide emissions, and the link to climate change in Australia and worldwide. Coal was responsible for 30% (164 million tonnes) of Australia's greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, not counting methane and export coal, in 2019. Coal as a fuel was responsible for 41% (160 million tonnes) of carbon dioxide emissions in Australia in 2020.
The


 Australian coal was first discovered in New South Wales by shipwreck survivors in August 1797, at Coalcliff, north of
Australian coal was first discovered in New South Wales by shipwreck survivors in August 1797, at Coalcliff, north of
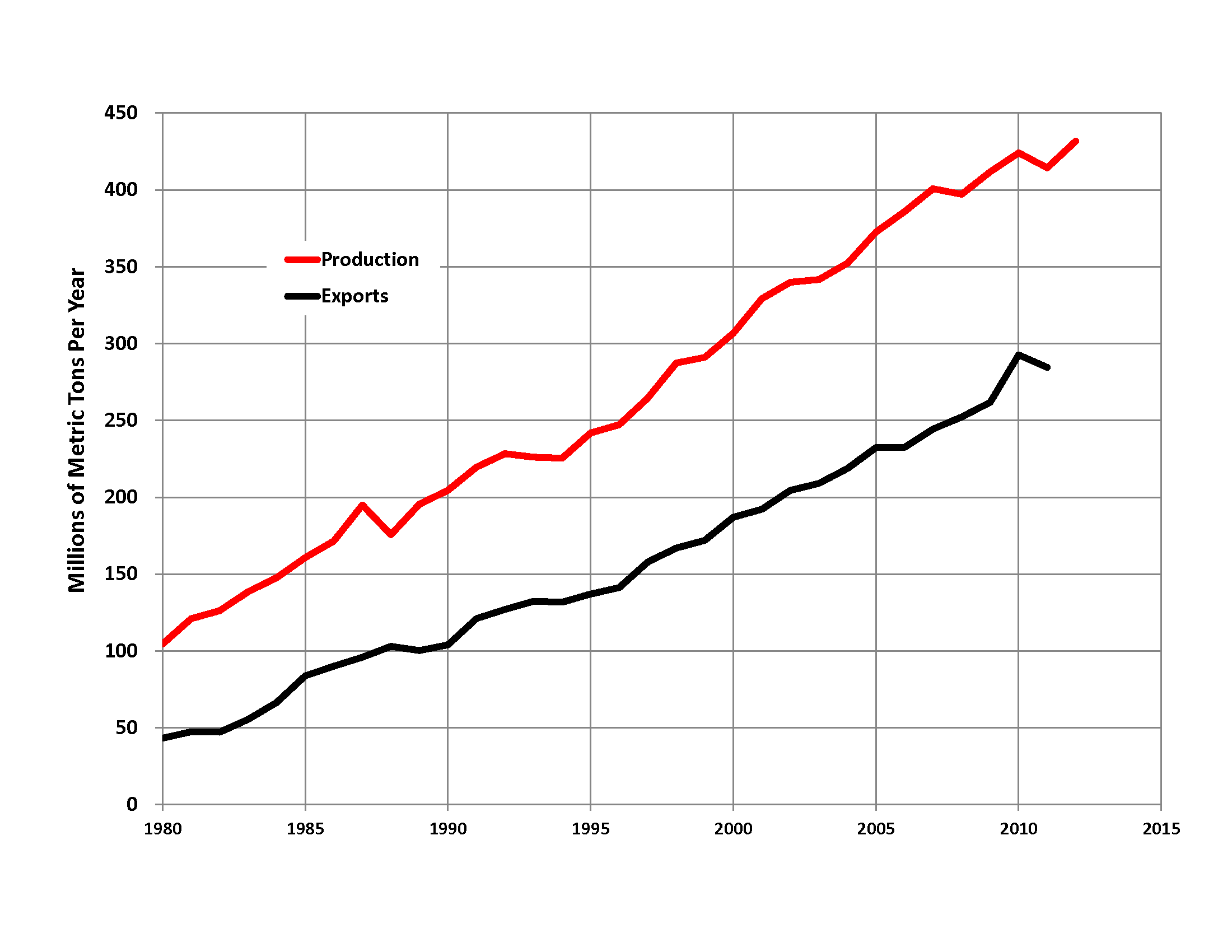
 In 2016, Australia was the biggest net exporter of coal, with 32% of global exports (389 Mt out of 1,213 Mt total). It was the fourth-highest producer with 6.9% of global production (503 Mt out of 7,269 Mt total). 77% of production was exported (389 Mt out of 503 Mt total).
In 2016, Australia was the biggest net exporter of coal, with 32% of global exports (389 Mt out of 1,213 Mt total). It was the fourth-highest producer with 6.9% of global production (503 Mt out of 7,269 Mt total). 77% of production was exported (389 Mt out of 503 Mt total).
 Australia exports the largest share of coal of any nation, at 54% of the total. In 2020, exports of coal accounted for 1% of national revenue, with a total value of A$55 billion.
Australia exports the largest share of coal of any nation, at 54% of the total. In 2020, exports of coal accounted for 1% of national revenue, with a total value of A$55 billion.
"Olive Downs Coking Coal Complex"
accessed 13 August 2019. In 2021, the federal government agreed to loan the project $175 million (AUS) to begin the first stages of its development. In April 2022, the construction of the mine commenced. Production is expected to begin in 2023.
 Both underground and open-cut mines generate significant environmental impacts, including modified topography, soil erosion,
Both underground and open-cut mines generate significant environmental impacts, including modified topography, soil erosion,
"Illawarra Coal"
- An unofficial history of coal mining in the Illawarra
Survey of Energy Resources 2007 for Australia
{{DEFAULTSORT:Coal in Australia
 Coal is mined in every state of Australia. The largest black coal resources occur in
Coal is mined in every state of Australia. The largest black coal resources occur in Queensland
)
, nickname = Sunshine State
, image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, establishe ...
and New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
. About 70% of coal mined in Australia is exported, mostly to eastern Asia, and of the balance most is used in electricity generation
Electricity generation is the process of generating electric power from sources of primary energy. For utilities in the electric power industry, it is the stage prior to its delivery ( transmission, distribution, etc.) to end users or its s ...
. In 2019-20 Australia exported 390 Mt of coal (177 Mt metallurgical coal
Metallurgical coal or coking coal is a grade of coal that can be used to produce good-quality coke. Coke is an essential fuel and reactant in the blast furnace process for primary steelmaking. The demand for metallurgical coal is highly coupled ...
and 213 Mt thermal coal) and was the world's largest exporter of metallurgical coal and second largest exporter of thermal coal.

 Coal mining in Australia has been criticized, due to carbon dioxide emissions during combustion. This criticism is primarily directed at thermal coal, for its connection to coal-fired power stations as a major source of carbon dioxide emissions, and the link to climate change in Australia and worldwide. Coal was responsible for 30% (164 million tonnes) of Australia's greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, not counting methane and export coal, in 2019. Coal as a fuel was responsible for 41% (160 million tonnes) of carbon dioxide emissions in Australia in 2020.
The
Coal mining in Australia has been criticized, due to carbon dioxide emissions during combustion. This criticism is primarily directed at thermal coal, for its connection to coal-fired power stations as a major source of carbon dioxide emissions, and the link to climate change in Australia and worldwide. Coal was responsible for 30% (164 million tonnes) of Australia's greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, not counting methane and export coal, in 2019. Coal as a fuel was responsible for 41% (160 million tonnes) of carbon dioxide emissions in Australia in 2020.
The Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme
The Carbon Pollution Reduction Scheme (or CPRS) was a cap-and-trade emissions trading scheme for anthropogenic greenhouse gases proposed by the Rudd government, as part of its climate change policy, which had been due to commence in Australia in ...
, which followed the draft report in the Garnaut Climate Change Review, placed a price on carbon emissions through a reducing cap and trade emissions trading
Emissions trading is a market-based approach to controlling pollution by providing economic incentives for reducing the emissions of pollutants. The concept is also known as cap and trade (CAT) or emissions trading scheme (ETS). Carbon emission ...
scheme and incentivised against carbon pollution temporarily, before it was revoked in 2014. Despite a target to reduce GHG emissions Australia continues to open new coal mines.
Forms of coal
Australian coal is either high-quality bituminous coal (black coal) or lower-quality lignite (brown coal). Bituminous coal is mined inQueensland
)
, nickname = Sunshine State
, image_map = Queensland in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of Queensland in Australia
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, establishe ...
and New South Wales
)
, nickname =
, image_map = New South Wales in Australia.svg
, map_caption = Location of New South Wales in AustraliaCoordinates:
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name = Australia
, established_title = Before federation
, es ...
. It is used for both domestic power generation and is exported. Mining is underground or open-cut. The coal is transported by rail to power stations or export shipping terminals.
Lignite is mined in Victoria
Victoria most commonly refers to:
* Victoria (Australia), a state of the Commonwealth of Australia
* Victoria, British Columbia, provincial capital of British Columbia, Canada
* Victoria (mythology), Roman goddess of Victory
* Victoria, Seychelle ...
and South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories ...
, and is of lower quality due to a lower thermal value largely caused by a high water content. Ash content varies significantly but some Australian lignites have relatively low ash content. In 2013 coal from three open cut lignite coal mines in Victoria was used for power generation.
History
 Australian coal was first discovered in New South Wales by shipwreck survivors in August 1797, at Coalcliff, north of
Australian coal was first discovered in New South Wales by shipwreck survivors in August 1797, at Coalcliff, north of Wollongong
Wollongong ( ), colloquially referred to as The Gong, is a city located in the Illawarra region of New South Wales, Australia. The name is believed to originate from the Dharawal language, meaning either 'five islands/clouds', 'ground near wa ...
. George Bass
George Bass (; 30 January 1771 – after 5 February 1803) was a British naval surgeon and explorer of Australia.
Early years
Bass was born on 30 January 1771 at Aswarby, a hamlet near Sleaford, Lincolnshire, the son of a tenant farmer, George ...
discovered coal soon afterwards in the cliffs
at Newcastle off of Point Solander. Coal exports first left Newcastle in 1799, with it being mined by convicts. Shipments left for India, marking Australia's first commodity export. Mining in the area was initially small scale and used in domestic heating.
In Queensland, coal mining began near Ipswich
Ipswich () is a port town and borough in Suffolk, England, of which it is the county town. The town is located in East Anglia about away from the mouth of the River Orwell and the North Sea. Ipswich is both on the Great Eastern Main Line ...
in 1825. The following year coal was discovered at Cape Paterson
Cape Paterson () is a cape and seaside village located near the town of Wonthaggi, south-east of Melbourne via the South Gippsland and Bass Highways, in the Bass Coast Shire of Gippsland, Victoria, Australia. Known originally for the disc ...
in Victoria. It wasn't until the 1850s that the deposits were mined, however it wasn't enough to sustain Victorian communities. Coal was discovered in Tasmania at Plunkett Point in 1833. In Western Australia, the first coal deposits were discovered in 1846 at Irwin River in what is known as the Coalseam Conservation Park.
By the 1900s coal had become integral to the economy as it was used in locomotives on railways and in steam mills cutting logs, and grinding wheat. In New South Wales development was particularly influenced by coal during the 20th century. During the 1940s Australian coal mines experienced significant strikes. The 1949 Australian coal strike
The 1949 Australian coal strike was the first time that Australian military forces were used during peacetime to break a trade union strike. The strike by 23,000 coal miners lasted for seven weeks, from 27 June 1949 to 15 August 1949, with troop ...
lasted for seven weeks. The Joint Coal Board was formed to aid in the resolution of workers' disputes. Before WWII underground mines dominated. After WWII, Australia began exporting coking coal to Japan to aid in their production of steel. Exports to South Korea and Taiwan soon followed. Australia became the number one coal exporter in 1984. By 1986 Australia was supplying around half of all its exports to Japan. As the Bowen Basin Coalfields
The Bowen Basin Coalfields contains the largest coal reserves in Australia. This major coal-producing region contains one of the world's largest deposits of bituminous coal. The Basin contains much of the known Permian coal resources in Queen ...
were developed, open-cut mines became more common. From the 1980s onwards the ratio of thermal coal exported to Asia increased significantly. High-grade coking coal extracted from the Illawarra
The Illawarra is a coastal region in the Australian state of New South Wales, nestled between the mountains and the sea. It is situated immediately south of Sydney and north of the South Coast region. It encompasses the two cities of Wollongo ...
region has supported a steel and steel products market with exports leaving via Port Kembla harbour. An anti-coal movement
Individual action on climate change can include personal choices in many areas, such as diet, travel, household energy use, consumption of goods and services, and family size. Individuals can also engage in local and political advocacy around issu ...
is a recent historical development.
Production, exports and reserves
Major export markets for Australian coal
 Australia exports the largest share of coal of any nation, at 54% of the total. In 2020, exports of coal accounted for 1% of national revenue, with a total value of A$55 billion.
Australia exports the largest share of coal of any nation, at 54% of the total. In 2020, exports of coal accounted for 1% of national revenue, with a total value of A$55 billion.
Major coal export ports
ThePort of Newcastle
The Port of Newcastle is a major seaport in the city of Newcastle, New South Wales, Australia. It is the world's largest coal port.
It is made up of facilities located at Port Hunter - Yohaaba in the Hunter River estuary. The port was the f ...
, New South Wales, is the world's largest and most efficient coal handling operation through its two terminals: Carrington and Kooragang. Australia has nine major coal-export ports, including:
Major coal mining companies
Future planned coal mining
Several new coal mines are planned for development in Australia. This includes Olive Downs mine, to be operated by Pembroke Resources, near Coppabella, Queensland.Pembroke Resources"Olive Downs Coking Coal Complex"
accessed 13 August 2019. In 2021, the federal government agreed to loan the project $175 million (AUS) to begin the first stages of its development. In April 2022, the construction of the mine commenced. Production is expected to begin in 2023.
Divestment from coal
Several mines have announced plans to wind-down operations in coal within set timeframes, alongside planned closures of coal power plants in Australia. This includes Werris Creek (2025). In 2016 Glencore announced that Tahmoor Complex would be closed by 2019. However, Glencore later sold the mine to SIMEC in 2018, who still operate it. BHP planned to sell the Mt Arthur mine in 2022, but failed to attract a viable offer and decided to continue operations there until financial year 2030. In August 2022 BHP completed its sale of the BHP Mitsui Coal to Stanmore Resources. Banks such as Westpac have introduced restrictions on lending for new thermal coal mines, including a limit of 6300 kilocalories per kilogram for new projects.Environmental impacts
 Both underground and open-cut mines generate significant environmental impacts, including modified topography, soil erosion,
Both underground and open-cut mines generate significant environmental impacts, including modified topography, soil erosion, water pollution
Water pollution (or aquatic pollution) is the contamination of water bodies, usually as a result of human activities, so that it negatively affects its uses. Water bodies include lakes, rivers, oceans, aquifers, reservoirs and groundwater. ...
, air pollution
Air pollution is the contamination of air due to the presence of substances in the atmosphere that are harmful to the health of humans and other living beings, or cause damage to the climate or to materials. There are many different typ ...
and acid water drainage. The coal industry claims that extensive rehabilitation of areas mined helps to ensure that land capability, after coal mining, meets agreed and appropriate standards.
Coal is the principal fossil fuel used in power generation not only in Australia but in many other countries. Links between coal mining, coal burning, and climate change are being discussed widely in Australia.
On 27 November 2006 the Land and Environment Court of New South Wales
The Land and Environment Court of New South Wales is a court within the Australian court hierarchy established pursuant to the to hear environmental, development, building and planning disputes. The Court’s jurisdiction, confined to the state ...
judge Justice Nicola Pain made the decision to set aside the Director-General's acceptance of the Environmental Assessment for the Anvil Hill coal mine, on the grounds that it did not include a comprehensive greenhouse gas assessment, even though the proposed mining of coal was for export. However, on 7 June 2007 the planning minister for NSW Frank Sartor reversed this decision and approved the mine, attaching a list of 80 conditions to the mines operation including conservation offsets.
Protests against coal
One of the first protests against coal development occurred to the south of Sydney in the early 1970s. Clutha Development wanted to build a new coal loading facility at Coalcliff. Coal was to be stored in heaps along the coast. Local activist, Judy Gjedsted, organised protests which successfully ended the proposal. In November 2021, anti-coal protestors led by Blockade Australia disrupted activity at the world’s largest coal terminal, the Port of Newcastle, by abseilling from equipment and obstructing railway tracks. The protests lasted for 10 days and 17 people were arrested. The Carmichael mine run by Adani Group, planned since 2012 and opened in 2021, drew national and international opposition, both from climate activists and traditional owners. In August 2019, the government extinguished 1,385 hectares of Wangan and Jaggalingou native title in order to grant Adani title to the land. Protestor activity at the mine has included 40 people blocking the entrance of the mine, with two chaining themselves to a drum of reinforced concrete.Environmental regulation of coal mining
The Australian commonwealth government is responsible for making policy on off-shore exploration of coal and resources, while the governments of the states and territories are responsible for policy on onshore exploration.Commonwealth law
The main Commonwealth environmental laws potentially applicable to coal mining are the ''Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999
The ''Environment Protection and Biodiversity Conservation Act 1999'' (Cth) is an Act of the Parliament of Australia that provides a framework for protection of the Australian environment, including its biodiversity and its natural and cult ...
'' (EPBC Act) and the ''Clean Energy Act 2011
The Clean Energy Act 2011 was an Act of the Australian Parliament, the main Act in a package of legislation that established an Australian emissions trading scheme (ETS), to be preceded by a three-year period of fixed carbon pricing in Australia ...
''. The EPBC Act is triggered if a proposed action is likely to have a significant impact on a matter of national environmental significance, for example federally listed threatened species and groundwater impacts.
State laws
New South Wales
Relevant laws are mining law, land use planning law, biodiversity law and water law.=Pollution law
= Coal mining requires a pollution control ('environment protection') licence under the ''Protection of the Environment Operations Act 1997'' (NSW) if it exceeds the following thresholds set out in Schedule 1 of the Act: if it is mining, processing or handling of coal (including tailings and chitter) at underground mines or open cut mines and (a) it has a capacity to produce more than 500 tonnes of coal per day, or (b) it has disturbed, is disturbing or will disturb a total surface area of more than 4 hectares of land by: (i) clearing or excavating, or (ii) constructing dams, ponds, drains, roads, railways or conveyors, or (iii) storing or depositing overburden or coal (including tailings and chitter).Queensland
In March, 2020, the Queensland Resources Council introduced safety protocols to promote the health of coal mine workers amidst the international spread ofCOVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. The disease quickly ...
. These included improvements to social distancing
In public health, social distancing, also called physical distancing, (NB. Regula Venske is president of the PEN Centre Germany.) is a set of non-pharmaceutical interventions or measures intended to prevent the spread of a contagious dis ...
of workers, disallowing visitors from the public to enter the sites and checking the temperature of workers at mine site entries.
See also
*Carbon capture and storage in Australia Carbon capture and storage (CCS) is a technology that can capture carbon dioxide emissions produced from fossil fuels in electricity, industrial processes which prevents from entering the atmosphere. Carbon capture and storage is also used to sequ ...
*Coal companies of Australia
÷Some of the more notable coal companies in Australia are the following:
Summary of coal companies
Anglo Coal Australia Ltd
Anglo Coal Australia Ltd owns and operates a number of mines in Queensland and New South Wales.
Mines
Callide mine: i ...
*Coal phase out
Coal phase-out is an environmental policy intended to stop using the combustion of coal in coal-burning power plants, and is part of fossil fuel phase-out. Coal is the most carbon-intensive fossil fuel, therefore phasing it out is critical ...
* Greenhouse Mafia
*Hunter Valley Coal Chain
The Hunter Valley Coal Chain (HVCC) is the chain of coal delivery in New South Wales, Australia from (mainly open-cut) coal mines in the Hunter Region to the Port of Newcastle and domestic coal-fired power stations in the Hunter Valley. The HVC ...
*List of coal fired power stations in Australia
These fossil fuel power stations burn coal to power steam turbines that generate some or all of the electricity they produce. Australia's fleet of coal-fired power stations are aging and many are due for decommissioning, and are being replace ...
*Mining in Australia
Mining in Australia has long been a significant primary sector industry and contributor to the Australian economy by providing export income, royalty payments and employment. Historically, mining booms have also encouraged population growth ...
* Mitigation of global warming in Australia
*Coastal coal-carrying trade of New South Wales
The Coastal coal-carrying trade of New South Wales involved the shipping of coal—mainly for local consumption but also for export or coal bunkering—by sea to Sydney from the northern and southern coal fields of New South Wales. It took place i ...
References
External links
"Illawarra Coal"
- An unofficial history of coal mining in the Illawarra
Survey of Energy Resources 2007 for Australia
{{DEFAULTSORT:Coal in Australia