Clipping (signal processing) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Clipping is a form of
Clipping is a form of
 In the
In the
 Clipping is a form of
Clipping is a form of distortion
In signal processing, distortion is the alteration of the original shape (or other characteristic) of a signal. In communications and electronics it means the alteration of the waveform of an information-bearing signal, such as an audio signal ...
that limits a signal
A signal is both the process and the result of transmission of data over some media accomplished by embedding some variation. Signals are important in multiple subject fields including signal processing, information theory and biology.
In ...
once it exceeds a threshold. Clipping may occur when a signal is recorded by a sensor
A sensor is often defined as a device that receives and responds to a signal or stimulus. The stimulus is the quantity, property, or condition that is sensed and converted into electrical signal.
In the broadest definition, a sensor is a devi ...
that has constraints on the range of data it can measure, it can occur when a signal is digitized
Digitization is the process of converting information into a digital (i.e. computer-readable) format.Collins Dictionary. (n.d.). Definition of 'digitize'. Retrieved December 15, 2021, from https://www.collinsdictionary.com/dictionary/english ...
, or it can occur any other time an analog or digital signal
A digital signal is a signal that represents data as a sequence of discrete values; at any given time it can only take on, at most, one of a finite number of values. This contrasts with an analog signal, which represents continuous values; ...
is transformed, particularly in the presence of gain or overshoot and undershoot.
Clipping may be described as hard, in cases where the signal is strictly limited at the threshold, producing a flat cutoff; or it may be described as soft, in cases where the clipped signal continues to follow the original at a reduced gain. Hard clipping results in many high-frequency harmonics
In physics, acoustics, and telecommunications, a harmonic is a sinusoidal wave with a frequency that is a positive integer multiple of the ''fundamental frequency'' of a periodic signal. The fundamental frequency is also called the ''1st harm ...
; soft clipping results in fewer higher-order harmonics and intermodulation distortion components.
Audio
frequency domain
In mathematics, physics, electronics, control systems engineering, and statistics, the frequency domain refers to the analysis of mathematical functions or signals with respect to frequency (and possibly phase), rather than time, as in time ser ...
, clipping produces strong harmonics in the high-frequency range (as the clipped waveform comes closer to a square wave Square wave may refer to:
*Square wave (waveform)
A square wave is a non-sinusoidal waveform, non-sinusoidal periodic waveform in which the amplitude alternates at a steady frequency between fixed minimum and maximum values, with the same ...
). The extra high-frequency weighting of the signal could make tweeter
A tweeter or treble speaker is a special type of loudspeaker (usually dome, inverse dome or horn-type) that is designed to produce high audio frequencies, typically from 2,000 to 20,000 Hertz, Hz. The name is derived from the high pitched sound ...
damage more likely than if the signal was not clipped.
Many electric guitar
An electric guitar is a guitar that requires external electric Guitar amplifier, sound amplification in order to be heard at typical performance volumes, unlike a standard acoustic guitar. It uses one or more pickup (music technology), pickups ...
players intentionally overdrive their amplifiers (or insert a "fuzz box") to cause clipping in order to get a desired sound (see guitar distortion).
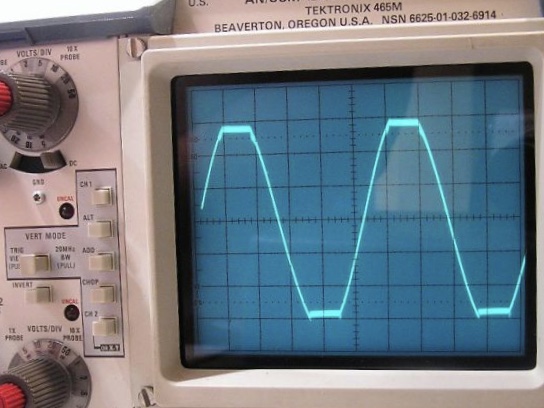
In general, the distortion associated with clipping is unwanted, and is visible on an oscilloscope
An oscilloscope (formerly known as an oscillograph, informally scope or O-scope) is a type of electronic test instrument that graphically displays varying voltages of one or more signals as a function of time. Their main purpose is capturing i ...
even if it is inaudible.
Images
In the image domain, clipping is seen as desaturated (washed-out) bright areas that turn to pure white if all color components clip. In digital colour photography, it is also possible for individual colour channels to clip, which results in inaccurate colour reproduction.Causes
Analog circuitry
A circuit designer may intentionally use a clipper or clamper to keep a signal within a desired range. When an amplifier is pushed to create a signal with more power than it can support, it will amplify the signal only up to its maximum capacity, at which point the signal will be amplified no further. *Anintegrated circuit
An integrated circuit (IC), also known as a microchip or simply chip, is a set of electronic circuits, consisting of various electronic components (such as transistors, resistors, and capacitors) and their interconnections. These components a ...
or discrete solid state amplifier cannot give an output voltage larger than the voltage it is powered by (commonly a 24- or 30-volt spread for operational amplifiers used in line-level
Line level is the specified strength of an audio signal used to transmit analog sound between audio components such as CD and DVD players, television sets, audio amplifiers, and mixing consoles.
Generally, line level signals sit in the middl ...
equipment).
*A vacuum tube
A vacuum tube, electron tube, thermionic valve (British usage), or tube (North America) is a device that controls electric current flow in a high vacuum between electrodes to which an electric voltage, potential difference has been applied. It ...
can only move a limited number of electrons
The electron (, or in nuclear reactions) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary charge, elementary electric charge. It is a fundamental particle that comprises the ordinary matter that makes up the universe, along with up qua ...
in an amount of time, dependent on its size, temperature, and metals.
*A transformer
In electrical engineering, a transformer is a passive component that transfers electrical energy from one electrical circuit to another circuit, or multiple Electrical network, circuits. A varying current in any coil of the transformer produces ...
(most commonly used between stages in tube equipment) will clip when its ferromagnetic
Ferromagnetism is a property of certain materials (such as iron) that results in a significant, observable magnetic permeability, and in many cases, a significant magnetic coercivity, allowing the material to form a permanent magnet. Ferromagne ...
core becomes electromagnetically saturated.
Digital processing
Indigital signal processing
Digital signal processing (DSP) is the use of digital processing, such as by computers or more specialized digital signal processors, to perform a wide variety of signal processing operations. The digital signals processed in this manner are a ...
, clipping occurs when the signal is restricted by the range of a chosen representation. For example in a system using 16-bit signed integers, 32767 is the largest positive value that can be represented, and if during processing the amplitude of the signal is doubled, sample values of 32000 should become 64000, but instead they are truncated to the maximum, 32767. Clipping is preferable to the alternative in digital systems — wrapping — which occurs if the digital hardware
Digital electronics is a field of electronics involving the study of digital signals and the engineering of devices that use or produce them. It deals with the relationship between binary inputs and outputs by passing electrical signals through ...
is allowed to " overflow", ignoring the most significant bit
In computing, bit numbering is the convention used to identify the bit positions in a binary numeral system, binary number.
Bit significance and indexing
In computing, the least significant bit (LSb) is the bit position in a Binary numeral sy ...
s of the magnitude, and sometimes even the sign of the sample value, resulting in gross distortion of the signal.
The incidence of clipping may be greatly reduced by using floating point numbers instead of integers. However, floating point numbers are usually less efficient to use, sometimes result in a loss of precision, and they can still clip if a number is extremely large or small.
Avoiding clipping
Clipping can be detected by viewing the signal (on an oscilloscope, for example), and observing that the tops and bottoms of waves aren't smooth anymore. When working with images, some tools can highlight allpixel
In digital imaging, a pixel (abbreviated px), pel, or picture element is the smallest addressable element in a Raster graphics, raster image, or the smallest addressable element in a dot matrix display device. In most digital display devices, p ...
s that are pure white, allowing the user to identify larger groups of white pixels and decide if too much clipping has occurred.
To avoid clipping, the signal can be dynamically reduced using a limiter. If not done carefully, this can still cause undesirable distortion, but it prevents any data from being completely lost.
Repairing a clipped signal
When clipping occurs, part of the original signal is lost, so perfect restoration is impossible. Thus, it is much preferable to avoid clipping in the first place. However, when repair is the only option, the goal is to make up a plausible replacement for the clipped part of the signal.See also
*Dynamic range
Dynamics (from Greek δυναμικός ''dynamikos'' "powerful", from δύναμις ''dynamis'' " power") or dynamic may refer to:
Physics and engineering
* Dynamics (mechanics), the study of forces and their effect on motion
Brands and ent ...
* Dynamic range compression
Dynamic range compression (DRC) or simply compression is an audio signal processing operation that reduces the volume of loud sounds or amplifies quiet sounds, thus reducing or ''compressing'' an audio signal's dynamic range. Compression is c ...
References
{{reflist Signal processing