Climate of the Philippines on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]


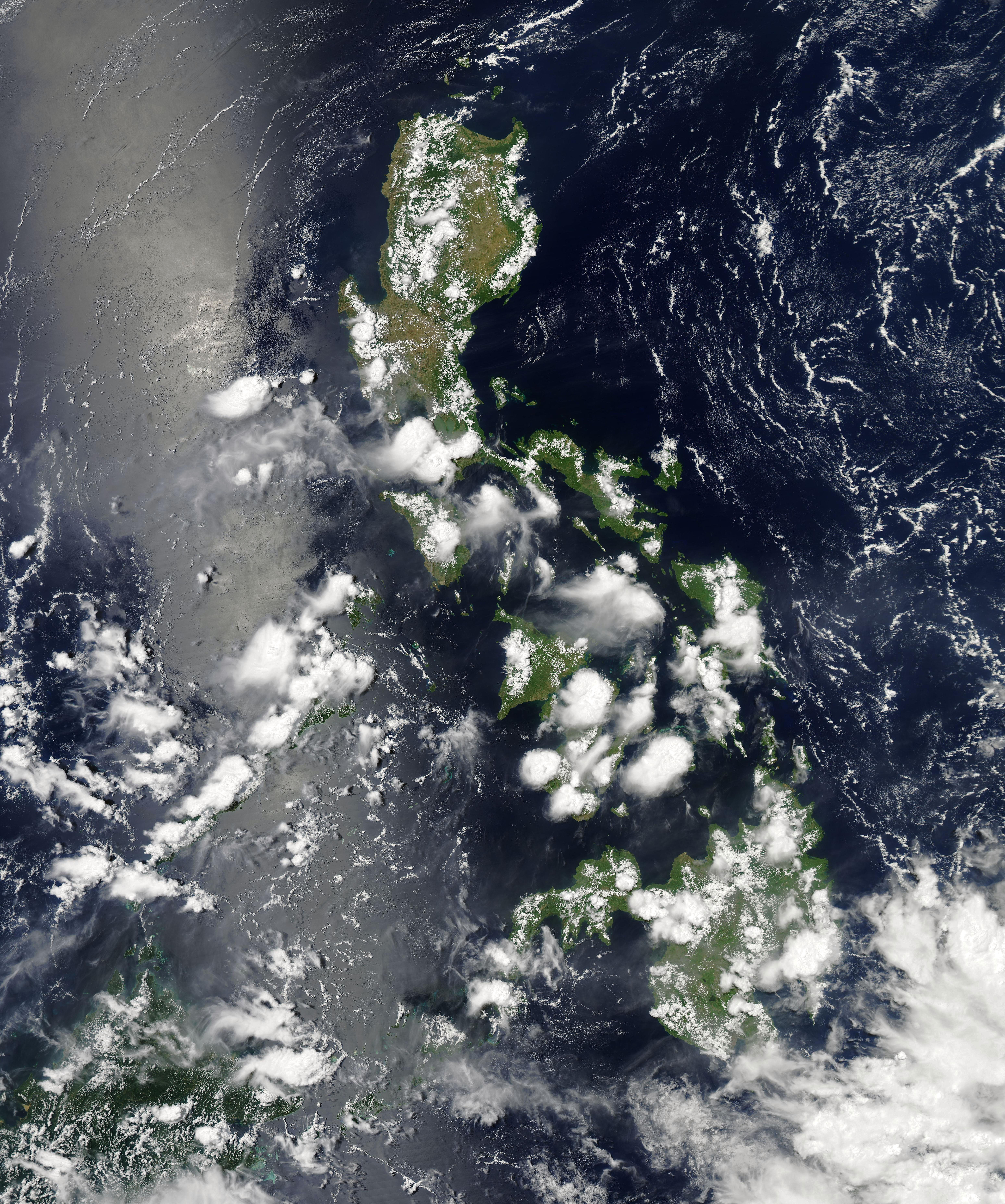 The
The
Baguio.
Retrieved on June 11, 2008. followed by extraordinary drought from October 1911 to May 1912, so that the annual amount of those two years were hardly noticeable.
Tropical Cyclone Statistics
". Retrieved on June 26, 2010. PAGASA categorises typhoons into five types according to wind speed. Once a tropical cyclone enters the PAR, regardless of strength, it is given a local name for identification purposes by the media, government, and the general public.

 The
The Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
has five types of climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorologi ...
s: tropical rainforest
Tropical rainforests are rainforests that occur in areas of tropical rainforest climate in which there is no dry season – all months have an average precipitation of at least 60 mm – and may also be referred to as ''lowland equator ...
, tropical monsoon, tropical savanna, humid subtropical
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25° and 40° ...
and oceanic (both are in higher-altitude areas) characterized by relatively high temperature, oppressive humidity and plenty of rainfall. There are two seasons
A season is a division of the year based on changes in weather, ecology, and the number of daylight hours in a given region. On Earth, seasons are the result of the axial parallelism of Earth's tilted orbit around the Sun. In temperate and po ...
in the country, the wet season and the dry season, based upon the amount of rainfall. This is also dependent on location in the country as some areas experience rain all throughout the year (see Climate types). Based on temperature, the warmest months of the year are March through October; the winter monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
brings cooler air from November to February. May is the warmest month, and January, the coolest.
Weather in the Philippines is monitored and managed by the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration
Pagasa may refer to:
* ''Pagasa'' (genus), an insect genus in the family Nabidae
* PAGASA, an acronym for the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration
*"May Pagasa", a pen-name of José Rizal
José Prot ...
(PAGASA).
Rainfall
Monsoon
A monsoon () is traditionally a seasonal reversing wind accompanied by corresponding changes in precipitation but is now used to describe seasonal changes in atmospheric circulation and precipitation associated with annual latitudinal oscil ...
s are large-scale sea breezes which occur when the temperature on land is significantly warmer or cooler than the temperature of the ocean. Most summer monsoons or southwest monsoons ( fil, Habagat) have a dominant westerly component and a strong tendency to ascend and produce copious amounts of rain (because of the condensation of water vapor in the rising air). The intensity and duration, however, are not uniform from year to year. Winter monsoons or northeast monsoons ( fil, Amihan), by contrast, have a dominant easterly component and a strong tendency to diverge, subside and cause drought.
The summer monsoon brings heavy rains to most of the archipelago from May to October. Annual average rainfall ranges from as much as in the mountainous east coast section of the country, to less than in some of the sheltered valleys. Monsoon rains, although hard and drenching, are not normally associated with high winds and waves.
At least 30 percent of the annual rainfall in the northern Philippines can be traced to tropical cyclones, while the southern islands receiving less than 10 percent of their annual rainfall from tropical cyclones. The wettest known tropical cyclone to impact the archipelago was the July 1911 cyclone, when the total precipitation for Baguio was distributed over the four days as: 14th – , 15th – , 16th – , 17th – ;Glossary of MeteorologyBaguio.
Retrieved on June 11, 2008. followed by extraordinary drought from October 1911 to May 1912, so that the annual amount of those two years were hardly noticeable.
Typhoons
The Philippines sit across the typhoon belt, making dangerous storms from July through October. Climate change exacerbates the situation with typhoons in the Philippines. ''Bagyo'' is the Filipino term for anytropical cyclone
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Dep ...
in the Philippine Islands. From the statistics gathered by PAGASA from 1948 to 2004, around an average of 28 storms and/or typhoons per year enter the PAR (Philippine Area of Responsibility) – the designated area assigned to PAGASA to monitor during weather disturbances. Those that made landfall or crossed the Philippines, the average was nine per year. In 1993, a record 19 typhoons made landfall in the country making it the most in one year. The fewest per year were 4 during the years 1955, 1958, 1992, and 1997.Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration.Tropical Cyclone Statistics
". Retrieved on June 26, 2010. PAGASA categorises typhoons into five types according to wind speed. Once a tropical cyclone enters the PAR, regardless of strength, it is given a local name for identification purposes by the media, government, and the general public.
Public Storm Warning System (PSWS)
For the past ten years, the Philippines has experienced a number of extremely damaging tropical cyclones, particularly typhoons with more than of sustained winds. Because of this, the Super Typhoon (STY) category with more than maximum sustained winds was officially adopted. PAGASA revises definition of super typhoon, signal system in 2022. However, according to different stakeholders, the extensive and devastating damages caused by strong typhoons such asTyphoon Haiyan
Typhoon Haiyan, known in the Philippines as Super Typhoon Yolanda, was one of the most powerful tropical cyclones ever recorded. On making landfall, Haiyan devastated portions of Southeast Asia, particularly the Philippines. It is one of the ...
(Yolanda) in 2013 and Typhoon Rai (Odette) in 2021 made the fourlevel warning system inadequate.
Strongest typhoons
Typhoon Haiyan (Yolanda, 2013)
The deadliest typhoon to impact the Philippines wasTyphoon Haiyan
Typhoon Haiyan, known in the Philippines as Super Typhoon Yolanda, was one of the most powerful tropical cyclones ever recorded. On making landfall, Haiyan devastated portions of Southeast Asia, particularly the Philippines. It is one of the ...
, locally known as Yolanda, in November 2013, in which more than 6,300 people died from its storm surges and powerful winds. Over 1,000 went missing and nearly 20,000 were injured. Winds reached in one–minute sustained and may have been the strongest storm in history in terms of wind speeds as wind speeds before the 1970s were too high to record.
Typhoon Angela (Rosing, 1995)
Back in 1995, where Typhoon Angela, known as Rosing was an extremely catastrophic category 5 typhoon that made landfall in Catanduanes and made across Manila. Winds reached 290 km/h (180 mph) on one-minute sustain winds. Rosing took 936 lives and the most powerful typhoon that ever hit Metro Manila.Typhoon Bopha (Pablo, 2012)
On late December 3, 2012,Typhoon Bopha
Typhoon Bopha, known in the Philippines as Typhoon Pablo, was the strongest tropical cyclone on record to ever affect the southern Philippine island of Mindanao, making landfall as a Category 5 super typhoon with winds of 175 mph (28 ...
or known as Pablo made landfall
Landfall is the event of a storm moving over land after being over water. More broadly, and in relation to human travel, it refers to 'the first land that is reached or seen at the end of a journey across the sea or through the air, or the fact ...
on Eastern Mindanao, damage was over US$1.04 billion by winds of 280 km/h (175 mph) on one-minute sustain winds. Typhoon Bopha was the most powerful typhoon ever hit Mindanao, killing 1,067 people and 834 people were missing. Most of the damage was caused by rushing storm surges and screaming winds.
Typhoon Megi (Juan, 2010)
Typhoon Megi (2010)
Typhoon Megi (), known in the Philippines as Super Typhoon Juan, was the strongest tropical cyclone of 2010 and is considered one of the most intense ever recorded. Megi, which means ''catfish'' in Korean (Hangul: 메기), was the only super ty ...
was the strongest storm ever to make landfall in the country in terms of pressure.
It reached wind speeds of 295 km/h (185 mph) on one-minute sustained winds, killing 67 people and costing over US$700 million in damage.
Climate types
There are four recognized climate types in the Philippines, and they are based on the distribution of rainfall ''(See the Philippine Climate Map at the top)''. They are described as follows:Temperature
The average year-round temperature measured from all the weather stations in the Philippines, exceptBaguio
Baguio ( ,
), officially the City of Baguio ( ilo, Siudad ti Baguio; fil, Lungsod ng Baguio), is a 1st class highly urbanized city in the Cordillera Administrative Region, Philippines. It is known as the "Summer Capital of the Philippines", ...
, is . Cooler days are usually felt in the month of January with temperature averaging at and the warmest days, in the month of May with a mean of . Elevation factors significantly in the variation of temperature in the Philippines. In Baguio, with an elevation of above sea level, the mean average is or cooler by about . In 1915, a one-year study was conducted
Conducting is the art of directing a musical performance, such as an orchestral or choral concert. It has been defined as "the art of directing the simultaneous performance of several players or singers by the use of gesture." The primary duti ...
by William H. Brown of the Philippine Journal of Science on top of Mount Banahaw
Mount Banahaw (; also spelled as Banahao and Banájao) is an active complex volcano on Luzon in the Philippines. The three-peaked volcano is located at the boundary of Laguna and Quezon provinces. It is the highest mountain in both provinces an ...
at elevation. The mean temperature measured was , a difference of from the lowland mean temperature.
Humidity
Relative humidity is high in the Philippines. A high amount of moisture or vapor in the air makes hot temperatures feel hotter. This quantity of moisture is due to different factors – the extraordinaryevaporation
Evaporation is a type of vaporization that occurs on the surface of a liquid as it changes into the gas phase. High concentration of the evaporating substance in the surrounding gas significantly slows down evaporation, such as when h ...
from the seas that surrounds the country on all sides, to the different prevailing winds
In meteorology, prevailing wind in a region of the Earth's surface is a surface wind that blows predominantly from a particular direction. The dominant winds are the trends in direction of wind with the highest speed over a particular point on ...
in the different seasons of the year, and finally, to the abundant rains so common in a tropical country. The first may be considered as general causes of the great humidity, which is generally observed in all the islands throughout the year. The last two may influence the different degree of humidity for the different months of the year and for the different regions of the archipelago.
Seasons
The climate of the country is divided into two main seasons: # the rainy season, from June and the early part of October; # the dry season, from the later part of October to May. The dry season may be subdivided further into (a) the cool dry season, from the later part of October to February; and (b) the hot dry season, from March to May. The months of April and May, the hot and dry months when schools are on their long break between academic years, is referred to assummer
Summer is the hottest of the four temperate seasons, occurring after spring and before autumn. At or centred on the summer solstice, the earliest sunrise and latest sunset occurs, daylight hours are longest and dark hours are shortest, wit ...
while in most of the northern hemisphere
The Northern Hemisphere is the half of Earth that is north of the Equator. For other planets in the Solar System, north is defined as being in the same celestial hemisphere relative to the invariable plane of the solar system as Earth's Nort ...
those months are part of spring
Spring(s) may refer to:
Common uses
* Spring (season), a season of the year
* Spring (device), a mechanical device that stores energy
* Spring (hydrology), a natural source of water
* Spring (mathematics), a geometric surface in the shape of a h ...
.
Climate change
Notes
References
Sources
* * * {{refend Geography of the Philippines