Climate of Mali on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Mali is one of the hottest countries in the world. The thermal equator, which matches the hottest spots year-round on the planet based on the mean daily annual temperature, crosses the country Most of Mali receives negligible rainfall and
Mali is one of the hottest countries in the world. The thermal equator, which matches the hottest spots year-round on the planet based on the mean daily annual temperature, crosses the country Most of Mali receives negligible rainfall and
 Geologically, Mali consists mostly of vast flatlands of
Geologically, Mali consists mostly of vast flatlands of
Mali: Floods DREF Bulletin No. MDRML004
. 13 July 2007. ReliefWeb site retrieved 13 August 2007. * Tropical thunderstorms in the south, which may bring wind and lightning damage as well as flash floods. * Occasional Niger River flooding

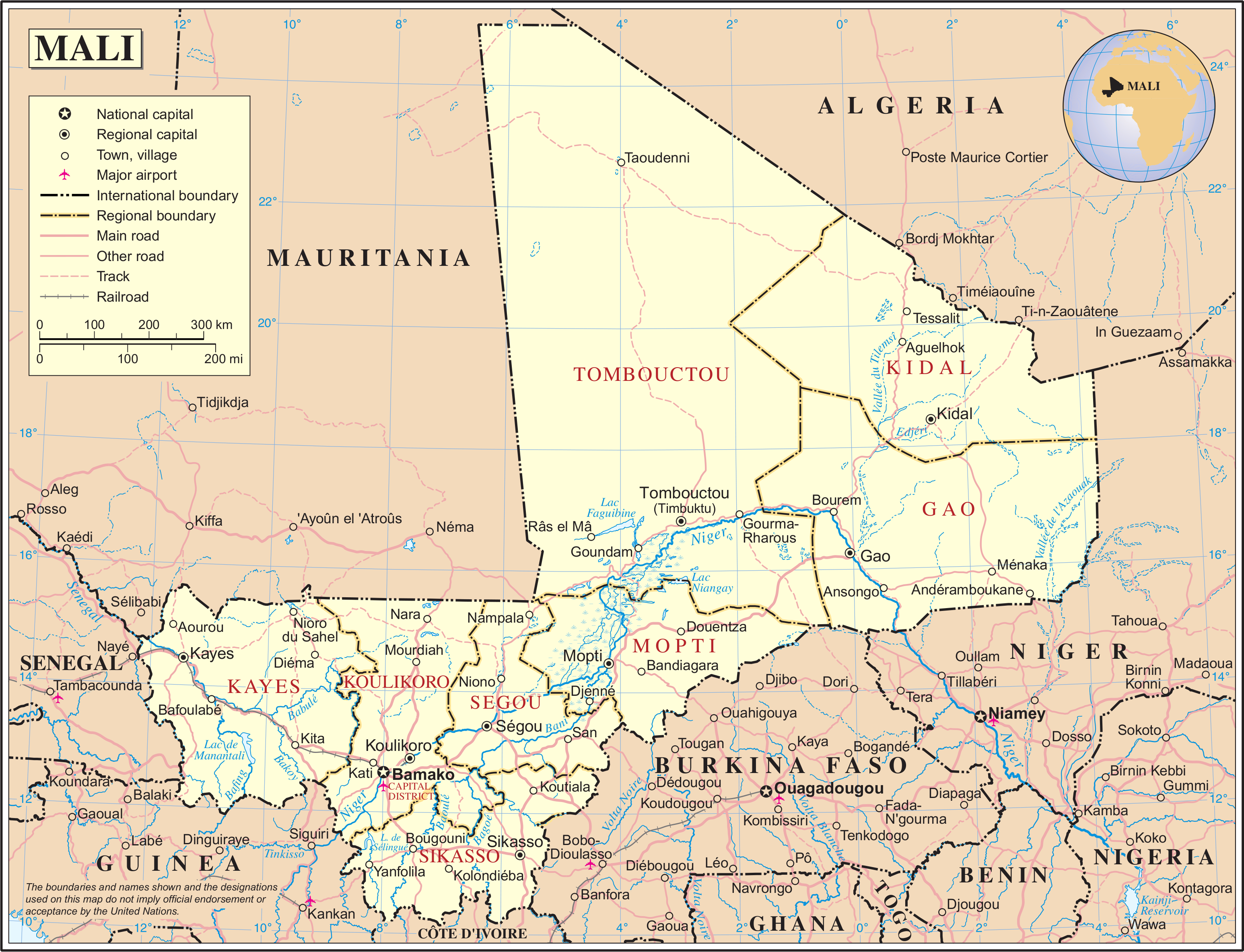
Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mali ...
is a landlocked nation in West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, Maurit ...
, located southwest of Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
, extending south-west from the southern Sahara Desert through the Sahel
The Sahel (; ar, ساحل ' , "coast, shore") is a region in North Africa. It is defined as the ecoclimatic and biogeographic realm of transition between the Sahara to the north and the Sudanian savanna to the south. Having a hot semi-arid c ...
to the Sudanian savanna zone. Mali's size is 1,240,192 square kilometers.
Desert or semi-desert covers about 65 percent of Mali's total area (1,240,192 square kilometers). The Niger River creates a large and fertile inland delta
A river delta is a landform shaped like a triangle, created by deposition of sediment that is carried by a river and enters slower-moving or stagnant water. This occurs where a river enters an ocean, sea, estuary, lake, reservoir, or (more rare ...
as it arcs northeast through Mali from Guinea before turning south and eventually emptying into the Gulf of Guinea.
The territory encompasses three natural zones: the southern cultivated Sudanese zone, central semi-desert Sahelian zone, and northern desert Saharan zone. The terrain is primarily savanna in the south and flat to rolling plains or high plateau (200–500 meters in elevation) in the north. There are rugged hills in the northeast, with elevations of up to 1,000 meters.
The Niger (with 1,693 kilometers in Mali) and Senegal are Mali's two largest rivers. The Niger is generally described as Mali's lifeblood, a source of food, drinking water, irrigation, and transportation.
The country's lowest point is on the Senegal River
,french: Fleuve Sénégal)
, name_etymology =
, image = Senegal River Saint Louis.jpg
, image_size =
, image_caption = Fishermen on the bank of the Senegal River estuary at the outskirts of Saint-Louis, Senegal ...
(23 m) and its highest point is Hombori Tondo
Mount Hombori (Hombori Tondo) is a mountain in Mali's Mopti Region, near the town of Hombori. At 1,155 meters, it is the highest point in Mali.
Biodiversity
Mount Hombori is an important location for biodiversity in the Sahel, with 150 diff ...
(1155 m).
Climate
drought
A drought is defined as drier than normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, an ...
s are very frequent Late April to early October is the rainy season in the southernmost area. During this time, flooding of the Niger River is common, creating the Inner Niger Delta. The vast northern desert part of Mali has a hot desert climate (Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, notabl ...
''BWh'') with long, extremely hot summers and scarce rainfall which decreases northwards. The central area has a hot semi-arid climate
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-ar ...
(Köppen climate classification ''BSh'') with very high temperatures year-round, a long, intense dry season and a brief, irregular rainy season. The southern areas have a tropical wet and dry climate (Köppen climate classification ''Aw'') very high temperatures year-round with a dry season and a rainy season. During the hottest season of the year, temperatures are high throughout the country. Timbuktu
Timbuktu ( ; french: Tombouctou;
Koyra Chiini: ); tmh, label=Tuareg, script=Tfng, ⵜⵏⴱⴾⵜ, Tin Buqt a city in Mali, situated north of the Niger River. The town is the capital of the Tombouctou Region, one of the eight administrativ ...
, Taghaza
, nickname =
, settlement_type =
, total_type =
, motto =
, translit_lang1 = , translit_lang1_
, translit_lang1_info2 =
, ...
, Taoudenni ar, تودني
, nickname =
, settlement_type =
, total_type =
, motto =
, translit_lang1=
, translit_lang1_type=
, translit_lang1_info=
, translit_lang1_type1=
, translit_lang1_info1=
, transli ...
, Araouane
Araouane or Arawan is a small village in the Malian part of the Sahara Desert, lying north of Timbuktu on the caravan route to the salt-mining centre of Taoudenni. The village once served as an entrepôt in the trans-Saharan trade.
History
Betw ...
, Gao
Gao , or Gawgaw/Kawkaw, is a city in Mali and the capital of the Gao Region. The city is located on the River Niger, east-southeast of Timbuktu on the left bank at the junction with the Tilemsi valley.
For much of its history Gao was an impor ...
, Kidal and Tessalit are some of the hottest spots on Earth during their warmest months. Kayes, with an average high temperature of about 44° (111.2°) in April is nicknamed "the pressure cooker of Africa" due to his extreme heat year-round. The heat is more extreme to the north in the Sahara Desert; the maximum average high temperature of the year reaches 46 °C (114.8 °F) in Araouane in June and comes close to 48° (118.4°) in the Taoudenni region during July sunshine duration
Sunshine duration or sunshine hours is a climatological indicator, measuring duration of sunshine in given period (usually, a day or a year) for a given location on Earth, typically expressed as an averaged value over several years. It is a gene ...
is high in Mali, reaching the highest levels in the northern arid zone with about 3,600 - 3,700 h a year. Mali has overall a hot, sunny and dry climate dominated by the subtropical ridge
The horse latitudes are the latitudes about 30 degrees north and south of the Equator. They are characterized by sunny skies, calm winds, and very little precipitation. They are also known as Subtropics, subtropical ridges, or highs. It is a h ...
.
Examples
Geology
 Geologically, Mali consists mostly of vast flatlands of
Geologically, Mali consists mostly of vast flatlands of granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained (phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies undergro ...
and shale
Shale is a fine-grained, clastic sedimentary rock formed from mud that is a mix of flakes of clay minerals (hydrous aluminium phyllosilicates, e.g. kaolin, Al2 Si2 O5( OH)4) and tiny fragments (silt-sized particles) of other minerals, especial ...
covered by sandstone and alluvial quartz. Mali extends over two main geological structures, the West African craton in the west and the Tuareg shield
The Tuareg Shield is a geological formation lying between the West African craton and the Saharan Metacraton in West Africa. Named after the Tuareg people, it has complex a geology, reflecting the collision between these cratons and later events. ...
in the southeast, which came together at the end of the Precambrian
The Precambrian (or Pre-Cambrian, sometimes abbreviated pꞒ, or Cryptozoic) is the earliest part of Earth's history, set before the current Phanerozoic Eon. The Precambrian is so named because it preceded the Cambrian, the first period of the ...
era between 600 and 550 million years ago. The suture zone is to the west of the Adrar des Ifoghas
The Adrar des Ifoghas (also Adrar des Iforas; Tamasheq: ⴰⴷⵔⴰⵔ ⵏ ⵉⴼⵓⵖⴰⵙ in Tifinagh; Adrar n Ifoghas; ar, أدرار إيفوغاس Ifoghas' Mountains) is a massif located in the Kidal Region of Mali, reaching into Algeri ...
mountains.
The underlying rocks of the West African craton are covered in the northwest by sediments of the Taoudeni basin
The Taoudeni Basin is a major Sedimentary basin in West Africa, named after the Taoudenni village in northern Mali. It covers large parts of the West African craton in Mauritania and Mali. It is of considerable interest due to its possible reserve ...
, with two main outcrops of crystalline rocks in the northern Reguibat shield in Mauritania
Mauritania (; ar, موريتانيا, ', french: Mauritanie; Berber: ''Agawej'' or ''Cengit''; Pulaar: ''Moritani''; Wolof: ''Gànnaar''; Soninke:), officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania ( ar, الجمهورية الإسلامية ...
and the southern Leo shield which includes the Bougouni
Bougouni is a commune and city in Mali, the administrative center of Bougouni Cercle, which is in turn found in the administrative region of Sikasso. Bougouni is located 170 km south of Bamako and 210 km west of the city of Sikasso. ...
and Kenieba outcrops, both of which contain valuable minerals. There may also be petroleum reserves in the Taoudeni basin.
Borders
Mali shares a total of 7,243 kilometers (4,500 miles) of land boundaries with seven bordering states: North and northeast:Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
- 1,376 km/855 mi
East: Niger- 821 km/510 mi
Southeast: Burkina Faso- 1,000 km/621 mi
South: Ivory Coast
Ivory Coast, also known as Côte d'Ivoire, officially the Republic of Côte d'Ivoire, is a country on the southern coast of West Africa. Its capital is Yamoussoukro, in the centre of the country, while its largest city and economic centre is ...
- 532 km/330 mi
Southwest: Guinea
Guinea ( ),, fuf, 𞤘𞤭𞤲𞤫, italic=no, Gine, wo, Gine, nqo, ߖߌ߬ߣߍ߫, bm, Gine officially the Republic of Guinea (french: République de Guinée), is a coastal country in West Africa. It borders the Atlantic Ocean to the we ...
- 858 km/533 mi
West: Senegal and Mauritania
Mauritania (; ar, موريتانيا, ', french: Mauritanie; Berber: ''Agawej'' or ''Cengit''; Pulaar: ''Moritani''; Wolof: ''Gànnaar''; Soninke:), officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania ( ar, الجمهورية الإسلامية ...
- 419 km/260 mi and 2,237 km/1,390 mi (respectively)
Natural resources
Mali is endowed with bauxite, copper, diamonds, gold, Granite, gypsum, iron ore, kaolin, limestone, lithium, manganese, phosphates, salt, silver, uranium, and zinc. Not all deposits are being exploited, and some may not be commercially viable. Mali also has ample hydropower.Land use
Sixty-five percent of Mali's land area is desert or semi-desert. According to estimates in 2011, only 5.63 percent of Mali's area can be classified as arable land, and 0.1 percent was planted to permanent crops. Mali was estimated to have 2,358 square kilometers of irrigated land in 2003. Mali has 100 cubic kilometers of total renewable water resources as off 2011 estimates.Environmental issues
Mali faces numerous environmental challenges, includingdesertification
Desertification is a type of land degradation in drylands in which biological productivity is lost due to natural processes or induced by human activities whereby fertile areas become increasingly arid. It is the spread of arid areas caused by ...
, deforestation, soil erosion, drought, and inadequate supplies of potable water. Deforestation is an especially serious and growing problem. According to the Ministry of the
Environment, Mali's population consumes 6 million tons of wood per year for timber and fuel. To meet this demand, 400,000 hectares of tree cover are lost annually, virtually ensuring destruction of the country's savanna woodlands.
Mali is a party to international treaties on Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol
The Kyoto Protocol was an international treaty which extended the 1992 United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) that commits state parties to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, based on the scientific consensus that (part ...
, Desertification
Desertification is a type of land degradation in drylands in which biological productivity is lost due to natural processes or induced by human activities whereby fertile areas become increasingly arid. It is the spread of arid areas caused by ...
, Endangered Species
An endangered species is a species that is very likely to become extinct in the near future, either worldwide or in a particular political jurisdiction. Endangered species may be at risk due to factors such as habitat loss, poaching and inv ...
, Hazardous Wastes, Law of the Sea, Ozone Layer Protection
The Montreal Protocol is an international treaty designed to protect the ozone layer by phasing out the production of numerous substances that are responsible for ozone depletion. It was agreed on 16 September 1987, and entered into force o ...
, Wetlands
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The ...
, and Whaling. It has signed, but not ratified the selected agreements.
Natural hazards
Natural hazards in Mali include: * Desert sandstorms in the north * Dust-ladenharmattan
The Harmattan is a season in West Africa that occurs between the end of November and the middle of March. It is characterized by the dry and dusty northeasterly trade wind, of the same name, which blows from the Sahara over West Africa into the ...
wind is common during dry seasons, bringing a dust haze which may ground aircraft and damage computers and sensitive electronics and machines, as well as aggravating respiratory diseases.
* Recurring drought
A drought is defined as drier than normal conditions.Douville, H., K. Raghavan, J. Renwick, R.P. Allan, P.A. Arias, M. Barlow, R. Cerezo-Mota, A. Cherchi, T.Y. Gan, J. Gergis, D. Jiang, A. Khan, W. Pokam Mba, D. Rosenfeld, J. Tierney, an ...
s
* Wildfires in the south
* Occasional floods, for example in July 2007.''International Federation of Red Cross And Red Crescent Societies (IFRC)'':Mali: Floods DREF Bulletin No. MDRML004
. 13 July 2007. ReliefWeb site retrieved 13 August 2007. * Tropical thunderstorms in the south, which may bring wind and lightning damage as well as flash floods. * Occasional Niger River flooding
Extreme points
This is a list of the extreme points ofMali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Mali ...
, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location.
* Northernmost point – the northern section of the border with Mauritania
Mauritania (; ar, موريتانيا, ', french: Mauritanie; Berber: ''Agawej'' or ''Cengit''; Pulaar: ''Moritani''; Wolof: ''Gànnaar''; Soninke:), officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania ( ar, الجمهورية الإسلامية ...
, Tombouctou Region*
* Easternmost point – the eastern section of the border with Niger**
* Southernmost point – Fonto Kourou on the border with Cote d'Ivoire, Sikasso Region
* Westernmost point - the tripoint with Senegal and Mauritania
Mauritania (; ar, موريتانيا, ', french: Mauritanie; Berber: ''Agawej'' or ''Cengit''; Pulaar: ''Moritani''; Wolof: ''Gànnaar''; Soninke:), officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania ( ar, الجمهورية الإسلامية ...
, Kayes Region
Kayes Region ( Bambara: ߞߊߦߌ ߘߌߣߋߖߊ tr. Kayi Dineja) is one of eight first level national subdivisions in Mali called Regions. It is the first administrative area of Mali and covers an area of . Its capital is the town of Kayes. The p ...
* *''Note: Mali does not have a northernmost point, the border being formed by a straight east–west line''
* **''Note: Mali does not have an easternmost point, the border being formed by a straight north–south line''
See also
* Inner Niger Delta *Manding Mountains
The Manding Mountains are a highland area in Mali, stretching between its western border with Guinea to an area 50km west of Bamako, Mali's capital. They reach above sea level. Kangaba, the spiritual home of the Mandinka people, is located at t ...
* 2010 Sahel famine
A large-scale, drought-induced famine occurred in Africa's Sahel region and many parts of the neighbouring Sénégal River Area from February to August 2010. It is one of many famines to have hit the region in recent times.
The Sahel is ...
* List of cities in Mali
* List of rivers of Mali
This is a list of rivers in Mali. This list is arranged by drainage basin, with respective tributaries indented under each larger stream's name.
Atlantic Ocean
*Sénégal River
** Falémé River
**Karakoro River
** Kolinbiné River
*** Sanaba ...
* Eburnean orogeny
* Kenieba inlier
* Bambouk
Bambouk (sometimes Bambuk or Bambuhu) is a traditional name for the territory in eastern Senegal and western Mali, encompassing the Bambouk Mountains on its eastern edge, the valley of the Faleme River and the hilly country to the east of the riv ...
* Birimian
References
{{DEFAULTSORT:Geography Of Mali